Abstract
Ammonia stripping has been widely used to recover ammonia nitrogen from biogas slurry; however, the inhibitory effects on biogas production cannot be fully eliminated if ammonia-stripped biogas slurry (ASBS) is recycled back to the high-solid anaerobic digestion (AD) of animal wastes. This study investigated the performance of swine manure AD with recycling of ASBS and confirmed that there was no positive effect on increasing biogas production for ASBS recycling in the swine manure AD system under high solids (15%). The lowest accumulated methane yield was 133.9 mL/g-VS when swine waste was diluted with only raw biogas slurry (RBS), which was 9.2% lower than that of the water group (C0). Notably, the performance of AD was enhanced by adding rice husk biochar (RHB), waste iron powder (WIP), or their combination with ammonia-stripped biogas slurry (ASBS) reflux in the swine manure AD system. By adding 9.0 g/L of RHB, the biogas yield increased by 21.1%, and the total ammonia concentration (TAN) reduced by 15.1% compared to ASBS reflux alone (C1). The methane content reached a maximum of 75.2%, which was 12.8% higher than C1, while the methane yield was 1.5-times higher with the addition of 9.0 g/L of WIP. Correspondingly, the TAN was reduced, while the degradation of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) increased. Both WIP and RHB can provide great potential to reuse biogas slurry in AD with a higher biogas yield and organic degradation rate. This approach facilitates source reduction in biogas slurry and nutrient recovery, while providing insights for reducing water consumption in manure treatment processes and enhancing biogas production efficiency.
1. Introduction
Anaerobic digestion (AD) has played a significant role in the development of renewable energy and the improvement of rural environments around the world [1,2]. Large-scale AD plants generate substantial quantities of biogas slurry as a by-product, with each cubic meter of biogas accompanied by approximately 50~100 kg of slurry [3]. However, the current treatment and utilization of biogas slurry still lack standardized procedures. Due to transportation costs, biogas slurry cannot be widely applied to agricultural land as fertilizer for crop production. Local farms especially have limited land for biogas slurry use; thus, it is necessary to reduce the discharge of biogas slurry from large-scale AD plants [4].
Biogas slurry recycling in AD systems has been regarded as one of the most economical and effective methods to reduce the discharge of biogas slurry. Biogas slurry can be used to replace water by diluting the substrate to an appropriate solid concentration [5,6]. The implementation of this methodology has the dual benefits of reducing biogas slurry treatment costs and enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the AD system. Theoretically, recycling of biogas slurry has the potential to enhance biogas yield by returning methanogens and water to the AD system, thereby promoting water conservation [7,8]. For example, it was determined that recycling biogas slurry in co-digestion of cow manure and steam-exploded Salix resulted in a 16% increase in methane production [9]. However, if the substrate contains nitrogen-rich materials, there might be some detrimental effects on the recycled biogas slurry AD system. Some studies found that recycling biogas slurry did not increase the methane yield; for example, methane production decreased by 43% due to excessive ammonia accumulation in the chicken manure AD system [10]. Therefore, inhibitory factors should be removed from biogas slurry before it is recycled back into an AD system.
Ammonia is one of the important inhibitory factors in the AD system, which ranges from 500 mg/L to 5000 mg/L in biogas slurry after AD of animal manure [11,12]. Ammonia nitrogen can be removed from biogas slurry via the ammonia stripping process to mitigate ammonia inhibition. The ammonia stripping technology has been widely used in Europe due to low investment and the simple method [13,14,15]. Although ammonia stripping can remove some ammonia nitrogen inhibition in the AD system, biogas slurry recycling may cause other problems, such as volatile acids, viscosity, and high ion concentration, which will cause AD inhibition [16]. Therefore, the recycling of ammonia-stripped biogas slurry in the AD system needs to be further investigated, and technology needs to be developed to overcome inhibition and achieve higher biogas yields.
The introduction of appropriate additives improves microbial activity in anaerobic fermentation systems but also reduces the concentration of inhibitory substances and improves the performance of the system in terms of gas production. Waste iron powder (WIP) and biochar might be used to stimulate the microbial activity in the AD system and reduce the concentration of inhibitory products. WIP produced by metal processing plants is sold for a low price and contains various valent iron ions. It was reported that the clean scrap iron powder could enhance the methane yield compared to the addition of zero-valent iron; however, the rusty scrap iron powder could further enhance the methane yield [17,18]. As iron plays an important role in the growth of microorganisms, its deficiency can impair the growth of methanogenic bacteria and propionic acid-oxidizing bacteria [19]. Researchers promoted butyric acid conversion by adding zero-valent iron to a kitchen waste fermentation system, resulting in methane production of up to 380 mL/g-VS [20]. In addition, trivalent iron ions can effectively reduce the concentration of ammonia nitrogen and decrease its inhibitory effect. The findings demonstrated that the incorporation of trivalent iron ions triggered the sustained occurrence of Feammox reactive oxidation within the AD systems. Furthermore, the TAN in the Fe(OH)3-added reactor exhibited a maximum of 20.1% [21]. Waste iron filings are considered an ideal additive due to their inclusion of multivalent iron ions and their low cost.
Due to its loose and porous structure, biochar is used as an additive material to improve anaerobic digestion performance. Researchers have also extensively summarized the impact of biochar on AD performance and its promotion mechanism, including CH4 production improvement and enhancement. AD system stability, shortening the lag period of biogas production, and upgrading biogas purification are important [22,23,24]. Especially under extreme conditions, it is effective in releasing the inhibition of harmful substances in the AD system, including ammonia inhibition, sulfide inhibition, volatile fatty acid accumulation, heavy metal accumulation and other issues [25,26,27,28]. Biochar is also capable of improving soil characteristics and affecting the redox process of the soil that will eventually improve plant growth [29]. Furthermore, as China is one of the world’s largest rice producers, biochar can be produced at low cost from rice husk waste. Therefore, the combination of biochar and WIP as composite additives in the AD system could provide a sustainable solution for the recycling of ammonia-stripped biogas slurry by both mitigating AD inhibition and improving soil quality. So far, to our best knowledge, this is the first time such sustainable solutions for biogas slurry recycling have been explored.
This study systematically evaluated the effects of recycling biogas slurry both before and after ammonia stripping on the AD performance of swine manure under thermophilic and high-solid conditions. To enhance system performance, rice husk biochar (RHB) and waste iron powder (WIP) were introduced into the AD system alongside recycled ammonia-stripped biogas slurry (ASBS). We also evaluated the effect of different addition concentrations on enhancing the biogas production potential. These findings provide a scientific basis for the utilization of biogas slurry in AD processes, thus supporting the development of strategies to reduce biogas slurry and improve overall treatment efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
The biogas slurry was collected from a biogas plant at Ezhou Hubei Swine Farm (Ezhou, China). Stripping was performed at 75 °C with an ambient air flow rate of 600 L/h, and the operational time was 5 h. The physical and chemical properties of the raw biogas slurry (RBS) and ammonia-stripped biogas slurry (ASBS), including total ammonia nitrogen (TAN), total solid content (TS), total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD), pH value, and total phosphorus (TP), are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of experimental materials.
The swine manure with a TS content of 28.2% and a VS content of 22.8% was used as feedstock for AD batch experiments. It was collected from a swine farm at Huazhong Agricultural University (Wuhan, China). The inoculum, which had a TS content of 7.4%, was taken from the biogas plant at Hubei Ezhou Swine Farm. The WIP was obtained from the manufacturing facility at Huazhong Agricultural University. The RHB was obtained from the processing facility at Huazhong Agricultural University via pyrolysis of the rice husks at 550 °C. To ensure uniform particle size and eliminate biological interference, all WIP and RHB were sieved through the 40 meshes, then dried in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h, after which they were exposed to ultraviolet light for 30 minutes before being added to the anaerobic digestion system.
2.2. Experimental Set-Up and Operation
To study the effect of biogas slurry recycling before and after ammonia stripping on AD performance, swine manure was diluted using the ASBS and RBS for the experiments, and resulting groups were defined as C1 and C2. Swine manure diluted with distilled water was used as the control (C0). Triplicates were conducted for each experiment.
Since the aforementioned experimental results showed that the methane yield of the ASBS was lower than that of the control (C0), further experiments were conducted to further optimize the biogas yield of the ASBS with the addition of WIP and RHB. Six groups were experimentally tested at 3 different doses of 3.0 g/L, 6.0 g/L and 9.0 g/L, with the addition of RHB and WIP, respectively. These levels were chosen based on previous studies of the AD process [18,30]. Meanwhile, the effects of mixing RHB and WIP in a 1:1 TS ratio with doses of 3.0 g/L and 6.0 g/L were also investigated. The detailed experimental parameters are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental scheme of RHB and WIP addition.
All the AD experiments were conducted at a TS content of 15% and a temperature of 55 ± 2 °C. The digester volume was 500 mL, with 400 mL workspace. The inoculum ratio was 40% (volume by volume—v/v), and the hydraulic retention time was 20 days. To maintain an anaerobic environment in the reactors, oxygen was removed from the headspace using flushed nitrogen. The biogas volumes, content and liquid samples were collected for further analysis periodically.
2.3. Analytical Methods
TS content and VS content were determined according to the procedures described by the American Public Health Association (2005) [31]. The pH value was measured using Mettler Toledo FE28 pH meter (Metier Toledo, Shanghai, China). TCOD was measured with a CM-03 COD meter (Beijing Shuanghui Jingcheng Electronics Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The TAN concentration was determined via salicylic acid spectrophotometry, and TP concentration was tested via ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry using a Smartchem 200 Discrete Auto Analyzer (AMS Alliance, Paris, France). The drainage method was used to measure the biogas volume [32]. Methane content was analyzed via gas chromatography (GC9790II, Zhejiang Fuli Analytical Instruments, Taizhou, China) manufactured with a TCD detector and a 1.5 m stainless-steel column (Hayesep Q, Lanzhou Atech Technologies, Lanzhou, China). The injector, oven, and detector temperatures were adjusted at 55, 50 and 100 °C, respectively. Argon (Wuhan Minghui Gas Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China), at a flow rate of 30 mL/min, was used as a carrier gas. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) were measured using GC9790II, manufactured with a FID detector and a KB-WAX capillary column 30 m × 0.32 mm × 0.25 μm. The injector, oven and detector temperatures were adjusted at 250, 130 and 280 °C, respectively. Nitrogen (Wuhan Minghui Gas Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) was used as a carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1. All liquid samples were filtered through 0.22 μm membrane filter before injection. Changes in morphological structure of straw fibers were examined using SEM (JSM6390LV, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). FTIR was carried out using a Nicolet Avatar 330FT-IR (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Madison, WI, USA) at 4000 and 400 cm−1 spectra range.
2.4. Data Analysis and Calculations
Free ammonia concentration (FAN) was calculated from ideal equilibrium equation (Equation (1)) [33]:
Here, and are the free (NH3) and total ammonia (NH3 + [NH4+-N]aq) concentrations, respectively, mg/L; t is temperature, °C.
TS degradation rate (TSt, %) was calculated using Equation (2) [33].
Here, TSf is the TS of the feed, %; TSd is the TS of the digestate, %.
All experiments were performed in triplicate, and results were calculated as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). And one-way ANOVA followed by LSD test was applied at a probability level (p) ≤ 0.05 using SPSS (IBM SPSS Statistics 20) in order to assess the significant differences between treatments.
3. Results
3.1. AD Performance with Different Biogas Slurry Reflux
As illustrated in Figure 1, the daily methane yield peaked around the sixth day of the AD process. C0 exhibited the highest accumulated methane yield of 146.3 mL/g-VS. The methane yield was 143.3 mL/g-VS with the ASBS reflux (C1), which was 2.4% less than that of C0. The lowest accumulated methane yield was 133.9 mL/g-VS with the RBS reflux (C2), which was 9.2% lower than that of the C0. The average methane content of C0, C1, and C2 was 63.6%, 64.3%, and 62.4%, respectively, with no significant difference (p > 0.05). It also reported that the specific methane productions (SMPs) were reduced by only 5% when cow manure was used as the substrate for AD with ASBS refluxing [8]. Similar results were obtained when the researcher reused the ASBS in a chicken manure AD system [34]. ASBS can replace fresh water as feed water distribution for the AD system; improving the performance of biogas production requires more in-depth research.
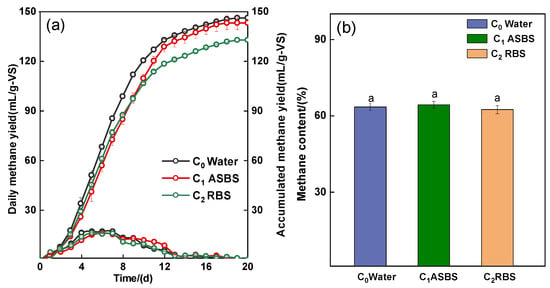
Figure 1.
Daily methane yield and accumulated methane yield. (a) Methane content (b) for AD with difference biogas slurry reflux. Intergroup differences were tested with statistical significance set at p ≤ 0.05.
The TAN, FAN concentration, pH value and TS degradation rate of AD with biogas slurry reflux are shown in Figure 2. The initial TAN concentration of C0 was 999.60 mg/L with a FAN concentration of 46.6 mg/L at pH 7.1. The TAN concentration rose to 1653 mg/L and 1126 mg/L, and pH rose to 7.5 and 7.8 with RBS and ASBS reflux, respectively. A positive correlation was observed between the FAN concentration and pH value, as indicated by Equation (1). Although most of the TAN was removed via ammonia stripping, the higher pH resulted in a higher FAN concentration of 221.9 mg/L with ASBS reflux (compared to only 163.2 mg/L with RBS reuse). FAN is the most toxic component of TAN, as it can directly penetrate cell membranes. The toxic range is between 150 and 1200 mg/L, depending on AD conditions (e.g., substrate, inoculum acclimatization) [35]. At the end of AD, the TAN concentration reached 2552 mg/L and 2188 mg/L, with a FAN concentration of 227 and 293 mg/L with RBS and ASBS reflux, respectively. It may cause potential ammonia toxicity during AD with ASBS reflux. It found that ammonia inhibition occurred at a TAN concentration of 1.8–2.4 g/L, which corresponded to a threshold concentration of 10% TS for dairy manure thermophilic AD [36]. To enhance biogas productivity, further mitigation of ammonia inhibition is needed for ASBS recycling.
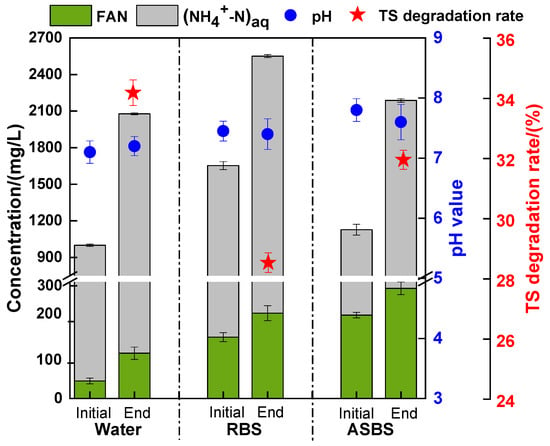
Figure 2.
pH value, calculated FAN concentration, (NH4+-N)aq concentration and TS degradation rate with difference biogas slurry reflux.
A decrease in the TAN concentration corresponded to an increase in the degradation rate of TS in the AD system. The degradation rate of TS was 32.0% with ASBS recycling, while it was only 28.5% with RBS recycling. This suggests that there is better potential for the biogas yield with ASBS recycling, because of the higher substrate degradation rate. In subsequent experiments, the optimization methods for mitigating the inhibition of the ASBS through additives to enhance biogas productivity were discussed.
3.2. Biogas Performance for ASBS Reflux with RHB and WIP Addition
Biogas yield performance was enhanced significantly with RHB and WIP addition, with performance increasing in correlation with the amendment concentration, as illustrated in Figure 3. The daily biogas yield reached the maximum at the 9th to 10th days in all experiments. The maximum daily biogas yield reached 41.3 mL/g-VS by adding 9.0 g/L WIP, while it was just 22.4 mL/g-VS on the 10th day of C1, shown in Figure 3a. With an increase in the dosage of WIP, the accumulated biogas yields also showed an increasing trend. The accumulated biogas yield was only 219.1 mL/g-VS with RSBS reflux, whereas the accumulated biogas yield reached 248.9, 265.2, and 292.6 mL/g-VS, which was 13.6%, 21.1% and 33.6% higher than that of the C1 with WIP addition of 3.0, 6.0 and 9.0 g/L, respectively. Also, the percentage of methane in the biogas increased significantly (p ≤ 0.05) with WIP addition (Table 3). The methane content reached a maximum of 75.2%, which was 12.8% higher than that of the C1, while the methane yield was increased 1.5-times by adding WIP of 9.0 g/L. This result indicated that WIP can significantly enhance the biogas production performance of ASBS reflux [19].
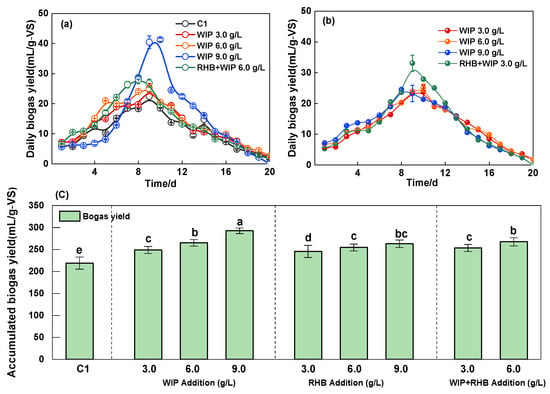
Figure 3.
Effects of different doses of WIP and RHB on biogas yield. Daily biogas yield with WIP addition (a), daily biogas yield with RHB addition (b). Accumulated biogas yield with WIP and RHB addition (c). Intergroup differences were tested with statistical significance set at p ≤ 0.05.

Table 3.
Biogas and methane yield when different additives are used in AD system.
It reported that the stimulating effects of iron on anaerobes were a major contributor to CH4 production, and CH4 production increased by 10.1% and 21.4% when 10.0 gFe/L waste iron scraps were added in the sludge acidogenic phase and methanogenic phase, respectively [37]. Moreover, zero-valent iron accelerated the recovery of the methanogenic activity, which was suppressed by the heat pretreatment. The biogas yield was 47.3% higher than that of the control by adding scrap iron of 10.0 g/L to AD. WIP contains a variety of valent iron ions, and different valent iron ions have different effects on the AD system. Zero-valent iron can directly participate in chemical reactions to produce hydrogen and methane, thereby increasing methane production and reducing carbon dioxide production (Equations (3) and (4)) [38]. It also reported that 1.0 g/L of microscale waste iron (20 μm) improved CH4 yields by 56.89% and enhanced the rate of hydrolysis (k) by 24.6% in AD of dairy manure [39].
8H+ + 4Fe0 + CO2→CH4 + 4Fe2+ + 2H2O
Fe0 + 2H2O→H2 + Fe2+ + 2OH−
For RHB addition, the accumulated biogas yield reached 245.7, 254.6, and 263.2 mL/g-VS, which was 12.1%, 16.2% and 20.1% higher than that of the C1 (Figure 3c), while the percentage of methane reached 67.2%, 69.8% and 70.5% (Table 3) with RHB addition of 3.0, 6.0 and 9.0 g/L, respectively. This result indicated that RHB has played a positive role in the recovery of methanogenic activity, which was suppressed by ASBS reuse. Methanogenic performance is statistically controlled by feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature and biochar concentration [40]. SMPs were mildly elevated with the addition of biochar by 7.9%, 9.4%, and 12.0% for bamboo, rice husk, and pecan shell-derived biochar additions, respectively, on mesophilic dry Co-AD (15%) batch digesters fed with pig manure and food [23].
The technical digestion time (T80) is defined as the time required to reach 80% of total biogas yield. T80 can be used to indicate the rate of biogas yield and the digestibility of the substrate [41]. Noteworthily, AD in the current study lasted up to 20 days, while T80 for C1 and the group of 3.0 g/L RHB addition were both 14 d, and others were 13 d. These results reflect that it has no positive effect on shortening the digestion time with a small amount of RHB addition via the ASBS reuse in thermophilic high AD. However, there is a significant difference between others. They found biochar shortened the lag phases of H2 and CH4 production in two-phase mesophilic AD of food waste [42]. The reason is that biochar is more conducive to improving the performance of mesophilic AD, compared with thermophilic AD, due to the weak adaptability of initial microflora to the temperature changes [43].
The accumulated biogas yield of the combination of WIP and RHB was 243.7 mL/g-VS of 3.0 g/L and 257.4 mL/g-VS. In the WIP and RHB of the 6.0 g/L group, which was 11.2% and 12.9% higher than that of C1, respectively, the investigation revealed no statistically significant discrepancy in biogas yield between the combined utilization of WIP and RHB and the isolated use of WIP (p > 0.05). However, a notable increase in the biogas yield was observed when RHB was used in isolation at an addition rate of 6.0 g/L (p ≤ 0.05). This could be speculated to have a synergistic effect when WIP and RHB are added at the same time in the AD system. WIP and RHB synergy promotes bacterial community reproduction and electron transfer to the flora in the AD system, while the porous structure of biochar provides a carrier for the flora; the scrap iron participates in the reaction and stimulates the enzyme activity by releasing electrons [42]. This finding enables the combination of WIP and RHB as composite additives, which have the capacity to mitigate AD inhibition and enhance soil quality.
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of AD for ASBS Reflux with RHB and WIP Addition
3.3.1. VFA Concentration and pH Value
Although VFAs are the main source of methane production and play an important role in the AD process, they are also regarded as one of the inhibitory factors for the instability of the AD system. The rapid accumulation of VFAs caused a rapid drop in the system pH, thereby inhibiting the activity of methanogens [27]. The initial pH level was 7.8–7.9 with ASBS reflux in the AD system (Figure 4). The VFA concentration decreased with WIP and RHB addition (Figure 4). On the 10th day, there was a significant reduction in the VFA concentration due to the effect of WIP. The addition of 9.0 g/L WIP reduced the VFA concentration by 22.6% compared to C1, resulting in a final VFA concentration of 3576 mg/L. Correspondingly, the pH was 7.0 with 9.0 g/L RHB addition, while the pH of C1 decreased to 6.3. This indicates that there was a better buffering effect on the pH of the AD system when WIP was added, which agrees with the results in the literature. The decrease in VFAs was attributable to the enrichment of hydrogen-trophic methanogens caused by WIP, in addition to the promotion of zoster bacteria reproduction, which accelerated the consumption of VFAs and the oxidation of propionic acid [37].
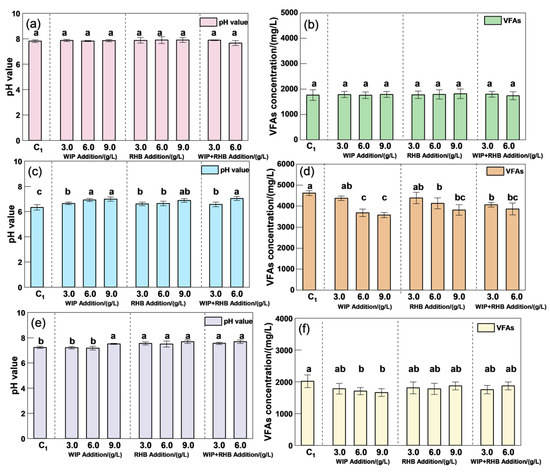
Figure 4.
Effects of different doses of RHB and WIP addition on pH value and VFA concentration. The initial pH value (a). The initial VFA concentration (b). The 10th day of the pH value (c). The 10th day of the VFA concentration (d). The final pH value (e). The final VFA concentration (f). Intergroup differences were tested with statistical significance set at p ≤ 0.05.
The addition of 9.0 g/L RHB resulted in the minimum VFA accumulation (3816 mg/L), representing a 17.4% reduction compared to C1. From the following chemical reaction (Equation (5)), the alkaline metal ions, including Ca, K, Na, and Mg, in biochar increased the buffering capacity of the system [43]. Moreover, the acidic and alkaline functional groups on the biochar can also provide a certain buffering capacity in solution. The degradation of intermediate acids was increased after adding biochar to the AD system [44].
Ca(Mg)CO3 + CxHyCOOH ↔ [CxHyCOO]2Ca(Mg) + H2O+ CO2
The addition of both WIP and RHB significantly reduced the VFA concentration to ranges of 1662~1784 mg/L and 1778~1872 mg/L, respectively, substantially lower than C1 (2019 mg/L). It showed that the WIP and RHB can effectively alleviate the accumulation of VFAs when the ASBS is recycled, thereby making the biogas production of the AD system more stable.
3.3.2. TAN Concentration
Ammonia is gradually released as a by-product from the proteins after they decompose in AD of animal manure. The TAN concentration is shown in Figure 5. The initial TAN concentration was between 1326 mg/L and 1420 mg/L in each experiment. There was no significant difference between the experiments (p > 0.05). On the 10th day, the TAN concentration of C1 reached 1809.5 mg/L, while the TAN concentration showed a decreasing trend with WIP and RHB addition. The TAN concentration was 1737 mg/L, 1664 mg/L, 1655 mg/L, respectively, with 3.0 g/L, 6.0 g/L, and 9.0 g/L WIP addition, which were 4.0%, 8.1%, and 8.6% lower than C1, respectively. And the final TAN concentration of C1 reached 2138 mg/L. The addition of 9.0 g/L WIP reduced the final TAN concentration to 1929 mg/L, which was 9.8% lower than C1. The reason for the lower TAN concentration with the addition of WIP may be that the trivalent iron reacts with the ammonia nitrogen ions (Equations (6) and (7)) in the biogas slurry. Furthermore, zero-valent iron has been demonstrated to encourage the formation of mineral precipitates with a high specific surface area, which are capable of adsorbing ammonia [17].
4Fe2O3 + NH4+ + 14H+→8Fe2+ + NO3− + 9H2O
3Fe(OH)3 + 5H+ + NH4+→3Fe2+ + 9H2O + 0.5N2
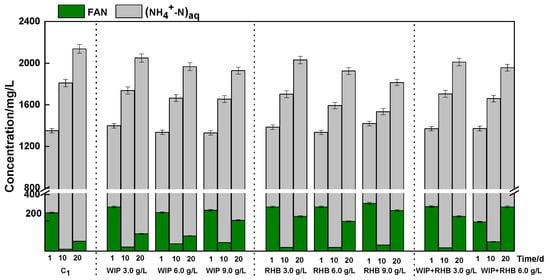
Figure 5.
Calculated FAN and (NH4+-N)aq concentration with different doses of WIP and RHB addition.
The addition of RHB resulted in a congruent trend of TAN alteration within the AD system, as observed in WIP, as illustrated in Figure 5. With the addition of 9.0 g/L RHB, the TAN concentration was 1534 mg/L, representing a 15.2% decrease compared to C1. At the microbiological level, biochar has been shown to promote cell fixation and facilitate the growth of microorganisms within an AD system [43]. Moreover, the addition of biochar has been demonstrated to enhance the ammonia tolerance of AD systems through the augmentation of ammonium ion adsorption capacity [45]. It can effectively delay the increase in TAN and with no inhibitory effects at a higher TAN concentration above 2450 mg/L by adding biochar in the AD system [46].
A major challenge of nitrogen-rich substrate AD is ammonia inhibition, which severely limits biogas production. Microorganisms involved in the process, particularly those in thermophilic systems, are highly sensitive to ammonia. This is exacerbated by thermophilic temperatures, which increase the proportion of free ammonia (FAN). FAN can freely penetrate microbial cell membranes, causing direct toxicity and disrupting cellular functions [47]. A key finding was that WIP and RHB addition, while lowering TAN, elevated pH and consequently increased FAN concentrations. At a dosage of 9.0 g/L, WIP and RHB amendments elevated FAN concentrations to 218 mg/L and 287 mg/L, representing increases of 67.49% and 75.38%, respectively, over C1. According to the FAN calculation formula (Equation (1)), this rise was directly attributable to the elevated pH resulting from higher WIP and RHB dosages. This observation is corroborated with findings from Kizito et al., 2022, who reported that the FAN concentration increased from 9.05 mg/L to 637.71 mg/L with an increase in biochar dosage, with the pH value increased from 7 to 35% [33]. A high FAN concentration in the range of (>500 mg/L) is considered to have a greater negative effect on the AD process because it can suppress methane-producing organisms [48]. It is noteworthy that, despite the final FAN (<300 mg/L) in this study not reaching the established inhibition threshold, the alkaline properties of biochar caused an increase in pH in reactors where biochar was added, suggesting a potential hazard that cannot be disregarded in the context of the AD systems operating over extended periods.
3.3.3. TCOD Concentration and TS Degradation Rate
The decrease in TCOD is attributable to the production of VFAs, methane, and carbon dioxide and is an important criterion for the degradation rate of the substrate. As shown in Figure 6, the TCOD concentration in the AD system exhibited a downward trend concomitant with an increase in digestion time. The initial concentration of TCOD utilized in each experiment was approximately 85,000 mg/L, with no statistically significant variation (p > 0.05). On the 10th day, the TCOD concentration of each experiment began to show a difference. The TCOD concentration of each experiment significantly decreased. The TCOD concentration of the C1 was 57,968 mg/L, in which the TCOD degradation rate was 30.9%, and the TS degradation rate was 27.5%. After the addition of RHB and WIP, the TCOD concentration was lower than C1, and it decreased with the increase in dosage of RHB and WIP. The addition of 9.0 g/L RHB resulted in the lowest TCOD concentration after AD, which was 44,217 mg/L with 9.0 g/L RHB addition. The degradation rate was 52.8%, and the degradation rate of TS was 35.6%. The degradation rates of TCOD and TS were increased compared with the C1 by 21.9% and 8.1%, respectively.
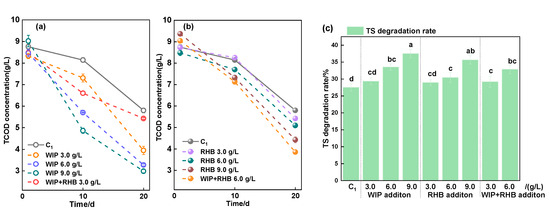
Figure 6.
TCOD concentration with different doses of WIP (a) and RHB (b) addition and TS degradation rate (c). Intergroup differences were tested with statistical significance set at p ≤ 0.05.
It increased the TCOD degradation rate from 22.6% to 37.0% when only zero-valent iron was added to the AD system [49]. In this study, the TCOD concentration reached the lowest value (29,861 mg/L) with 9.0 g/L WIP for the ASBS reuse AD system, the TCOD degradation rate increased from 30.9% to 66.9%, and the TS degradation rate increased from 27.52% to 37.5%, which corresponded to the biogas yield. Thus, with the addition of RHB and WIP to AD of swine manure with ASBS recycling, the degradation rates of TCOD and TS can be significantly improved.
3.4. Surface Changes in RHB and WIP and Analysis of Functional Groups in Swine Manure
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) were used to study the effects of AD with ASBS recycling on swine manure RHB and WIP (Figure 7). The relative amount of each functional group in swine manure before and after thermophilic AD was examined. The results showed that swine manure is mainly composed of organic compounds, such as sugars, proteins, lipids, phenols, etc. Among them, polysaccharides account for the highest content, which is similar to previous reports [50]. The main absorption peak near 3285 cm−1 is the intramolecular hydroxyl (O-H) stretching vibration band, which is related to the presence of cellulose and polysaccharides. The peak was weakened, suggesting that the degradation of cellulose in swine manure was enhanced by adding WIP and RHB to AD with the ASBS reflux. With the conversion of organic compounds to biogas during AD, the peak around 2024 cm−1 and 2850 cm−1 (C-Hx) was weakened, resulting in the degradation of fat in swine manure with WIP and RHB addition. The vibration peak around 1650 cm−1 (C=O, N-H) was related to the degradation of aromatic compounds and acyl compounds containing nitrogen in swine manure. The vibration peak around 1530 cm−1 (C=O, N-H) was related to the degradation of amino compounds. The weakened intensity of this band confirmed that degradation of protein and carbohydrate enhanced in swine manure by adding biochar and scrap iron in AD with the ASBS recycling.
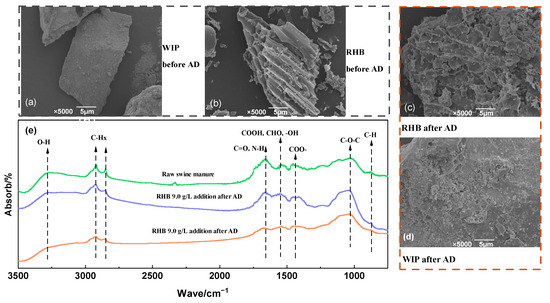
Figure 7.
SEM image and analysis of functional groups. SEM of WIP before AD (a), SEM of RHB before AD (b), SEM of RHB after AD (c). SEM of WIP after AD (d), FTIR of anaerobic digestate and swine manure (e).
There were differences in the microstructures of WIP and RHB before and after AD. Before AD, there was an obvious pore structure on the surface of the biochar. After AD, particulate attachment was generated on the surface of the biochar. This is because the bacterial flora adhered to the surface of the biochar during AD, and certain destructive effects occurred on the biochar surface. The surface of the WIP was smooth before AD; however, the surface of WIP became rough, with shedding after AD. This indicated that the scrap iron participated in biochemical reactions in AD, which resulted in an increase in the biogas yield and a decrease in the TAN concentration and the total VFAs.
4. Conclusions
This study confirmed that there was no positive effect on increasing methane production for the ASBS reflux in the thermophilic high-solid anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Methane yields decreased by 2.4% and 9.2% with the reflux of ASBS and RBS, respectively, while TAN concentrations increased significantly by 12.7% and 65.3%. Notably, amending with WIP or RHB markedly enhanced biogas production with ASBS reflux. At 9.0 g/L WIP, the accumulative biogas yield increased by 33.6% over C1; RHB at the same concentration also raised production by 20.7%, functioning as a microbial support and adsorbent. FTIR spectra revealed improved cellulose degradation in manure with both additives. Moreover, SEM imaging showed clear surface changes: WIP exhibited corrosion and flaking, confirming its reactivity, while RHB surfaces accumulated biofilm and granular deposits, evidencing active microbial colonization. These morphological and chemical insights jointly explain the enhanced gas production. Overall, the findings provide a practical strategy to reduce biogas slurry in large-scale biogas plants and to mitigate the inhibitory effects associated with biogas slurry reflux in the AD system.
Author Contributions
J.P.: Investigation, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft. X.Z.: Methodology, data curation, X.W.: Conceptualization, supervision, Z.L.: Validation, writing—review and editing. P.A.: Conceptualization, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Chongqing Rural Revitalization Project by Chongqing Agricultural and Rural Affairs, grant No. XCZX0036.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| SMPs | Specific methane productions |
| RBS | Raw biogas slurry |
| ASBS | Ammonia-stripped biogas slurry |
| WIP | Waste iron powder |
| RHB | Rice husk biochar |
| TS | Total solids |
| VS | Volatile solids |
| TAN | Total ammonia nitrogen |
| FAN | Free Ammonia |
| TCOD | Total chemical oxygen demand |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| VFAs | Volatile fatty acids |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Simeonov, I.; Chorukova, E.; Kabaivanova, L. Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion for Green Energy Production: A Review. Processes 2025, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Witaszek, K.; Dach, J. Current State of Development of Demand-Driven Biogas Plants in Poland. Processes 2025, 13, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.; Abomohra, A.E.F.; Ai, P.; Jin, K.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Acetogenesis and methanogenesis liquid digestates for pretreatment of rice straw: A holistic approach for efficient biomethane production and nutrient recycling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K. Anaerobic digestate management for carbon neutrality and fertilizer use: A review of current practices and future opportunities. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 180, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wu, B.; Yang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.L.; Qin, H.; Tan, F.R.; Ruan, Z.Y.; Ma, K.D.; et al. Replacing process water and nitrogen sources with biogas slurry during cellulosic ethanol production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Fei, S.; Yuan, H.R.; Zou, D.X.; Pang, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhu, B.N.; Chufo, W.A.; Jaffar, M.; Li, X.J. Influence of recirculation of liquid fraction of the digestate (LFD) on maize stover anaerobic digestion. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 127, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Liu, T.; Chu, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y. Effects of biogas slurry reflux mode and reflux rate on methane production by mixed anaerobic digestion of corn straw and pig manure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 411, 137214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, I.; Ma, J.; Frear, C.; Zhao, Q.; Ndegwa, P.; Yao, Y.; Kafle, G.K. Recycling separated liquid-effluent to dilute feedstock in anaerobic digestion of dairy manure. Energy 2017, 119, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, M.M.; Sapci, Z.; Linjordet, R.; Schnürer, A.; Morken, J. Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and steam-exploded Salix with recirculation of liquid digestate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 136, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ni, P.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Dach, J.; Dong, R. Integrated approach to sustain biogas production in anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under recycled utilization of liquid digestate: Dynamics of ammonium accumulation and mitigation control. Bioresour. Technol 2016, 205, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrbai, M.; Al-Dahidi, S.; Shboul, B.; Abusorra, M.; Hayajneh, H. Techno-economic feasibility study of ammonia recovery from sewage sludge digestate in wastewater treatment plants. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2024, 15, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Wu, X.-Q.; Zhao, Q.-B.; Yu, L.; Xie, J.-F.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhou, T.-T.; Li, J. Prediction and Optimization of Ammonia Removal in Direct Aeration Process Based on Wastewater Properties: An Integrated Experimental and Machine Learning Approach. ACS EST Eng. 2025, 5, 1760–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ruan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L. New progress of ammonia recovery during ammonia nitrogen removal from various wastewaters. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Singh, R.; Gurian, P.L.; Hendricks, A.; Kohl, P.; McKelvey, S.; Spatari, S. Life cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis of nitrogen recovery by ammonia air-stripping from wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakodeti, A.; Azman, S.; Rossi, B.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. A critical review of ammonia recovery from anaerobic digestate of organic wastes via stripping. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Lyu, T.; Sun, H.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Liquid digestate recycled utilization in anaerobic digestion of pig manure: Effect on methane production, system stability and heavy metal mobilization. Energy 2017, 141, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure by the Addition of Zero-Valent Iron. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 12441–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Shirai, T.; Yamashiro, T.; Yasui, S.; Iwasaki, M.; Ihara, I.; Nishida, T.; Tangtaweewipat, S.; Umetsu, K. Valorizing waste iron powder in biogas production: Hydrogen sulfide control and process performances. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 208, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, J.; Jing, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, C. Effects of waste rusted iron shavings on enhancing anaerobic digestion of food wastes and municipal sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S. Inhibiting excessive acidification using zero-valent iron in anaerobic digestion of food waste at high organic load rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Peng, H. Nitrogen removal during anaerobic digestion of wasted activated sludge under supplementing Fe (III) compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fang, W.; Liang, J.; Nabi, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G. Biochar application in anaerobic digestion: Performances, mechanisms, environmental assessment and circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Xie, S.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, J.; Wu, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, X. Stimulatory effects of biochar addition on dry anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste under mesophilic conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19212–19223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavali, M.; Libardi Junior, N.; de Almeida Mohedano, R.; Belli Filho, P.; da Costa, R.H.R.; de Castilhos Junior, A.B. Biochar and hydrochar in the context of anaerobic digestion for a circular approach: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Xu, C.; Huang, W.; Jiang, M.; Yan, J.; Fan, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Xiao, B.; Song, G. Improving anaerobic digestion of piggery wastewater by alleviating stress of ammonia using biochar derived from rice straw. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Mannina, G.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, L.; Ni, B.-J. Enhanced high-quality biomethane production from anaerobic digestion of primary sludge by corn stover biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Hu, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.-Q. The role of rice husk biochar addition in anaerobic digestion for sweet sorghum under high loading condition. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Tang, J.; Niu, Q. The dosage-effect of biochar on anaerobic digestion under the suppression of oily sludge: Performance variation, microbial community succession and potential detoxification mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Wang, J.-X.; Shi, Y.-X.; Guo, X.-P. Chemical stabilization remediation for heavy metals in contaminated soils on the latest decade: Available stabilizing materials and associated evaluation methods–A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wen, Q.; Chen, Z. Effect of KH2PO4-modified biochar on immobilization of Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn and as during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination for Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xi, J.; Ai, P.; Yu, L.; Zhai, H.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing ethanol production from thermophilic and mesophilic solid digestate using ozone combined with aqueous ammonia pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 2016, 207, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Jjagwe, J.; Mdondo, S.W.; Nagawa, C.B.; Bah, H.; Tumutegyereize, P. Synergetic effects of biochar addition on mesophilic and high total solids anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Jacobi, H.F.; Strach, K.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Liebetrau, J. Mono-fermentation of chicken manure: Ammonia inhibition and recirculation of the digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenigün, O.; Demirel, B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: A review. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yu, L.; Ghogare, R.; Dunsmoor, A.; Davaritouchaee, M.; Chen, S. Simultaneous ammonia stripping and anaerobic digestion for efficient thermophilic conversion of dairy manure at high solids concentration. Energy 2017, 141, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Wei, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Cao, D. Analysing the mechanisms of sludge digestion enhanced by iron. Water Res. 2017, 117, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, L.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Accelerated CO2 reduction to methane for energy by zero valent iron in oil reservoir production waters. Energy 2018, 147, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.; Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Ahmed, M.M.; Kotb, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamashiro, T.; Umetsu, K. Prospects for biogas production and H2S control from the anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: The influence of microscale waste iron powder and iron oxide nanoparticles. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lichtfouse, E.; Kumar, P.S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F. Biochar promotes methane production during anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3557–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jin, K.; Yi, R.; Chen, M.; Peng, J.; Pan, Y. Enhancement of bioenergy recovery from agricultural wastes through recycling of cellulosic alcoholic fermentation vinasse for anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyoto, N.M.S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of biochar addition on hydrogen and methane production in two-phase anaerobic digestion of aqueous carbohydrates food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, F.; Davaritouchaee, M. A review on biochar-mediated anaerobic digestion with enhanced methane recovery. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Lü, F.; Shao, L.; He, P. Application of eco-compatible biochar in anaerobic digestion to relieve acid stress and promote the selective colonization of functional microbes. Water Res. 2015, 68, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Wandera, S.M.; Guo, L.; Dong, R. Evaluation of ammonium adsorption in biochar-fixed beds for treatment of anaerobically digested swine slurry: Experimental optimization and modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, A.S.; Xu, H.; Chang, F.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Ali, N.; Ding, S.; Wang, K. Effect of biochar on reactor performance and methane generation during the anaerobic digestion of food waste treatment at long-run operations. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, R.; Grohmann, E.; Krakat, N. Anaerobic digestion of nitrogen rich poultry manure: Impact of thermophilic biogas process on metal release and microbial resistances. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiao, F.; Yan, M.; Tang, S.; Duan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of ammonia on anaerobic digestion: Focusing on energy flow and electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Quan, X. Zero-valent iron enhanced methanogenic activity in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge after heat and alkali pretreatment. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, F.Y.; Wang, J.F. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the composition of DOM in manure-derived biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).