Abstract
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is a type of biomass composed entirely of cellulose. This characteristic favors the presence of a multitude of active sites, which facilitate the exchange of heavy metals present in polluting effluents. Upon contact with water contaminated with metals such as chromium, arsenic, and lead, among others, this biomass offers a potential solution to the environmental problem of industrial pollutants in water. This is particularly pertinent given the well-documented harmful effects of heavy metals in aquatic ecosystems. In this context, the objective is to determine the impact of temperature on Cr (IV) adsorption using bacterial cellulose biomass as an adsorbent, under different temperature scenarios, similar to the conditions of discharge of contaminated effluents into rivers, lagoons, and wetlands. In this study, the biomass was previously characterized through FTIR and SEM images, and isothermal models were subsequently evaluated along with batch adsorption kinetics. The findings demonstrate that bacterial cellulose biomass has great potential for Cr (VI) removal at various temperatures, with an adsorption capacity of 140 mg/g at high temperatures and a reduction of up to 125 mg/g at low temperatures. The findings of this study constitute a valuable contribution to decision-making when considering the expansion of these treatment processes, facilitating this task by offering a comparative analysis of effluent discharge conditions in relation to various scenarios involving contaminated liquid temperatures. The use of this biomaterial in an environmental sustainability initiative focused on water resource conservation is a very promising prospect.
1. Introduction
A considerable number of studies in the field of environmental sciences are currently focusing on the identification of industrial wastewater treatment systems that are not only effective in their function, but also straightforward to assemble and economically viable [1,2]. This focus is largely driven by the pressing issue of water contamination by heavy metals. The presence of these pollutants poses a threat not only to the environment but also has significant social and economic implications, as evidenced by the decline in ecosystem services provided by water bodies such as rivers, wetlands, and lagoons [3,4]. As demonstrated in previous studies [5,6,7,8,9], the heavy metal chromium (Cr) is a substantial source of contamination in wastewater. Cr is an essential element for humans, but it is toxic in high concentrations. Consequently, global research efforts are predominantly oriented towards the management of Cr (VI) exposure and toxicity [10,11]. The contamination of water bodies by Cr (VI) represents a significant environmental concern, given its deleterious effect on ecosystem services. This is due to the fact that it bioaccumulates in animal and plant tissues and is non-biodegradable, therefore posing a long-term risk to human health [12,13,14,15]. The C-OH groups on cellulose have been identified as the primary reactive sites for the reduction of Cr (VI) to Cr (III). In this process, the resulting Cr (III) reacts with cellulose, forming an inner sphere bidentate complex with the carboxyl groups that are the by-products of the oxidation of the C-OH groups by Cr (VI) [16]. A cost-effective and straightforward technique for extracting heavy metals is through the utilization of adsorbent biomasses [17,18,19]. Bacterial cellulose has emerged as a promising solution due to its high adsorption capacities. The cellulose composition of bacterial cellulose provides a multitude of active sites within its cellulose matrix, where the exchange of heavy metals occurs through a process known as cation exchange [20,21,22]. The presence of hydroxyl groups in bacterial cellulose serves to attract heavy metals, thus facilitating the adsorption of these contaminants [23,24,25]. Bacterial cellulose has been demonstrated to be an effective absorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions. It has also been shown that this biomass can remove different types of heavy metals from mixed effluents [26]. The adsorption mechanism for Cr (VI) is understood to generally consist of chemical reactions between functional groups on the adsorbent and metal ions or cation exchange reactions due to the high cation exchange capacity of the adsorbent [27]. Laboratory-scale experiments are conducted to ascertain behaviors and adaptations in heavy metal removal, thereby informing decisions when designing processes at larger scales. The parameters that are considered include pH, various concentrations of heavy metals, and notably, temperature. Through the careful manipulation of variables such as temperature, it is possible to ascertain the predominant isotherm in the adsorption process, thereby facilitating the selection of the most suitable isotherm for the given context [28,29,30,31]. The evaluations of thermodynamic parameters represent a fundamental and integral component within the scope of adsorption research projects, as they are critical to delineate the nature of the process by reporting physical or chemical interactions [32,33]. In order to reuse biomass and thus obtain a product that meets the criteria of the circular economy, biomass elution processes must be in place [34]. An effective elution agent is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), a powerful chelator that optimizes the adsorption process of heavy metals in adsorbent biomasses [35,36]. Therefore, it is imperative to develop laboratory-scale treatment systems with bacterial cellulose biomass, using adsorption models, to identify the optimal parameters for the development of a larger-scale treatment system. For this reason, the present project was initiated with the objective of determining the impact of temperature on the adsorption of Cr (IV) using bacterial cellulose biomass as an adsorbent.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Cellulose (BC) Production
The production of this biomass involved the use of tea, glucose (3 g), and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) (5 g), mixed with distilled water (1 L). The mixture was subsequently heated to 85 °C to form the initial culture medium. Then, 300 mL of kombucha (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast) was added to a 3 L glass container and placed in a 15 L incubator (IO Xtemp Series Dual Incubator Oven, Hettich, Föhrenstr, Germany) at a temperature of 37 °C. During the incubation process, pH, humidity, and temperature were kept constant for all samples. The production of cellulose films was completed in approximately three weeks. After this process, the BC films were dried to remove excess water. After drying, the bacterial cellulose biomass was ground to obtain particles below 0.222 mm using a squat mill.
2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
Test solutions of 300, 400, and 600 mg/L Cr (VI) were prepared using a 1000 (mg/L) Cr (VI) stock solution prepared with distilled water and potassium dichromate. The batch adsorption study was carried out at 20 °C. The adsorption capacity was determined by suspending 0.3 g of biomass in 100 mL of Cr (VI) solution for 140 min at 200 rpm. The sample size was 20 µm, which was subsequently transferred to a centrifuge (KASAI MIKRO 200, Staufen, Germany). The experiments were carried out in a 100 mL glass vessel with constant stirring (IKA KS 4000 stirrer, Staufen, Germany) at 20 °C and 150 rpm. Data were recorded at 20 min intervals until 160 min had elapsed. For greater reliability, the experiments were performed in triplicate, using arithmetic averages. All tests were carried out at neutral pH and at three different temperatures.
2.3. Analysis of Treatment
The treatment was conducted at different temperatures, controlled in the laboratory by an incubator (IO Xtemp Series Dual Incu-bator Oven, Hettich, Föhrenstr, Germany).
BC (1): Biomass cellulose to temperature 10 °C and 283 K;
BC (2): Biomass cellulose to temperature 25 °C and 298 K;
BC (3): Biomass cellulose to temperature 45 °C and 318 K.
Chromium determination. A solution was prepared by mixing 900 microliters of 0.5% diphenylcarbazide (97% purity) with 120 microliters of acetone (97% purity, w/v) and 80 microliters of diphenylcarbazide (1,5-diphenylcarbazide), adjusting it to a pH of 2 and a purity of 90% (H3PO4). Subsequently, 100 microliters of the chromium sample was added to an Eppendorf tube. Then, it was transferred to an adsorption cell, measuring the adsorbance at 540 nm. The measurement uncertainty of heavy elements, specifically Cr (VI), was approximately 4%.
Chromium measurement. The Cr (VI) content was measured using an Evolution 300 spectrophotometer, which monitors changes in light absorption. All of these analyses for determining chromium in water complied with APHA (American Public Health Association) and Standard Methods for the Analysis of Water and Wastewater.
Desorption–adsorption process. The bacterial cellulose saturated with Cr (VI) was placed in a 200 mL Erlenmeyer flask at 20 °C for 2 h, stirring constantly, with 100 mL of EDTA (0.1 g/mL). The biomass was then filtered off.
2.4. Biomass Characterization
Bacterial cellulose was observed using an integrated scanning electron microscope (SEM-EDS) coupled with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (FTIR) microanalysis system (University of Los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia).
FTIR. The biomasses were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (79 Jasco FTIR 430). IR spectra were measured between 4000 and 400 cm−1, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and a scan speed of 2 mm s−1.
Adsorption models. Table 1 shows the summary of the isotherm and kinetic models.

Table 1.
Models of isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics.
3. Results
3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
As illustrated in Figure 1, the characteristic functional groups of bacterial cellulose have been determined by this tool. In this context, the hydroxyl group (OH) is of particular significance due to its ability to interact with heavy metals [37,38], as evidenced by the 3448 cm−1 stretching band.

Figure 1.
Production of bacterial cellulose (BC).
Figure 2 represents the spectra of a special cellulose with 100% purity of this polysaccharide. The biomass is shown before and after the removal of Cr (VI), observing the intensities of (OH, C=O, and CO) and characteristic peaks of bacterial cellulose [39], and a change can be observed due to the adsorption process of Cr (VI). These changes are due to the biochemical modification in the biomass [40], especially of the hydroxyl group (OH), located at 3340 cm−1, indicating a possible interaction between this group and Cr (VI) [41]. Specific changes can also be seen in the peaks at 1632 cm−1 and 1000 cm−1, corresponding to the C = O and CO groups, respectively, due to the incorporation of this heavy metal in the structure of bacterial cellulose [42,43].
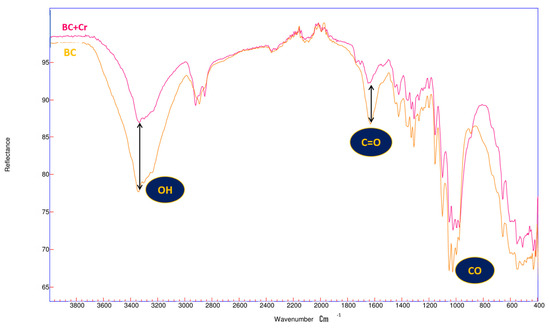
Figure 2.
FTIR characterizations of BC.
3.2. FE-SEM
Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was utilized to examine the microstructure of bacterial cellulose biomass. Figure 3 shows some characteristics of BC.
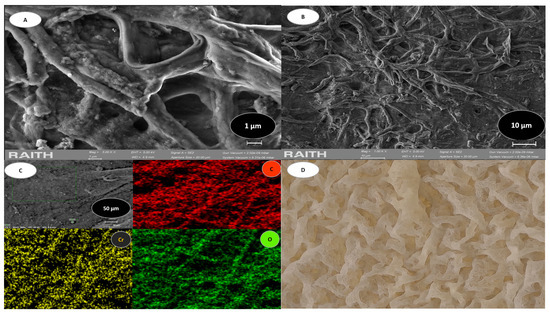
Figure 3.
BC analysis. (A) shows the SEM morphology at 1 µm. (B) shows the SEM morphology at 10 µm. (C) shows the EDS mapping that revealed the distribution of elements. (D) is an image of the bacterial cellulose biomass.
Microphotographs revealed the presence of nanofibers forming three-dimensional cellulose networks with porous channels with openings of approximately 0.1 μm (Figure 3A,B). Figure 3C represents an EDS mapping, revealing a distribution of the characteristic elements of this biomass, which are oxygen (O) and carbon (C), and also shows chromium (Cr) after adsorption. Figure 3D shows a biomass characteristic of bacterial cellulose. Table 2 represents the EDS mapping in the characterization of the elements.

Table 2.
Composition of the BC sample with Cr (VI).
As shown in Table 2, the analysis indicates that the biomass exhibited a predominance of carbon and oxygen compositions; similar results were reported in [44,45,46,47]. After the adsorption process, the Cr (VI) occupancy in the biomass is approximately 9% due to the incorporation of this heavy metal into the biochemical structure [48], somewhat aligning with similar investigations [49].
3.3. Chemical Analysis of Adsorption
After analyzing the FTIR results, micrographs, and EDS analysis, Figure 4 shows the bacterial cellulose and adsorption process.
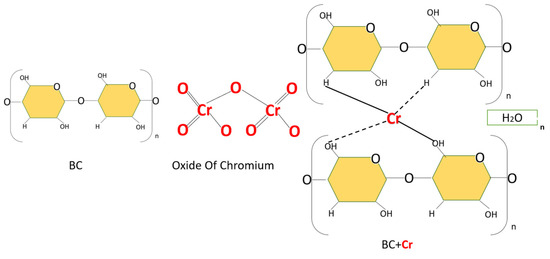
Figure 4.
Representations of the cellulose bacterial and adsorption of Cr (VI).
The adsorption process involves reactions between the adsorbent’s functional groups and Cr (VI) metal ions and cation exchange reactions due to the adsorbent’s high cation exchange capacity [50,51,52].
3.4. Removal Results Under Three Temperature Scenarios
Cr (VI) removal by BC bacterial cellulose was analyzed under three different temperature conditions in order to assess which of these conditions has the greatest impact on the process. As illustrated in Figure 5, BC (1) biomass was observed at a temperature of 288 K.
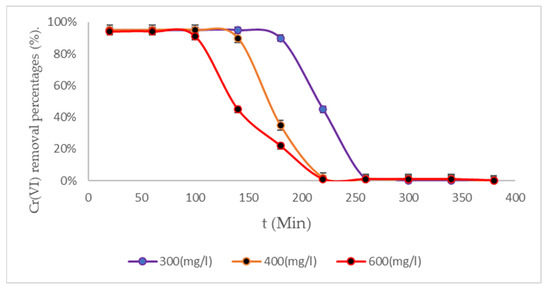
Figure 5.
Cr (VI) removal percentages from BC (1) biomass to 288 K.
BC (1) biomass has demonstrated its excellent capacity to adsorb heavy metals (see Figure 6), with removals above 90% being achieved at 120 min under an initial concentration of 600 mg/L, 180 min at an initial concentration of 400 mg/L, and 200 min at an initial concentration of 300 mg/L. As illustrated in Figure 6, the treatment system utilizing BC (2) demonstrates its efficacy in this regard.
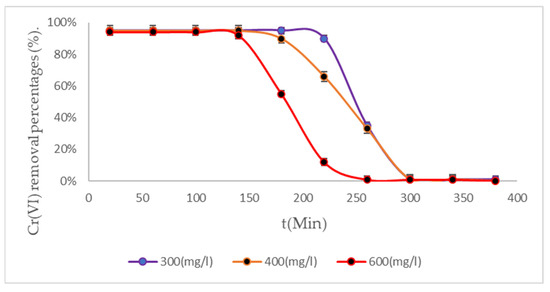
Figure 6.
Cr (VI) removal percentages from BC (2) biomass to 298 K.
The BC (2) biomass showed ideal performances when treating water contaminated with Cr (VI) for 160 min, under initial concentrations of 600 mg/L. This biomass, at room temperature, removes interesting percentages of Cr (VI), making this biomass an ideal material for treating industrial wastewater due to its excellent experimental results [53,54]. Figure 7 shows the treatment system with the BC (3) biomass.
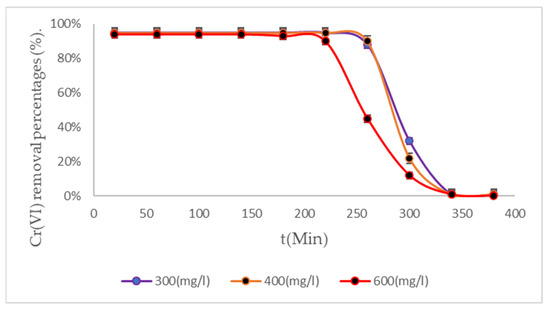
Figure 7.
Cr (VI) removal percentages from BC (3) biomass to 318 K.
It is evident that after treatment for more than 200 min, at low initial concentrations of 600 mg/L, the bacterial cellulose biomass increased its adsorption capacities with increasing temperature due to an increase in its chemisorbing potential. Given the industrial nature of the BC (100% bacterial cellulose), it was observed that removals increase due to the activation of the active sites of this biomass [55,56,57]. The enhanced interaction of the adsorbent material with Cr (VI) present in the water is particularly advantageous when utilizing water treatment systems with a post-humus design at elevated temperatures [58,59]. For example, E. crassipes biomass has also been used in Cr (VI) removal processes, achieving the removal of 90% of the contaminant, at an initial 300 mg/L in 100 min [60], but when this same biomass is used with a chelating chemical agent, such as iron chloride, the process is optimized by 20% more in Cr (VI) removals [61]. Zeolites remove 99% of the Cr (VI) present in water at initial concentrations of 600 mg/L [62,63], but this material is very difficult to obtain. High removals have also been achieved with activated carbon [64,65,66], around 95%, which is an ideal component of adsorbents but has high energy expenditure, increasing its operating costs. Table 3 shows the research on the process of removing Cr (VI).

Table 3.
Research’s on the Cr (VI) removal efficiency.
3.5. Isotherms
Thermodynamic studies using isothermal evaluations of the adsorption processes are ideal due to their ability to accurately investigate the nature and mechanisms of heavy metal adsorption in the different biomasses under evaluation [70]. The isothermal studies were carried out at three temperatures (288, 298, and 318 K). Table 4 shows a summary of the parameters.

Table 4.
Summary of the parameters.
As demonstrated in Figure 8, the various isotherms are represented graphically. The adsorption capacities of each biomass are evident, with the BC (3) biomass demonstrating superior performance due to an increased number of active sites in the biomass matrix, resulting from specific activation by elevated temperatures.
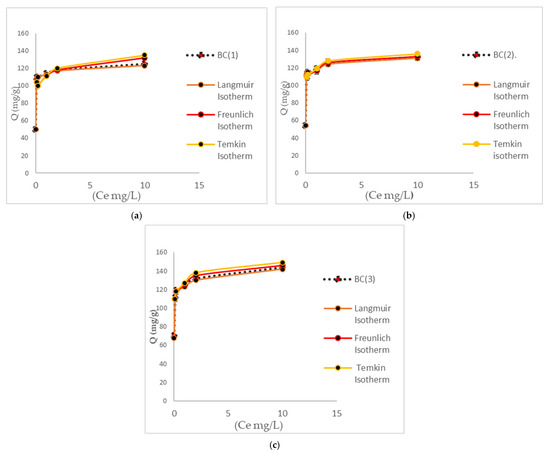
Figure 8.
Adsorption capacities of each biomass, along with the adjustments of its isotherm. (a) Graphic isotherm of BC (1). (b) Graphic isotherm of BC (2). (c) Graphic isotherm of BC (3).
It can be observed that the Langmuir isotherm model best represents the adsorption process. These results demonstrate that bacterial cellulose aligns with this isotherm in adsorption processes, due to its characteristic homogeneity of this biomass [71]. Because of this, the Langmuir isotherm parameter (KL), numerically equivalent to the thermodynamic model constant, could be used. Thermodynamic evaluations during Cr (VI) adsorption processes by bacterial cellulose are imperative in practical applications in decision-making in the design of treatment systems with adsorbent biomasses [72]. From the adsorption isotherm data at different temperatures, the enthalpy (ΔH°ads), entropy (ΔS°ads), and free energy of adsorption (ΔG°ads) can be calculated using Equations (7)–(9). The thermodynamic results of the biomasses at different temperatures are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Summary of thermodynamic parameters.
In Table 5, it is observed that the free energy (ΔG°) values were negative, indicating a spontaneous interaction in the chemical adsorption involving bacterial cellulose and Cr (VI). It was concluded that the active sites, such as the hydroxyl groups (OH), of this biomass were associated with cation exchanges, thus contributing to the high removal rates of this biological material [73]. Furthermore, the negative values of ∆G° that also increase with increasing temperature suggest that the Cr (VI) removal process becomes increasingly favorable, spontaneous, and feasible at higher temperatures [74]. The positive enthalpy values, ∆H°, for Cr (VI) ions imply that the process is endothermic. The positive value of ΔS° can be attributed to the randomness of Cr (VI) ions during the chemisorption process in biomass [75], and an increase in these values indicates an increase in disorder during the adsorption process.
3.6. Kinetic Studies
Bacterial cellulose at different concentrations and at the three temperatures fitted second-order models due to the high speeds of the adsorption processes. The kinetics of Cr (VI) removal by bacterial cellulose under three different temperatures are ideal due to the rapidity and durability over time. Figure 9 shows the process kinetic studies.
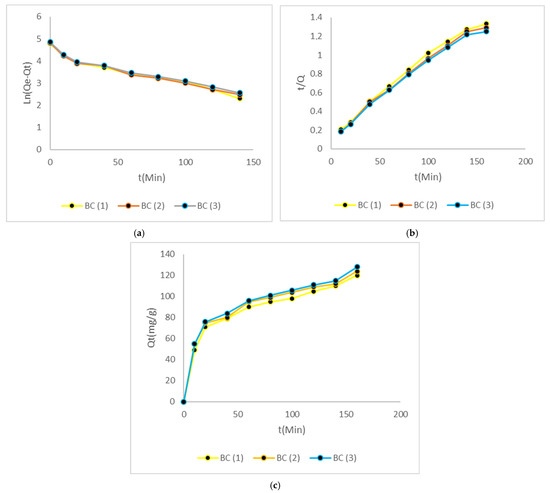
Figure 9.
Process kinetic studies. (a) Graphic of first order. (b) Graphic of second order. (c) Intraparticle diffusion.
As demonstrated in the figures illustrating the removal of this heavy metal, particularly at higher temperatures, the removal exceeded 100 mg/g within the initial 100 min, and subsequently, adsorption equilibrium was attained after approximately 200 min. Table 6 gives a summary of the parameters for each of the models.

Table 6.
Parameters of model kinetics.
Furthermore, the adsorption data can be adequately described by the pseudo-second order kinetic model, as evidenced by the high correlation coefficient R2 of 99%, which suggests the predominance of chemisorption processes [76]. The rapid adsorption kinetics can be attributed to 100% bacterial cellulose and better interaction at higher temperatures with the contaminant Cr (VI). The rate constant for the BC (3) biomass is 1.25 × 10−3 (g/mg/min), which increases with increasing temperature. However, when the temperature is decreased, as in the case of the BC (2) biomass, its rate also decreases to 1.22 × 10−3 (g/mg/min). The adjustment of the BC (1) biomass to the second-order model suggests that the low temperature affected the adsorption process to a certain extent, but not significantly [77].
3.7. Elutions and Reutilizations of Biomass
Elutions were performed through EDTA, in which the biomasses were recycled at different temperatures after the adsorption processes. The removal processes continued under conditions that replicated those of the laboratory. As illustrated in Figure 10, the adsorption capacities of the BC biomasses following elutions and reuse were also examined.
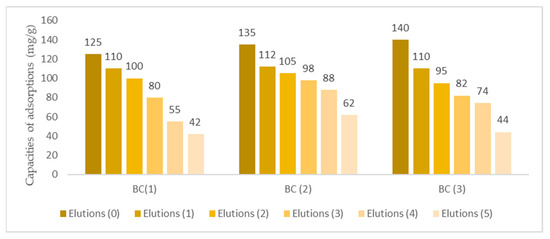
Figure 10.
Illustration of various elution processes with EDTA.
As shown in Figure 11, a continuous loss of adsorption capacities is evident in each process in bacterial cellulose. Although the capacities were lost, no significant loss was observed. However, a greater loss is evident in BC (3) due to high temperatures, and a loss is also evident in the BC (1) biomass, but less than in the other two experiments. The elution and reuse experiments demonstrate the biomass’s notable resilience to temperature fluctuations and repeated elution with EDTA. This process has been shown to enhance adsorption capacities, underscoring the potential for effective recycling of this biomass. Such recycling is crucial for subsequent scaling designs in industrial wastewater treatment applications. Bacterial cellulose is particularly well-suited for this purpose due to its high resistance to this chemical mechanism [77]. The elution process of bacterial cellulose is illustrated in Figure 11.
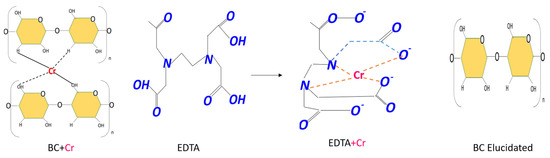
Figure 11.
BC biomass with adsorbed Cr (VI) and EDTA is utilized to form a chelate complex between EDTA and Cr (VI). This complex is then eluted or left free from bacterial cellulose for a subsequent Cr (VI) removal process. The BC biomasses demonstrated resilience, withstanding five cycles under varied temperature conditions.
EDTA, a compound known to be effective in elutions of heavy metals, is able to bind with the metals through its hydroxyl groups, which become protonated in the process [77]. This results in the adsorption and subsequent chemisorption of the heavy metal into the biomass, forming a chelate between EDTA and, in this instance, Cr (VI). This reagent is considered to be one of the most effective due to its non-toxic nature and its applicability across various recycling cycles and subsequent removal processes of heavy metals [78]. It is highly effective in the chelation of heavy metals present in adsorbent biomasses, particularly cellulose [79]. The composition of Cr (VI) in the biomass and its elution with EDTA cause the wear of the bacterial cellulose biomass by the chelating agent [80,81]. Notwithstanding, the biomass remains available for subsequent adsorption cycles and further capacities of adsorption.
4. Conclusions
A treatment system for the removal of Cr (VI) from industrial wastewater has been designed and developed. This has been achieved through the use of industrial biomass, such as bacterial cellulose, in a batch adsorption process. The result of this process is superior adsorption performance, including high adsorption capacity, rapid capture kinetics, and optimal fit to a Langmuir isotherm adsorption model. The development of thermodynamic models has been shown to facilitate decision-making when effluents have different discharge temperatures. The study concluded that bacterial cellulose biomass is a promising material for the removal of Cr (VI) at different adsorption temperatures. The highest adsorption power was observed at higher temperatures, and significant removal of this heavy metal was also achieved at lower temperatures. Furthermore, the special importance of the elution and recycling process was evident, as it optimized the sum of all adsorption capacities. This, in turn, has the potential to increase the economic viability of the material in the context of developing large-scale industrial water treatment systems. The findings are relevant to the field of environmental sciences, as they demonstrate that treatment systems using this biosorbent can be designed on a larger scale. This approach has the potential to prevent the ongoing environmental, social, and health impacts caused by Cr (VI).
Funding
The university Los Libertadores is the company that contributed to development of this article and related processes through the macroproject “Development of isothermal models in biomass pollutant adsorption processes” on adsorbent biomasses with code ING-07-25.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Carreño Sayago, U.F. Diseño y evaluación de un biosistema de tratamiento a escala piloto de aguas de curtiembres a través de la Eichhornia crassipes. Rev. Colomb. Biotecnol. 2016, 18, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R. Heavy metals in chrome-tanned shaving of the tannery industry are a potential hazard to the environment of Bangladesh. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Castro, Y.P. Development of a composite material between bacterial cellulose and E crassipes, for the treatment of water contaminated by chromium (VI). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 6285–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin-Shafique, S.; Huang, J.; Malla, S.; Mitra, M.C.; Rehman, S. Stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash and its effect on strength. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2022, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri-and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.K.; Moktadir, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.M. Progress in surface-modified silicas for Cr (VI) adsorption: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.H.; Huang, S.T.; Liang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Guo, Z.W.; Guo, P.R.; Qian, W.; Diao, Z.H.; et al. Simultaneous adsorption of Cr (VI) and phenol by biochar-based iron oxide composites in water: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Aguilar, A.M.L. Designing, Modeling and Developing Scale Models for the Treatment of Water Contaminated with Cr (VI) through Bacterial Cellulose Biomass. Water 2024, 16, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, W.; Shi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Carboxymethylated-bacterial cellulose for copper and lead ion removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.; Zakeel, M.C.M.; Zavahir, J.S.; Marikar, F.M.; Jahan, I. Heavy metal accumulation in rice and aquatic plants used as human food: A general review. Toxics 2021, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; Rao, F.; Zhang, K.; Qin, Z.; Song, Z.; Na, Z. Behaviors and mechanisms of adsorption of MB and Cr (VI) by geopolymer microspheres under single and binary systems. Molecules 2024, 29, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jimmy, C.Y. Converting cellulose waste into a high-efficiency photocatalyst for Cr (VI) reduction via molecular oxygen activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 295, 120253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhu, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and Cr (VI) adsorption performance of carbonaceous nanofibers derived from bacterial cellulose. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Guo, M.; Guo, Z. Fluorescent carbon dots crosslinked cellulose Nanofibril/Chitosan interpenetrating hydrogel system for sensitive detection and efficient adsorption of Cu (II) and Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Recent advances in the treatment of industrial wastewater from different celluloses in continuous systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Lee, J.F. Reaction mechanism of hexavalent chromium with cellulose. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a pilot-scale industrial wastewater treatment system with plant biomass and EDTA. Water 2023, 15, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qiao, J.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. A 3D porous structured cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel with carbon dots-enhanced synergetic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis for effective Cr (VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Mousavi, S.M. Bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite aerogels as novel bioadsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium: Experimental and simulation study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, Z.; Deng, Y.; Deng, W.; Xiao, H.; Wu, W. Fluorescent bacterial cellulose@ Zr-MOF via in-situ synthesis for efficient enrichment and sensitive detection of Cr (VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, K.; Kumar, N.; Verma, V. Bacterial cellulose/PANi mat for Cr(VI) removal at acidic pH. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F.; Piñeros Castro, Y.; Conde Rivera, L.R. Design of a fixed-bed column with vegetal biomass and its recycling for Cr (VI) treatment. Recycling 2022, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, G.M.; Palladino, F.; Nucci, E.R.; Machado, A.R.T.; Rosa, C.A.; Santos, I.J.B. Bacterial nanocellulose produced as a by-product of the brewing industry and used as an adsorbent for synthetic solutions of Co (II), Cu (II), Ni (II) AND Fe (III). J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 6803–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.S.; Riaz, A.; Roy, J.S.; Fréchette, J.; Morency, S.; Gomes, O.P.; Dumée, L.F.; Greener, J.; Messaddeq, Y. Removal of cadmium and chromium heavy metals from aqueous medium using composite bacterial cellulose membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, P.; Du, Z.; Cai, Z. Copper ion-imprinted bacterial cellulose for selectively removing heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2022, 29, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyo, A.N.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A. Recent advances in cellulose, chitosan, and alginate based biopolymeric composites for adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Luo, W.; Luo, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Jing, L. A study on adsorption of Cr (VI) by modified rice straw: Characteristics, performances and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhan, E.Y.; Yildirim, A.; Kocer, M.B.; Uysal, A.; Yilmaz, M. A cellulose-based material as a fluorescent sensor for Cr (VI) detection and investigation of antimicrobial properties of its encapsulated form in two different MOFs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Lozano, A.M. Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride. Toxics 2025, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiravi-Rivash, O.; Mashreghi, M.; Baigenzhenov, O.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Producing bacterial nano-cellulose and keratin from wastes to synthesize keratin/cellulose nanobiocomposite for removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from waters and wastewaters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2023, 656, 130355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Ahmad, W.; Park, J.H.; Kumar, V.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Vaya, D.; Kim, H. One-step functionalization of chitosan using EDTA: Kinetics and isotherms modeling for multiple heavy metals adsorption and their mechanism. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Tran, T.V. Bacterial cellulose and composites for the treatment of water pollution: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2025, 23, 707–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.U.; Zhang, Y.M.; Guan, X.H.; Xu, X.H.; Gao, T.T. Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions onto surface amino-bacterial cellulose. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Ficai, D.; Trusca, R.; Dolete, G.; Andronescu, E.; Turculet, S.C. Chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite membranes as adsorbents with applications in water purification. Materials 2020, 13, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Peräniemi, S.; Leiviskä, T.; Kim, T.; Tripathi, K.M.; Bhatnagar, A. Synthesis of clay-cellulose biocomposite for the removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Pham, C.D.; Nguyen, K.D.; Tran, A.T.; Le, N.T.; Ho, P.H.; Le, H.V. Bacterial Cellulose-Based Material from Coconut Water as Efficient Green Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Cations. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Amr, A.; Asker, M.S.; El-Shafie, A. Preparation and characterization of ion exchanger based on bacterial cellulose for heavy metal cation removal. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019, 62 Pt 2, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; El-Assal, A.A.; El Sikaily, A.; Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Ragab, S. New magnetic cellulose nanobiocomposites for Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions removal: Kinetics, thermodynamics and analytical evaluation. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricou, P.; Lecuyer, I.; Le Cloirec, P. Removal of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+ by adsorption onto fly ash and fly ash/lime mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rocky, M.M.H.; Rahman, I.M.; Biswas, F.B.; Rahman, S.; Endo, M.; Wong, K.H.; Mashio, A.S.; Hasegawa, H. Cellulose-based materials for scavenging toxic and precious metals from water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ye, Z. Study on adsorption mechanism of Pb (II) and Cu (II) in aqueous solution using PS-EDTA resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Hierarchically porous poly (amidoxime)/bacterial cellulose composite aerogel for highly efficient scavenging of heavy metals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 600, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, L.; Rodrigues, R.; Fischer, D.; Tovar-Castro, J.D.; Payne, A.; Navone, L.; Hu, Y.; Yan, H.; Pinmanee, P.; Barro, E.; et al. Bacterial cellulose cookbook: A systematic review on sustainable and cost-effective substrates. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2024, 9, 379–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, R.; Hooda, A. Fungal biosorption–an alternative to meet the challenges of heavy metal pollution in aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Angove, M.J.; Morton, D.W. Recent innovative research on chromium (VI) adsorption mechanism. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, D.T.; Le, G.T.; Tomul, F.; Lima, E.C.; Woo, S.H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, P.T.; Chao, H.P.; et al. Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium onto layered double hydroxides-based adsorbents: A systematic in-depth review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, D.J. Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption equilibrium of heavy metals and dyes from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Lozano, A.M. Design of Biomass Adsorbents Based on Bacterial Cellulose and E. crassipes for the Removal of Cr (VI). Polymers 2025, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Development of a treatment for water contaminated with Cr (VI) using cellulose xanthogenate from E. crassipes on a pilot scale. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. A comprehensive review of cellulose nanomaterials for adsorption of wastewater pollutants: Focus on dye and heavy metal Cr adsorption and oil/water separation. Collagen Leather 2024, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmoune, M.N. Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, A.; Hamid, A.; Muhammad, N.; Naseer, A.; Ghauri, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rafiq, S.; Shah, N.S. Cellulose-based materials for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater—An overview. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, S.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, H. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II) onto diethylenetriamine-bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Li, X.; Qiao, H.; Ke, H.; Luo, L.; Wei, Q. Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, H.I.; Yap, P.S. A review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels for the removal of heavy metals from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Zhao, D.; Lu, A.; Zhong, C.; Shen, X.C.; Ruan, C. One-pot green synthesis of poly (hexamethylenediamine-tannic acid)-bacterial cellulose composite for the reduction, immobilization, and recovery of Cr (VI). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.A.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Strachota, B.; Strachota, A.; Pavlova, E.; Mares Barbosa, S.; Kamel, S. Temperature-and pH-responsive super-absorbent hydrogel based on grafted cellulose and capable of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. Gels 2023, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.W.; Kamari, A.; Fatinathan, S.; Ng, P.W. Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution using chitosan beads. Adsorption 2006, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a biotreatment of E. crassipes for the decontamination of water with Chromium (VI). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno Sayago, U.F. Design, scaling, and development of biofilters with E crassipes for treatment of water contaminated with Cr (VI). Water 2021, 13, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Dou, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hu, M. Removal difference of Cr (VI) by modified zeolites coated with MgAl and ZnAl-layered double hydroxides: Efficiency, factors and mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 621, 126583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, G.; Baikousi, M.; Salmas, C.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R.; Karakassides, M.A. Advanced Cr (VI) sorption properties of activated carbon produced via pyrolysis of the “Posidonia oceanica” seagrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, N.; Gündoğdu, A.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.; Soylak, M. Application of cherry laurel seeds activated carbon as a new adsorbent for Cr(VI) removal. Membr. Water Treat. 2021, 12, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabar, J.M.; Adebayo, M.A.; Owokotomo, I.A.; Odusote, Y.A.; Yılmaz, M. Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous ZnCl2–activated cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) leaves biochar derived via pyrolysis for crystal violet dye removal. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, M.B.; Mallek, M.; Valverde, A.; Monclús, H.; Myers, T.G.; Salvadó, V.; Cabrera-Codony, A. Competitive heavy metal adsorption on pinecone shells: Mathematical modelling of fixed-bed column and surface interaction insights. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.P.; Chang, C.C.; Nieva, A. Biosorption of heavy metals on Citrus maxima peel, passion fruit shell, and sugarcane bagasse in a fixed-bed column. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3408–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, M.; Mohamed, M.H.; Udoetok, I.A.; Steiger, B.G.; Wilson, L.D. Evaluation of a granular Cu-modified chitosan biocomposite for sustainable sulfate removal from aqueous media: A batch and fixed-bed column study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Flores, G.; Alvarado-Reyna, S.; Elvir-Padilla, L.G.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Avila, H.E.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. Kinetics, thermodynamics, and competitive adsorption of heavy metals from water using orange biomass. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Su, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, S. Cr (VI) removal by cellulose-based composite adsorbent with a double-network structure. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liao, W.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Qiu, R.; Gao, T.; Xian, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, M. Cellulose nanocrystals for green remediation of contaminated soil with multiple heavy metals. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaffa, E.; Ramsheh, N.A.; Banerjee, A.; Ghafuri, H. Bacterial cellulose microfilament biochar-architectured chitosan/polyethyleneimine beads for enhanced tetracycline and metronidazole adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeedi, H.; Ahmad, H.; Altowairqi, M.F.; Alhamed, A.A.; Alsalme, A. Covalently Functionalized Cellulose Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Enrichment of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Cu (II) Ions. Polymers 2023, 15, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, M.; Ali, J.; Hou, J.; Chen, Y.; Juan, L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Shaoya, M. Bacterial cellulose modified with thiomolybdate sulfides: An outstanding eco-friendly adsorbent for the removal of multiple heavy metals from aqueous medium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 374, 133656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosen, J.; Binnemans, K. Adsorption and chromatographic separation of rare earths with EDTA-and DTPA-functionalized chitosan biopolymers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, R.K. Solid phase extraction studies on cellulose based chelating resin for separation, pre-concentration and estimation of Cu2+ and Ni2+. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Gao, K.; Yu, W.; Liu, L. Fabrication of cellulose-based carboxylate-functionalized materials via cosolubilization-crystallization for reversible Pb2+ adsorption. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J. Adsorption and coadsorption mechanisms of Cr (VI) and organic contaminants on H3PO4 treated biochar. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, S.; Wan, T.; Jia, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Zhong, C. Biosynthesis of spherical Fe3O4/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).