Real-Time Prediction of Bottom Hole Pressure via Graph Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Datasets
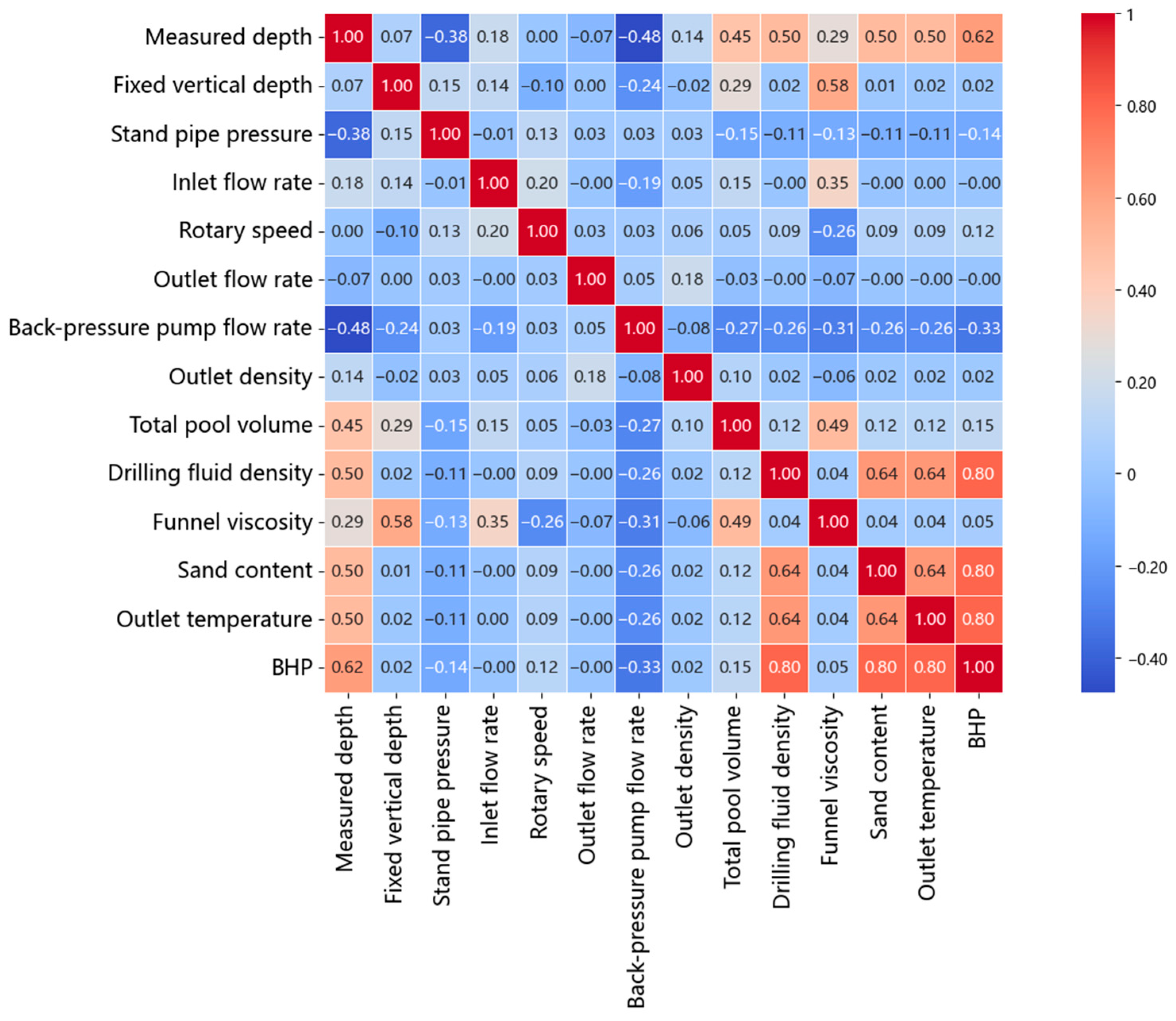
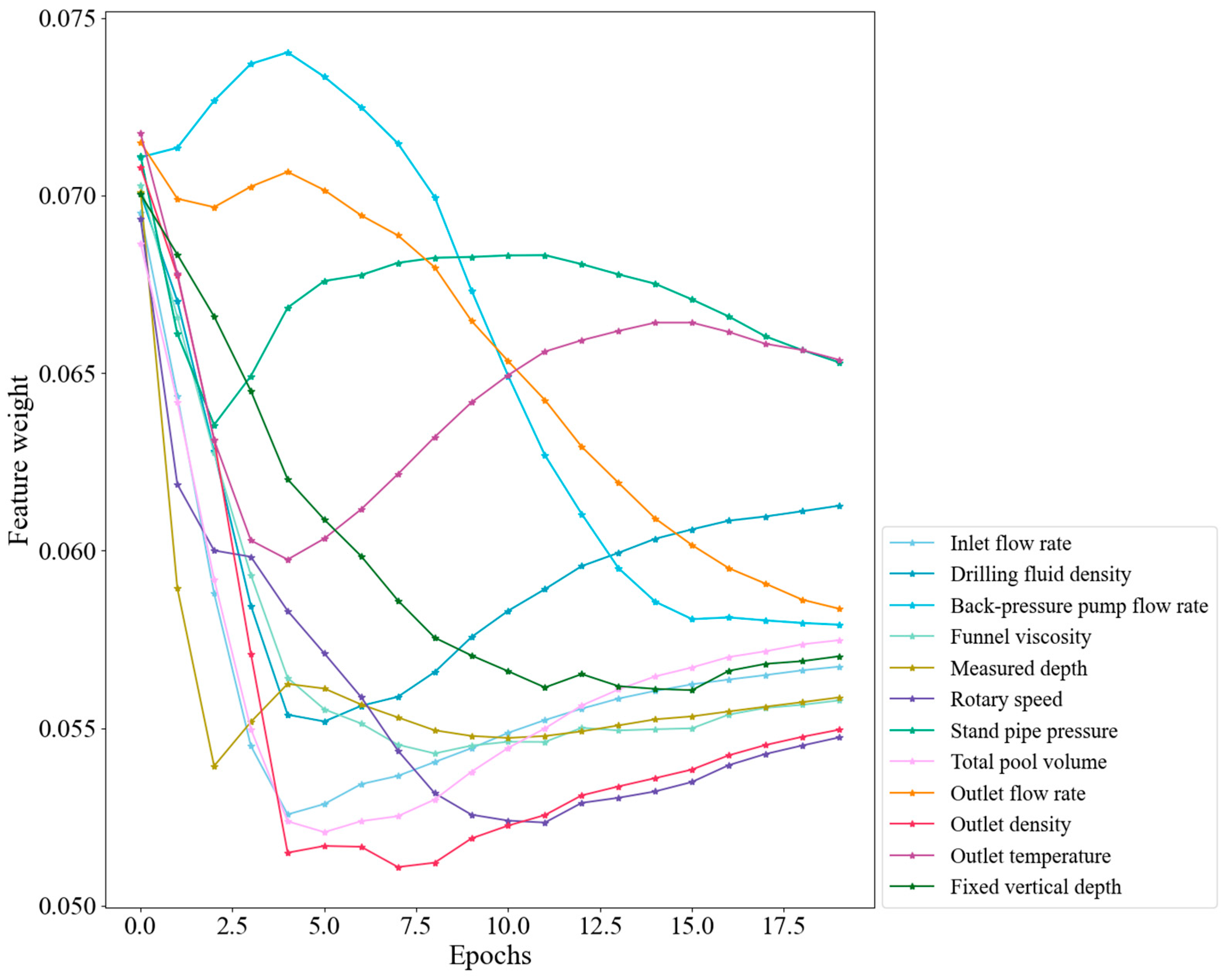
2.2. Feature Engineering
- (1)
- Mechanism-driven initial feature screening
- (2)
- Correlation-based feature selection
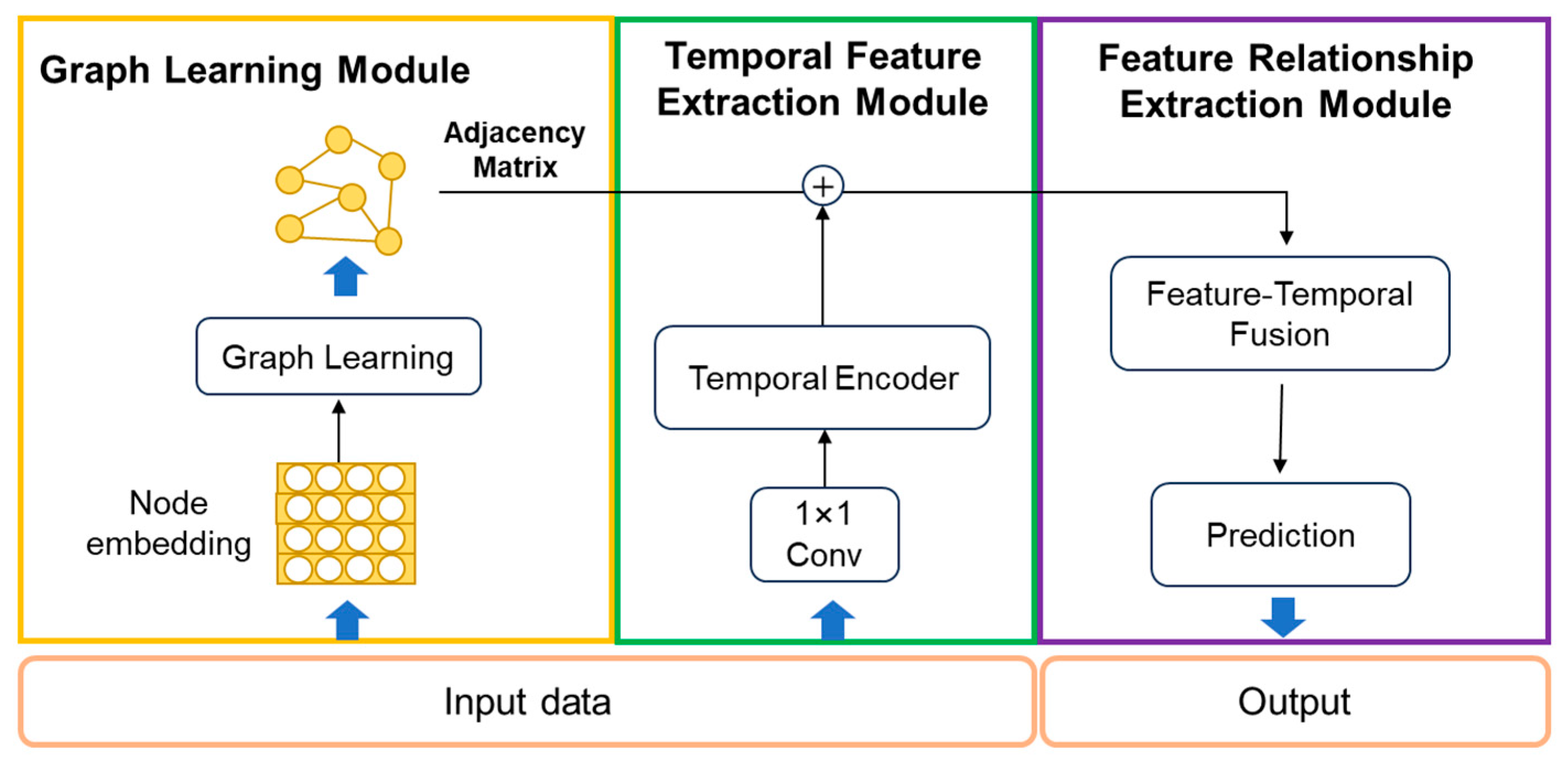
2.3. Improved Hybrid Graph Learning Network
- (3)
- Graph learning module
- (4)
- Temporal feature extraction module
- (5)
- Feature relationship extraction module
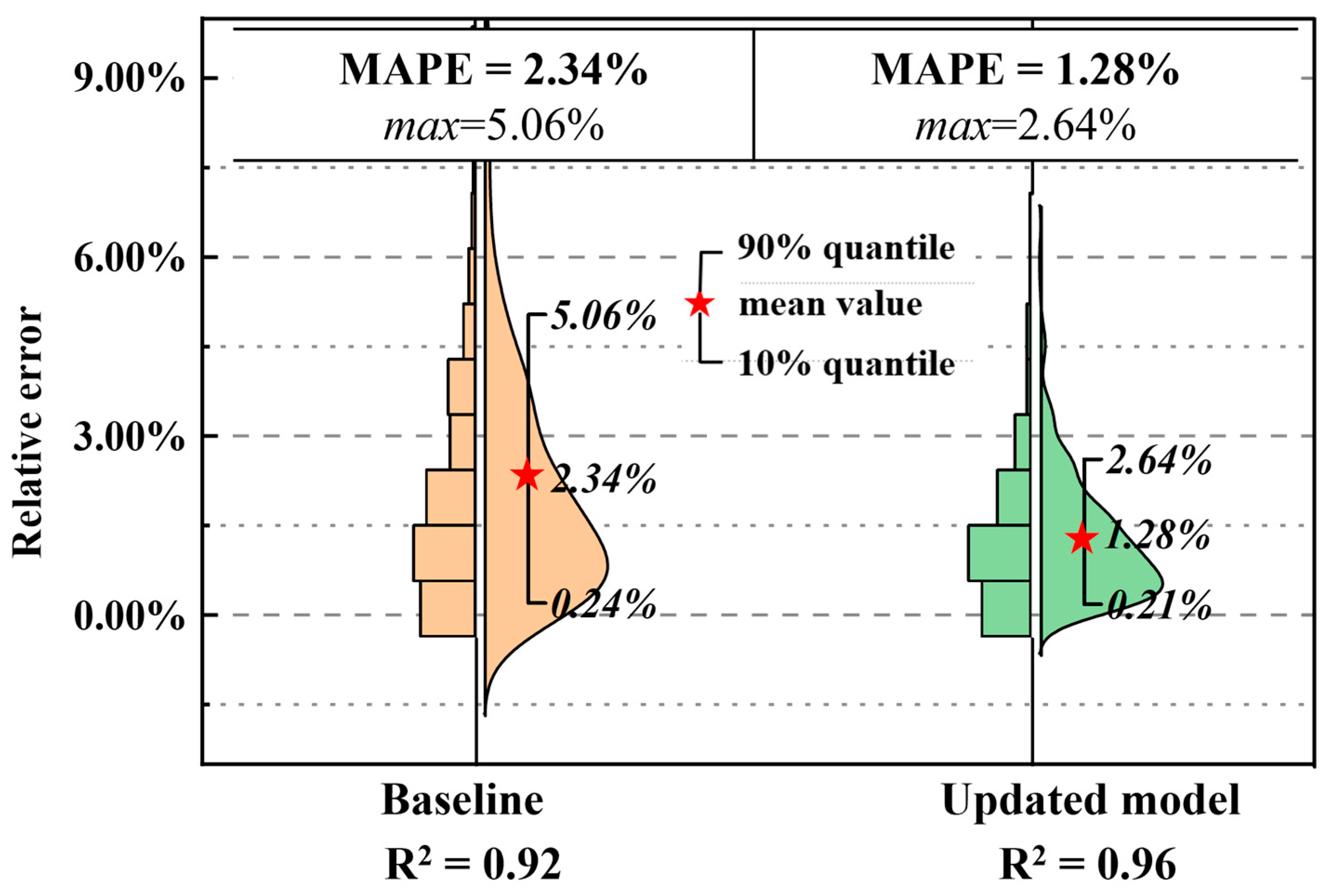
2.4. Incremental Updating Workflow
2.5. Training Configuration
3. Results and Discussion
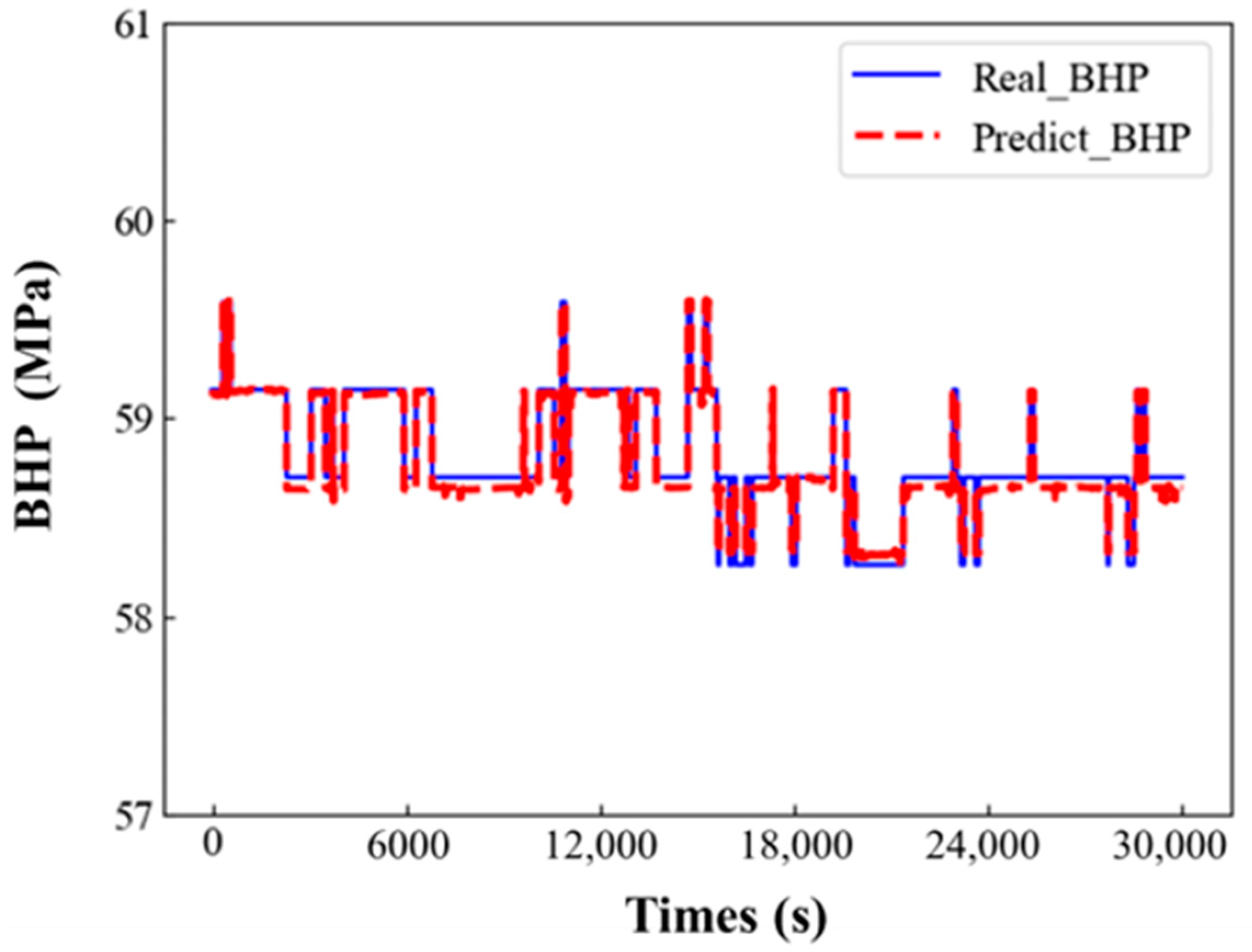
3.1. Model Performance Analysis
3.2. Model Interpretability
3.3. Model Comparison
3.4. Ablation Study
- IHGLN-w/o GL: Replacing the Graph Learning (GL) module with a fixed, identity adjacency matrix I.
- IHGLN-w/LSTM: Replacing the TCN with a standard LSTM layer (maintaining similar parameter counts).
- IHGLN-w/o Feature-Temporal Fusion: Simplifying the Feature Relationship Extraction Module by feeding the TCN output directly to the final Fully Connected layer.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BHP | Bottomhole pressure |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| IHGLN | Improved hybrid graph learning network |
| Conv | Convolution |
| TCN | Temporal convolutional network |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Song, X.; Su, Y.; Li, G.; Han, L. Bottom Hole Pressure Prediction Based on Hybrid Neural Networks and Bayesian Optimization. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 3712–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, X.; Tian, S.; Zhu, Z. Intelligent Drilling and Completion: A Review. Engineering 2022, 18, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, D.; Liu, J. Multi-Objective Sidetracking Horizontal Well Trajectory Optimization in Cluster Wells Based on DS Algorithm. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 147, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, C.; Gao, L. Multi-Objective Cellular Particle Swarm Optimization for Wellbore Trajectory Design. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Song, X.; Cui, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Fu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D. Intelligent Kick Warning Based on Drilling Activity Classification. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Song, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, X.; Hemmati, A.; Verma, S. Wellbore Pressure Inversion Model Based on Wavelet Analysis During Gas Kick. SPE J. 2025, 30, 3416–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, Z.; Mahmoud, M.; Abdulraheem, A. Real-Time Prognosis of Flowing Bottom-Hole Pressure in a Vertical Well for a Multiphase Flow Using Computational Intelligence Techniques. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 1411–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Sheng, M.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Tian, S.; Li, G. Optimization of Fracturing Stages/Clusters in Horizontal Well Based on Unsupervised Clustering of Bottomhole Mechanical Specific Energy on the Bit. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2023, 10, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C. A Knowledge-Guided Temporal Graph Neural Network for Predicting Rate of Penetration in Complex Formations. SPE J. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, D.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Osei, A. Novel Method to Estimate Bottom Hole Pressure in Multiphase Flow Using Quasi-Monte Carlo Method. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference (IPTC), Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 13–14 January 2020; p. D021S050R001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, E.E.; Obomanu, T.; Sanni, S.E.; Olatunji, D.I.; Igbinedion, P. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Predicting the Dynamics of Bottom Hole Pressure for Under-Balanced Drilling: Extra Tree Compared with Feed Forward Neural Network Model. Petroleum 2022, 8, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Lv, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Gong, C. A Novel Hybrid Transfer Learning Method for Bottom Hole Pressure Prediction. In Proceedings of the ASME 2023 42nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering (OMAE 2023), Melbourne, Australia, 11–16 June 2023; Volume 9: Offshore Geotechnics; Petroleum Technology. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Xiao, X.; Shen, M.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y. TCGNN: Packet-Grained Network Traffic Classification via Graph Neural Networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Ryu, J.-G.; Kim, J. Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Network for Multivariate Multi-Step Ahead Time-Series Forecasting of Sea Temperature. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q.; Meng, L.; Gao, F. PM2.5-GNN: A Domain Knowledge Enhanced Graph Neural Network for PM2.5 Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 November 2020; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharroshan, M.; Khamehchi, E. Accurate Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods in Predicting Bottom-Hole Pressure in Multiphase Flow Wells, a Comparison Approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann Rüdiger 3σ-Rule for Outlier Detection from the Viewpoint of Geodetic Adjustment. J. Surv. Eng. 2013, 139, 157–165. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, B.; Lv, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, G.; Zhu, Z. Real-Time and Multi-Objective Optimization of Rate-of-Penetration Using Machine Learning Methods. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q. Research on Adaptive Prediction Model of Rate of Penetration under Dynamic Formation Conditions. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, C.; Vidal, R.; Reiter, A.; Hager, G.D. Temporal Convolutional Networks: A Unified Approach to Action Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops; Hua, G., Jégou, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-Generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measured Depth (m) | Fixed Vertical Depth (m) | Stand Pipe Pressure (MPa) | Inlet Flow Rate (L/s) | Rotary Speed (rpm) | Outlet Flow Rate (L/s) | Back-Pressure Pump Flow Rate (L/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 6087.99 | 4935.39 | 19.37 | 13.75 | 11.68 | 13.74 | 8.84 |
| Min | 5832.82 | 4930.15 | 16.54 | 13.30 | 6.28 | 13.40 | 6.78 |
| Max | 6705.78 | 4942.07 | 22.17 | 19.47 | 23.50 | 19.47 | 10.78 |
| Outlet Density (g/cm3) | Total Pool Volume (m3) | Drilling Fluid Density (g/cm3) | Outlet Temperature (℃) | Funnel Viscosity (s) | Sand Content (%) | BHP (MPa) | |
| Mean | 1.19 | 146.44 | 1.1 | 51 | 44 | 0.2 | 58.58 |
| Min | 1.17 | 124.38 | 1.1 | 50 | 43 | 0.2 | 56.94 |
| Max | 1.82 | 175.23 | 1.2 | 52 | 45 | 0.2 | 59.58 |
| Hyperparameter | Optimal Values |
|---|---|
| Channels | (16, 32, 64) |
| Fully connected neurons | (8, 16, 32, 64) |
| Dropout | (0.1, 0.2, 0.3) |
| Learning rate | (0.01, 0.001, 0.0001) |
| Epoch | (50, 80, 100) |
| Model | MAPE (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| IHGLN | 1.28 ± 0.03 | 0.9563 ± 0.0031 |
| MLP | 15.36 ± 0.13 | 0.8894 ± 0.0043 |
| CNN | 8.30 ± 0.08 | 0.8572 ± 0.0056 |
| LSTM | 4.12 ± 0.06 | 0.8991 ± 0.0039 |
| TCN | 4.01 ± 0.05 | 0.9013 ± 0.0032 |
| CNN-LSTM | 2.93 ± 0.03 | 0.9190 ± 0.0032 |
| Models | MAPE (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| w/o GL | 1.85 | 0.9320 |
| w/LSTM | 1.51 | 0.9450 |
| w/o Feature-Temporal Fusion | 1.76 | 0.9365 |
| IHGLN | 1.28 | 0.9563 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ma, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, C. Real-Time Prediction of Bottom Hole Pressure via Graph Neural Network. Processes 2025, 13, 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13124081
Pang Z, Zhang R, Ma M, Wang H, Li Q, Wang C. Real-Time Prediction of Bottom Hole Pressure via Graph Neural Network. Processes. 2025; 13(12):4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13124081
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Zhaoyu, Rui Zhang, Mengnan Ma, Haizhu Wang, Qihao Li, and Chaochen Wang. 2025. "Real-Time Prediction of Bottom Hole Pressure via Graph Neural Network" Processes 13, no. 12: 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13124081
APA StylePang, Z., Zhang, R., Ma, M., Wang, H., Li, Q., & Wang, C. (2025). Real-Time Prediction of Bottom Hole Pressure via Graph Neural Network. Processes, 13(12), 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13124081





