A Variational Mode Snake-Optimized Neural Network Prediction Model for Agricultural Land Subsidence Monitoring Based on Temporal InSAR Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
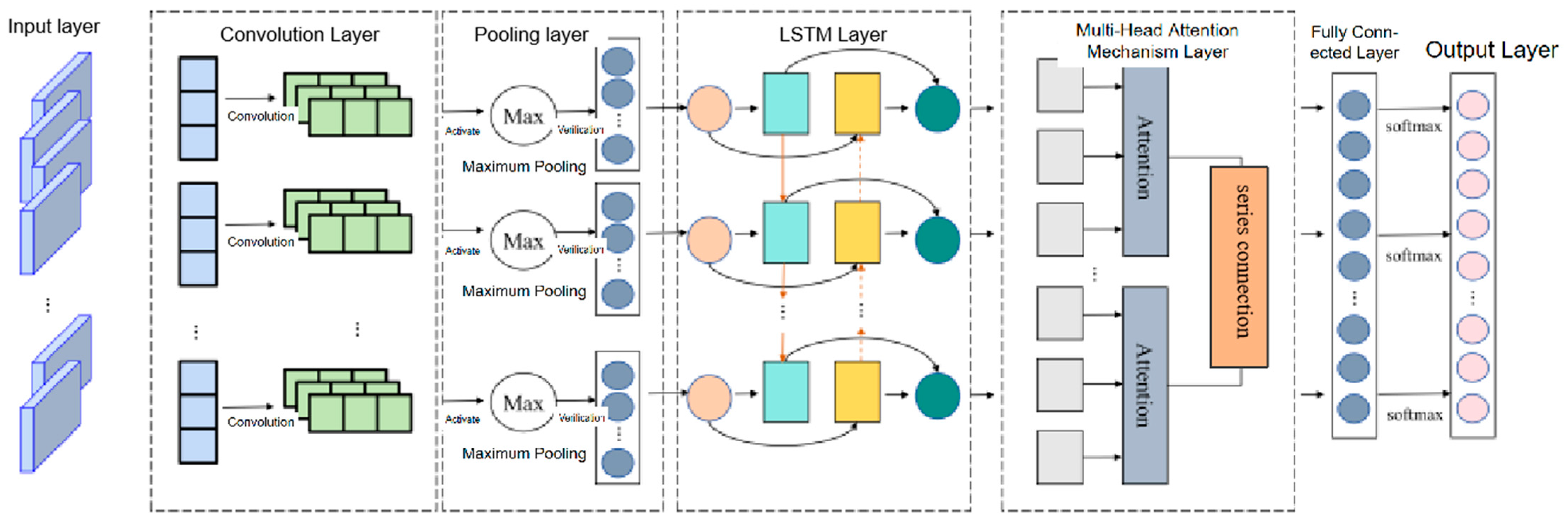
2. Design of Subsidence Prediction Network for Hilly and Mountainous Area
- (1)
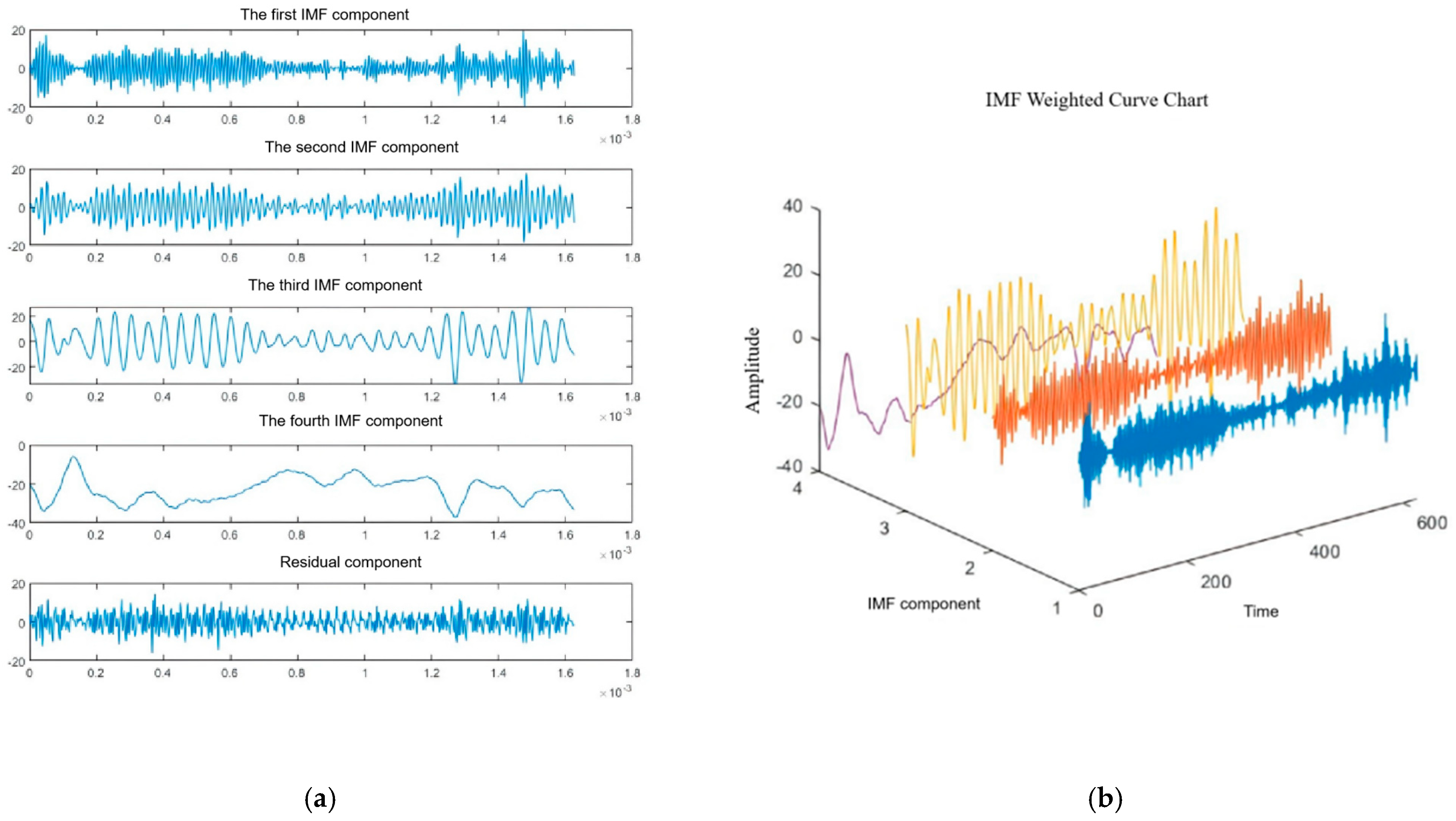
- In the VMD module, the original InSAR cumulative subsidence time series is decomposed into four IMF components with distinct frequency characteristics. The model input consists of the normalized time series of each modality, and the output is the predicted subsidence value for future time steps. The residual term does not participate in the prediction process; the overall subsidence prediction is obtained by summing the predicted values of all modalities.
- (2)
- In the CNN-LSTM-MATT network structure, in addition to the main layers, a dropout layer is added to suppress overfitting, with a dropout rate set to 0.2 and applied after the multi-head attention output.
- (3)
- Considering the characteristics of InSAR data, the subsidence time series exhibits periodic trends. CNN is suitable for capturing spatial neighborhood features, LSTM is effective for modeling temporal dependencies, and MATT enhances the influence of key time windows. Together, they form a deep prediction framework tailored for non-stationary surface deformation scenarios.
3. Identification of Farmland Surface Subsidence in Hilly Areas Based on SBAS-InSAR
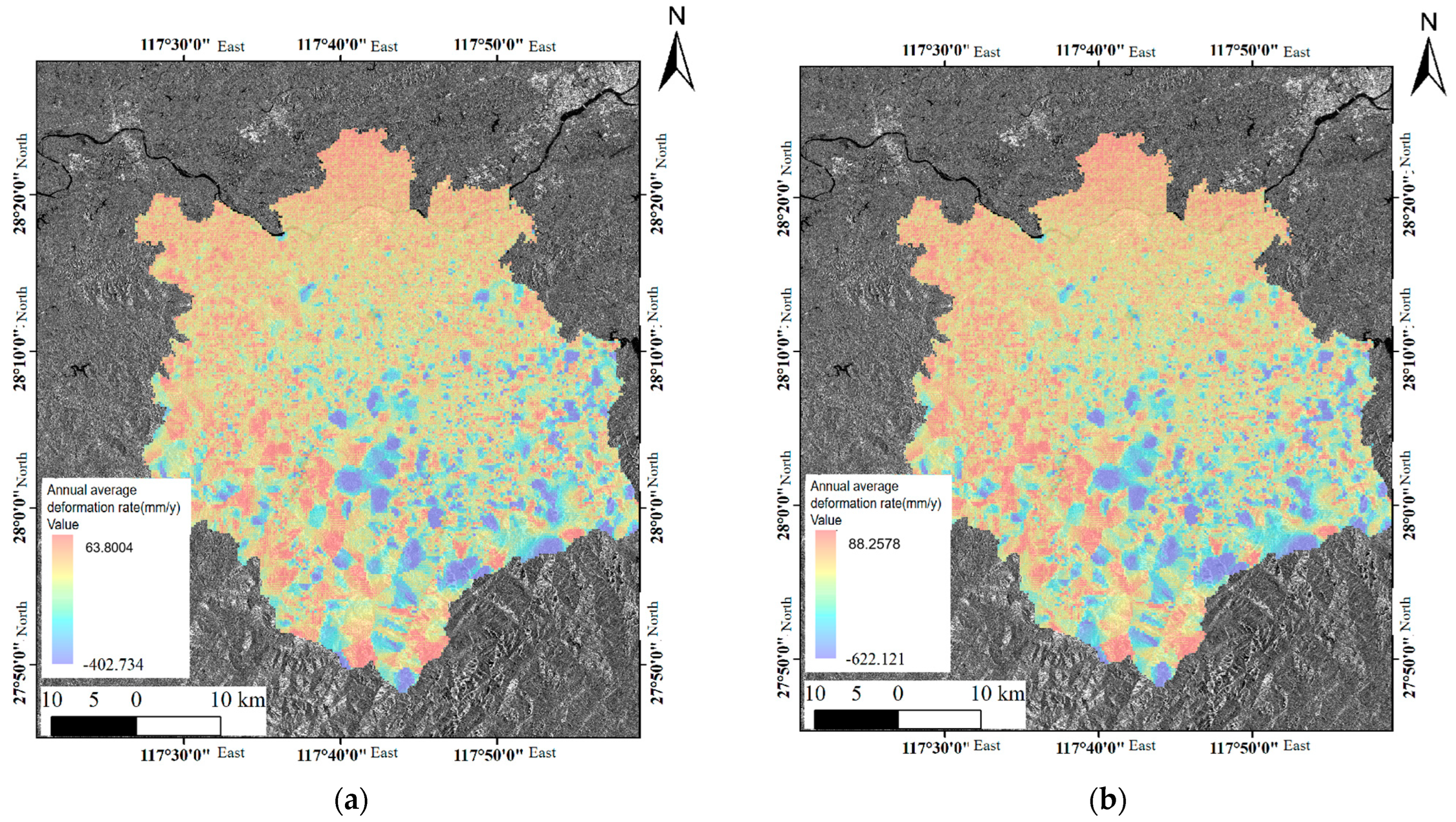
3.1. Study Area Overview and Data Sources
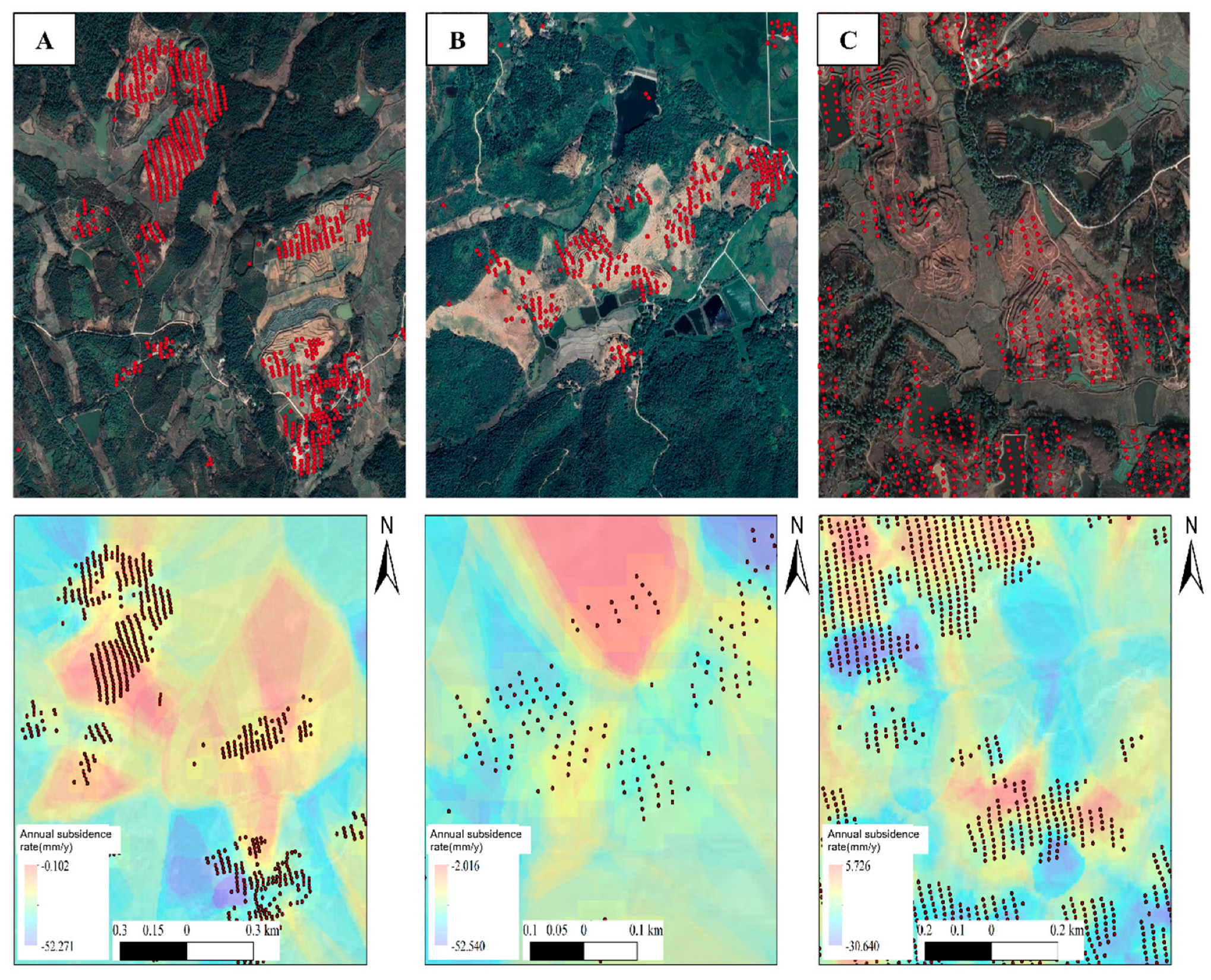
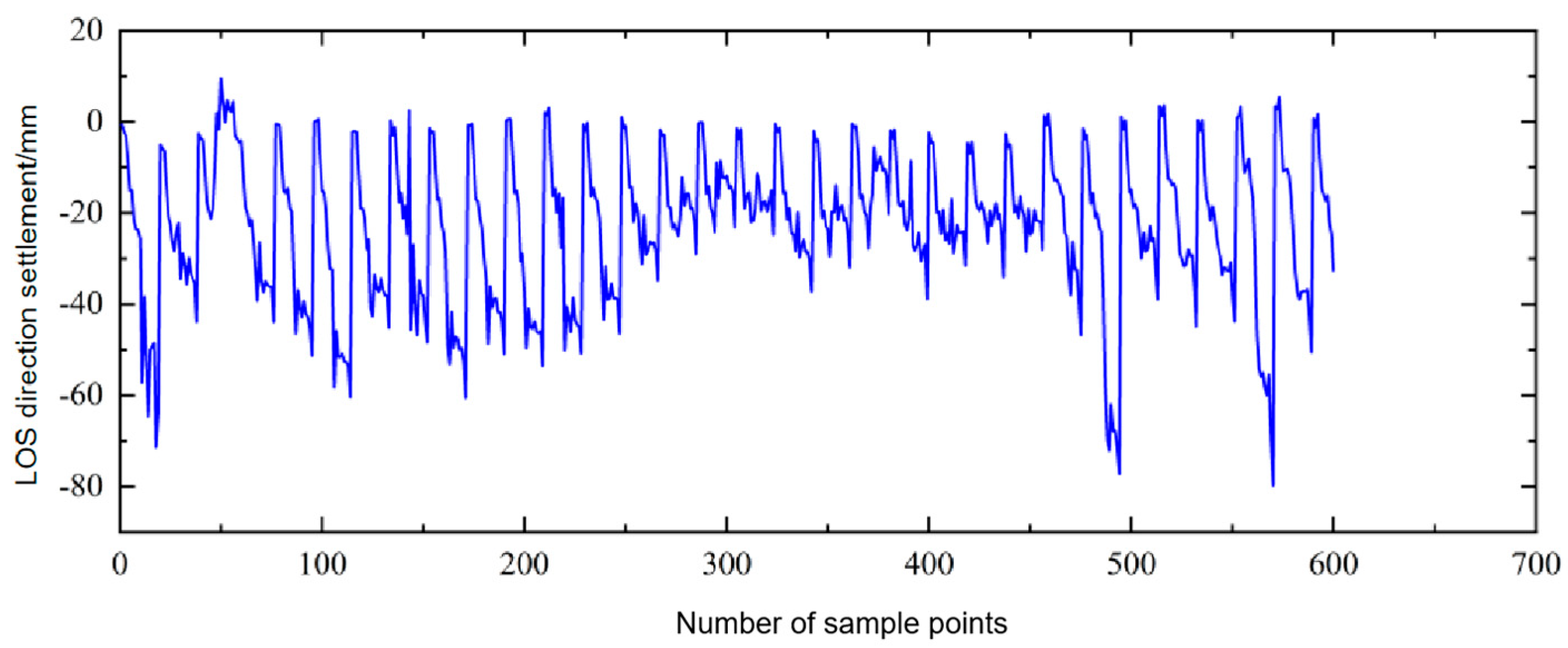
3.2. Monitoring, Identification, and Analysis of Farmland Subsidence in Hilly Areas of Yanshan County
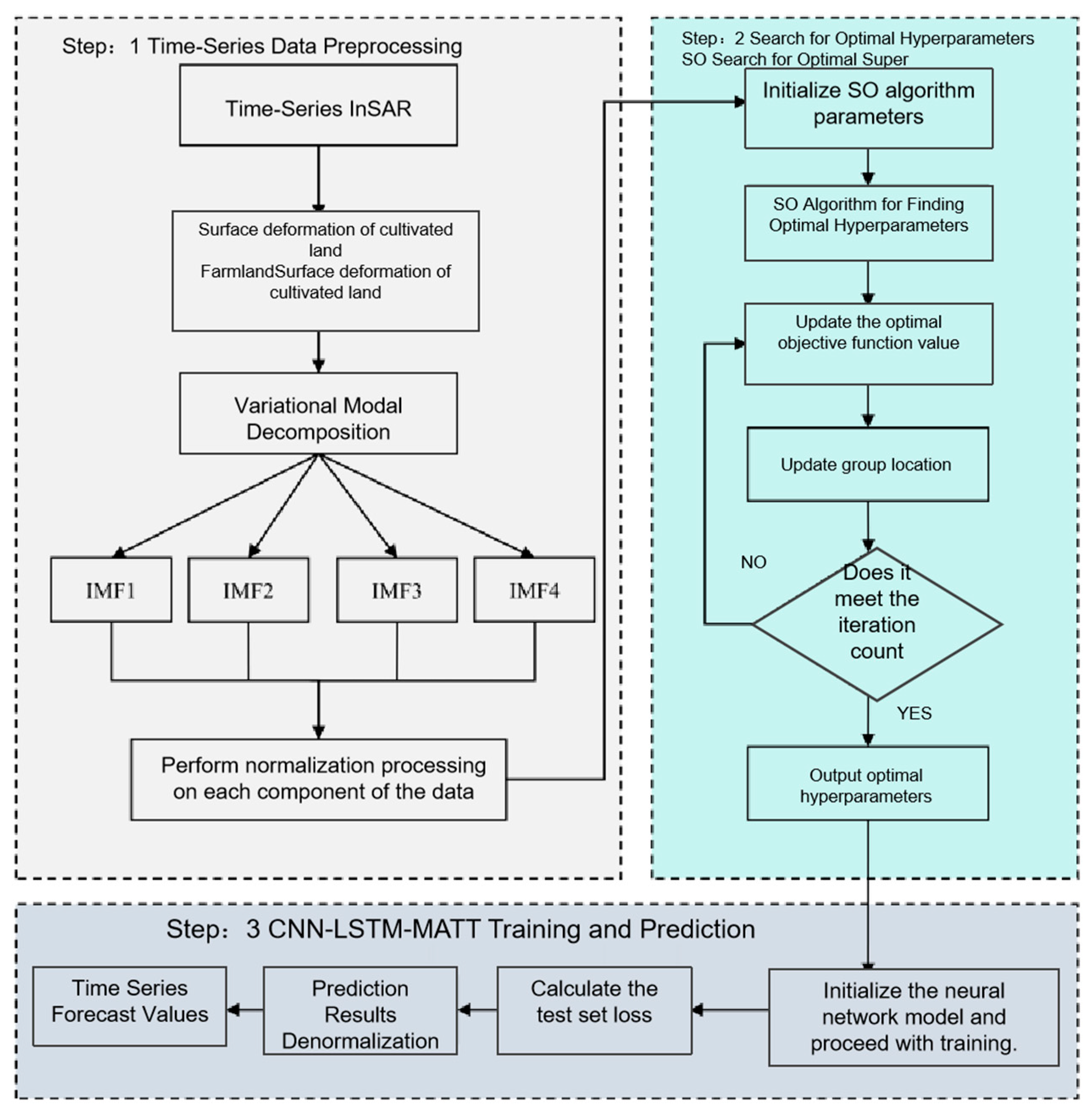
4. Farmland Surface Subsidence Prediction in Hilly Areas Based on the VMD-SO-CNN-LSTM-MATT Model
4.1. Experimental Analysis of VMD Decomposition
4.2. SO-CNN-LSTM-MATT Model Prediction and Analysis
4.2.1. Evaluation Metrics
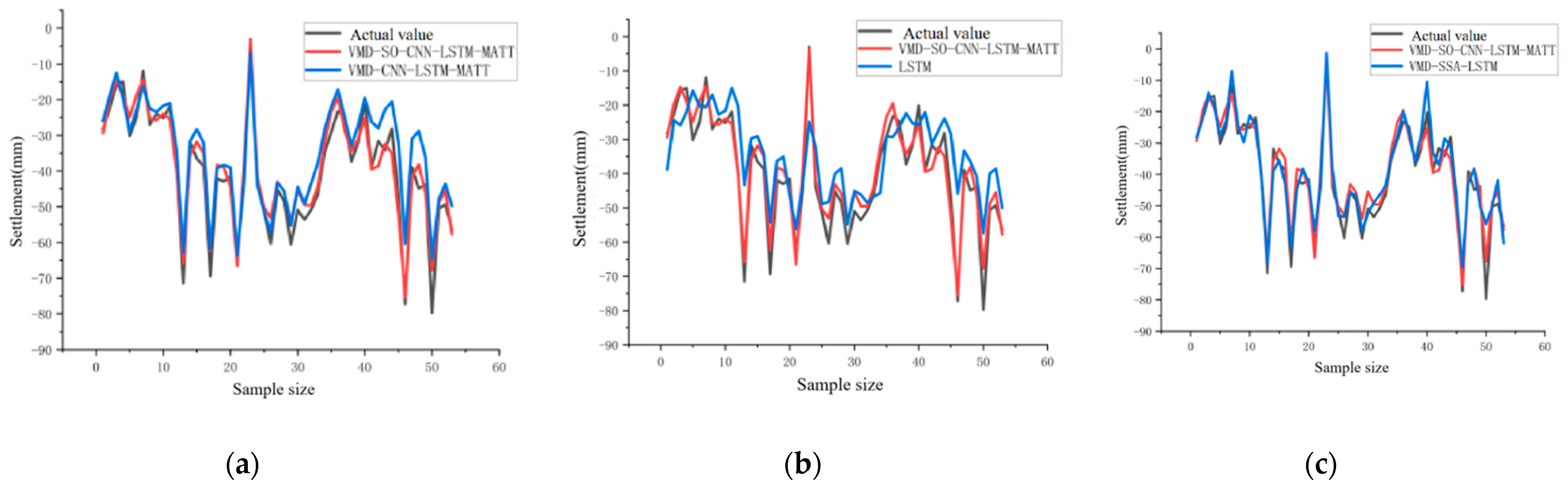
4.2.2. Accuracy Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Q.; Mou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Tian, T.; He, Q. Evolution and prediction of cultivated land landscape pattern in multi-level watersheds of Chongqing based on ANN-CA model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Balz, T.; Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Li, J.; Han, Y. Multi-sensor InSAR time series fusion for long-term land subsidence monitoring. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 27, 1424–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Sheng, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence in Wuhan, China from 2017 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2023, 14, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Caleca, F.; Del Soldato, M.; Festa, D.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S. Review of satellite radar interferometry for subsidence analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, T.; Pan, D. Dynamic change monitoring of Qianlong Garden rockery in the Forbidden City based on InSAR and LIDAR technology. ISPRS Arch. 2020, 43, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, R.; Scaioni, M. Validation of full-resolution DInSAR-derived vertical displacement in cultural heritage monitoring: Integration with geodetic levelling measurements. ISPRS Ann. 2023, X-M-1–2023, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Mróz, M.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Anders Moldestad, D.; Bateson, L.; Guerrieri, L.; et al. The evolution of wide-area DInSAR: From regional and national services to the European Ground Motion Service. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Tao, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, F. Accuracy verification and correction of D-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR in monitoring mining surface subsidence. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Peng, H.; Zeng, M.; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Pi, P.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, A.; Liu, F. Land subsidence in a coastal city based on SBAS-InSAR monitoring: A case study of Zhuhai, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Tao, Y.; Kou, P.; Alonso, A.; Luo, X.; Gong, C.; Fan, Y.; Lei, C.; Gou, Y. Monitoring and evaluation of gully erosion in China’s largest loess tableland based on SBAS-InSAR. Nat. Hazards 2023, 117, 2435–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, S.; Si, J.; Hui, W.; Li, S. Hu Deformation interpretation of Ankang expansive soil airport using integrated SBAS-InSAR and CR-InSAR. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2023, 43, 1112–1116+1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Niu, R.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. Potential landslides identification based on temporal and spatial filtering of SBAS-InSAR results. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Integrating SBAS-InSAR and AT-LSTM for time-series analysis and prediction method of ground subsidence in mining areas. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z. A deep-learning-facilitated, detection-first strategy for operationally monitoring localized deformation with large-scale InSAR. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S. Application of the Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) method to river tides. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 261, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ren, H.; Duan, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Tang, H. Fusion of Multi-Layer Attention Mechanisms and CNN-LSTM for Fault Prediction in Marine Diesel Engines. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.; Ahsan, M.; Hasanat, S.M.; Haris, M.; Yousaf, H.; Raza, S.F.; Tandon, R.; Abid, S.; Ullah, Z. Short-term load forecasting: A comprehensive review and simulation study with CNN-LSTM hybrids approach. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 111858–111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wei, A.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, H.; Tang, S. A CNN-LSTM based deep learning model with high accuracy and robustness for carbon price forecasting: A case of Shenzhen’s carbon market in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Application of integrated model based on EEMD-CNN-LSTM for landslide-displacement prediction. J. Geomech. 2024, 30, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yan, H.; Yang, W.; Yao, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T. Time-series analysis and prediction of surface deformation in the Jinchuan mining area, Gansu Province, by using InSAR and CNN–PhLSTM network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6732–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hua, D.; Bao, P.; Li, T.; Yao, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hu, P. A short-term electricity price forecasting method based on improved VMD-PSO-CNN-LSTM. J. Electr. Power Sci. Technol. 2024, 39, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Zhu, L. Short-term wind power prediction by an extreme learning machine based on an improved Hunter–Prey Optimization Algorithm. Sustainability 2023, 15, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L. Ultra-short-term wind power prediction based on VMD-SO-BP. Hongshui River 2023, 42, 50–54+59. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Huang, X.; Tang, W. Prediction method for sandstone fracture process based on improved VMD and GA-BP neural network. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2021, 12, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Geng, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, R. Research on fault diagnosis of optical fiber composite submarine cable based on VMD and SO optimized SVM. Electron. Meas. Technol. 2023, 46, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, F.A.; Hussien, A.G.; Mabrouk, M.S.; Al-Atabany, W.; Mirjalili, S. Snake Optimizer: A Metaheuristic Algorithm Inspired by Snake Behavior. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 172, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, F.A.; Hussien, A.G. Snake Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 242, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, J.; Wang, P.; Rong, H.; Chai, Y. Research on photovoltaic power prediction model based on TDE-SO-AWM-GRU. China Electr. Power 2024, 57, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3045118.3045167 (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Mining, D. Concepts and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 340, pp. 94104–103205. ISBN 978-0-12-381479-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, J.; Ma, P.; Lin, H. Identification and Analysis on Surface Deformation in the Urban Area of Nanchang Based on PS-InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Xi, W.; Zhou, D. The monitoring and analysis of land subsidence in Kunming (China) supported by time series InSAR. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, W.; Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. SinoLC-1: The first 1 m resolution national-scale land-cover map of China created with a deep learning framework and open-access data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 4749–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, J.; Tadono, T.; Tsutsui, K. Generation of High Resolution Global DSM from ALOS PRISM. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| k | IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | IMF6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 10.77 × 10−5 | 0.535 | ||||
| 3 | 10.76 × 10−5 | 0.336 | 0.624 | |||
| 4 | 10.74 × 10−5 | 0.321 | 0.615 | 0.183 | ||
| 5 | 10.71 × 10−5 | 0.328 | 0.610 | 0.205 | 0.183 | |
| 6 | 10.71 × 10−5 | 0.324 | 0.603 | 0.952 | 0.154 | 0.185 |
| Parameter Name | Note | Parameter Name | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum number of training iterations | 300 | Gradient threshold | 1 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.001 | Initial population size | 20 |
| Regularization parameter | 0.0005 | Maximum evolutionary generations | 10 |
| Prediction Model | RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | MAPE/% | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMD-SO-CNN-LSTM-MATT | 4.3813 | 3.7236 | 10.52 | 19.1955 |
| VMD-CNN-LSTM-MATT | 6.7246 | 5.3089 | 15.85 | 45.2203 |
| LSTM | 10.9966 | 8.6513 | 34.94 | 120.9256 |
| VMD-SSA-CNN-LSTM | 4.7837 | 4.5153 | 26.15 | 21.5032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, R.; Guo, M.; Li, L.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Variational Mode Snake-Optimized Neural Network Prediction Model for Agricultural Land Subsidence Monitoring Based on Temporal InSAR Remote Sensing. Processes 2025, 13, 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113480
Wang Z, Huang H, Wang R, Guo M, Li L, Teng Y, Zhang Y. A Variational Mode Snake-Optimized Neural Network Prediction Model for Agricultural Land Subsidence Monitoring Based on Temporal InSAR Remote Sensing. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113480
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhenda, Huimin Huang, Ruoxin Wang, Ming Guo, Longjun Li, Yue Teng, and Yuefan Zhang. 2025. "A Variational Mode Snake-Optimized Neural Network Prediction Model for Agricultural Land Subsidence Monitoring Based on Temporal InSAR Remote Sensing" Processes 13, no. 11: 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113480
APA StyleWang, Z., Huang, H., Wang, R., Guo, M., Li, L., Teng, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). A Variational Mode Snake-Optimized Neural Network Prediction Model for Agricultural Land Subsidence Monitoring Based on Temporal InSAR Remote Sensing. Processes, 13(11), 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113480





