Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers
2.1. Templates
2.2. Monomers and Crosslinkers
| Template | Monomers and Ligands | Crosslinker | Supporting Material | Polymerisation Technique | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(II) and Pb(II) | Popain | APTES | Fe3O4-SiO2 | Surface imprinting combined with sol-gel | [48] |
| Cd(II) | Waste beer yeast | TEOS | Fe3O4-SiO2 | Surface imprinting combined with sol-gel | [65] |
| Au(III) | TEOS and Y-MAPS | EDGMA | Hybrid monolithinic vinyl functionalised Fe3O4 | One-pot synthesis (sol-gel combined with free radical polymerisation | [67] |
| Ag(I) | Methacrylic acid | EDGMA | Core-shell of Fe3O4, SiO2, and TIO2 | Sol-gel combined with surface imprinting | [68] |
| Li(I) | Sing N-propylacrylamide and benzo-12-crown 4-ether | EDGMA | Magnetic carbon nanosphere | Surface imprinting | [69] |
| Cd(II) | 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid | N,N′-Methylenebisacrylamide | Fe3O4@SiO2 | Surface imprinting and chemical grafting | [37] |
| Cr(VI) | 4-vinyl pyridine | EDGMA | Fe3O4 | Surface imprinting | [32] |
| Ni(II) | Chitosan+ Acrylic acid | N′ N-methylene bis-acrylamide | Fe3O4 Multi-walled carbon nanotubes | Inverse emulsion system | [63] |
| Ni(II) | Citric acid | Polyvinyl alcohol | Bentonite/CoFe2O4/SiO2 @ Polyvinyl alcohol | Surface imprinting | [70] |
| Cd(II) and Pb(II) | Methacrylic acid | EDGMA | Fe3O4@SiO2@NH2 | Ultrasonic-mediated precipitation polymerisation | [51] |
| Ni(II) | Methacrylic acid | EDGMA | Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 | Surface imprinting | [71] |
| Pb(II) | Itaconic acid | EDGMA | Fe3O4@itonic acid | Surface imprinting | [72] |
2.3. Solid Matrix
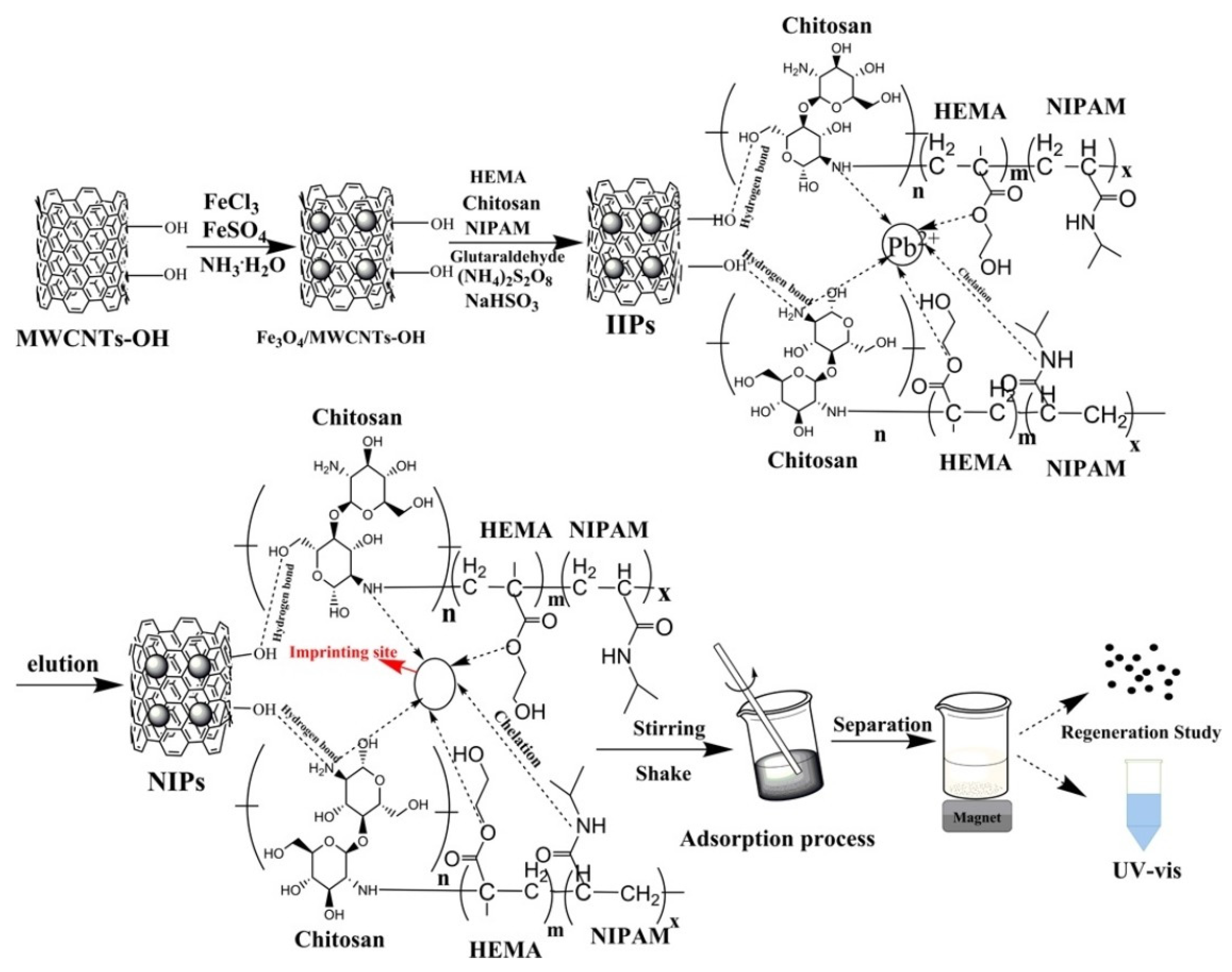
2.3.1. Magnetic Carbon Nanotubes
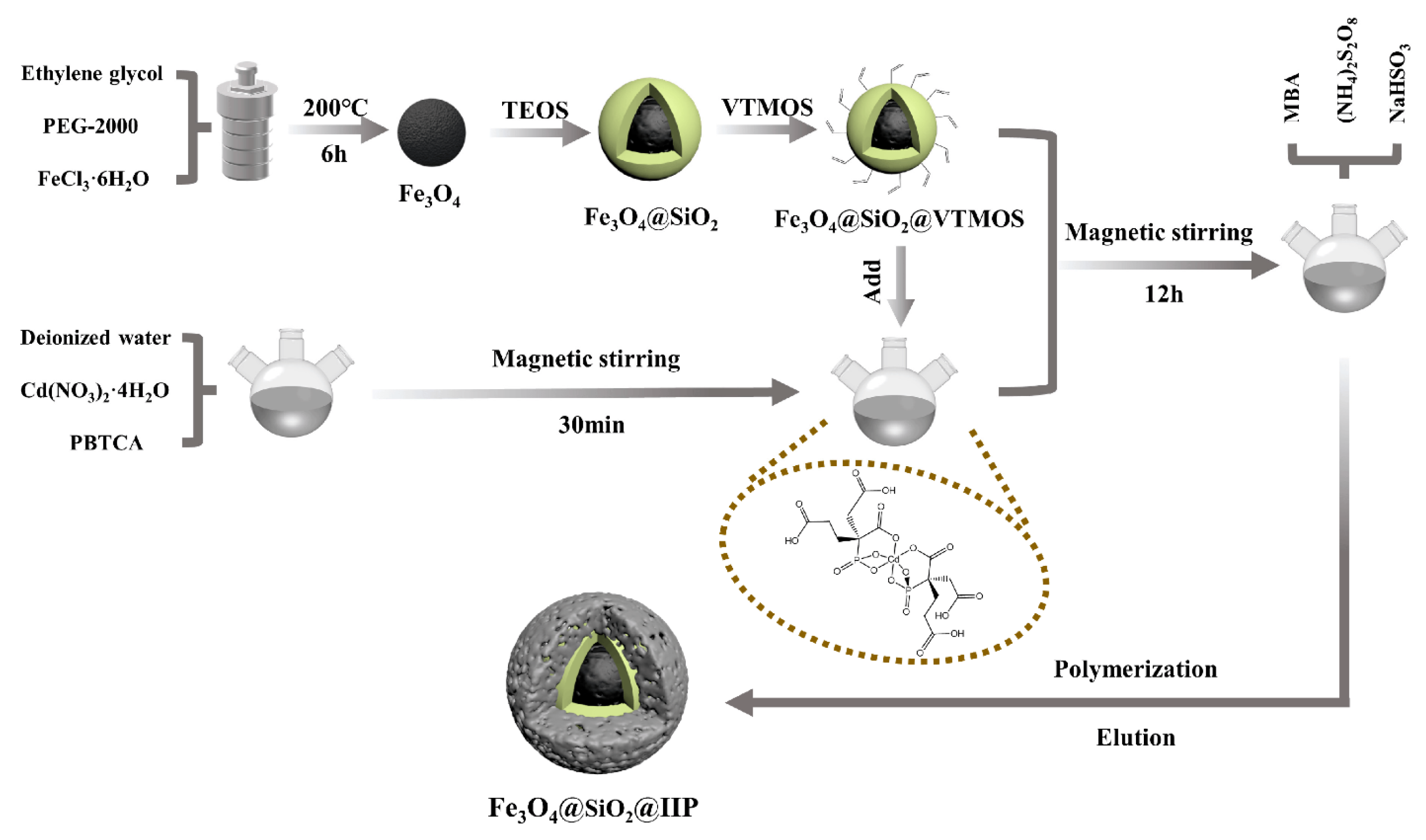
2.3.2. Magnetic Silica
2.3.3. Magnetic Graphene Oxide
2.3.4. Magnetic Chitosan
2.3.5. Other Supporting Materials
3. Application of Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers
3.1. Electrochemical Detection of Metals
3.2. Preconcentration of Heavy Metals
3.3. Adsorption Performance of IIPs
Influential Parameters in the Adsorption of Metals
- Sample pH
- Adsorbent dose
- Contact time
- Initial metal ion concentration
- Temperature
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIIPs | Magnetic ion-imprinted polymers |
| WHO | The World Health Organisation |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| Fe3O4 | Iron oxide |
| Fe@MgO | Iron magnesium oxide |
| IIPs | ion-imprinted polymers |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-IIP | Iron oxide-coated silicon dioxide ion-imprinted polymers |
| SMACNT-MIIP | silanised magnetic amino-functionalised carbon nanotube-based multi-ion-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@AECS-IIP | Functionalised silica-coated magnetite aminoethyl chitosan imprinted polymers |
| NIP | Non-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4@VTES-IIP | Iron(III) oxide functionalised with vinyltriethoxysilane ion-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4@SBA-15-NH2-IIP | Magnetic SBA silica NH2 ion-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4@MWCNT-IIP | Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube ion-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4/SiO2/CS-IIP | Magnetic silica chitosan ion-imprinted polymer |
| Fe3O4/MWCNTs-COOH | Iron(III) oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalised with carboxyl groups. |
| IIP/MNPs-oxine/GCE | Ion-imprinted polymer/magnetic nanoparticles modified with oxine/glassy carbon electrode |
| APTES | 3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl orthosilicate |
| EDGMA | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| Bentonite/CoFe2O4/SiO2 @ Polyvinyl alcohol | Bentonite/cobalt ferrite/silicon dioxide encapsulated with polyvinyl alcohol |
| Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 | Iron(III) oxide coated with silica and functionalised with amine groups |
| Fe3O4@ITA | Itaconic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles |
| TIO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| Fe3O4@MWCNT-IIP | Magnetic multiwalled ion-imprinted polymer |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2/GO-IIP | Manganese ferrite silicon dioxide graphene oxide ion-imprinted polymer |
| MnFe2O4 | Manganese oxide |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| MDMS@MAH-Cd-IIP | Magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica functionalised with maleic anhydride cadmium ion-imprinted polymer |
References
- Nazaripour, M.; Reshadi, M.A.M.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Nazaripour, M.; Bazargan, A. Research Trends of Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Environments. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, L.; Yu, H. Application of Co-Pyrolysis Biochar for the Adsorption and Immobilization of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Environmental Substrates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ahmed, A.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Simultaneous Adsorption of Heavy Metals and Organic Dyes by β-Cyclodextrin-Chitosan Based Cross-Linked Adsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, R.; Gopinath, K.P.; Kumar, P.S. Adsorptive Separation of Toxic Metals from Aquatic Environment Using Agro Waste Biochar: Application in Electroplating Industrial Wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthi, D.; Jose, J.M.A.; Gladis, E.H.E.; Shinu, P.M.S.; Joseph, J. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water Using Adsorbents from Agro Waste Materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 1794–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; An, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wei, X.; Lai, B. Efficiencies and Mechanisms of Heavy Metals Adsorption on Waste Leather-Derived High-Nitrogen Activated Carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Electrospun SiO2-MgO Hybrid Fibers for Heavy Metal Removal: Characterization and Adsorption Study of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Lagerquist, L.; Qin, M.; Willför, S.; Xu, C.; Fatehi, P. Ultrafast Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions onto Functionalized Lignin-Based Hybrid Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fato, F.P.; Li, D.W.; Zhao, L.J.; Qiu, K.; Long, Y.T. Simultaneous Removal of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions from River Water Using Ultrafine Mesoporous Magnetite Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7543–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Baloch, H.A.; Griffin, G.J.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Mubarak, N.M.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Tanksale, A. Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes From Wastewater. In Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Almomani, F.; Bhosale, R.; Khraisheh, M.; Kumar, A.; Almomani, T. Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, S.; Zhou, R.; Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Miller, R.H.B.; Hao, T.; Yang, R. Synthesis of Ion Imprinted Magnetic Nanocomposites and Application for Novel Selective Recycling of Ni(II). J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, K.; Chen, Q.; Wang, A.; Chen, W. Application of Magnetic Ferrite Nanoparticles for Removal of Cu(II) from Copper-Ammonia Wastewater. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Magnetic Zr-MOFs Nanocomposites for Rapid Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Dyes from Water. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, A.; Alipour, E.; Sadeghi, M. Superabsorbent Magnetic Fe3O4-Based Starch-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Efficient Removal of Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions from Water. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, D.; Kong, X.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, C. Anionic Polypeptide Poly(Γ-Glutamic Acid)-Functionalized Magnetic Fe3O4-GO-(o-MWCNTs) Hybrid Nanocomposite for High-Efficiency Removal of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) Heavy Metal Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wang, W.; Peng, Z.; Tan, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X. Facile Fabrication of Fe@MgO Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ion and Dye from Water. Powder Technol 2018, 326, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wu, L.; Yu, N.; Luo, Z.; Geng, W. Preparation of Magnetic Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Functionalized Fe3O4 for Fast and Selective Adsorption of Cobalt Ions from Water. Water 2022, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sedki, M.; Shen, Y.; Mulchandani, A.; Gao, G. Chemiresistor Sensor Based on Ion-Imprinted Polymer (IIP)-Functionalized RGO for Cd(II) Ions in Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashami, Z.S.; Taheri, A.; Alikarami, M. Synthesis of a Magnetic SBA-15-NH2@Dual-Template Imprinted Polymer for Solid Phase Extraction and Determination of Pb and Cd in Vegetables; Box Behnken Design. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1204, 339262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, S.J. Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Mesoporous Silica for Selective Removal of Co(II) from Radioactive Wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Javed, H.; Chauhan, A.; Ahmad, I.; Rais, S. Triethylenetetramine-Grafted Magnetite Graphene Oxide-Based Surface-Imprinted Polymer for the Adsorption of Ni(II) in Food Samples. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Shao, N.; Hou, L.; Zhu, X. Fabrication of an Efficient Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Sandwich-like Graphene Oxide Composite Materials for Fast and Selective Removal of Lead Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 566, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shang, H.; Sun, X.; Hou, L.; Wen, M.; Qiao, Y. Preparation of Thermo-Sensitive Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymers Based on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composites for Selective Adsorption of Lead(II) Ion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, F.H. The Preparation of Specific Adsorbents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1949, 35, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Jia, M.; Zhao, H.; Kang, L.; Shi, L.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Optical Sensors for Pesticides in Foods: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; He, C.; Liu, S. Recent Advances and Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Solid-Phase Extraction for Real Sample Analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 274–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, J.; Qin, M.; Guo, T. Molecularly Imprinted Nanocapsule Mimicking Phosphotriesterase for the Catalytic Hydrolysis of Organophosphorus Pesticides. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Malivindi, R.; Delbue, S.; Ferrante, P.; Parapini, S.; Galeazzi, R.; Cavarelli, M.; Cilurzo, F.; et al. Design and Development of Plastic Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 RBD Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers That Inhibit in Vitro Virus Infection. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16885–16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Guerreiro, A.; Karim, K.; Sandström, N.; Ostanin, V.P.; van der Wijngaart, W.; Piletsky, S.A.; Ghosh, S.K. Direct Detection of Small Molecules Using a Nano-Molecular Imprinted Polymer Receptor and a Quartz Crystal Resonator Driven at a Fixed Frequency and Amplitude. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158, 112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Du, J.; Zhang, B.; Ren, Z. Preparation of Highly Efficient Ion-Imprinted Polymers with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Carrier for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, H.; Deguchi, J.; Tsuchida, E. Selective Adsorption of Metal Ions on Crosslinked Poly (Vinylpyridine) Resin Prepared with a Metal Ion as a Template. Chem. Lett. 1976, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cao, H.; Mai, D.; Ye, T.; Wu, X.; Yuan, M.; Yu, J.; Xu, F. A Novel Morphological Ion Imprinted Polymers for Selective Solid Phase Extraction of Cd(II): Preparation, Adsorption Properties and Binding Mechanism to Cd(II). React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 151, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.M.; Ghiorghita, C.A.; Dragan, E.S.; Humelnicu, D.; Dinu, M.V. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2023, 28, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Huang, C.; Ma, S.; Gong, B.; Ou, J. Rapid Adsorption and Detection of Copper Ions in Water by Dual-Functional Ion-Imprinted Polymers Doping with Carbon Dots. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Li, Y.; Deng, X. Selective Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism for Cd(II) in Aqueous Solution with a Recoverable Magnetie-Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer. Polymers 2023, 15, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, F.; Ning, H.; He, M.; Chi, R.; Yin, W. Highly Effective and Selective Recovery of Gd(III) from Wastewater by Defective MOFs-Based Ion-Imprinted Polymer: Performance and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nchoe, O.B.; Klink, M.J.; Mtunzi, F.M.; Pakade, V.E. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of β-Cyclodextrin-Based Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Selective Sequestration of Cr(VI) Ions from Aqueous Media: Kinetics and Isotherm Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 111991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rais, S.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, I.; Kumar, S.; Chauhan, A.; Javed, H. Preparation of a New Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer and Optimization Using Box-Behnken Design for Selective Removal and Determination of Cu(II) in Food and Wastewater Samples. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagirani, M.S.; Balouch, A.; Mahesar, S.A.; Kumar, A.; Baloch, A.R.; Abdullah; Bhanger, M.I. Fabrication of Cadmium Tagged Novel Ion Imprinted Polymer for Detoxification of the Toxic Cd2+ ion from Aqueous Environment. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumkar, V.V.; Galamboš, M.; Viglašová, E.; Daňo, M.; Šmelková, J. Ion-Imprinted Polymers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption of Radionuclides. Materials 2021, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Cadmium Ion-Imprinted Polymers for Adsorption and Detection of Cadmium Ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivián-Castro, E.Y.; Zepeda-Navarro, A.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Flores-Alamo, M.; Mata-Ortega, B. Ion-Imprinted Polymer Structurally Preorganized Using a Phenanthroline-Divinylbenzoate Complex with the Cu(II) Ion as Template and Some Adsorption Results. Polymers 2023, 15, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giove, A.; El Ouardi, Y.; Sala, A.; Ibrahim, F.; Hietala, S.; Sievänen, E.; Branger, C.; Laatikainen, K. Highly Selective Recovery of Ni(II) in Neutral and Acidic Media Using a Novel Ni(II)-Ion Imprinted Polymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, N.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, M. In-Suit Ion-Imprinted Bio-Sorbent with Superior Adsorption Performance for Gallium(III) Capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakavula, S.; Biata, N.R.; Dimpe, K.M.; Pakade, V.E.; Nomngongo, P.N. Multi-Ion Imprinted Polymers (MIIPs) for Simultaneous Extraction and Preconcentration of Sb(III), Te(IV), Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Drinking Water Sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Wei, S.; Xiao, C.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z. Novel Dual-Template Magnetic Ion Imprinted Polymer for Separation and Analysis of Cd2+ and Pb2+ in Soil and Food. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, M.; Yin, J.; Shui, R.; Yang, S.; Hua, D. Dual Ion-Imprinted Mesoporous Silica for Selective Adsorption of U(VI) and Cs(I) through Multiple Interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6322–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L. Synthesis of Multi-Ion Imprinted Polymers Based on Dithizone Chelation for Simultaneous Removal of Hg2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from Aqueous Solutions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44087–44095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Balouch, A.; Alveroglu, E.; Ullah, R.; Shah, M.T.; Jagirani, M.S.; Mahar, A.M.; Chang, S.A. Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Ultrasonic Assisted Dual Metal Imprinted Polymer: A Real Magnetic Sorbent for Simultaneous Removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from Water Samples. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.; Lu, H.; Xu, S. Ion Imprinted Dual Reference Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe for Respective and Simultaneous Detection of Fe3+ and Cu2+. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 6404–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yu, C.; Xu, S. A Dual Reference Ion-Imprinted Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe for Simultaneous Detection of Silver (I) and Lead (II). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahangdale, D.; Kumar, A. Chitosan as a Substrate for Simultaneous Surface Imprinting of Salicylic Acid and Cadmium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Qiu, F.; Yan, Y. A Versatile Strategy to Fabricate Dual-Imprinted Porous Adsorbent for Efficient Treatment Co-Contamination of Λ-Cyhalothrin and Copper(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Hu, T.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Deng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J. Highly Efficient Extraction of Lead Ions from Smelting Wastewater, Slag and Contaminated Soil by Two-Dimensional Montmorillonite-Based Surface Ion Imprinted Polymer Absorbent. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Deng, Y.; Merchant, A.; Su, J.; Zeng, G.; Long, X.; Zhong, M.E.; Yang, L.; Gong, D.; Bai, L.; et al. Insights into Surface Ion-Imprinted Materials for Heavy Metal Ion Treatment: Challenges and Opportunities. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2022, 52, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Liu, X.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Hao, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, F. “One-Pot” Synthesis of Mesoporous Ion Imprinted Polymer for Selective Adsorption and Detection of As(V) in Aqueous Phase via Cooperative Extraction Mechanism. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Xu, Q. Nanomaterials-Based Ion-Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for Heavy Metal Ions Detection: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushani, M.; Saedi, Z.; Hamdi, F.; Dizajdizi, B.Z. Preparation of an Electrochemical Sensor for Detection of Manganese (II) Ions Using Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Chitosan-Ionic Liquid Nanocomposite Decorated with Ion Imprinted Polymer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 804, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, H.; Xing, J. Synthesis of Multidentate Functional Monomer for Ion Imprinting. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Green Multi-Functional Monomer Based Ion Imprinted Polymers for Selective Removal of Copper Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Colloid Interface. Sci. 2019, 541, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Shang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. Synthesis and Application of Ion Imprinting Polymer Coated Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Selective Adsorption of Nickel Ion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Peng, J. Highly Selective Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Wei, S.; Chen, D.; Lan, W.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Z. Preparation of Magnetic Ion Imprinted Polymer with Waste Beer Yeast as Functional Monomer for Cd(Ii) Adsorption and Detection. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23474–23483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A. A Note about Crosslinking Density in Imprinting Polymerization. Molecules 2021, 26, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Song, R.; Zhu, Z. Fe3O4/SiO2/CS Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitivity and Selectivity Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 113, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Chen, L. Sensitive, Selective and Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Multiple Heavy Metals in Environment and Food Using a Lowcost Fe3O4 Nanoparticles/Fluorinated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Sensor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Rais, S. A Facile Approach for Grafting Ion Imprinted Polymer onto Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Selective Removal and Preconcentration of Cadmium in Food and Wastewater Samples Prior to Atomic Spectrometric Determination. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Taher, M.A.; Afzali, D.; Mostafavi, A.; Ghanei-Motlagh, M. Synthesis and Application of Novel Ion-Imprinted Polymer Coated Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Selective Solid Phase Extraction of Lead(II) Ions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, E.; Arabkhani, P.; Haddadi, H.; Asfaram, A.; Varma, R.S. A Silanized Magnetic Amino-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Multi-Ion Imprinted Polymer for the Selective Aqueous Decontamination of Heavy Metal Ions. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 21704–21716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C.; Sun, C. Determination of Cesium Ions in Environmental Water Samples with a Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Imprinted Potentiometric Sensor. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 10075–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.E.; Rahman, M.M.; Dhahi, T.S.; Kashif, M.; Sarkar, M.S.; Basirun, W.J.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Bhargava, S.K. Nanostructured Materials: Bioengineering Platforms for Sensing Nucleic Acids. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Xie, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. A Novel Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Graphene Oxide-Mesoporous Silica Nanosheet for Fast and Efficient Removal of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Solution. J. Colloid Interface. Sci. 2018, 514, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Xia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ai, Z.; Yin, W.; Xia, M.; Yu, J.; Chi, R.A.; Yue, Q. Ion-Imprinted Mesoporous Silica/Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composites Functionalized with Schiff-Base for Selective Cu(II) Capture and Simultaneously Being Transformed as a Robust Heterogeneous Catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Huang, R.F.; Ma, X.G.; Guo, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.M. Selective Fluorescence Sensor Based on Ion-Imprinted Polymer-Modified Quantum Dots for Trace Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7165–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Dolgormaa, A.; Fang, H.; Guo, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, J. A Novel Magnetic Cd(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymer as a Selective Sorbent for the Removal of Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 1874–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh, F.; Taghizadeh, M.; Hassanpour, S. Preparation of a Novel Magnetic Pd(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymer for the Fast and Selective Adsorption of Palladium Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18493–18508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Alveroǧlu, E.; Balouch, A.; Talpur, F.N.; Jagirani, M.S.; Abdullah; Mahar, A.M.; Pato, A.H.; Mal, D.; Lal, S. Fabrication of Chromium-Imprinted Polymer: A Real Magneto-Selective Sorbent for the Removal of Cr(vi) Ions in Real Water Samples. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 18668–18678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar-Motlagh, M.; Es’haghi, Z. Magnetic Porous Ion Imprinted Polymer Based on Surface Polymerization and Nano-ZnO as Sacrificial Support for Selective Extraction and Determination of Pb (II) in Water Samples and Cosmetics. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Zhu, Z.; Song, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. An Ion-Imprinted Sensor Based on Chitosan-Graphene Oxide Composite Polymer Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Environmental Sensing Application. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 317, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Song, G.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Ni, X.; Xu, W. A Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor Based on Ion Imprinted Polymers with Gold Nanoparticles for High Selective Detecting Cd (II) Ions in Real Samples. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Koduru, J.R.; Karri, R.R. A Comprehensive Review of Applications of Magnetic Graphene Oxide Based Nanocomposites for Sustainable Water Purification. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C. Adsorption of Radionuclides on Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; Li, H. Selective Removal of As(III) Using Magnetic Graphene Oxide Ion-Imprinted Polymer in Porous Media: Potential Effect of External Magnetic Field. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yang, C.; Rao, X.; Hu, L.; Bao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X. Fabrication of Recoverable Magnetic Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Graphene Oxide for Fast and Selective Removal of Lead Ions from Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, X. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Surface Lithium Ion-Imprinted Material towards Lithium Extraction from Salt Lake. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Ye, S.Q.; Yang, X.T.; Zhu, B.S.; Li, W.L.; He, H.X.; Deng, X.J. A Recoverable Magnetic Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Graphene Oxide for Fast and Selective Adsorption of Ni(Ii) from Aqueous Solution: Experimental and DFT Calculations. New J. Chem. 2022, 47, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, C.; Lacin, G.; Yilmaz, V.; Coldur, F.; Caglar, B.; Cubuk, O.; Isildak, I. Electrochemical Determination of Copper(II) in Water Samples Using a Novel Ion-Selective Electrode Based on a Graphite Oxide–Imprinted Polymer Composite. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 1890–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lu, T.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Preparation and Properties of GO-Based Lanthanum Ion-Imprinted Polymer, La-IIP-MAA/Fe3O4-GO. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, F.; Taheri, A.; Shahmari, M. Application of Selective Solid-Phase Extraction Using a New Core-Shell-Shell Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer for the Analysis of Ultra-Trace Mercury in Serum of Gallstone Patients. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2758–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Chitosan as an Environment-Friendly Biomaterial—A Review on Recent Modifications and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatullayeva, S.; Tagiyev, D.; Zeynalov, N.; Mammadova, S.; Aliyeva, E. Recent Advances of Chitosan-Based Polymers in Biomedical Applications and Environmental Protection. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, E487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Tu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liao, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, N. A Novel Ion-Imprinted Polymer Induced by the Glycylglycine Modified Metal-Organic Framework for the Selective Removal of Co(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, K. Study on the Adsorption Behavior of Glutaric Acid Modified Pb(II)Imprinted Chitosan-Based Composite Membrane to Pb(II)in Aqueous Solution. Mater. Lett. 2019, 251, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, X. Adsorption of Ni(II) Ion on Ni(II) Ion-Imprinted Magnetic Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, Q. Selective Adsorption Behavior of Ion-Imprinted Magnetic Chitosan Beads for Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Tang, D.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Q. Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polyacrylonitrile-Chitosan Electro-Spun Nanofibrous Membrane as Recyclable Adsorbent with Selective Heavy Metal Removal and Antibacterial Fouling in Water Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.; Dadfarnia, S.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Ranjbar, M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of a Zn (II)-Imprinted Polymer Grafted on Graphene Oxide/Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite for Selective Extraction of Zinc Ions from Different Food Samples. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Liu, S.; Shao, N.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetic Chitosan-Mediated GO Dual-Template Imprinted Polymer for the Simultaneous and Selective Removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Cui, K.; Li, H.; Feng, J.; Pu, X.; Xiong, W.; Liu, N.; Yuan, G. Novel MOFs-Based Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Selective Separation of Cobalt Ions from Waste Battery Leaching Solution. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2022, 536, 120922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahaghin, Z.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Mousavi, H.Z. Novel Ion Imprinted Polymer Electrochemical Sensor for the Selective Detection of Lead(II). Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfà, J.; Pupin, R.R.; Sotomayor, M.; Pividori, M.I. Magnetic-Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6141–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanei-Motlagh, M.; Taher, M.A. Magnetic Silver(I) Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles on a Carbon Paste Electrode for Voltammetric Determination of Silver(I). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkashvand, M.; Gholivand, M.B.; Azizi, R. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of a Novel Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based Voltammetric Sensor for Selective Extraction and Trace Determination of Cobalt (II) Ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D. Double-Ion Imprinted Polymer @magnetic Nanoparticles Modified Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for Simultaneous Analysis of Cerium and Gadolinium Ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 875, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.H.; Alatawi, A.; Monier, M. Diacetylmonoxine Modified Chitosan Derived Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Selective Solid-Phase Extraction of Nickel (II) Ions. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 151, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Min, H.; Wu, X.H.; Cui, X.B.; Chen, Y.J.; Lian, H.Z.; Sheng, D. Hybrid Monolith Assisted Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer Extraction Coupled with ICP-MS for Determination of Trace Au(III) in Environmental and Mineral Samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, Z.; Afkhami, A.; Madrakian, T.; Kamalabadi, M. Application of Magnetic Ion Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Quantification of Al3+ and Be2+ Ions Using the Mean Centering of Ratio Spectra Method. Talanta 2021, 225, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landarani, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A. A Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer Composed of Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and Polymerized 4-Vinyl Pyridine and 2,6-Diaminopyridine for Selective Extraction and Determination of Lead Ions. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 7561–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahaghin, Z.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Mousavi, H.Z. Determination of Cadmium(II) Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with a Cd-Ion Imprinted Polymer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 810, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; AlJarrah, M.; Alrebaki, M.; Mayyas, M. Nanoionic Exchanger with Unprecedented Loading Capacity of Uranium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Balouch, A.; Alveroğlu, E.; Jagirani, M.S.; Abdullah; Mughal, M.A.; Mal, D. Fabrication of Nickel-Tagged Magnetic Imprinted Polymeric Network for the Selective Extraction of Ni(II) from the Real Aqueous Samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40022–40034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibmehr, Z.; Faghihian, H. Preparation of Highly Selective Magnetic Cobalt Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Functionalized SBA-15 for Removal Co2+ from Aqueous Solutions. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, G.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Zhu, X. Histidine-Mediated Dendritic Mesoporous Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer toward Effective and Recoverable Cadmium Removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.H.; Beyki, M.H. Construction of 1, 10-Phenanthroline Functionalized Magnetic Starch as a Lead (II) Tagged Surface Imprinted Biopolymer for Highly Selective Targeting of Toxic Lead Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, X.; Ye, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, L.; Li, W.; He, H. Selective Removal and Recovery of Ni(Ii) Using a Sulfonic Acid-Based Magnetic Rattle-Type Ion-Imprinted Polymer: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34571–34583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Chauhan, A. Tailored-Designed Material for the Preconcentration of Cd(II) on Glycidyl Methacrylate-Based Ion–Imprinted Polymer for Flame Atomic Absorption for Trace Determination in Real Samples: Multivariate Optimization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69068–69081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Shu, H.; Huang, Y.; Tu, X. Novel Cu (II) Magnetic Ion Imprinted Materials Prepared by Surface Imprinted Technique Combined with a Sol-Gel Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


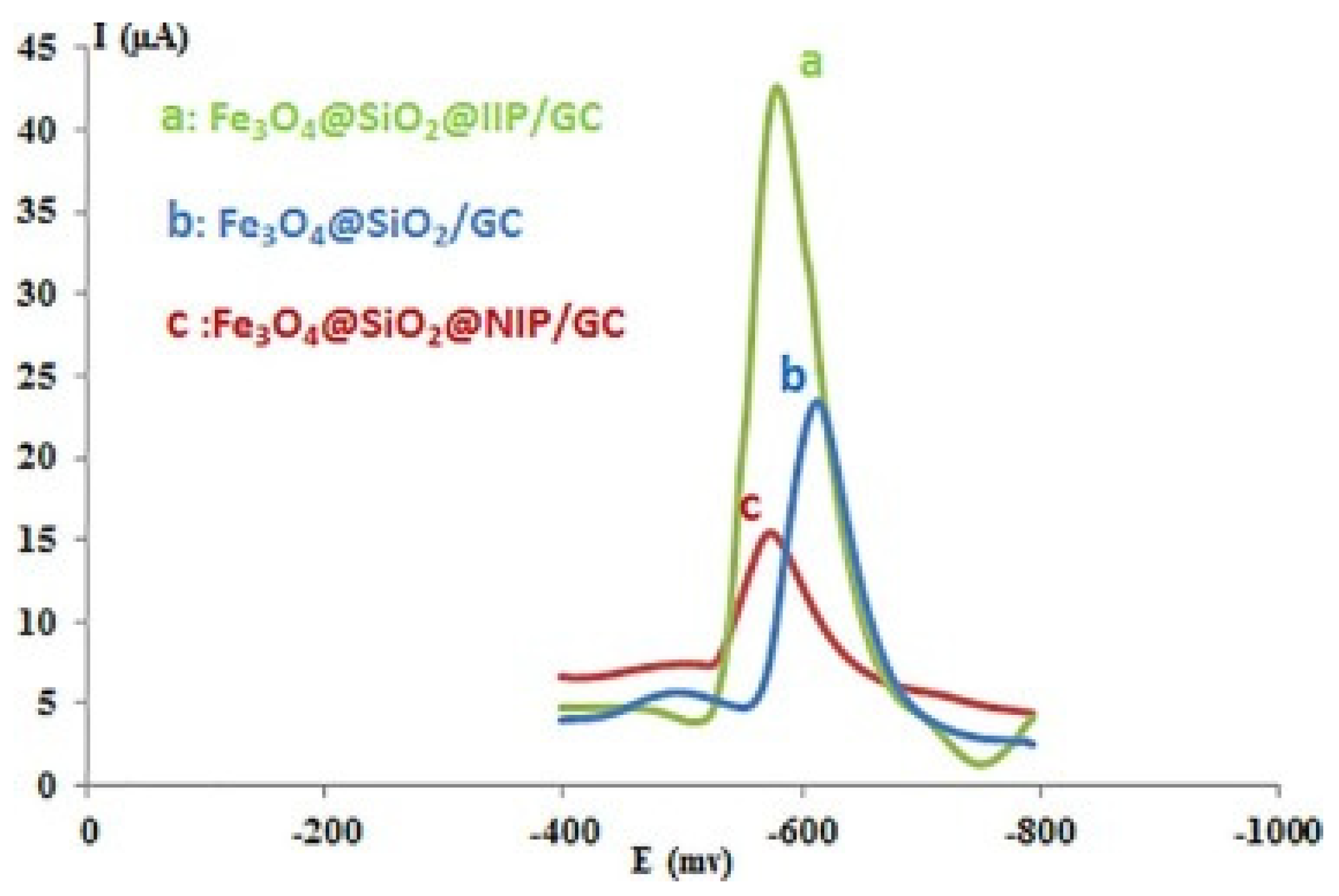
| Analyte | Electrochemical Method | Monomer | Composition of Nanoparticle | LOD | Linear Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb(II) | Differential pulse voltammetry | 4-vinyl pyridine | Fe3O4@SiO2@IIP | 0.05 ng mL−1 | 0.1–80 ng mL−1 | [103] |
| Au(II) | Glassy carbon electrodes | Chitosan | Fe3O4/SiO2/CS-IIP | 5 nmol L−1 | 0.01 to 20 μmol L−1 | [67] |
| Ni(II) | Carbon paste electrode | Chitosan and acrylic acid | Fe3O4/MWCNTs-COOH | * | * | [63] |
| Co(II) | Differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry | Acryl amide | IIP/MNPs-oxine/GCE | 0.1 Nm | 0.5 to 20 nM and 20 to 500 nM | [106] |
| Ce(IV) and Gd(III) | Screen-printed carbon electrode | but-2-enedioic acid bis-[(2-amino-ethyl)-amide]) | MNPs-COOH and MNPs-COCl | 0.07 ng mL−1 and 0.19 ng mL−1 | 0.07 ng mL−1 and 0.19 ng mL−1 | [107] |
| Magnetic IIP | Analyte | Matrices | Preconcentration Factor | LOD | LOQ | Recoveries (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2–IIP | Hg(II) | Sera | 100 | 0.05 µg L−1 | 0.20–28.00 µg L−1 | * | [91] |
| Fe3O4@SBA-15-NH2-IIP | Cd(II) and Pb(II) | vegetable sample | 88.8 83.3 | 0.35 μg L−1 | * | 96.60–104.750 | [20] |
| Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-IIPs | Cd(II) | tea, coffee, bread, tobacco, radish, spinach, water, and wastewater | 50 | 1.13 µg L−1 | 3.21 µg L−1 | >99 | [69] |
| MNPs@IIP MNPs@HM@PVIM-Au-IIP | AU(III) | Environmental and mineral samples | * | 0.002 μg L−1 for Au(III) | * | 86.105 | [110] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@IIPs | Al3+ and Be2+ | Water samples (Tap and Well) | 50 | 3.2 and 0.9 ng mL−1 | 5.0–50.0 ng mL−1 and 2.0–40.0 ng mL−1 | 92.0–108.0 | [111] |
| Fe3O4@VTES-IIP | Pb(II) | Water samples and several types of agricultural products | 125 | 0.71 ng mL−1 | 2.34 ng mL−1 | 93.70–97.80 | [111] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-IIP-sensor | Cd(II) | Water samples | * | * | 0.008 to 0.05 μM | 93.18–101.57 | [112] |
| Analytes | Adsorbent | Mass of Adsorbent | Contact | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Isotherms and Kinetics | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2-IIP | 50 mg | 20 min | Nip = 24.2 IIP = 5.2 | Langmuir adsorption isotherm and pseudo-second-order rate | [120] |
| Cd(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2@IIP | 30 mg | 20 min | IIP = 62.74 NIP = 32.32 | pseudo-second order | [65] |
| Cd(II) and Pb(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2@IIP | - | 30 min | 41.69 for Cd2+ and 76.39 for Pb2+ | second order | [48] |
| Pd(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2IIP | 1 g L−1 | 20 min | 65.75 | Langmuir isotherm pseudo-second order | [78] |
| Hg(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) | SMACNT-MIIP | 20 | 30 min | 105.34, 91.79, 75.03, and 63.54 | Langmuir pseudo-second-order kinetic model | [71] |
| Cd(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2@AECS (Cd(II)-IIP) | 5 | 60 min | 26.1 and 6.7 | pseudo-first or second-order model, Langmuir | [77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mabaso, N.B.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Nyaba, L. Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices. Processes 2024, 12, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081601
Mabaso NB, Nomngongo PN, Nyaba L. Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices. Processes. 2024; 12(8):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMabaso, Nyeleti Bridget, Philiswa Nosizo Nomngongo, and Luthando Nyaba. 2024. "Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices" Processes 12, no. 8: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081601
APA StyleMabaso, N. B., Nomngongo, P. N., & Nyaba, L. (2024). Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices. Processes, 12(8), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081601







