Abstract
Textile dyes discharged into aquatic systems can have significant environmental impacts, causing water pollution and toxicity to aquatic life, and constituting a human health risk. To manage these effects, the sorption ability of wood biowaste chemically modified by Bi2O3 for textile dye removal was investigated. Sorbent characterization was performed using scanning electron microscopy, and elemental analysis by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method for the specific surface area, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy–attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR). The optimization of the sorption process was carried out, and optimal parameters, such as contact time, pH, the dose of sorbent, the concentration of dye, and temperature, were defined. Also, desorption studies were conducted. Kinetics and isotherms studies were carried out, and the data fits to a pseudo-second order model (r2 ≥ 0.99) and Langmuir model (r2 ≥ 0.99), indicating that the process occurs in the monolayer form and the dye sorption depends on the active sites of the sorbent surface. The maximal sorption capacity of the sorbent was 434.75 mg/g.
1. Introduction
Water pollution is a pressing environmental issue that endangers both human health and natural ecosystems. It occurs when harmful substances, such as chemicals, waste, and microorganisms, contaminate water bodies, including rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater. These pollutants degrade the water quality and disrupt the balance of aquatic environments [1]. The main sources of water pollution are industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, improper waste disposal, and urbanization [2]. Industrial activities often discharge heavy metals and toxic chemicals, such as textile dyes, into waterways, posing serious health risks to humans and animals [3]. Textile dyes contribute significantly to water pollution due to their complex chemical structures and extensive use in the textile industry [4,5]. These dyes, which are often synthetic, are designed to be resistant to fading, thus also making them resistant to natural degradation processes [6], such as reactive blue 19, which is a very stable and resistant dye [7]. When wastewater containing dyes is released into water bodies without proper treatment, it can cause severe environmental and health problems. Textile dyes can discolor water bodies, reducing light penetration and disturbing the balance of aquatic ecosystems [8]. This can negatively impact habitats and hinder the growth and reproduction of aquatic plants and animals. Also, some studies suggested that dyes such as reactive blue 19, due to their electrophilic vinyl sulfone groups, have mutagenic properties [7].
Ensuring safe drinking water, protecting wildlife, and maintaining environmental health requires urgent action to address water pollution. According to the World Health Organization, contaminated water is a significant cause of diseases and deaths worldwide, underscoring the need for effective pollution control and remediation measures [1]. It is crucial to implement effective management practices and policies. Solutions include improving wastewater treatment, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, and enforcing stricter regulations on industrial emissions [9].
Synthetic dyes are chemically complex and resistant to conventional wastewater treatment methods such as coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation, making their removal from wastewater difficult. More effective treatment methods include advanced oxidation processes, membrane filtration, and biological treatments [10]. However, these methods are more expensive and require advanced infrastructure and expertise. Recent advancements in wastewater treatment have introduced sorption as an innovative technique to enhance the removal of contaminants and improve sustainability. Sorption is a highly effective method for treating wastewater from the textile industry, particularly for dyes removal. This process involves the adhesion of molecules of dye onto the adsorbent material surface [11]. The method is praised for its high efficiency, cost effectiveness, and relative simplicity in implementation. Creating sorbents from waste materials involves transforming discarded or byproduct materials into substances that can sorb pollutants. This approach not only repurposes waste but also contributes to environmental remediation. Common waste materials used include agricultural residues, industrial byproducts, and even municipal solid waste, such as plastic [12,13]. Sorbents based on waste lignocellulose biomass, such as wood and agricultural residues, provide a green alternative for various environmental and industrial applications. Their continued development is promising, focusing on enhancing their efficiency and usability [14]. Waste lignocellulose biomass consists of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin [15,16]. Cellulose provides structural support and a high surface area [17]. Hemicellulose adds versatility and enhances sorptive properties [18]. Lignin contributes hydrophobic qualities and structural rigidity [19]. Also, wood biowaste has various functional groups, such as hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, phenolic, and amide, which are responsible for the binding of pollutants, predominantly cationic pollutants, such as heavy metals [20,21,22,23]. These functional groups can also be used for chemically or physically modified metal oxides to enhance their adsorption capabilities, uptake capacity, or sorption rate [24]. In recent studies, metal oxide, such as bismuth oxide (Bi2O3), was used as a nanocomposite with zeolite as a promising sorbent material for Rhodamine B and Methylene Blue dyes, which are cationic [25]. So, the main objective of this work was the synthesis of low-cost sorbents from wood biowaste chemically modified with bismuth oxide Bi2O3, for the removal of anionic pollutants, such as the commonly used textile dye reactive blue 19 from a model solution. The main sorption parameters, such as contact time, the solution’s pH, sorbent dose, dye concentration, and temperature, were investigated. The isotherm and kinetics sorption models were used to determinate the sorption equilibrium, mechanism, and sorbent capacity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Bi(NO3)3 × 5H2O, NaOH, HNO3, NaNO3, Bi2O3 and reactive blue 19 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification. The deionized water (18 MΩ) was used to prepare all solutions.
2.2. Synthesis
Wood sawdust, an industrial biowaste, was obtained from a furniture factory and used for sorbent synthesis. The wood biowaste was fractionized and the 0.4–0.8 mm fraction was used for chemical modification. After that, the wood biowaste was washed using deionized water and treated with 0.5 M NaOH for 30 min to activate the surface functional groups. Then, in the first step, the 10 g of wood biowaste were incorporated in a solution of 2.0 g of Bi(NO3)3 × 5H2O in 30.0 cm3 of 2 M HNO3. After mixing the mixtures for 30 min, they were filtered, and then in the second step the residue was treated with trimethylamine vapor for 90 min, which was used to create the conditions necessary to produce Bi2O3. Then, the material was washed and dried at 65 °C for 6 h. The obtained wood biowaste–Bi2O3 sorbents were abbreviated as W-Bi. The schematic illustration for the synthesis process of the W-Bi sorbent is shown in Scheme S1 in Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Characterization
The morphology of the sorbent was investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, SUPRA 35VP (Carl Zeiss), Jena, Germany) at an accelerating voltage of 1.0 kV. All samples were attached to carbon tape and coated with thin and thick conductive Cr layer to avoid electrical discharge. Magnifications of ×5000 were used for imaging the samples. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) was investigated on the JSM-5300 SEM (SEM, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with QX2000 system (Link Analytical, High Wycombe, UK). Samples were attached to aluminum stubs with Leit-c conductive carbon cement. Secondary electron images were collected with a Hitachi High Technologies SU8030 (Tokyo, Japan) field emission gun SEM. Samples were imaged uncoated, at 20 kV with a Thermo Scientific System 7 Ultradry EDX detector (Waltham, MA, USA). Five random areas were analyzed on each sample. The crystalline structure and compositions were examined using theta–theta geometry in reflection mode with a D8 Advance X-ray diffraction (XRD) instrument (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). The analysis employed Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 40 mA, with a LynxEye silicon strip detector. Data were collected over a range of 2–80° 2θ, with a step size of 0.02° and a counting time of 0.5 s per step. Data acquisition was managed through DIFFRAC plus XRD Commander software version 2.6.1 (Bruker-AXS), while qualitative analysis utilized EVA version 5 (Bruker-AXS) and the PDF-2 2020 database (ICDD). Quantitative analysis was conducted using TOPAS version 5 (Bruker-AXS). The specific surface area was measured by nitrogen adsorption using the Micromeritics Gemini 5 Surface Area Analyzer, USA, using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method [26]. Samples were degassed overnight under flowing nitrogen gas. The Barret–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method was used for pore size and pore volume analysis [27]. The molecular structure was investigated using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy–attenuated total reflectance (FTIR–ATR, Vertex 70v (Bruker), Billerica, MA, USA) in the spectral range 4000–600 cm−1. The net surface charge of the sorbent was determined by the point of zero charge (PZC) drift method. The series of 0.1 dm3 0.1 M NaNO3 solutions were adjusted to the initial pH (pHi) range 2.0–10.0 using 0.1/0.01 M HNO3 and 0.1/0.01 M NaOH. A total of 0.2 g of sorbents were added to each solution into stopped glass tubes and stirred. The final pH (pHf) was measured after 24 h. The PZC was obtained at the intersection of the pHi and pHf curves.
2.4. Sorption and Desorption Study
The W-Bi sorbent was used to remove textile dye reactive blue 19 from aqueous solution. For the sorption experiments, freshly prepared dye working solutions were utilized. The pH was adjusted to the required level using HNO3 and NaOH solutions. Once the appropriate amount of sorbents was added to the dye solution, the mixture was stirred at 500 rpm until equilibrium was achieved. Dye concentration was measured by analyzing samples of the solution at 569 nm using a UV-1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The removal efficiency (RE, %) and sorption capacity (qt, mg/g) over time (t, s) were calculated using Equations (1) and (2), respectively:
where ci (mg/dm3) is the initial dye concentration, cf (mg/dm3) is the final dye concentration, V (dm3) is the dye volume solution and m (g) is the sorbent mass. The sorption study was carried out to analyze the effects of the initial pH of dye solution (2.0–10.0), the W-Bi dose (0.5–6.0 g/dm3), initial dye concentration (50.0–1000.0 mg/dm3) and temperature (5.0–55.0 °C). Also, the sorption study for dye removal using unmodified waste biomass and commercial Bi2O3 was carried out for comparison. The desorption was carried out using 0.5 M NaOH.
2.5. Kinetic and Isotherm Study
The kinetic and isotherm examination was conducted with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose in range of 10.0–1000.0 mg/dm3, with the dye solutions mixed up to equilibrium. Two kinetic models, the pseudo-first order and the pseudo-second order, and two isotherm models, Langmuir and Freundlich, were employed for the kinetics and isotherm examination of dye sorption onto W-Bi. The pseudo-first order model describes the sorption rate, which is dependent on the number of active sites available on the sorbent surface for binding the sorbate molecules [28]. The pseudo-second order model assumed that the sorption rate is controlled by the amount of sorbate sorbed on the sorbent surface [29]. The pseudo-first order and the pseudo-second order model are represented in Equations (3) and (4), respectively:
where k1 (1/min) and k2 (g/mg·min) are the the pseudo-first order and the pseudo-second order rate constant, qe (mg/g) is the sorbed dye amount at equilibrium, and r2 is the determination coefficient.
The Langmuir isotherm suggests that sorbate uptake occurs through monolayer adsorption on a surface that is energetically uniform, with no interaction between the sorbate molecules [30]. The Freundlich isotherm indicates that sorption happens on a heterogeneous surface, where sites with higher energy are occupied first. As the occupation of these sites increases, the binding strength decreases [31]. These models are expressed by the Equations (5) and (6), respectively:
where ce (mg/dm3) is the equilibrium dye concentration, qm (mg/g) is the maximum capacity, KL and KF are the Langmuir and the Freundlich constants, respectively, and 1/nF is the Freundlich exponent.
All parameter evaluations were conducted using Origin 2021 software (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. SEM-EDX
The morphologies and microstructures of the wood biowaste (Figure 1a) and the W-Bi sorbent (Figure 1b–d) were examined by SEM. The samples before and after modification show a very similar smooth surface and a porous morphology, containing specific channels and pores, which means that the modification process did not cause any significant morphological change in the wood biowaste surface. The size of the particles on the W-Bi sorbent surface is near 1 mm, with about 100-µm-sized cell-like units. These unites have randomly positioned holes whose dimensions are around 1 µm. On the surface of some particles of the W-Bi sorbent, there was a smooth layer consisting of a higher atomic number, meaning that Bi2O3 was highly and homogeneously dispersed, without a change in the wood biowaste structure. The chemical composition of the wood biowaste (Figure 2a) and W-Bi sorbent (Figure 2b) was confirmed by EDX analysis. The wood biowaste consists of 59.7% carbon and 39.4% oxygen, and W-Bi sorbent consists of 23.4% carbon, 57.9% oxygen and 18.7 bismuth. With the increase of bismuth content in the samples, oxygen content also increased, meaning that there was no incorporation of individual bismuth atoms in the wood biowaste structure, but it is most likely an oxide form of bismuth.
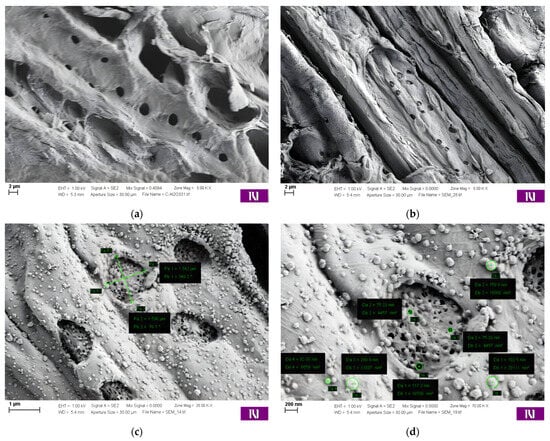
Figure 1.
SEM image of (a) wood biowaste at 5.00 K and W-Bi sorbent at (b) 35.00 K, (c) 35.00 K and (d) 70.00 K.
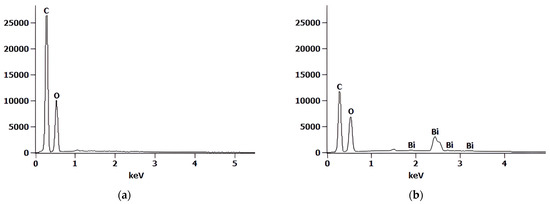
Figure 2.
EDX spectrum of (a) wood biowaste and (b) W-Bi sorbent.
3.1.2. XRD
The mineral properties of the wood biowaste (Figure 3a) and the W-Bi sorbent (Figure 3b) were examined by XRD. The samples before and after modification show a very similar structure, which is predominantly amorphous. The W-Bi sorbent has broad reflections of 2θ at 23 and 16, with a significantly weaker broad reflection of 2θ at 43. These are reminiscent of a partially amorphous, poorly crystalline material in the W-Bi sorbent, and no characteristic peaks of crystal Bi2O3, which occurred in the Bi2O3 with a crystal structure [32], meaning that Bi2O3 does not occur as a separate or individual form on the W-Bi sorbent surface, and indicating that Bi is chemically bonded to the wood biowaste.
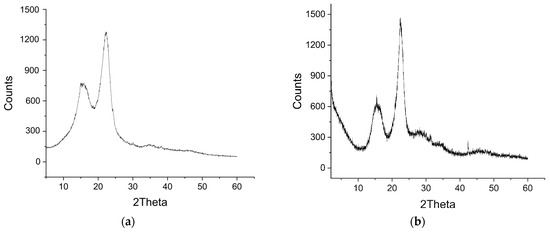
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of (a) wood biowaste and (b) W-Bi sorbent.
3.1.3. BET
The specific surface area of the wood biowaste (Figure 4a) and the W-Bi sorbent (Figure 4b) was estimated using the BET method. Surface area measurements showed that the wood biowaste and W-Bi sorbent has a BET surface area of 5.70 and 1.70 m2/g, respectively. The BJH pore size distribution of the wood biowaste was 5.13 nm with a BJH pore volume of 0.0067 cm3/g. The BJH pore size distribution of W-Bi sorbent was 7.11 nm with a BJH pore volume of 0.0033 cm3/g. Wood-based sorbents can have varying BET surface areas depending on their treatment and preparation. Generally, untreated wood has a relatively low BET surface area, often in the range of 1–10 m2/g [33]. The activated carbon derived from wood can have a significantly higher BET surface area depending on the activation process [34]. However, wood-based sorbents which are not carbonated have generally relatively low BET surface areas, such as the W-Bi sorbent [33].
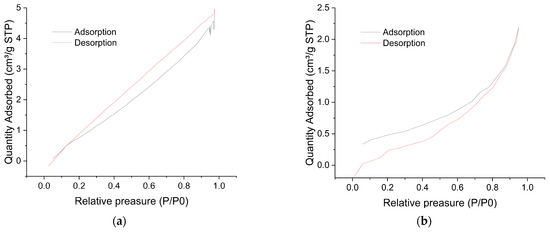
Figure 4.
Adsorption–desorption plot for BET method of (a) wood biowaste and (b) W-Bi sorbent.
3.1.4. FTIR
The functional groups content of the wood biowaste and the W-Bi sorbent was examined by FTIR-ATR (Figure 5a). The samples before and after modification show that the modification using Bi2O3 generated several changes in the IR region of 4000–400 cm−1. The bands in the region 3500–3000 cm−1 are related to the stretching vibration of hydroxyl and methyl/methylene groups in the hemicellulose and lignin molecules in both spectra, and the peak at around 3350 cm−1 is related to the band of hydroxyl groups [35]. The peaks observed in the 1700–1380 cm−1 range in the spectra of the W-Bi sorbent correspond to the bending vibrations of Bi–OH groups. These peaks are overlapped by other vibrations, including the stretching vibrations of C=O groups in carboxylic acids and esters, aromatic ring bands, and the stretching vibrations associated with lignin and hemicellulose. The bands in the region 1200–800 cm−1 are related by the presence of carbohydrate components and correspond to the vibration of C–O–C, C–O and O–H of cellulose in both spectra [35]. The series of minor absorption peaks around 550 cm−1 in the spectra of the W-Bi sorbent correspond to Bi–O vibrations. These peaks exhibit lower intensity due to the relatively low concentration of Bi in the W-Bi sorbent [36]. This indicates that Bi2O3 is chemically bonded to functional groups of wood biowaste, creating new specific active centers.
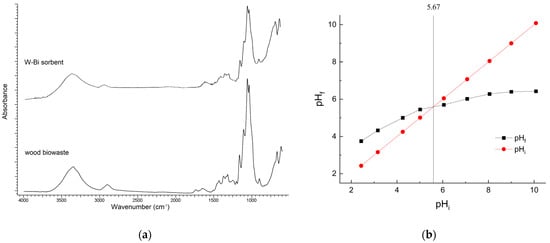
Figure 5.
(a) FTIR−ATR spectrum of wood biowaste and W-Bi sorbent; (b) PZC plot for W-Bi sorbent.
3.1.5. PZC
The PZC of the W-Bi sorbent was estimated using the PZC drift method (Figure 5b). It was found that the PZC of W-Bi was 5.67. When the pH of the solution is below the PZC, the surface of the sorbent typically carries a positive charge, which can attract anions (negatively charged ions). Conversely, when the pH is above the PZC, the sorbent’s surface usually carries a negative charge, making it more likely to attract cations (positively charged ions) [37].
3.2. Sorption and Desorption Study
3.2.1. Contact Time
The contact time is a critical factor which affects the sorption of dyes and directly influences the equilibrium state of the sorption process. The effect of the contact time was explored in a period of time of 150 min at a pH value of 2.0 with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose and a 100.0 mg/dm3 dye concentration at 25.0 °C. The results presented in Figure 6a show that the dye sorption efficiency increased with time and took place in two phases. The first one was fast, and dye removal efficiency increased from 0 to 95.3% in less than 20 min. After that, the slower phase took place, until reaching equilibrium for 60 min. An increase in contact time generally enhances the dye sorption efficiency until equilibrium is reached. Initially, the sorption rate was high due to the abundance of active sites on the W-Bi sorbent’s surface, but as these sites became occupied, the rate decreased, leading to a plateau phase, indicating equilibrium [38]. The sorption removal of dye using unmodified wood biowaste and commercial Bi2O3 was investigated in period of 150 min, after which the dye removal efficiency was 0.95 and 12.24%, respectively. These experiments show that the chemical modification of wood biowaste using Bi2O3 improved the capability of wood biowaste to remove anionic pollutants such as reactive blue 19 dye, and the obtained W-Bi sorbent displayed very high and rapid sorption.
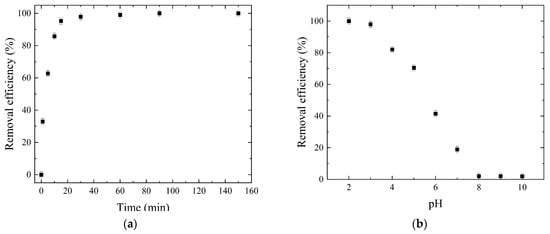
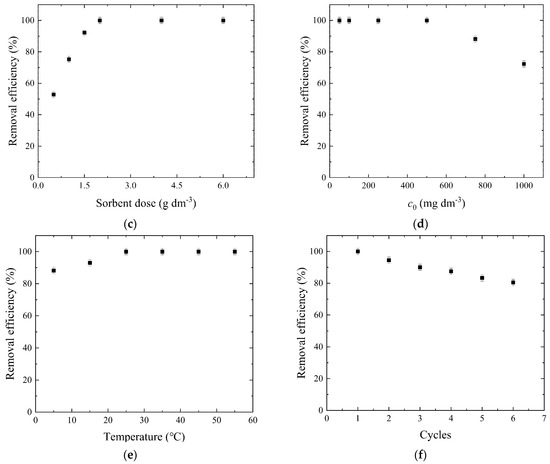
Figure 6.
Sorption process optimization: (a) effect of contact time; (b) effect of pH; (c) effect of sorbent dose, (d) effect of dye concentration; (e) effect of temperature, and (f) desorption study.
3.2.2. pH
The pH of the solution is a key factor in the sorption process of textile dyes, influencing dye ionization, sorbent surface charge, and overall sorption mechanisms. Optimizing pH conditions is essential for enhancing dye removal efficiency in wastewater treatment processes. The effect of the pH was explored by changing its values from 2.0 up to 10.0, with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose and a 100.0 mg/dm3 dye concentration at 25.0 °C. The results presented in Figure 6b show that, with the increase in the pH up to 5.0, the removal efficiency decreased from 100 to 70.5%. An additional increase in pH to 10.0 led to a significant decrease in the removal efficiency (1.9%). The maximal dye uptake was achieved at pH 2.0. Reactive blue 19 is an anionic dye, due to the sulfonic group in the molecule, which has a negative charge, and influences dye interaction with sorbents. The surface charge of the W-Bi sorbent changes with pH. In acidic environments, at a pH lower than the PZC of the W-Bi sorbent, the W-Bi sorbent’s surface becomes positively charged due to the protonation of surface groups. This positive charge enhances the sorption of dye molecules because opposite charges attract [39]. At higher pH levels, at a pH higher than the PZC of W-Bi sorbent, the W-Bi sorbent’s surface becomes more negatively charged due to deprotonation. This increased the negative charge and repelled dye molecules, reducing their sorption [40]. Generally, a lower pH enhances dye adsorption due to increased attraction, while a higher pH can decrease adsorption due to increased repulsion (Scheme S2 in Supplementary Materials).
3.2.3. Sorbent Dose
The sorbent dose has a critical role in optimizing dye removal processes, and it is crucial to determine the optimal dose to avoid inefficiencies and unnecessary costs and achieve effective and cost-efficient dye removal from wastewater. The effect of the sorbent dose was explored by changing its values from 0.5 up to 6.0 g/dm3 at a pH value of 2.0 with a 100.0 mg/dm3 dye concentration at 25.0 °C. The results presented in Figure 6c show that increasing the W-Bi dose to 2.0 g/dm3 increased removal efficiency from 52.9 to 100%; after that, the dye removal efficiency negligibly changed, with higher W-Bi doses up to 6.0 g/dm3. The maximal dye uptake was achieved at 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose. Increasing the sorbent dose generally enhances the removal of textile dyes from aqueous solutions, due to the increase in surface area and more sorption sites available for the dye molecules [41]. Also, a higher sorbent dose led to more effective dye removal due to enhanced sorption capacity and better interactions between the dye molecules and the sorbent surface.
3.2.4. Dye Concentration
The effect of dye concentration on removal efficiency in the sorption process is a significant factor influencing the performance of adsorption systems used in wastewater treatment. Recent studies have elucidated how varying dye concentrations can impact the efficiency of dye removal, providing insights into optimizing sorption processes for enhanced environmental management. As dye concentration increases, the removal efficiency of the sorption process typically shows a trend of decreasing effectiveness. The effect of the dye concentration was explored by changing its values from 50.0 up to 1000.0 mg/dm3 at a pH value of 2.0 with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose at 25.0 °C. The results depicted in Figure 6d indicate that as the dye concentration increases, the removal efficiency of the dye decreases. At lower dye concentrations (50.0–500.0 mg/dm3), the removal efficiency is very high, approaching nearly 100%. The maximal dye uptake was achieved at lower dye concentrations from 50.0 to 500.0 mg/dm3. Further increasing the dye concentration up to 1000.0 mg/dm3 reduces the removal efficiency to 72.3%. This occurs because, at higher concentrations, the number of dye molecules exceeds the number of available active sites on the sorbent material. Consequently, the sorption sites become saturated, leading to a reduction in the overall efficiency of the removal process [42,43]. The comparison of maximum sorption capacities for reactive blue 19 dye of the W-Bi sorbent and other novel sorbents from the literature are presented in Table 1, and it is noticeable that the sorption capacities depend on nature of the used sorbent. The W-Bi sorbent shows very high dye sorption efficiency among the other sorbents, which proves the advantages of chemical modification using Bi2O3 in comparison with other physical/chemical modification methods reported in the literature. The use of wood waste sorbents for the removal of organic dyes, particularly reactive blue 19, offers several advantages that make them an attractive choice for treating dye-contaminated water. The biggest advantage of W-Bi sorbent compared to other sorbents from the literature is the cost-effectiveness due to wood biowaste abundant availability and low acquisition costs. The removal of such a high dye concentration using sorbents is crucial, particularly in the textile industry, where wastewater often contains significant levels of dye. The textile sector is known for generating large volumes of effluent with high concentrated dyes due to the processes of dyeing and finishing. Implementing W-Bi sorbent for the removal of high dye concentrations not only helps in mitigating the environmental impact of textile effluents but also supports compliance with regulatory standards for wastewater discharge.

Table 1.
The comparison of various novel sorbents used for reactive blue 19 dye removal.
3.2.5. Temperature
The effect of temperature on removal efficiency plays a significant role in the sorption process, influencing both the rate and capacity of sorbents to remove pollutants from water. Sorption is sensitive to temperature changes due to its impact on the interaction dynamics between the sorbent and the pollutants. The effect of the temperature was explored by changing its values from 5.0 up to 55.0 °C at a pH value of 2.0 with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose and a 100.0 mg/dm3 dye concentration. The results presented in Figure 6e show that increasing the temperature from 5.0 to 55.0 °C led to an increase in the removal efficiency of dye from 88.2% to 100%, indicating that the sorption process is endothermic in nature. The maximal dye uptake was achieved at 25 °C. Such an influence of temperature may be a result of the fact that higher temperatures generally increase the mobility of both the sorbate and the sorbent molecules, which can lead to more frequent collisions and interactions [51].
3.2.6. Desorption and Reusability
Desorption studies are critical for understanding environmental impact and the effectiveness of the W-Bi sorbent. The pH levels significantly affect the desorption process. Increasing the pH can enhance the desorption of anionic dyes from substrates due to the reduction in electrostatic interactions between the dye molecules and the substrate [52]. The results presented in Figure 6f show that the dye removal efficiency using W-Bi sorbent was reduced gradually from 100 to 80.5 %, after six sorption–desorption cycles, meaning that W-Bi sorbent had good reusability properties. The decrease in dye removal efficiency is probably attributed to the loss of the W-Bi sorbent in the sorption–desorption processes or the inactivation of surface sorption centers. The desorption did not lead to visible changes on the surface and in the structure of the sorbent (Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials).
3.3. Kinetic and Isotherm Study
3.3.1. Sorption Kinetic
Sorption kinetics refers to the rate at which dye molecules are sorbed by the W-Bi sorbent. This concept is crucial in environmental science, chemistry, and materials science for understanding how quickly dye molecules interact with surfaces of W-Bi sorbent. The results presented in Figure 7a,b show the plot of qt vs. t for the pseudo-first order and the pseudo-second order model for dye removal using W-Bi sorbent, respectively. The obtained value of the parameters presented in Table 1 shows that the determined values of qe for dye sorption using W-Bi showed similarity with the obtained experimental qe values, but in the case of the pseudo-second order model, they are closer to the experimental values. The obtained r2 for the pseudo-second order model was from 0.999 to 0.993, which was relatively higher than the r2 for the pseudo-first-order model, which was from 0.997 to 0.960, meaning that the pseudo-second order model better fitted experimental data than the pseudo-first order. The obtained results indicate that the pseudo-second order model can be successfully used for the study of dye sorption by W-Bi and implies that the sorption process is controlled by the interaction between the sorbate and specific binding sites on the sorbent [53]. This can reflect the involvement of chemisorption or the formation of new chemical bonds, which often occurs when the sorbate and sorbent have a high affinity for each other (Table 2).
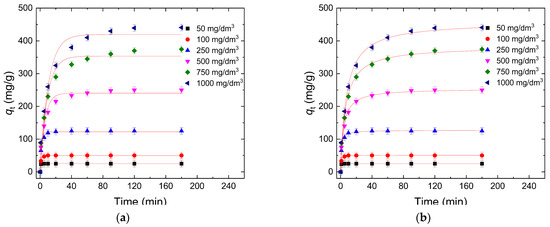
Figure 7.
Sorption kinetic study: (a) pseudo-first order model, and (b) pseudo-second order model.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters obtained for dye sorption using W-Bi sorbent and their 98% confidence intervals.
3.3.2. Sorption Isotherm
Sorption isotherms describe how dye molecules interact with a W-Bi sorbent, illustrating the relationship between the quantity of the dye molecules sorbed and its concentration in the surrounding phase at equilibrium. The results presented in Figure 8a,b show the plot of qe versus ce for the Langmuir and the Freundlich isotherm for dye removal using the W-Bi sorbent, respectively. The obtained parameter values presented in Table 3 show that the r2 obtained for the Langmuir model was 0.991, which was relatively higher than the r2 for the Freundlich model, which was 0.999, meaning that the Langmuir model better fitted experimental data than the Freundlich model, which achieved a value of 0.671. This outcome means that for systems where adsorption sites are homogeneously distributed and a maximum capacity is reached, the Langmuir model can provide a more accurate representation of the adsorption process compared to the Freundlich model [41]. The maximal sorption capacity of the W-Bi sorbent for reactive blue 19 calculated from Langmuir model was 434.75 mg/g.
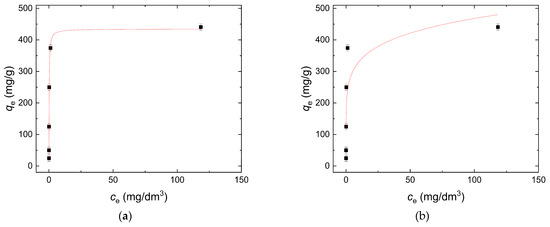
Figure 8.
Sorption isotherm study: (a) Langmuir model, and (b) Freundlich model.

Table 3.
Isotherm parameters obtained for dye sorption using W-Bi sorbent.
4. Conclusions
The morphology analysis revealed that the W-Bi sorbent consists of particles approximately 1 mm in size, featuring cell-like units around 100 µm in diameter, each with holes of about 1 µm. The chemical analysis confirmed that the W-Bi sorbent consisted of 23.4% carbon, 57.9% oxygen and 18.7 bismuth. The mineral analysis proved that the W-Bi sorbent has an amorphous structure, meaning that Bi2O3 does not appear as a separate or individual form on the W-Bi sorbent surface. Surface area measurements showed that the W-Bi sorbent has a BET surface area of 1.70 m2/g with a BJH pore size distribution of 7.11 nm and BJH pore volume of 0.0033 cm3/g. The sorption study of dye using the W-Bi sorbent confirmed that removal efficiency increased from 0 to 95.3% in less than 20 min, reaching equilibrium for 60 min, and the maximal dye uptake was achieved at a pH of 2.0, with a 2.0 g/dm3 sorbent dose at lower tested dye concentrations from 50.0 to 500.0 mg/dm3. The desorption study showed that dye removal efficiency using the W-Bi sorbent was reduced from 100 to 80.5%, after six sorption–desorption cycles. Kinetics and isotherms studies revealed that the data were best fitted to pseudo-second order model (r2 ≥ 0.99) and Langmuir model (r2 ≥ 0.99), indicating that the process occurs in the monolayer form and the dye sorption depends on the active sites of the sorbent surface. The maximal sorption capacity of the W-Bi sorbent for dye was 434.75 mg/g. All these results suggest that the W-Bi sorbent could be a viable option for reactive blue 19 dye removal from polluted waters or wastewaters, particularly in the textile industry, where wastewater often contains significant levels of dye.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr12092025/s1, Scheme S1: Schematic illustration for the synthesis of W-Bi sorbent. Scheme S2: Schematic illustration for proposed sorption mechanism of Reactive blue 19 dye using W-Bi sorbent. Figure S1: The characterization of W-Bi sorbent after desorption: (a) SEM; (b) EDX; (c) XRD; (d) FTIR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization N.V. and M.R.V.; methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation: N.V.; resources: I.J. and A.B.; writing—review and editing: D.M.N., G.N. and D.B.; supervision: I.J. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia: 451-03-66/2024-03/200124, 451-03-65/2024-03/200124 and 451-03-65/2024-03/200133.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the technical support of Matic Šobak and Helena Spreizer, from the Department of Materials Chemistry at National Institute of Chemistry, Ljubljana, Slovenia, for their support in the SEM and FTIR-ATR analyses, as well as Andrew Hurt, from the Faculty of Engineering and Science, University of Greenwich, London, UK, for his support in the EDX, XRD and BET analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Drinking-Water. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Nutrient Pollution: Sources and Solutions. 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nutrientpollution/sources-and-solutions (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). What Causes Tap Water Contamination. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drinking-water/causes/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/drinking/contamination.html (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- European Parliament (EP). The Impact of Textile Production and Waste on the Environment (Infographics). 2020. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20201208STO93327/the-impact-of-textile-production-and-waste-on-the-environment-infographics (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Christie, R.M. Environmental Aspects of Textile Dyeing; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2007; pp. 1–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, M.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z. Textile Dyeing Wastewater Treatment. In Advances in Treating Textile Wastewater; Hauser, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, T.A.; Abdelrahman, M.S.; Rehan, M. Textile Dyeing Industry: Environmental Impacts and Remediation. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 27, 3803–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivan, M.; Simsek, S.; Ozbek, S.; Ozbek, B. An optimization study on adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 dye from aqueous solutions by extremely effective and reusable novel magnetic nanoadsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 191, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Water Pollution from Agriculture: A Global Review. 2018. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca0146en/CA0146EN.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, H.; Ri, C.; Liu, Q.; Tang, J. Characteristics of ball-milled PET plastic char for the adsorption of different types of aromatic organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 77685–77697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barracco, F.; Parisi, E.; Pipitone, G.; Simone, E.; Bensaid, S.; Fino, D. Valorization of pyrolytic plastic-derived char for adsorption of wastewater contaminants: A kinetic and thermodynamic investigation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 6513–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, H.C.; Woo, S.H.; Nguyen, T.V. Removal of Various Contaminants from Water by Renewable Lignocellulose-Derived Biosorbents: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2155–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, S.; Hameed, A.; Noman, M.; Ahmed, T. Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Sustainable Bioenergy Source for the Future. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, S.; Pong, R.R.; Tan, Y.C.; Leow, Y. Advances in Sustainable Polymeric Materials from Lignocellulosic Biomass. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Crombeen, M. Cellulose-Based Materials in Wastewater Treatment of Petroleum Industry. J. Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Lv, Z.; Chen, G.; Peng, F. Hemicellulose: Structure, Chemical Modification, and Application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, M.; Ahmadpoor, F.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Lignin-Derived (Nano) Materials for Environmental Pollution Remediation: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 178, 394–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.J.; Ghosh, R.K.; Das, A.K.; Nath, S.C.; Islam, M.R.; Akhter, S.; Rahman, M.S. Investigation of the chemical profiles of seven wood species for their potential applications. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 18, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, P.; Sahu, O. Arsenate and fluoride removal from groundwater by sawdust impregnated ferric hydroxide and activated alumina (SFAA). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Motiee, F. Application of a Sawdust/Fe3O4 and Sawdust/Fe3O4/PEI as a Selective Adsorbent for Pb(II) Removal. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, E.; Pelé-Meziani, C.; Macchioni, N.; Lemoine, G.; Guilminot, E.; Shen, D.; Pizzo, B. The removal of iron from waterlogged archaeological wood: Efficacy and effects on the room temperature wood properties. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 18, 672–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, S.M.; Idowu, K.S.; Adejuwon, O.M.; Adeyemi-Adejolu, T. A review on the influence of chemical modification on the performance of adsorbents. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.A.; Kapanga, P.M.; Ntale, M.; Lusamba, S.N.; Tshimanga, R.M.; Ammari, A.; Shehu, Z.S. Synthesis, characterization and application of Zeolite/Bi2O3 nanocomposite in removal of Rhodamine B dye from wastewater. Clean. Water 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Kungl. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.Z. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57A, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Oudghiri-Hassani, H.; Rakass, S.; Al Wadaani, F.T.; Al-ghamdi, K.J.; Omer, A.; Messali, M.; Abboudi, M. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of α-Bi2O3 nanoparticles. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.I.; Armynah, B.; Tahir, D. Comprehensive review of wood-based composites as microwave absorbers: Utilizing wood-derived materials such as carbon, metal/metal oxides, and polymer composites as fillers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, J.; Louhelainen, J.; Kłosińska, T.; Drożdżek, M.; Alén, R. Characterization of alkali-extracted wood by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy. Biomass Conv. Biorefin. 2018, 8, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, A.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous zirconia made by using a poly(methyl methacrylate) template. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Taoufik, N.; García, A.M.; Korili, S.A. Comparative removal of emerging contaminants from aqueous solution by adsorption on an activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Karishma, S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Jeyasri, S.; Kiruthika, A.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Optimization and Modeling of Reactive Yellow Adsorption by Surface Modified Delonix regia Seed: Study of Nonlinear Isotherm and Kinetic Parameters. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N. Cationic and Anionic Dye Adsorption by Agricultural Solid Wastes: A Comprehensive Review. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2013, 5, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, X. Anionic Dye Adsorption on Chemically Modified Ordered Mesoporous Carbons. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 14070–14083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, H.-Y.; Gollakota, A.R.K.; Wen, J.-C.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Shu, C.-M.; Reddy, G.M.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Wen, J.-H.; Tian, Z. Removal of Sulfonated Azo Reactive Red 195 Textile Dye from Liquid Phase Using Surface-Modified Lychee (Litchi chinensis) Peels with Quaternary Ammonium Groups: Adsorption Performance, Regeneration, and Mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, B.T.; Ozel, H.U.; Ozel, H.B. Removal of Methylene Blue onto Forest Wastes: Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M. Solar Red and Brittle Blue Direct Dyes Adsorption onto Eucalyptus angophoroides Bark: Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Sahu, U.K.; Jani, N.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Wilson, L.D. Magnetic crosslinked chitosan-tripolyphosphate/MgO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for reactive blue 19 dye removal: Optimization using desirability function approach. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, A.S.; Hapiz, A.; Musa, S.A.; Kashi, E.; Wu, R.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Jawad, A.H.; Algburi, S. Organically modified montmorillonite composited with magnetic glyoxal-chitosan Schiff base for reactive blue 19 dye removal: Process optimization and adsorptive mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Surip, S.N.; Alothman, Z.A. Hybrid multifunctional biocomposite of chitosan grafted benzaldehyde/montmorillonite/algae for effective removal of brilliant green and reactive blue 19 dyes: Optimization and adsorption mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 393, 136334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doondani, P.; Panda, D.; Gomase, V.; Peta, K.R.; Jugade, R. Novel Chitosan-ZnO nanocomposites derived from Nymphaeaceae fronds for highly efficient removal of Reactive Blue 19, Reactive Orange 16, and Congo Red dyes. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, K.; Reghioua, A.; Atia, D.; Mbuvi, H.M.; Moussaoui, Y.; Jawad, A.H. Magnetic chitosan-benzoin Schiff’s base/fly ash for reactive blue 19 dye removal: Characterization and parametric optimization. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 169, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Geng, Z.; She, D. Three-dimensional lignin-based polyporous carbon@polypyrrole for efficient removal of reactive blue 19: A synergistic effect of the N and O groups. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Abd Malek, N.N.; ALOthman, Z.A. Statistical optimization and modeling for color removal and COD reduction of reactive blue 19 dye by mesoporous chitosan-epichlorohydrin/kaolin clay composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4218–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumeier, B.M.; Augustin, A.; Thönes, M.; Sablotny, J.; Wintgens, T.; Wessling, M. Linking the effect of temperature on adsorption from aqueous solution with solute dissociation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Meng, Y.; Wei, Z.; DeLaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Adsorption/Desorption Behavior of Cationic and Anionic Dyes by Biochars Prepared at Normal and High Pyrolysis Temperatures. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 572, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Lahuri, A.H.; Rahim, A.A.; Nordin, N.; Adnan, R.; Jaafar, N.F.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Comparative Studies on Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetic for CO2 Capture Using Iron Oxide Impregnated Activated Carbon. Catal. Today 2023, 418, 114111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).