Abstract
This study evaluated the effectiveness of photodynamic treatment (PDT) using riboflavin (Rbf) and blue light-emitting diode (BL) irradiation for microbial inactivation and quality preservation in fresh betel leaves (Piper betle L.). Non-pathogenic surrogates Escherichia coli K-12 and Listeria innocua were used to model Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The combined Rbf-BL treatment significantly reduced microbial populations by up to 5.3 log CFU/g for E. coli and 6.2 log CFU/g for L. innocua on leaf surfaces (p < 0.05) and 1.3–1.5 log CFU/mL in broth cultures. Treated samples showed significantly higher total soluble solids (12.0 ± 0.0 °Brix), total phenolic content (0.17 ± 0.02 mmol GAE/g, p < 0.05), and antioxidant activity (62.0 ± 3.1% DPPH inhibition, p < 0.05), with minimal color alteration after treatment (ΔE = 4.68). The total fluence measured at the leaf surface was approximately 11.72 J/cm2. As a mild thermal treatment utilizing a GRAS photosensitizer, riboflavin-assisted PDT presents a promising strategy for enhancing microbial safety and promoting phytochemical quality in betel leaves.
1. Introduction
Betel leaf (Piper betle L.) is a traditional plant widely consumed across Southeast Asia, often fresh and raw, due to its aromatic properties and cultural significance. Besides its use in culinary and medicinal practices, the leaf is recognized for its bioactive compounds, including phenolics and essential oils with antimicrobial and antioxidant potential. Nevertheless, its consumption without thermal processing introduces considerable risks associated with microbial contamination. The delicate structure and high moisture content of the leaf also predispose it to rapid quality degradation during storage, posing challenges for safe distribution and export [1,2].
Ensuring the microbial safety of fresh produce without compromising quality remains a pressing issue in food science. Conventional approaches, such as heat treatments, chemical disinfectants, and irradiation can be effective in microbial reduction but may negatively impact the sensory and nutritional properties of the food. This has driven interest in alternative mild-thermal preservation methods. One such approach, photodynamic inactivation, utilizes the combined action of a light source and a photosensitizing compound to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which disrupt microbial cell structures and lead to cell death [3,4].
The mechanism underlying PDT involves the excitation of photosensitizers under visible light. These excited molecules transfer energy to surrounding oxygen, producing highly reactive oxidative species such as singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and superoxide radicals. These ROS can compromise cellular membranes, nucleic acids, and enzymes, ultimately inactivating microorganisms. Importantly, the oxidative damage affects multiple targets, making the development of microbial resistance to PDT relatively uncommon [5,6].
Among the various light sources investigated for PDT, blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are of particular interest. Operating within the 450–470 nm range, blue LEDs can activate both endogenous chromophores found in microbial cells and externally applied photosensitizers. They offer several advantages, including low energy consumption, minimal heat generation, and the absence of chemical residues. These properties make blue LEDs especially attractive for applications in fresh and sensitive food matrices [7].
Riboflavin (vitamin B2), a water-soluble and naturally occurring compound in many foods, has emerged as a promising photosensitizer for food applications. It is classified as generally recognized as safe (GRAS), exhibits strong light absorption in the blue region, and has demonstrated effectiveness in producing ROS under blue light exposure. Several studies have reported the success of riboflavin-assisted PDT in inactivating foodborne pathogens in liquid matrices and on fresh produce surfaces [8,9]. Moreover, riboflavin’s photodegradability and water solubility contribute to its safety and ease of application in postharvest processing.
While PDT using riboflavin and blue LEDs has shown efficacy in laboratory conditions, its performance on complex plant surfaces, particularly those with irregular topography like betel leaves—requires further investigation. Additionally, beyond microbial inactivation, it is essential to consider how such treatments affect the overall physicochemical quality of the produce. Factors such as color, total soluble solids (TSS), antioxidant capacity, and phenolic content are important indicators of freshness and nutritional value. Oxidative stress generated by PDT may induce both beneficial and detrimental effects, including the stimulation of secondary metabolite production or the degradation of structural pigments like chlorophyll [10,11].
Moreover, evaluating the impact of such treatments over time is critical. Changes in antioxidant properties, enzymatic activity, and tissue integrity may occur throughout storage. Therefore, understanding the dynamics of quality attributes after PDT is necessary for its practical implementation.
In this context, the present study explores the effectiveness of blue LED light in combination with riboflavin for reducing microbial contamination on fresh betel leaves. Escherichia coli K12 and Listeria innocua were selected as model organisms representing Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively, due to their relevance as non-pathogenic surrogates in food safety research. The treatment was applied both in nutrient media and directly on the leaf surface to assess microbial inactivation efficiency under different conditions. Furthermore, the effects of photodynamic treatment on the physicochemical characteristics of betel leaves were evaluated throughout storage, focusing on TSS, total phenolic content, DPPH antioxidant activity, and color parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fresh betel leaves (Piper betel L.) were obtained from a local market in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Leaves of uniform size, free of physical damage and microbial decay, were selected for experimentation. Riboflavin (≥98% purity), used as the photosensitizer, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). All reagents used in the physicochemical analyses were of analytical grade. Methanol (≥99.8%) was used for phenolic extraction and antioxidant assays. The Folin–Ciocalteu phenol reagent and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) were employed for total phenolic content (TPC) determination. Gallic acid (≥99%) served as the calibration standard for phenolic quantification. For antioxidant capacity analysis, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical reagent was used. Peptone (1%) was prepared for microbial sample dilution, and sterile distilled water was used throughout all procedures. All chemicals were sourced from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) or equivalent suppliers.
2.2. Microbial Strains and Culture Preparation
Escherichia coli K-12 (JCM 20135) and Listeria innocua (JCM 32814) were obtained from the Japan Collection of Microorganisms (JCM, RIKEN BRC, Tsukuba, Japan). Each strain was streaked onto Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. A single colony was transferred to 25 mL of Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and incubated under the same conditions to reach the stationary phase. Cell concentrations were adjusted to approximately 7 log CFU/mL by serial dilution with sterile distilled water prior to inoculation. These strains are widely used in food safety studies as non-pathogenic substitutes for E. coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes, respectively. They have been shown to share key physiological and genetic characteristics with their pathogenic counterparts, which allows them to serve as practical and scientifically accepted models in challenge studies. Additionally, their use enables safer handling under Biosafety Level 1 conditions, avoiding the need for high-containment laboratories [12].
2.3. Preparation of Betel Leaf Samples
Betel leaves were washed under running tap water, rinsed with sterile distilled water, and air-dried in a laminar flow hood. For microbial inoculation, 1 mL of bacterial suspension was evenly pipetted onto the upper (adaxial) surface of each leaf and allowed to dry under sterile airflow for 1 h. Leaves were randomly assigned to four treatment groups; (Untreated): No riboflavin and no light exposure. BL: Exposed to blue LED light only. Rbf: Treated with riboflavin in the dark. BL + Rbf: Treated with riboflavin followed by blue light exposure. The treatment groups and procedures is provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Experimental treatment groups and procedures.
For concentration-dependent experiments, leaves were immersed in riboflavin solutions of 50, 75, 125, or 175 µM (prepared in sterile distilled water) for 5 min in darkness. Leaves were then drained and kept in the dark for 10 min before illumination. For quality analyses during storage were performed at 125 µM riboflavin, the concentration giving the highest microbial inactivation without adverse quality changes.
2.4. Photodynamic Treatment Protocol
The blue LED chamber (custom-built) contained 180 diodes (3 W each) emitting at a peak wavelength of 470 nm. The total electrical power was 540 W. The internal chamber dimensions were 30 × 30 × 52 cm. Leaves were placed horizontally on a perforated stainless-steel tray at a vertical distance of 20 cm from the light source. Irradiation was performed for 30 min under ambient laboratory conditions (25 ± 2 °C, ~55% RH, no forced airflow). Optical irradiance at the sample plane was empirically measured using a PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) meter (PM-01, Apogee Instruments Inc., Logan, UT, USA). The recorded irradiance was 300 μmol photons/m2/s at a vertical distance of 20 cm. Assuming an average photon energy of 2.64 × 10−19 J (at 470 nm), the total energy dose over a 30 min exposure was calculated as 11.72 J/cm2.
2.5. Microbial Enumeration
Each betel leaf sample (~4–5 g, approximately 12 cm2 surface area) was inoculated with 1 mL of bacterial suspension (either E. coli K-12 or L. innocua) to achieve a target load of ~7.0 log CFU/g. To ensure even distribution and minimize pooling, the inoculum was gently pipetted in droplets across the adaxial (upper) surface and spread with a sterile bent glass rod. After inoculation, samples were air-dried in a biosafety cabinet for 30 min to facilitate bacterial attachment.
After treatment, 1 g of each leaf sample was aseptically transferred to a sterile stomacher bag containing 9 mL of 0.1% peptone water and homogenized for 1 min. Ten-fold serial dilutions were prepared up to 10−6. One-milliliter aliquots from appropriate dilutions were plated onto selective media. E. coli K-12 was enumerated using 3M Petrifilm™ E. coli/Coliform Count Plates (3M, St. Paul, MN, USA), with only red colonies being counted. Listeria innocua was enumerated on PALCAM Listeria Selective Agar (HiMedia, M1064, Himedia Laboratories, Mumbai, India), with only gray-green colonies surrounded by black halos recorded as presumptive Listeria. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 h depending on colony visibility and reported as logCFU/g. The detection limit was 1.0 log CFU/g based on 1 colony per plate.
2.6. Physicochemical Analyses
After treatment, the samples were aseptically packed in sterile low-density polyethylene (LDPE) bags containing ambient air and wrapped in aluminum foil. The packaging atmosphere was not modified (i.e., no vacuum or gas flushing applied), and headspace gas composition (O2/CO2) was not measured. Aluminum foil was used to prevent exposure to ambient light during storage, minimizing any unintended photochemical reactions from residual riboflavin. All samples were stored at 4 ± 1 °C for 10 days. Sampling was performed at Day 0 and Day 10 for subsequent analyses.
2.6.1. Total Soluble Solids (TSS)
Leaf juice was extracted by macerating 1 g of tissue and filtering through cheesecloth. TSS was measured using a handheld digital refractometer (PAL-1, Atago, Tokyo, Japan) and reported in °Brix.
2.6.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
TPC was determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu method with slight modifications. One gram of ground leaf tissue was extracted in 10 mL of 80% methanol for 1 h at room temperature with constant shaking. The extract was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 min, and 100 µL of the supernatant was reacted with 1.25 mL of 10% Folin–Ciocalteu reagent and 600 µL of 7.5% sodium carbonate. The mixture was incubated in the dark for 90 min before measuring absorbance at 760 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Results were calculated from a gallic acid standard curve and expressed as mmol gallic acid equivalents per gram (mmol GAE/g) of fresh weight. Prior to extraction, all treated leaves were rinsed twice with sterile distilled water to remove residual riboflavin. Absorbance at 470 nm of the rinse water was monitored, showing a sharp decline from 1.62 to ~0.10 since second rinse onward, suggesting effective removal of riboflavin from the leaf surface (Supplement data).
2.6.3. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
Antioxidant activity was assessed via DPPH assay. A 250 µL aliquot of methanolic leaf extract (as prepared in Section 2.6.2) was added to 2 mL of 0.1 mM DPPH solution in methanol. After mixing and incubation in the dark for 30 min, absorbance was measured at 517 nm. Percentage inhibition was calculated as follows:
2.6.4. Color Measurement
Color attributes were recorded using a calibrated colorimeter (CR-400, Konica Minolta, Tokyo, Japan) with D65 standard illuminant and a 10° observer angle. Parameters L* (lightness), a* (green-red), and b* (blue-yellow) were measured at three random points per sample and averaged. Measurements were conducted on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 during storage at 4 ± 1 °C under dark conditions.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
For microbial enumeration, each treatment was performed in three independent biological replicates. One plate was prepared and counted for each replicate. For physicochemical analyses (TSS, color, TPC, and DPPH), three independent leaf samples were used per treatment group. Each sample was measured in triplicate to ensure instrumental consistency. Data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 16.0, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). One-way ANOVA followed by Turkey’s HSD (p < 0.05) was used to determine significant differences among treatment means. Storage-related parameters were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with treatment and storage day as fixed factors, followed by Tukey’s HSD post hoc test (p < 0.05)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Compatibility Between Light Source and Photosensitizer
Figure 1 illustrates the emission spectrum of the blue light-emitting diode (LED) used in this study and the absorption spectrum of riboflavin at 125 µM. The LED displayed a peak emission at approximately 470 nm, which aligns closely with the primary absorption band of riboflavin in the visible spectrum, particularly between 445 and 470 nm. This spectral overlap is essential for ensuring effective photoexcitation of the photosensitizer and is a fundamental requirement in photodynamic inactivation systems [13]. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) acts as a photoactive molecule capable of initiating both Type I and Type II photochemical reactions. Upon absorption of blue light, riboflavin transitions to an excited singlet state and subsequently to a more stable triplet state. This triplet riboflavin can then engage in electron transfer reactions with substrates (Type I), forming radicals such as superoxide anions, or in energy transfer to molecular oxygen (Type II), producing singlet oxygen [4]. Both ROS types are highly reactive and are capable of causing irreversible oxidative damage to microbial components including membranes, proteins, and nucleic acids [14].
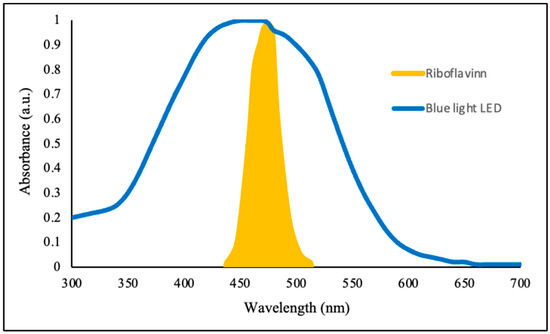
Figure 1.
Emission spectrum of blue light emitting diode and absorption spectrum of 80 μM riboflavin.
Moreover, the narrow-band emission of LED light provides a well-defined excitation source, allowing precise control of the photodynamic process. The use of LEDs also eliminates the production of UV radiation, which could otherwise accelerate degradation of the photosensitizer and damage the users [7]. Hence, the emission characteristics of the selected blue LED are well-suited for activating riboflavin.
3.2. Dose-Dependent Microbial Inactivation by Riboflavin and Blue LED Light
Figure 2 illustrates the microbial reductions of Escherichia coli K-12 and Listeria innocua populations in nutrient broth and on betel leaf surfaces following treatments with riboflavin (Rbf), blue LED light (BL), and their combination (BL + Rbf) at varying Rbf concentrations (50–175 µM). The combined BL + Rbf treatment exhibited a clear dose-dependent microbial inactivation pattern.
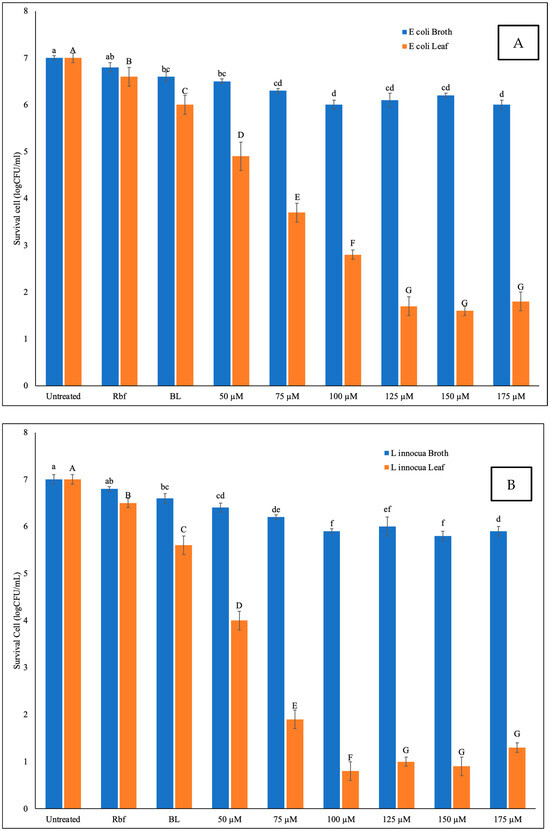
Figure 2.
Microbial populations of E. coli K-12 and L. innocua after treatment with BL, Rbf, or their combination at various riboflavin concentrations (50–175 µM) on (A) betel leaf surfaces and (B) in nutrient broth. Bars represent means ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters above bars indicate significant differences among treatments within broth samples, while uppercase letters indicate differences within leaf samples (p < 0.05, Tukey’s HSD).
In broth, the maximum reductions observed were approximately 0.95 log CFU/mL for E. coli and 1.25 log CFU/mL for L. innocua at 175 µM Rbf. Conversely, on leaf surfaces, reductions reached approximately 5.8 log CFU/g for E. coli and 6.0 log CFU/g for L. innocua. The enhanced efficacy on leaf surfaces may be attributed to increased light scattering and localized photosensitizer concentration, despite potential surface irregularities.
The synergistic effect of Rbf and BL confirms the photodynamic mechanism. Upon excitation, riboflavin generates singlet oxygen and other reactive oxygen species (ROS) that oxidize microbial membranes and cellular components [5,8]. The dose-dependent response aligns with findings that higher photosensitizer concentrations lead to increased ROS production, up to a saturation point [3].
In comparison to previous published works, our results show substantially greater antimicrobial efficacy under much lower fluence. For example, Kim et al. (2021) [15] demonstrated that riboflavin-mediated 405 nm LED illumination in phosphate-buffered saline at 25 °C achieved about 6.2 log CFU/mL reduction of Listeria monocytogenes at ~19.2 J/cm2, whereas LED alone required a much higher dose (57.6 J/cm2) to reach ~1.9 log reduction. In our work, on betel leaf surfaces, we achieved ~6.2 log CFU/g reduction in L. innocua with the Rbf-BL treatment, with a measured fluence of ~11.72 J/cm2. This suggests that PDT using riboflavin + blue light in this matrix may be more efficient, likely due to surface topology, leaf-mediated light scattering, or enhanced photosensitizer localization. However, we caution that direct comparisons remain challenging due to differences in light delivery, bacterial species/strain, and matrix (leaf vs. PBS).
Interestingly, in our study, L. innocua exhibited slightly higher reductions than E. coli on leaf surfaces, despite being Gram-positive. This may relate to species-specific susceptibility and differences in antioxidant enzyme expression or riboflavin uptake. Additionally, while Gram-positive bacteria possess a thicker peptidoglycan layer, the absence of an outer membrane may allow hydrophilic photosensitizers such as riboflavin to diffuse more effectively into the cell wall matrix, facilitating ROS penetration. In contrast, the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria like E. coli contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which can act as a partial barrier or ROS scavenger, potentially reducing PDT efficacy [16].
Conversely, in broth, both strains responded similarly, with modest but consistent reductions. At higher riboflavin concentrations, the optical density at 470 nm increased markedly in broth, reaching OD470 values of 0.83 and 1.06, respectively, when measured at a 1 cm path length (see Supplementary Materials). These high absorbance levels can lead to inner-filter effects that attenuate light penetration observed in other fluorescence or photochemical systems [17]. Similar limitations have been noted in microplate-based fluorescence assays, where absorbance above 1 can significantly reduce fluorescence or light transmission, reducing the effective fluence received by cells suspended in the medium.
In addition to ROS-mediated bacterial inactivation, the relatively higher reductions observed on betel leaf surfaces may be partially influenced by the presence of intrinsic antimicrobial phytochemicals. Piper betle leaves are known to contain bioactive compounds such as eugenol, hydroxychavicol, chavicol, and polyphenols, which exhibit antimicrobial activity [18]. While the present study did not directly quantify the release or activation of these compounds during PDT, their presence may complement the photodynamic mechanism. Future investigations should examine the potential synergistic effects between ROS and endogenous phytochemicals using targeted metabolite profiling.
While our results indicate that riboflavin-mediated photodynamic inactivation effectively reduced E. coli and L. innocua, it is important to acknowledge that microbial resistance to oxidative treatments, though uncommon, has been reported. Mackay (2022) [19] noted that certain bacteria may develop increased tolerance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) via enhanced antioxidant enzyme expression, particularly under repeated or sublethal photodynamic exposures. However, such adaptations are rarely observed in single-use applications like those applied in this study, especially on fresh produce surfaces [19].
From a food safety perspective, riboflavin (vitamin B2) is classified as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by the U.S. FDA and has an established acceptable daily intake (ADI) of up to 0.5 mg/kg body weight per day [20]. The estimated residual riboflavin on betel leaf after treatment and rinsing is expected to be <1 mg per portion, well below the ADI for an average adult. Furthermore, riboflavin photoproducts such as lumichrome and lumiflavin are generally regarded as non-toxic at trace levels and do not pose safety concerns [21]. Therefore, the use of riboflavin in photodynamic treatment presents minimal toxicological risk for consumers.
3.3. Residual Survival of Microbes Following Photodynamic Treatment
Figure 3 shows the time-dependent survival of Escherichia coli K-12 and Listeria innocua subjected to photodynamic treatment (BL + Rbf) on betel leaf surfaces and in broth. Both species started with an initial population of 7.0 log CFU/mL.
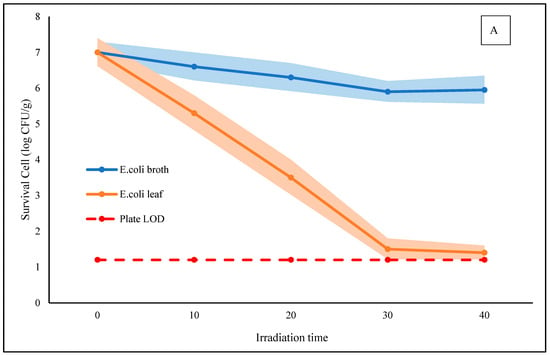
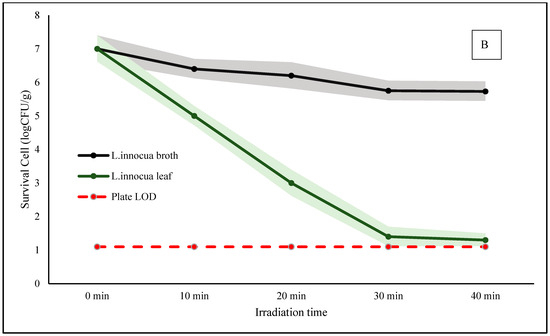
Figure 3.
Time–kill curves of E. coli K12 (A) and L. innocua (B) under photodynamic treatment using riboflavin (Rbf, 125 µM) and blue LED irradiation (470 nm, fluence = 11.72 J/cm2) over 30 min. Survival counts were measured in broth and on betel leaf surfaces at 10 min intervals. Shaded bands represent ± standard deviation (n = 3). The red dashed line indicates the plate detection limit (LOD).
On the betel leaf surface, the most significant reductions were achieved after 30 min of treatment. E. coli counts decreased to 1.5 log CFU/mL, and L. innocua dropped even further to 1.0 log CFU/mL, corresponding to 5.5 and 6.0 log reductions, respectively. Notably, extending the treatment to 40 min did not lead to further significant reduction for either microorganism, indicating that 30 min is sufficient for maximal inactivation under the tested conditions.
In contrast, bacterial inactivation in broth was significantly lower. After 30 min, E. coli and L. innocua were reduced to approximately 5.7 and 5.5 log CFU/mL, equivalent to 1.3 and 1.5 log reductions, respectively. This difference reflects the limited diffusion range and short half-life of ROS like singlet oxygen in aqueous environments, which reduces their contact time with planktonic cells [22].
The markedly higher efficacy on the leaf surface may result from localized ROS accumulation near attached bacterial cells, enhanced riboflavin retention on the cuticle, and increased light scattering that improves photon exposure. Additionally, ROS-induced disruption of leaf tissues may promote the release of antimicrobial compounds such as eugenol and hydroxychavicol, which are naturally abundant in Piper betle [23]. These phytochemicals may act synergistically with ROS to enhance bacterial killing.
In our study, a total fluence of ~11.72 J/cm2 applied over 30 min led to microbial reductions of up to 6.2 log CFU/g for L. innocua and 5.3 log CFU/g for E. coli on betel leaf surfaces. These results are comparable to the findings of Li et al. (2021), who reported that riboflavin-mediated PDT using 9.36 J/cm2 fluence achieved >6.0 log CFU/mL inactivation of Salmonella in planktonic suspension [24]. Despite differences in matrix and bacterial species, the comparable fluence and effectiveness support the antimicrobial potential of our system. In addition, the relatively high inactivation observed on betel leaves may be partly influenced by the presence of intrinsic phytochemicals. Although not directly measured in this study, oxidative stress from illumination might have contributed to the release or activation of compounds such as hydroxychavicol and eugenol, which are known for their antimicrobial activity [25].
3.4. Morphological Changes in Bacteria Observed by SEM
Leaf samples were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde (v/v) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) at 4 °C overnight. Samples were then rinsed in PBS and subjected to a graded ethanol dehydration series (30%, 50%, 70%, 90%, and 100%, 10 min each step). After critical point drying, specimens were sputter-coated with a thin layer of gold and examined under a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM; TESCAN CLARA, Czech Republic) at an accelerating voltage of 15 kV. This preparation approach follows standard SEM protocols for biological samples to minimize structural collapse or artifacts during imaging [26,27].
Figure 4 shows scanning electron micrographs of Escherichia coli K-12 and Listeria innocua on betel leaf surfaces before and after photodynamic treatment (BL + Rbf). Untreated E. coli cells (Figure 4A) exhibited smooth, rod-shaped morphology with intact membranes. After treatment (Figure 4C), many cells appeared deformed, with wrinkled surfaces and signs of membrane collapse.
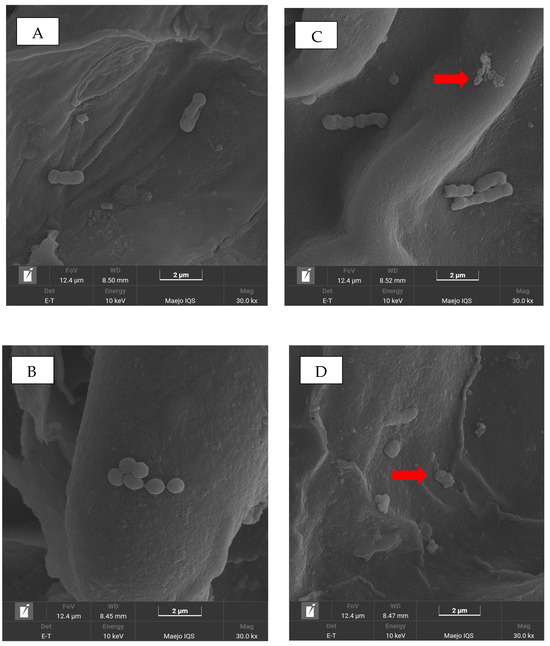
Figure 4.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of Escherichia coli K12 (A) and Listeria innocua (B) on the surface of betel leaf before treatment. Images (C,D) show E. coli K12 and L. innocua, respectively, after exposure to photodynamic treatment with blue light and riboflavin (BL + Rbf). Red arrows highlight microbial cells exhibiting structural damage induced by the treatment.
Similarly, untreated L. innocua cells (Figure 4B) showed smooth, spherical to short-rod shapes typical of Gram-positive bacteria. Post-treatment images (Figure 4D) revealed distorted shapes, surface rupture, and irregular outlines, indicating structural damage.
These visible alterations in both species are consistent with structural damage typically attributed to reactive oxygen species (ROS) during PDT [28]. In summary, SEM analysis provides morphological evidence that PDT effectively damages bacterial cells and contributes to microbial inactivation.
3.5. Physicochemical Properties of Betel Leaf
Table 2 summarizes the temporal changes in total soluble solids (TSS), total phenolic content (TPC), antioxidant activity (DPPH assay), and color parameters (L*, a*, b*) in betel leaves subjected to photodynamic treatment (BL + Rbf) compared to untreated controls during 10 days of storage at 4 °C.

Table 2.
The effects of photodynamic treatment using BL and Rbf on physicochemical properties of betel leaf.
3.5.1. Total Soluble Solids (TSS)
TSS values increased over time in both groups. However, leaves treated with BL + Rbf consistently showed higher °Brix readings, reaching 12.0 °Brix on day 3. This effect is likely due to increased membrane permeability caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can facilitate the leakage of intracellular sugars into the apoplast [23]. Additionally, blue light has been shown to stimulate sugar metabolism and soluble carbohydrate accumulation in plant tissues [7].
3.5.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
TPC gradually increased over the 10-day storage period, with significantly higher levels observed in the BL + Rbf group, peaking at 0.17 mmol GAE/g. The measured TPC in our study is comparable to values reported by [29], who found 0.18–0.28 mmol GAE/g in Piper betle leaves extracted with various solvents. This increase may result from oxidative stress-induced upregulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), a key enzyme in the phenylpropanoid pathway [30]. Furthermore, membrane disruption from ROS could enhance the extractability of phenolics, making them more readily detected [31].
3.5.3. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH)
Antioxidant activity, as measured by DPPH radical scavenging, increased in all samples during storage, with the BL + Rbf-treated group reaching 62.01% inhibition on day 10, compared to 46.12% in the control. This improvement aligns with the observed TPC increase, as phenolic compounds are major contributors to antioxidant capacity [25]. Riboflavin-mediated ROS may have also induced mild stress signaling in the leaves, triggering the synthesis of antioxidant compounds [5].
3.5.4. Color Parameter
Significant changes (p < 0.05) were observed in L*, a*, and b* values during storage for both untreated and BL+Rbf-treated leaves. In general, L* values (lightness) of treated leaves were lower than those of the untreated control, particularly at later storage days, indicating a slight darkening effect possibly due to oxidative stress or partial chlorophyll degradation induced by photodynamic treatment. The a* values (green–red axis) increased markedly over time, especially in treated samples, suggesting a progressive loss of green coloration and a shift toward red tones, consistent with chlorophyll breakdown and possible accumulation of pheophytin derivatives during storage. The b* values (yellow–blue axis) decreased significantly in both groups, with a sharper decline in treated leaves, indicating a reduction in yellow pigments such as carotenoids, which are known to be sensitive to oxidative processes. Similar trends have been reported in postharvest vegetables exposed to blue light and oxidative treatments [30].
To reconcile the observed L*, a*, and b* shifts with perceptual changes, we calculated the total color difference (ΔE*) using untreated Day 0 as the reference. The ΔE* value immediately after treatment (Day 0) was 4.68, indicating a moderate but acceptable color change. According to sensory guidelines, ΔE* values between 2 and 3 are just noticeable, while those in the 2–10 range are slightly perceptible at a glance, yet often acceptable in food applications [32]. Thus, although surface color changes were instrumentally measurable, they are likely modest in terms of human visual perception immediately after PDT. After 10 days of refrigerated storage, ΔE* values increased to 15.27 in untreated leaves and 14.89 in BL+Rbf-treated samples. These high values suggest that most of the visual color degradation occurred during storage, likely due to natural senescence, chlorophyll breakdown, and oxidative changes over time [33].
While the present study demonstrates the potential of riboflavin-assisted blue light photodynamic treatment (PDT) for microbial inactivation and quality preservation in betel leaves, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the use of non-pathogenic surrogates (E. coli K-12 and L. innocua) limits the direct extrapolation of results to actual pathogenic strains, although such models are widely accepted for safety and regulatory purposes. Second, the experimental setup was performed in a laboratory-scale chamber under controlled conditions; scaling the system to industrial or commercial applications may require optimization of LED configurations, fluence uniformity, and temperature control. Moreover, the possible contributions of leaf intrinsic phytochemicals to microbial inactivation, though supported by literature, were not directly quantified in this study. Future research should investigate the mechanistic synergy between ROS and plant-derived antimicrobials, evaluate residue safety, and validate the system’s efficacy on real-world pathogens and in diverse leafy matrices.
4. Conclusions
Photodynamic treatment using riboflavin and blue LED effectively reduced E. coli K-12 and L. innocua on betel leaves and in broth. SEM confirmed structural cell damage, supporting oxidative inactivation. The treatment also enhanced physicochemical properties, including increased TSS, phenolic content, and antioxidant activity, with small color changes. These results suggest that riboflavin-mediated PDT is a promising, mild-thermal preservation method for improving both safety and quality of fresh betel leaves.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13103130/s1.
Author Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: R.R.: Experimental set-up, Formal analysis and Original draft. V.P.: Experimental set-up and Formal analysis. R.P.: Experimental set-up and Formal analysis. S.J.: Experimental set-up and Formal analysis. S.P.: Review and Editing. W.K.: Methodology, Review and Editing. T.K.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Faculty of Agro-Industry, Chiang Mai University.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors of this research have any financial interest or conflict with industries or parties.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PDT | Photodynamic treatment |
| Rbf | Riboflavin |
| BL | Blue Light |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
References
- Dada, A.C.; Somorin, Y.M.; Ateba, C.N.; Onyeaka, H.; Anyogu, A.; Kasan, N.A.; Odeyemi, O.A. Microbiological Hazards Associated with Food Products Imported from the Asia-Pacific Region Based on Analysis of the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) Notifications. Food Control 2021, 129, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Murray, C.K.; Hamblin, M.R.; Hooper, D.C.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Pathogenic Microbes: State of the Art. Drug Resist. Updates 2017, 33–35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Shin, M.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, D.H. Inactivation Efficacy of Combination Treatment of Blue Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and Riboflavin to Control E. coli O157:H7 and S. typhimurium in Apple Juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Leung, A.W.; Hua, H.; Rao, X.; Xu, C. Photodynamic Action of LED-Activated Curcumin against Staphylococcus Aureus Involving Intracellular ROS Increase and Membrane Damage. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 637601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ran, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanisms of Obligate Anaerobes Involved in Biological Waste Treatment Processes: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; van Iersel, M.W. Photosynthetic Physiology of Blue, Green, and Red Light: Light Intensity Effects and Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 619987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwannasom, N.; Kao, I.; Pruß, A.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, N.; Chin, V.K.; Chong, P.P.; Lim, W.F.; Lim, C.W.; Basir, R.; Chang, S.K.; Lee, T.Y. Riboflavin as a Promising Antimicrobial Agent? A Multi-Perspective Review. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatansever, F.; de Melo, W.C.M.A.; Avci, P.; Vecchio, D.; Sadasivam, M.; Gupta, A.; Chandran, R.; Karimi, M.; Parizotto, N.A.; Yin, R.; et al. Antimicrobial Strategies Centered around Reactive Oxygen Species—Bactericidal Antibiotics, Photodynamic Therapy, and Beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 955–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songca, S.P.; Adjei, Y. Applications of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy against Bacterial Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Gurtler, J.B. Selection of Surrogate Bacteria for Use in Food Safety Challenge Studies: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1506–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algorri, J.F.; Ochoa, M.; Roldán-Varona, P.; Rodríguez-Cobo, L.; López-Higuera, J.M. Light Technology for Efficient and Effective Photodynamic Therapy: A Critical Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, H.; Coenye, T. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Antibiotic-Mediated Killing of Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Da Jeong, M.; Zheng, Q.; Yuk, H.G. Antimicrobial Activity of 405 Nm Light-Emitting Diode (LED) in the Presence of Riboflavin against Listeria Monocytogenes on the Surface of Smoked Salmon. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Pathogen Clearance: The Killing Mechanisms, the Adaption Response, and the Side Effects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 622534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitner, T.; Friganovic, T.; Šakic, D. Inner Filter Effect Correction for Fluorescence Measurements in Microplates Using Variable Vertical Axis Focus. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7107–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Anand, U.; Saha, S.C.; Kant, N.; Mishra, T.; Masih, H.; Bar, A.; Pandey, D.K.; Jha, N.K.; Majumder, M.; et al. Betelvine (Piper betle L.): A Comprehensive Insight into Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological, Biomedical and Therapeutic Attributes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3083–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, A.M. Microbial Resistance to Photodynamic Therapy. J. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 4, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; König, J.; Lambré, C.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Mosesso, P.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the Re-Evaluation of Riboflavin (E 101(i)) and Riboflavin-5′-Phosphate Sodium (E 101(Ii)) as Food Additives. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.G.K.; Rhodes, C.; Dessent, C.E.H. Photodegradation of Riboflavin under Alkaline Conditions: What Can Gas-Phase Photolysis Tell Us about What Happens in Solution? Molecules 2021, 26, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, G.; Mokrzyński, K.; Sarna, T. Generation of Singlet Oxygen inside Living Cells: Correlation between Phosphorescence Decay Lifetime, Localization and Outcome of Photodynamic Action. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2024, 23, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, M.; Gui, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; et al. Blue Light Combined with Salicylic Acid Treatment Maintained the Postharvest Quality of Strawberry Fruit during Refrigerated Storage. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, L.; Chen, B.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.J. Antibacterial Potency of Riboflavin-Mediated Photodynamic Inactivation against Salmonella and Its Influences on Tuna Quality. LWT 2021, 146, 111462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, P.; Muthukrishnan, S. Evaluation of Total Phenolic Content and Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Boerhavia Erecta. J. Acute Med. 2013, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relucenti, M.; Familiari, G.; Donfrancesco, O.; Taurino, M.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Selan, L. Microscopy Methods for Biofilm Imaging: Focus on SEM and VP-SEM Pros and Cons. Biology 2021, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Běhalová, H.; Tremlová, B.; Kalčáková, L.; Pospiech, M.; Dordevic, D. Assessment of the Effect of Secondary Fixation on the Structure of Meat Products Prepared for Scanning Electron Microscopy. Foods 2020, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, J.; Lin, S. Curcumin-Mediated Sono-Photodynamic Treatment Inactivates Listeria Monocytogenes via ROS-Induced Physical Disruption and Oxidative Damage. Foods 2022, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.Q. Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase, a Key Component Used for Phenylpropanoids Production by Metabolic Engineering. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62587–62603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Khare, T.; Srivastav, A.; Surekha, C.; Shriram, V.; Wani, S.H. Oxidative Stress and Leaf Senescence: Important Insights. In Senescence Signalling and Control in Plants; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Sazwi, N.; Nalina, T.; Rahim, Z.H.A. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Activities of Piper Betle, Areca Catechu, Uncaria Gambir and Betel Quid with and without Calcium Hydroxide. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, M.; Nemli, S.K.; Güngör, M.B.; Bal, B.T.; Öztürk, E. Perceptibility and Acceptability Thresholds for Color Differences of Light and Dark Maxillofacial Skin Replications. Vis. Res. 2024, 223, 108474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonto, T.C.; Cimini, S.; Grasso, S.; Zompanti, A.; Santonico, M.; De Gara, L.; Locato, V. Methodological Pipeline for Monitoring Post-Harvest Quality of Leafy Vegetables. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).