Determining the Impact of Temperature on Cr (IV) Adsorption Using Bacterial Cellulose Biomass as an Adsorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Cellulose (BC) Production
2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Analysis of Treatment
2.4. Biomass Characterization
3. Results
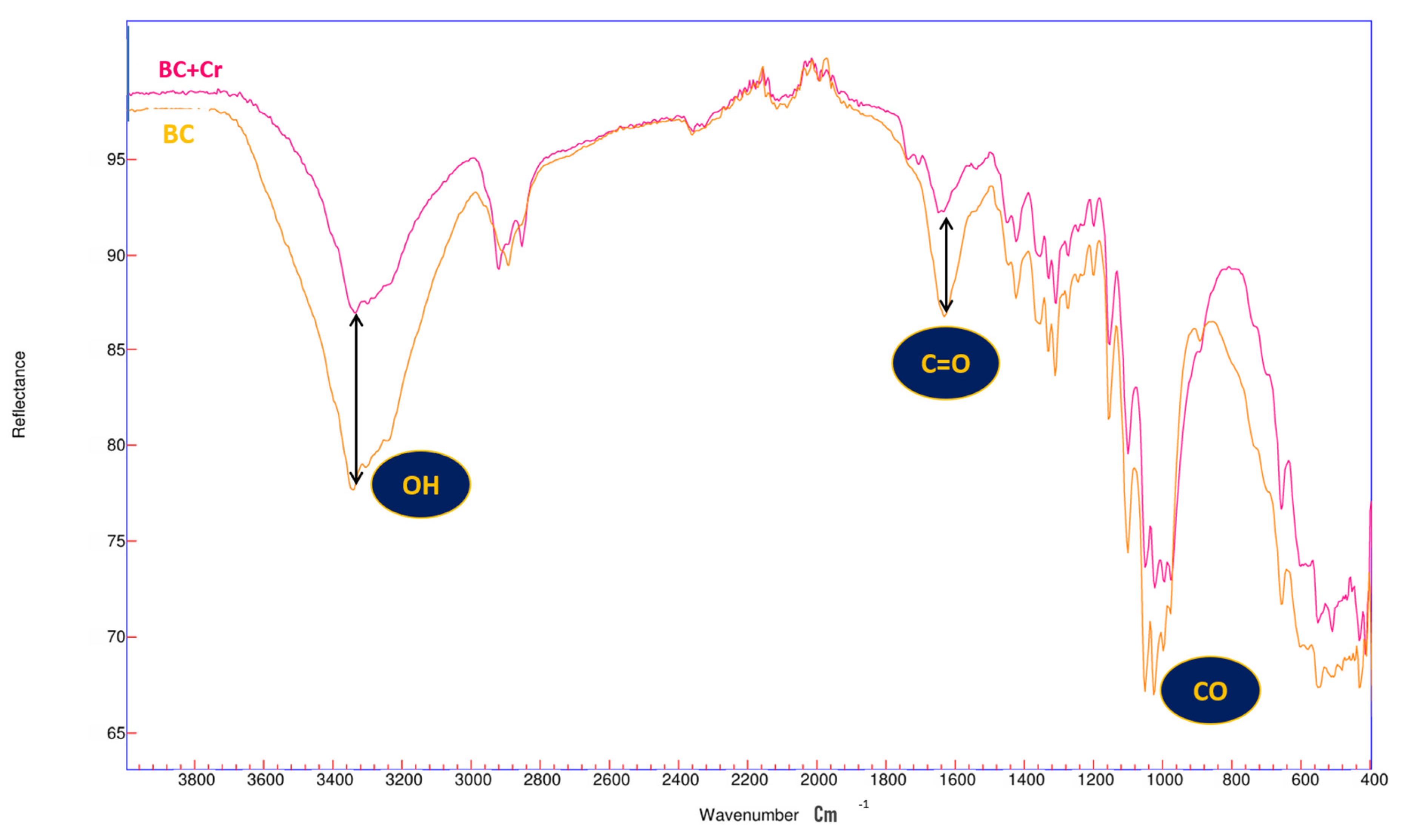
3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
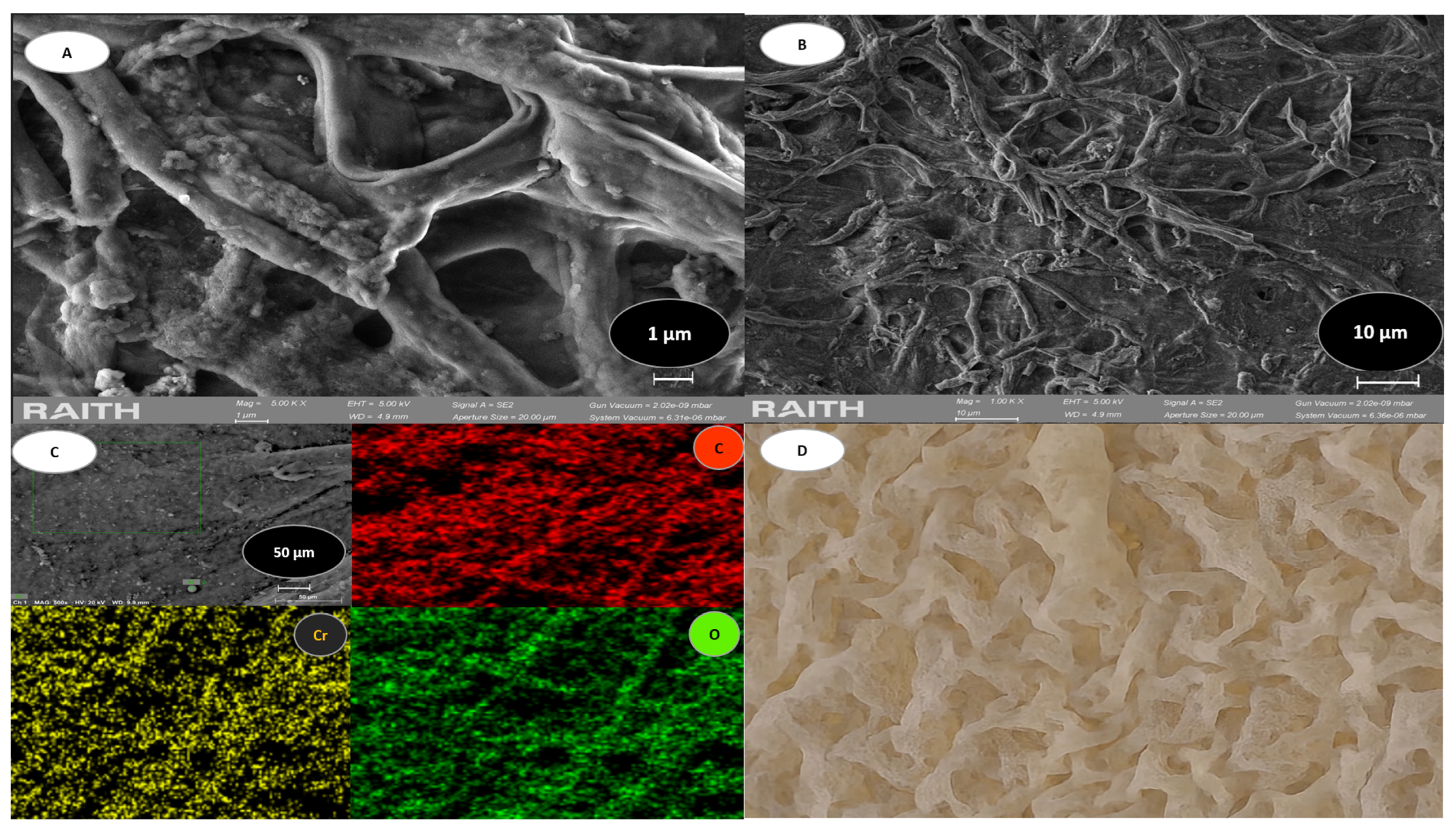
3.2. FE-SEM
3.3. Chemical Analysis of Adsorption
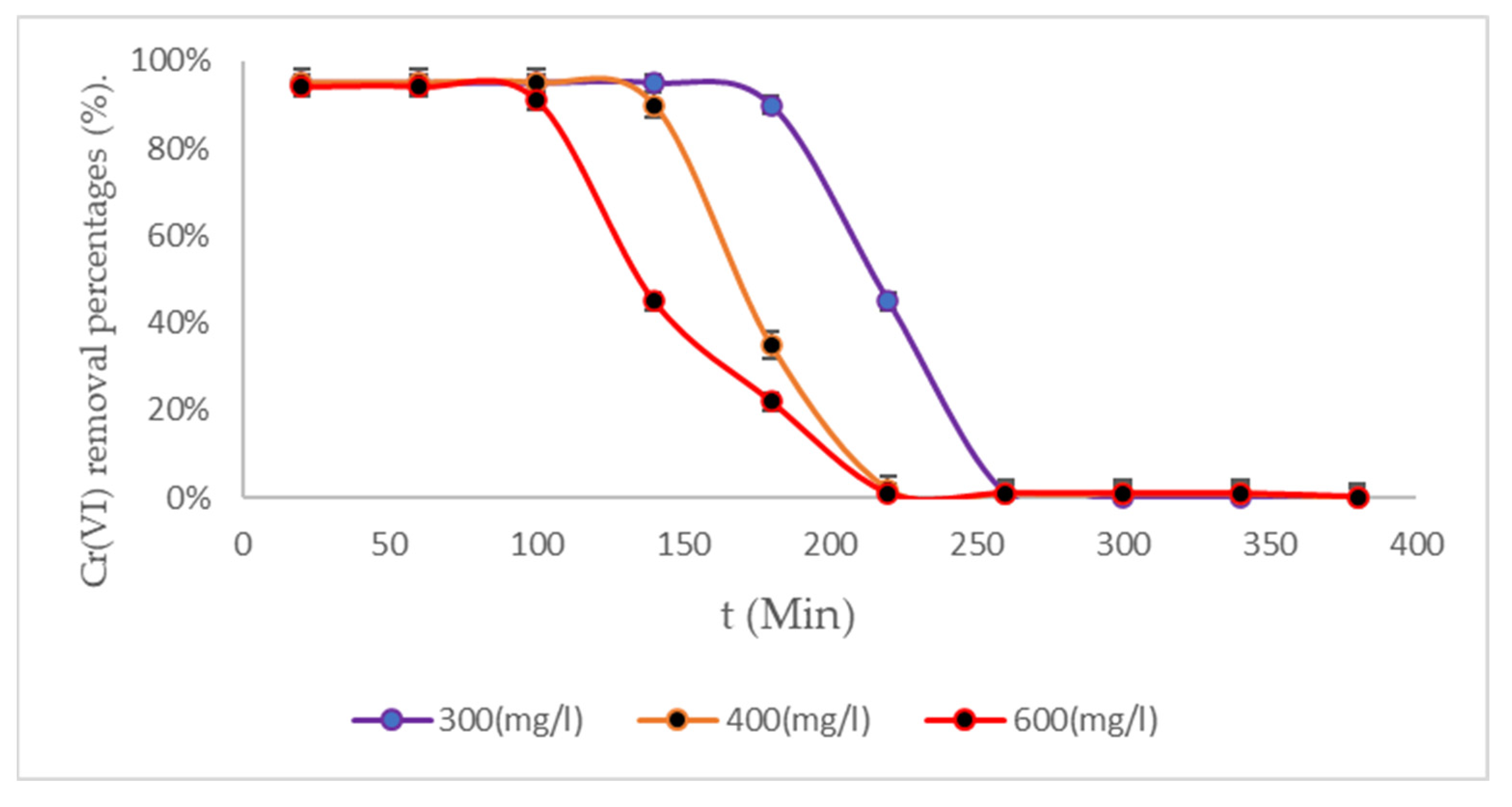
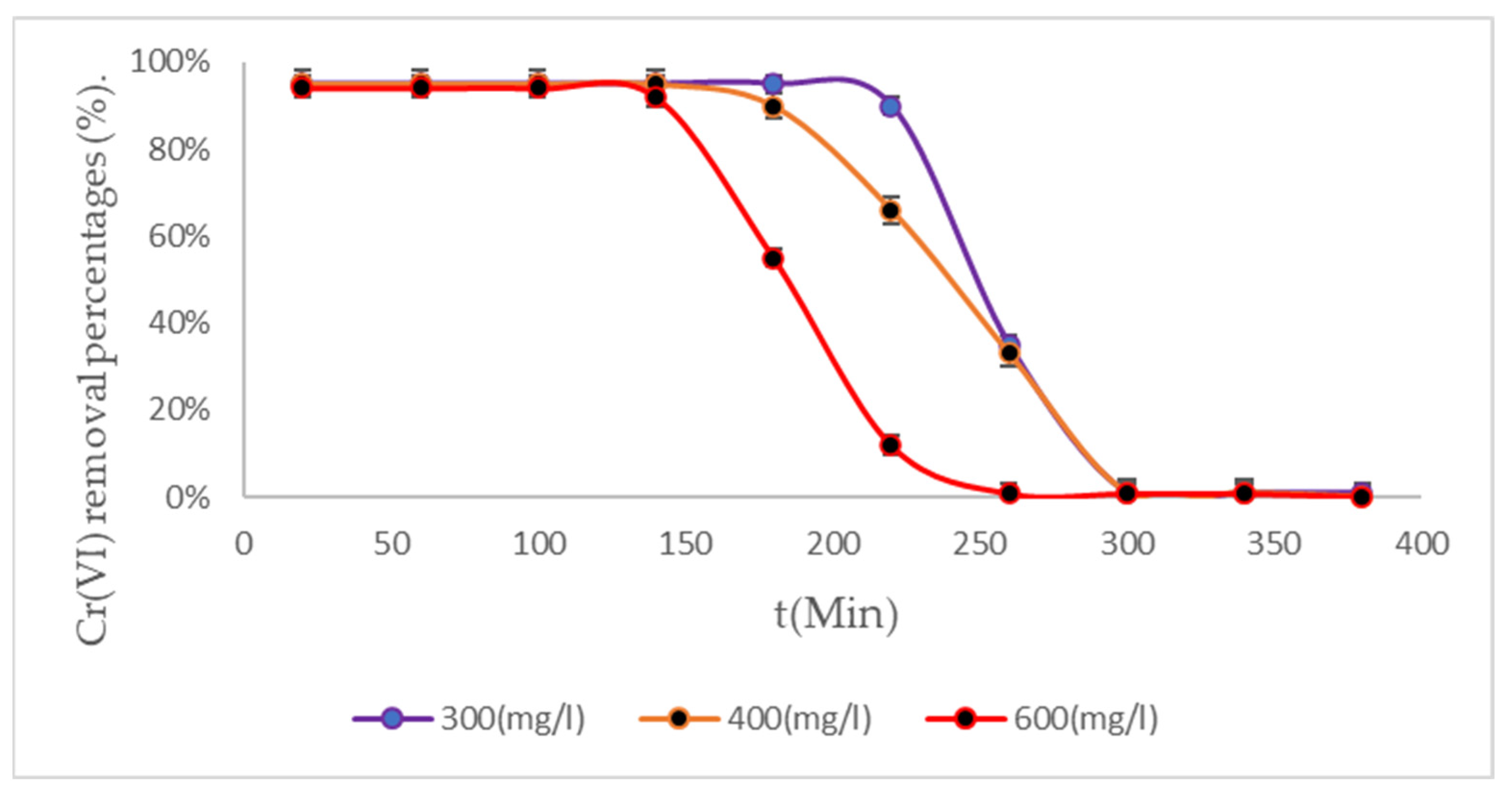
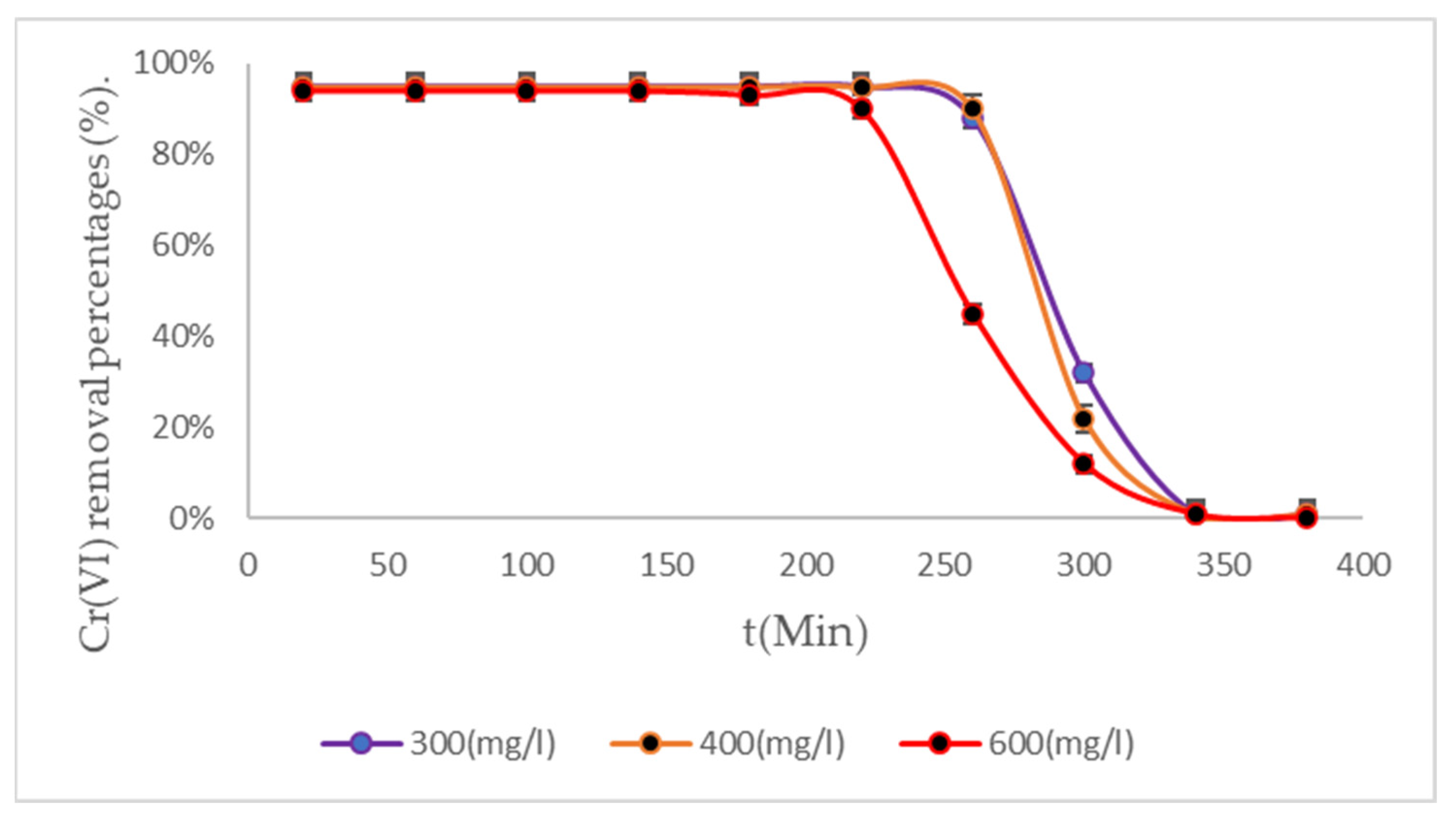
3.4. Removal Results Under Three Temperature Scenarios
3.5. Isotherms
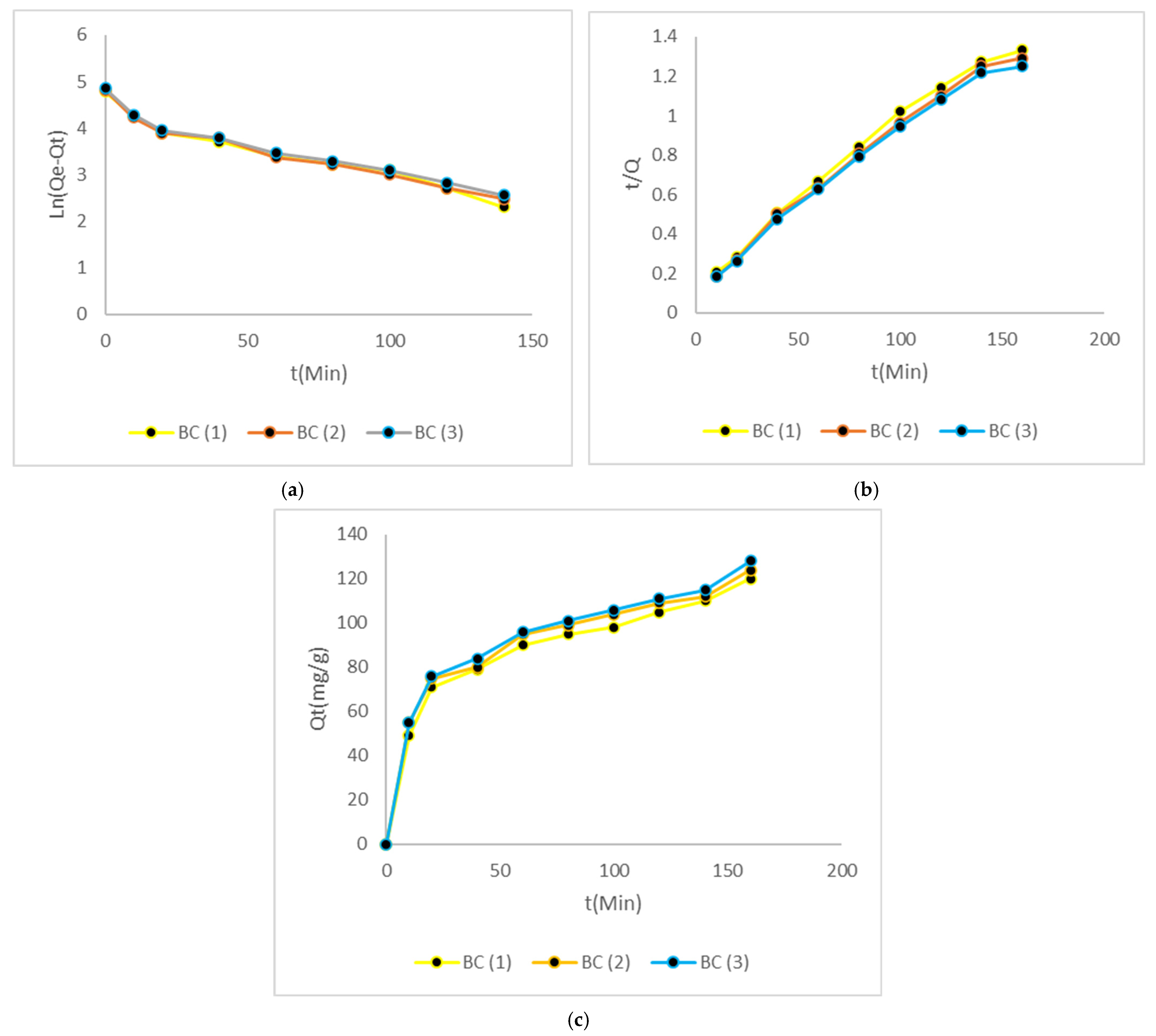
3.6. Kinetic Studies
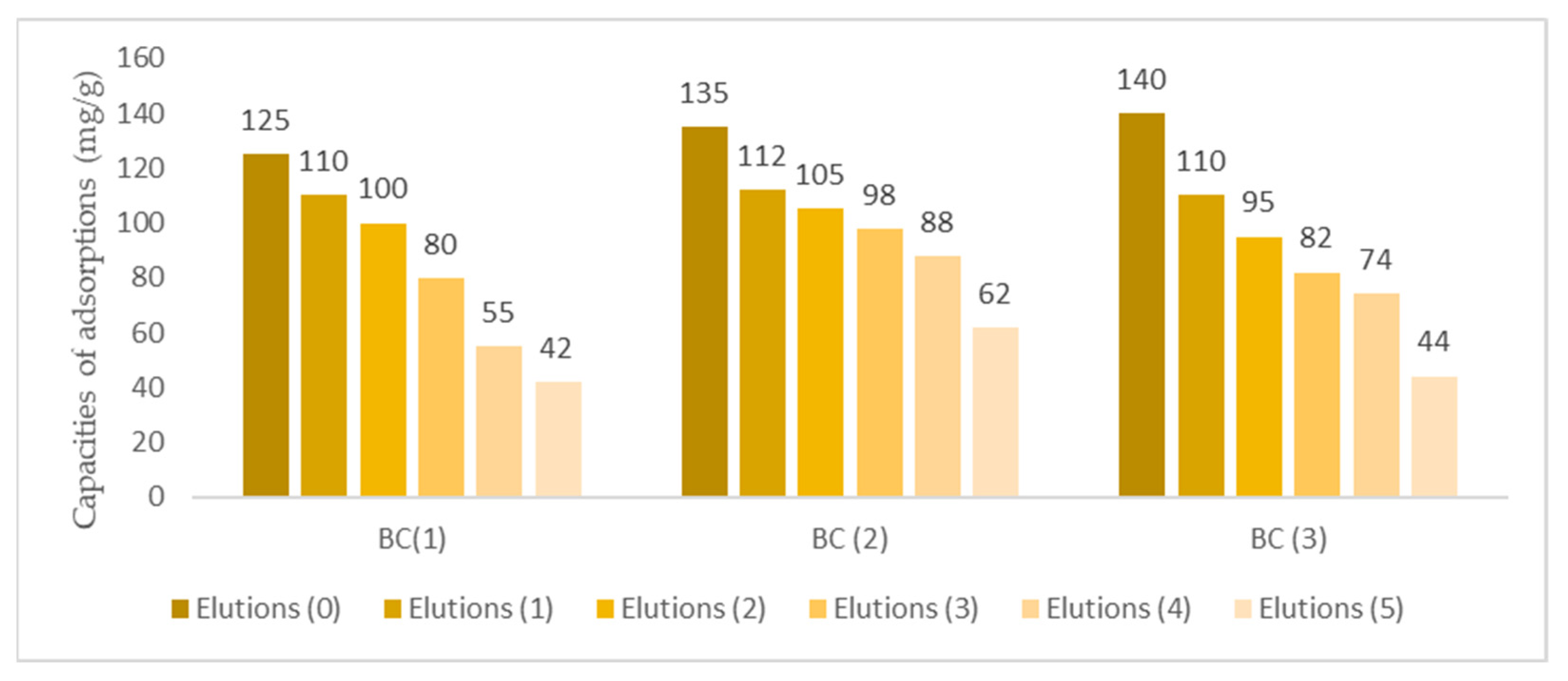
3.7. Elutions and Reutilizations of Biomass
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carreño Sayago, U.F. Diseño y evaluación de un biosistema de tratamiento a escala piloto de aguas de curtiembres a través de la Eichhornia crassipes. Rev. Colomb. Biotecnol. 2016, 18, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R. Heavy metals in chrome-tanned shaving of the tannery industry are a potential hazard to the environment of Bangladesh. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Castro, Y.P. Development of a composite material between bacterial cellulose and E crassipes, for the treatment of water contaminated by chromium (VI). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 6285–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin-Shafique, S.; Huang, J.; Malla, S.; Mitra, M.C.; Rehman, S. Stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash and its effect on strength. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2022, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri-and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.K.; Moktadir, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.M. Progress in surface-modified silicas for Cr (VI) adsorption: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.H.; Huang, S.T.; Liang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Guo, Z.W.; Guo, P.R.; Qian, W.; Diao, Z.H.; et al. Simultaneous adsorption of Cr (VI) and phenol by biochar-based iron oxide composites in water: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Aguilar, A.M.L. Designing, Modeling and Developing Scale Models for the Treatment of Water Contaminated with Cr (VI) through Bacterial Cellulose Biomass. Water 2024, 16, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, W.; Shi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Carboxymethylated-bacterial cellulose for copper and lead ion removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.; Zakeel, M.C.M.; Zavahir, J.S.; Marikar, F.M.; Jahan, I. Heavy metal accumulation in rice and aquatic plants used as human food: A general review. Toxics 2021, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; Rao, F.; Zhang, K.; Qin, Z.; Song, Z.; Na, Z. Behaviors and mechanisms of adsorption of MB and Cr (VI) by geopolymer microspheres under single and binary systems. Molecules 2024, 29, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jimmy, C.Y. Converting cellulose waste into a high-efficiency photocatalyst for Cr (VI) reduction via molecular oxygen activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 295, 120253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhu, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and Cr (VI) adsorption performance of carbonaceous nanofibers derived from bacterial cellulose. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Guo, M.; Guo, Z. Fluorescent carbon dots crosslinked cellulose Nanofibril/Chitosan interpenetrating hydrogel system for sensitive detection and efficient adsorption of Cu (II) and Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Recent advances in the treatment of industrial wastewater from different celluloses in continuous systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Lee, J.F. Reaction mechanism of hexavalent chromium with cellulose. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a pilot-scale industrial wastewater treatment system with plant biomass and EDTA. Water 2023, 15, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qiao, J.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. A 3D porous structured cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel with carbon dots-enhanced synergetic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis for effective Cr (VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Mousavi, S.M. Bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite aerogels as novel bioadsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium: Experimental and simulation study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, Z.; Deng, Y.; Deng, W.; Xiao, H.; Wu, W. Fluorescent bacterial cellulose@ Zr-MOF via in-situ synthesis for efficient enrichment and sensitive detection of Cr (VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, K.; Kumar, N.; Verma, V. Bacterial cellulose/PANi mat for Cr(VI) removal at acidic pH. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F.; Piñeros Castro, Y.; Conde Rivera, L.R. Design of a fixed-bed column with vegetal biomass and its recycling for Cr (VI) treatment. Recycling 2022, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, G.M.; Palladino, F.; Nucci, E.R.; Machado, A.R.T.; Rosa, C.A.; Santos, I.J.B. Bacterial nanocellulose produced as a by-product of the brewing industry and used as an adsorbent for synthetic solutions of Co (II), Cu (II), Ni (II) AND Fe (III). J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 6803–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.S.; Riaz, A.; Roy, J.S.; Fréchette, J.; Morency, S.; Gomes, O.P.; Dumée, L.F.; Greener, J.; Messaddeq, Y. Removal of cadmium and chromium heavy metals from aqueous medium using composite bacterial cellulose membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, P.; Du, Z.; Cai, Z. Copper ion-imprinted bacterial cellulose for selectively removing heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2022, 29, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyo, A.N.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A. Recent advances in cellulose, chitosan, and alginate based biopolymeric composites for adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Luo, W.; Luo, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Jing, L. A study on adsorption of Cr (VI) by modified rice straw: Characteristics, performances and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhan, E.Y.; Yildirim, A.; Kocer, M.B.; Uysal, A.; Yilmaz, M. A cellulose-based material as a fluorescent sensor for Cr (VI) detection and investigation of antimicrobial properties of its encapsulated form in two different MOFs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Lozano, A.M. Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride. Toxics 2025, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiravi-Rivash, O.; Mashreghi, M.; Baigenzhenov, O.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Producing bacterial nano-cellulose and keratin from wastes to synthesize keratin/cellulose nanobiocomposite for removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from waters and wastewaters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2023, 656, 130355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Ahmad, W.; Park, J.H.; Kumar, V.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Vaya, D.; Kim, H. One-step functionalization of chitosan using EDTA: Kinetics and isotherms modeling for multiple heavy metals adsorption and their mechanism. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Tran, T.V. Bacterial cellulose and composites for the treatment of water pollution: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2025, 23, 707–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.U.; Zhang, Y.M.; Guan, X.H.; Xu, X.H.; Gao, T.T. Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions onto surface amino-bacterial cellulose. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Ficai, D.; Trusca, R.; Dolete, G.; Andronescu, E.; Turculet, S.C. Chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite membranes as adsorbents with applications in water purification. Materials 2020, 13, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Peräniemi, S.; Leiviskä, T.; Kim, T.; Tripathi, K.M.; Bhatnagar, A. Synthesis of clay-cellulose biocomposite for the removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Pham, C.D.; Nguyen, K.D.; Tran, A.T.; Le, N.T.; Ho, P.H.; Le, H.V. Bacterial Cellulose-Based Material from Coconut Water as Efficient Green Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Cations. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Amr, A.; Asker, M.S.; El-Shafie, A. Preparation and characterization of ion exchanger based on bacterial cellulose for heavy metal cation removal. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019, 62 Pt 2, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; El-Assal, A.A.; El Sikaily, A.; Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Ragab, S. New magnetic cellulose nanobiocomposites for Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions removal: Kinetics, thermodynamics and analytical evaluation. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricou, P.; Lecuyer, I.; Le Cloirec, P. Removal of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+ by adsorption onto fly ash and fly ash/lime mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rocky, M.M.H.; Rahman, I.M.; Biswas, F.B.; Rahman, S.; Endo, M.; Wong, K.H.; Mashio, A.S.; Hasegawa, H. Cellulose-based materials for scavenging toxic and precious metals from water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ye, Z. Study on adsorption mechanism of Pb (II) and Cu (II) in aqueous solution using PS-EDTA resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Hierarchically porous poly (amidoxime)/bacterial cellulose composite aerogel for highly efficient scavenging of heavy metals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 600, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, L.; Rodrigues, R.; Fischer, D.; Tovar-Castro, J.D.; Payne, A.; Navone, L.; Hu, Y.; Yan, H.; Pinmanee, P.; Barro, E.; et al. Bacterial cellulose cookbook: A systematic review on sustainable and cost-effective substrates. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2024, 9, 379–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, R.; Hooda, A. Fungal biosorption–an alternative to meet the challenges of heavy metal pollution in aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Angove, M.J.; Morton, D.W. Recent innovative research on chromium (VI) adsorption mechanism. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, D.T.; Le, G.T.; Tomul, F.; Lima, E.C.; Woo, S.H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, P.T.; Chao, H.P.; et al. Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium onto layered double hydroxides-based adsorbents: A systematic in-depth review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, D.J. Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption equilibrium of heavy metals and dyes from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Lozano, A.M. Design of Biomass Adsorbents Based on Bacterial Cellulose and E. crassipes for the Removal of Cr (VI). Polymers 2025, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Development of a treatment for water contaminated with Cr (VI) using cellulose xanthogenate from E. crassipes on a pilot scale. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. A comprehensive review of cellulose nanomaterials for adsorption of wastewater pollutants: Focus on dye and heavy metal Cr adsorption and oil/water separation. Collagen Leather 2024, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmoune, M.N. Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, A.; Hamid, A.; Muhammad, N.; Naseer, A.; Ghauri, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rafiq, S.; Shah, N.S. Cellulose-based materials for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater—An overview. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, S.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, H. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II) onto diethylenetriamine-bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Li, X.; Qiao, H.; Ke, H.; Luo, L.; Wei, Q. Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, H.I.; Yap, P.S. A review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels for the removal of heavy metals from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Zhao, D.; Lu, A.; Zhong, C.; Shen, X.C.; Ruan, C. One-pot green synthesis of poly (hexamethylenediamine-tannic acid)-bacterial cellulose composite for the reduction, immobilization, and recovery of Cr (VI). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.A.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Strachota, B.; Strachota, A.; Pavlova, E.; Mares Barbosa, S.; Kamel, S. Temperature-and pH-responsive super-absorbent hydrogel based on grafted cellulose and capable of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. Gels 2023, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.W.; Kamari, A.; Fatinathan, S.; Ng, P.W. Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution using chitosan beads. Adsorption 2006, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a biotreatment of E. crassipes for the decontamination of water with Chromium (VI). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno Sayago, U.F. Design, scaling, and development of biofilters with E crassipes for treatment of water contaminated with Cr (VI). Water 2021, 13, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Dou, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hu, M. Removal difference of Cr (VI) by modified zeolites coated with MgAl and ZnAl-layered double hydroxides: Efficiency, factors and mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 621, 126583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, G.; Baikousi, M.; Salmas, C.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R.; Karakassides, M.A. Advanced Cr (VI) sorption properties of activated carbon produced via pyrolysis of the “Posidonia oceanica” seagrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, N.; Gündoğdu, A.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.; Soylak, M. Application of cherry laurel seeds activated carbon as a new adsorbent for Cr(VI) removal. Membr. Water Treat. 2021, 12, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabar, J.M.; Adebayo, M.A.; Owokotomo, I.A.; Odusote, Y.A.; Yılmaz, M. Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous ZnCl2–activated cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) leaves biochar derived via pyrolysis for crystal violet dye removal. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, M.B.; Mallek, M.; Valverde, A.; Monclús, H.; Myers, T.G.; Salvadó, V.; Cabrera-Codony, A. Competitive heavy metal adsorption on pinecone shells: Mathematical modelling of fixed-bed column and surface interaction insights. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.P.; Chang, C.C.; Nieva, A. Biosorption of heavy metals on Citrus maxima peel, passion fruit shell, and sugarcane bagasse in a fixed-bed column. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3408–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, M.; Mohamed, M.H.; Udoetok, I.A.; Steiger, B.G.; Wilson, L.D. Evaluation of a granular Cu-modified chitosan biocomposite for sustainable sulfate removal from aqueous media: A batch and fixed-bed column study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Flores, G.; Alvarado-Reyna, S.; Elvir-Padilla, L.G.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Avila, H.E.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. Kinetics, thermodynamics, and competitive adsorption of heavy metals from water using orange biomass. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Su, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, S. Cr (VI) removal by cellulose-based composite adsorbent with a double-network structure. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liao, W.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Qiu, R.; Gao, T.; Xian, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, M. Cellulose nanocrystals for green remediation of contaminated soil with multiple heavy metals. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaffa, E.; Ramsheh, N.A.; Banerjee, A.; Ghafuri, H. Bacterial cellulose microfilament biochar-architectured chitosan/polyethyleneimine beads for enhanced tetracycline and metronidazole adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeedi, H.; Ahmad, H.; Altowairqi, M.F.; Alhamed, A.A.; Alsalme, A. Covalently Functionalized Cellulose Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Enrichment of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Cu (II) Ions. Polymers 2023, 15, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, M.; Ali, J.; Hou, J.; Chen, Y.; Juan, L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Shaoya, M. Bacterial cellulose modified with thiomolybdate sulfides: An outstanding eco-friendly adsorbent for the removal of multiple heavy metals from aqueous medium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 374, 133656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosen, J.; Binnemans, K. Adsorption and chromatographic separation of rare earths with EDTA-and DTPA-functionalized chitosan biopolymers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, R.K. Solid phase extraction studies on cellulose based chelating resin for separation, pre-concentration and estimation of Cu2+ and Ni2+. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Gao, K.; Yu, W.; Liu, L. Fabrication of cellulose-based carboxylate-functionalized materials via cosolubilization-crystallization for reversible Pb2+ adsorption. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J. Adsorption and coadsorption mechanisms of Cr (VI) and organic contaminants on H3PO4 treated biochar. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, S.; Wan, T.; Jia, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Zhong, C. Biosynthesis of spherical Fe3O4/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model Isotherm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity of adsorption | (1) | Q (mg/g) Adsorption capacity (mg/L) Vol: volume (ml); M: Biomass (g), C0 Concentrations initial mg/L; CF Concentrations final. | |
| Freundlich equation | (2) | Q (mg/g) Adsorption capacity (mg/L) KF (mg/g) (L/mg), n is constant for Freundlich. | |
| Langmuir equation | (3) | Q (mg/g) Adsorption capacity; Qm (mg/g) is the maximum adsorption capacity; KL (mg/g) constant for Langmuir | |
| Temkin equation | (4) | Q (mg/g) Adsorption capacity at equilibrium; Kt (mg/g) constants for Temkin | |
| Model Kinetic | |||
| Pseudo-first order | (5) | Qt and Qe (mg/g) of pollutions at equilibrium and time t (h); K1 (min−1) is the pseudo-first order | |
| Pseudo-second order | (6) | Qt and Qe (mg/g); K2 is the model second order. | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | (7) | Qt (mg/g) (mg/g)h0.5 is intraparticle diffusion; C (mg/g) is the thickness of the boundary layer | |
| Model Thermodynamic | |||
| (8) | R (8.314 J/mol.K) is the gas constant, T (Kelvin), ∆H° (kJ/mol) is the enthalpy change, and ∆S° (J/mol.K) is the entropy change. | ||
| (9) | ∆G° (kJ/mol) is the change in Gibbs energy of the processes, ΔG° | ||
| (10) |
| Element | Weight | Percentages % |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 45.1 | 44.1 |
| Oxygen | 41.3 | 39.2 |
| Chromium | 10 | 9.1 |
| Reference | Adsorbents | Concentrations (mg/L) of Cr (VI) | Remotion’s % |
|---|---|---|---|
| [60] | E. crassipes | 300 | 90 |
| [61] | E. crassipes + FeOOH | 300 | 99 |
| [62] | Zeolites | 1000 | 99 |
| [64] | Activated carbon | 500 | 95 |
| [67] | pinecone shells | 500 | 90 |
| [68] | Citrus maxima peel | 100 | 90 |
| [69] | Chitosan biocomposite | 500 | 99 |
| Isotherm | Constante | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC (1) | Langmuir | KL = 0.8; Qm; 125 | 0.99 |
| Freundlich | KF = 0.16 | 0.91 | |
| Temkin | KT = 16.33 | 0.90 | |
| BC (2) | Langmuir | KL = 1.0; Qm; 135 | 0.99 |
| Freundlich | KF = 0.14 | 0.91 | |
| Temkin | KT = 16.2 | 0.89 | |
| BC (3) | Langmuir | KL = 1.1; Qm; 140 | 0.99 |
| Freundlich | KF = 0.12 | 0.91 | |
| Temkin | KT = 16.1 | 0.90 |
| ΔS° (J/mol.K) | ∆H° (kJ/mol) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | Temperature (k) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC (1) | 111.0 | 7.3 | −24.59 | 288 |
| BC (2) | 109.2 | 7.0 | −26.14 | 298 |
| BC (3) | 108.5 | 6.9 | −28.96 | 318 |
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | Intraparticle Diffusion | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | Qe (mg/g) | K1 (min) | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K2 × 10−3 (g/mg·min) | R2 | C (mg/L) | Kd (mg/g × 0.5 h) | R2 |
| BC (1) | 124 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 125 | 1.17 | 0.99 | 18.2 | 4.4 | 0.91 |
| BC (2) | 133 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 135 | 1.22 | 0.98 | 18.1 | 4.5 | 0.91 |
| BC (3) | 141 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 140 | 1.25 | 0.96 | 18.0 | 4.6 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernando, C.S.U. Determining the Impact of Temperature on Cr (IV) Adsorption Using Bacterial Cellulose Biomass as an Adsorbent. Processes 2025, 13, 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113493
Fernando CSU. Determining the Impact of Temperature on Cr (IV) Adsorption Using Bacterial Cellulose Biomass as an Adsorbent. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113493
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernando, Carreño Sayago Uriel. 2025. "Determining the Impact of Temperature on Cr (IV) Adsorption Using Bacterial Cellulose Biomass as an Adsorbent" Processes 13, no. 11: 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113493
APA StyleFernando, C. S. U. (2025). Determining the Impact of Temperature on Cr (IV) Adsorption Using Bacterial Cellulose Biomass as an Adsorbent. Processes, 13(11), 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113493








