Fault Intelligent Diagnosis for Distribution Box in Hot Rolling Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Bi-LSTM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fault Diagnosis for Distribution Box
2.1. Distribution Box in Rolling Mill
2.2. Installation of Sensors
2.3. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis for Distribution Box
3. Framework of Proposed Model
3.1. Spatial Feature Extraction Based on Convolutional Neural Networks
3.2. Temporal Feature Extraction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network
3.3. Fault Diagnosis Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction
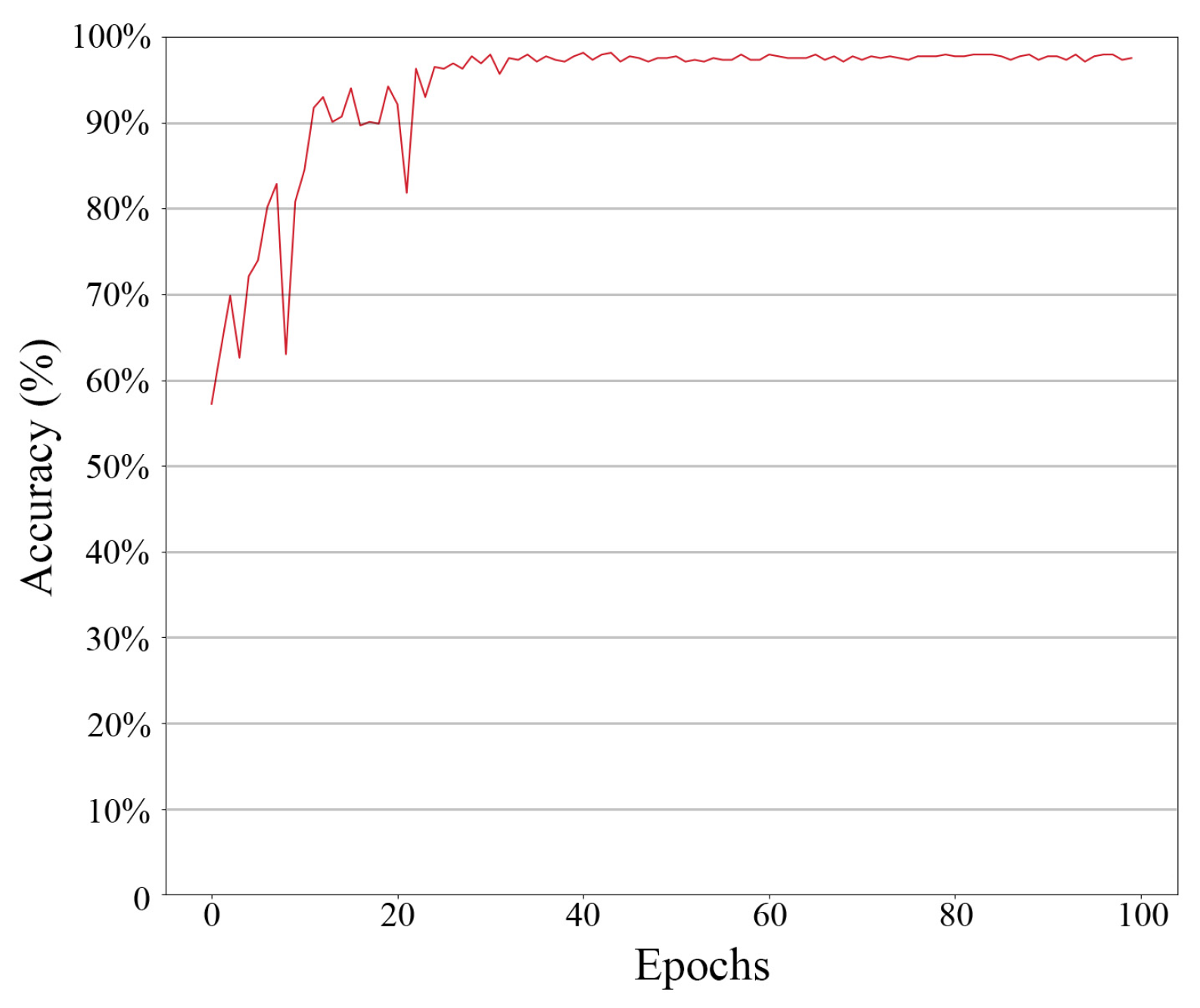
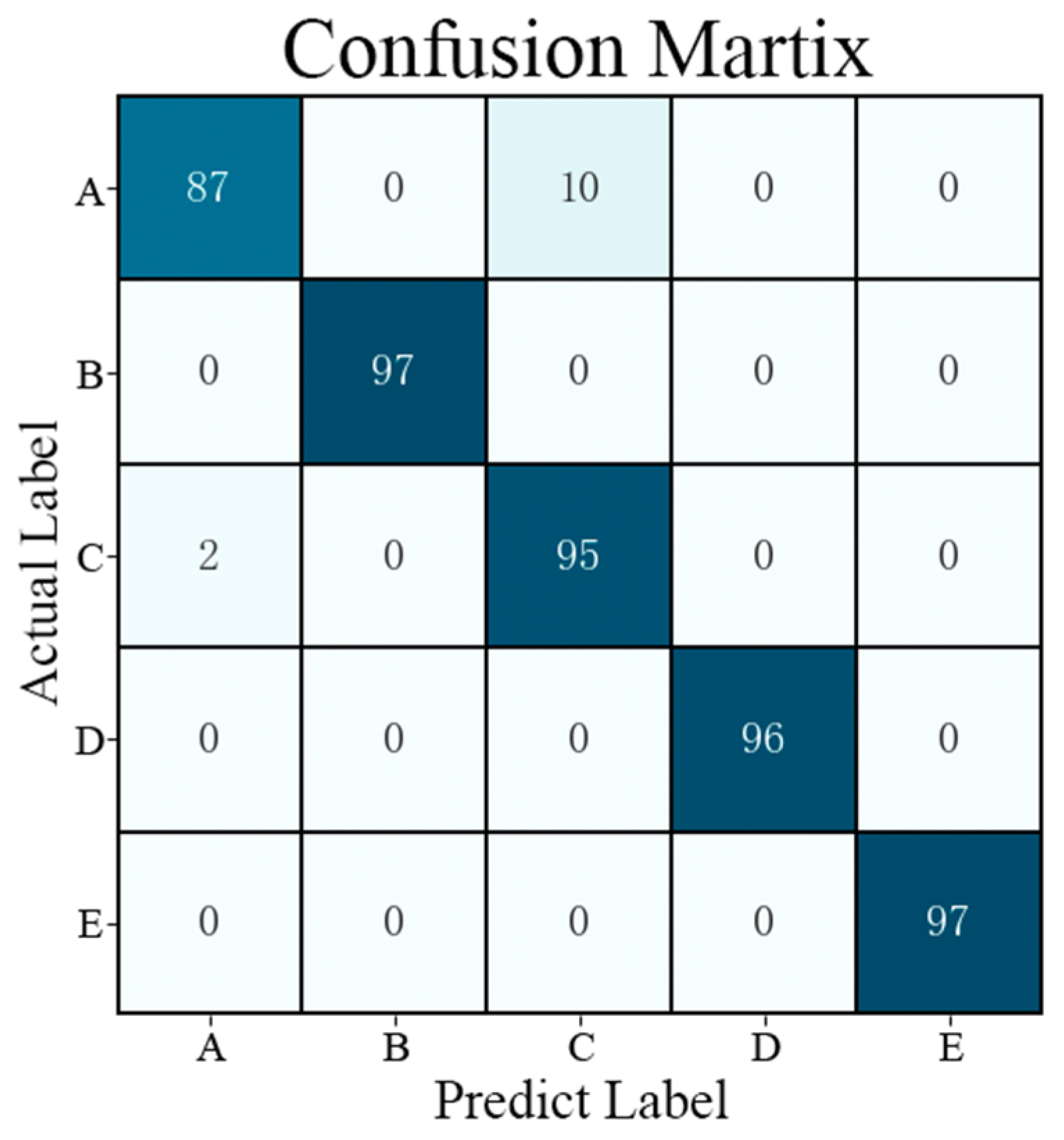
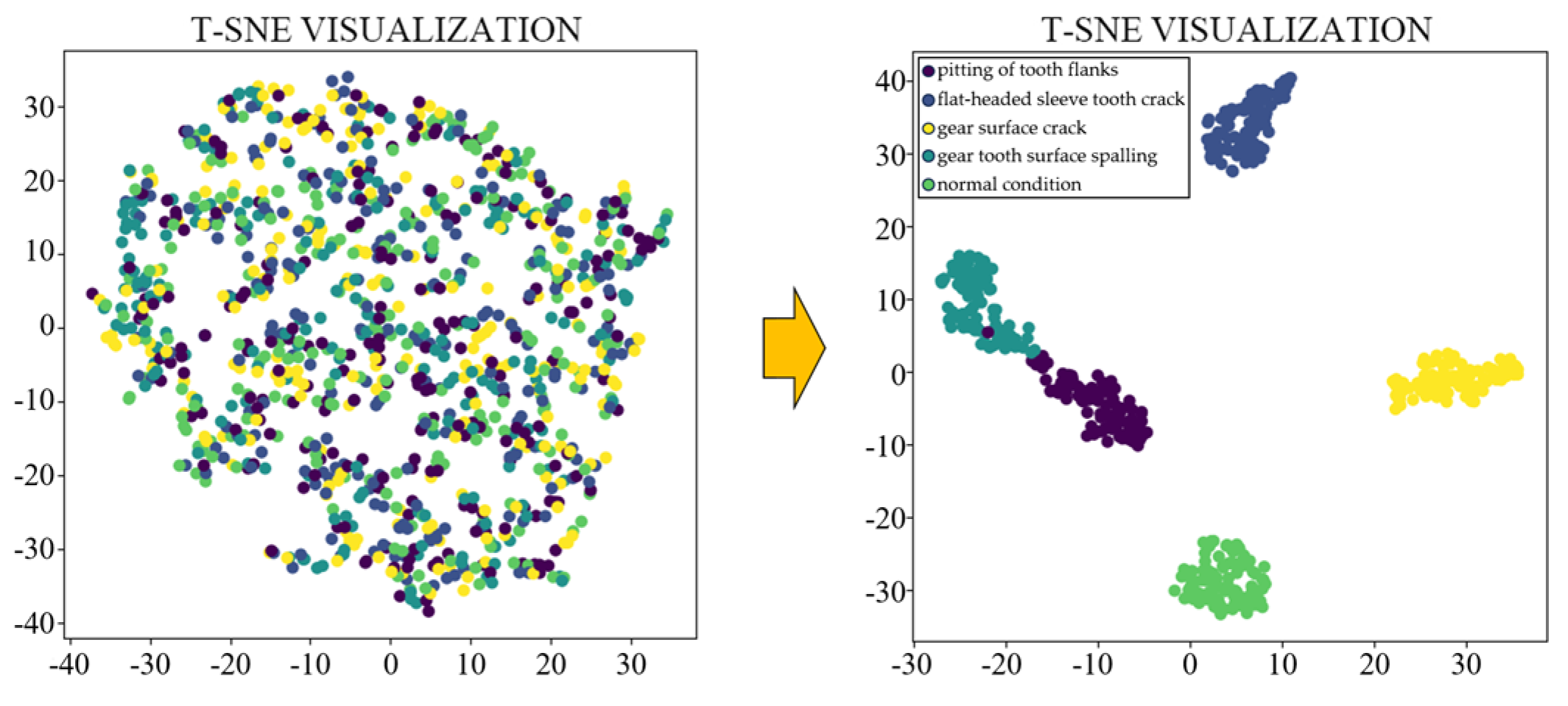
4. Model Performance Analysis of Fault Diagnosis
4.1. Dataset Introduction
4.2. Model Parameters and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Model Comparison
4.4. Verification of Noise Robustness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Chen, Z. System-Level Predictive Maintenance Optimization for No-Wait Production Machine–Robot Collaborative Environment under Economic Dependency and Hybrid Fault Mode. Processes 2024, 12, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.K.; Forbes, J.F.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Vaculik, V.; Dudzic, M. Dynamic modelling and simulation of a hot strip finishing mill. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 3208–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ben, X. Maintenance modelling for work rolls in hot finishing mill group with constraint of thermal character. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 62, 1846–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-N.; Shao, J.; Wang, X.-C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, Y.-Z. Research and application of approximate rectangular section control technology in hot strip mills. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Tang, T.; Sun, Y. Data-driven technology of fault diagnosis in railway point machines: Review and challenges. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2022, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; He, Z.; Zi, Y.; Liu, H. Gearbox fault diagnosis of rolling mills using multiwavelet sliding window neighboring coefficient denoising and optimal blind deconvolution. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Lin, S.; Peng, Y. Rolling mill bearings fault diagnosis based on improved multivariate variational mode decomposition and multivariate composite multiscale weighted permutation entropy. Measurement 2022, 195, 111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Kang, H.K.; Park, C.J.; Shin, K.H. Fault diagnosis of roll shape under the speed change in hot rolling mill. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2005, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Chen, M.; Gu, J.Y.; Cheng, L. Remote fault diagnosis system based on EMD and SVM for heavy rolling-mills. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 889–890, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zong, S.; Ling, Z. Fault diagnosis using kernel principal component analysis for hot strip mill. J. Eng. 2017, 2017, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wan, Z.; Pan, J.; Zi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Sun, H.; Yuan, J.; He, Z. Customized maximal-overlap multiwavelet denoising with data-driven group threshold for condition monitoring of rolling mill drivetrain. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 68–69, 44–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tang, T.; Tan, L.; Zhang, H. Fault Detection for Point Machines: A Review, Challenges, and Perspectives. Actuators 2023, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Peng, K. A novel parallel feature extraction-based multibatch process quality prediction method with application to a hot rolling mill process. J. Process. Control 2024, 135, 103166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shi, P.; Tian, J.; Xu, X.; Hua, C. Rolling mill health states diagnosing method based on multi-sensor information fusion and improved DBNs under limited datasets. ISA Trans. 2023, 134, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Shi, P. Improved GNN based on Graph-Transformer: A new framework for rolling mill bearing fault diagnosis. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Gao, H.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.; Han, D. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling mills based on dual attention- guided deep learning method under imbalanced data conditions. Measurement 2022, 204, 111993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Bao, L.; Hou, C.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Y. Multi-source domain adversarial graph convolutional networks for rolling mill health states diagnosis under variable working conditions. Struct. Health Monit. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Du, Y.; Li, Y. Railway Switch Machine Fault Diagnosis Considering Sensor Abnormality Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Bilbao, Spain, 24–28 September 2023; Volume 9, pp. 4834–4839. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Mauricio, A.; Li, W.; Gryllias, K. A deep learning method for bearing fault diagnosis based on Cyclic Spectral Coherence and Convolutional Neural Networks. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 140, 106683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.M.; Bouamama, B.O.; Boukerdja, M.; Pekpe, K.M. Bond Graph-CNN based hybrid fault diagnosis with minimum labeled data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 131, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiao, Y. A Fault Diagnosis Method for Rotating Machinery Based on CNN With Mixed Information. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 9091–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Yu, M. Fault diagnosis of bearings based on deep separable convolutional neural network and spatial dropout. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Fu, Q.; Goh, H.H. Thermal Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Equipment in Substations Using Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5005709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Wu, Q.; Huang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. A Lightweight Bearing Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Multi-Channel Depthwise Separable Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Bearing Intelligent Fault Diagnosis in the Industrial Internet of Things Context: A Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87329–87340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Liu, C.; Jiang, D. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine based on Long Short-term memory networks. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Zhang, H.; Sang, S.; Li, X.; He, W.; Liu, X. Bearing fault diagnosis based on combined multi-scale weighted entropy morphological filtering and bi-LSTM. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6647–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Qian, Z.; Zareipour, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, F. Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Deep Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory Under Time-Varying Non-Stationary Operating Conditions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 155219–155228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X. A novel fault diagnosis method based on CNN and LSTM and its application in fault diagnosis for complex systems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 1289–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Hu, C. Fault Detection of the Harmonic Reducer Based on CNN-LSTM With a Novel Denoising Algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Fault Detection for Motor Drive Control System of Industrial Robots Using CNN-LSTM-based Observers. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2023, 7, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, F. Reinforced convolutional neural network fault diagnosis of industrial production systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 299, 120466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Yan, S.; Tang, X.; Xu, C. Deep Convolutional and LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks for Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Under Strong Noises and Variable Loads. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66257–66269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, G. A Siamese CNN-BiLSTM-based method for unbalance few-shot fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. Meas. Control 2024, 57, 551–565. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, W.; Ullah, A.; Haq, I.U.; Muhammad, K.; Sajjad, M.; Baik, S.W. CNN features with bi-directional LSTM for real-time anomaly detection in surveillance networks. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2020, 80, 16979–16995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, M.; Weng, J.; Liu, Z.; Geng, G. Anomaly Detection for In-Vehicle Network Using CNN-LSTM With Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10880–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, E.; Xi, L. An ensemble framework based on convolutional bi-directional LSTM with multiple time windows for remaining useful life estimation. Comput. Ind. 2020, 115, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, J. Transfer remaining useful life estimation of bearing using depth-wise separable convolution recurrent network. Measurement 2021, 176, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilesanmi, A.E.; Ilesanmi, T.O. Methods for image denoising using convolutional neural network: A review. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2179–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Z.; Pang, S. Deep multi-scale convolutional transfer learning network: A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearings under variable working conditions and domains. Neurocomputing 2020, 24, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, W.; Montavon, G.; Lapuschkin, S.; Anders, C.J.; Muller, K.-R. Explaining Deep Neural Networks and Beyond: A Review of Methods and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhao, S. Improving Accuracy and Interpretability of CNN-Based Fault Diagnosis through an Attention Mechanism. Processes 2023, 11, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Ke, R.; Pu, Z.; Wang, Y. Stacked bidirectional and unidirectional LSTM recurrent neural network for forecasting network-wide traffic state with missing values. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 118, 102674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, X. Residual Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings Based on a CEEMDAN Algorithm Fused with CNN–Attention-Based Bidirectional LSTM Modeling. Processes 2024, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Yang, W.; Dong, R.; Hu, J. Limited Data Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis With Few-Shot Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 2169–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


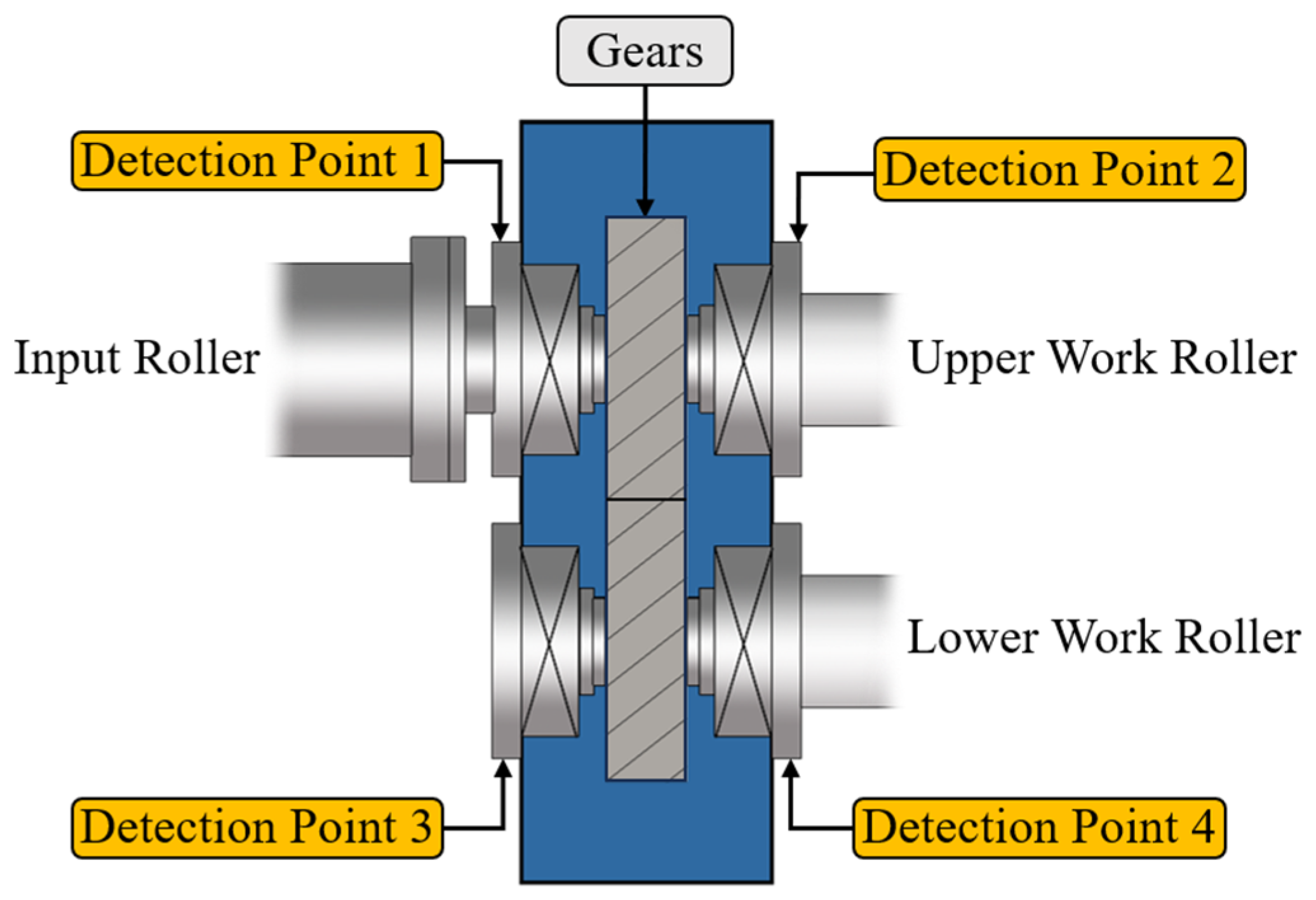


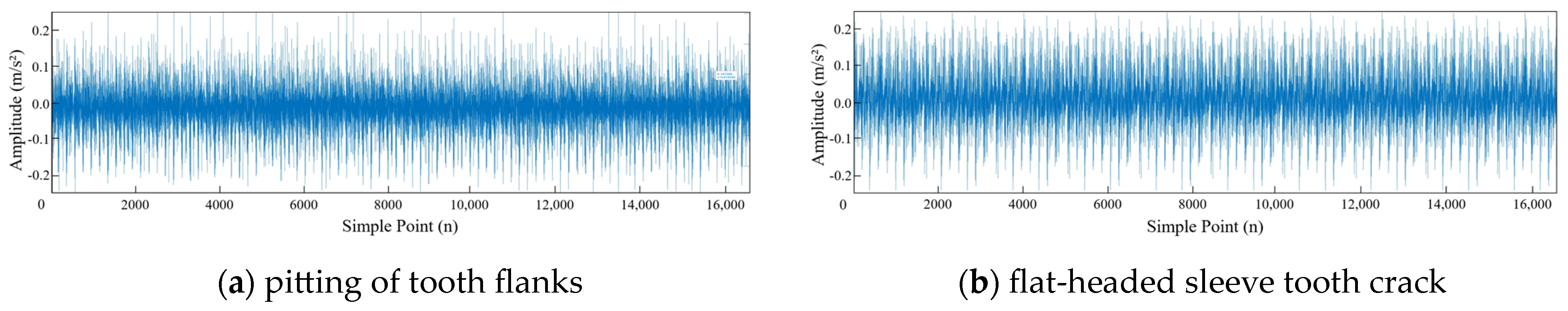
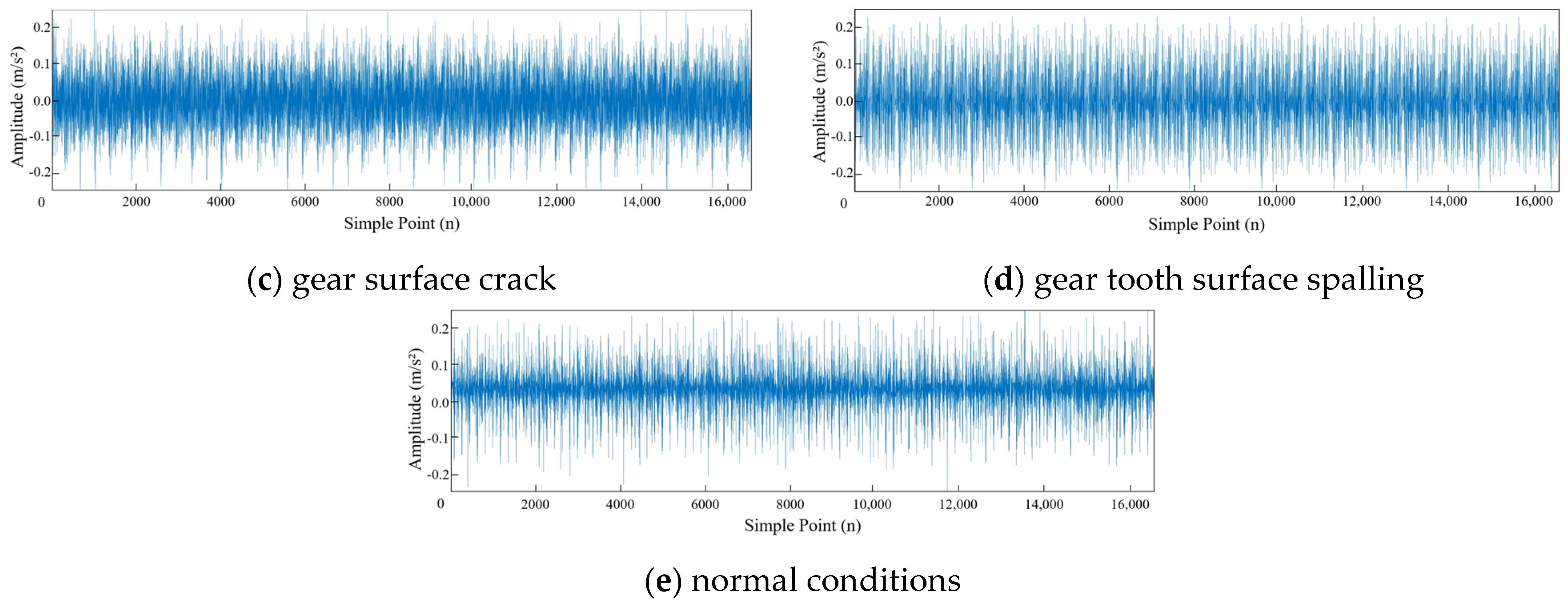
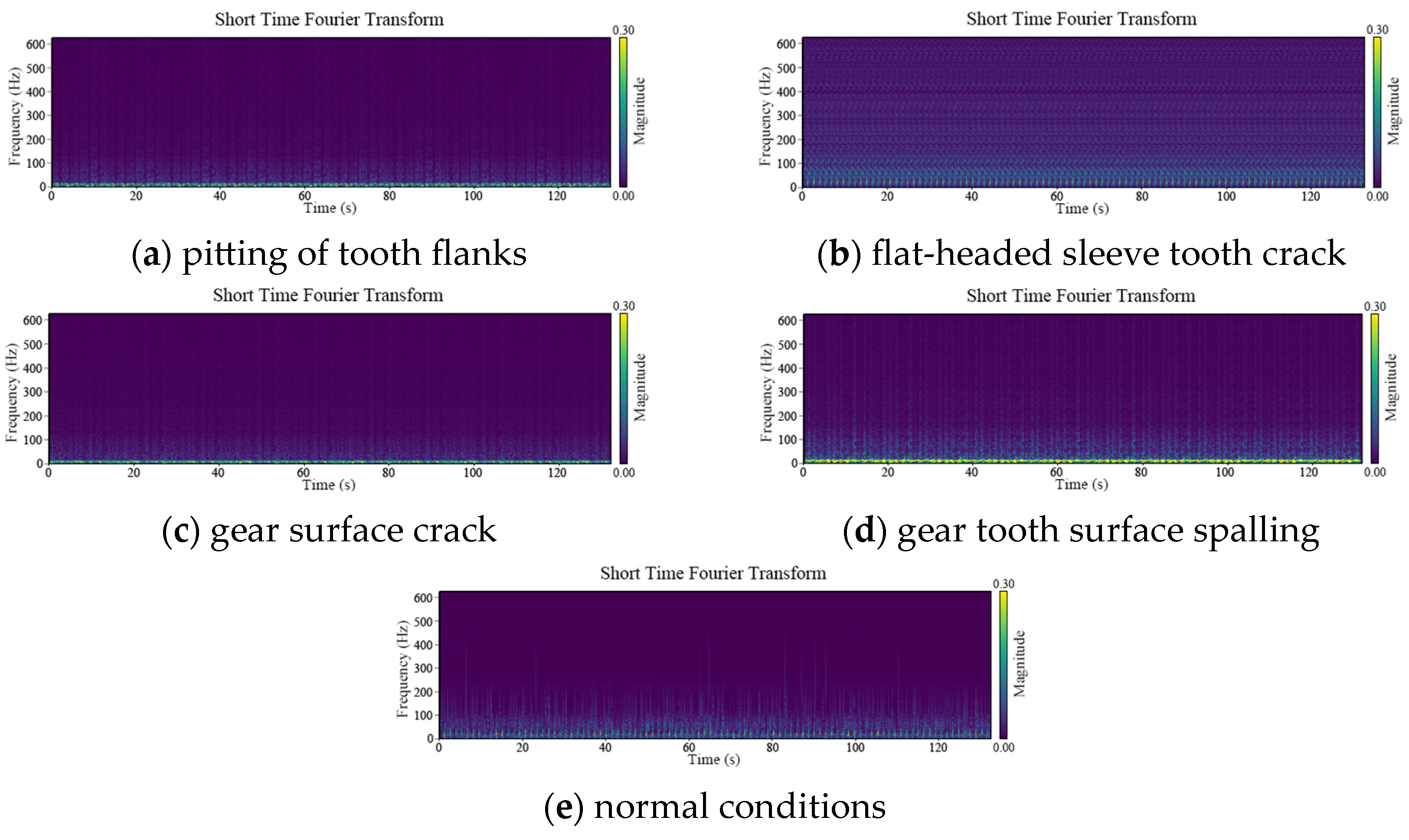



| Specifications | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Production line name | Hot rolling 1580 |
| Capacity | 3 million tons per year |
| Thickness range | 1.2 mm to 12.5 mm |
| Maximum width | 1580 mm |
| Production speed | 5 m/s to 15 m/s |
| On year | Since 2000 |
| Number of stands | 7 finishing mills |
| Fault Location | Label | Sample Number | Training/Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pitting of tooth flanks | A | 322 | 225/97 |
| Flat-headed sleeve tooth crack | B | 322 | 225/97 |
| Gear surface crack | C | 322 | 225/97 |
| Gear tooth surface spalling | D | 322 | 225/97 |
| Normal conditions | E | 322 | 225/97 |
| Network Layer | Parameter | Output Size |
|---|---|---|
| Input | 512 × 1 | |
| ConV | Kernel Size = 32; Stride = 4; Channel Size = 24 | 121 × 24 |
| Deep_ConV | Kernel Size = 16; Stride = 1; Channel Size = 24; Padding = same | 121 × 24 |
| ReLU | ||
| BatchNormal | ||
| Point_ConV | Kernel Size = 1; Stride = 1; Channel Size = 24; Padding = same | 121 × 24 |
| Dropout | Dropout = 0.5 | |
| Permute | ||
| BiLSTM | Input size = 24; hidden size = 16; batch first = True; bidirectional = True | 2 × 16 |
| Permute | ||
| AdaptiveAvgPool | ||
| Linear | 16 × 2; out features = 5 | 1 × 5 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 86.99% | 86.78% | 86.87% | 86.78% |
| MCCNN | 90.13% | 90.08% | 9011% | 90.08% |
| WDCNN | 88.11% | 87.81% | 87.87% | 87.81% |
| Bi-LSTM | 76.73% | 76.86% | 76.57% | 76.86% |
| CNN | 90.62% | 90.08% | 90.10% | 90.08% |
| Proposed Model | 97.64% | 97.46% | 97.46% | 97.46% |
| Model | Parameters | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 6.2 × 104 | 3.2 × 107 |
| MCCNN | 5.7 × 104 | 3.2 × 107 |
| WDCNN | 8.7 × 104 | 5.1 × 106 |
| Bi-LSTM | 1.2 × 106 | 2.1 × 106 |
| CNN | 2.5 × 105 | 4.7 × 106 |
| Proposed Model | 7.1 × 103 | 4.6 × 106 |
| Model | 4DB | 6DB | 8DB |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 61.36% | 68.18% | 58.06% |
| MCCNN | 83.88% | 72.52% | 70.87% |
| WDCNN | 88.22% | 73.55% | 78.10% |
| Bi-LSTM | 69.42% | 66.94% | 70.04% |
| CNN | 85.74% | 44.21% | 59.09% |
| Proposed model | 88.22% | 87.40% | 91.12% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, H.; Yue, X.; Cheng, Y. Fault Intelligent Diagnosis for Distribution Box in Hot Rolling Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Bi-LSTM. Processes 2024, 12, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091999
Guo Y, Zhou D, Chen H, Yue X, Cheng Y. Fault Intelligent Diagnosis for Distribution Box in Hot Rolling Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Bi-LSTM. Processes. 2024; 12(9):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091999
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yonglin, Di Zhou, Huimin Chen, Xiaoli Yue, and Yuyu Cheng. 2024. "Fault Intelligent Diagnosis for Distribution Box in Hot Rolling Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Bi-LSTM" Processes 12, no. 9: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091999
APA StyleGuo, Y., Zhou, D., Chen, H., Yue, X., & Cheng, Y. (2024). Fault Intelligent Diagnosis for Distribution Box in Hot Rolling Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Bi-LSTM. Processes, 12(9), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12091999






