Enzymatic Potential of Schizophyllum commune BNT39 in BHET Hydrolysis and PET Biodegradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolation and Identification
2.1.1. Fungal Isolation and Culture Conditions
2.1.2. Molecular Identification
2.2. BHET Degradation Assays
2.2.1. Hydrolysis on Solid Medium
2.2.2. Degradation in Liquid Medium Analyzed by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
2.2.3. Quantitative Analysis by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. PET Degradation Assays
2.4. Cutin Extraction and Characterization
2.5. Effect of Cutin on Enzymatic Activity
2.6. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
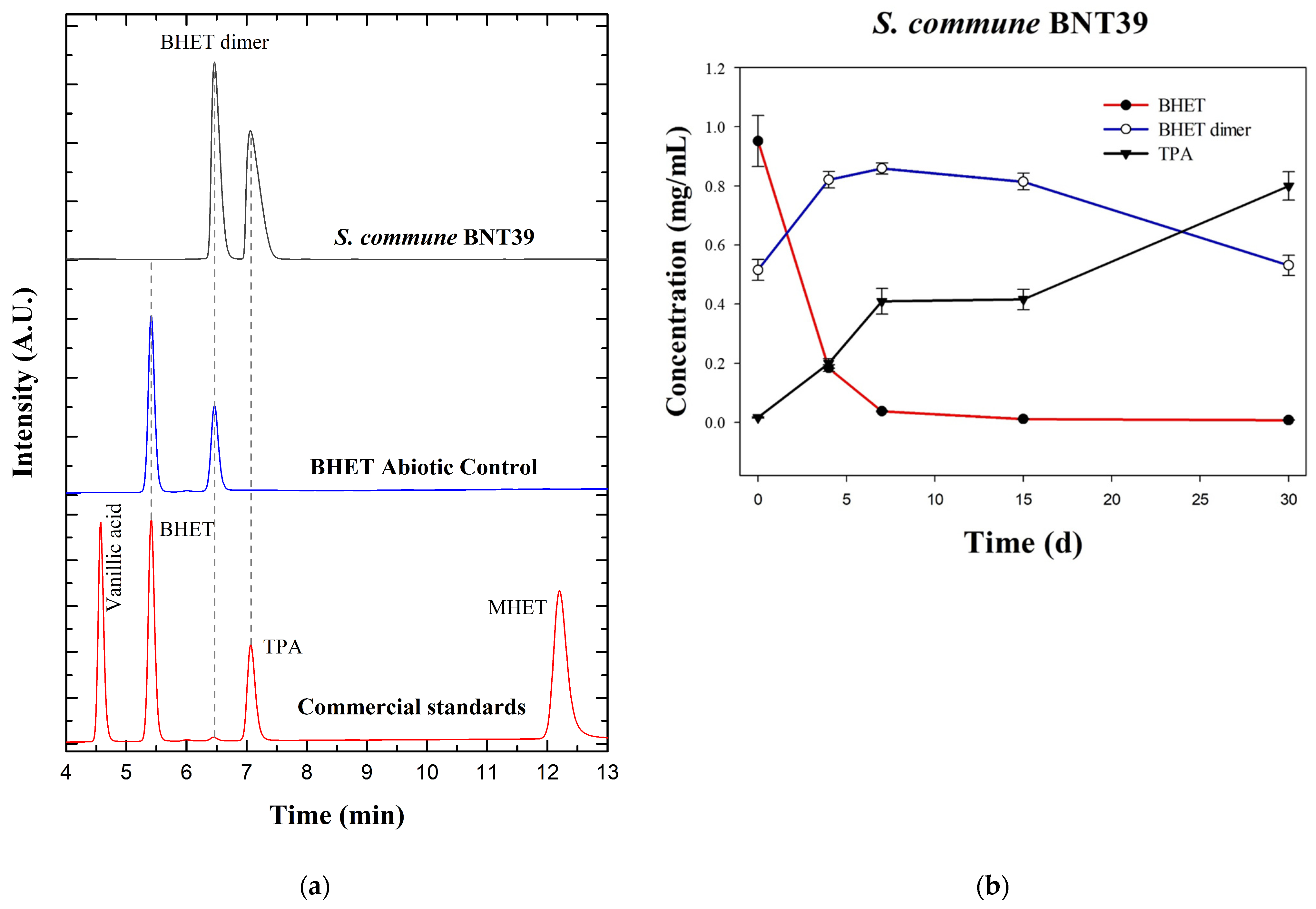
3.1. Degradation of BHET by Schizophyllum commune BNT39
3.2. Biodegradation of PET by Schizophyllum commune BNT39
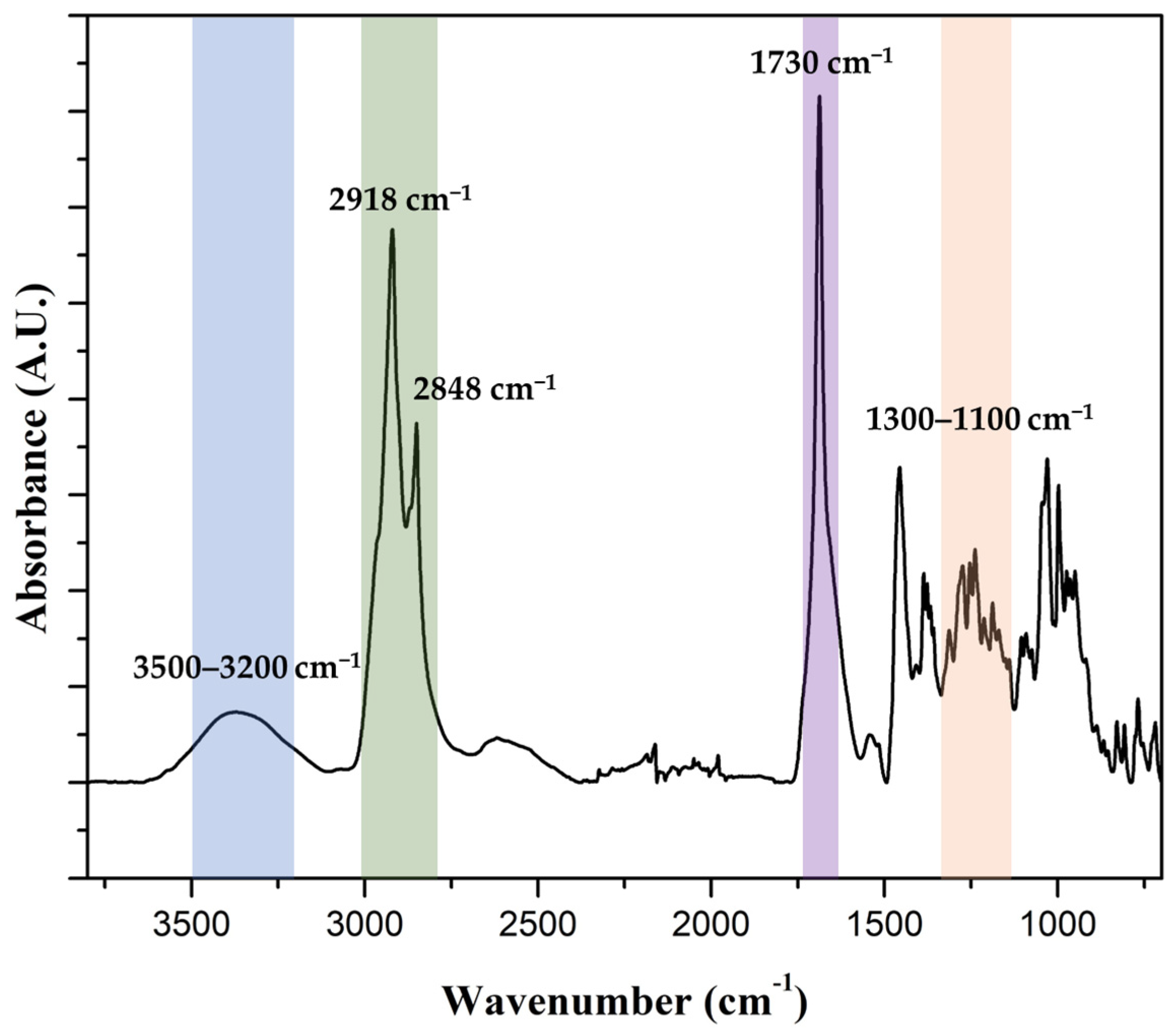
3.3. Extraction and Confirmation of Cutin
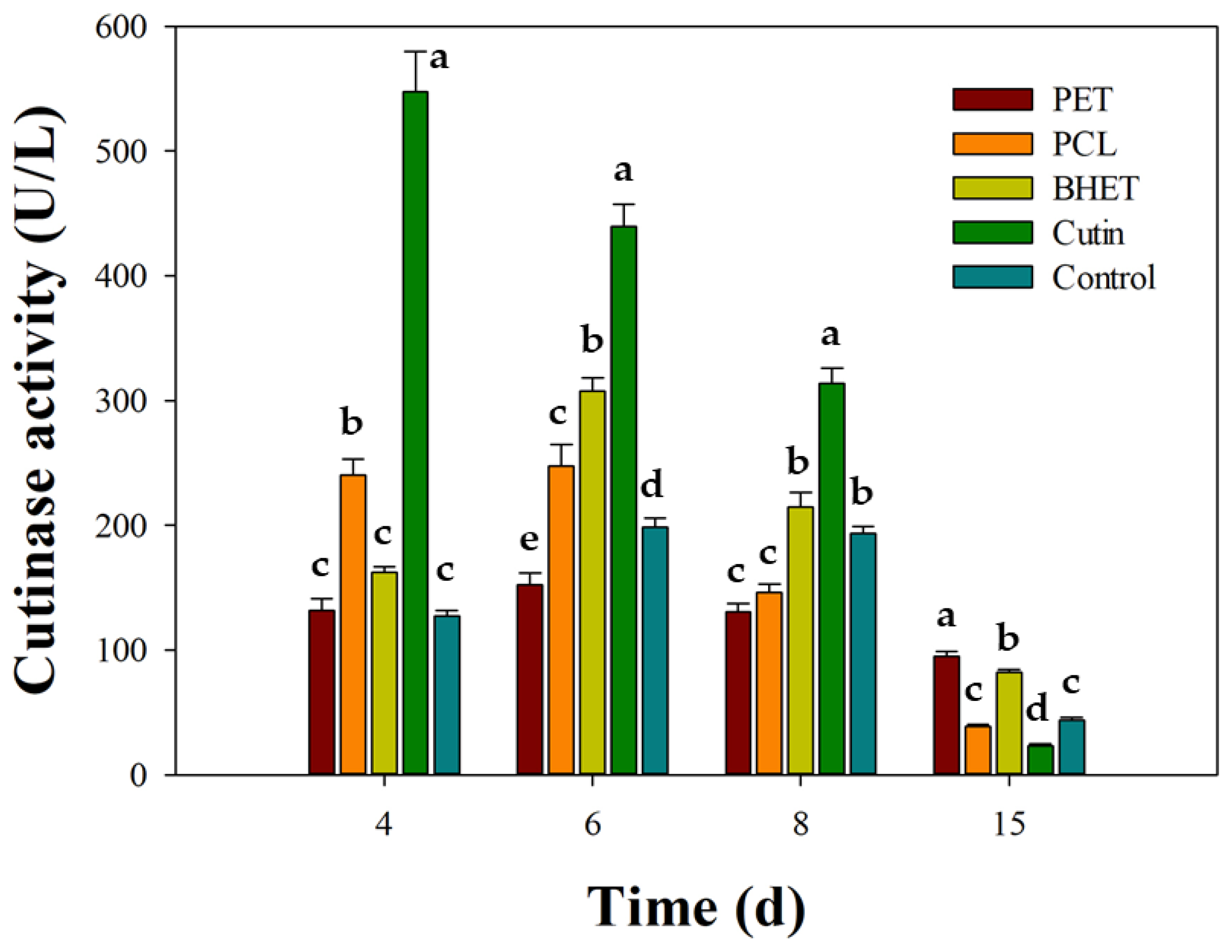
3.4. Stimulation of Cutinase Activity in Schizophyllum commune BNT39
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BHET | bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate |
| MHET | mono (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate |
| TPA | terephthalic acid |
| TLC | thin-layer chromatography |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
References
- Verschoor, J.-A.; Croese, M.R.; Lakemeier, S.E.; Mugge, A.; Burgers, C.M.; Innocenti, P.; Willemse, J.; Crooijmans, M.E.; Van Wezel, G.P.; Ram, A.F. Polyester degradation by soil bacteria: Identification of conserved BHETase enzymes in Streptomyces. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegariyanto, M.; Titah, H.; Pratikno, H. Biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastics using a combination of Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma harzianum. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Alcántara, L.; Oliart-Ros, R.M.; García-Bórquez, A.; Peña-Montes, C. Expression of a cutinase of Moniliophthora roreri with polyester and PET-plastic residues degradation activity. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00976-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.-S.; Chen, S.-Q.; Zhao, X.-M.; Song, L.-J.; Deng, Y.-M.; Xu, K.-W.; Yan, Z.-F.; Wu, J. Enhanced degradation of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics by an engineered Stenotrophomonas pavanii in the presence of biofilm. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temporiti, M.E.E.; Nicola, L.; Nielsen, E.; Tosi, S. Fungal enzymes involved in plastics biodegradation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Iizuka, R.; Kawabata, T. Engineered polyethylene terephthalate hydrolases: Perspectives and limits. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Duquesne, S.; Guillamot, F.; Cramail, H.; Taton, D.; Marty, A.; André, I. Enzymes’ power for plastics degradation. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5612–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Sharma, S.; Shree, N.; Mehrotra, R. A Comprehensive Review on the Diverse Arsenal of PET-Degrading Organisms. Int. J. Innov. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 3, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ion, S.; Voicea, S.; Sora, C.; Gheorghita, G.; Tudorache, M.; Parvulescu, V.I. Sequential biocatalytic decomposition of BHET as valuable intermediator of PET recycling strategy. Catal. Today 2021, 366, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Kaur, A.; Khatri, M.; Singh, G.; Arya, S.K. A review on cutinases enzyme in degradation of microplastics. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaditabatabaei, S.; Kyazze, G.; Iqbal, H.M.; Keshavarz, T. Fungal enzymes as catalytic tools for polyethylene terephthalate (PET) degradation. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.-J.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, H.-K. Functional production, characterization, and immobilization of a cold-adapted cutinase from Antarctic Rhodococcus sp. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 195, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyses, D.N.; Teixeira, D.A.; Waldow, V.A.; Freire, D.M.; Castro, A.M. Fungal and enzymatic bio-depolymerization of waste post-consumer poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET) bottles using Penicillium species. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaraj, R.; Suresh Kumar, S.M.; Kim, S.C.; Santhamoorthy, M. A review on sustainable upcycling of plastic waste through depolymerization into high-value monomer. Processes 2025, 13, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhai, K.; Wright, R.C.; Chen, J. Engineered Yeasts Displaying PETase and MHETase as Whole-Cell Biocatalysts for the Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). ACS Synth. Biol. 2025, 14, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.D.; Bulacio, N.; Álvarez, A.; Pajot, H.; Aragón, R. Fungal decomposers of leaf litter from an invaded and native mountain forest of NW Argentina. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, G.M.; Dominguez, F.G.; Pajot, H.; Flores, J.R.; Catania, M.D.V. Octospora tucumanensis (Pezizales), a new bryophilous ascomycete on Dimerodontium balansae (Bryophyta) from Argentina. Mycol. Prog. 2023, 22, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Novoa, J.G.; Domínguez, F.G.; Pajot, H.; De Cabo, L.I.; Navarro Llorens, J.M.; Marconi, P.L. Isolation and assessment of highly sucrose-tolerant yeast strains for honey processing factory’s effluent treatment. AMB Express 2024, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melinas Ciller, A.C.; Jiménez Migallón, A.; Garrigós Selva, M.d.C. Method for Obtaining Cutin from Plant Waste and Cutin Obtained. WO2023/198943 A1, 19 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, L.-F.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yuan, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; Chai, Y.-J.; Shan, S.-D. Application and comparison in biosynthesis and biodegradation by Fusarium solani and Aspergillus fumigatus cutinases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijburg, F.E.; Wösten, H.A. The versatility of Schizophyllum commune in nature and application. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2025, 53, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Kim, B.-K.; Han, M.; Cho, B.G.; Kim, D.H. Sub-and supercritical glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) into the monomer bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.; Seo, H.; Hong, H.; Park, J.; Ki, D.; Kim, K.-J. Characterization and engineering of a fungal poly (ethylene terephthalate) hydrolyzing enzyme from Aspergillus fumigatiaffinis. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-H.; Jin, J.-L.; Sun, H.-T.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.-F.; Yu, X.-H.; Cao, Q.-Z.; Song, Y.-X.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.-H. Perspectives on the microorganisms with the potentials of PET-degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1541913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soong, Y.H.V.; Abid, U.; Chang, A.C.; Ayafor, C.; Patel, A.; Qin, J.; Xu, J.; Lawton, C.; Wong, H.W.; Sobkowicz, M.J. Enzyme selection, optimization, and production toward biodegradation of post-consumer poly (ethylene terephthalate) at scale. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 18, 2300119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahova, S.; Tsacheva, I.; Troev, K.; Mitova, V. Conventional and MW assisted PET glycolysis promoted by titanium based catalyst. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 212, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Park, I.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.F.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, H. Chemical recycling of polyethylene terephthalate using a micro-sized MgO-incorporated SiO2 catalyst to produce highly pure bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate in high yield. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, T.; Weigert, S.; Gagsteiger, A.; Eich, Y.; Sittl, S.; Papastavrou, G.; Ruckdäschel, H.; Altstädt, V.; Höcker, B. Impact of enzymatic degradation on the material properties of poly (ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2021, 13, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, N.; Tsai, S.-L.; Lee, C.-K. Class I hydrophobins pretreatment stimulates PETase for monomers recycling of waste PETs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z. Deconstructing PET: Advances in enzyme engineering for sustainable plastic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.-H.; Lee, M.-E.; Cho, B.-H.; Oh, J.W.; You, S.K.; Ko, Y.J.; Hyeon, J.E.; Han, S.O. Enhanced biodegradation of waste poly (ethylene terephthalate) using a reinforced plastic degrading enzyme complex. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Dong, X.; Sun, Y. Sequentially co-immobilized PET and MHET hydrolases via Spy chemistry in calcium phosphate nanocrystals present high-performance PET degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Haugwitz, G.; Han, X.; Pfaff, L.; Li, Q.; Wei, H.; Gao, J.; Methling, K.; Ao, Y.; Brack, Y.; Mican, J. Structural insights into (tere) phthalate-ester hydrolysis by a carboxylesterase and its role in promoting PET depolymerization. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 15259–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiorowska, K.E.; Biniarz, P.; Dobrowolski, A.; Leluk, K.; Mirończuk, A.M. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for poly (ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiorowska, K.E.; Moreno, A.D.; Iglesias, R.; Leluk, K.; Mirończuk, A.M. Production of PETase by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica for efficient poly (ethylene terephthalate) biodegradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, Z.; Ding, M.; Yuan, Y. Current advances in the biodegradation and bioconversion of polyethylene terephthalate. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Taniguchi, I.; Oda, K. Ideonella sakaiensis, PETase, and MHETase: From identification of microbial PET degradation to enzyme characterization. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Long, R.; Lin, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, L. Development and characterization of a bacterial enzyme cascade reaction system for efficient and stable PET degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingwekar, D.; Laster, H.; Kemp, H.; Mellies, J.L. Two-step chemo-microbial degradation of post-consumer polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic enabled by a biomass-waste catalyst. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Benítez, J.J.; Domínguez, E.; Bayer, I.S.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A.; Heredia, A. Infrared and Raman spectroscopic features of plant cuticles: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafatti-Picca, L.; Bucioli, E.C.; De Barros Chaves, M.R.; De Castro, A.M.; Valoni, É.; De Oliveira, V.M.; Marsaioli, A.J.; Govone, J.S.; De Franceschi de Angelis, D.; Brienzo, M. Fungal screening for potential PET depolymerization. Polymers 2023, 15, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, P.; Reinikainen, T.; Nyyssölä, A.; Buchert, J. A high throughput profiling method for cutinolytic esterases. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2009, 44, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.-W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, F.G.; Canal Martínez, V.; Pereira, C.E.; Zannier, F.; Arnau, V.G.; Romero, C.M.; Álvarez, A. Enzymatic Potential of Schizophyllum commune BNT39 in BHET Hydrolysis and PET Biodegradation. Processes 2025, 13, 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113663
Martínez FG, Canal Martínez V, Pereira CE, Zannier F, Arnau VG, Romero CM, Álvarez A. Enzymatic Potential of Schizophyllum commune BNT39 in BHET Hydrolysis and PET Biodegradation. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113663
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Fernando Gabriel, Verónica Canal Martínez, Claudia Elizabeth Pereira, Federico Zannier, Víctor Gonzalo Arnau, Cintia Mariana Romero, and Analía Álvarez. 2025. "Enzymatic Potential of Schizophyllum commune BNT39 in BHET Hydrolysis and PET Biodegradation" Processes 13, no. 11: 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113663
APA StyleMartínez, F. G., Canal Martínez, V., Pereira, C. E., Zannier, F., Arnau, V. G., Romero, C. M., & Álvarez, A. (2025). Enzymatic Potential of Schizophyllum commune BNT39 in BHET Hydrolysis and PET Biodegradation. Processes, 13(11), 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113663








