Abstract
Overlapping uranium and coal resources are widely distributed in the basins of China. The current uranium–coal coordinated mining model, mining interaction, and multi-phase and multi-field coupling mechanisms remain unclear, thereby substantially restricting the mining of overlapping uranium and coal resources. This article reviews the overlapping uranium–coal mining technology and conditions, summarizes the main problems faced by the coordinated mining of coexisting uranium–coal resources, proposes a dynamic coordinated mining technology system for the entire life cycle of coexisting uranium–coal resources, and describes the multiphase and multifield coordinated mining of co-associated uranium–coal resources. The multifield coupling mechanism clarifies the solid–liquid–gas three-phase spatiotemporal coupling effects of the stress, fracture, seepage, geochemical, pressure, and microbial fields, and explains the safe and efficient mining technology of uranium and coal resources, and the coordinated mining and isolation technology of uranium and coal. “Trinity” pollution prevention and control technology and other key research directions are discussed to promote green, efficient, joint, and coordinated mining of uranium and coal.
1. Introduction
The Chinese energy structure is characterized by the depletion of oil and gas and the relative enrichment of coal. Coal, oil, gas, and uranium meet most of the demand for energy resources in China and globally. In past decades, fossil energy and nuclear energy consumption have significantly increased with the rapid development of Chinese economy. In 2023, China’s consumption of coal, oil, and uranium was approximately 5 billion, 756 million, and 10,000 tons, respectively. Therefore, Chinese energy development faces new challenges against the background of global warming. Uranium is an important clean energy resource because it does not produce carbon dioxide. Its proportion in the Chinese energy structure continues to increase, owing to the increasing demand for uranium resources. In 2023, the annual demand for natural uranium for nuclear power exceeded 10,000 tons and is expected to exceed 30,000 tons in 2035. Therefore, meeting the demand for uranium has become urgent for the Chinese government.
Notably, 57.4% of the global natural uranium production comes from sandstone uranium deposits, and this proportion in China exceeds 90% [1]. Oil, gas, coal, and sandstone uranium deposits commonly occur in the basin [2,3,4]. Of the 31 uranium-bearing basins in the world, 26 bear uranium and coal; 12 of these are in China [5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Therefore, coordinated uranium–coal mining is of great significance for guaranteeing Chinese energy demand and environmental security [12,13].
Interactions exist between coal and sandstone uranium mining [12,13]. First, during coal mining, underground goafs and a new stress environment are created [14]. Caving, fissure, and curved subsidence zones develop from the goaf to the surface. The caving and fissure zones can cause the formation of a falling funnel with the goaf as the core. The cracks passing through the aquifer form channels for water migration, eventually causing the groundwater level to drop and the water to converge on the goaf. However, the in situ leaching mining of sandstone uranium deposits requires the maintenance of a certain pressure head and relatively closed water circulation [15,16,17]. Therefore, the mining of coal may significantly affect the in situ leaching mining of sandstone uranium deposits and may even render uranium deposits impossible to mine. In addition, deformation within the curved subsidence zone can lead to borehole deformation, which may cause casing ruptures in extreme cases. In contrast, in situ leaching mining of uranium ores causes uranium minerals that were originally insoluble in water to begin to dissolve in the water body and migrate with it [18,19]. In the normal process of in-situ uranium leaching, the diffusion range of the leaching solution is strictly controlled by making the pumping volume slightly larger than the injection volume [15]. However, if cracks penetrate an ore-bearing aquifer during uranium mining, the diffusion range of the leachate is no longer controllable, eventually causing serious radioactive contamination. Therefore, solving the problem of safe and economical exploitation of the two resources in the overlapping areas of uranium and coal, or areas where uranium and coal are close and may interact with each other, has become an urgent problem [20,21,22].
Scholars have conducted corresponding studies to address these problems [2,13,23,24,25]. However, many problems remain in the realization of dynamic and coordinated mining of uranium coal throughout its life cycle. In particular, some content is still at the conceptual level and cannot be implemented to guide production. However, whether certain concepts are applicable and economically feasible remains questionable. The aim of this paper is to realize the coordinated mining of uranium and coal; the main issues and key technologies involved in the coordinated mining of uranium and coal throughout the life cycle are discussed under the scenario of “staggered time and space avoidance.”
2. Challenges Facing Coordinated Uranium–Coal Mining
2.1. Deformation of Overlying Strata Induced by Coal Seam Mining
2.1.1. Strata Deformation
After the coal seam mining face is goafed, the overlying rocks in the goaf area bend and move downward under the action of their own weight and the pressure of the overlying rock and soil mass. It initially appears as weak cracks in the layer joints of the roof and slowly evolves into a separation layer. When the goaf loses its effective support and the tensile stress formed inside the roof rock layers exceeds the tensile strength limit of the rock layers, the roof of the coal-bearing seam fractures and collapses, forming caving zones [14,26,27]. The formation of caving zones is directly related to factors such as the regional geological structure, roof properties, support conditions, and mining speed. When the stress on the upper part of the caving zone exceeds its own strength under the action of gravity, the rock layer bends downward, causing cracks, separation, and fractures, but still maintains the original overlapping relationship of the rock layers, forming a fissure zone. The rock layer on the upper part of the fissure zone also bends downward owing to its own gravity and the weight of the overlying rock layer. However, neither breaks nor falls form in the curved subsidence zone (Figure 1).
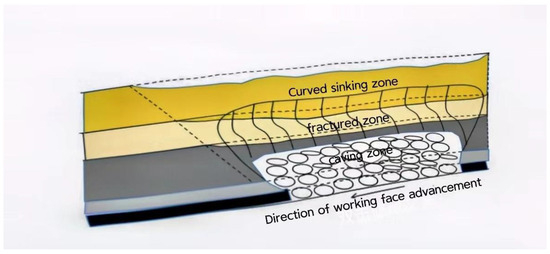
Figure 1.
Schematic of strata damage in long-wall comprehensive mechanized coal mining.
2.1.2. Impact on Groundwater Environment
To ensure safe coal mining, aquifers must be manually drained prior to coal mining [28,29]. Generally, this lowers the aquifer water level to the aquifer floor. However, when water is released, owing to the influence of many factors, such as the seepage resistance of the aquifer and the layout of drainage boreholes, the water level of the aquifer within the working surface cannot fully drop to the aquifer floor [14]. Combined with the size of the static reserves in the mining area, the water pressure of the aquifer is reduced to a safe level, and mining can proceed only after a pre-mining safety assessment. During the mining process, groundwater from the periphery of the working face must be discharged, which may affect mining safety. After the working face is mined, as the roof collapses and is lifted, a water-conducting fissure zone is formed, which further drains the groundwater [30,31]. From the release of water before coal mining to the end of coal mining, the mining process disrupts the original natural balance of the groundwater, forming a falling funnel centered on the mine. Within its scope of influence, the water level drops, and some sections change from positive pressure to no pressure.
2.2. Disturbance of Groundwater Environment by Uranium In-Situ Leaching
Currently, in situ leaching uranium mining is the main method of uranium mining in China. Compared to conventional hard-rock uranium mining methods, in situ leaching mining has the advantages of a short construction period, low production cost, and high safety [15]. The leaching process consists of two parts: orebody leaching and leaching solution treatment. The former involves injecting a leaching solution into the underground ore-bearing layer through a liquid injection pipe to selectively oxidize and dissolve the uranium in the ore. Tetravalent uranium in water is oxidized into hexavalent uranium ions to form a uranium-containing solution, which is the leachate. The leachate is pumped to a surface water smelting plant through a liquid extraction pipe. The latter obtains the product after the extracted leachate is adsorbed on resin, washed, precipitated, thickened, and filtered (Figure 2).
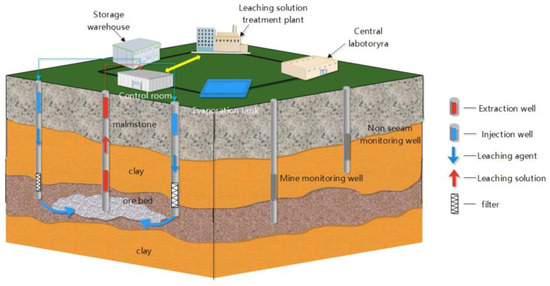
Figure 2.
Ground leaching production process.
The in situ leaching uranium mining process constructs only pumping, injection, and monitoring wells during the production process and does not effectuate tunnel development or underground ore mining. No waste rock yard or tailing (slag) storage, which has evident environmental protection advantages, exist. In the process of uranium leaching in the ground, to minimize the loss of leaching liquid to the periphery of the mining area, an operating principle is often adopted in which the liquid pumping volume is greater than the liquid injection volume to ensure the well site maintains a falling funnel centered on the well site, thereby controlling the leaching liquid within a certain range [16,17]. However, because in situ uranium leaching involves ore-rock reactions directly in ore-bearing aquifers, it is still possible that the leaching solution will spread to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in the concentration of radionuclides in groundwater near the uranium mining area.
2.3. Physical and Chemical Responses Trigged by Co-Mining of Uranium and Coal Deposits
Coal mining requires the drainage of groundwater from the upper part of the coal seam to achieve safe mining, whereas uranium mining requires stable water-isolating roofs and floors and sufficient groundwater headwater. Therefore, a conflict between coal mine drainage and uranium mine water conservation is likely. Taking the Nalinggou uranium mine and Tarangol coal mine area in the Ordos Basin of Inner Mongolia as an example, uranium and coal resources overlap and coexist in this mining area [2,31,32,33,34]. The uranium mine is located in the upper part of the coal mine, with a structure of “uranium on top and coal below.” Mineral seams occur mainly in the aquiferous rock group in the lower section of the Jurassic Zhiluo formation. This aquifer is a direct water-filled aquifer in the coal seam (Figure 3). Co-mining of uranium and coal results in a series of mining, safety, and environmental issues, including the following:
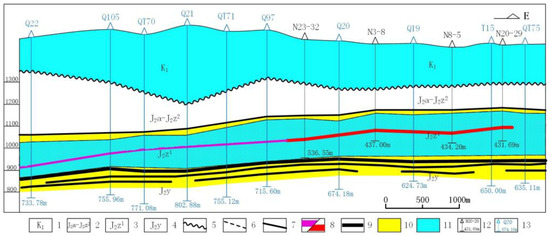
Figure 3.
Regional hydrogeological profile. 1: lower Cretaceous; 2: diazepam group, Upper Zhiluo formation; 3: Lower Zhiluo formation; 4: Yan’an formation; 5: angular unconformity boundary; 6: parallel unconformity boundary; 7: integration boundary; 8: coal logging gamma elevation anomaly body/uranium ore body; 9: coal seam; 10: aquifuge; 11: aquifers; 12: uranium mine boreholes; 13: coalfield boreholes.
- (1)
- Coal mining requires dewatering, which causes the groundwater level in uranium mining areas to continuously decline [35]. The uranium deposit is a sandstone uranium mine suitable for in-situ leaching. Mining must maintain a certain pressure head. If coal mine dewatering causes the groundwater level to exceed the lower levels suitable for in situ leaching, it will destroy the mining conditions of the Nalinggou uranium mine, resulting in unusable dead ore or rendering the uranium mine unusable.
- (2)
- Mining activities in lower coal mines may result in the spillage of uranium-containing leachates, posing the risk of radioactive contamination. During the mining activities of the lower coal mine, the formation of three zones causes changes in the groundwater seepage field, causing radionuclides to diffuse with the groundwater to the environment outside the uranium mine, polluting the surrounding groundwater environment, and even entering the coal mining area, affecting the safe operation of the coal mine.
2.4. Application of Numerical Methods in Coal-Uranium Co-Mining
The mining of rock layers disturbs the original stress field of the rock, inducing the development of a fracturing field. Moreover, the spatial development of the fracture field significantly impacts the spatial distribution of seepage fields and the transport of solutes. During the coal mining process, as the mining face advances, vertical advance support pressure is generated in the direction of face, causing the overlying rock layers to exhibit an elasto-plastic state within a range of 10–30 m ahead of the face. This leads to a large number of fractures [14,26,36]. The advance support pressure gradually increases in the direction of face advancement and then decreases significantly, with the peak point of vertical stress being 1.5–7 times the original rock stress. Compared to the vertical stress, the horizontal stress decreases gradually from ahead of the mining face to the face itself. Simultaneously, coal and uranium mining cause complex changes in gravel aquifers and sandy mudstone layers, creating a complex water seepage environment. Therefore, Darcy’s law cannot effectively describe the flow state of underground fluids under disturbed conditions. Non-Darcy flow should be used to study the coupling characteristics of multiphase media and fractured media.
By establishing a non-Darcy flow coupling model between stress and seepage in fractured media and combining it with the FLAC3D-CFD fluid-solid simulator for numerical simulations, we observe that during solute transport in fractured media, the stress field and seepage field exhibit non-uniform distributions in the fractures and matrix [34,37]. An overall decrease in stress, with localized stress concentration and dissipation on the fracture surface exist near the fracture surface. Pore pressure primarily increases locally and decreases on the fracture surface. The solute transport velocity in fractured media is positively correlated with hydraulic pressure, while solute concentration is negatively correlated with hydraulic pressure and time. Increasing hydraulic pressure enhances the connectivity of voids in the fracture surface, accelerating seepage velocity and the effective seepage area. The non-uniform distribution of rough fracture surfaces results in localized stress concentration and dissipation, leading to eddy currents and solute retention on some fracture surfaces. Solute concentration in fractures is positively correlated with the stress value on the fracture; the greater the stress, the higher the residual solute amount within the fracture over a certain period.
3. Coordinated Mining Technology System for the Entire Uranium and Coal Mining Lifecycle
The lifecycle coordinated mining technology system is a multi-agent, multi-dimensional system based on the “staggered time and space avoidance” scenario, with the premise of protecting the ecological environment and a goal of reducing the interaction of resource development and realizing the full recovery of resources. The system is based on the perspective of the geological characteristics of uranium and coal deposits, supported by the multi-phase and multifield coupling theory, and with the technical means of intelligent sensing and control, the internet of things, and big data computing for multi-level safe and efficient mining technology integration [12,13]. The core scientific issue of this technical system is the solid–liquid–gas three-phase spatiotemporal coupling problem and the stress, fracture, seepage, geochemical, and diffusion migration fields in the coordinated mining process of uranium and coal. Its main technologies include: (1) See-through uranium and coal deposit geological characteristics technology; clarifying the macro- and micro-geological characteristics of uranium and coal deposits is a prerequisite for designing specific process routes for uranium and coal-assisted mining. (2) Safe and efficient uranium and coal mining technology, covering rapid construction, rapid mining, and rapid leaching technology, as well as coal mine subsidence reduction and water conservation mining technology. (3) Uranium–coal coordinated mining safety isolation technology, focusing on uranium–coal spatiotemporal isolation technology and curtain isolation technology. (4) “Trinity” pollution prevention and control technology of source control, process interruption, and terminal emergency treatment, involving in-situ precision injection technology, microbial space blocking technology, ex situ and in situ groundwater physical and chemical restoration technology, and pollution prevention and dynamic sensing and control technology [38]. (5) Construction of an intelligent disaster early warning and decision-making platform (Figure 4).
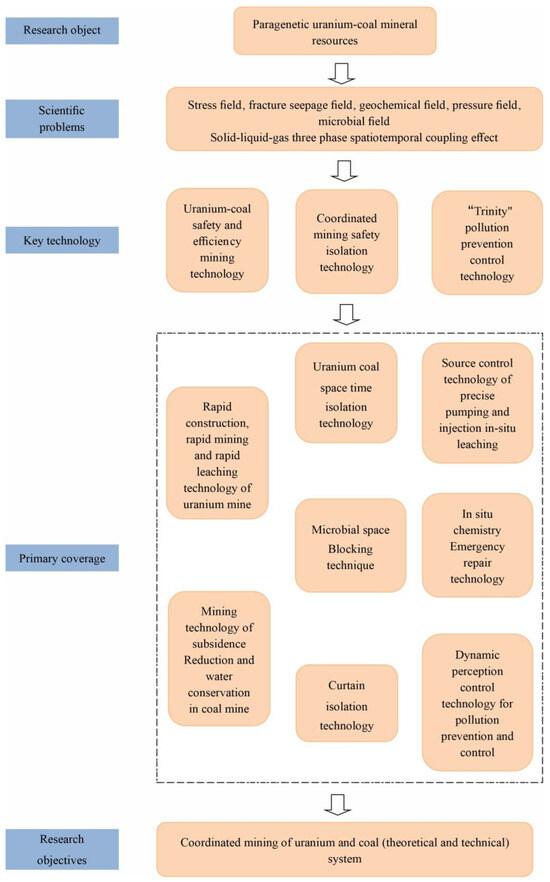
Figure 4.
Coordinated mining of uranium and coal theoretical technology system diagram.
4. Key Scientific Issues in Coordinated Uranium and Coal Mining
The process of coordinated mining of symbiotic uranium and coal involves changes in the regional stress field, fissure field, and groundwater seepage field caused by the collapse of coal mines (Figure 5); the chemical field when the leaching solution interacts with the ores during in situ leaching of uranium mines; and the evolution of the diffusion and migration fields of various chemical substances in water bodies. The coupling mechanism between the stress, fracture, seepage, chemical, and diffusion fields is the theoretical basis for guiding uranium–coal co-mining and building disaster early warning systems. Owing to the radiation of uranium ores, when mining resources in uranium–coal overlay areas, any accident may cause significant economic losses, serious radioactive pollution, and strong social repercussions, which may ultimately be fatal to the industry. Here, we emphasize that uranium–coal mining is conducted under time-staggered and spatial avoidance scenarios, and the purpose of multi-field coupling theoretical research is to obtain a scientific and reasonable spatial avoidance distance that can maximize economic benefits and enable dynamic adjustments during actual mineral extraction. Existing theories have discussed the changing rules of the stress, fissure, and seepage fields in coal mining; the evolution of the geochemical field of uranium ore in situ leaching; and the migration and diffusion of radionuclides in the seepage field. However, for the stress field in coordinated mining, the solid–liquid–gas three-phase spatiotemporal coupling mechanisms of the fracture, seepage, geochemical, and diffusion migration fields remain unclear [21,23,24,39]. Therefore, coordinated uranium–coal mining research focuses on two levels.
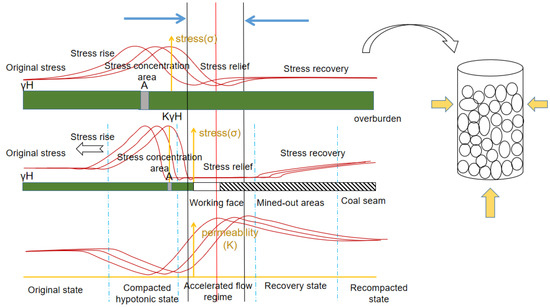
Figure 5.
Multi-parameter coupling relationship and temporal and spatial evolution law of strata movement.
- (1)
- The evolutionary characteristics and mechanisms of multiple phases and fields involved in uranium–coal mining process. Coal mining involves phenomena such as stress disturbances, surface subsidence, rock fractures, increases in underground fissures, and changes in groundwater seepage [30]. In addition, the underground leaching process of uranium ore involves a chemical reaction between the leaching solution and the ore-bearing layer, diffusion of various chemical substances, and migration of the leaching solution. Clarifying the changing rules of the rock stress, fissure, and groundwater seepage fields in coal mining and the evolution characteristics and rules of the chemical, diffusion, and solute transport fields involved in uranium mining are key to constructing a multiphase uranium–coal mining process.
- (2)
- Accurate characterization of multiphase and multifield cross-scale, full-time spatiotemporal coupling in coordinated uranium–coal mining areas. During the entire period of coordinated mining of uranium and coal, on the basis of the study of cross-scale spatial evolution rules and integration of time characteristics, we aim to establish a cross-scale multifield, including a cross-scale and full-time regional stress field, fracture field seepage field, geochemical field, and multiphase (including gas–liquid–solid) coupling model, to accurately characterize regional crack development rules, hydrodynamic field evolution, radionuclide migration and diffusion rules, and solute concentration change characteristics throughout the life of uranium–coal coordinated mining.
The multi-field coupling mechanism is represented by a large number of physical simulation experiments and numerical simulation studies conducted by Zhang Tong on the stress field, crack field, seepage field, and solute chemical reaction-transport dynamic coupling process under uranium–coal co-mining conditions. The mechanism and evolution process of multifield coupling were obtained in their research. However, research on the chemical and diffusion migration fields of uranium ore in in situ leaching mining has been simplified. Therefore, further studies are warranted. The physical simulation experiments and numerical simulations were performed under static or unchanged parameters. However, in a real uranium–coal mining process, the geological, hydrogeological, stress, fissure, seepage, and chemical fields change dynamically in real time with mineral mining. The realization of a multifield coupling simulation and the precise characterization of uranium coal mining throughout its life cycle will be the focus of future research. In addition, previous research was conducted in laboratories rather than uranium or coal mining sites. Taking the Nalinggou uranium mine and Tarangola coal mine as examples, further research should focus on monitoring the hydro geochemistry during on-site mining of the Nalinggou uranium mine to invert the chemical seepage field during real uranium mining. In addition, the stress, fissure, and seepage fields in the Tarangola coal mine mining area should be monitored, and tracer tests should be conducted at different distances from the coal mining area to simulate the actual conditions of the coal mining fissure field, seepage field, strain field, and uranium. Owing to the similarity in geological conditions, these data are a reliable reference to support the scientific determination of reasonably safe distances. Additionally, current research on multifield coupling focuses on normal coal and uranium mining processes. Hence, research on multifield coupling under possible emergencies such as earthquakes is scant. These issues should be included in the scope of multifield coupling research in uranium–coal assisted mining.
5. Key Technologies for Coordinated Uranium and Coal Mining
The key technologies for coordinated uranium and coal mining mainly include the technology of seeing through the geological characteristics of uranium and coal deposits, the technology for safe and efficient uranium coal mining, the technology for coordinated uranium and coal mining isolation, the “trinity” pollution prevention and control technology, and intelligent early warning decision-making technology. Among them, seeing through uranium and coal deposits and safe and efficient uranium–coal mining technology are fundamental, isolation technology is pivotal, and intelligent early warning and pollution prevention and control technologies are guaranteed.
5.1. Technology to See through the Geological Characteristics of Uranium and Coal Deposits
The coordinated mining of uranium coal throughout its lifecycle begins with resource exploration. Traditional resource exploration and mining are aimed at a single mineral resource, and no exploration of other co-associated resources exist in the area. Correspondingly, in the subsequent mining process, mining planning is performed only for a single specific resource. If overlapping resources or resources that interact with each other during the mining process are blindly mined without detection, resources will inevitably be wasted, and it may even cause radioactive contamination when overlying uranium ores. Therefore, reforms must be implemented from the perspective of both exploration and development, and comprehensive exploration, development, and utilization of various associated resources must be carried out. These issues include reform of the evaluation system for mineral rights and resource taxes, reform of relevant laws, and overall coordination between the government and enterprises. This will change the government’s approval functions and the mining concepts of coal mining companies, ultimately realizing the co-mining of various associated resources. From a technical perspective, coal and uranium exploration are complementary. For example, coal mines were discovered during uranium mine exploration in the Ili Basin, providing information on coal mine burial conditions and ore-prospecting clues. Similarly, coal mine exploration is characterized by large project spacing, wide control range, and large detection depth. The exploration data can provide clues for uranium ore prospecting and a basis for the analysis of the uranium ore metallogenic environment and origin. The sharing of geological data from uranium mines and coal mines, and the simultaneous exploration of uranium and coal mines can not only save costs but also improve the comprehensive utilization of mineral resources.
When it has been proven that uranium–coal resources overlap or partially overlap, to carry out scientific and reasonable planning for the entire life cycle of coordinated uranium–coal mining, it is necessary to know the conditions for the occurrence of uranium and coal ore. This knowledge is needed not only for obtaining the ore body, but also for the location, thickness, and grade information. It is necessary to obtain all information about uranium and coal mines, including the geology, hydrogeology, rock mineral composition, structure, fracture and void development, and physical parameters of the rocks. This information forms the basis for coordinated planning of uranium–coal mining. Although it is extremely difficult to achieve the precise characterization of centimeter-level geological features, the accurate depiction of macro- and micro-features of geology and hydrogeology in three-dimensional space with decimeter-level accuracy is still worth investigating. This not only involves intuitively obtaining underground geological characteristics through traditional drilling projects but also involves innovating multi-directional comprehensive detection methods such as magnetic, nuclear, acoustic, optical, and electrical parameters. Research and development for detection instruments includes multidimensional visual reconstruction, other data fusion processing, and multi-source massive geological holographic transparent display technology (Figure 6).
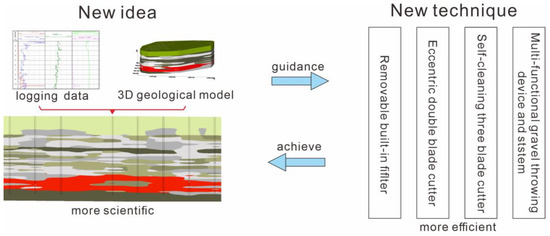
Figure 6.
Technical system of rapid well construction.
5.2. Safe and Efficient Mining of Uranium Coal and Interference Reduction Technology
Research on safe and efficient uranium–coal mining technologies includes coal mine subsidence reduction technology, water retention technology [38,39,40], and rapid construction, mining, and recycling technologies for uranium mines.
Coal mine subsidence reduction and water conservation technologies mainly include filling, partial mining, coordinated mining, and grouting of the overlying rock separation layer [41,42,43]. Backfill mining uses coal gangue, paste, and (super) high water as supports instead of coal. Partial mining uses strip mining, Wongawilli coal mining, thickness-limited mining, room-and-pillar mining, and other methods to effectively control the overlying rock. Coordinated mining uses two or more adjacent working faces to offset mining effects when the working face advances based on the spatiotemporal evolution of the overlying rock during the mining process. It can be divided into two layers of coal (layered) or the same coal layer. Overlying rock separation layer grouting refers to the use of ultrahigh water and other materials to fill the cavities and caving zones between rock layers to control the movement of the overlying rock. It is a near-source technology that reduces overall surface movement and deformation [29]. Using this technology, the expansion and penetration of primary and new fissures into aquifers can be effectively controlled to achieve water-preserving mining.
During coordinated uranium–coal mining, coal mining drainage inevitably leads to a continuous decline in the water level of the uranium mine aquifers. To achieve safe uranium coal mining, it is necessary to first perform staggered mining of uranium and then coal in overlapping or partially overlapping uranium–coal areas. Therefore, accelerating the leaching of uranium minerals is an important method to reduce the impact of uranium mining on coal mining and achieve coordinated uranium and coal mining, including the rapid construction of well sites, rapid leaching of underground uranium minerals, and removal of uranium from the leaching solution. Rapid recovery technology involves the scientific issue of multifield coupled seepage in the coordinated mining of coal and uranium.
Rapid well site construction applies secondary construction well formation technology in the uranium–coal coordinated development area, subverting the traditional uranium well formation model of in situ leaching and using virtual well site construction technology based on three-dimensional geological models to develop the geology of existing exploration boreholes in the area. On the basis of geophysical prospecting data, three-dimensional geological modeling is used to finely describe the distribution patterns of uranium ore bodies and ore-bearing sand bodies, and a new in situ uranium production well network is constructed. By means of a visual expression of the leaching flow field and optimization of the filter layout, the implementation of a tailor-made design of the leaching channels during the drilling and construction processes can achieve precise development of uranium ore bodies. In the process of rapid well formation, the speed and quality of secondary well formation are crucial. Rapid well-formation technology with screw motor compound power, supporting a high-efficiency compound drilling fluid formula, and convenient and efficient drilling rigs dedicated to in situ immersion can ensure rapid and high-quality secondary well formation on a large scale. With these advancements, the efficiency of a single unit can be increased by 30%.
Rapid leaching of uranium ore uses high-intensity extraction methods and segmented leaching processes to accelerate the uranium leaching reaction and solute exchange speed and improve the efficiency of pumping and uranium mineral leaching. Pumping and injection use centralized filtration technology such as a “limestone + quartz sand” filter tower with a backwash function that replenishes bicarbonate in the leachate. Enhanced leaching is implemented in the production stage using two means: strong oxidation and strong complexation reaction. To accelerate the chemical reaction rate under the conditions of CO2 + O2 in the in situ uranium leaching process, advanced oxidation and strong oxidation leaching are used in the first and second leaching stages. The strong oxidation method uses a gas–liquid mixed micro/nanobubble generator. Millimeter-scale oxygen bubbles are dispersed to improve the oxygen dissolution efficiency. In the third leaching stage, strong complexation leaching is used, and the key measure is to maintain the HCO3− concentration in the leaching agent above 1.5 g/L. In the production stage, the pumping and injection well network is rotated during the production stage of well pattern scheduling. In the early and middle stages of production in the mining area, as well as in the later stages of production, different well pattern arrangements are used to reorganize the well patterns to reduce leaching dead corners and improve resource recovery rates. A series of proprietary and dedicated high-pressure pipelines are used to achieve continuous group-hole pumping and injection under high-pressure leaching conditions. High-intensity pumping is implemented throughout the production stage using high-lift and large-flow submersible pump operations to improve the liquid pumping quantity, accelerate the replacement of the leaching liquid flow, and increase the speed of resource recovery (Figure 7).
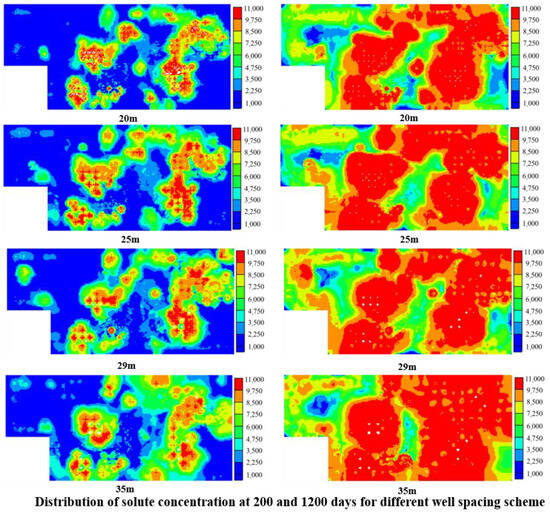
Figure 7.
Optimization of a rapid leaching scheme based on digital–analog quantitative optimization.
For rapid extraction of uranium solution, the efficient and rapid recovery of low-concentration and large-flow uranium-containing leach solutions depends mainly on the upgrading of hydrometallurgical treatment equipment and optimization of the timely adjustment of process parameters [43,44]. Presently, newly developed large-flux ion-exchange tower equipment has achieved a single-tower processing capacity of 2000 m3/h, solving the problem of large-flow adsorption. In the first Chinese U-shaped integrated tower with multiple functions, such as adsorption, elution, and transformation, the concentration of the qualified liquid was approximately 43–50 g/L, meeting the requirements of industrial indicators. Developing new high-efficiency resin adsorption materials to further increase the uranium adsorption capacity of saturated resins increased the saturation capacity by approximately 23%. Intelligent analysis methods transform the elution through the adaptive adjustment of process parameters and preliminary research on resin blocking and prevention mechanisms. A set of high-throughput hydrometallurgical treatment technologies with early warning effects was constructed to achieve the rapid recovery of uranium in uranium-containing leachate (Figure 8).
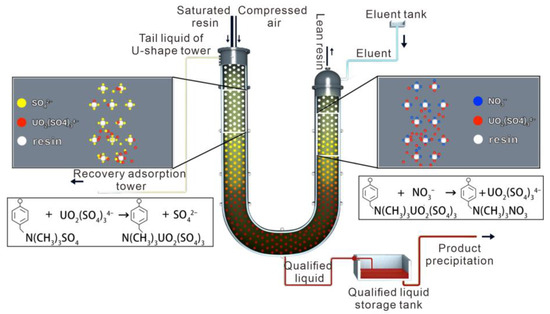
Figure 8.
Schematic of U-shaped rapid adsorption treatment.
5.3. Uranium–Coal Coordinated Mining Isolation Technology
Uranium–coal coordinated mining isolation technology is mainly realized through two methods: space–time isolation and curtain isolation.
Spatiotemporal isolation technology refers to optimizing the spatiotemporal layout of coordinated uranium and coal mining and constructing a reserved corridor based on changes in the height of the water-conducting fissure zone in the coal mining fissure field, which results in changes in the groundwater seepage field combined with the hydrogeological conditions of the hydrodynamic field required for uranium mining. First, full use of geological exploration and three-dimensional geological technology is required to ascertain the occurrence of uranium coal in coordinated uranium–coal mining areas; the horizontal and vertical spatial distribution characteristics of uranium and coal; and the composition, thickness, and anti-interference properties of aquifers, groundwater zoning, and water supply conditions. Second, based on the “three zones” theory of coal mining, numerical simulations, physical experiments, and on-site monitoring are used to determine the spatiotemporal variation patterns of the seepage field in coal mining fissures. Subsequently, on the basis of the hydraulic characteristics of uranium ore in situ leaching mining, studies should be performed under the hydrodynamic conditions of uranium ore mining, and the seepage field requirements for in situ leaching mining should be determined. Finally, combined with the safe and efficient uranium–coal mining technology, a reserved corridor is constructed according to the principle of “staggered time and distance in space” to determine the coordinated development sequence of uranium coal [2] (Figure 9).
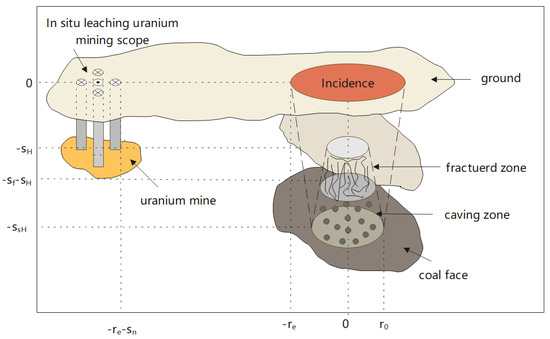
Figure 9.
Space–time diagram for coordinated mining of uranium and coal.
Curtain isolation is a key means of ensuring the hydraulic conditions for the coordinated mining of uranium and coal. The main curtaining methods include hydraulic curtaining, curtain grouting, and freeze isolation.
A hydraulic curtain uses water-injection wells to inject water into an aquifer. By adjusting the well spacing and water volume, a complete hydraulic lifting zone is formed along the water injection well to prevent a decrease in the water level of the aquifer in the uranium mining area [45]. First, the source and quality requirements of the injected water should be investigated. The injected water source can be coal mine drainage or uranium mine in situ leaching adsorption tail liquid. Studies on the treatment methods for recharged water pollutants should be performed according to the water and groundwater quality requirements of the recharged water. Second, according to the groundwater level protection requirements of the uranium mining area and regional hydrogeological conditions, combined with changes in the coal-mining seepage field, the relative position of the hydraulic curtain, number and distance of water injection wells, and the amount and distribution of reinjection water are studied and determined (Figure 10).
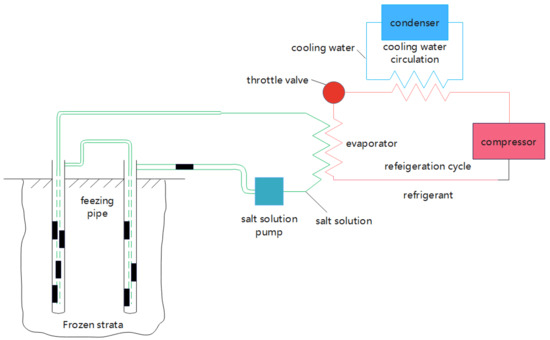
Figure 10.
Process flow of freezing technology.
Curtain grouting began in the 1950s and is currently widely used in many fields, such as water conservation, construction, railways, and mining [35]. Curtain grouting pushes grout that can be fixed in water into water-bearing rock formations (cracks, pores, and caves) through grouting holes. After the filling, compaction, and solidification processes, a similar line is formed in the main water-passing section. Curtain-like relative water-isolation zones are implemented to achieve water retention [21,46,47]. First, grouting materials with a low grout viscosity, good groutability, high stone rate, and good impermeability should be selected. Second, combined with hydrogeological conditions, the relative position of the curtain, number of injection wells, and well spacing are studied. Finally, relevant parameters such as the grouting method, curtain grouting thickness, grouting concentration, and grouting pressure are studied [48].
Freeze isolation involves transferring cold energy to the stratum through frozen tubes, absorbing the heat of the soil around the tubes, and freezing the soil to reinforce, stabilize, and isolate the groundwater [49]. Freezing technology was first used in gold mining in Russia and was first used in China in 1955 for the wind shaft excavation of the Linxi Coal Mine in Kailuan. The freezing isolation technology focuses on refrigerant selection, freezing drilling layouts and structures, and freezing period selection [50].
5.4. “Trinity” Pollution Prevention and Control Technology
Radioactive pollution prevention and control technologies include source control technology for precise injection at subsurface well sites, microbial space isolation zone process blocking technology, in situ chemical remediation emergency treatment technology, and pollutant dynamic sensing and control technology [51,52].
Precision pumping technology for in situ leaching wells minimizes the outward diffusion of leachate by accurately adjusting the flow rate of each pumping liquid well according to the hydrogeological conditions of the uranium mining area. First, by establishing the hydrogeology of the uranium mining area, the relationship between the pumping–injection ratio and leachate diffusion range in the drilling field area is studied. Second, combined with the basic requirements of the production process, the impact of the boundary unit injection ratio on the radionuclide diffusion distance is studied. Finally, the radioactive impact is minimized by optimizing the injection ratio of each unit in the field area [18,52].
Microbial space blocking and isolation technology is used to construct a microbial reduction isolation zone along the migration and diffusion paths of radionuclides to reduce and solidify radionuclides that may diffuse, thereby controlling the spread of radioactive contamination. First, through the screening and recycling of microorganisms, the dominant species for radionuclide reduction are selected. Second, key parameters such as microbial quantity, distribution, and reduction characteristics are studied, as well as the effects of temperature, humidity, and light on the reduction effect. Finally, the relative position of the microbial reduction zone, number and spacing of the injection wells, injection concentration, and quantity of microorganisms are optimized and studied.
In-situ chemical remediation emergency treatment technology refers to a technology that efficiently and quickly fixes radionuclides by injecting chemical reducing agents underground under the conditions of acute diffusion of uranium ore leachate. The first choice is to study the selection of in situ emergency, rapid, and efficient reducing agents based on the physical and chemical properties of radionuclides. Second, the concentration and quantity of the chemical reducing agent are determined experimentally, and the correlation between the change in radionuclide concentration and the dosage and concentration distribution of the chemical reducing agent is studied. Finally, combined with the regional groundwater seepage characteristics, the relative position, number, and spacing of emergency treatment injection wells are studied.
Radionuclide dynamic sensing and control technology refers to building an online radionuclide monitoring and environmental risk early warning platform through the internet and big-data technology, and regulating the proportion of ground immersion injection liquid according to the changing law of nuclide concentration, which has reached the macro level of radioactive pollution. First, studies on rapid dynamic identification technologies and early warning methods for radionuclides should be conducted to determine the correlation between radionuclide concentrations and indicator factors. Second, based on the migration and diffusion laws of radionuclides, a risk identification and early warning network is built to study the spatiotemporal characteristics of multiple data sources, and a regional and timely environmental risk early warning cloud platform is built. Finally, based on closed-loop reciprocating technology, the precision pumping and injection system of the in situ well site is integrated, an emergency decision-making platform is established, and the organic unity of environmental risk early warning and macro-control of the well site is achieved.
5.5. Establishment of Intelligent Early Warning and Decision-Making Platform
This section focuses on innovative disaster precursor sensing, early warning, and pre-analysis technologies to create intelligent decision-making models. A disaster early warning and intelligent and accurate decision-making platform for coordinated uranium–coal mining is necessary to ensure coordinated uranium–coal mining throughout its lifecycle. It is based on multiphysics dynamic information, conducts real-time dynamic analysis, and adjusts the impact of the two during the mining process. Coal-seam mining changes the stress field distribution and promotes the expansion and development of the fissure and seepage fields. In turn, the seepage and fissure fields promote the evolution of the stress field. In situ uranium leaching involves water-rock interactions, which are solute reactions of hydrodynamics and chemical dynamics. Transport coupling dynamic processes involve many dynamic parameters based on time effects, such as stress, cracks, fluids, solutes, and chemical reaction processes. Therefore, the identification, digital quantification, collection, and transmission of multi-field and multi-parameter dynamic information can provide coordination, and the pre-adjustment of mining modes and real-time updates of specific parameters can provide effective guarantees.
This direction is based on big-data in-depth mining and machine-learning theory, is oriented toward the holographic global learning method of disaster area prediction models, and masters the spatiotemporal coupling characteristics of uranium–coal coordinated development composite disaster-causing factors and the inherent laws of disaster mechanisms and disaster accidents. A disaster multi-information data warehouse will be constructed to quickly identify and dynamically delineate dangerous areas that may be involved in disasters during the uranium and coal mining processes. Multidata fusion theory is used to intelligently evaluate and grade the hidden dangers, risks, and danger levels of the delineated dangerous areas and to make intelligent and precise response suggestions based on risk assessment. Ultimately, early disaster warning and intelligent and accurate decision-making platforms for the coordinated development of uranium and coal will be realized to ensure the accurate and coordinated development of coal and associated resources.
6. Overlook into Conclusions
Safe and efficient mining of resources guarantees national defense and energy security strategies. The realization of safe, green, and coordinated mining of co-associated uranium and coal resources can provide an important guarantee for meeting the domestic demand for natural uranium production and the country’s demand for coal energy. Coordinated uranium and coal mining provides support for the formation of a complete method system, including planning, theoretical, technical, and engineering practices for coordinated uranium and coal mining.
- (1)
- Based on the spatial superposition rules and superposition types of co-associated uranium coal, through the uranium coal mining process characteristics, mechanisms, control mechanisms, and geological process response rules and evolution characteristics, a coordinated mining model of avoidance, distance, and interference reduction throughout the lifecycle is constructed to form uranium planning methodology for safe, efficient and green mining of coal resources.
- (2)
- Our studies focused on constructing an adaptation mechanism for co-associated uranium coal coordinated mining, establishing a coupling evolution mechanism of the stress field, seepage field, chemical field, and solute transport process under the disturbance conditions of coordinated uranium coal mining, and revealing the strata deformation and contaminant leaching of coordinated uranium coal mining. The liquid migration law provides a theoretical model and important theoretical support for the coordinated and efficient development of uranium and coal resources, thus forming a theoretical system for coordinated uranium and coal mining.
- (3)
- Based on the co-associated uranium–coal coordinated mining technology system, joint studies on key technologies such as safe and efficient uranium–coal mining technology, uranium–coal coordinated mining isolation technology, and “trinity” pollution prevention and control technology are performed through a combination of industry, academia, research, and application. These points lead to areas, and areas lead to bodies that form a technical methodology for coordinated uranium and coal mining.
- (4)
- On the basis of obtaining planning, theoretical, and technical methodologies for coordinated uranium and coal mining, we will focus on co-associated uranium and coal in the Ordos Basin, conduct demonstration applications and promotions, and establish engineering practices for coordinated uranium and coal mining.
Author Contributions
X.S.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Data processing, writing reviewing and editing. X.L.: Conceptualization, writing—reviewing and editing. Z.D.: Investigation, discussion and reviewing. C.H.: Investigation, discussion and reviewing, writing—reviewing and editing. M.L.: Discussion and reviewing. F.C.: Discussion and reviewing. M.C.: Discussion and reviewing. T.Z.: Discussion and reviewing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the China National Nuclear Corporation (Grant No. A105-2).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from China National Nuclear Corporation. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
References
- Fu, Y.; Wei, S.; Jin, R.; Li, J.; Ao, C. Research status and existing problems of zoning characteristics of sandstone type uranium deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 3519–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.X.; Ren, B.; Hao, X.J.; Xu, C. Precise coordinated mining of coal and associated resources: A case of environmental coordinated mining of coaland associated rare metal in Ordos basin. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Dai, S. Potential associated mineral resources in coal and coal bearing rock series—A problem worthy of attention. China Coal Geol. 2009, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Yao, D.; Huang, W.; Tang, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sha, J. Abundance, distribution, and modes of occurrence of uranium in Chinese coals. Minerals 2017, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Meng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Jiao, W.; Sun, Y. Foreign multi energy coexistence of minerals in the same basin Preliminary study on enrichment law. J. Hebei Inst. Archit. Technol. 2005, 22, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L. Resultant compilation Comparative analysis of uranium bearing properties of cover rocks in Russian platforms. World J. Nucl. Geosci. 2004, 21, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yang, J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Liu, H.; Garrison, T.M.; French, D.; O’Keefe, J.M. Geochemical and mineral evidence for a coal-hosted uranium deposit in the Yili basin, Xinjiang, northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Luo, J.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, S. The relationship between uranium and organic matter, oil and gas and coal in uranium bearing sandstone: Ten red beaches in the basin area as an example. J. Northwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2006, 6, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, A. Relationship between Jurassic coal and uranium deposits in Dongsheng area, Ordos Basin. J. Geosci. Environ. 2006, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, M.; He, Z. Temporal and spatial distribution of uranium, oil and coal and uranium mineralization in Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. World Nucl. Geosci. 2009, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Yin, J. Lincang, Yunnan Regional Bangmai Basin Uranium-bearing Germanium in coal Research. Uranium Geol. 1987, 5, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L. Scientific problems and Countermeasures of precise mining of coal and associated resources. J. Coal 2019, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; He, G.; Yue, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Theory and technical conception of coordinated mining of coal and associated strategic metal minerals. Acta Coal Sin. 2022, 47, 2516–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, H. An estimation method for cover pressure re-establishment distance and pressure distribution in the goaf of longwall coal mines. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2004, 41, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W. Sandstone type uranium deposit In situ leaching of uranium Overview of process methods. Min. Technol. 2011, 11, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Du, Y.; Su, X. In Situ Leaching Uranium Well Site Technology; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, G.; Li, M.; Tang, Q.; Sun, J.; Cao, F.; He, Z.; Bai, X. Somewhere Immersion Well pad pumping is greater than Note proportion Study on the relationship between groundwater and environmental impact. Uranium Min. Metall. 2017, 36, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.L.; Santos, I.R.; Perkins, A.; Maher, D.T. Dissolved radon and uranium in groundwater in a potential coal seam gas development region (Richmond river catchment, Australia). J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 154, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burow, K.R.; Belitz, K.; Dubrovsky, N.M.; Jurgens, B.C. Large decadal-scale changes in uranium and bicarbonate in groundwater of the irrigated western U.S. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 586, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Nie, X.; Song, S.; Hao, X.; Yang, X. Modeling uranium transport in rough-walled fractures with stress-dependent non-darcy fluid flow. Mathematics 2022, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; He, Y. Reactive transport model of uranium by CO2 + O2 in situ leaching. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65976–65989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Mao, J.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Xie, Z. Alkaline in-situ leaching of uranium in low-permeability sandstone: An experimental study using online low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) spectroscopy on multiphase response. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 225, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Hydrogeology response to the coordinated mining of coal and uranium: A transparent physical experiment. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6236455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Wei, J.; Feng, X.-T.; Liu, J.; Elsworth, D.; Chen, T.; Xiong, W. Preliminary study on the feasibility of co-exploitation of coal and uranium. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2019, 123, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Vuik, C.; Hajibeygi, H. A stabilized mixed-fe scheme for frictional contact and shear failure analyses in deformable fractured media. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 267, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, K.; Kumar, S.A.; Kumar, M.A.; Rajendra, S. Underground mining of thick coal seams. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y. Scientific conception of precise coal mining. J. Coal 2017, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ma, Z.; Bai, E. Current status and prospect of coal mining technology under buildings, water bodies and railways, and above confined water in China. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 47, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gläser, D.; Helmig, R.; Flemisch, B.; Class, H. A discrete fracture model for two-phase flow in fractured porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 110, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Mathews, J.P.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Tao, S.; Li, S. Evaluation of coal macrolithotypes distribution by geophysical logging data in the hancheng block, eastern margin, Ordos basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yu, R.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Sima, X.; Tang, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Si, Q.; Li, G.; et al. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and fluid action process of uranium deposits in the Zhiluo formation, Ordos basin, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 111, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Yang, X.; Pirajno, F. Sandstone type uranium deposits in the Ordos basin, Northwest China: A case study and an overview. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 146, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y. Coupled multifield response to coordinate mining of coal and uranium: A case study. Water 2019, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.C.; Wei, C.H. Numerical simulation on mining-induced water inrushes related to geologic structures using a damage-based hydromechanical model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lin, B.-Q.; Qu, Y.-A.; Li, Z.-W.; Zhai, C.; Jia, L.-L.; Zhao, W.-Q. Stress evolution with time and space during mining of a coal seam. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2011, 48, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Nie, X.; Yang, K.; Li, J. Investigations into Mining-Induced Stress–Fracture–Seepage Field Coupling Effect Considering the Response of Key Stratum and Composite Aquifer. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 4017–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wei, F.; Yu, X. Modeling of multiphysical–chemical coupling for coordinated mining of coal and uranium in a complex hydrogeological environment. Nat. Resour. Res. 2020, 30, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Miao, H.; Liu, K. Discussion on water environment problems induced by coal mining in Jining City. Met. Mines 2013, 5, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allow, K.A. The use of injection wells and a subsurface barrier in the prevention of seawater intrusion: A modelling approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 5, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, K.; Perera, M.; Elsworth, D.; Matthai, S.; Ranjith, P.; Dong-Yin, L. Discrete fracture matrix modelling of fully-coupled CO2 flow—Deformation processes in fractured coal. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2021, 138, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wei, M.; Elsworth, D. Coal permeability maps under the influence of multiple coupled processes. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 187, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Werner, J.; Ali, Z.A.; Bertucci, L.; Groppo, J. Kinetics and Modeling of Counter-Current Leaching of Waste Random-Access MemoryChips in a Cu-NH3-SO4 System Utilizing Cu(II) as an Oxidizer. Materials 2023, 16, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lien, T.; Dinh, T.T.; Dung, N.T.K. Study on leaching systems and recovery for PALUA–PARONG low grade uranium sandstone ores. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Mechanism and application of hydraulic curtain in water injection wells to prevent seawater intrusion. J. Yangtze River Acad. Sci. 2009, 26, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemcov, I. Impact assessment of grout curtain on the hydraulic behavior in karst, based on time a series analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Y. Hydrological effects of the underground hydraulic curtain with different design parameters based on numerical modeling for a co-exploitation of coal and uranium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 257, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hou, K. Application status and development trend of curtain grouting technology in mine water control. Mod. Min. 2010, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Yue, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, L. The temperature distribution along a freezing pipe wall during liquid nitrogen freezing. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2013, 42, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J. Ground controlled by freezing technology: Leaching uranium extraction: The feasibility analysis on control of drawing and injecting liquid flow rate by the technology of freezing in-situ leaching uranium. Uranium Min. Metall. 2017, 36, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baborowski, M.; Bozau, E. Impact of former mining activities on the uranium distribution in the River Saale (Germany). Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bister, S.; Birkhan, J.; Lüllau, T.; Bunka, M.; Solle, A.; Stieghorst, C.; Riebe, B.; Michel, R.; Walther, C. Impact of former uranium mining activities on the floodplains of the Mulde River, Saxony, Germany. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 144, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lian, G.; Cao, F.; Yang, B. Non-uniform sampling Injection technology in-situ leaching Application of groundwater environmental protection. Uranium Min. Metall. 2017, 36 (Suppl. S1), 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).