Screening and Evaluation of Sorbents for the Detection of Oil Field VOC Microseepage †
Abstract
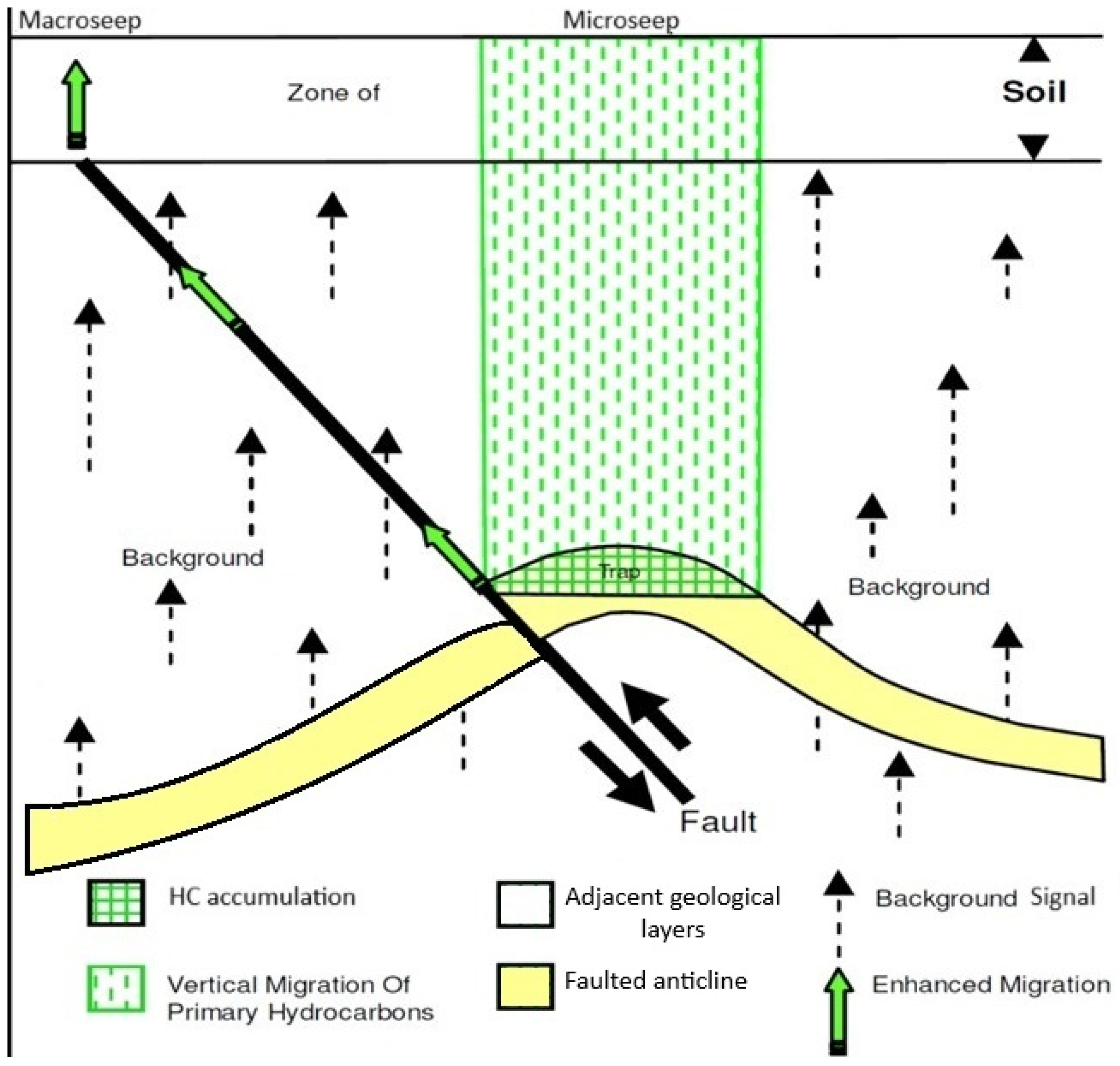
1. Introduction
2. Revision of Materials for Volatile Organic Compounds Sensing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Method of Determining the Porous Structures of Sorbent Samples
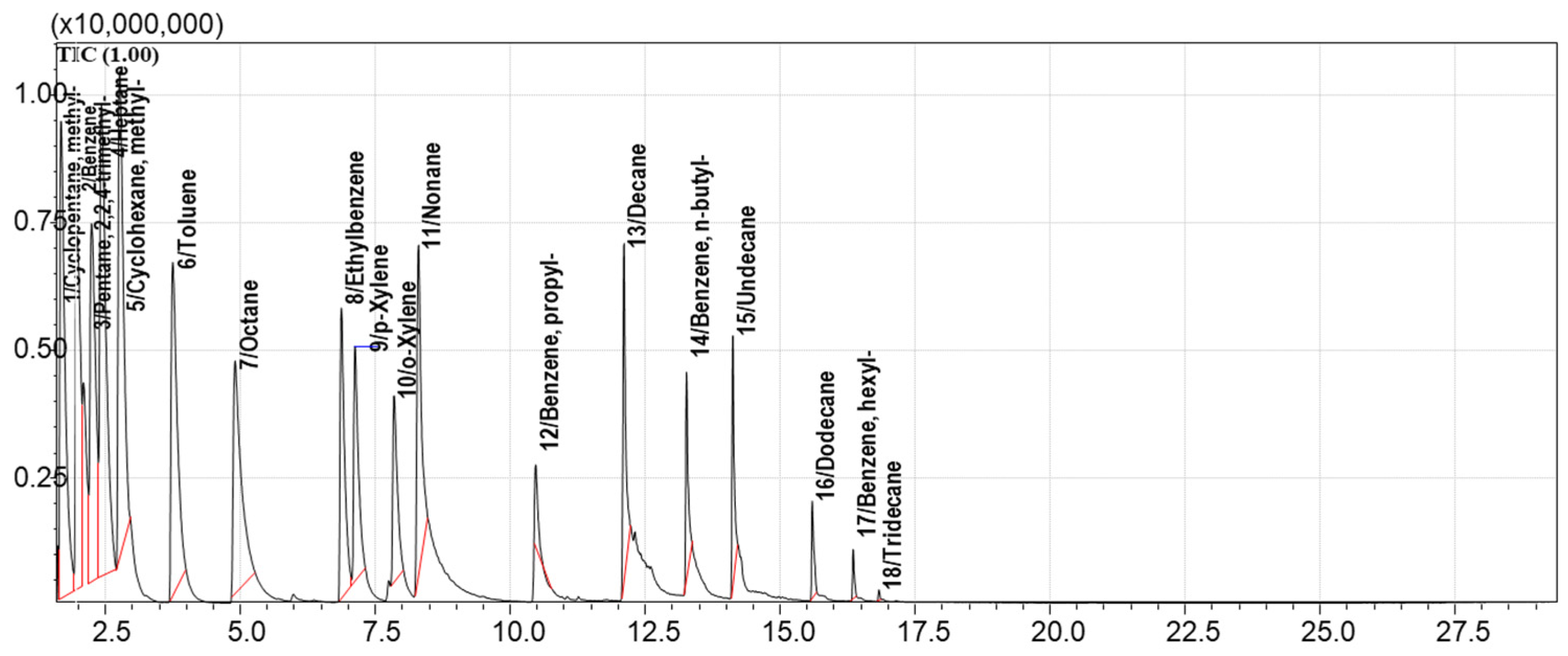
3.3. Model Mixture of Hydrocarbons for Evaluation of Adsorption Capacities of Sorbents
3.4. Method of Saturation of Sorbents by Hydrocarbon VOCs
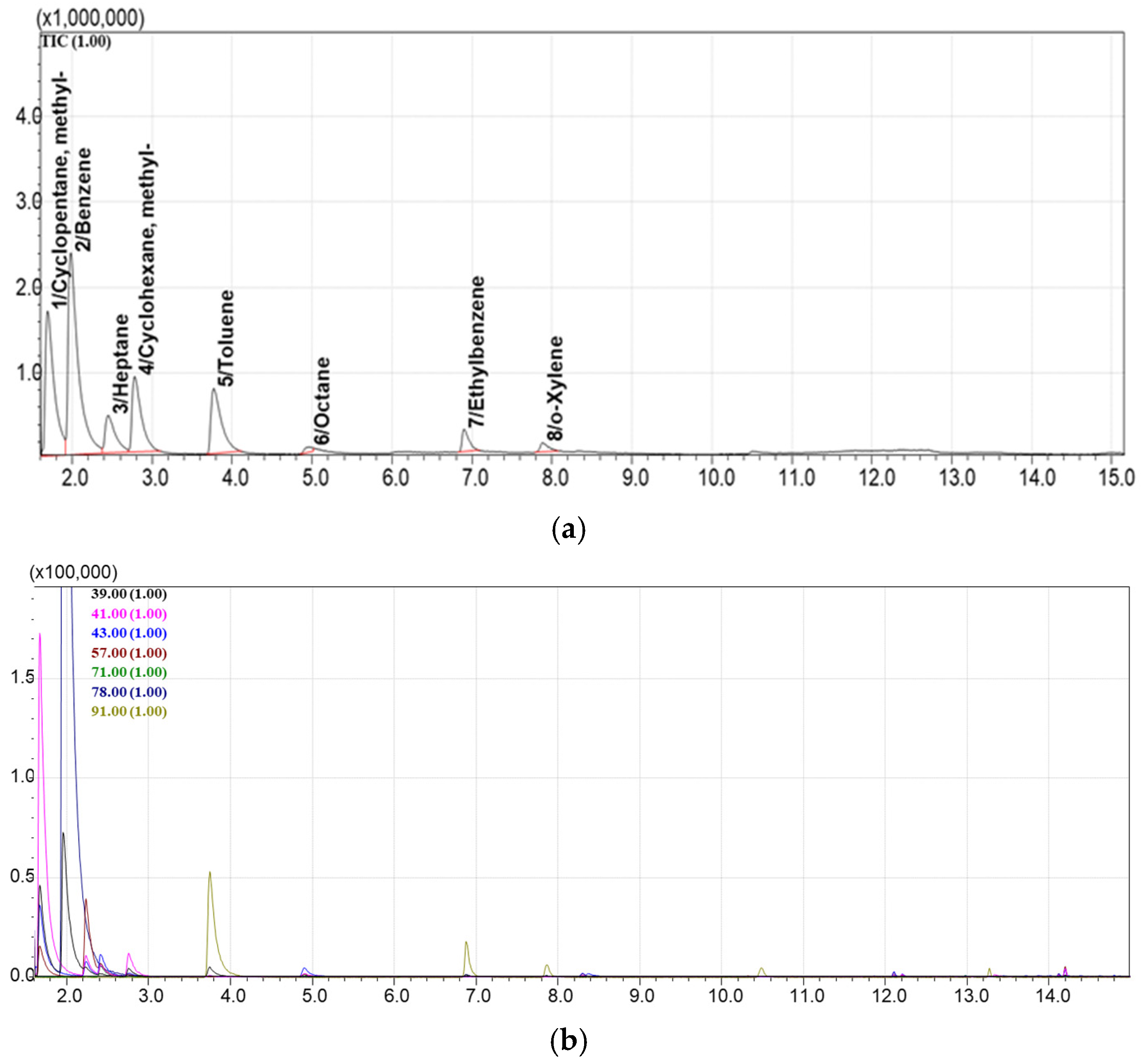
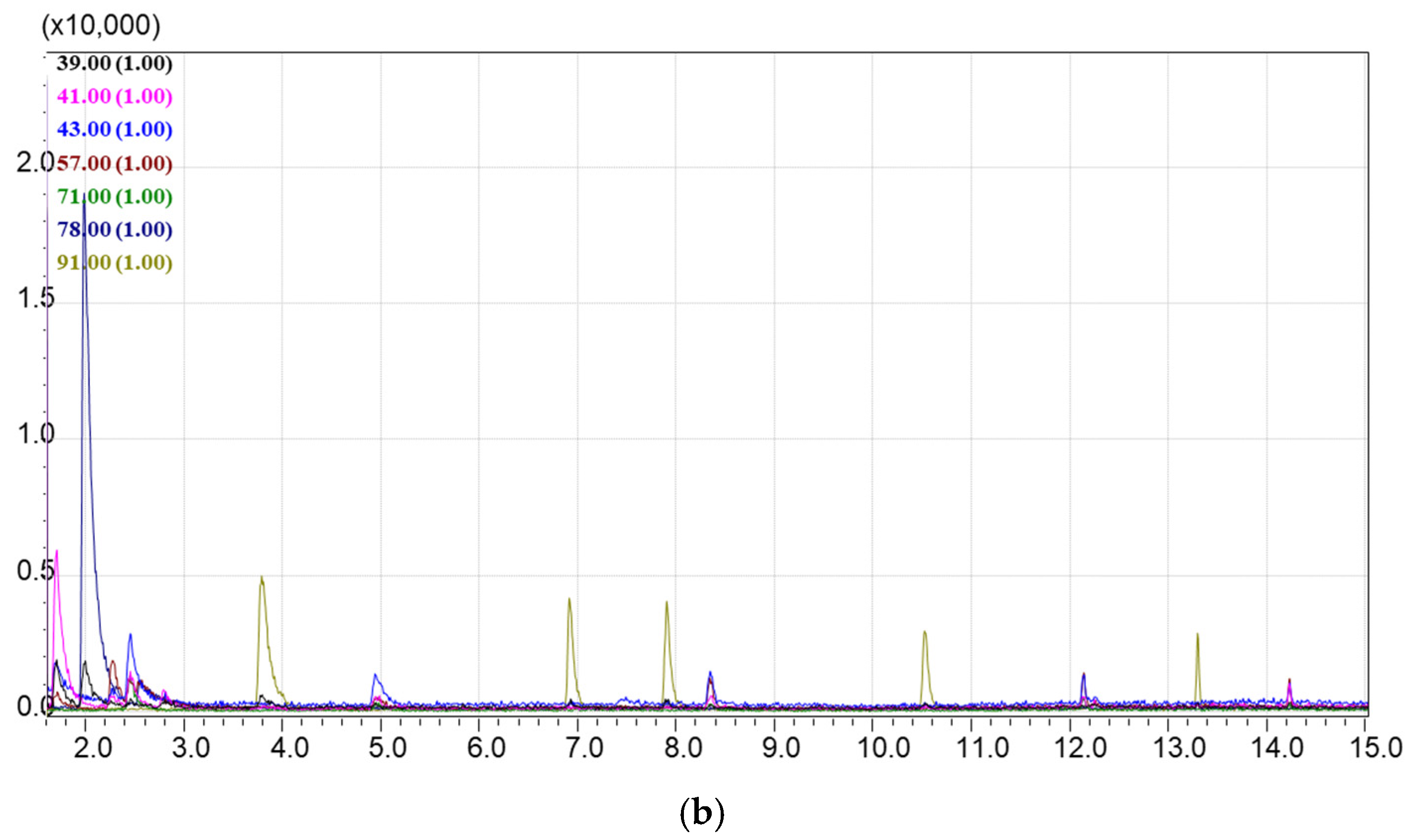
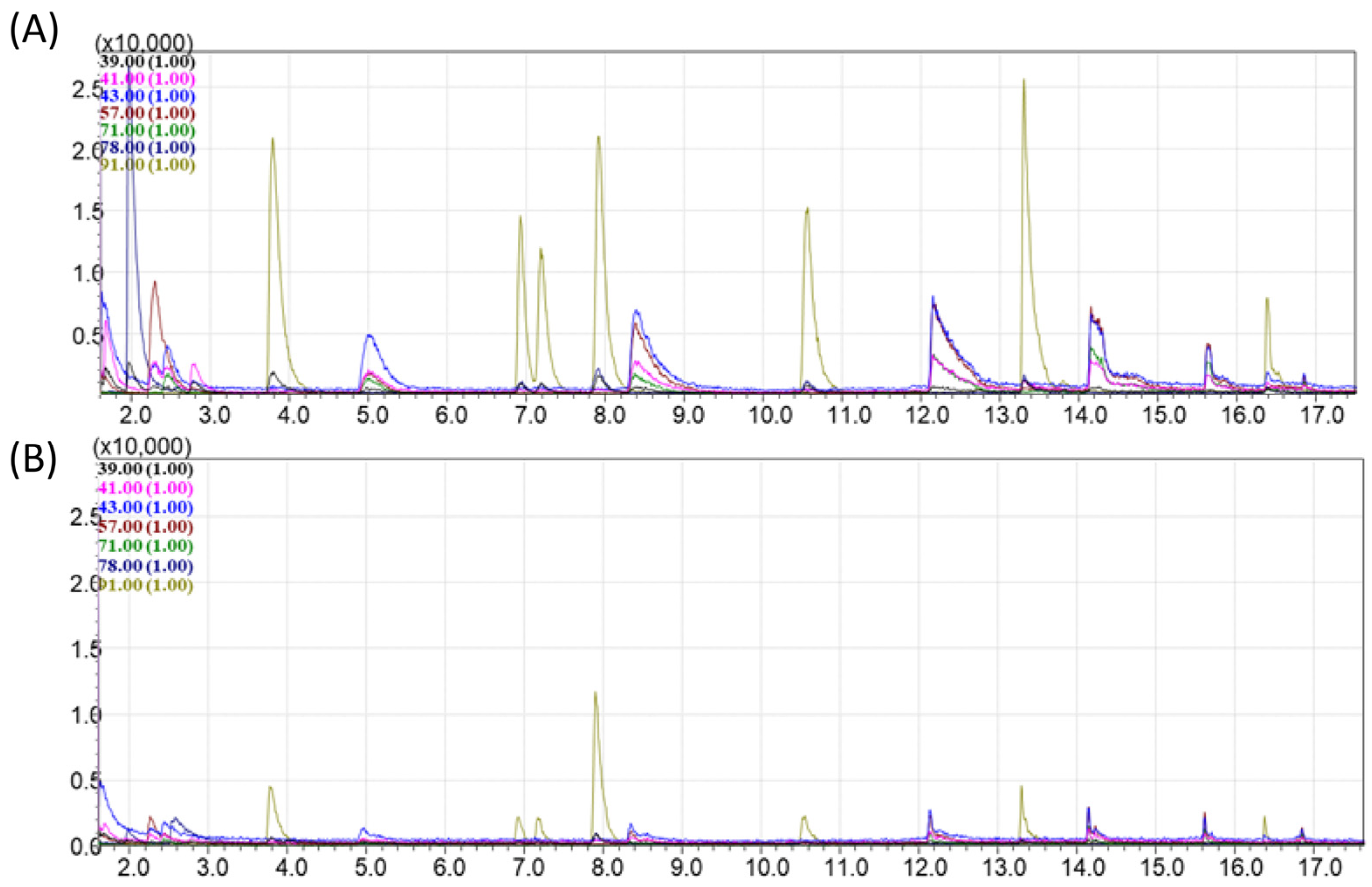
3.5. Method for GCMS Separation and Detection of Hydrocarbon VOCs Adsorbed on Sorbents
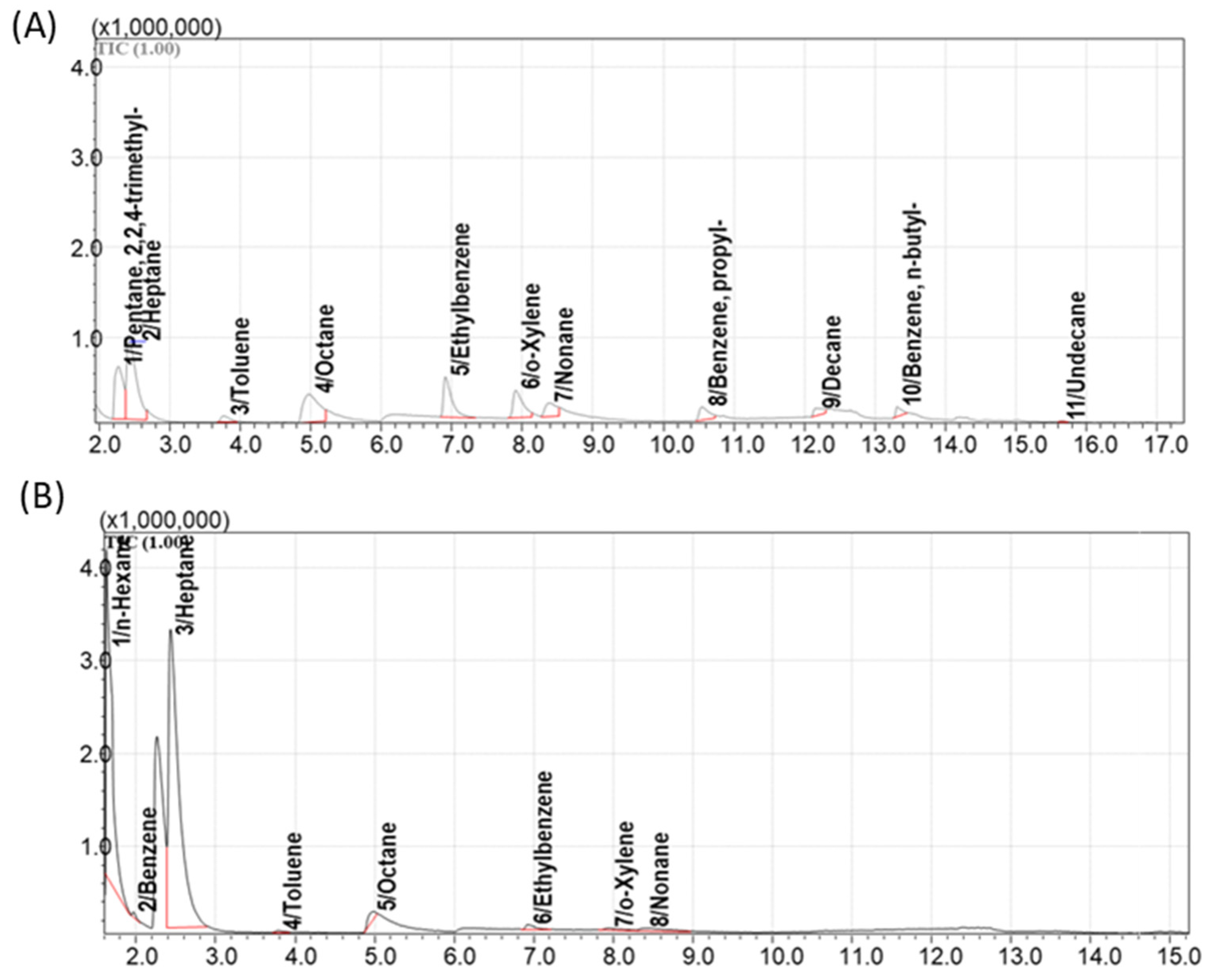
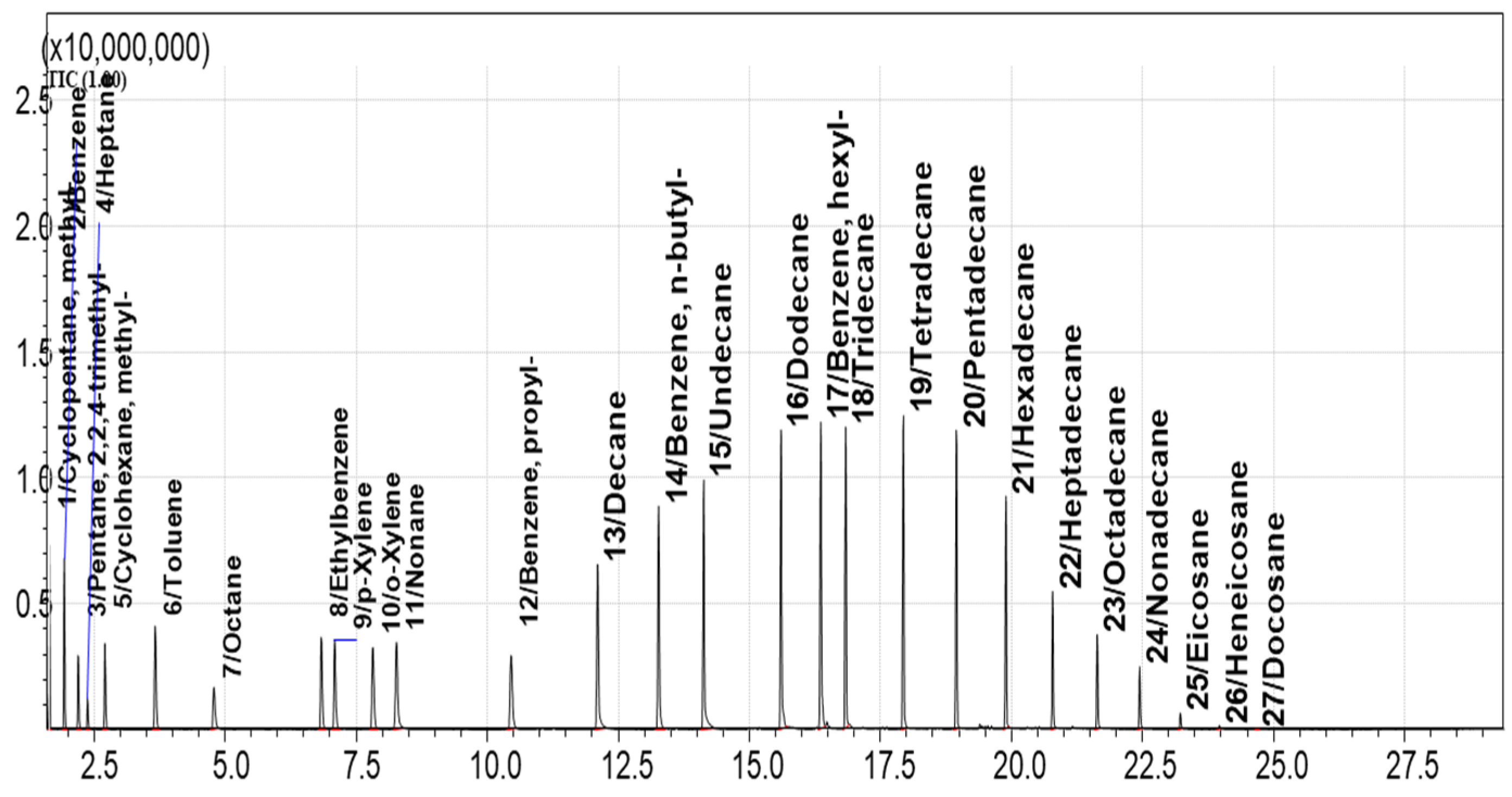
3.6. Passive Sampling of Crude Oil VOCs
3.7. Thermal Desorption and GCxGC/MS Analysis of Crude Oil VOCs
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Selection of the Best Adsorbents from the Library of Porous Materials
4.2. Evaluation of the Adsorption and Desorption Parameters for the Best Selected Sorbents
4.3. The SEM-Microscopy Characterization of the Surface of the Best-Performing Adsorbents and Their Composition
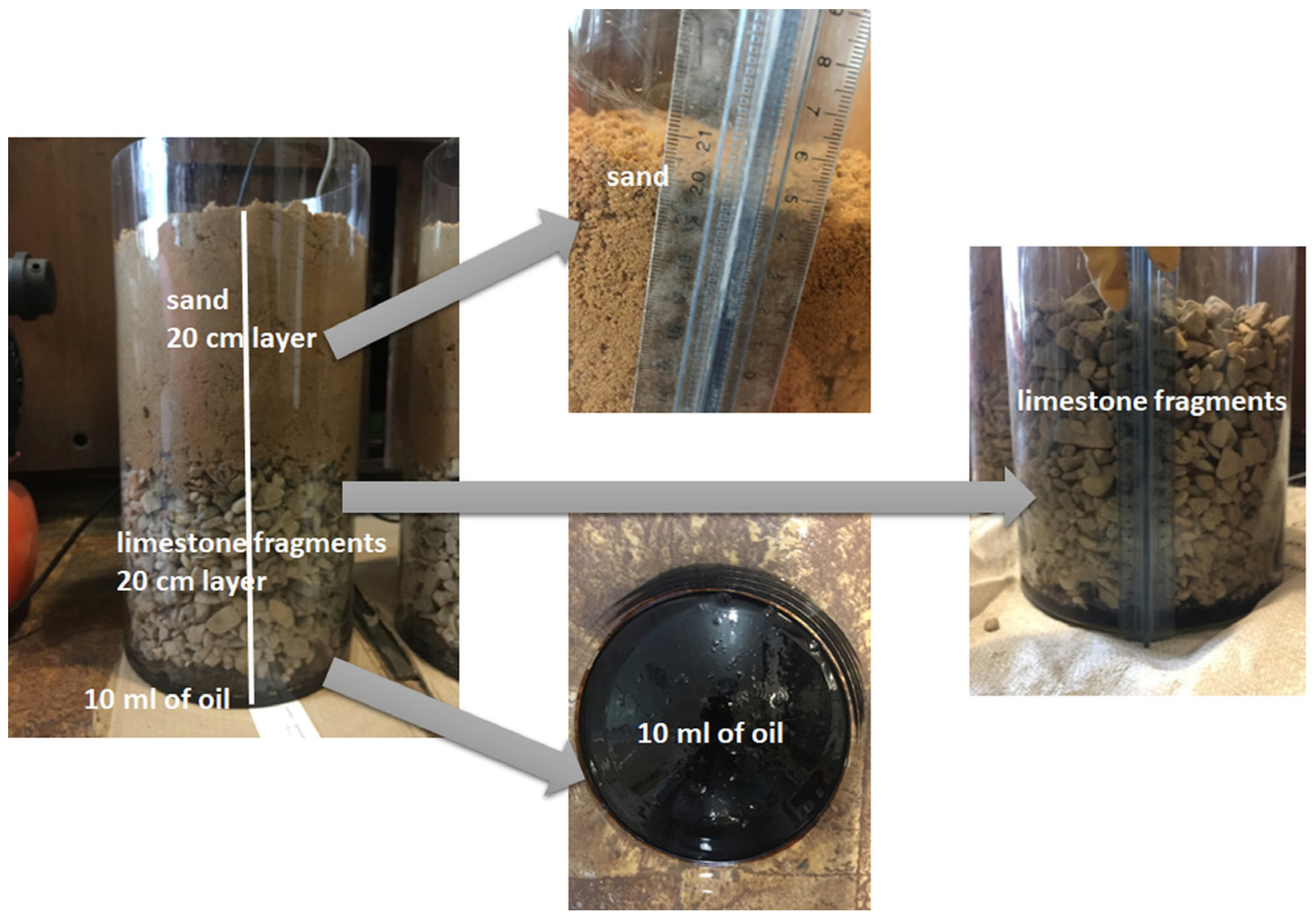
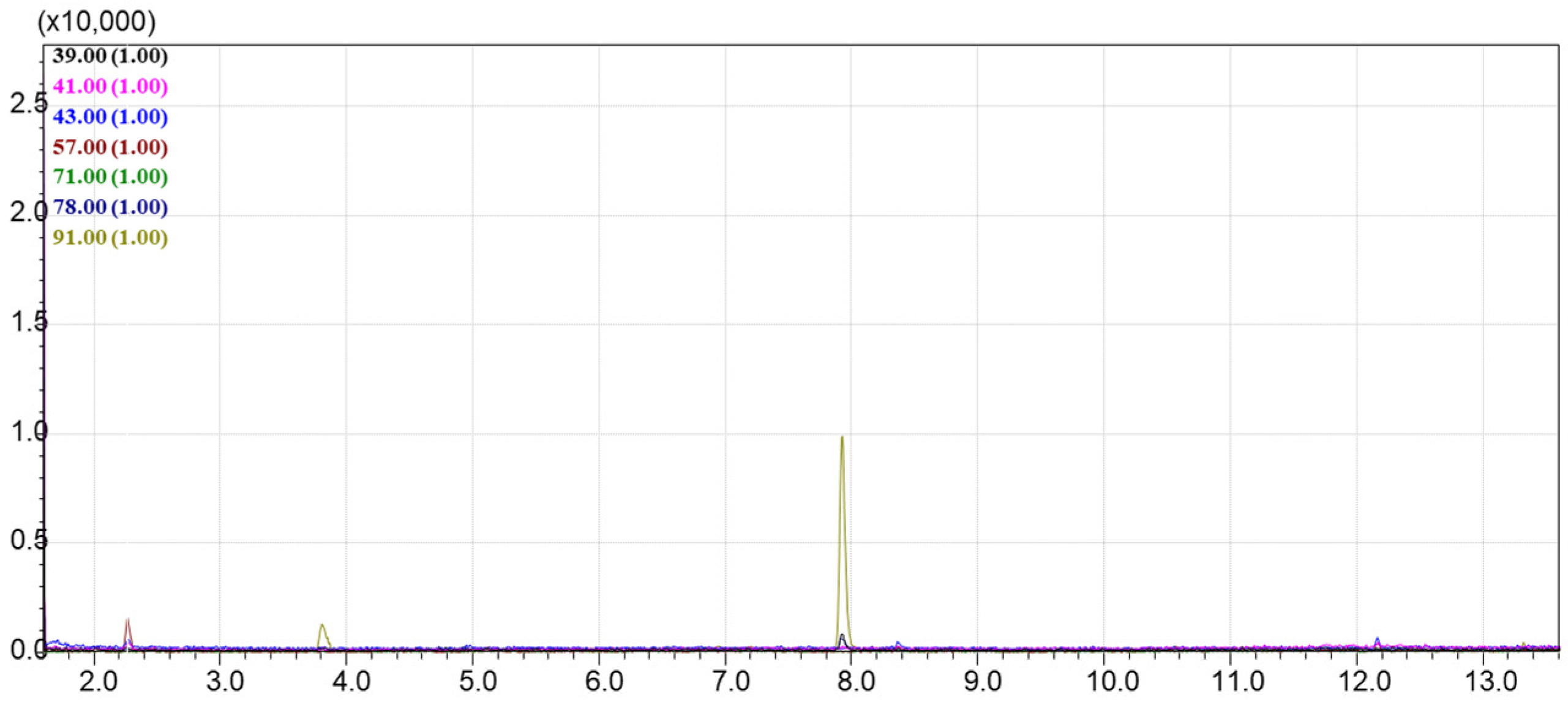
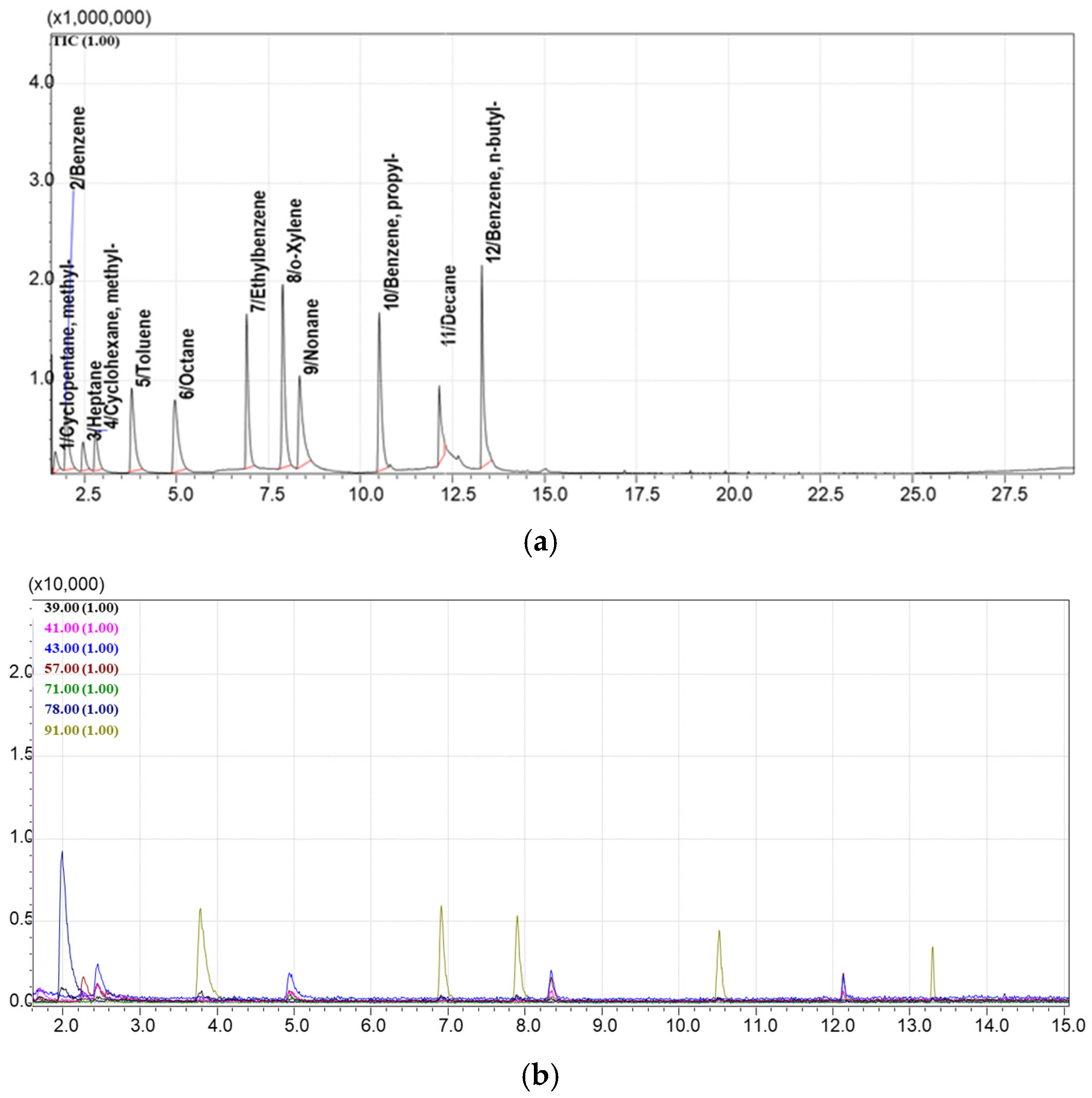
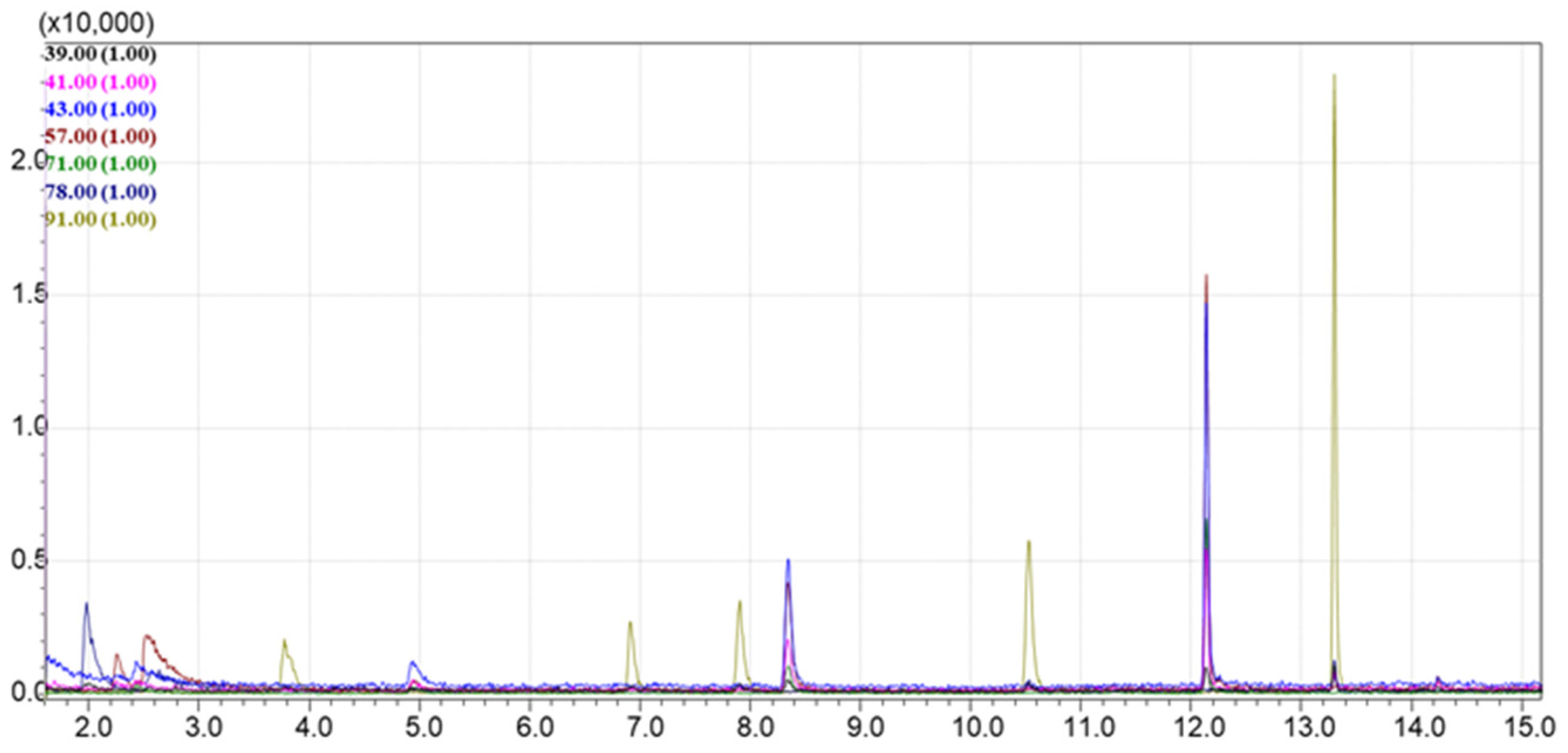
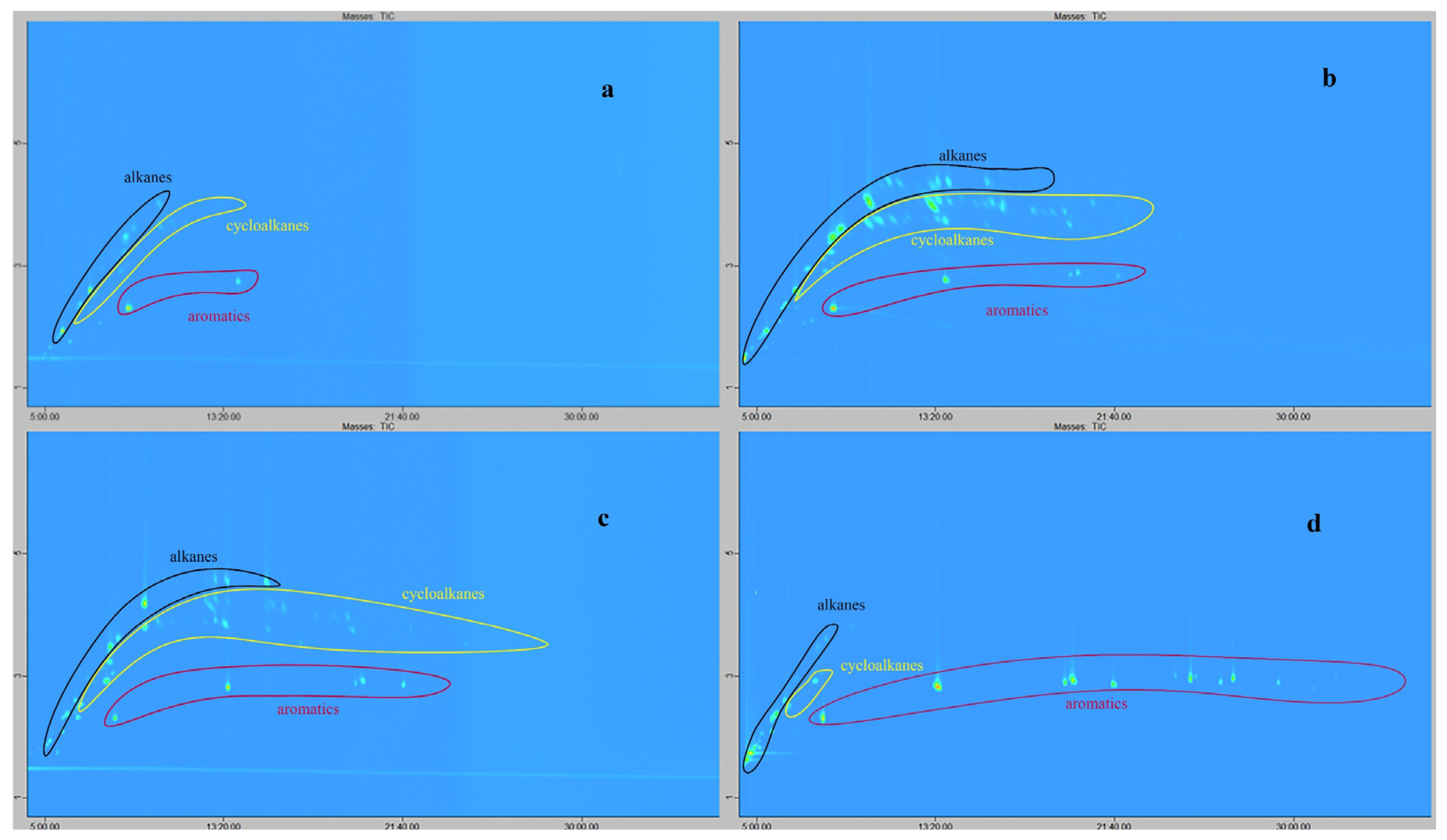
4.4. The Passive Sampling of VOCs from Natural Oils in Laboratory Conditions
4.5. Temperature Effects on Sorbent Selection and Thermal Desorption Protocol
- Reliable sealing of the sample before analysis.
- Automated and stringent leak testing.
- Complete desorption of the analytes.
4.6. Laboratory Safety and Environmental Concerns for Sorbent-Based Microseepage Sensing
4.7. Field Validation and Future Directions for Sorbent-Based Microseepage Detection
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schumacher, D. (Ed.) Hydrocarbon Migration and Its Near-Surface Expression. In Proceedings of the Overgrowth of the AAPG Hedberg Research Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 April 1994; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chapter 10. Geochemical Methods of Exploration for Petroleum and Natural Gas. In Developments in Petroleum Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 307–341. [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.A. Microseepage vs. Macroseeepage: Defining Seepage Type and Migration Mechanisms for Differing Levels of Seepage and Surface Expressions. In 2019 AAPG Hedberg Conference: Hydrocarbon Microseepage: Recent Advances, New Application, and Remaining Challenges; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, S.; De Souza Filho, C.R. Spectral remote sensing for onshore seepage characterization: A critical overview. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 168, 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.A. Concepts of Microseepage. In Surface Geochemistry in Petroleum Exploration; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, V.; Orlov, M.; Atwah, I.; Abu Alreesh, M. Custom-Made Sorbent-Based Sensors for Subsurface Microseepage of Volatile Organic Markers of Oil and Gas Fields. Presented at the 3rd International Electronic Conference on Processes—Green and Sus-tainable Process Engineering and Process Systems Engineering (ECP 2024). Proceedings 2024, 105, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, D. Integrating Hydrocarbon Microseepage Data with seismic Data Doubles Exploration Success. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Convention of the Indonesian Petroleum Association (IPA), Jakarta, Indonesia, 18–20 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, L. ON GEOCHEMICAL PROSPECTING—I. Geophysics 1939, 4, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conolly, J.R.; Moffitt, R.S.; Adams, N.P. Soil-Gas Microseepage Surveys Help Locate New Oil and Gas Accumulations; Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia (PESA): Beaumaris, VIC, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schrynemeeckers, R. Combining Surface Geochemical Surveys and Downhole Geochemical Logging for Mapping Hydrocarbons in the Utica Shale. In Proceedings of the AAPG Annual Convention and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 April 2014; AAPG Publisher: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Atwah, I.; AlSaif, M.; Yeadon, A.; Srinivasan, P. Depth dimension in seepage detection: Insights for exploration and geological gas storage surveillance. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 243, 213242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, M. Sorbent trapping of volatile organic compounds from air. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 885, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Tsimnadis, K.; Sebos, I.; Charabi, Y. Investigating the Effect of Pore Size Distribution on the Sorption Types and the Adsorption-Deformation Characteristics of Porous Continua: The Case of Adsorption on Carbonaceous Materials. Crystals 2024, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.; Doulia, D.; Anagnostopoulos, E. Adsorption of pesticides on porous polymeric adsorbents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfenden, E. Sorbent-based sampling methods for volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in air. Part 2. Sorbent selection and other aspects of optimizing air monitoring methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, V.M.; Crump, D.R. An investigation into the performance of a multi-sorbent sampling tube for the measurement of VVOC and VOC emissions from products used indoors. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.S.H.; Wang, L.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Xue, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, B.; Dai, W.; Li, L.; et al. Optimization and evaluation of multi-bed adsorbent tube method in collection of volatile organic compounds. Atmospheric. Res. 2018, 202, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, T.; Kim, D. Practical Application of a Multi-Bed Adsorbent Tube Coupled with GC-MS for Low-Level VOCs Identification to Achieve Comprehensive Odor Management. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A. Intra-workday fluctuations of airborne contaminant concentration and the time-weighted average. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2022, 19, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabiegała, B.; Sărbu, C.; Urbanowicz, M.; Namieśnik, J. A Comparative Study of the Performance of Passive Samplers. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odencrantz, J.E.; O’Neill, H. Passive to active tie-in for soil gas surveys: Improved technique for source-area, spatial variability, remediation-monitoring, and vapor-intrusion assessment. Remediat. J. 2009, 19, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrin, D.L.; Kerfoot, H.B. Soil-gas surveying techniques. Environ Sci Technol. 1988, 22, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, D.C.; Alarsa, M.; Salvador, M.C.; Kupferschmid, C. Environmental Soil and Ground Water Assessment Using High Resolution Passive Soil-Gas Samplers—Petrex Method: Methodology and Results of a Case Study Performed in Brazil. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, B.; Gelencsér, A.; Gál, C.; Hlavay, J. Evaluation of the reliability of diffusive sampling in environmental monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 408, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelencsér, A.; Kiss, G.; Hlavay, J.; Hafkenscheid, T.L.; Peters, R.J.B.; De Leer, E.W.B. The evaluation of a tenax GR diffusive sampler for the determination of benzene and other volatile aromatics in outdoor air. Talanta 1994, 41, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannov, A.G.; Popov, M.V.; Kurmashov, P.B. Thermal analysis of carbon nanomaterials: Advantages and problems of interpretation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 142, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwah, I.; Sweet, S.; Pantano, J.; Knap, A. Light Hydrocarbon Geochemistry: Insight into Mississippian Crude Oil Sources from the Anadarko Basin, Oklahoma, USA. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 2795017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.; Arguello, E.M.E.; Atwah, I. Evaluating the reliability of solid phase extraction techniques for hydrocarbon analysis by GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1737, 465435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwah, I.; Adeboye, O.O.; Zhang, J.; Wilcoxson, R.; Marcantonio, F. Linking biomarkers with elemental geochemistry to reveal controls on organic richness in Devonian-Mississippian mudrocks of Oklahoma. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2023, 611, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.W.; Birrell, R.D.; Mann, A.T.; Humphreys, D.B.; Perdrix, J.L. Application of the mobile metal ion technique to routine geochemical exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 1998, 61, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, A.; Lushpeev, V.; Sokolov, A.; Sultanbekov, R.; Tyan, Y.; Ovchinnikov, E.; Shvets, A.; Bushuev, V.; Islamov, S. Experimental Research of the Possibility of Applying the Hartmann–Sprenger Effect to Regulate the Pressure of Natural Gas in Non-Stationary Conditions. Processes 2025, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwah, I.; Solovyeva, V.; Orlov, M. Methods and Systems for Detecting Hydrocarbon Microseepage from Deep Geological Formations. Patent WO/2024/237802, 21 November 2024. [Google Scholar]




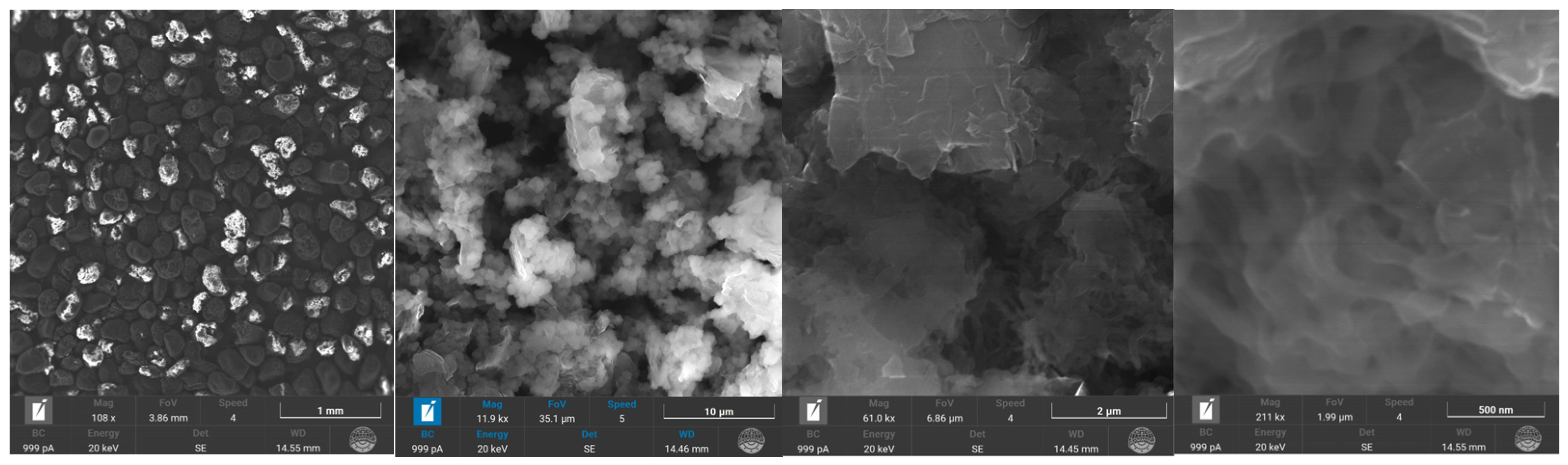

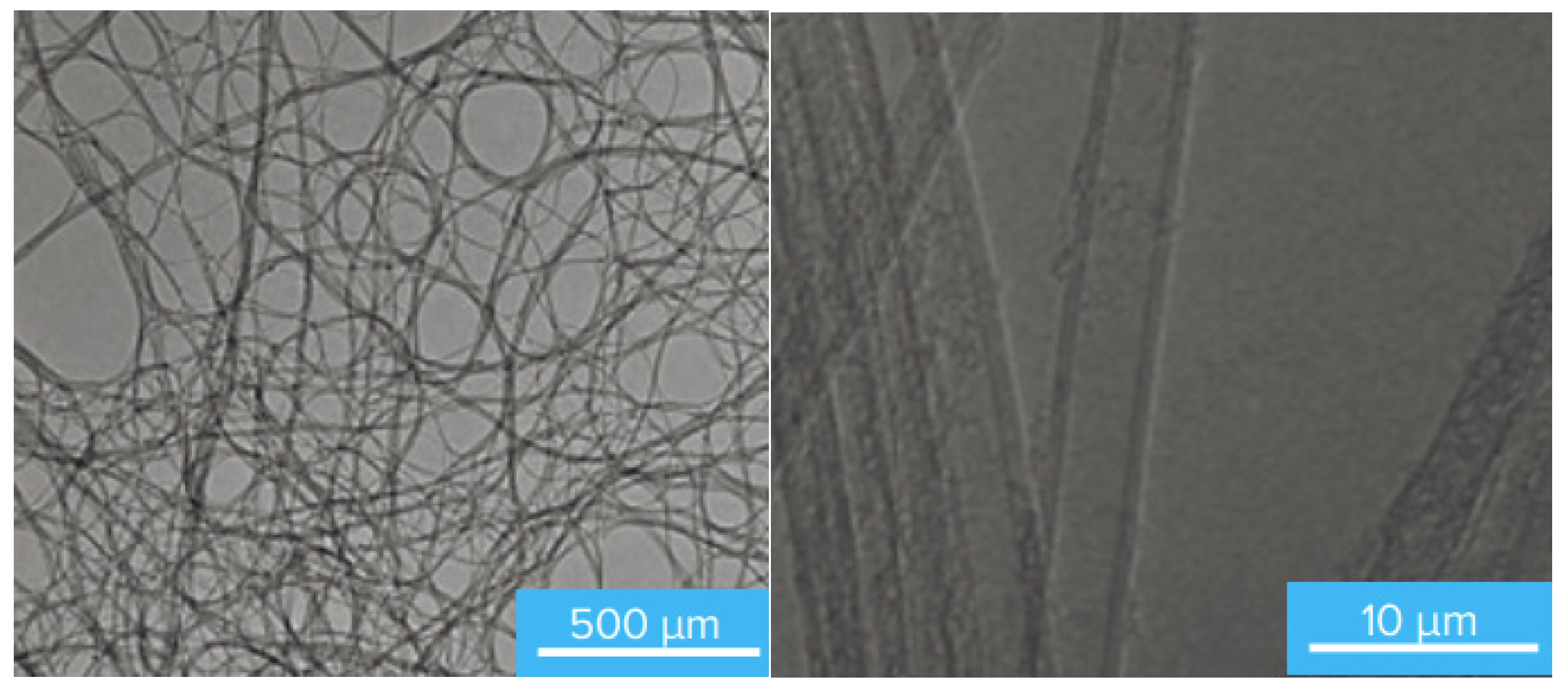
| # | Sorbent | Micropores Parameters | SMe, m2/g (γ-method) | VMe, cm3/g | Vs, cm3/g | S BET, m2/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W0, cm3/g | E0, kJ/mol | x0, nm | ||||||
| 1 | SKT | 0.61 | 19.39 | 0.52 | 90 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 420 |
| 2 | AUkon-s | 0.58 | 22.24 | 0.45 | 10 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 940 |
| 3 | VSK | 0.61 | 18.68 | 0.53 | 60 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 643 |
| 4 | Meks | 0.40 | 20.94 | 0.48 | 76 | 0.06 | 0.46 | 700 |
| 5 | UPK-B | 0.29 | 14.710 | 0.68 | 35 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 660 |
| 6 | DAS | 0.13 | 22.62 | 0.44 | 35 | 0.003 | 0.133 | 250 |
| 7 | FAS | 0.14 | 21.80 | 0.46 | 74 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 750 |
| 8 | Polystyrene, Cross-linked 150% | 0.17 | 26.63 | 0.37 | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | UNHT | 0.12 | 14.90 | 0.67 | 90 | 0.18 | 0.31 | 235 |
| 10 | Zeolite 13X | 0.23 | 30.84 | 0.32 | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | CNT | - | - | - | - | - | - | 460 * |
| 12 | Tenax | - | - | - | - | - | - | 18 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solovyeva, V.; Orlov, M.; Grokhovsky, V.; Borisov, R.; Kanateva, A.; Petukhova, G.; Pytskii, I.; Atwah, I.; Abu Alreesh, M. Screening and Evaluation of Sorbents for the Detection of Oil Field VOC Microseepage. Processes 2025, 13, 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113703
Solovyeva V, Orlov M, Grokhovsky V, Borisov R, Kanateva A, Petukhova G, Pytskii I, Atwah I, Abu Alreesh M. Screening and Evaluation of Sorbents for the Detection of Oil Field VOC Microseepage. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113703
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolovyeva, Vera, Maxim Orlov, Vyacheslav Grokhovsky, Roman Borisov, Anastasiya Kanateva, Galina Petukhova, Ivan Pytskii, Ibrahim Atwah, and Mohammed Abu Alreesh. 2025. "Screening and Evaluation of Sorbents for the Detection of Oil Field VOC Microseepage" Processes 13, no. 11: 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113703
APA StyleSolovyeva, V., Orlov, M., Grokhovsky, V., Borisov, R., Kanateva, A., Petukhova, G., Pytskii, I., Atwah, I., & Abu Alreesh, M. (2025). Screening and Evaluation of Sorbents for the Detection of Oil Field VOC Microseepage. Processes, 13(11), 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113703







