Mitigation of Asphaltene Deposit Formation via Chemical Additives: A Review
Abstract
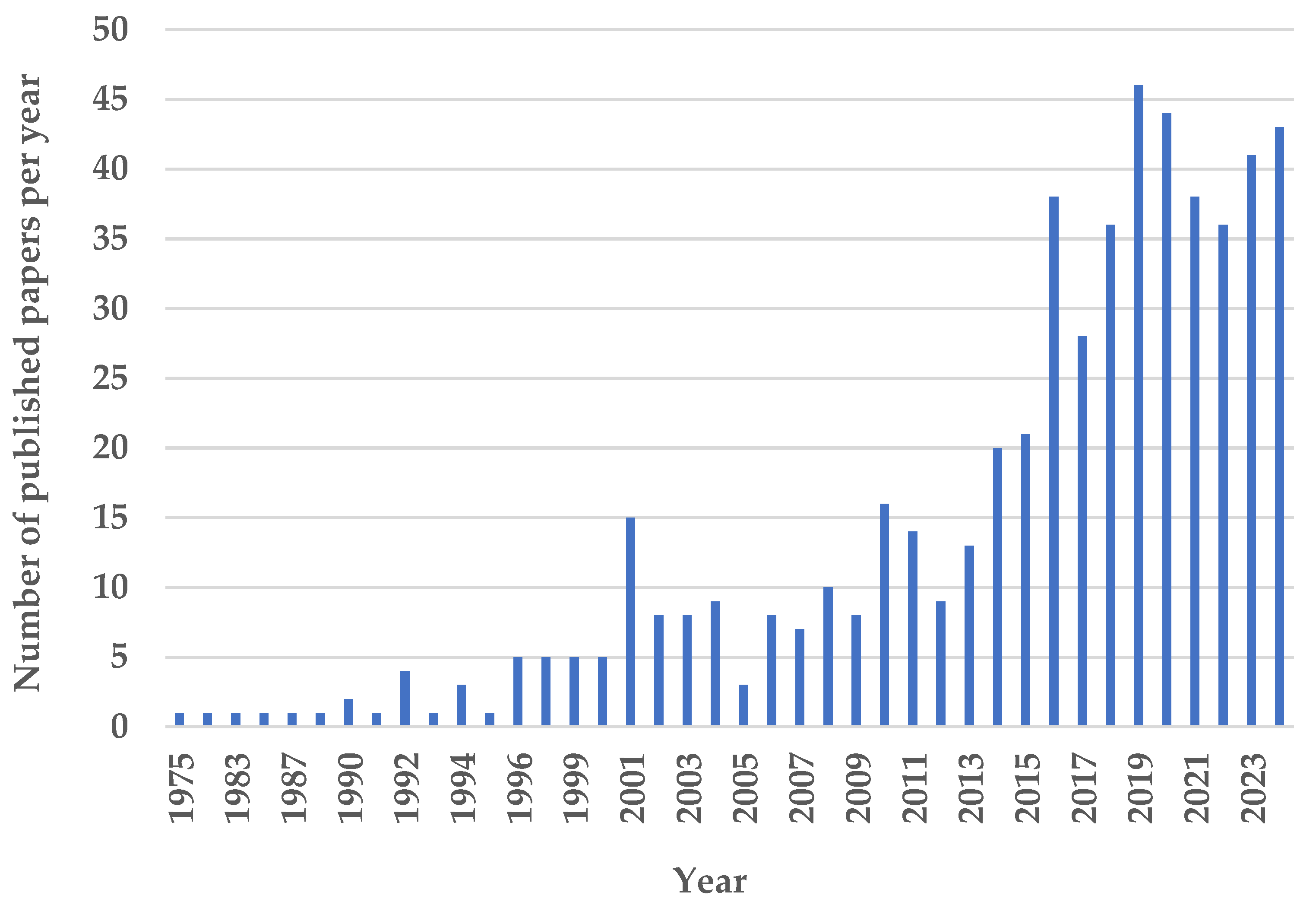
1. Introduction
2. Review on Asphaltene Characteristics, Aggregation and Deposit Formation
| No. | Asphaltene Type | %C | %H | %N | %S | %O | MW (Method) | Sa * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C7 Kuwait MG-130 asphaltenes | 89.69 | 6.23 | 0.6 | 3.48 | 1692 (VPO) | 0.444 | [100] | |
| 2 | C7 Kuwait MN-33 asphaltenes | 88.4 | 8.27 | 0.35 | 2.13 | 1940 (VPO) | 0.68 | [100] | |
| 3 | C7 Kuwait MG-144 asphaltenes | 90.38 | 6.33 | 0.49 | 2.8 | 1752 (VPO) | 0.45 | [100] | |
| 4 | C7 Kuwait MN-39 asphaltenes | 88.77 | 6.28 | 0.41 | 4.54 | 1215 (VPO) | 0.458 | [100] | |
| 5 | C5 Arab Light asphaltenes | 84.23 | 7.76 | 0.75 | 6.3 | 0.96 a | 0.668 | [101] | |
| 6 | C5 Arab Heavy asphaltenes | 83.17 | 8.28 | 0.84 | 7.18 | 0.53 a | 0.729 | [101] | |
| 7 | C5 Arab Medium asphaltenes | 83.65 | 8.31 | 0.65 | 6.41 | 0.98 a | 0.728 | [101] | |
| 8 | C5 Arab Berri asphaltenes | 85.05 | 7.24 | 0.27 | 6.3 | 1.12 a | 0.605 | [101] | |
| 9 | C7 Maya asphaltenes | 82.54 | 8.46 | 1.11 | 7.1 | 5190 (VPO) | 0.752 | [102] | |
| 10 | C7 Maya asphaltenes | 81.62 | 7.26 | 1.46 | 8.46 | 1.02 a | 5190 (VPO) | 0.64 | [103] |
| 11 | C7 Isthmus asphaltenes | 83.99 | 7.3 | 1.35 | 6.48 | 0.79 a | 3375 (VPO) | 0.622 | [103] |
| 12 | C7 Olmeca asphaltenes | 87.16 | 7.38 | 1.34 | 3.48 | 0.64 a | 2663 (VPO) | 0.601 | [103] |
| 13 | C5 Maya asphaltenes | 81.23 | 8.11 | 1.32 | 8.25 | 0.97 a | 3680 (VPO) | 0.732 | [103] |
| 14 | C5 Isthmus asphaltenes | 83.9 | 8 | 1.33 | 6.06 | 0.71 a | 2603 (VPO) | 0.695 | [103] |
| 15 | C5 Olmeca asphaltenes | 86.94 | 7.91 | 1.33 | 3.2 | 0.62 a | 1707 (VPO) | 0.658 | [103] |
| 16 | C6 A-dead oil asphaltenes | 88.5 | 10.3 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 1.01 | 0.853 | [65] | |
| 17 | C6 F-dead oil asphaltenes | 88.29 | 10.68 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.884 | [65] | |
| 18 | C7 PC asphaltenes | 84.56 | 6.78 | 0.93 | 5.79 | 1.43 a | 3100 (VPO) | 0.558 | [104] |
| 19 | C7 Iri asphaltenes | 81.92 | 7.15 | 1.15 | 4.66 | 5.12 a | 7400 (VPO) | 0.625 | [104] |
| 20 | C7 Karamay asphaltenes | 84.44 | 8.49 | 1.75 | 0.82 | 4.06 | 0.737 | [104] | |
| 21 | C7 Lungu asphaltenes | 83.99 | 7.31 | 1.41 | 4.38 | 2.74 | 0.623 | [104] | |
| 22 | C7 OL1-Furrial field | 84.4 | 6.75 | 1.31 | 3.5 | 4.04 a | 2100 (ND) | 0.556 | [105] |
| 23 | C7 OL2-Barua-Motatan field | 84.9 | 8.6 | 1.31 | 4.5 | 0.69 a | 3098 (ND) | 0.743 | [105] |
| 24 | C7 LO asphaltenes | 83.6 | 6.95 | 1.06 | 4.64 | 2.6 | 3346 (VPO) | 0.586 | [66] |
| 25 | C7 M1-O asphaltenes | 83.09 | 7.4 | 1.34 | 5.9 | 1.29 | 4550 (VPO) | 0.641 | [66] |
| 26 | C7 M2-O asphaltenes | 82.78 | 7.2 | 1.28 | 6.91 | 1.4 | 3380 (VPO) | 0.622 | [66] |
| 27 | C7 Maya-type asphaltenes | 85.07 | 7.21 | 818 (ND) | 0.602 | [106] | |||
| 28 | C7 Kuwait asphaltenes | 79.65 | 8.31 | 0.77 | 7.48 | 3.79 | 1520 (VPO) | 0.767 | [107] |
| 29 | C7 El Furrial asphaltenes | 85.5 | 6.9 | 1.73 | 3.4 | 2.50 a | 0.563 | [108] | |
| 30 | C5 Cold Lake asphaltenes | 79.9 | 7.5 | 1.3 | 7.6 | 2000 (GPC) | 0.683 | [109] | |
| 31 | C5 Mobil oil asphaltenes | 84 | 8 | 2.7 | 12170 (ND) | 0.694 | [110] | ||
| 32 | C5 Gulf of Mexico asphaltenes | 85.17 | 8.63 | 1.24 | 1.14 | 2.38 | 0.743 | [111] | |
| 33 | C5 West of Africa asphaltenes | 84.91 | 8.2 | 1.44 | 1.78 | 2.27 | 0.705 | [111] | |
| 34 | C5 North Sea asphaltenes | 82.56 | 8.48 | 0.72 | 1.71 | 2.86 | 0.754 | [111] | |
| 35 | C5 Brazilian asphaltenes | 85.67 | 8.15 | 1.89 | 1.36 | 1.86 | 0.693 | [111] | |
| 36 | C5 Gulf of Mexico asphaltenes | 79.5 | 7.9 | 0.8 | 3.95 | 6.68 | 0.728 | [111] | |
| 37 | C7 Iran asphaltenes | 74.56 | 6.74 | 0.85 | 6.86 | 10.99 | 1622 (ND) | 0.653 | [112] |
| 38 | C7 Iran asphaltenes | 74.47 | 6.1 | 1 | 3.14 | 15.29 a | 0.575 | [113] | |
| 39 | C7 Kuwaiti oil well Asphaltenes | 84.61 | 5.79 | 1.08 | 4.15 | 3.17 | 815 (MALDI/MS) | 0.432 | [72] |
| 40 | C7 Asphaltenes | 78.64 | 7.56 | 0.8 | 9.04 | 1.21 | 0.702 | [114] | |
| 41 | C7 Asphaltenes A1 | 75.2 | 8.14 | 0.78 | 15.78 | 0.796 | [115] | ||
| 42 | C7 Asphaltenes A2 | 57.64 | 5.99 | 0.93 | 10.91 | 1.83 | 0.763 | [115] | |
| 43 | C7 Asphaltenes A3 | 64.75 | 7.2 | 0.84 | 13.38 | 4.36 | 0.817 | [115] | |
| MIN | 57.64 | 5.79 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 815 | 0.432 | ||
| MAX | 90.38 | 10.68 | 2.7 | 15.78 | 15.29 | 12170 | 0.884 | ||
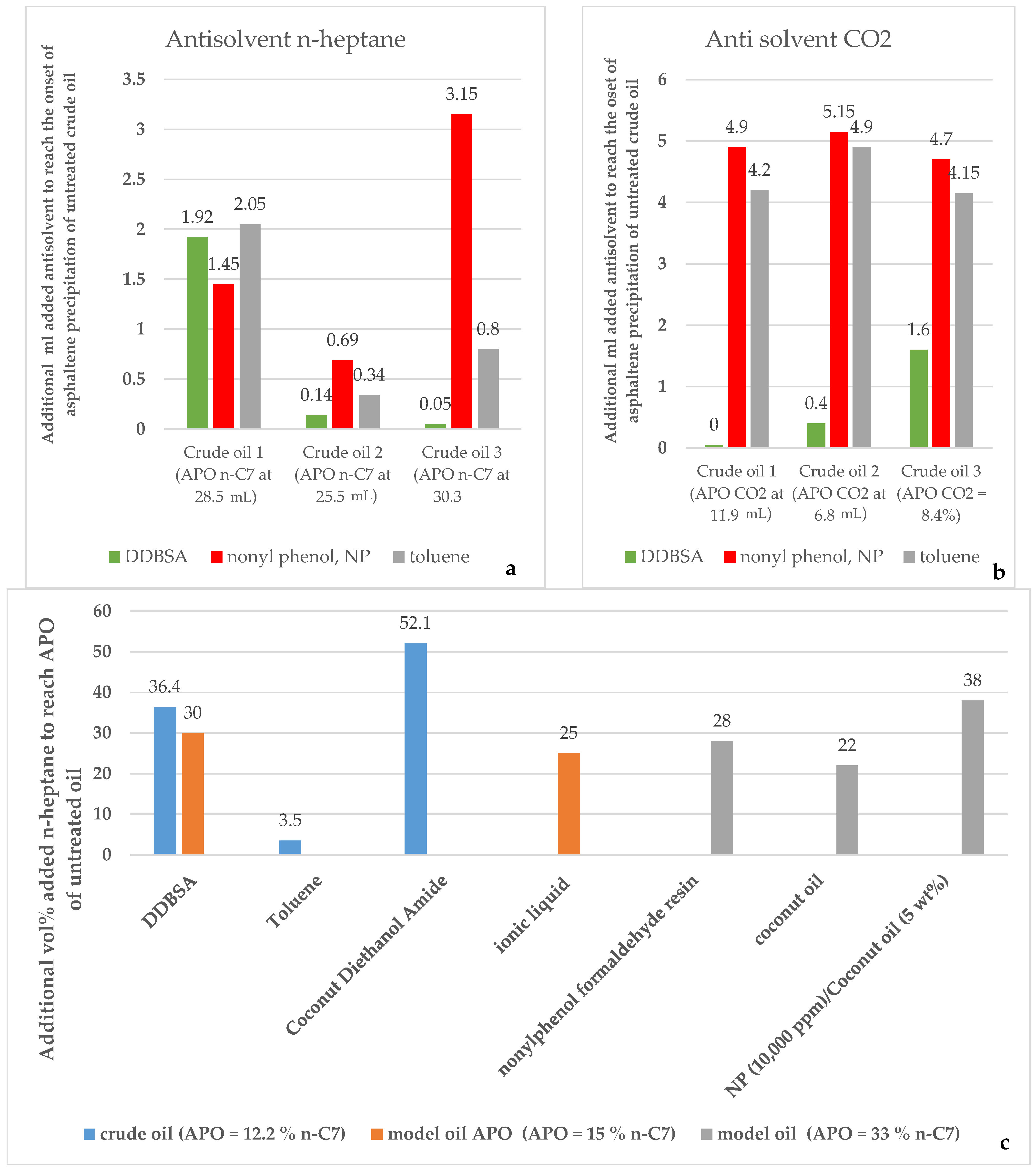
3. Review of the Chemical Additives Used to Prevent Asphaltene Deposit Formation
4. Conclusions
5. Knowledge Gaps and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammed, I.; Mahmoud, M.; Al Shehri, D.; El-Husseiny, A.; Alade, O. Asphaltene Precipitation and Deposition: A Critical Review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 197, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, M.Z.; Ahmadi, M.A.; Behbahani, R.M. Solving Asphaltene Precipitation Issue in Vertical Wells via Redesigning of Production Facilities. Petroleum 2015, 1, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Alvarez, A.A.; Garcia-Bermudes, M.; Tavakkoli, M.; Doherty, R.H.; Meng, S.; Abdallah, D.S.; Vargas, F.M. On the Evaluation of the Performance of Asphaltene Dispersants. Fuel 2016, 179, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, S.; Zendehboudi, S.; James, L. A Comprehensive Review of Asphaltene Deposition in Petroleum Reservoirs: Theory, Challenges, and Tips. Fuel 2019, 252, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.; Angelico, R.; Caputo, P.; Abe, A.A.; Teltayev, B.; Rossi, C.O. The Structure of Bitumen: Conceptual Models and Experimental Evidences. Materials 2022, 15, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.M.; Creek, J.L.; Chapman, W.G. On the Development of an Asphaltene Deposition Simulator. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2294–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, D.; Ratulowski, J.; Akbarzadeh, K.; Andersen, S. Modeling of Asphaltene Deposition in a Production Tubing. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 2936–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.J. Asphaltene Adsorption, a Literature Review. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2831–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.S. Asphaltene Deposition. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4086–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, D.; Mohammadzadeh, O.; Akbarzadeh, K.; Taylor, S.D.; Ratulowski, J. Reservoir Impairment by Asphaltenes: A Critical Review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 1202–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammadi, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Yen, A.; Wang, J.; Creek, J.L.; Vargas, F.M.; Chapman, W.G. Effect of the Gas Composition and Gas/Oil Ratio on Asphaltene Deposition. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 3610–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ren, T. Influence of Injection Pressure and Injection Volume of CO2 on Asphaltene Deposition. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.M.; Tavakkoli, M. Asphaltene Deposition: Fundamentals, Prediction, Prevention, and Remediation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Campen, S.M.; Moorhouse, S.J.; Wong, J.S.S. Effect of Aging on the Removal of Asphaltene Deposits with Aromatic Solvent. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11995–12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, A. Essentials of Flow Assurance Solids in Oil and Gas Operations Understanding Fundamentals, Characterization, Prediction, Environmental Safety, and Management; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wiehe, I.A. Asphaltene Solubility and Fluid Compatibility. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4004–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Lezcano, M.; Yee, N.; Witt, M. Effect of Aging on Deposit Characteristics Obtained by Crude Oil Blending. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Miao, T.; Vien, J.; Roye, M. Comparing Asphaltenes: Deposit versus Crude Oil. Fuel 2015, 147, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Ovalles, C.; Vien, J.; Moir, M. Asphaltene Characterization of Paraffinic Crude Oils. Fuel 2016, 178, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Syliangco, C.; Hudson, J. Wax Adsorption on Carbonaceous Materials Including Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 5276–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehe, I.A.; Kennedy, R.J.; Dickakian, G. Fouling of Nearly Incompatible Oils. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 1057–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, F.G.A.; Kapusta, S.D.; Ooms, A.C.; Smith, A.J. Fouling and Compatibility of Crudes as Basis for a New Crude Selection Strategy. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Watkinson, P. A Study of Asphaltene Solubility and Precipitation. Fuel 2004, 83, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, Z.S.; Sheikholeslami, R.; Watkinson, A.P. Blending Effects on Fouling of Four Crude Oils. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Heat Exchanger Fouling and Cleaning—Challenges and Opportunities, Kloster Irsee, Germany, 5–10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, E.; Watkinson, A.P. Precipitation and Fouling in Heavy Oil-Diluent Blends. Heat Transf. Eng. 2009, 30, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.P. Deposition from Crude Oils in Heat Exchangers. Heat Transf. Eng. 2007, 28, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hosani, A.; Ravichandran, S.; Daraboina, N. Review of Asphaltene Deposition Modeling in Oil and Gas Production. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 965–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Moir, M. Effect of Precipitation Time and Solvent Power on Asphaltene Characteristics. Fuel 2017, 208, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambinek, K.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Compatibility of Crude Oil Blends─Processing Issues Related to Asphaltene Precipitation, Methods of Instability Prediction—A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.A.; Rueda-Chacón, H.; Agudelo, J.L.; Molina, V.D. Prediction of the Stability and Compatibility of Colombian Heavy Crude Oils by 1D Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxometry and Chemometric Methods. Fuel 2021, 298, 120721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamartale, A.; Zendehboudi, S. Asphaltene and Asphaltene Precipitation/Deposition. In Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kor, P.; Kharrat, R.; Ayoubi, A. Comparison and Evaluation of Several Models in Prediction of Asphaltene Deposition Profile along an Oil Well: A Case Study. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2017, 7, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abutaqiya, M.I.L.; Sisco, C.; Kuang, J.; Lin, P.; Wang, F.; Tavakkoli, M.; Vargas, F.M. Case Studies and Field Applications. In Asphaltene Deposition: Fundamentals, Prediction, Prevention, and Remediation; Tavakkoli, M., Vargas, F.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; Volume 91, pp. 284–323. [Google Scholar]
- Stratiev, D.S.; Shishkova, I.K.; Nikolaychuk, E.; Anastasov, M.; Stanulov, K.; Toteva, V. Effect of Catalyst Condition on Sedimentation and Conversion in the Ebullated Bed Vacuum Residue H-Oil Hydrocracking. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.W.; Kuramae, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yoon, S.H.; Mochida, I. Plugging Problems Observed in Severe Hydrocracking of Vacuum Residue. Fuel 2009, 88, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega García, F.; Mar-Juárez, E.; Schacht Hernández, P. Controlling Sediments in the Ebullated Bed Hydrocracking Process. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2948–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislaus, A.; Hauser, A.; Marafi, M. Investigation of the Mechanism of Sediment Formation in Residual Oil Hydrocracking Process through Characterization of Sediment Deposits. Catal. Today 2005, 109, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Zhao, X.; Sakanishi, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Takashima, H.; Uemura, S. Structure and Properties of Sludges Produced in the Catalytic Hydrocracking of Vacuum Residue. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Ovalles, C.; Pradhan, A.; Leung, P.; Chen, N. Sediment Formation in Residue Hydroconversion Processes and Its Correlation to Asphaltene Behavior. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6587–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Dinkov, R.; Shishkova, I.; Sharafutdinov, I.; Ivanova, N.; Mitkova, M.; Yordanov, D.; Rudnev, N.; Stanulov, K.; Artemiev, A.; et al. What Is behind the High Values of Hot Filtration Test of the Ebullated Bed Residue H-Oil Hydrocracker Residual Oils? Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7037–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, E.; Merdrignac, I.; Rebours, B.; Harlé, V.; Kressmann, S.; Colyar, J. Contribution of Analytical Tools for the Understanding of Sediment Formation: Application to H-Oil® Process. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Patil, A.; Panjwani, B.; Simonsen, G. Review on Application of Nanotechnology for Asphaltene Adsorption, Crude Oil Demulsification, and Produced Water Treatment. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 19191–19210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.P.; Costa, G.M.N.; Vieira de Melo, S.A.B. A Comparative Study of CPA and PC-SAFT Equations of State to Calculate the Asphaltene Onset Pressure and Phase Envelope. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 494, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Lalji, S.M.; Haneef, J.; Ahsan, U.; Tariq, S.M.; Tirmizi, S.T.; Shamim, R. Critical Analysis of Different Techniques Used to Screen Asphaltene Stability in Crude Oils. Fuel 2021, 299, 120874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, F.G.A. History and Review of Dual Solvent Titration Methods. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 8639–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanbekov, R.R.; Schipachev, A.M. Manifestation of Incompatibility of Marine Residual Fuels: A Method for Determining Compatibility, Studying Composition of Fuels and Sediment. J. Min. Inst. 2022, 257, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanbekov, R.; Islamov, S.; Mardashov, D.; Beloglazov, I.; Hemmingsen, T. Research of the Influence of Marine Residual Fuel Composition on Sedimentation Due to Incompatibility. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, R.; Ancheyta, J.; Trejo, F.; Rodríguez, S. Methods for Determining Asphaltene Stability in Crude Oils. Fuel 2017, 188, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, E.A.; Lira-Galeana, C.; Ancheyta, J. Analysis of Asphaltene Precipitation Models from Solubility and Thermodynamic-Colloidal Theories. Processes 2023, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Chaudhuri, P.; Kumar, B.; Panja, S.S. Review on Aggregation of Asphaltene Vis-a-Vis Spectroscopic Studies. Fuel 2016, 185, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S. Challenges in Asphaltenes Inhibitor Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Oil & Gas Chemistry & Additives Conference, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, 24–26 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Juyal, P.; Ho, V.; Yen, A.; Allenson, S.J. Reversibility of Asphaltene Flocculation with Chemicals. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.; Naderi, K.; Firoozabadi, A. Asphaltene Deposition and Removal in Flowlines and Mitigation by Effective Functional Molecules. SPE J. 2020, 25, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.M.; Quintiliano, L.A.; Firoozabadi, A. Polymeric Dispersants Delay Sedimentation in Colloidal Asphaltene Suspensions. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8021–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.M.; Vafaie-Sefti, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Assaf, M.A.; Veisi, S. Effect of Dispersants on the Kinetics of Asphaltene Settling Using Turbidity Measurement Method. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhreez, M.; Wen, D.; Ali, L. A Novel Inhibitor for Controlling Iraqi Asphaltene Problems. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Environmental Impacts of the Oil and Gas Industries: Kurdistan Region of Iraq as a Case Study (EIOGI), Koya-Erbil, Iraq, 17–19 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Firoozinia, H.; Fouladi Hossein Abad, K.; Varamesh, A. A Comprehensive Experimental Evaluation of Asphaltene Dispersants for Injection under Reservoir Conditions. Pet. Sci. 2016, 13, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiwattanawong, K.; Fogler, H.S.; Gharfeh, S.G.; Singh, P.; Thomason, W.H.; Chavadej, S. Effect of Asphaltene Dispersants on Aggregate Size Distribution and Growth. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Cervantes, V.Y.; Hernández-Altamirano, R.; Buenrostro-González, E.; Beltrán, H.I.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S. Development of Oxazolidines Derived from Polyisobutylene Succinimides as Multifunctional Stabilizers of Asphaltenes in Oil Industry. Fuel 2013, 110, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Cervantes, V.Y.; Hernández-Altamirano, R.; Buenrostro-González, E.; Beltrán, H.I.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S. Tin and Silicon Phthalocyanines Molecularly Engineered as Traceable Stabilizers of Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamartale, A.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. Alternation of Asphaltene Binding Arrangement in the Presence of Chemical Inhibitors: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Strategy. Fuel 2023, 336, 127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomkar, A.; Reza Nasriani, H. The Role of Direct Asphaltene Inhibitors on Asphaltene Stabilization during Gas Injection. Fuel 2020, 282, 118827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehe, I.A.; Jermansen, T.G. Design of Synthetic Dispersants for Asphaltenes. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, M.A. Production Chemicals for the Oil and Gas Industry, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Horeh, N.B.; Hosseinpour, N.; Bahramian, A. Asphaltene Inhibitor Performance as a Function of the Asphaltene Molecular/Aggregate Characteristics: Evaluation by Interfacial Rheology Measurement and Bulk Methods. Fuel 2023, 339, 127420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.H.; Idem, R.O. Interrelationships between Asphaltene Precipitation Inhibitor Effectiveness, Asphaltenes Characteristics, and Precipitation Behavior during n-Heptane (Light Paraffin Hydrocarbon)-Induced Asphaltene Precipitation. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Malayeri, M.R.; Busse, O.; Weigand, J.J. Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation Using Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents and Ionic Liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayat, S.; Tavakkoli, M.; Yen, A.; Misra, S.; Vargas, F.M. Review of the Current Laboratory Methods to Select Asphaltene Inhibitors. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15488–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Moghadam, S.M.A.; Zahedi-Nejad, A.; Bahrami, M.; Torkaman, M.; Ghayyem, M.A. Experimental and Modeling Investigations of Temperature Effect on Chemical Inhibitors of Asphaltene Aggregation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Brunner, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Atkin, R. Dissolution and Suspension of Asphaltenes with Ionic Liquids. Fuel 2019, 238, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, S.; Niu, M.; Cheng, R.; Gong, Y.; Xu, J. Asphaltene Inhibition and Flow Improvement of Crude Oil with a High Content of Asphaltene and Wax by Polymers Bearing Ultra-long Side Chain. Energies 2021, 14, 8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashidi, H.; Afra, S.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Application of Natural Fatty Acids as Asphaltenes Solvents with Inhibition and Dispersion Effects: A Mechanistic Study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 172, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamartale, A.; Afzali, S.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. Experimental Investigation of Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors. In Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical Prospects; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 101–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamartale, A.; Afzali, S.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. Modeling and Simulation Investigations of Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors. In Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors Theoretical and Practical Prospects; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 181–218. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Rowland, S.M.; Rodgers, R.P. Advances in Asphaltene Petroleomics. Part 1: Asphaltenes Are Composed of Abundant Island and Archipelago Structural Motifs. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13509–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F. Molecular Composition and Structure of Metal Compounds in Asphaltene. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Pau et des Pays de l’Adour, Pau, France, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; de Klerk, A.; Prado, G.H.C. Visbreaking of Vacuum Residue Deasphalted Oil: New Asphaltenes Formation. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5135–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, L.M.Y.; de Klerk, A. Is Solubility Classification a Meaningful Measure in Thermal Conversion? Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 8649–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, O.C.; Sabbah, H.; Eyssautier, J.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Barré, L.; Andrews, A.B.; Ruiz-Morales, Y.; Mostowfi, F.; McFarlane, R.; Goual, L.; et al. Advances in Asphaltene Science and the Yen–Mullins Model. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3986–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strausz, O.P.; Safarik, I.; Lown, E.M.; Morales-Izquierdo, A. A Critique of Asphaltene Fluorescence Decay and Depolarization-Based Claims about Molecular Weight and Molecular Architecture. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Qian, K.; Olmstead, W.N.; Freund, H.; Yung, C.; Gray, M.R. Quantitative Evidence for Bridged Structures in Asphaltenes by Thin Film Pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3581–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, A.H.; Scherer, A.; Tan, X.; Azyat, K.; Stryker, J.M.; Tykwinski, R.R.; Gray, M.R. Formation of Archipelago Structures during Thermal Cracking Implicates a Chemical Mechanism for the Formation of Petroleum Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, D.C.; Corilo, Y.E.; Nyadong, L.; Lobodin, V.V.; Bythell, B.J.; Robbins, W.K.; McKenna, A.M.; Marshall, A.G.; Rodgers, R.P. Heavy Petroleum Composition. 5. Compositional and Structural Continuum of Petroleum Revealed. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgich, J. Molecular Simulation and the Aggregation of the Heavy Fractions in Crude Oils. Mol. Simul. 2003, 29, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strausz, O.P.; Mojelsky, T.W.; Lown, E.M. The Molecular Structure of Asphaltene: An Unfolding Story. Fuel 1992, 71, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Gray, M.R.; Rüger, C.; Smith, D.F.; Glattke, T.J.; Niles, S.F.; Neumann, A.; Weisbrod, C.R.; Yen, A.; McKenna, A.M.; et al. Lessons Learned from a Decade-Long Assessment of Asphaltenes by Ultrahigh-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Implications for Complex Mixture Analysis. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 16335–16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Rowland, S.M.; Rodgers, R.P. Advances in Asphaltene Petroleomics. Part 2: Selective Separation Method That Reveals Fractions Enriched in Island and Archipelago Structural Motifs by Mass Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-PatinÌo, M.L.; Rowland, S.M.; Rodgers, R.P. Advances in Asphaltene Petroleomics. Part 3. Dominance of Island or Archipelago Structural Motif Is Sample Dependent. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9106–9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, O.C.; Sheu, E.Y.; Hammami, A.; Marshall, A.G. Asphaltenes, Heavy Oils, and Petroleomics, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, O.C.; Martínez-Haya, B.; Marshall, A.G. Contrasting Perspective on Asphaltene Molecular Weight. This Comment vs the Overview of AA Herod, KD Bartle, and R. Kandiyoti. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenzin, H.; Mullins, O.C. Molecular Size and Structure of Asphaltenes from Various Sources. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badre, S.; Carla Goncalves, C.; Norinaga, K.; Gustavson, G.; Mullins, O.C. Molecular Size and Weight of Asphaltene and Asphaltene Solubility Fractions from Coals, Crude Oils and Bitumen. Fuel 2006, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, O.C. Rebuttal to Comment by Professors Herod, Kandiyoti, and Bartle on “Molecular Size and Weight of Asphaltene and Asphaltene Solubility Fractions from Coals, Crude Oils and Bitumen”. Fuel 2007, 86, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Petro, D.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Nelson, R.K.; Latifzai, A.S.; Nouvelle, X.; Zuo, J.Y.; Reddy, C.M.; Mullins, O.C. New Thermodynamic Modeling of Reservoir Crude Oil. Fuel 2014, 117, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Andrews, A.B.; Gross, L.; Pauchard, V.; Banerjee, S.; Mullins, O.C. Overview of Asphaltene Nanostructures and Thermodynamic Applications. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15082–15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehe, I.A. A Solvent-Resid Phase Diagram For Tracking Resid Conversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.R.; Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Rodgers, R.P. Structure–Reactivity Relationships for Petroleum Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 4370–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, O.C. The Modified Yen Model. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2179–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Meyer, J.; Campbell, T.; Canas, J.; Betancourt, S.S.; Dumont, H.; Forsythe, J.C.; Mehay, S.; Kimball, S.; Hall, D.L.; et al. Applicability of Simple Asphaltene Thermodynamics for Asphaltene Gradients in Oilfield Reservoirs: The Flory-Huggins-Zuo Equation of State with the Yen-Mullins Model. Fuel 2018, 221, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghloum, E.F.; Al-Qahtani, M.; Al-Rashid, A. Effect of Inhibitors on Asphaltene Precipitation for Marrat Kuwaiti Reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 70, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirokoff, J.W.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Ali, M.F. Characterization of the Structure of Saudi Crude Asphaltenes by X-Ray Diffraction. Energy Fuels 1997, 11, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, F.; Ancheyta, J.; Centeno, G.; Marroquín, G. Effect of Hydrotreating Conditions on Maya Asphaltenes Composition and Structural Parameters. Catal. Today 2005, 109, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancheyta, J.; Centeno, G.; Trejo, F.; Marroquín, G.; García, J.A.; Tenorio, E.; Torres, A. Extraction and Characterization of Asphaltenes from Different Crude Oils and Solvents. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Que, G.; Li, Z. The Properties of Asphaltenes and Their Interaction with Amphiphiles. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Contreras, E.; Rogel, E. Amphiphile Adsorption on Asphaltene Particles: Adsorption Isotherms and Asphaltene Stabilization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 189, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Miyauchi, T.E.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S.; Barba-López, V.; Buenrostro-Gonzalez, E.; Martínez-Magadán, J.M. N-Aryl Amino-Alcohols as Stabilizers of Asphaltenes. Fuel 2013, 110, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahhaf, T.A.; Fahim, M.A.; Elkilani, A.S. Retardation of Asphaltene Precipitation by Addition of Toluene, Resins, Deasphalted Oil and Surfactants. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2002, 194–197, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.C.; Delgado-Linares, J.; Briones, A.; Guevara, M.; Scorzza, C.; Salager, J.L. The Effect of Solvent Nature and Dispersant Performance on Asphaltene Precipitation from Diluted Solutions of Instable Crude Oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, K.M.; Cyr, N.; Fedorak, P.M.; Westlake, D.W.S. Characterization of Asphaltenes from Cold Lake Heavy Oil: Variations in Chemical Structure and Composition with Molecular Size. Can. J. Chem. 1990, 68, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; Fogler, H.S. Peptization and Coagulation of Asphaltenes in Apolar Media Using Oil-Soluble Polymers. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 1996, 14, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudášová, D.; Simon, S.; Hemmingsen, P.V.; Sjöblom, J. Study of Asphaltenes Adsorption onto Different Minerals and Clays. Part 1. Experimental Adsorption with UV Depletion Detection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, V.; Abolghasemi, E.; Hosseini, A.; Ayatollahi, S.; Dehghani, F. Electrokinetic Properties of Asphaltene Colloidal Particles: Determining the Electric Charge Using Micro Electrophoresis Technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 541, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadbaygi, A.; Bayati, B.; Mansouri, M.; Rezaei, H.; Riazi, M. Chemical Study of Asphaltene Inhibitors Effects on Asphaltene Precipitation of an Iranian Oil Field. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. d’IFP Energ. Nouv. 2020, 75, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhreez, M.; Wen, D. Controlled Releases of Asphaltene Inhibitors by Nanoemulsions. Fuel 2018, 234, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazikeh, S.; Sayyad Amin, J.; Zendehboudi, S.; Shafiei, A. Effects of Asphaltene Structure and Polythiophene-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles on Surface Topography and Wettability Alteration of Silica Surface. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Shishkova, I.; Tsaneva, T.; Mitkova, M.; Yordanov, D. Investigation of relations between properties of vacuum residual oils from different origin, and of their deasphalted and asphaltene fractions. Fuel 2016, 170, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Nenov, S.; Shishkova, I.; Georgiev, B.; Argirov, G.; Dinkov, R.; Yordanov, D.; Atanassova, V.; Vassilev, P.; Atanassov, K. Commercial Investigation of the Ebullated-Bed Vacuum Residue Hydrocracking in the Conversion Range of 55–93%. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 33290–33304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Shishkova, I.; Nedelchev, A.; Kirilov, K.; Nikolaychuk, E.; Ivanov, A.; Sharafutdinov, I.; Veli, A.; Mitkova, M.; Tsaneva, T.; et al. Investigation of Relationships between Petroleum Properties and Their Impact on Crude Oil Compatibility. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 7836–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarranton, H.W.; Ortiz, D.P.; Barrera, D.M.; Baydak, E.N.; Barré, L.; Frot, D.; Eyssautier, J.; Zeng, H.; Xu, Z.; Dechaine, G.; et al. On the Size Distribution of Self-Associated Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 5083–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.R.; Yarranton, H.W. Quantitative Modeling of Formation of Asphaltene Nanoaggregates. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 8566–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, I.N.; Fesan, A.A. Multi-Step Formation of Asphaltene Colloids in Dilute Solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 492, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, I.N.; Fesan, A.A.; Losev, A.P. New Answers to the Optical Interrogation of Asphaltenes: Complex States of Primary Aggregates from Steady-State Fluorescence Studies. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8226–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, G.; Vargas, V.; Feo, L.; Castellano, O.; Castillo, J.; Giusti, P.; Acavedo, S.; Lienemann, C.P.; Bouyssiere, B. Size Distributions of Sulfur, Vanadium, and Nickel Compounds in Crude Oils, Residues, and Their Saturate, Aromatic, Resin, and Asphaltene Fractions Determined by Gel Permeation Chromatography Inductively Coupled Plasma High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7783–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shaw, J.M. Composition and Size Distribution of Coherent Nanostructures in Athabasca Bitumen and Maya Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyssautier, J.; Hénaut, I.; Levitz, P.; Espinat, D.; Barré, L. Organization of Asphaltenes in a Vacuum Residue: A Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)-Viscosity Approach at High Temperatures. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2696–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulier, F.; Barbier, J.; Guichard, B.; Levitz, P.; Espinat, D. Asphaltenes Transport into Catalysts under Hydroprocessing Conditions. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 6250–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.R.; Yarranton, H.W.; Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Rodgers, R.P.; Bouyssiere, B.; Giusti, P. Distributed Properties of Asphaltene Nanoaggregates in Crude Oils: A Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 18078–18103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.R.; Tykwinski, R.R.; Stryker, J.M.; Tan, X. Supramolecular Assembly Model for Aggregation of Petroleum Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3125–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgich, J. Intermolecular Forces in Aggregates of Asphaltenes and Resins. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.; Lechner, M.P.; Stryker, J.M.; Tykwinski, R.R. Aggregation of Asphaltene Model Compounds Using a Porphyrin Tethered to a Carboxylic Acid. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 6984–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Siskin, M.; Gray, M.R.; Walters, C.C.; Rodgers, R.P. Mechanisms of Asphaltene Aggregation: Puzzles and a New Hypothesis. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 9094–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.; Scherer, A.; Hampel, F.; Stryker, J.M.; Tykwinski, R.R. Synthesis and Aggregation Behavior of Chiral Naphthoquinoline Petroporphyrin Asphaltene Model Compounds. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Fenniri, H.; Gray, M.R. Pyrene Derivatives of 2,2′-Bipyridine as Models for Asphaltenes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Supramolecular Organization. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Fenniri, H.; Gray, M.R. Water Enhances the Aggregation of Model Asphaltenes in Solution via Hydrogen Bonding. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fechtenkötter, A.; Gauss, J.; Watson, M.D.; Kastler, M.; Fechtenkötter, C.; Wagner, M.; Müllen, K. Controlled Self-Assembly of Hexa-Peri-Hexabenzocoronenes in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11311–11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisula, W.; Tomović, Ž.; Simpson, C.; Kastler, M.; Pakula, T.; Müllen, K. Relationship between Core Size, Side Chain Length, and the Supramolecular Organization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4296–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.X.; Tan, X.; Müllen, K.; Stryker, J.M.; Gray, M.R. Associative π − π Interactions of Condensed Aromatic Compounds with Vanadyl or Nickel Porphyrin Complexes Are Not Observed in the Organic Phase. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, C.; Scott, D.E.; Tykwinski, R.R.; Gray, M.R.; Stryker, J.M. Scalable, Chromatography-Free Synthesis of Alkyl-Tethered Pyrene-Based Materials. Application to First-Generation “Archipelago Model” Asphaltene Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Patiño, M.L.; Smith, D.F.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Marshall, A.G.; Rodgers, R.P. Advances in Asphaltene Petroleomics. Part 4. Compositional Trends of Solubility Subfractions Reveal That Polyfunctional Oxygen-Containing Compounds Drive Asphaltene Chemistry. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 3013–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, F.G.A.; Heijnis, R.M.A.; Stamps, P.A.; Kramer, P.A. A Geochemical Framework for Understanding Residue Properties. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.M.; Tavakkoli, M.; Boggara, M.; Garcia-Bermudes, M.; Evangelista, R.; Melendez, A.; Wang, F.; Sisco, C.; Mathew, N.T.; Prasad, S.; et al. Advances in Understanding Asphaltene Precipitation and Deposition. In Proceedings of the Petro Phase 2014 the 15th International Conference on Petroleum Phase Behavior and Fouling, Galveston, TX, USA, 8–12 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Duran, J.A.; Schoeggl, F.F.; Yarranton, H.W. Kinetics of Asphaltene Precipitation/Aggregation from Diluted Crude Oil. Fuel 2019, 255, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chaisoontornyotin, W.; Hoepfner, M.P. Structure of Asphaltenes during Precipitation Investigated by Ultra-Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10371–10380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarranton, H.W.; Alboudwarej, H.; Jakher, R. Investigation of Asphaltene Association with Vapor Pressure Osmometry and Interfacial Tension Measurements. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Li, R.; Yang, Z.; Yin, C.X.; Gray, M.R.; Bohne, C. Evaluating Steady-State and Time-Resolved Fluorescence as a Tool to Study the Behavior of Asphaltene in Toluene. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.; Perron, S.P. Size Characterization of Petroleum Asphaltenes and Maltenes. In Chemistry of Asphaltenes; Bunger, J.W., Li, N.C., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; Volume 195, pp. 137–153. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, D.P.; Sadeghi, H.; Yarranton, H.W.; Van Den Berg, F.G.A. Regular Solution Based Approach to Modeling Asphaltene Precipitation from Native and Reacted Oils: Part 1, Molecular Weight, Density, and Solubility Parameter Distributions of Asphaltenes. Fuel 2016, 178, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, A.T.; Sisco, C.J.; Tavakkoli, M.; Vargas, F.M. An Investigation of the Effect of Asphaltene Polydispersity on Asphaltene Precipitation and Deposition Tendencies. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 8799–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, G.; Ancheyta, J. Regular Solution Model to Predict the Asphaltenes Flocculation and Sediments Formation during Hydrocracking of Heavy Oil. Fuel 2020, 260, 116160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.; Baydak, E.N.; Schoeggl, F.F.; Taylor, S.D.; Hay, G.; Yarranton, H.W. Regular Solution Based Approach to Modeling Asphaltene Precipitation from Native and Reacted Oils: Part 3, Visbroken Oils. Fuel 2019, 257, 116079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, M.; Panuganti, S.R.; Taghikhani, V.; Pishvaie, M.R.; Chapman, W.G. Understanding the Polydisperse Behavior of Asphaltenes during Precipitation. Fuel 2014, 117, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J.; De Klerk, A.; Gary, J.H.; Handwerk, G.E. Petroleum Refining: Technology, Economics, and Markets, 6th ed; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Shi, Q.; Vallverdu, G.; Giusti, P.; Bouyssiere, B. Fractionation and Characterization of Petroleum Asphaltene: Focus on Metalopetroleomics. Processes 2020, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Shishkova, I.; Palichev, G.N.; Atanassov, K.; Ribagin, S.; Nenov, S.; Nedanovski, D.; Ivanov, V. Study of Bulk Properties Relation to SARA Composition Data of Various Vacuum Residues Employing Intercriteria Analysis. Energies 2022, 15, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.I.; Speight, J.G. Petroleum resins, separation, character, and role in petroleum science and technology. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utin, M.C.; Ofodile, S.E.; Ogali, R.E.; Achugasim, O. Resins In The Heavy Organics Precipitate From Crude Oil With Single N-Alkane And Binary Mixture N-Alkane Solvents. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 6, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshani-Molayousefi, M.; McCullagh, M. Deterring Effect of Resins on the Aggregation of Asphaltenes in N-heptane. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 16081–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboor, A.; Yousaf, N.; Haneef, J.; Ali, S.I.; Lalji, S.M. Performance of Asphaltene Stability Predicting Models in Field Environment and Development of New Stability Predicting Model (ANJIS). J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafi, M.; Al-Barood, A.; Stanislaus, A. Effect of Diluents in Controlling Sediment Formation During Catalytic Hydrocracking of Kuwait Vacuum Residue. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, A.; Ancheyta, J. Batch Reactor Study of the Effect of Aromatic Diluents to Reduce Sediment Formation during Hydrotreating of Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiev, D.; Dinkov, R.; Shishkova, I.; Yordanov, D. Can We Manage the Process of Asphaltene Precipitation during the Production of IMO 2020 Fuel Oil? Erdoel Erdgas Kohle 2020, 12, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Rogel, E.; Morazan, H.; Moir, M.E. Synthesis, Characterization, and Mechanism of Asphaltene Inhibition of Phosphopropoxylated Asphaltenes. Fuel 2016, 180, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oschmann, H.-J. New Methods for the Selection of Asphaltene Inhibitors in the Field. In Chemistry in the Oil Industry VII: Performance in a Challenging Environment; Balson, T., Craddock, H.A., Dunlop, J., Frampton, H., Payne, G., Reid, P., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2002; pp. 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamartale, A.; Afzali, S.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. Fundamentals of Chemical Inhibitors of Asphaltenes. In Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical Prospects; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 47–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.L.; Fogler, H.S. Stabilization of Asphaltenes in Aliphatic Solvents Using Alkylbenzene-Derived Amphiphiles. 1. Effect of the Chemical Structure of Amphiphiles on Asphaltene Stabilization. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, E.; Vafaie-Sefti, M.; Shadman, M.M.; Naderi, H.; Amiri, M.; Noorbakhsh, A. Experimental Investigation of Dodecylbenzene Sulfonic Acid and Toluene Dispersants on Asphaltene Precipitation of Dead and Live Oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karambeigi, M.A.; Nikazar, M.; Kharrat, R. Experimental Evaluation of Asphaltene Inhibitors Selection for Standard and Reservoir Conditions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 137, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östlund, J.A.; Nydén, M.; Fogler, H.S.; Holmberg, K. Functional Groups in Fractionated Asphaltenes and the Adsorption of Amphiphilic Molecules. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 234, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Rogel, E.; Morazan, H.; Chen, K.; Moir, M.E. The Use of Nonylphenol Formaldehyde Resins for Preventing Asphaltene Precipitation in Vacuum Residues and Hydroprocessed Petroleum Samples. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zou, R.; He, L.; Liu, L.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Xu, J. Effect of Aromatic Pendants in a Maleic Anhydride- Co-Octadecene Polymer on the Precipitation of Asphaltenes Extracted from Heavy Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 10562–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lin, B.; Yan, Z.; Yao, Z.; Cao, K. Influences of Molecular Structure of Poly(Styrene-Co-Octadecyl Maleimide) on Stabilizing Asphaltenes in Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, L.C.M.; Lucas, E.F. Asphaltene Aggregation: Influence of Composition of Copolymers Based on Styrene-Stearyl Methacrylate and Styrene-Stearyl Cinnamate Containing Sulfate Groups. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukherissa, M.; Mutelet, F.; Modarressi, A.; Dicko, A.; Dafri, D.; Rogalski, M. Ionic Liquids as Dispersants of Petroleum Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-hoshoudy, A.N.; Ghanem, A.; Desouky, S.M. Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids for Asphaltene Dispersion; Experimental and Computational Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 114698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, A.; Alharthy, R.D.; Desouky, S.M.; El-Nagar, R.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Evaluating Their Performance as Asphaltene Dispersants. Materials 2022, 15, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghersaei, S.; Mokhtari, B.; Pourreza, N.; Soulgani, B.S. Tetraalkylammonium and Phosphonium Salt for Asphaltene Dispersion; Experimental Studies on Interaction Mechanisms. Egypt. J. Pet. 2022, 31, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Vitale, G. Comparing Kinetics and Mechanism of Adsorption and Thermo-Oxidative Decomposition of Athabasca Asphaltenes onto TiO2, ZrO2, and CeO2 Nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 484, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniela Contreras–Mateus, M.; Sánchez, F.H.; Cañas-Martínez, D.M.; Nassar, N.N.; Chaves–Guerrero, A. Effect of Asphaltene Adsorption on the Magnetic and Magnetorheological Properties of Heavy Crude Oils and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Systems. Fuel 2022, 318, 123684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizkhani, A.; Gandomkar, A. A Novel Method for Application of Nanoparticles as Direct Asphaltene Inhibitors during Miscible CO2 Injection. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, E.; Doryani, H.; Malayeri, M.R.; Riazi, M. Asphaltene Stability during Heptane Injection in a Glass Micromodel in the Presence of Co3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, N.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Bahramian, A.; Mortazavi, Y. Asphaltene Adsorption onto Acidic/Basic Metal Oxide Nanoparticles toward in Situ Upgrading of Reservoir Oils by Nanotechnology. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14135–14146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Pereira-Almao, P. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Asphaltene Adsorption and Oxidation. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Pereira-Almao, P. Effect of the Particle Size on Asphaltene Adsorption and Catalytic Oxidation onto Alumina Particles. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3961–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoodeh, N.; Darvishi, P.; Lashanizadegan, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, F. A Comparative Study for Evaluating the Performance of Five Coatings Applied on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation from Crude Oil. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1616–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaati, F.; Riazi, M.; Mousavi, S.H.; Derikvand, Z. Experimental Investigation of the Inhibitory Behavior of Metal Oxides Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Precipitation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrin, L.B.D.S.; Francisco, R.D.; Bertran, C.A.; Cardoso, M.B.; Loh, W. Direct Assessment of Inhibitor and Solvent Effects on the Deposition Mechanism of Asphaltenes in a Brazilian Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.S.; Loh, W.; Ramos, A.C.S.; Delgado, C.C.; Almeida, V.R. Reversibility and Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation in Brazilian Crude Oils. Pet. Sci. Technol. 1999, 17, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Chen, Z. Comprehensive Molecular Scale Modeling of Anionic Surfactant-Asphaltene Interactions. Fuel 2021, 288, 119729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Guo, T.M. Effect of the Structures of Ionic Liquids and Alkylbenzene-Derived Amphiphiles on the Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation from CO2 Injected Reservoir Oils. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8168–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newberry, M.E.; Barker, K.M. Method for the Removal of Asphaltenic Deposits. USA patent 4,414,035, 8 November 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, A.; Nikazar, M.; Dehghani, S.A.M.; Dabir, B.; Gohari, O. The Role of Inhibitors’ Molecular Structure on Asphaltene Deposition in Reservoir Conditions. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, T.; Solntsev, K.M.; Kahs, T.; Saleh, N.; Commins, P.; Whelan, J.; Mohamed, S.; Naumov, P. Formation of Noncovalent Complexes between Complex Mixtures of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Asphaltenes) and Substituted Aromatics Studied by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 8742–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; Fogler, H.S. Asphaltene Stabilization in Alkyl Solvents Using Oil-Soluble Amphiphiles. In Proceedings of the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–5 March 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Safaie, K.; Nazar, A.R.S. Evaluation of Asphaltene Inhibitors Effect on Aggregation Coupled Sedimentation Process. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghaffar, A.M.; Kabel, K.I.; Farag, R.K.; Maysour, N.E.; Zahran, M.A.H. Synthesis of Poly(Dodecyl Phenol Formaldehyde)-b-Poly(Oxypropylene) Block Copolymer, and Evaluation as Asphaltene Inhibitor and Dispersant. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, D.; Wu, K.; Firoozabadi, A. Ionic Liquids as Viscosity Modifiers for Heavy and Extra-Heavy Crude Oils. Fuel 2015, 143, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries-Harris, M.J.; Coppel, C.P. Solvent Stimulation in Low Gravity Oil Reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol. 1969, 21, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Lin, J.R.; Yen, T.F. Peptization Studies of Asphaltene and Solubility Parameter Spectra. Fuel 1994, 73, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Contreras, E.; León, O. An Experimental Theoretical Approach to the Activity of Amphiphiles as Asphaltene Stabilizers. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Miyauchi, T.E.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S.; Barba-López, V. Aromatic Polyisobutylene Succinimides as Viscosity Reducers with Asphaltene Dispersion Capability for Heavy and Extra-Heavy Crude Oils. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, M.; Kharrat, R.; Hamoule, T. Screening of Inhibitors for Remediation of Asphaltene Deposits: Experimental and Modeling Study. Petroleum 2018, 4, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Ezzat, A.O.; Abdullah, M.M.; Hashem, A.I. Effect of Different Families of Hydrophobic Anions of Imadazolium Ionic Liquids on Asphaltene Dispersants in Heavy Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 8045–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.M.; Dehghanizadeh, M.; Saeedi Dehaghani, A.H.; Vafaie Sefti, M.; Mokhtarian, N. An Investigation of the Effect of Aromatic, Anionic and Nonionic Inhibitors on the Onset of Asphaltene Precipitation. J. Oil Gas Petrochem. Technol. 2014, 1, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auflem, I.H.; Havre, T.E.; Sjöblom, J. Near-IR Study on the Dispersive Effects of Amphiphiles and Naphthenic Acids on Asphaltenes in Model Heptane-Toluene Mixtures. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; He, P.; Tavakkoli, M.; Mathew, N.T.; Fatt, Y.Y.; Chai, J.C.; Goharzadeh, A.; Vargas, F.M.; Biswal, S.L. Characterizing Asphaltene Deposition in the Presence of Chemical Dispersants in Porous Media Micromodels. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 11660–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefi, S.; Shahrabadi, A.; Jahangiri, S.; Lotfollahi, M.N.; Bagherzadeh, H. Investigation of the Performance of Several Chemical Additives on Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2016, 38, 3647–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, G.; Middea, A. Peptization of Asphaltene by Various Oil Soluble Amphiphiles. Colloids Surf. 1991, 52, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.M.; Firoozabadi, A. Tuning Size and Electrostatics in Non-Polar Colloidal Asphaltene Suspensions by Polymeric Adsorption. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8384–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goual, L.; Sedghi, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z. Asphaltene Aggregation and Impact of Alkylphenols. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5394–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamartale, A.; Zendehboudi, S.; Rezaei, N.; Chatzis, I. Effects of Inhibitor Concentration and Thermodynamic Conditions on N-Octylphenol-Asphaltene Molecular Behaviours. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 116897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Malayeri, M.R. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent and Glycolipid Biosurfactant as Green Asphaltene Inhibitors: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 4791–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peramanu, S.; Clarke, P.F.; Pruden, B.B. Flow Loop Apparatus to Study the Effect of Solvent, Temperature and Additives on Asphaltene Precipitation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1999, 23, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permsukarome, P.; Chang, C.; Fogler, H.S. Kinetic Study of Asphaltene Dissolution in Amphiphile/Alkane Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 3960–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillon, L.Z. Effect of Dispersants and Flocculants on the Colloidal Stability of Asphaltenes. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Contreras, E.; Rogel, E.; Dambakli, G.; Espidel, J.; Acevedo, S. The Influence of the Adsorption of Amphiphiles and Resins in Controlling Asphaltene Flocculation. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcenas, M.; Orea, P. Molar-Mass Distributions of Asphaltenes in the Presence of Inhibitors: Experimental and Computer Calculations. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2100–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubov, M.R.; Yakubova, S.G.; Borisov, D.N.; Romanov, G.V.; Arbuzov, A.E.; Yakubson, K.I. Asphaltene Precipitation Inhibitors and Phase Behaviour Control for Bitumen Recovery by Solvent Injection. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers—SPE Heavy Oil Conference, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 10 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Merino-Garcia, D.; Andersen, S.I. Interaction of Asphaltenes with Nonylphenol by Microcalorimetry. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Rogel, E.; Urbina, A.; Andújar, A.; Lucas, A. Study of the Adsorption of Alkyl Benzene-Derived Amphiphiles on Asphaltene Particles. Langmuir 1999, 15, 7653–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, C.; Qi, Y.; Shi, H.; Sun, G.; Yao, B.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y. Asphaltene Dispersants Weaken the Synergistic Modification Effect of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate and Asphaltene for Model Waxy Oil. Fuel 2023, 341, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yang, Y.; Chaisoontornyotin, W.; Ovalles, C.; Rogel, E.; Moir, M.E.; Hoepfner, M.P. Effect of Chemical Inhibitors on Asphaltene Precipitation and Morphology Using Ultra-Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 3681–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Daneshfar, R.; Dehaghani, A.H.S.; Su, C.H. The Effect of Shear Rate on Aggregation and Breakage of Asphaltenes Flocs: Experimental Study and Model-Based Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 114861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaghani, A.H.S.; Badizad, M.H. Inhibiting Asphaltene Precipitation from Iranian Crude Oil Using Various Dispersants: Experimental Investigation through Viscometry and Thermodynamic Modelling. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 442, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.C.; Ferreira, M.S.; da Silva Ramos, A.C. Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation in Brazilian Crude Oils Using New Oil Soluble Amphiphiles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 51, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos da Silva Ramos, A.; Haraguchi, L.; Notrispe, F.R.; Loh, W.; Mohamed, R.S. Interfacial and Colloidal Behavior of Asphaltenes Obtained from Brazilian Crude Oils. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2001, 32, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétuya, R.; Punase, A.; Bosoni, E.; de Oliveira Filho, A.P.; Sarria, J.; Purkayastha, N.; Wylde, J.J.; Mohr, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Asphaltene Aggregation: Machine-Learning Identification of Representative Molecules, Molecular Polydispersity, and Inhibitor Performance. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4862–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguele, R.; Sasaki, K. Asphaltene Behavior at the Interface Oil-Nanofluids: Implications to Adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 622, 126630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.F.; Pruden, B.B. Asphaltene Precipitation from Cold Lake and Athabasca Bitumens. Pet. Sci. Technol. 1998, 16, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.F.; Pruden, B.B. Asphaltene Precipitation: Detection Using Heat Transfer Analysis, and Inhibition Using Chemical Additives. Fuel 1997, 76, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.F.; Mansur, C.R.; Lucas, E.F.; Gonzalez, G. Polycardanol or Sulfonated Polystyrene as Flocculants for Asphaltene Dispersions. Energy Fuels 2009, 24, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghloum, E.F.; Rashed, A.M.; Safa, M.A.; Sablit, R.C.; Al-Jouhar, S.M. Mitigation of Asphaltenes Precipitation Phenomenon via Chemical Inhibitors. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhreez, M.; Xiao, X.; Wen, D. Kinetic Study of Controlled Asphaltene Inhibitor Release from Nanoemulsions. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10795–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, C.R.E.; De Melo, A.R.; Lucas, E.F. Determination of Asphaltene Particle Size: Influence of Flocculant, Additive, and Temperature. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4988–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.; Wilfred, C.D.; Iyyaswami, R.; Appusamy, A.; Thanabalan, M. Investigating the Solubility of Petroleum Asphaltene in Ionic Liquids and Their Interaction Using COSMO-RS. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 79, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Sulemana, N.; Banat, F.; Mathew, N. Ionic Liquid in Stabilizing Asphaltenes during Miscible CO2 Injection in High Pressure Oil Reservoir. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 180, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlaja, A.S.; Hosten, E.; Tshentu, Z.R. Dispersion of Asphaltenes in Petroleum with Ionic Liquids: Evaluation of Molecular Interactions in the Binary Mixture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18390–18401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Melendez-Alvarez, A.A.; Yarbrough, J.; Garcia-Bermudes, M.; Tavakkoli, M.; Abdallah, D.S.; Punnapala, S.; Vargas, F.M. Assessment of the Performance of Asphaltene Inhibitors Using a Multi-Section Packed Bed Column. Fuel 2019, 241, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, D.; Firoozabadi, A. Effect of Surfactants and Water on Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation and Deposition. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, S.M.; Firoozabadi, A. Effect of Dispersant on Asphaltene Suspension Dynamics: Aggregation and Sedimentation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 15780–15788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.M.; Firoozabadi, A. Controlling Nonpolar Colloidal Asphaltene Aggregation by Electrostatic Repulsion. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4438–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar-Vara, L.A.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S.; Buenrostro-González, E.; Hernández-Altamirano, R.; Mena-Cervantes, V.Y.; Ramírez-Pérez, J.F. Multifunctional Properties of Zwitterionic Liquids. Application in Enhanced Oil Recovery and Asphaltene Aggregation Phenomena. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2868–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joonaki, E.; Burgass, R.; Tohidi, B. Experimental and Modelling Study on Application of New Class of Asphaltene Inhibitors for Enhanced Oil Recovery Purposes: Adsorption and Wettability Alteration. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 7–10 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamartale, A.; Zendehboudi, S.; Rezaei, N. New Molecular Insights into Aggregation of Pure and Mixed Asphaltenes in the Presence of N-Octylphenol Inhibitor. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 13186–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Yarbrough, J.; Enayat, S.; Edward, N.; Wang, J.; Vargas, F.M. Evaluation of Solvents for In-Situ Asphaltene Deposition Remediation. Fuel 2019, 241, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytting, B.M.K.; Harper, M.R.; Edmond, K.V.; Zhang, Y.; Kilpatrick, P.K. High-Purity Vanadyl Petroporphyrins: Their Aggregation and Effect on the Aggregation of Asphaltenes. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Silva, H.; Alfarra, A.; Vallverdu, G.; Bégué, D.; Bouyssiere, B.; Baraille, I. Impact of H-Bonds and Porphyrins on Asphaltene Aggregation as Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11153–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, F.B.; Mejía, J.M.; Ruiz, M.A.; Benjumea, P.; Riffel, D.B. Sorption of Asphaltenes onto Nanoparticles of Nickel Oxide Supported on Nanoparticulated Silica Gel. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, F.M.; Dehghani, S.A.M.; Rashidi, A.; Hosseinpour, N.; Mohammadi, S. A Mechanistic Study toward the Effect of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Asphaltene Precipitation and Aggregation in Unstable Crude Oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguele, R.; Mbouopda Poupi, A.B.; Anombogo, G.A.M.; Alade, O.S.; Saibi, H. Influence of Asphaltene Structural Parameters on Solubility. Fuel 2022, 311, 122559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, H.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Sharifi, M.; Riazi, M.; Shojaei, S. A New Insight into Fe3O4 Based Nanocomposites for Adsorption of Asphaltene at the Oil/Water Interface: An Experimental Interfacial Study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 177, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, Y.; Sharifi, M.; Riazi, M. Optimization of Fe3O4/Chitosan Nanocomposite Concentration on the Formation and Stability of W/O Emulsion. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.M.; Firoozabadi, A. Effective Removal of Asphaltene Deposition in Metal-Capillary Tubes. SPE J. 2016, 21, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sultan, A.; Zirrahi, M.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Abedi, J. Effect of the Surfactant on Asphaltene Deposition on Stainless-Steel and Glass Surfaces. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goual, L.; Firoozabadi, A. Effect of Resins and DBSA on Asphaltene Precipitation from Petroleum Fluids. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Khamehchi, E.; Ghaffarzadeh, M.; Kardani, N. Laboratory Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Chemical Solution for Asphaltene Precipitation and Aggregation Problem: Comparison with an Industrial Chemical Solution. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 193, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschy, G.; Papirer, E. Interactions between a Bitumen, Its Components and Model Fillers. Fuel 1978, 57, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Duan, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Zhang, H.; Yao, B. Multi-Alkylated Aromatic Amides Amphiphiles Effectively Stabilize the Associated Asphaltene Particles in Crude Oil. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboudwarej, H.; Pole, D.; Svrcek, W.Y.; Yarranton, H.W. Adsorption of Asphaltenes on Metals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5585–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, Z.; Farhadian, A.; Hu, J. Asphaltene Adsorption of Co3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by SiO2 Film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 602, 154367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Quan, H.; Chang, S.; Huang, Z. Research on a Fluorine-Containing Asphaltene Dispersant and Its Application in Improving the Fluidity of Heavy Oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, B.; Miri, R.; Bazyari, A.; Thompson, L.T. Asphaltene Adsorption on MgO, CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 Nanoparticles Synthesized via the Pechini-Type Sol−Gel Method. Fuel 2022, 321, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, N.M.M.; Dhevarajan, S.; Wilfred, C. Studies on the Effect of Sulfonate Based Ionic Liquids on Asphaltenes. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Khamehchi, E.; Ghaffarzadeh, M.; Kardani, N. Static and Dynamic Evaluation of a Novel Solution Path on Asphaltene Deposition and Drag Reduction in Flowlines: An Experimental Study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Khamehchi, E.; Ghaffarzadeh, M. Experimental Investigation of a Novel Multifunctional Chemical Solution on Preventing Asphaltene Precipitation Using Two Crude Oil Samples with Different Molecular Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Yao, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Sun, G. Synergistic Effect of Asphaltenes and Octadecyl Acrylate-Maleic Anhydride Copolymers Modified by Aromatic Pendants on the Flow Behavior of Model Waxy Oils. Fuel 2020, 260, 116381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Bouyssiere, B.; Vargas, V. Asphaltenes, Subfractions A1 and A2 Aggregation and Adsorption onto RH-SiO2 Nanoparticles: Solvent Effect on the Aggregate Size. Fuel 2023, 331, 125635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Vargas, V.; Piscitelli, V.; Le Beulze, A.; Bouyssiere, B.; Carrier, H.; Castillo, J. SiO2 Biogenic Nanoparticles and Asphaltenes: Interactions and Their Consequences Investigated by QCR and GPC-ICP-HR-MS. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6566–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.A.; Nassar, N.N.; Ruiz, M.A.; Pereira-Almao, P.; Cortés, F.B. Nanoparticles for Inhibition of Asphaltenes Damage: Adsorption Study and Displacement Test on Porous Media. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazikeh, S.; Sayyad Amin, J.; Zendehboudi, S.; Dejam, M.; Chatzis, I. Bi-Fractal and Bi-Gaussian Theories to Evaluate Impact of Polythiophene-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Precipitation and Surface Topography. Fuel 2020, 272, 117535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazikeh, S.; Sayyad Amin, J.; Zendehboudi, S. Experimental Study of Asphaltene Precipitation and Metastable Zone in the Presence of Polythiophene-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazikeh, S.; Kondori, J.; Zendehboudi, S.; Sayyad Amin, J.; Khan, F. Molecular Dynamics Simulation to Investigate the Effect of Polythiophene-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Precipitation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 237, 116417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, J.; An, N.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q. Study of Asphaltene Dispersion and Removal for High-Asphaltene Oil Wells. Pet. Sci. 2012, 9, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, S.; Carmona, J.C.; Nassar, N.N.; Franco, C.A.; Cortés, F.B. Role of Particle Size and Surface Acidity of Silica Gel Nanoparticles in Inhibition of Formation Damage by Asphaltene in Oil Reservoirs. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6122–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schantz, S.S.; Stephenson, W.K. Asphaltene Deposition. Development and Application of Polymeric Asphaltene Dispersants. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 6–9 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan, N.; Salager, J.L.; Anton, R. Effect of Resins on Stability of Asphaltenes. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 30 April–3 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Madhi, M.; Bemani, A.; Daryasafar, A.; Khosravi Nikou, M.R. Experimental and Modeling Studies of the Effects of Different Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Adsorption. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi Alemi, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Mousavi Dehghani, S.A.; Rashidi, A.; Hosseinpour, N.; Seif, A. Experimental and DFT Studies on the Effect of Carbon Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Precipitation and Aggregation Phenomena. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.M.S.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Tannic Acid Esters and Their Performances as Asphaltenes Dispersants. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Akbari, M.; Fakhroueian, Z.; Bahramian, A.; Azin, R.; Arya, S. Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation by TiO2, SiO2, and ZrO2 Nanofluids. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, S.; Riazi, M.; Riazi, M.; Cortés, F.B.; Mousavi, S.H. Investigating the Performance of Carboxylate-Alumoxane Nanoparticles as a Novel Chemically Functionalized Inhibitor on Asphaltene Precipitation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16149–16164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayat, S.; Safa, M.A.; Tavakkoli, M.; Valdes, H.; Rashed, A.M.; Ghloum, E.F.; Gharbi, R.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Vargas, F.M. Novel Nanoparticle-Based Formulation to Mitigate Asphaltene Deposition. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12974–12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatifar, M.; Toghraie, D.; Khosravi, A.; Saberi, F.; Soltani, F.; Sabetvand, R.; Goldanlou, A.S. The Study of Asphaltene Desorption from the Iron Surface with Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafashi, S.; Rasaei, M.R.; Eshraghi, E.; Kuhar, L.; Bona, A.; Nikoloski, A.N. Visual Study of TiO2 Nanofluid Stabilization Methods on Inhibition of Asphaltene Precipitation in Porous Media. Miner. Eng. 2021, 169, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanzadeh, M.R.; Sharifi, M. Stabilizing Silica Nanoparticles in High Saline Water by Using Polyvinylpyrrolidone for Reduction of Asphaltene Precipitation Damage under Dynamic Condition. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi Alemi, F.; Mousavi Dehghani, S.A.; Rashidi, A.; Hosseinpour, N.; Mohammadi, S. Synthesize of MWCNT-Fe2O3 Nanocomposite for Controlling Formation and Growth of Asphaltene Particles in Unstable Crude Oil. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igder, M.; Hosseinpour, N.; Biyouki, A.A.; Bahramian, A. Control of Asphaltene Aggregation in Reservoir Model Oils along the Production Streamline by Fe3O4 and NiO Nanoparticles. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 6689–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, Y.; Malayeri, M.R.; Riazi, M.; Parsaei, R. Impact of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles on Asphaltene Precipitation during CO2 Injection. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 22, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goual, L.; Sedghi, M. Role of Ion-Pair Interactions on Asphaltene Stabilization by Alkylbenzenesulfonic Acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varamesh, A.; Hosseinpour, N. Prediction of Asphaltene Precipitation in Reservoir Model Oils in the Presence of Fe3O4 and NiO Nanoparticles by Cubic Plus Association Equation of State. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 4293–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wei, H.; Tan, Z.; Xue, S.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, S. Biodiesel as Dispersant to Improve the Stability of Asphaltene in Marine Very-Low-Sulfur Fuel Oil. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Lalji, S.M.; Haneef, J.; Ahsan, U.; Khan, M.A.; Yousaf, N. Estimation of Asphaltene Adsorption on MgO Nanoparticles Using Ensemble Learning. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 208, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N. Asphaltene Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles: Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4116–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Q. Nanoparticles for Inhibition of Asphaltenes Deposition during CO2 Flooding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6723–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C. Application of a Nanofluid for Asphaltene Inhibition in Colombia. J. Pet. Technol. 2014, 66, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Acuna, H.M.; Cortes, F.; Patino, J.E.; Chavarro, C.C.; Mora, E.; Botero, O.F.; Guarin, L. Application and Evaluation of a NanoFluid Containing NanoParticles for Asphaltenes Inhibition in Well CPSXL4. In Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 29–30 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.I.; Fazelabdolabadi, B.; Moradi, S.; Rashidi, A.M.; Shahrabadi, A.; Bagherzadeh, H. On the Application of NiO Nanoparticles to Mitigate in Situ Asphaltene Deposition in Carbonate Porous Matrix. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Al-Jabari, M.E.; Husein, M.M. Removal of Asphaltenes from Heavy Oil by Nickel Nano and Micro Particle Adsorbents. In Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference Nanotechnology and Applications, Crete, Greece, 1 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, E.; Sedghi, M.; Goual, L. Polymers for Asphaltene Dispersion: Interaction Mechanisms and Molecular Design Considerations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.F.; Pruden, B.B. Heat Transfer Analysis for Detection of Asphaltene Precipitation and Resuspension. In Proceedings of the Annual Technical Meeting, Calgary, Alberta, 9–11 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Barcenas, M.; Orea, P.; Buenrostro-González, E.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S.; Duda, Y. Study of Medium Effect on Asphaltene Agglomeration Inhibitor Efficiency. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; León, O.; Espidel, Y.; González, Y. Asphaltene Stability in Crude Oils. SPE Prod. Facil. 2001, 16, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.F.; Klein, G.C.; Yen, A.T.; Squicciarini, M.P.; Rodgers, R.P.; Marshall, A.G. Crude Oil Polar Chemical Composition Derived from FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry Accounts for Asphaltene Inhibitor Specificity. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, A.E.; Ershov, M.A.; Savelenko, V.D.; Lobashova, M.M.; Rogova, M.Y.; Makhova, U.A.; Tikhomirova, E.O.; Burov, N.O.; Aleksanyan, D.R.; Kapustin, V.M.; et al. Use of Asphaltene Stabilizers for the Production of Very Low Sulphur Fuel Oil. Energies 2023, 16, 7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliev, A.M. Chemistry and Technology of Additives to Oils and Fuels; Chemistry: Leningrad, Russia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tankov, I.; Yankova, R. DFT Analysis, Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism of Esterification Using Pyridinium Nitrate as a Green Catalyst. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankov, I.; Yankova, R.; Veli, A.; Nikolova, R.; Mustafa, Z.; Stoycheva, I. Effect of the Active Phase-Support Interaction on the Electronic, Thermal and Catalytic Properties of [H–Pyr]+[HSO4]−/Support (Support = Rice Husk Ash; Corundum). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, M.A.; Choudhury, K.P.; Neogi, N. Advances with Molecular Nanomaterials in Industrial Manufacturing Applications. Nanomanufacturing 2021, 1, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.S.; Daraee, M.; Sobat, Z. Advanced Development in Upstream of Petroleum Industry Using Nanotechnology. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Zhao, L.; An, Y. Advanced Developments in Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials for the Oil and Gas Industry: A Review. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 238, 212872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Martin, C.A.; Montes-Pinzon, D.; Meneses Motta da Silva, M.; Montes-Paez, E.; Guerrero-Martin, L.E.; Salinas-Silva, R.; Camacho-Galindo, S.; Fernandes Lucas, E.; Szklo, A. Asphaltene Precipitation/Deposition Estimation and Inhibition through Nanotechnology: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2023, 16, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, U.J.; Bai, P.; Yan, Z. Nanotechnology Applications in Petroleum Refining. In Topics in Mining, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering; Saleh, T., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 37–65. [Google Scholar]
- Murgich, J.; Rogel, E.; León, O.; Isea, R. A Molecular Mechanics-Density Functional Study of the Adsorption of Fragments of Asphaltenes and Resins on the (001) Surface of Fe2O3. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tarboush, B.J.; Husein, M.M. Inferring the Role of NiO Nanoparticles from the Thermal Behavior of Virgin and Adsorbed Hydrocarbons. Fuel 2015, 147, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tarboush, B.J.; Husein, M.M. Dispersed Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Preparation in Heavy Oil and Their Uptake of Asphaltenes. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 133, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.; Giraldo, L.J.; Lucas, E.F.; Riazi, M.; Franco, C.A.; Cortés, F.B. Cardanol/SiO2 Nanocomposites for Inhibition of Formation Damage by Asphaltene Precipitation/Deposition in Light Crude Oil Reservoirs. Part I: Novel Nanocomposite Design Based on SiO2 Cardanol Interactions. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7048–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yan, C.; Cai, J.; Pan, Y.; Han, Q. Research Progress in Nanoparticle Inhibitors for Crude Oil Asphaltene Deposition. Molecules 2024, 29, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, M.A.; Zabala, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Cortés, F.B. Asphaltenes Inhibition by Using New Generation of Nanofluids in Tenay Field. In Proceedings of the SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference and Exhibition, Moscow, Russia, 24–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, H.H.; Idem, R.O. Correlations of characteristics of Saskatchewan crude oils/asphaltenes with their asphaltenes precipitation behavior and inhibition mechanisms: Differences between CO2 and n-heptane-induced asphaltene precipitation. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 1354–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel, E.; Hench, K.; Miao, T.; Lee, E.; Dickakian, G. Evaluation of the Compatibility of Crude Oil Blends and Its Impact on Fouling. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9233–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
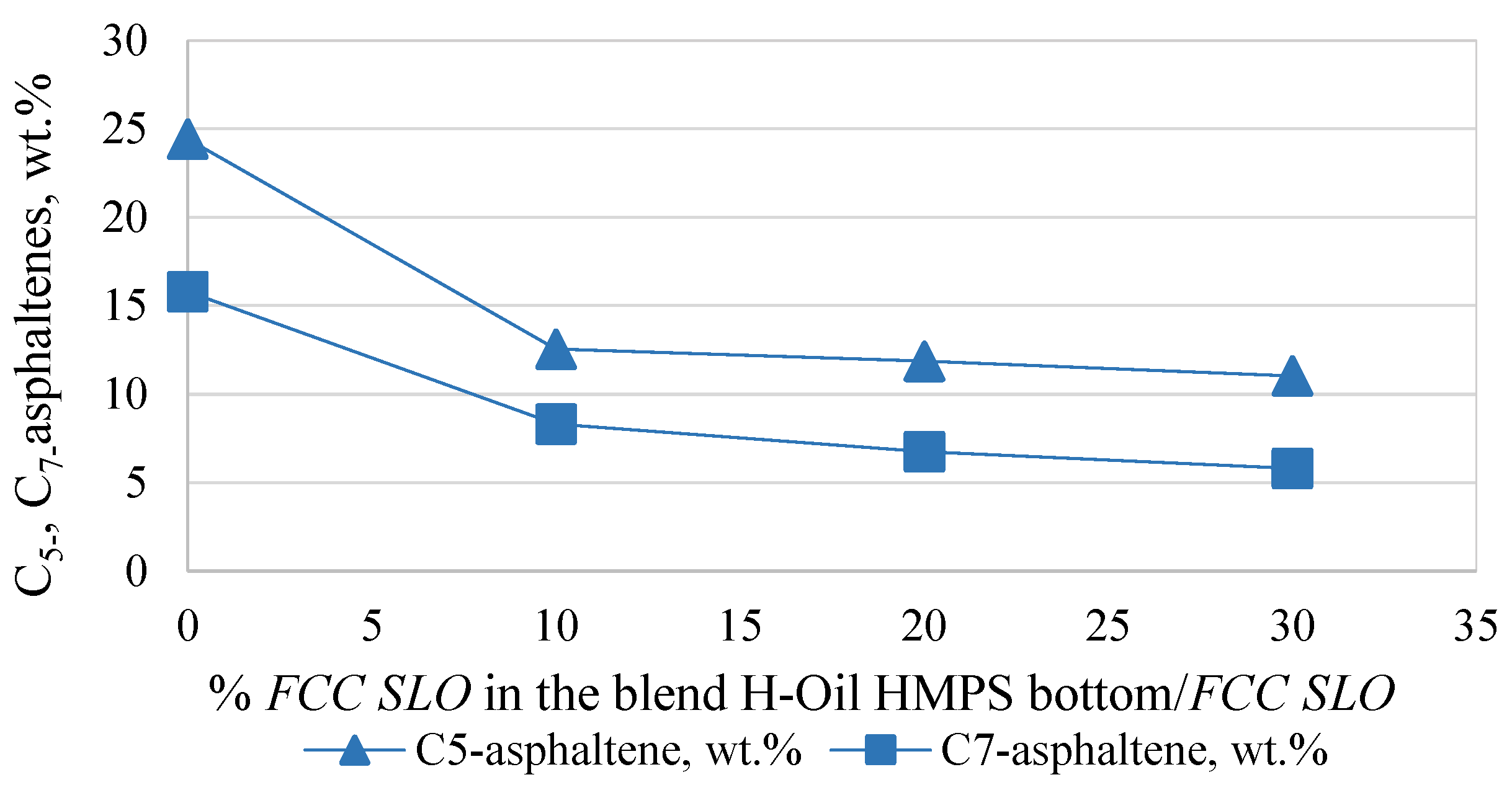
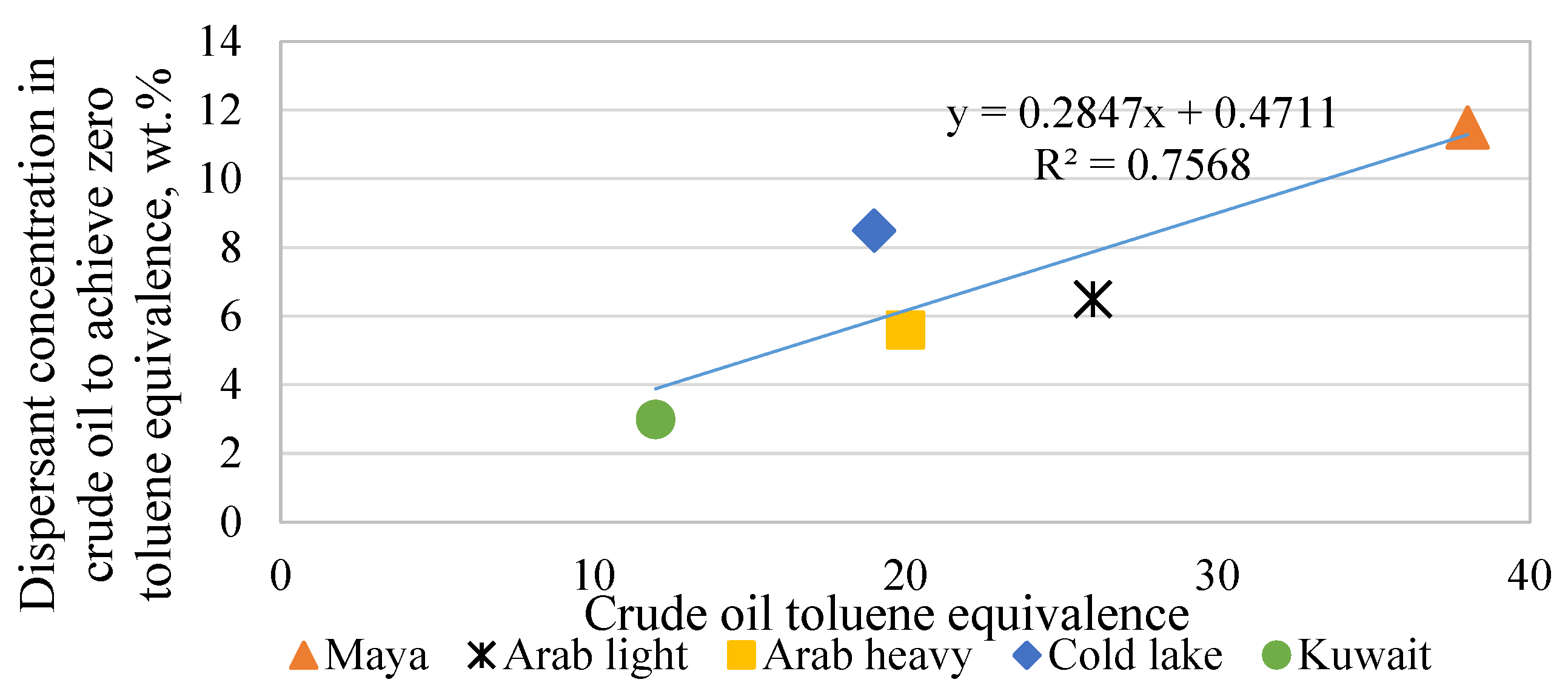
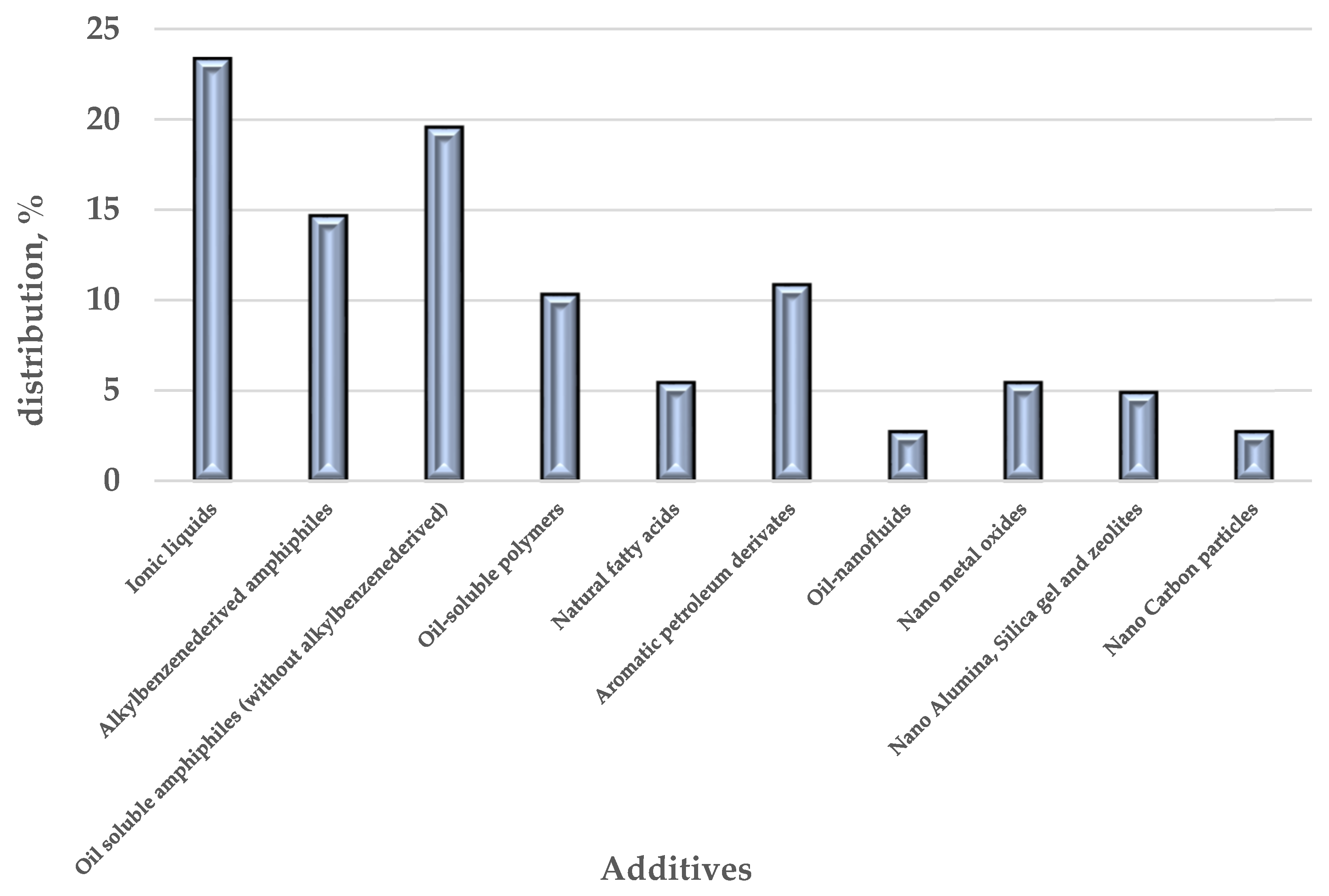
| Asphaltenes | FCC SLO Added to the H-Oil HMPS Bottom Product | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 20% | 30% | |
| Asphaltene Reduction, % | |||
| C5 asphaltenes | −48.6 | −39.3 | −35.5 |
| C7 asphaltenes | −47.4 | −46.6 | −47.5 |
| Nr | Additive | Nr | Additive | Nr | Additive | Nr | Additive | Nr | Additive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate [187,188,189] | 21 | phenol [190,191,192] | 41 | 4-dodecylresorcinol [57,107,165,193,194] | 61 | propoxylated poly(dodecylphenol formaldehyde) [195] | 81 | dodecyl pyridinium chloride [196] |
| 2 | sodium octylbenzenesulfonate [189] | 22 | cresol [165,193,197,198] | 42 | sorbitan monooleate [199] | 62 | aromatic polyisobutylene succinimides [200] | 82 | 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [196] |
| 3 | sodium dodecyl sulfate [201] | 23 | ethylphenol [165,189,193] | 43 | PL (two functional groups of hydroxyls connected to a benzene) [191] | 63 | poly(vinyltoluene-co-alpha-methylstyrene) [56] | 83 | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium oleate [202] |
| 4 | triethanolamine lauryl ether sulfate [203] | 24 | butylphenol [165,189] | 44 | hexylamine [197,204] | 64 | polyisobutylene succinimide [57] | 84 | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium abeitate [202] |
| 5 | sodium lauryl ether sulfate [203] | 25 | hexylphenol [165,189,193,205] | 45 | dodecylamine [206,207] | 65 | polyisobutylene succinic ester [57] | 85 | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium cardanoxy [202] |
| 6 | dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate [208] | 26 | octylphenol [61,165,189,193,205,209,210] | 46 | hexadecylamine [198] | 66 | nonylphenol-formaldehyde resin (modified by polyamines) [57] | 86 | synthesized deep eutectic solvent [206,211] |
| 7 | acetic acid [197] | 27 | nonylphenol [66,105,107,165,167,191,193,198,199,207,212,213,214,215,216,217,218] | 47 | diethanoldodecylamine [199] | 67 | p-octylpyridinium chloride [189] | 87 | nonylphenol formaldehyde resin/Toluene [72] |
| 8 | isopropanol [197] | 28 | dodecylphenol [110,165,189,193,205,209,214,219,220,221] | 48 | coconut diethanol amide [203,222,223] | 68 | p-butylpyridinium chloride [189] | 88 | nonylphenol formaldehyde resin/Xylene [72] |
| 9 | caprylic acid [190,224,225] | 29 | secbutylphenol [165,189,193,219] | 49 | N-aryl amino-alcohols [106] | 69 | p-dodeylpyridinium chloride [189] | 89 | nonylphenol formaldehyde resin/Coconut oil [72] |
| 10 | oleic acid [190,225] | 30 | tertbutylphenol [219] | 50 | poly(maleic anhydride l-octadecene) [110] | 70 | p-dodeylpyridinium tetrafluoroborate [189] | 90 | nonylphenol formaldehyde resin/Andiroba oil [72] |
| 11 | lauric acid [206] | 31 | tertoctylphenol [165,193,219] | 51 | nonylphenolic resin [219,226] | 71 | p-dodeylpyridinium hexafluorophosphate [189] | 91 | mPVOH-1 (standard polymer) [227] |
| 12 | palmitic acid [223] | 32 | creosol [212,228,229] | 52 | dodecyl phenolic resin [110] | 72 | N-butylisoquinolinium chloride [189] | 92 | mPVOH-2 (non-ionic polymer) [227] |
| 13 | stearic acid [198] | 33 | heptyloxyphenol [165,193] | 53 | sulfonated polystyrene [230] | 73 | 1-propylboronic acid-3-alkylimidazolium bromides [173] | 93 | mPVOH-1 (anionic polymer) [227] |
| 14 | benzoic acid [69,167,190,191,201] | 34 | methanol [197] | 54 | polycardanol [230] | 74 | 1-propenyl-3-alkylimidazolium bromide [173] | 94 | dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid [67,69,186,192,211,220,222,231,232] |
| 15 | octylbenzoic acid [233] | 35 | 1-octanol [204,207] | 55 | nonylphenol formaldehyde resins [221] | 75 | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide [61,173,234,235] | 95 | auric alcohol [220] |
| 16 | salicylic acid [69,167,201,231] | 36 | dodecanol [108] | 56 | polyolefin amide alkeneamine [54] | 76 | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [61,173,235,236] | 96 | BZSS-012 inhibitor [65] |
| 17 | phthalic acid [167,191] | 37 | 2-ethyl-1-hexanol [201] | 57 | alkylated phenol [54,208] | 77 | didecyldimethylammonium nitrate [173] | 97 | I-8 commercial inhibitor [237] |
| 18 | sebacic acid [224] | 38 | benzyl alcohol [198,201] | 58 | poly olefin esters [52] | 78 | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium nitrate [236] | 98 | I-9 commercial inhibitor [237] |
| 19 | etyltrimethylammonium bromide [104,187,201] | 39 | Triton X-100 [198] | 59 | polyolefin alkeneamine [205,238,239,240] | 79 | 1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-carboxybenzoate [236] | 99 | I-15 commercial inhibitor [237] |
| 20 | zwitterionic liquid [241,242] | 40 | ethoxylated nonylphenol [105,111,165,187,191,193,198,199,207,219,225] | 60 | poly(dodecylphenol formaldehyde) [195] | 80 | dodecyl thiazolium chloride [195] | 100 | 4-hexylphenol [237] |
| 101 | 4-octylphenol [237,243] | 121 | poly(styrene-co-octadecyl maleimide) [171] | 141 | tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate [176] | 161 | vanadyl petroporphyrins [244,245,246] | 181 | nanoparticles of NiO supported on silica gel: SNi5; SNi15 [247] |
| 102 | 4-dodecylphenol [237] | 122 | 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [223] | 142 | cetyltrimethylammoniun bromide [176] | 162 | Ni petroporphyrins [246] | 182 | carbon nanotubes [248] |
| 103 | sodium dodecyl sulfonic acid [188] | 123 | 1-butylpyridinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [234] | 143 | tetrabutylphosphonium bromide [176] | 163 | ethylbenzene [249] | 183 | Fe3O4/Chitosan nanocomposite [250,251] |
| 104 | CA 2 inhibitor [186] | 124 | 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate [234] | 144 | toluene [66,107,165,189,190,204,212,233,249,252,253,254] | 164 | nanoparticles of Al2O3; Fe3O4; NiO [185] | 184 | nanoparticles of Fe3O4; Fe3O4/SiO2; Fe3O4/TiO2; Fe3O4/ Chitosan [250] |
| 105 | CA 1 inhibitor [186] | 125 | PL5001 [255] | 145 | cyclohexane [197] | 165 | nanoparticles of SiO2; Al2O3; MgO; ZnO;TiO2; kaolin [256] | 185 | TiO2, ZrO2, CeO2 nanoparticles [177] |
| 106 | 4-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid/4-nonylphenol mixture [186] | 126 | multi-alkylated aromatic amides [257] | 146 | dicyclopentadiene [197] | 166 | nanoparticle of stainless steel (304L), iron, and aluminum [258] | 186 | Co3O4 nanoparticles modified by SiO2 [259] |
| 107 | trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(2,4,4-trimethylphentyl) phosphinate [67,70] | 127 | fluorine-containing tetrameric copolymer [260] | 147 | naphthalene [198,201,212,228,229] | 167 | nanoparticles of kaolin, CaCO3, TiO2, BaSO4, Fe3O4, FeS, SiO2 (hydrophilic/hydrophobic) [111] | 187 | nanoparticles of MgO, CaO, SiO2, Al2O3 [261] |
| 108 | trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate [70] | 128 | trioctylmethylammonium dodecylsulfate [262] | 148 | quinoline [212,229] | 168 | nanoparticles of NiO; Fe2O3; WO3; MgO; CaCO3; ZrO2 [181] | 188 | Co3O4 nanoparticles [180] |
| 109 | AUT Force 110 [263,264] | 129 | polyoctadecylacrylate [265] | 149 | indole (solid) [212,228,229] | 169 | nanoparticles of Co3O; Fe3O4; MgO; CaO; TiO2; NiO [182] | 189 | SiO2 nanoparticles from rice husks [266,267] |
| 110 | X2; Y1; Y2; Y3; Z1 inhibitors [192] | 130 | polyoctadecylacrylate-maleic anhydride [265] | 150 | phenanthrene [186,202] | 170 | nanoparticles of Slica gel, SNi5, SNi15, Zeolite, Al, AlNi5, AlNi15, PdNi/Al, [268] | 190 | polythiophene-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles [115,269,270,271] |
| 111 | rhamnolipid [67] | 131 | polyoctadecylacrylate-maleic anhydride-aniline [265] | 151 | benzene [190,201,212,249,272] | 171 | nanoparticles of Slica gel: S11, S11A, S11N, S11B, S58, S240 [273] | 191 | DBSA nanoemulsion [114] |
| 112 | 3-hexadecyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetrachloroferrate(III) [174] | 132 | polyoctadecyl-acrylate-maleic anhydride-naphthylamine [265] | 152 | m-xylene [190,191,197,212,228,249,274,275] | 172 | nanoparticle of SiO2 [111,227,273,276] | 192 | carbon nanoparticles [277] |
| 113 | 1-ethyl-3-hexadecyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetrachloroferrate(III) [174] | 133 | esters of tannic acid and heptanoyl chloride [278] | 153 | 1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene [212] | 173 | nanoparticles of SiO2; Al2O3; MgO [276,279] | 193 | carboxylate-alumoxane nanoparticles [280] |
| 114 | 1-butyl-3-hexadecyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetrachloroferrate(III) [174] | 134 | tetramethylammonium bromide [176] | 154 | decalin [212,228,229] | 174 | nanoparticles of TiO2, ZrO2, SiO2 [279] | 194 | oil/water nanoemulsions and oil/water nanoemulsions with DBSA [232] |
| 115 | tetrahydrofuran [248] | 135 | tetraethylammonium bromide [176] | 155 | tetralin [164,188,209,225] | 175 | nanoparticle of TiO2 [111,182,281,282,283] | 195 | nanoparticles of SiO2 and polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilizer [284,285] |
| 116 | furan [249] | 136 | tetrapropylammonium bromide [176] | 156 | pyridine [187,209] | 176 | nanoparticle of iron (II and III) oxide [111,178,179,181,182,185,250,286,287] | 196 | multi-walled carbon nanotubes-Fe3O4 nanoparticles [285] |
| 117 | furfural [249] | 137 | tetrabutylammonium fluoride [176] | 157 | benzothiophene [209,225,288] | 177 | nanoparticles of NiO; Fe2O3 [286,289] | 197 | nanoparticles of graphene oxide, TiO2, SiO2, MgO [62] |
| 118 | methyl acetate [249] | 138 | tetrabutylammonium chloeide [176] | 158 | nonylbenzene [162,190,290] | 178 | nanoparticles of MgO [181,182,276,291] | ||
| 119 | ethyl acetate [249] | 139 | tetrabutylammonium bromide [176] | 159 | p-xylene [241] | 179 | nanoparticles of Al2O3 [72,179,183,185,292,293,294,295] | ||
| 120 | ethyl propionate [249] | 140 | tetrabutylammonium iodide [176] | 160 | aromatic naphtha A 150 [244] | 180 | nanoparticles of NiO [181,182,185,286,296,297] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stratiev, D.; Nikolova, R.; Veli, A.; Shishkova, I.; Toteva, V.; Georgiev, G. Mitigation of Asphaltene Deposit Formation via Chemical Additives: A Review. Processes 2025, 13, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010141
Stratiev D, Nikolova R, Veli A, Shishkova I, Toteva V, Georgiev G. Mitigation of Asphaltene Deposit Formation via Chemical Additives: A Review. Processes. 2025; 13(1):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010141
Chicago/Turabian StyleStratiev, Dicho, Radoslava Nikolova, Anife Veli, Ivelina Shishkova, Vesislava Toteva, and Georgi Georgiev. 2025. "Mitigation of Asphaltene Deposit Formation via Chemical Additives: A Review" Processes 13, no. 1: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010141
APA StyleStratiev, D., Nikolova, R., Veli, A., Shishkova, I., Toteva, V., & Georgiev, G. (2025). Mitigation of Asphaltene Deposit Formation via Chemical Additives: A Review. Processes, 13(1), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13010141








