Influence of Tectonic Movements on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Dongying Formation, Western Bohai Bay Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
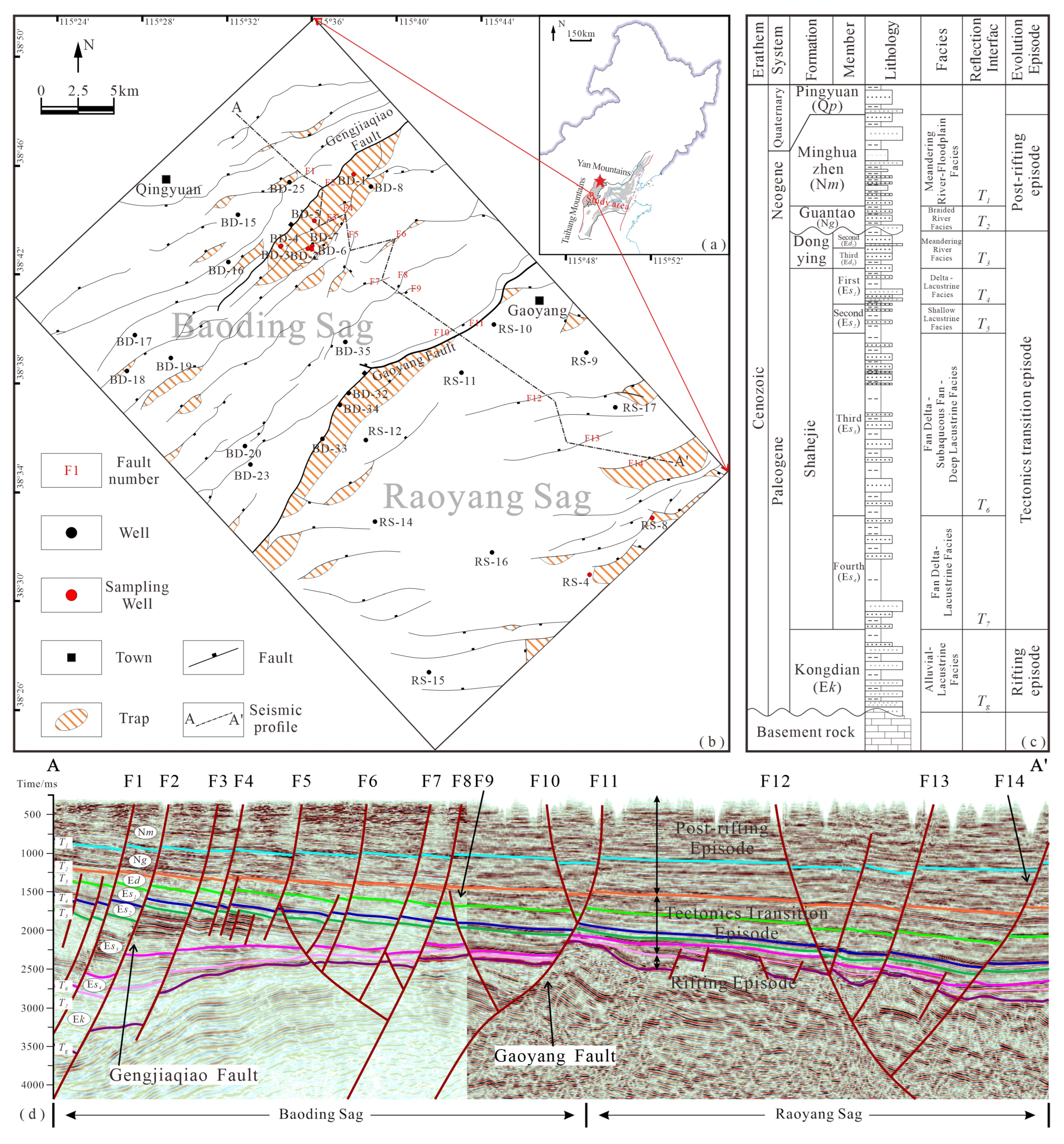
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
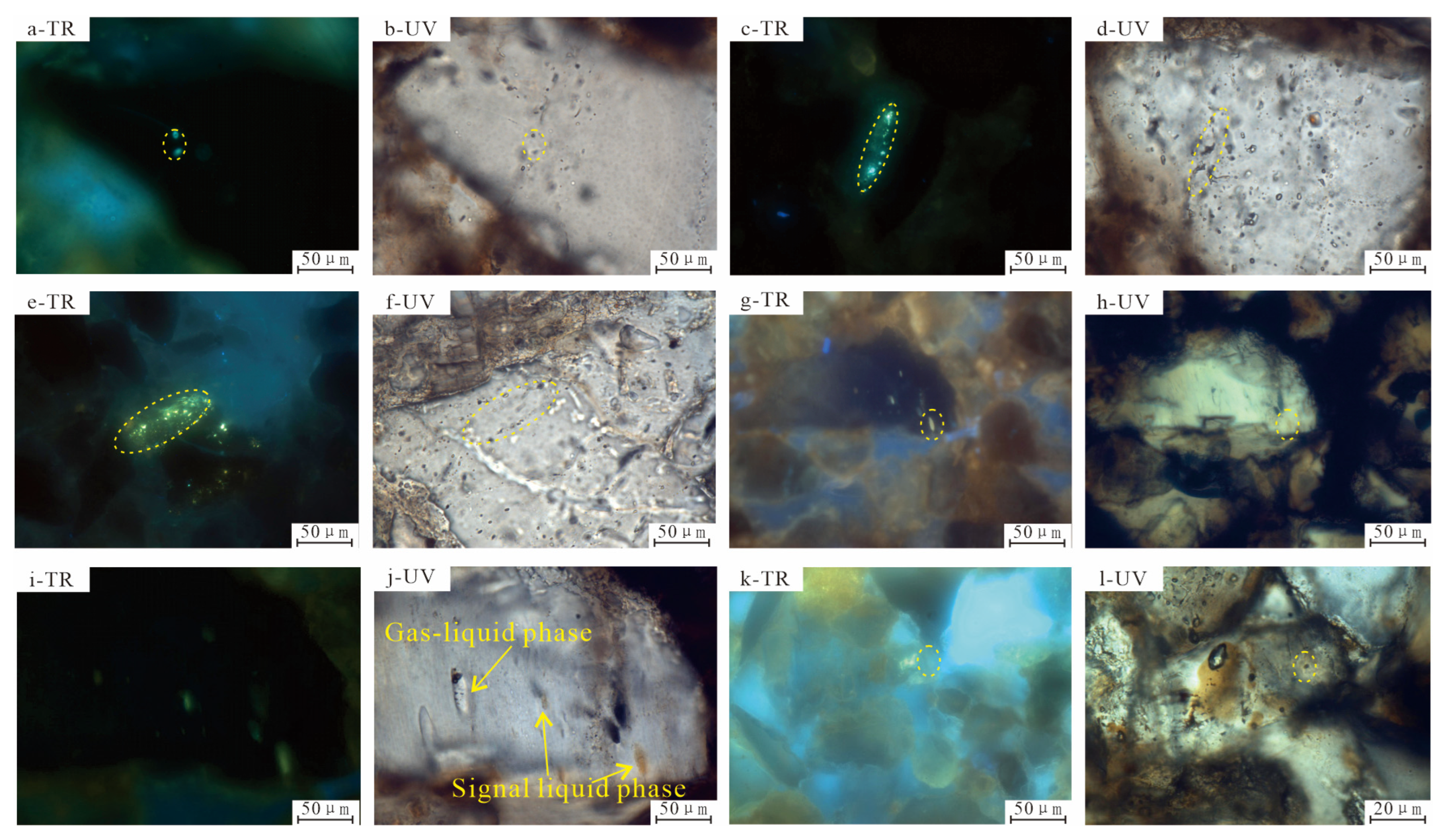
3.1. Fluid Inclusion Testing
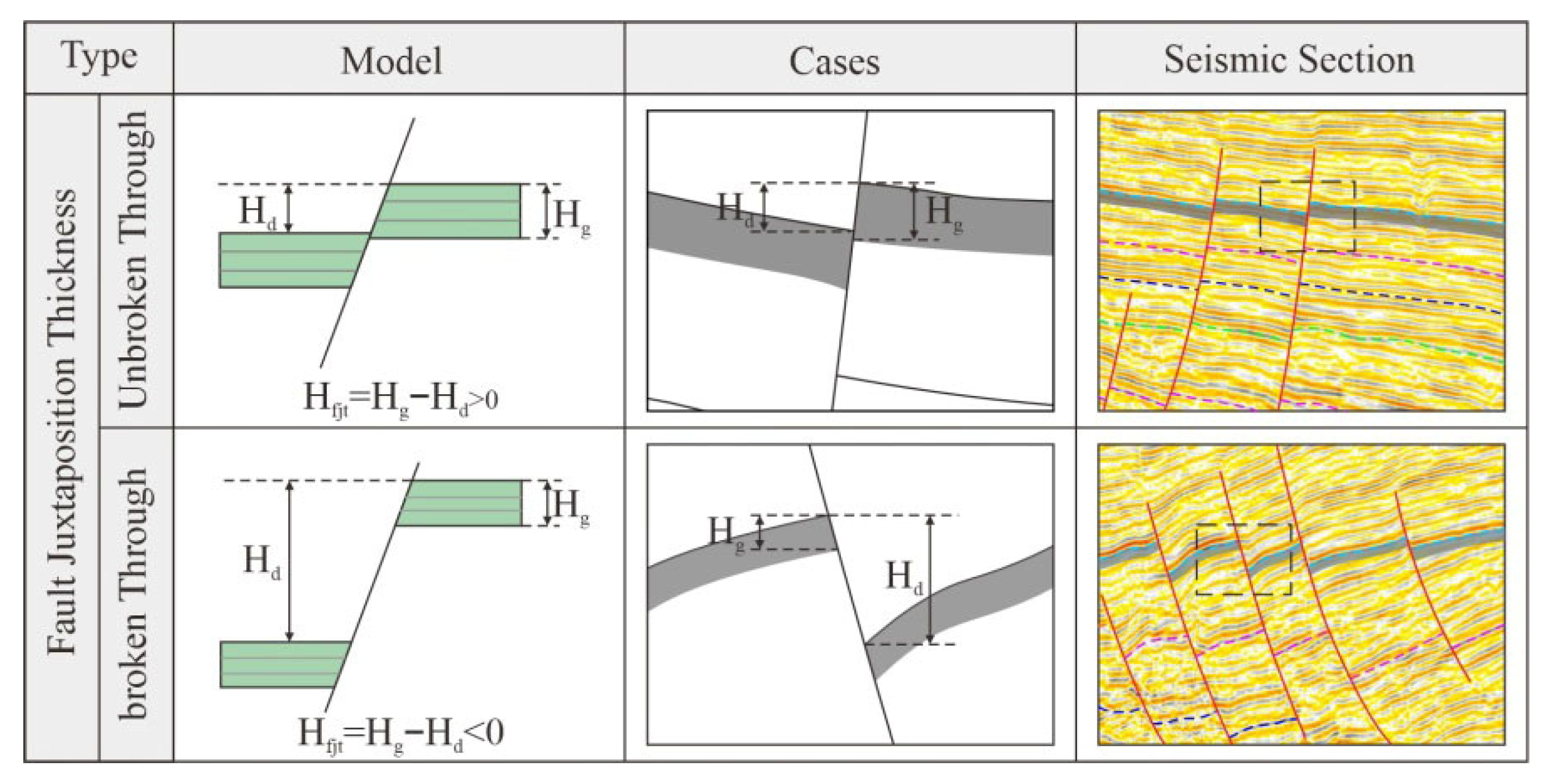
3.2. Fault–Cap Sealing Properties Estimation
4. Results
4.1. Fluid Inclusion Character
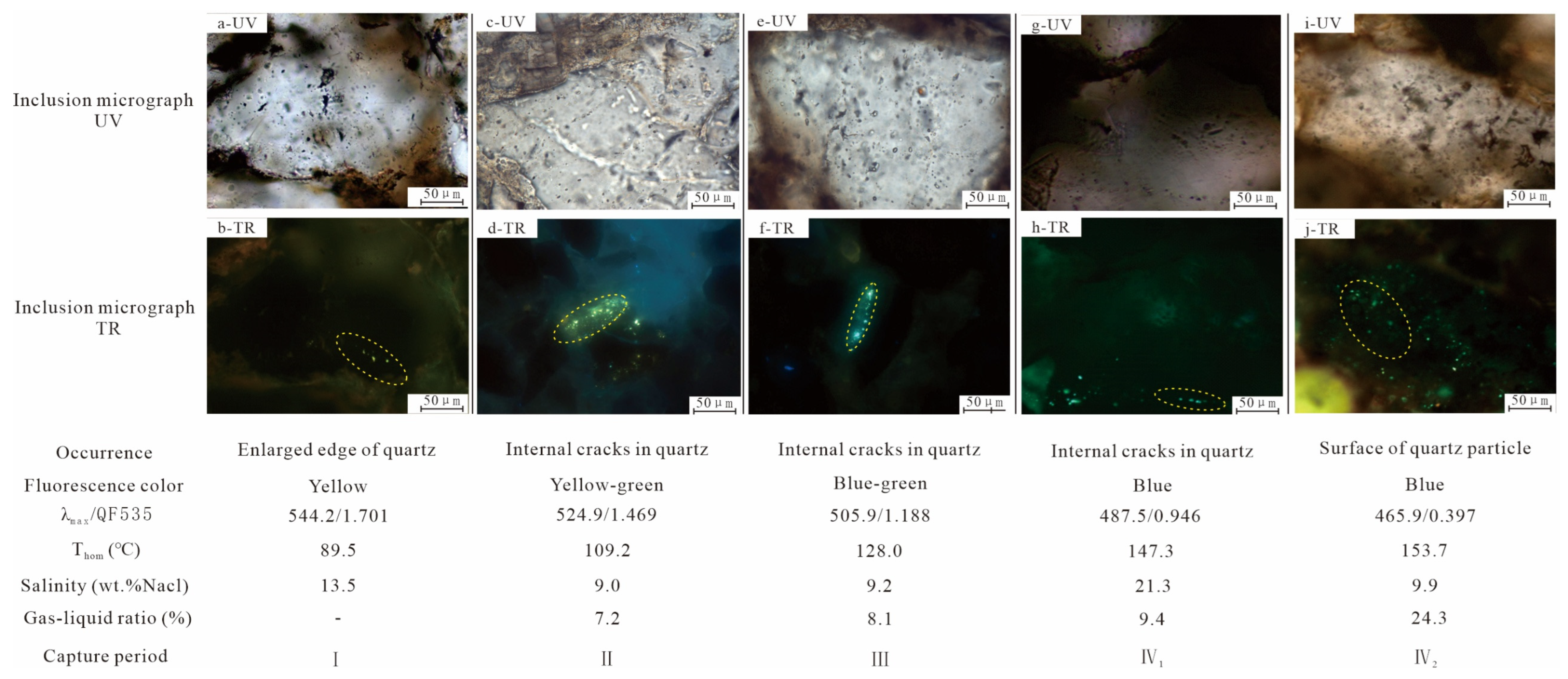
4.1.1. Fluid Inclusion Petrography
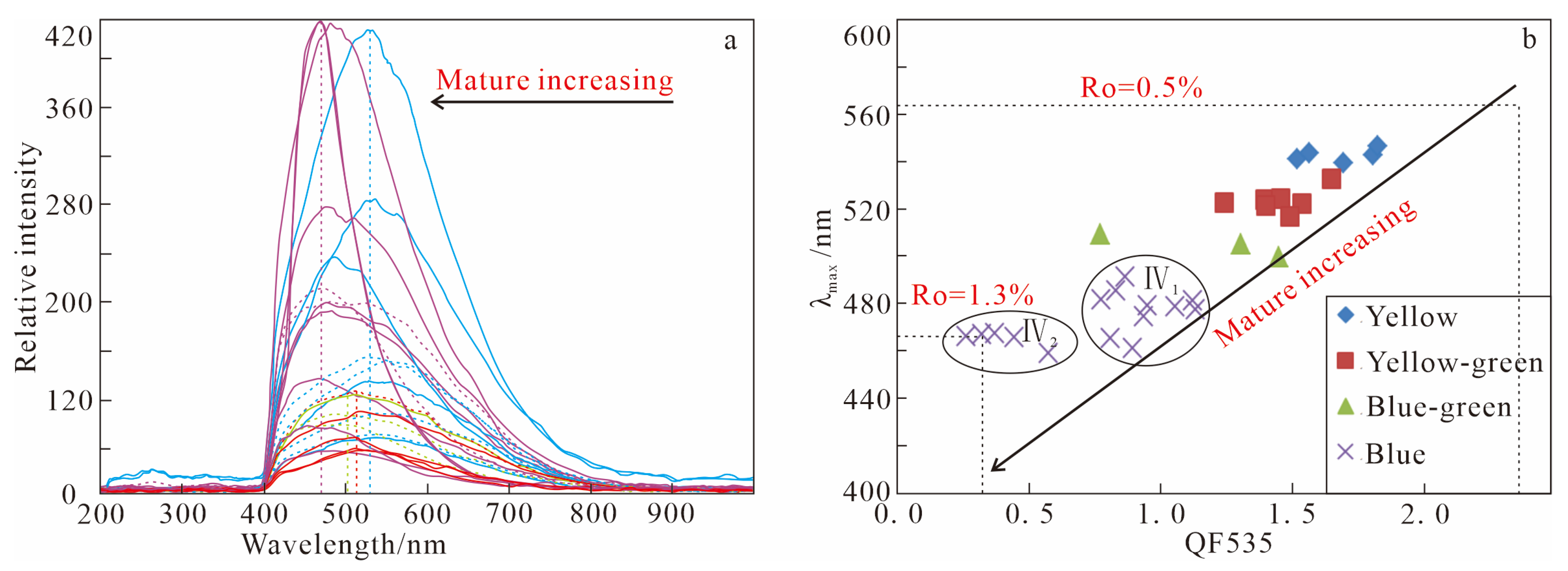
4.1.2. Fluid Inclusion Fluorescence Spectral Character
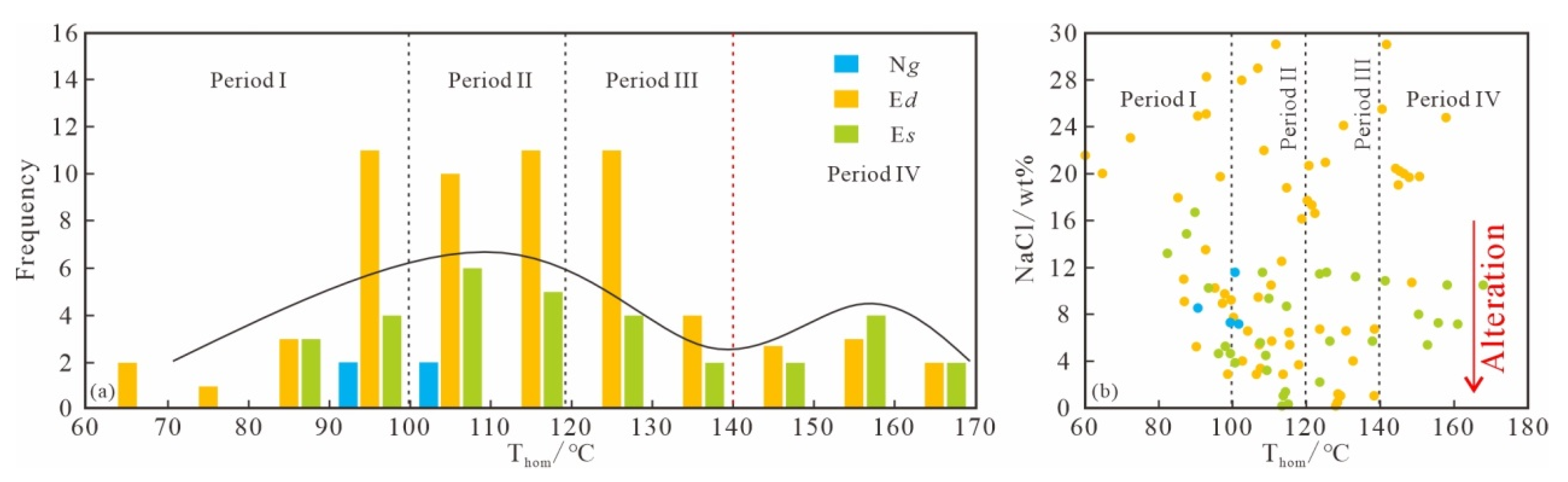
4.1.3. Microthermometric
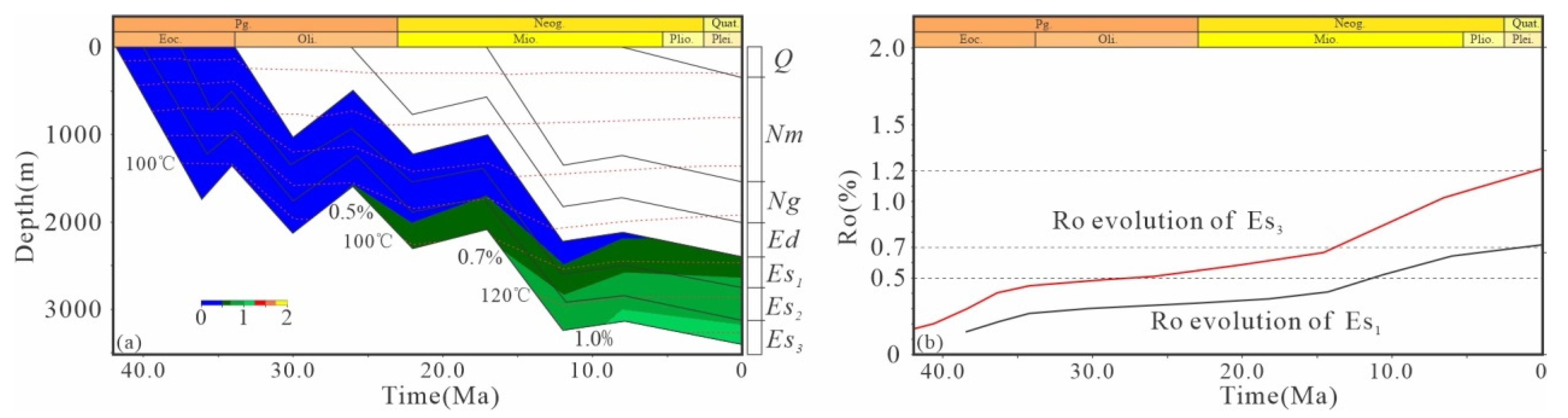
4.2. Burial–Thermal History Recovery
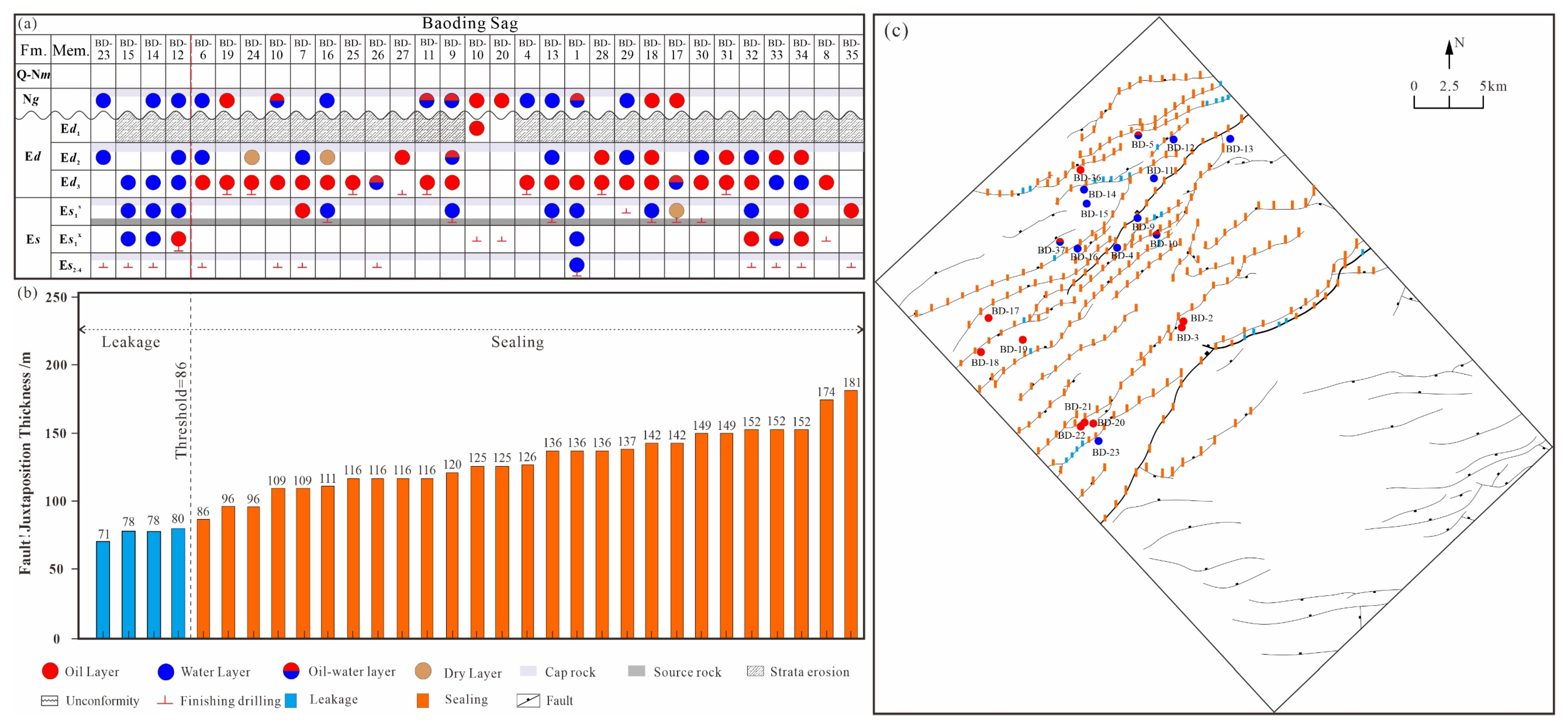
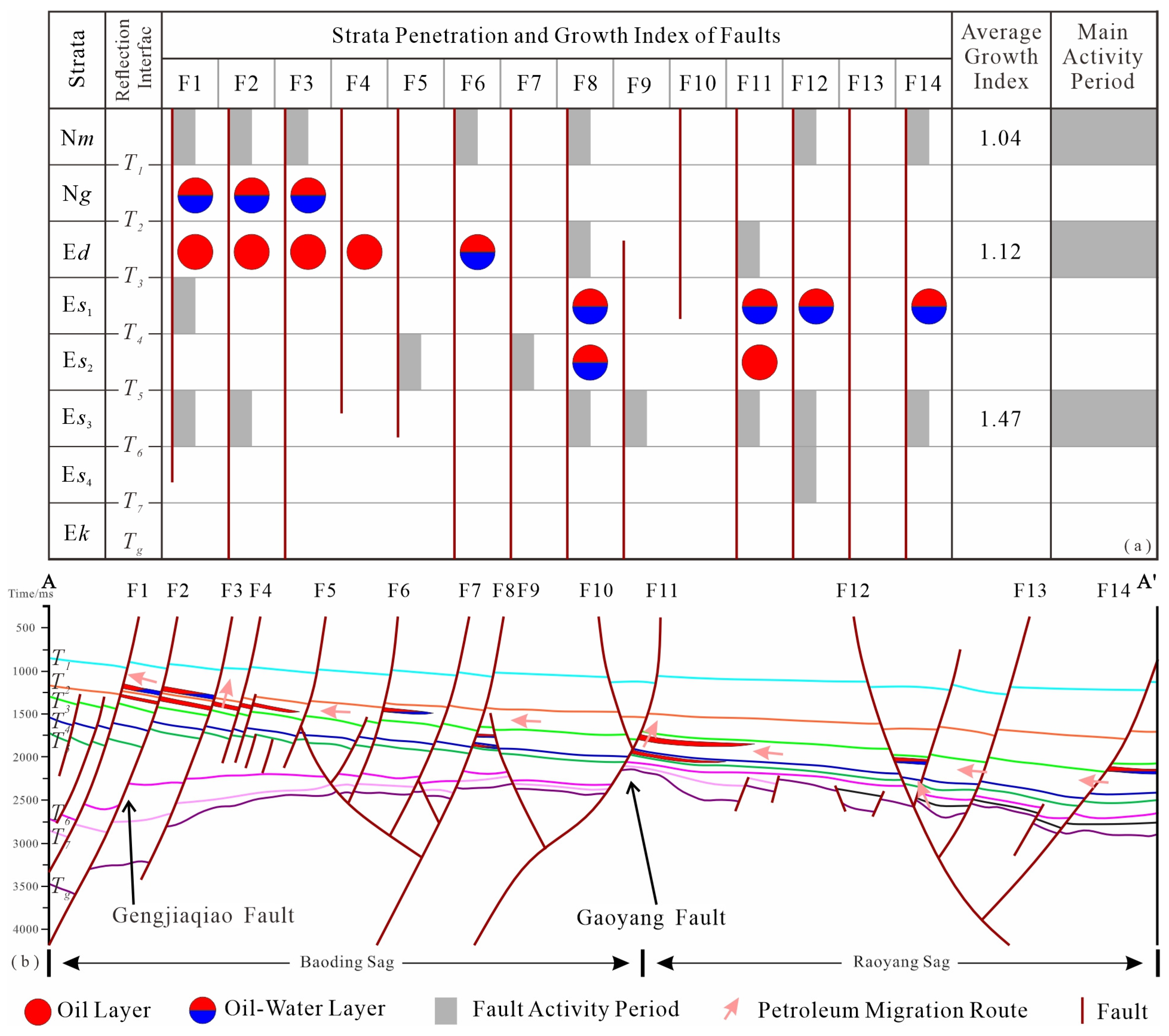
4.3. Fault–Cap Sealing Distribution Character
5. Discussion
5.1. Hydrocarbon Charging Process of Dongying Formation
5.2. Adjustment and Alteration of the Dongying Formation
5.2.1. Adjustment and Alteration Construed by Inclusion Salinity
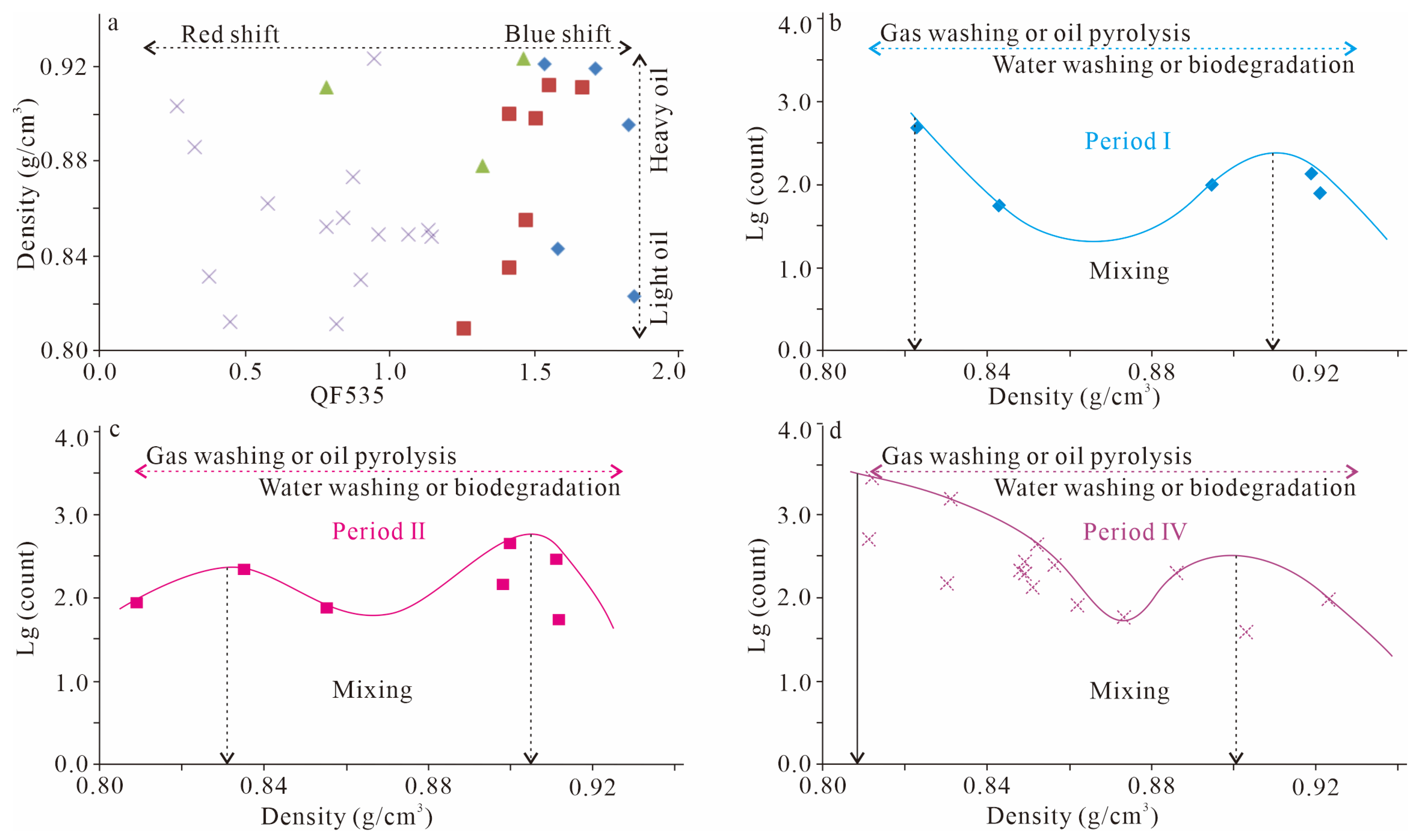
5.2.2. Adjustment and Alteration Constrained by Fluorescence Spectral
5.3. The Coupling Characteristics Between Hydrocarbon Distribution and Fault–Cap Sealing
5.3.1. The Hydrocarbon Relation Between the Dongying and Guantao Formations
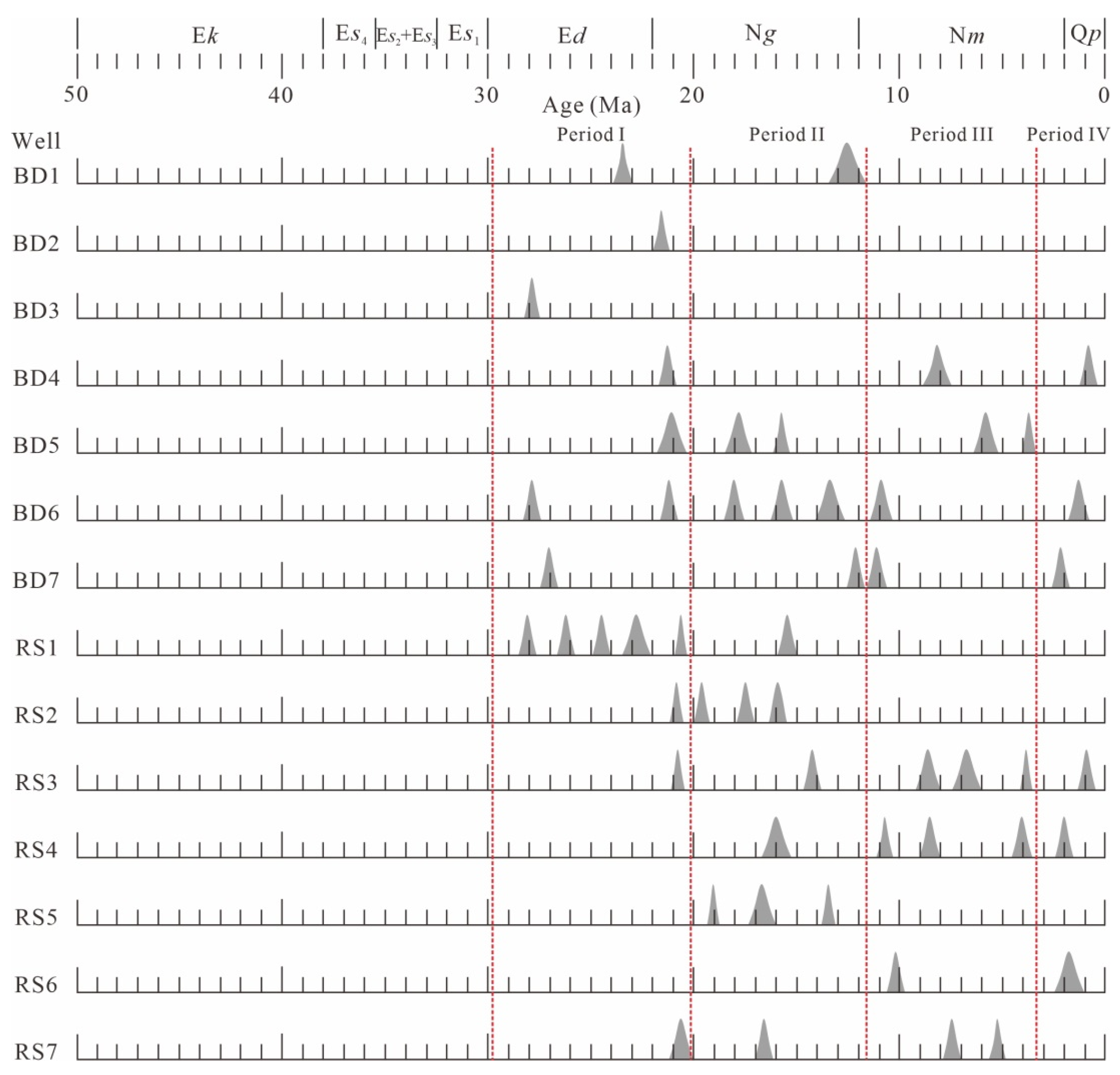
5.3.2. The Relation Between Hydrocarbon Accumulation and Fault Activity Time
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The study area has experienced at least two distinct stages of hydrocarbon charging. Based on microthermometric and fluorescence characteristics, these stages can be further divided into four sub-periods (I–IV), with fluorescence colors ranging from yellow (indicating marginal maturity) to blue (indicating maturity).
- (2)
- The salinity characteristics of the inclusions suggest that the Dongying Formation has undergone adjustments and alterations due to two significant tectonic events: the 22.3 Ma uplift erosion and the 11.8 Ma strike-slips fracturing. Fluorescence spectral data also indicate that the reservoir has been subjected to both gas and water washing processes, with gas washing occurring much later (after 0.36 Ma).
- (3)
- There are two source rocks supplying hydrocarbons to the Dongying Formation (Es1 and Es3; the burial history indicates that the latter released hydrocarbons relatively late). The inclusions exhibit a mixing characteristic, and this mixing is most evident in period IV, which can be further divided into IV1 and IV2 based on fluorescence spectral data.
- (4)
- The strike-slip fracturing around 11.8–7.8 Ma caused hydrocarbons of periods I and II to leak from the Dongying Formation and accumulate in the Guantao Formation, and this finding aligns with the fault activity characteristics. Additionally, the oil–water distribution characteristics suggest a fault juxtaposition thickness threshold for hydrocarbon leak at 86 m.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jian, Y.; Tang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ren, C.; et al. Potentials and favorable directions for new fields, newtypes of oil-gas exploration in Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 69–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Tian, Y. Discussion on influencing factors of hydrocarbon generation in deep source rocks: A case study of Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay basin. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 6, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, V.; Simon, C. Using petroleum inclusions to trace petroleum systems—A review. Org. Geochem. 2019, 129, 99–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Gong, Y.; Zhuo, Q.; Lu, X.; Huang, W. Fluid inclusion characteristics of the Jurassic reservoir and hydrocarbon accumulation process in the eastern Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2023, 13, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Hydrocarbon accumulation and alteration of the Upper Carboniferous Keluke Formation in the eastern Qaidam Basin: Insights from fluid inclusion and basin modeling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 211, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W. Tight Oil and Gas Charging Period andIts Accumulation Contribution of Fuyu Oil Layerin Sanzhao Sag, Songliao Basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2023, 54, 1457–1467. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Liu, K.; Moussa, H.; Liu, J.; Ahmed, H.A.; Kra, K.L. Assessment of petroleum system elements and migration pattern of Borno (Chad) Basin, northeastern Nigeria. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Jia, C.; Pang, H.; Yang, H. Destruction of hydrocarbon reservoirs due to tectonic modifications: Conceptual models and quantitative evaluation on the Tarim Basin, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2018, 91, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrence, P. A review of fluid inclusions in diagenetic systems. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2015, 89, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osukuku, G.; Osinowo, O.; Sonibare, W.; Makhanu, E.; Orora, C. Integrated fluid inclusion studies and source rock parameters in constraining hydrocarbon potential in offshore Lamu Basin, Kenya. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhaom, Z.; Gao, J.; Fu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. Hydrocarbon accumulation periods in the Upper Paleozoic strata of the Western Ordos Basin, China, based on fluid inclusions and basin modeling. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 20536–20549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wei, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tang, M. Hydrocarbon charge history of the Upper Paleozoic, Ordos Basin as revealed by fluid inclusions. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 836977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Characterization of Fluid Inclusions in Chang 7 Shale Oil in Ordos Basin. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an, China, 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Ulrich, T.; Zhong, H. A numerical model for the quantification of fluid inclusion property variations caused by heterogeneous entrapment and post-entrapment modifications in the H2O-NaCl system. Chem. Geol. 2024, 661, 122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, F.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X. Fluid inclusion characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation process in Lungu Area, Tarim Basin. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 2407–2419. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Peng, J.; Wu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Ye, T. Vertical dominant migration channel and hydrocarbon migration in complex fault zone, Bohai Bay Sag, China. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Lou, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pang, Q.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhong, X.; et al. Characteristics and hydrocarbon generation mechanism of early low-mature oil in Baoding sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 500–516. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Qiu, N.; Qin, M.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y. Main controlling factors and models of hydrocarbon accumulation in the Shulu buried-hill belt, Jizhong depression, Bohai Bay basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 897–910. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Han, Y.; Du, M. Fluid inclusions characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation Period of the reservoir in the Northern Section, Lixian Slope. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2016, 35, 53–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Morakinyo, A.; Mohamed, A.; Bowden, S. The release of petroleum from Central Africa rift basins over geological time as deduced from petroleum systems modelling. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 183, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Yan, D.; Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q. Quantitative constraints on hydrocarbon vertical leakage: Insights from underfilled fault-bound traps in the Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 149, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhao, K. Hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism and model of sub-sags in hydrocarbon-rich sag: A case study of Raoyang Sag in Jizhong Depression. Acta Pet. Sin. 2017, 38, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S. Structural Geometry and Kinematics of the Taihang Mountain Piedmont Fault and Its Controlling on the Development of the Bohai Bay Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Study on the Difference in the Evolution Mechanism of Strike-Slip Fault System and Its Relationship with Oil and Gas Distribution in the Western Depression of Liaohe Sub-Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, N.; Murphy, F.; Walsh, J.; Watterson, J. Outcrop studies of shale smears on fault surfaces. Int. Assoc. Sedimentol. 1993, 15, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Yan, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, X. Deformation mechanism and vertical sealing capacity of fault in the mudstone caprock. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 30, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrolijk, P.; Urai, J.L.; Kettermann, M. Clay smear: Review of mechanisms and applications. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 86, 95–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, M. Quantitative evaluation method and its application for vertical fault seal of thick caprock intervals. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2024, 43, 95–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y. Geological Structure Characteristics and the Influence on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Jizhong Depression. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (EastChina), Qingdao, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Jiang, Z.; Han, C.; Zhang, R. Organic Matter Enrichment and Hydrocarbon Accumulation Models of the Marlstone in the Shulu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Northern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 217, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Xiao, Y.; Ming, J.; Tian, R.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C. Geochemical Characteristics and Oil-Source Correlation of Crude Oils of Buried Hills in Shulu Sag, Jizhong Depression. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 3630–3644. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; You, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, R. A type of continuous petroleum accumulation system in the Shulu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. AAPG Bull. 2017, 101, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, R.; Klitzke, P.; Weniger, P.; Blumenberg, M.; Franke, D.; Reinhardt, L.; Ehrhardt, A.; Berglar, K. Basin and petroleum systems modelling in the northern Norwegian Barents Sea. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2021, 130, 105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Song, G. Quantitative analyses in fault sealing properties. Acta Pet. Sin. 1996, 17, 39–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R. Fluid inclusion in the sedmentary and diagenetic systems. Lithos 2001, 55, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, K.; He, S.; Song, G.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.; Wang, B. Petroleum generation and charge history of the northern Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Insight from integrated fluid inclusion analysis and basin modelling. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2012, 32, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Yan, G. Application of fluorescence spectroscopy in identification of aromatic components in single oil inclusions. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 1736–1740. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Quantitative evaluation of petroleum maturity of different periods of charging of Ordovician reservoirs in Tahe Area using fluorescence spectrum parameters of oil. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 2434–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Li, P.; Lei, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X. Identifying gas-washing and water-washing of oil reservoir by fluorescence and infrared spectra of single oil inclusion. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, H.; Chen, H.; Jia, G. Petroleum accumulation in the deeply buried reservoirs in the northern Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: New insights from fluid inclusions, natural gas geochemistry, and 1–D basin modeling. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2017, 80, 70–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, C.; Dong, C.; Luan, G.; Ren, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, B. Diagenetic fluid evolution and its implication for hydrocarbon accumulation in Ordovician carbonate of the Tazhong area, Tarim Basin: Constraints from petrology, fluid inclusions, and geochemistry of calcite cements. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2025, 176, 107360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shan, X.; Wu, C.; Yi, J.; Hao, G.; Wang, P. Formation and evolution of the Changbaishan volcanic geothermal system in a convergent plate boundary back-arc region constrained by boron isotope and gas data. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Member | Occurrences | Fluorescence | /℃ | /wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ng | Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | ||
| Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green | |||
| Ed | Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | ||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green | |||
| Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | blue-green | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | blue | |||
| Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | blue-green | |||
| Es | Enlarged edge of quartz | yellow | ||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | blue-green | |||
| Intergranular pores of quartz | blue | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | blue-green | |||
| Surface of quartz particle | blue | |||
| Internal cracks in quartz | yellow-green |
| Well | Layer | Depth (m) | λmax | Q | QF535 | Type | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD-1 | Ng | 1546.78 | 525.5 | 0.518 | 1.412 | II | 0.9 |
| BD-7 | Ed3 | 1692.07 | 534.1 | 0.652 | 1.667 | II | 0.911 |
| 462.0 | 0.363 | 0.901 | IV | 0.83 | |||
| BD-30 | Ed3 | 1766.35 | 542.7 | 0.596 | 1.535 | I | 0.921 |
| 540.9 | 0.699 | 1.713 | I | 0.919 | |||
| BD-4 | Ed3 | 1987.65 | 466.6 | 0.152 | 0.447 | IV | 0.812 |
| 478.5 | 0.452 | 1.145 | IV | 0.848 | |||
| 479.9 | 0.421 | 1.066 | IV | 0.849 | |||
| RS-3 | Es1 | 3111.09 | 480.3 | 0.362 | 0.96 | IV | 0.849 |
| 506.3 | 0.548 | 1.32 | III | 0.878 | |||
| 482.2 | 0.442 | 1.135 | IV | 0.851 | |||
| BD-6 | Ng | 1704.76 | 548.2 | 0.783 | 1.845 | I | 0.923 |
| 1705.66 | 525.9 | 0.59 | 1.471 | II | 0.895 | ||
| Ed3 | 1904.76 | 482.6 | 0.264 | 0.782 | IV | 0.852 | |
| 1905.31 | 486.3 | 0.278 | 0.837 | IV | 0.856 | ||
| 1904.93 | 467.0 | 0.067 | 0.264 | IV | 0.823 | ||
| 468.4 | 0.126 | 0.373 | IV | 0.811 | |||
| 1905.34 | 475.3 | 0.387 | 0.947 | IV | 0.873 | ||
| 1906.16 | 500.9 | 0.474 | 1.463 | III | 0.843 | ||
| 1906.56 | 522.7 | 0.529 | 1.415 | II | 0.912 | ||
| 1907.06 | 459.7 | 0.215 | 0.579 | IV | 0.809 | ||
| 1907.23 | 510.4 | 0.231 | 0.78 | III | 0.855 | ||
| 1907.56 | 518.2 | 0.586 | 1.507 | II | 0.903 | ||
| 1910.1 | 468.0 | 0.081 | 0.323 | IV | 0.831 | ||
| RS-4 | Es1 | 3552.65 | 544.1 | 0.776 | 1.828 | I | 0.923 |
| 3555.1 | 466.1 | 0.293 | 0.816 | IV | 0.835 | ||
| 492.2 | 0.325 | 0.874 | IV | 0.862 | |||
| 545.0 | 0.667 | 1.582 | I | 0.911 | |||
| 523.6 | 0.641 | 1.553 | II | 0.898 | |||
| 524.1 | 0.541 | 1.256 | II | 0.886 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Pu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Influence of Tectonic Movements on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Dongying Formation, Western Bohai Bay Basin, China. Processes 2025, 13, 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113744
Zhu J, Li X, Pu L, Li X, Chen K, Wang C, Zhang J, Li Y, Li Y, Zhao Y, et al. Influence of Tectonic Movements on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Dongying Formation, Western Bohai Bay Basin, China. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113744
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jieqiong, Xiaodong Li, Longchuan Pu, Xiwei Li, Ketong Chen, Chengyun Wang, Jichao Zhang, Yawen Li, Yan Li, Yi Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Influence of Tectonic Movements on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Dongying Formation, Western Bohai Bay Basin, China" Processes 13, no. 11: 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113744
APA StyleZhu, J., Li, X., Pu, L., Li, X., Chen, K., Wang, C., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Song, Z., Liu, Z., & Zhao, R. (2025). Influence of Tectonic Movements on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Dongying Formation, Western Bohai Bay Basin, China. Processes, 13(11), 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113744





