A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality in the Lake and Rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
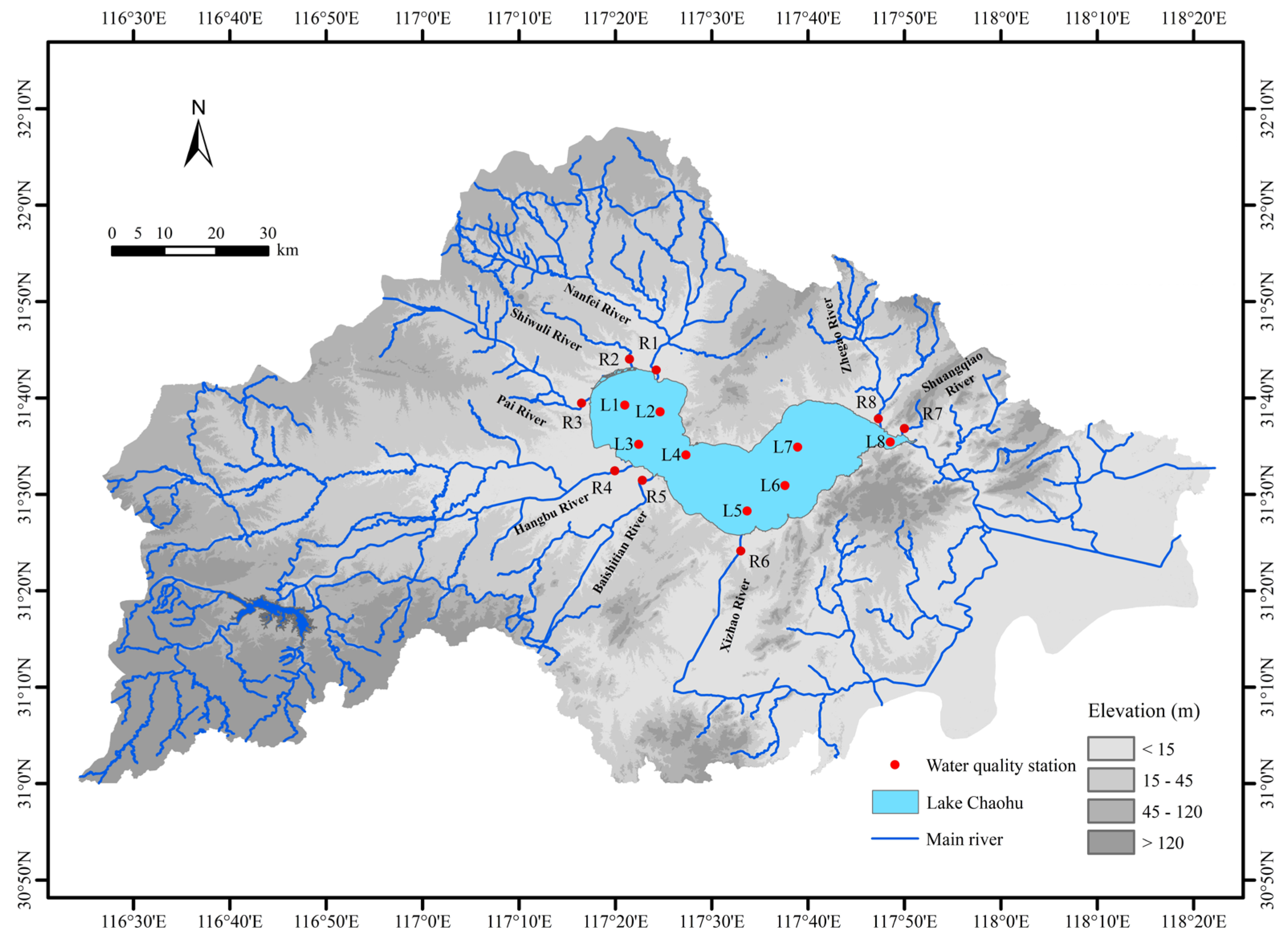
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. WQI and WQImin Calculations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Features of Water Quality Metrics in the LCB
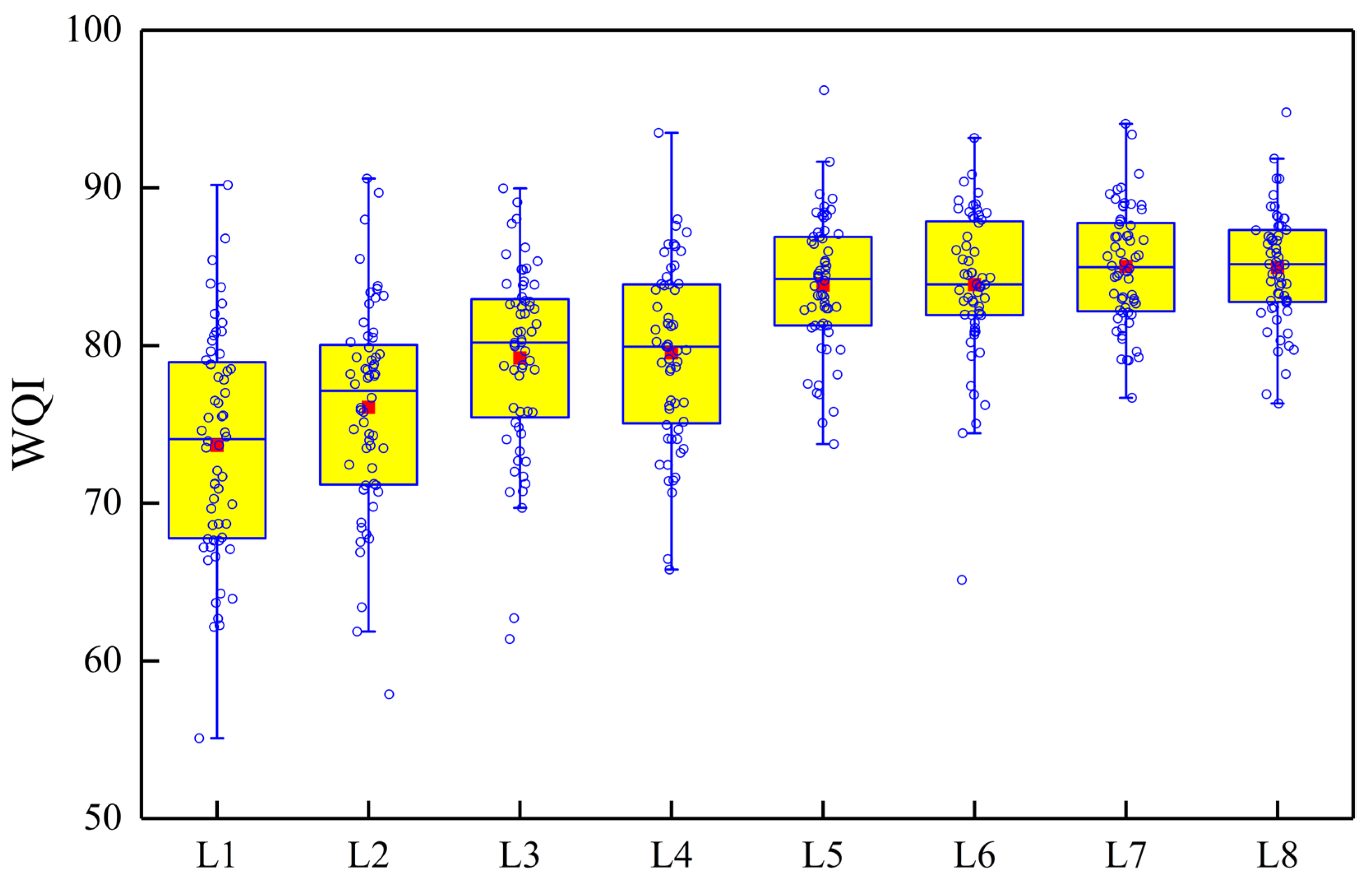
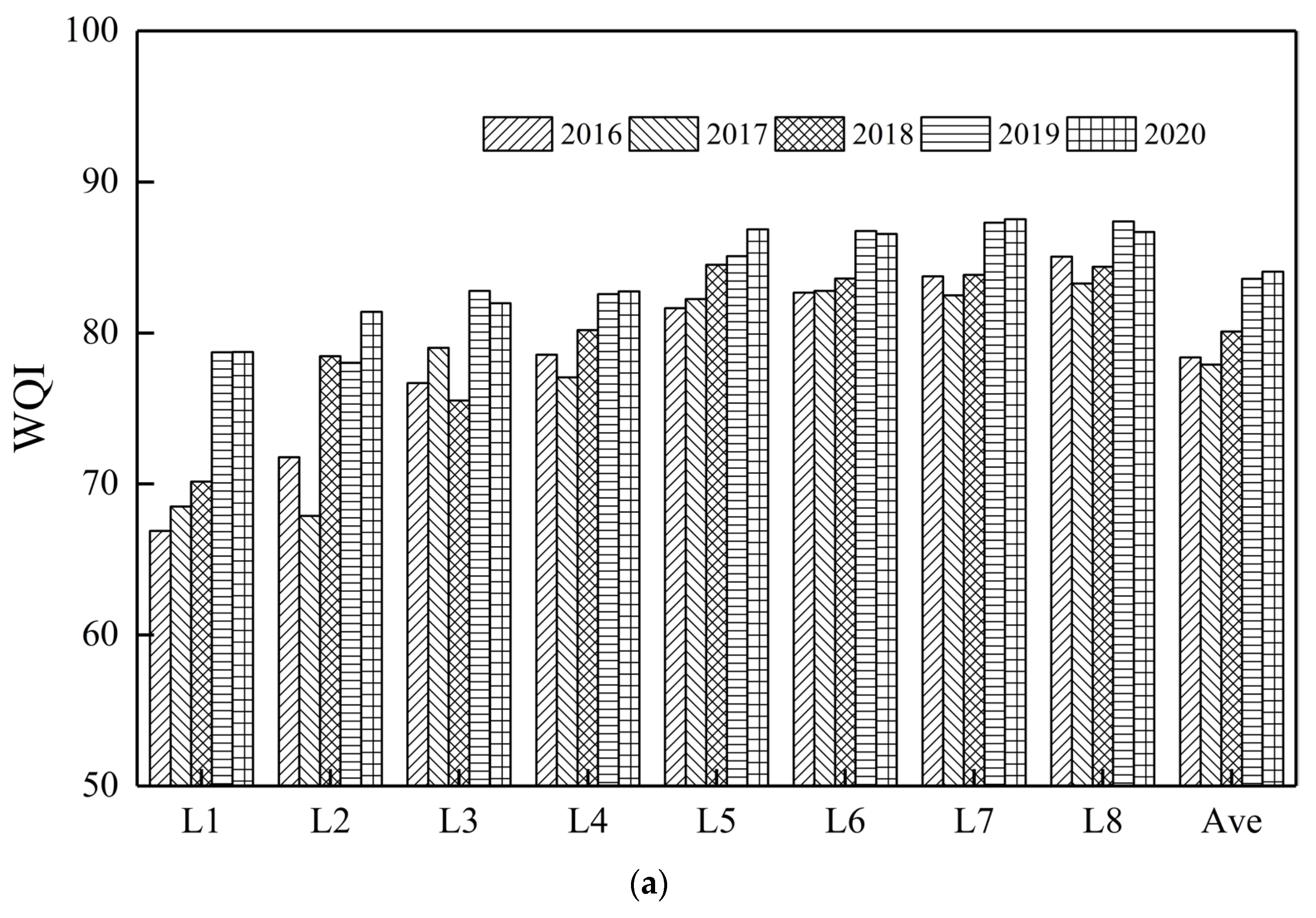
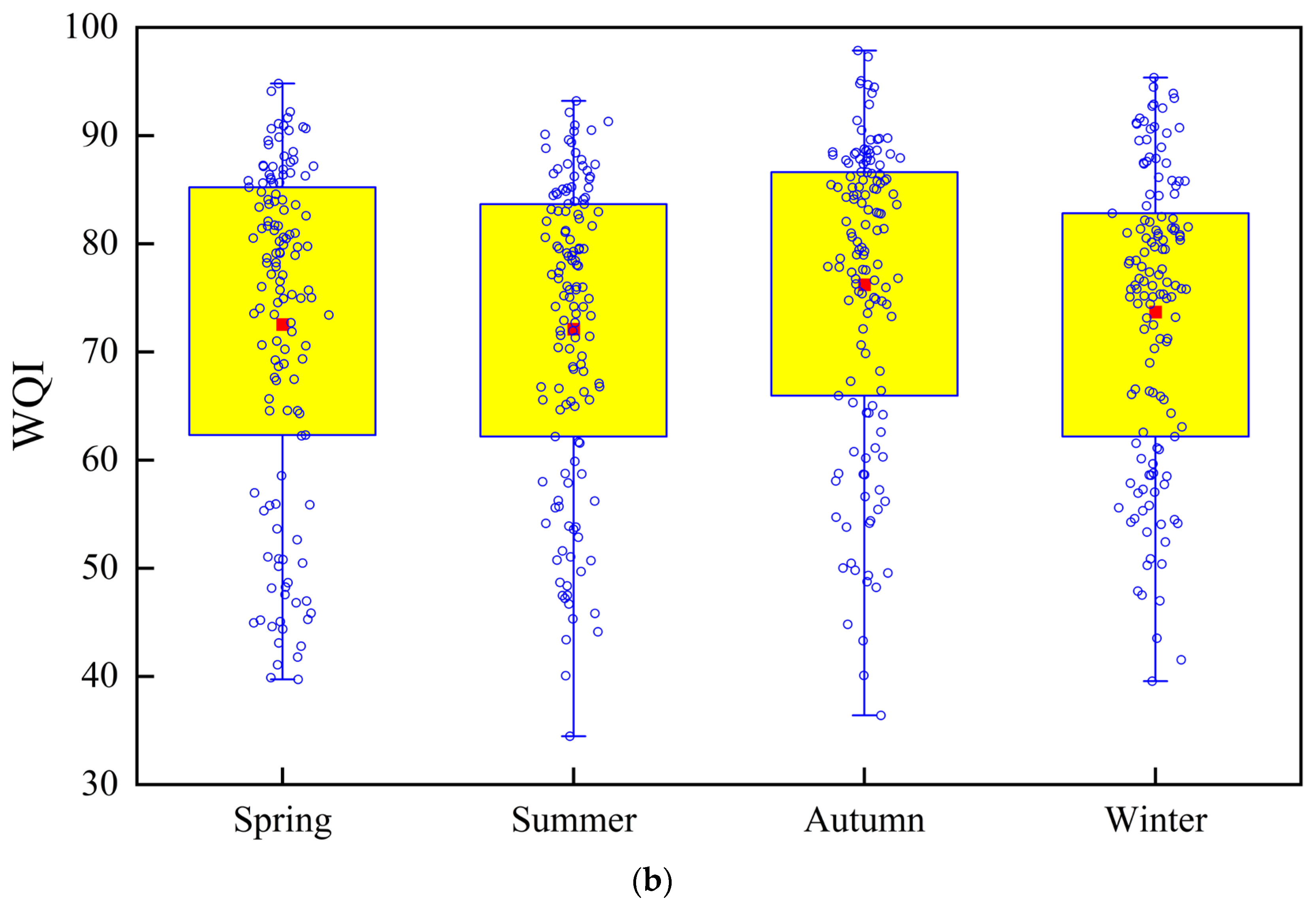
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Water Quality in Lake Chaohu Using the WQI
3.3. Spatiotemporal Patterns in Water Quality of Inflowing Rivers Based on the WQI
3.4. Relationship Between Lake and Inflowing River Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Crucial Parameters Affecting Water Quality and the WQImin
4.2. Recommendations for Water Pollution Control in the LCB
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LCB | Lake Chaohu Basin |
| WQI | Water quality index |
| WQImin | Minimum WQI |
References
- Mammides, C. A Global Assessment of the Human Pressure on the World’s Lakes. Glob. Environ. Change 2020, 63, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y.; Shao, K.; Tang, X.; Gong, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, Q.; Gao, G. Relationships between Environmental Factors and N-cycling Microbes Reveal the Indirect Effect of Further Eutrophication on Denitrification and DNRA in Shallow Lakes. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S. Drivers to Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Column Integrated Phytoplankton Biomass in the Shallow Lake of Chaohu, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Xiao, P.; Heino, J.; Tan, F.; Soininen, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Eutrophication Increases the Similarity of Cyanobacterial Community Features in Lakes and Reservoirs. Water Res. 2024, 250, 120977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Z.-P.; Chu, Y.-X.; Tian, G.; He, R. Eutrophication Levels Increase Sulfur Biotransformation and Emissions from Sediments of Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M. Eutrophication, Harmful Algae and Biodiversity—Challenging Paradigms in a World of Complex Nutrient Changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, S.; Mao, B. Eutrophication Causes Analysis Under the Influencing of Anthropogenic Activities in China’s Largest Fresh Water Lake (Poyang Lake): Evidence from Hydrogeochemistry and Reverse Simulation Methods. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication Control of Large Shallow Lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Uyl, P.A.; Thompson, L.R.; Errera, R.M.; Birch, J.M.; Preston, C.M.; Ussler, W.; Yancey, C.E.; Chaganti, S.R.; Ruberg, S.A.; Doucette, G.J.; et al. Lake Erie Field Trials to Advance Autonomous Monitoring of Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1021952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yindong, T.; Xiwen, X.; Miao, Q.; Jingjing, S.; Yiyan, Z.; Wei, Z.; Mengzhu, W.; Xuejun, W.; Yang, Z. Lake Warming Intensifies the Seasonal Pattern of Internal Nutrient Cycling in the Eutrophic Lake and Potential Impacts on Algal Blooms. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Kang, X.; Quan, D.; Sun, B.; Arvola, L.; Li, G. Spatiotemporal Variation in Water Quality and Identification and Quantification of Areas Sensitive to Water Quality in Hulun Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitau, M.W.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z. Water Quality Indices as Tools for Decision Making and Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2591–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Feng, J.; Chang, X.; Li, Y. Evaluation of the Effectiveness and Effects of Long-term Ecological Restoration on Watershed Water Quality Dynamics in Two Eutrophic River Catchments in Lake Chaohu Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyenje, P.M.; Foppen, J.W.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Kulabako, R.; Muwanga, A. Eutrophication and Nutrient Release in Urban Areas of Sub-Saharan Africa—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Dong, F.; Huang, A.; Lei, Y.; Wang, W.; Tong, Z.; Long, J. Research on Water Quality Assessment Using the Water Quality Index for the Eastern Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water 2023, 15, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; You, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H. Water Quality Assessment and the Influence of Landscape Metrics at Multiple Scales in Poyang Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, A.; Akiner, M.E. Pollution Evaluation in Streams Using Water Quality Indices: A Case Study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A Critical Review on the Application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.; Ahmad, M.I.; Umar, K.; Md Yusuff, M.S.; Anees, M.T.; Qadir, A.; Ali Almanasir, Y.K. Modification of the Water Quality Index (WQI) Process for Simple Calculation Using the Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) Method: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhang, W.; Cao, S.; Hao, S.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Li, W.; Jiang, M. Optimization of Water Quality Index Models Using Machine Learning Approaches. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Xin, X.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Jia, R. Assessing Water Quality of Five Typical Reservoirs in Lower Reaches of Yellow River, China: Using a Water Quality Index Method. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A Review of Water Quality Index Models and Their Use for Assessing Surface Water Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M. Comparison of Seven Water Quality Assessment Methods for the Characterization and Management of Highly Impaired River Systems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 188, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Xia, W.; Lu, Y.; Gang, D.-D.; Lin, L.-S. A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality Condition and Spatiotemporal Patterns in Impounded Lakes Along the Eastern Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of Water Quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China Using the Water Quality Index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zou, Y. A comprehensive water quality assessment for a typical river–lake watershed in Northeast China: Implications for the water management of boundary lake. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 113942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruq, O.; Malak, M.A.; Hossain, N.J.; Sami, M.S.; Sajib, A.M. Investigating the relationship between land use and water quality in urban water bodies. Clean. Water 2025, 3, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, S.-P.; He, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yue, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xu, N. Assessing Water Quality in the Pearl River for the Last Decade Based on Clustering: Characteristic, Evolution and Policy Implications. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of Water Quality Indices to Verify the Impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J. Assessing River Water Quality Using Water Quality Index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lai, X.; Li, K. Water Quality Assessment of Rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) Using Water Quality Index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Ren, B.; Wu, B.; Deng, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics and optimization of water quality assessment in the Nantong section of the Yangtze River Basin: A WQImin approach. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, F.d.S.; Moreira, A.B.; Bisinoti, M.C.; Gimenez, S.M.N.; Yabe, M.J.S. Water Quality Index as a Simple Indicator of Aquaculture Effects on Aquatic Bodies. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Luo, J.; Xiong, Z.; Wan, N.; Ma, J.; Yuan, J.; Duan, H. Can the Establishment of a Protected Area Improve the Lacustrine Environment? A Case Study of Lake Chaohu, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yan, R.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, L. Modeling the Impacts of Water Transfer on Water Transport Pattern in Lake Chao, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Tang, M.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Song, C. Organic Carbon Quantity and Composition Jointly Modulate the Differentiation of Nitrate Reduction Pathways in Sediments of the Chinese Eutrophic Lake, Lake Chaohu. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Alatalo, J.M.; Li, C.; Ni, C. Tracking Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Harmful Algal Blooms Using Long-term MODIS Observations of Chaohu Lake in China from 2000 to 2021. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhang, M.; Fan, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.C.; Shi, X. Difference in Temporal and Spatial Distribution Pattern of Cyanobacteria between the Sediment and Water Column in Lake Chaohu. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment Internal Nutrient Loading in the Most Polluted Area of a Shallow Eutrophic Lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its Contribution to Lake Eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yi, Y. Spatial Distribution of Nutrient Loads and Thresholds in Large Shallow Lakes: The Case of Chaohu Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Cao, Z.; Chu, Q.; Jing, Y. Optimized Remote Sensing Estimation of the Lake Algal Biomass by Considering the Vertically Heterogeneous Chlorophyll Distribution: Study Case in Lake Chaohu of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, R. Modelling the Effects of Joint Operations of Water Transfer Project and Lake Sluice on Circulation and Water Quality of a Large Shallow Lake. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Hu, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, R.; Wei, W. Development and Evaluation of a Real-time Forecasting Framework for Daily Water Quality Forecasts for Lake Chaohu to Lead Time of Six Days. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 3838-2002Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Koçer, M.A.T.; Sevgili, H. Parameters Selection for Water Quality Index in the Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Land-based Trout Farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Mhere, G. Water Quality of the Odzi River in the Eastern Highlands of Zimbabwe. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, J. When and Where to Reduce Nutrient for Controlling Harmful Algal Blooms in Large Eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China? Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, L. Combining hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes to reveal the influence of human activities on surface water quality in Chaohu Lake Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Lake | ||||
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| pH | 8.19 ± 0.33, I | 8.25 ± 0.31, I | 8.22 ± 0.38, I | 8.16 ± 0.50, I | 8.25 ± 0.69, I |
| DO (mg/L) | 10.11 ± 2.04, I | 9.83 ± 1.77, I | 9.71 ± 2.07, I | 10.09 ±2.30, I | 9.58 ± 2.29, I |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 4.52 ± 0.99, III | 4.23 ± 1.10, III | 3.50 ± 1.07, II | 3.50 ± 0.67, II | 3.47 ± 0.92, II |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 2.44 ± 1.01, I | 2.37 ± 0.86, I | 1.53 ± 0.83, I | 1.90 ± 0.93, I | 1.83 ± 0.95, I |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 0.27 ± 0.41, II | 0.23 ± 0.33, II | 0.25 ± 0.55, II | 0.17 ± 0.20, II | 0.10 ± 0.13, I |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.09 ± 0.05, IV | 0.11 ± 0.06, V | 0.10 ± 0.04, IV | 0.08 ± 0.04, IV | 0.07 ± 0.03, IV |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.65 ± 0.82, V | 1.64 ± 0.91, V | 1.44 ± 1.06, IV | 1.18 ± 0.70, IV | 1.36 ± 0.73, IV |
| F- (mg/L) | 0.46 ± 0.08, I | 0.41 ± 0.07, I | 0.37 ± 0.07, I | 0.41 ± 0.06, I | 0.41 ± 0.04, I |
| Cu (μg/L) | 2.95 ± 1.69, I | 2.88 ± 0.22, I | 8.73 ± 8.02, I | 20.00 ±0.00, II | 20.00 ±0.00, II |
| Zn (μg/L) | 5.72 ± 9.37, I | 14.52 ± 29.41, I | 5.41 ± 4.74, I | 5.42 ± 2.56, I | 9.32 ±12.72, I |
| Se (μg/L) | 0.26 ± 0.16, I | 0.38 ± 0.34, I | 0.20 ± 0.00, I | 0.20 ± 0.00, I | 0.20 ± 0.00, I |
| As (μg/L) | 0.73 ± 0.70, I | 2.37 ± 2.41, I | 2.37 ± 1.92, I | 1.29 ± 1.34, I | 1.01 ± 0.70, I |
| Hg (μg/L) | 0.03 ± 0.00, I | 0.03 ± 0.01, I | 0.02 ± 0.00, I | 0.02 ± 0.01, I | 0.02 ± 0.01, I |
| Parameter | Rivers | ||||
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| pH | 7.91 ± 0.37, I | 7.83 ± 0.38, I | 7.63 ± 0.44, I | 7.54 ± 0.44, I | 7.29 ± 0.46, I |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.53 ± 2.74, I | 7.75 ± 2.42, I | 7.11 ± 2.49, II | 7.22 ± 2.45, II | 7.11 ± 3.21, II |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 5.11 ± 1.13, III | 4.87 ± 1.42, III | 4.30 ± 1.08, III | 4.10 ± 1.07, III | 4.75 ± 1.36, III |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 3.54 ± 1.41, III | 3.35 ± 1.98, III | 2.84 ± 1.98, I | 2.64 ± 1.91, I | 2.58 ± 1.01, I |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 2.60 ± 3.22, V | 2.07 ± 2.43, V | 1.39 ± 1.83, IV | 1.00 ± 1.56, III | 0.68 ± 0.63, II |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.23 ± 0.22, IV | 0.21 ± 0.21, IV | 0.15 ± 0.13, III | 0.11 ± 0.10, III | 0.15 ± 0.30, III |
| TN (mg/L) | 4.40 ± 3.87 | 4.14 ± 3.39 | 3.63 ± 3.22 | 2.92 ± 2.41 | 3.40 ± 2.64 |
| F- (mg/L) | 0.49 ± 0.12, I | 0.45 ± 0.11, I | 0.38 ± 0.12, I | 0.40 ± 0.11, I | 0.42 ± 0.14, I |
| Cu (μg/L) | 2.95 ± 1.61, I | 2.88 ± 0.22, I | 9.61 ± 9.02, I | 20.00 ± 0.00, II | 21.07 ± 8.69, II |
| Zn (μg/L) | 5.03 ± 11.14, I | 31.92 ± 84.51, I | 28.56 ± 71.04, I | 12.34 ± 12.90, I | 13.47 ± 15.78, I |
| Se (μg/L) | 0.31 ± 0.25, I | 0.35 ± 0.27, I | 0.28 ± 0.27, I | 0.23 ± 0.10, I | 0.21 ± 0.04, I |
| As (μg/L) | 0.70 ± 1.44, I | 2.24 ± 2.53, I | 1.64 ± 1.29, I | 1.28 ± 1.38, I | 1.20 ± 0.91, I |
| Hg (μg/L) | 0.03 ± 0.00, I | 0.03 ± 0.01, I | 0.02 ± 0.01, I | 0.02 ± 0.01, I | 0.02 ± 0.01, I |
| Models | Parameters Included | Weights Considered | PE | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
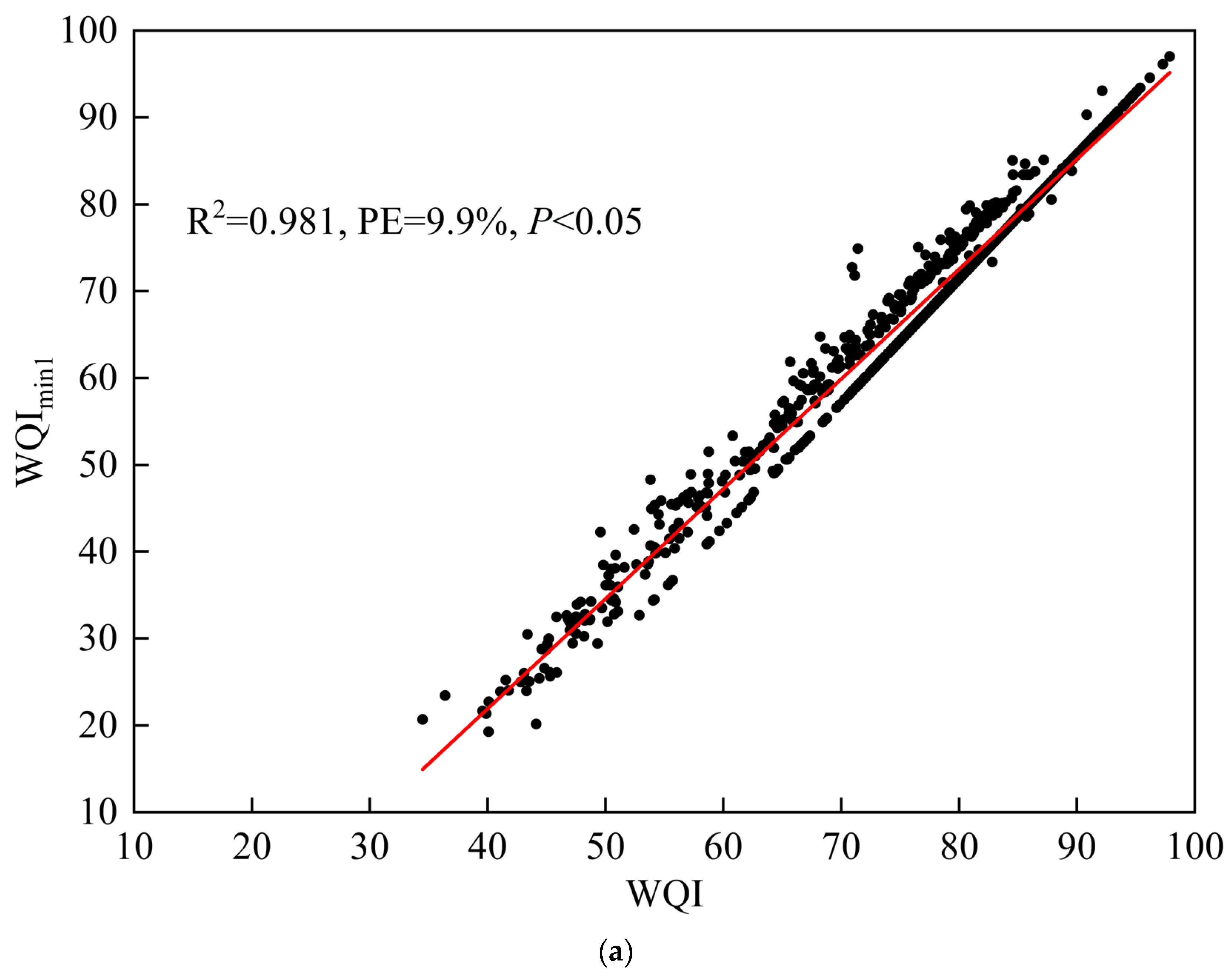
| WQImin1 | NH3-N, TP, TN, DO, CODMn | Yes | 0.981 | 9.9% | <0.05 |
| WQImin2 | NH3-N, TP, TN, DO, CODMn | No | 0.978 | 10.3% | <0.05 |
| WQImin3 | NH3-N, TP, TN, DO, CODMn, BOD5 | Yes | 0.998 | 8.4% | <0.05 |
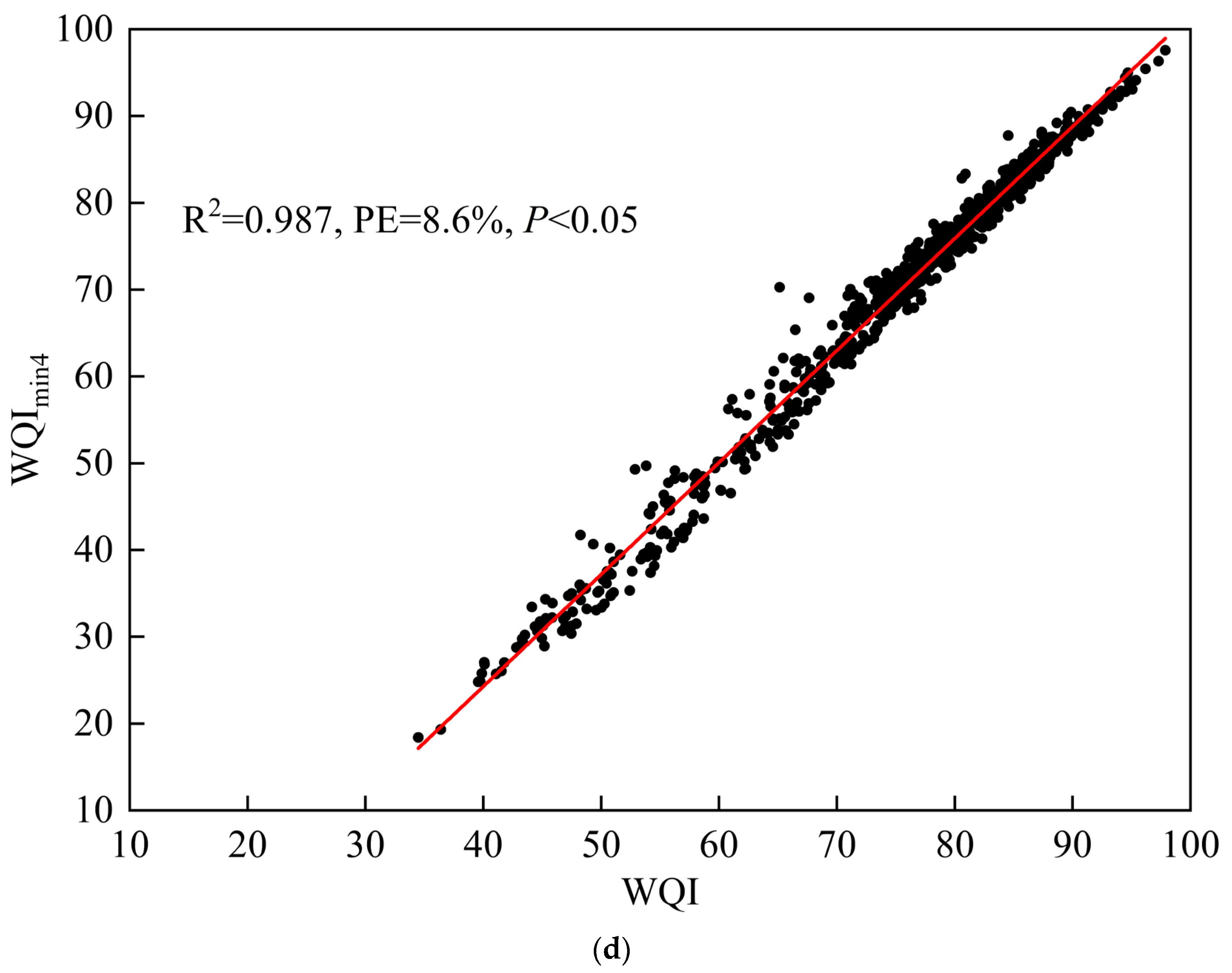
| WQImin4 | NH3-N, TP, TN, DO, CODMn, BOD5 | No | 0.987 | 8.6% | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Peng, W.; Yang, X.; Ma, B.; Lei, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z. A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality in the Lake and Rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China. Processes 2025, 13, 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103125
Huang A, Liu X, Dong F, Peng W, Yang X, Ma B, Lei Y, Wang W, Wang Z. A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality in the Lake and Rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103125
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Aiping, Xiaobo Liu, Fei Dong, Wenqi Peng, Xiaochen Yang, Bing Ma, Yang Lei, Weihao Wang, and Zhuowei Wang. 2025. "A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality in the Lake and Rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China" Processes 13, no. 10: 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103125
APA StyleHuang, A., Liu, X., Dong, F., Peng, W., Yang, X., Ma, B., Lei, Y., Wang, W., & Wang, Z. (2025). A Holistic Assessment of Water Quality in the Lake and Rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China. Processes, 13(10), 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103125





