Assessing Soil and Water Pollution: A Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Mine for Remediation and Repurposing in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
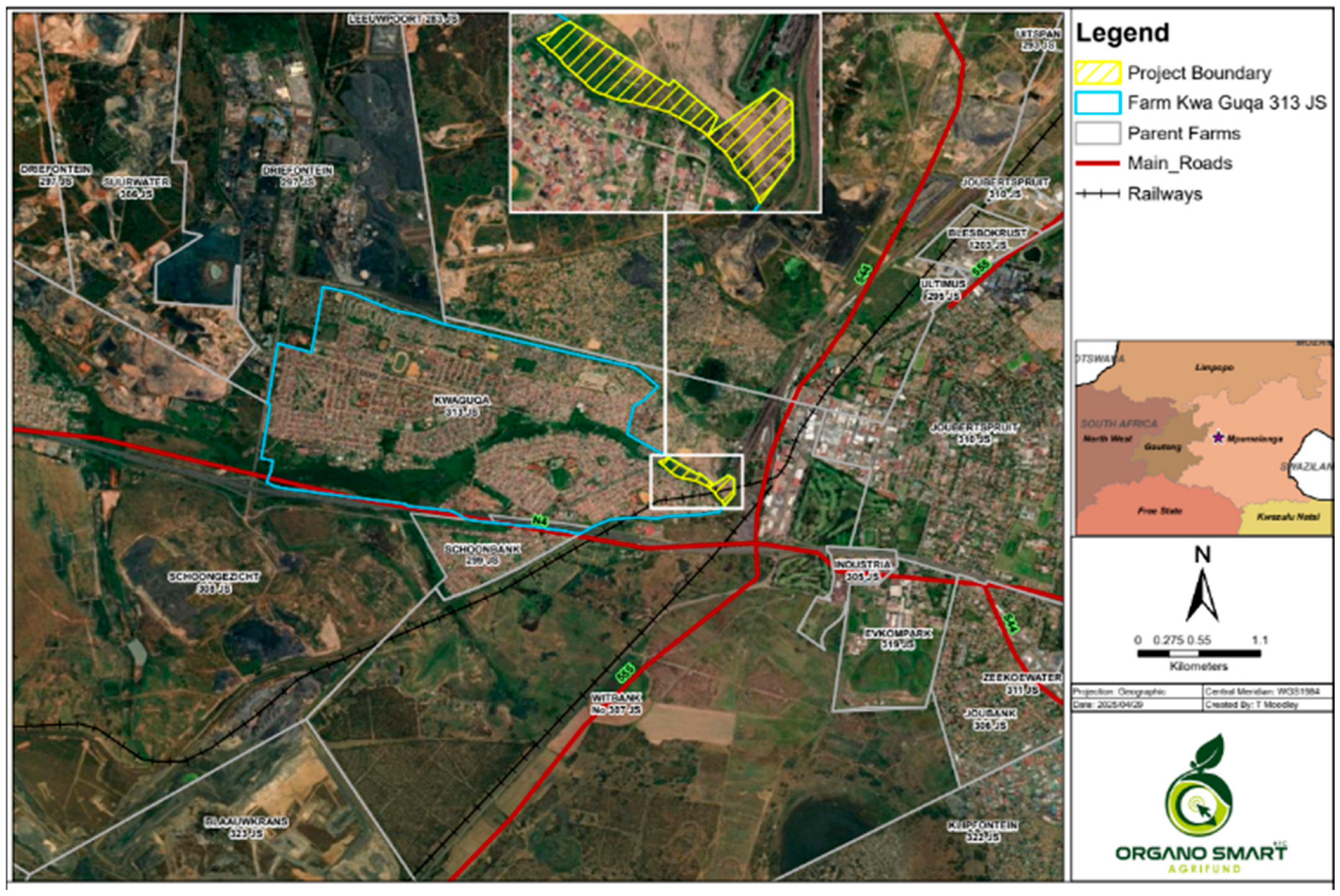
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis Techniques
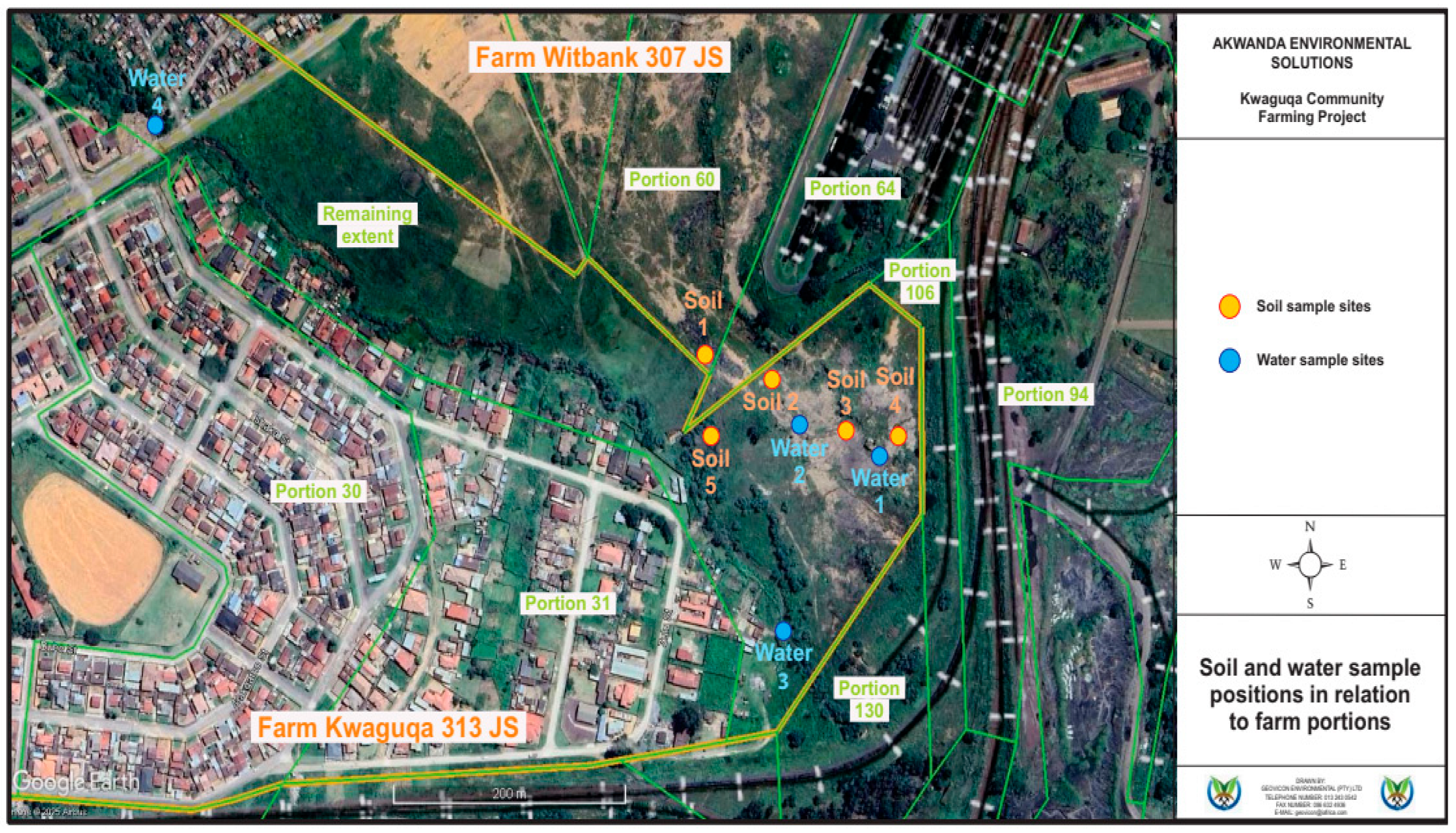
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2.2. Surface Water Sampling
2.3. Analysis
2.4. Water Quality Assessment Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Data: Soils
3.2. Physico-Chemical Data: Water
4. Opportunities for Remediation and Value-Added Benefits
4.1. AMD Treatment
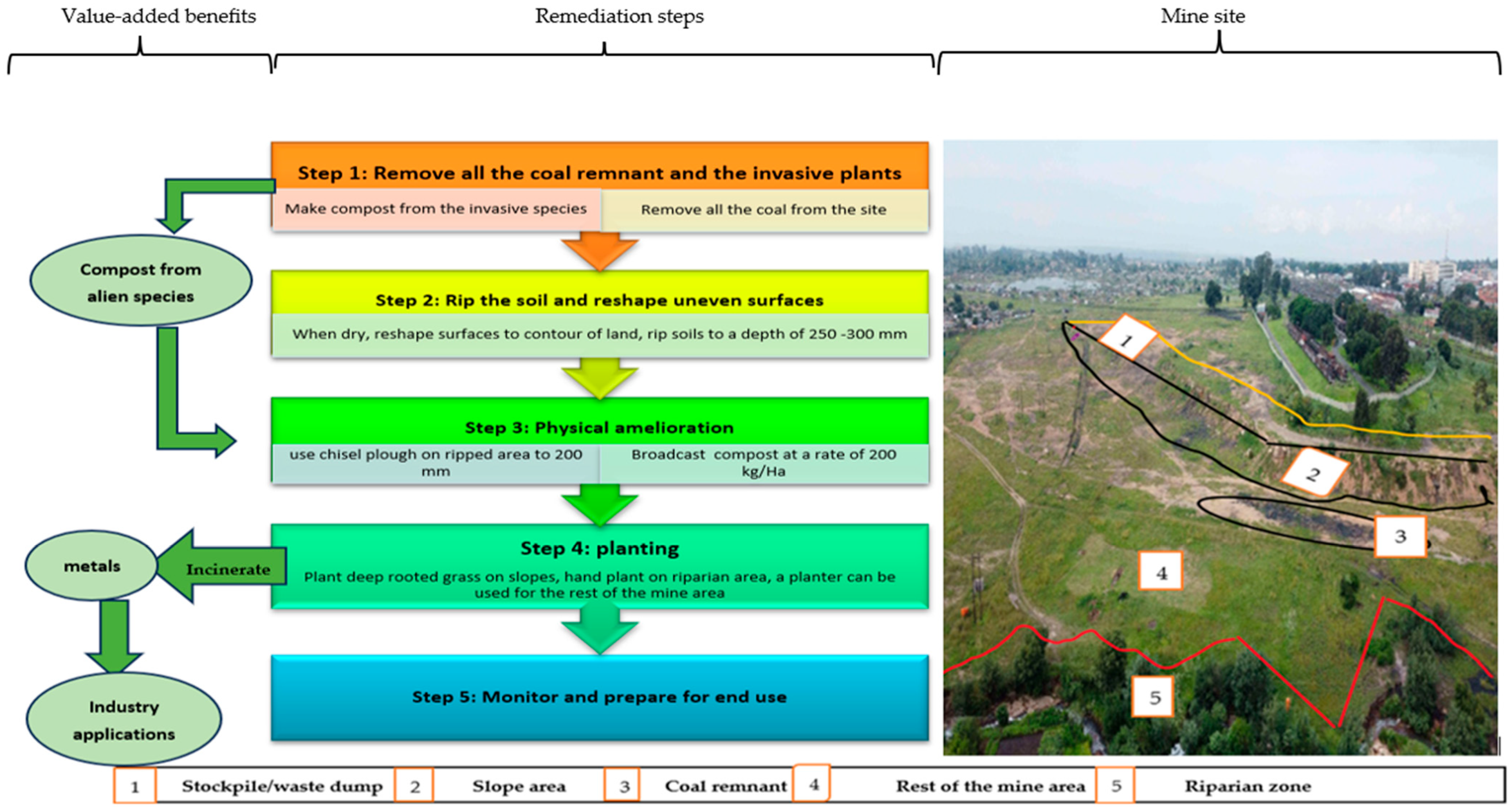
4.2. Remediation, Reclamation, and Restoration of the Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zocche, J.J.; Sehn, L.M.; Pillon, J.G.; Schneider, C.H.; Olivo, E.F.; Raupp-Pereira, F. Technosols in coal mining areas: Viability of combined use of agro-industry waste and synthetic gypsum in the restoration of areas degraded. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, W.; le Roux, M. Statistics of Utility-Scale Power Generation in South Africa; CSIR Energy Centre: Pretoria, South Africa. 2023. Available online: https://researchspace.csir.co.za/dspace/bitstream/handle/10204/12067/Statistics_of_utility-scale_powergeneration_in_South_Africa_ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Minerals Council South Africa. Facts & Figures Pocketbook 2022; Minerals Council South Africa: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chamber of Mines of South Africa. National Coal Strategy for South Africa 2018; Minerals Council South Africa: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2018; Available online: https://www.mineralscouncil.org.za/downloads?task=download.send&id=535&catid=22&m=0 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Hassan, A.S. Coal mining and environmental sustainability in South Africa: Do institutions matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 20431–20449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almano, Z. The Rehabilitation and Closure of Mines: A Failure in the Protection of Human Rights; Mineral Law in Africa; University of Cape Town: Cape Town, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mpanza, M.; Adam, E.; Moolla, R. A critical review of the impact of South Africa’s mine closure policy and the winding-up process of mining companies. J. Transdiscipl. Res. South. Afr. 2021, 17, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Mpanza, M.; Adam, E.; Moolla, R. Dust deposition impacts at a liquidated gold mine village: Gauteng province in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humby, T.L. ‘One environmental system’: Aligning the laws on the environmental management of mining in South Africa. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law 2015, 33, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Environmental Rights. The Truth About Mining Rehabilitation in South Africa; Centre for Environmental Rights: Cape Town, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mabaso, S.M. Legacy gold mine sites & dumps in the Witwatersrand: Challenges and required action. Nat. Resour. 2023, 14, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Mineral Resources and Energy. Progress in Dealing with Derelict and Ownerless Mines; Department of Mineral Resources: Pretoria, South Africa. 2019. Available online: http://pmg-assets.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/141112derelict.ppt (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Akbar, W.A.; Rahim, H.U.; Irfan, M.; Sehrish, A.K.; Mudassir, M. Assessment of heavy metal distribution and bioaccumulation in soil and plants near coal mining areas: Implications for environmental pollution and health risks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Majumder, S.; Mandal, J.; Roy, P.K.; Bhattacharyya, P. Appraisal of pollution and health risks associated with coal mine contaminated soil using multimodal statistical and Fuzzy-TOPSIS approaches. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, J. Characteristics and treatment technologies for acid mine drainage from abandoned coal mines in major coal-producing countries. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 4521–4535. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Ren, M. Distribution, source and health risk assessment based on the Monte Carlo method of heavy metals in shallow groundwater in an area affected by mining activities, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Luan, H. Distribution and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils around coal industrial areas: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 135292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Miller, S.A.; Ellis, B.R. Comparative human toxicity impact of electricity produced from shale gas and coal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13018–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Kuang, X.; Cao, Y.; Bai, Z. The soil chemical properties of reclaimed land in an arid grassland dump in an opencast mining area in China. Rsc. Adv. 2018, 8, 41499–41508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerizghi, T.; Guo, Q.; Tian, L.; Wei, R.; Zhao, C. An integrated approach to quantify ecological and human health risks of soil heavy metal contamination around coal mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasii, O.; Gasii, G. Coal mining and water resources: Impacts, challenges, and strategies for sustainable environmental management. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Online, 8–10 November 2023; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024; Volume 1348, p. 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, G.B.; Badenhorst, J.; Jewitt, G.P.; Berchner, M.; Davies, E. Competition for land: The water-energy-food nexus and coal mining in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bench Marks Foundation. South African Coal Mining, Corporate Grievance Mechanisms, Community Engagement Concerns, and Mining Impacts; Policy Gap 9; Bench Marks Foundation: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for Environmental Rights. Zero Hour: Poor Governance of Mining and the Violation of Environmental Rights in Mpumalanga; Centre for Environmental Rights: Cape Town, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Magagula, M.; Atangana, E.; Oberholster, P. Assessment of the Impact of Coal Mining on Water Resources in Middelburg, Mpumalanga Province, South Africa: Using Different Water Quality Indices. Hydrology 2014, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, E.; Oberholster, P.J. Using heavy metal pollution indices to assess water quality of surface and groundwater on catchment levels in South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 182, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.L.; Jamal, A. Assessment of water quality in coal mines: A quantitative approach. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, C.T.; Giang, N.T.H.; Thao, T.P.; Nui, N.H.; Lam, N.T.; Cong, V.H. Assessment of Cau River water quality assessment using a combination of water quality and pollution indices. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2020, 69, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water quality indices: Challenges and application limits in the literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Das, S.K.; Paul, S.C.; Islam, M.F.; Hossain, M.S. Water quality assessment of Karrnaphuli River, Bangladesh using multivariate analysis and pollution indices. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2018, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholster, P.F.; Goldin, J.; Xu, Y.; Kanyerere, T.; Oberholster, P.J.; Botha, A.M. Assessing the adverse effects of a mixture of AMD and sewage effluent on a sub-tropical dam situated in a nature conservation area using a modified pollution index. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharma, M.P.; Kumar, A. Assessment of surface water quality in Surha Lake using pollution index, India. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Yu, C. Exploring the accumulation capacity of dominant plants based on soil heavy metals forms and assessing heavy metals contamination characteristics near gold tailings ponds. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Qian, W.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Evaluation of soil heavy metals pollution and the phytoremediation potential of copper-nickel mine tailings ponds. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, S.E.; Quiroz, I.A.; Magni, C.R.; Yáñez, M.A.; Martínez, E.E. Long-term effects of copper mine tailings on surrounding soils and sclerophyllous vegetation in Central Chile. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South African Weather Service. Climate Data for Mpumalanga; South African Weather Service: Pretoria, South Africa, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, M.C.; Mucina, L.; Powrie, L.W. Biomes and bioregions of southern Africa. Veg. S. Afr. Lesotho Swazil. 2006, 19, 30–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cairncross, B.; McCarthy, T.S. A geological investigation of Klippan in Mpumalanga province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2008, 111, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.G.C.; Anhaeusser, C.R. The Mineral Resources of South Africa, 6th ed.; Handbook 16; Council for Geoscience: Pretoria, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 17025; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Ramakrishnaiah, C.R.; Sadashivaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.R.; Ye, B.; Ye, C. Acid sulfate soils: Formation, identification, environmental impacts, and sustainable remediation practices. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Favas, P.J.C.; Pratas, J.; Prasad, M.N.V. Review of the environmental impacts of abandoned mines in South Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Steyn, C.E.; Herselman, J.E. Trace element concentrations in soils under different land uses in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2006, 23, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantcharova, M.M.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C. Soil acidification, mineral neoformation and heavy metal contamination driven by weathering of sulphide wastes in a Ramsar wetland. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Zhao, W.; Feng, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, X. The impacts of aging pH and time of acid mine drainage solutions on Fe mineralogy and chemical fractions of heavy metals in the sediments. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Chou, C.L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orem, W.H.; Finkelman, R.B. Coal formation and geochemistry. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 7, pp. 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ketris, M.Á.; Yudovich, Y.E. Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Heavy metal pollution in soil and its impact on human health: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159746. [Google Scholar]
- Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Ali, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Feng, S.; Lei, K. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of mining area soil based on land type changes: An information network environ analysis. Ecol. Model. 2021, 455, 109633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.M.; Van Wilgen, B.W. Invasive alien plants in South Africa: How well do we understand the ecological impacts?: Working for water. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2004, 100, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- van Wilgen, B.W.; Richardson, D.M.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Marais, C.; Magadlela, D. The economic consequences of alien plant invasions: Examples of impacts and approaches to sustainable management in South Africa. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2001, 3, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L. Alien Weeds and Invasive Plants. A Complete Guide to Declared Weeds and Invaders in South Africa; Food and Agriculture Organization of the Unites States: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Le Maitre, D.C.; Versfeld, D.B.; Chapman, R.A. Impact of Invading Alien Plants on Surface Water Resources in South Africa: A Preliminary Assessment; CSIR Division of Water, Environment and Forestry Technology, Stellenbosch: Capetown, South Africa, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D. Status of heavy metals in water and bed sediments of river Gomti–A tributary of the Ganga river, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 105, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigua, G.C.; Tweedale, W.A. Watershed scale assessment of nitrogen and phosphorus loadings in the Indian River Lagoon basin, Florida. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 67, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Mitra, A.K. Mobilization of heavy metals from mine spoils in a part of Raniganj coalfield, India: Causes and effects. Environ. Geosci. 2004, 11, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddick, J. Environmental impacts of coal mining. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 157, 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, A.M.; Baumgartl, T.; Matthew, P.; Glenn, V. The impact of underground longwall mining on prime agricultural land: A review and research agenda. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Xu, R.; Li, X.; Min, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Soil reconstruction and heavy metal pollution risk in reclaimed cultivated land with coal gangue filling in mining areas. Catena 2023, 228, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovleva, E.V.; Gabov, D.N.; Beznosikov, V.A.; Kondratenok, B.M. Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and plants of the tundra zone under the impact of coal-mining industry. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, L.; Olías, M.; Cerón, J.C.; de Villaran, R.F. Inputs and fate of contaminants in a reservoir with circumneutral water affected by acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, L.M.; Biswas, T.K.; Dang, T.; Palmer, D.; Cummings, C.; Daly, R.; Kirby, J. Fate and dynamics of metal precipitates arising from acid drainage discharges to a river system. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laisani, J.; Jegede, A.O. Impacts of coal mining in Witbank, Mpumalanga province of South Africa: An eco-legal perspective. J. Rev. Glob. Econ. 2019, 8, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cloquet, C.; Zhu, C.; Fan, H.; Luo, C. Tracing sources of pollution in soils from the Jinding Pb–Zn mining district in China using cadmium and lead isotopes. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 52, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosai, A.K.; Ndlovu, G.; Tutu, H. Improving acid mine drainage treatment by combining treatment technologies: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of passive systems for acid mine drainage treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.J.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.Q.; Bi, Y.X.; Ding, Z.; Dai, H.X.; Wen, S.M. An innovative option for the activation of chalcopyrite flotation depressed in a high alkali solution with the addition of acid mine drainage. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, B.; Anderson, A. Sustainable resolutions for environmental threat of the acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramla, B.; Sheridan, C. The potential utilisation of indigenous South African grasses for acid mine drainage remediation. Water SA 2015, 41, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghoum, I.; Edahbi, M.; Melián, J.A.H.; Doña Rodriguez, J.M.; Durães, N.; Pascual, B.A.; Salmoun, F. Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage Effluents Using Constructed Wetlands: Case of an Abandoned Iron Mine, Morocco. Water 2025, 17, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, E.O.; Njoku, K.I.; Osuntoki, A.A.; Akinola, M.O. A review of current techniques of physico-chemical and biological remediation of heavy metals polluted soil. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2015, 8, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, T. Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafle, A.; Timilsina, A.; Gautam, A.; Adhikari, K.; Bhattarai, A.; Aryal, N. Phytoremediation: Mechanisms, plant selection and enhancement by natural and synthetic agents. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; van Zyl, D. Distinguishing reclamation, revegetation and phytoremediation, and the importance of geochemical processes in the reclamation of sulfidic mine tailings: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedrite, E.; Klavins, L.; Dobkevica, L.; Purmalis, O.; Ievinsh, G.; Klavins, M. Sustainable control of invasive plants: Compost production, quality and effects on wheat germination. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, Y.; Linghu, J. Influence of carbon dioxide on the adsorption of methane by coal using low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 6113–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, S.; Wu, J.; Chang, L. Study on the relationship between microscopic functional group and coal mass changes during low-temperature oxidation of coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 171, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.H.M.; Kaksonen, A.H. Towards circular economy in mining: Opportunities and bottlenecks for tailings valorization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, D. Australian Resource Reviews: Iron Ore 2019; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Santander, M.; Valderrama, L. Recovery of pyrite from copper tailings by flotation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4312–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, G.; Ryu, S.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S. A critical review on remediation, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlalazi, N.; Chimuka, L.; Simatele, M.D. Synergistic effect of compost and moringa leaf extract biostimulants on the remediation of gold mine tailings using chrysopogon zizanioides. Sci. Afr. 2024, 26, e02358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Ndunagu, J.N.; Osibote, O.A.; Emegha, J.O.; Darmokoesoemo, H. An overview of the emergence and challenges of land reclamation: Issues and prospect. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 5889823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcombe, S.; Keenan, J. Mining as a Temporary Land Use Scoping Project: Transitions and Repurposing; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Paulo Farias, D.; dos Santos Gomes, M.G. COVID-19 outbreak: What should be done to avoid food shortages? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the intensification of agriculture for global food security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, D.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E. Building beyond land: An overview of coastal land reclamation in 16 global megacities. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method No. | Based on | Instrument | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | EPL-WL-003 | Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater | Electrode |
| EC | EPL-WL-001 | Probe | |
| TDS | EPL-WL-004 | Gravimetric | |
| TSS | EPL-WL-014 | Gravimetric | |
| Metals (Total) | EPL-WL-007 | EPA6010 | ICP-OES |
| SSV1 All Land Uses Protective of the Water Resources | Protection of the Ecosystem Health (SSV3) | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.16 ± 0.28 | 4.99 ± 0.67 | 4.22 ± 0.14 | 3.82 ± 0.09 | 4.66 ± 0.45 | ||
| EC (mS/m) | 14.5 ± 1.37 | 1.6 ± 0.21 | 14.2 ± 1.28 | 27.4 ± 1.67 | 34.7 ± 2.97 | ||
| NH3 as N | 41.04 ± 2.25 | 11.67 ± 1.44 | 14.61 ± 1.66 | 15.89± 1.13 | 53.94 ± 4.29 | ||
| SO4 | 4000 | 2648.00 ± 133.54 | <200 | 1815.00 ± 78.05 | 6130.00 ± 115.28 | 12,868.00 ± 401.38 | |
| Ca | 3307.00 ± 107.11 | 225.70 ± 7.29 | 600.80 ± 29.34 | 1930.00 ± 203.27 | 4562.00 ± 53.21 | ||
| Fe | 9373.00 ± 205.29 | 15,176.00 ± 629.56 | 25,573.00 ± 923.21 | 24,781.00 ± 523.41 | 58,497.00 ± 800.25 | ||
| Mg | 81.08 ± 9.98 | 73.43 ± 7.11 | 73.95 ± 5.97 | 125.50 ± 9.32 | 164.40 ± 7.21 | ||
| Mn | 740 | 36,000 | 67.82 ± 5.23 | 54.53 ± 7.57 | 45.44 ± 1.33 | 64.17 ± 4.22 | 43.70 ±1.98 |
| Pb | 20 | 100 | 13.83 ± 1.11 | 8.61 ± 0.89 | 13.83 ± 0.98 | 45.48 ± 3.33 | 29.76 ± 1.09 |
| Discharge General Standard (mg/L) | Irrigation General Standard (mg/L) | Livestock Watering (DWA) (mg/L) | Aquatic Ecosystem (DWA) (mg/L) | Domestic Use SANAS 241(15) (mg/L) | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | ||||||
| pH | 5.5–9.5 | 5.5–9.5 | - | - | 5–9.7 | 3.41 ± 0.22 | 3.39 ± 0.31 | 3.64 ± 0.23 | 3.76 ± 0.28 |
| EC * (mS/m) | 150 | 150 | - | - | ≤170 | 314.10 ± 9.87 | 257.93 ± 10.45 | 130.05 ± 6.76 | 124.21 ± 6.45 |
| TDS | - | - | ≤2000 | - | ≤2000 | 3337.78 ± 78.21 | 2803.02 ± 81.89 | 1226.12 ± 69.56 | 1093.15 ± 57.65 |
| TSS | 25 | 25 | - | - | - | 670.11 ± 11.23 | 437.33 ± 7.76 | 385.11 ± 13.98 | 360.24 ± 22.69 |
| SO4 | - | - | ≤1500 | - | ≤500 | 1955.00 ± 87.25 | 1766.00 ± 75.44 | 731.40 ± 47.94 | 681.00 ± 53.98 |
| Ca | - | - | ≤1000 | - | - | 647.70 ± 43.23 | 367.40 ± 29.67 | 156.10 ± 10.95 | 140.20 ± 14.77 |
| Fe | 0.3 | - | - | - | ≤2 | 2.95 ± 0.76 | 1.95 ± 0.20 | 7.73 ± 0.94 | 4.93 ± 0.11 |
| Mg | - | - | ≤500 | - | - | 60.42 ± 3.34 | 64.96 ± 9.09 | 20.08 ± 3.26 | 20.88 ± 4.45 |
| Mn | 0.1 | - | ≤10 | ≤0.18 | ≤0.5 | 12.86 ± 2.65 | 12.64 ± 3.86 | 10.23 ± 1.11 | 10.57 ± 0.45 |
| Pb | 0.01 | 0.01 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.0012 | ≤0.01 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mlalazi, N.; Mbohwa, C.; Ramuhaheli, S.; Chimwani, N. Assessing Soil and Water Pollution: A Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Mine for Remediation and Repurposing in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Processes 2025, 13, 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103307
Mlalazi N, Mbohwa C, Ramuhaheli S, Chimwani N. Assessing Soil and Water Pollution: A Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Mine for Remediation and Repurposing in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103307
Chicago/Turabian StyleMlalazi, Nkanyiso, Charles Mbohwa, Shumani Ramuhaheli, and Ngonidzashe Chimwani. 2025. "Assessing Soil and Water Pollution: A Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Mine for Remediation and Repurposing in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa" Processes 13, no. 10: 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103307
APA StyleMlalazi, N., Mbohwa, C., Ramuhaheli, S., & Chimwani, N. (2025). Assessing Soil and Water Pollution: A Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Mine for Remediation and Repurposing in Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Processes, 13(10), 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103307





