Abstract
The adsorption of CO2 fracturing fluid into coal reservoirs causes the expansion of the coal matrix volume, resulting in changes in the fracture opening, which alters the permeability of the coal reservoir. However, it is not yet clear whether thermal expansion during CO2 adsorption on coal is the main cause of coal adsorption expansion. Therefore, by testing the thermal properties, expansion coefficient, and adsorption heat of the three coal samples, the adsorption thermal expansion characteristics of coal and their impact on the permeability of coal reservoirs are clarified. The results reveal the following: (1) Under the same conditions, the adsorption heat increases with increasing pressure, while it decreases with increasing temperature. The relationship between adsorption heat and pressure conforms to the Langmuir equation before 40 °C, and it follows a second-order equation beyond 40 °C. At 100 °C, the adsorption heat of coal samples to CO2 is primarily determined by temperature. (2) The maximum temperature variation in coal samples from Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang during CO2 adsorption is 95.767 °C, 87.463 °C, and 97.8 °C, respectively. The maximum thermal expansion rates are 12.66%, 5.74%, and 14.37%, and the maximum permeability loss rates are 16.16%, 7.51%, and 18.24%, respectively, indicating that thermal expansion is the main reason for coal adsorption expansion. (3) This research can elucidate the impact of CO2 fracturing fluid on coal reservoirs and its potential application value, thus providing theoretical support for coalbed methane development and CO2 geological storage.
1. Introduction
The adsorption and desorption of CO2 fracturing fluid into coal reservoirs result in the expansion and contraction of the coal matrix, respectively. The expansion and contraction alter the fracture openings, thereby altering the permeability of the coal reservoir, and affecting the output of coalbed methane [1,2,3]. Generally, higher reservoir pressure results in more significant adsorption expansion and desorption contraction effects [4]. Scholars worldwide [5,6,7] have long studied the deformation effects of coal during adsorption and desorption reaching a consensus that adsorption causes expansion while desorption causes contraction. There are three main theories explaining the adsorption expansion and desorption contraction mechanisms of coal: First, gas adsorption drives gas molecules into the pores and fractures of the coal, causing the sorption layer to wedge open micropores and cracks similar in size to the gas molecules, thus triggering coal expansion [8,9]; second, the interaction between gas molecules adsorbed on the coal surface and the coal surface molecules causes expansion [10,11]; third, gas adsorption weakens the van der Waals forces between coal macromolecules, reducing the internal attraction energy of the coal and increasing the expansion energy, which leads to coal expansion [12,13]. However, these theories are based on the exothermic nature of adsorption and the endothermic nature of adsorption and are not entirely convincing.
Coal is an organic material composed of high-molecular polymers, making it a unique substance. Like any material, coal exhibits thermal expansion and contraction and is sensitive to temperature changes. Variations in the thermal expansion and contraction coefficients of coal are due to differences in coal rank, petrological composition, molecular structure, and rock mass structure [14,15,16]. Heating experiments on coal indicate that, as the temperature increases, the deformation of coal gradually increases, and its permeability decreases [17,18]. Additionally, the heat released during gas adsorption (adsorption heat) causes changes in coal temperature. This adsorption heat is influenced by factors such as adsorption pressure, coal rank, coal rock composition, gas type, adsorption capacity, and temperature. The greater the adsorption heat of coal to gas, the more significant the temperature change in the coal, and the more pronounced the thermal expansion caused by heating [19]. There are no clear conclusions on whether thermal expansion during adsorption is the main cause of coal adsorption. The thermal properties of coal, the variation in coal temperature, and the change in thermal expansion rate with adsorption pressure caused by the adsorption heat of adsorbed gas have not been comprehensively studied. Additionally, the impact of coal deformation during thermal expansion on the permeability of coal reservoirs is rarely addressed in comprehensive research.
Therefore, this paper selects three types of primary structural coal with different metamorphic grades from China’s coalbed methane exploration and development hot spots as experimental samples. By testing the thermal properties, expansion coefficient, and adsorption heat of these coal samples, the study investigates the adsorption heat generated during CO2 adsorption, the resulting coal temperature variation, the thermal expansion rate, and the permeability loss rate at different adsorption pressures. This research aims to clarify the thermal expansion characteristics of coal during adsorption and their impact on the permeability of coal reservoirs. Through this study, we seek to further elucidate the effects of CO2 fracturing fluid on coal reservoirs, thereby providing theoretical support for coalbed methane development and CO2 geological storage.
2. Coal Sample Source and Experimental Test
2.1. Coal Sample Source
Three types of primary structural coals with different metamorphic grades from the southern margin of the Junggar Basin (Xinjiang), the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin (Liulin), and the central and southern parts of the Qinshui Basin (Zhaozhuang) were selected as experimental samples (Table 1).

Table 1.
Basic parameters of coal samples.
2.2. Experimental Test
2.2.1. Thermal Property Test
The coal sample was processed into a thin sheet with a diameter of 10 mm and a thickness of 2 mm, and then, the thermal capacity, thermal conductivity, and thermal diffusivity of the coal sample were tested using the LFA 467 laser-flash apparatus produced by NETZSCH located in Selb, Germany (Table 2). The sample preparation process is as follows: grind the coal sample into a powder of about 60 mesh, then take the appropriate amount of powder into the powder tablet press mold, pressurize to more than 10 Mpa, wait for five minutes, and then the tablet production is completed.

Table 2.
Thermal properties and linear expansion coefficient of coal samples.
2.2.2. Linear Expansion Coefficient Test
The coal sample was processed into a rod with a diameter of 10 mm and a height of 25 mm. The linear expansion coefficient of the coal sample was then tested using the DIL 402 PC thermal expansion coefficient tester produced by NETZSCH located in Europe (Table 2).
2.2.3. Adsorption Heat Test
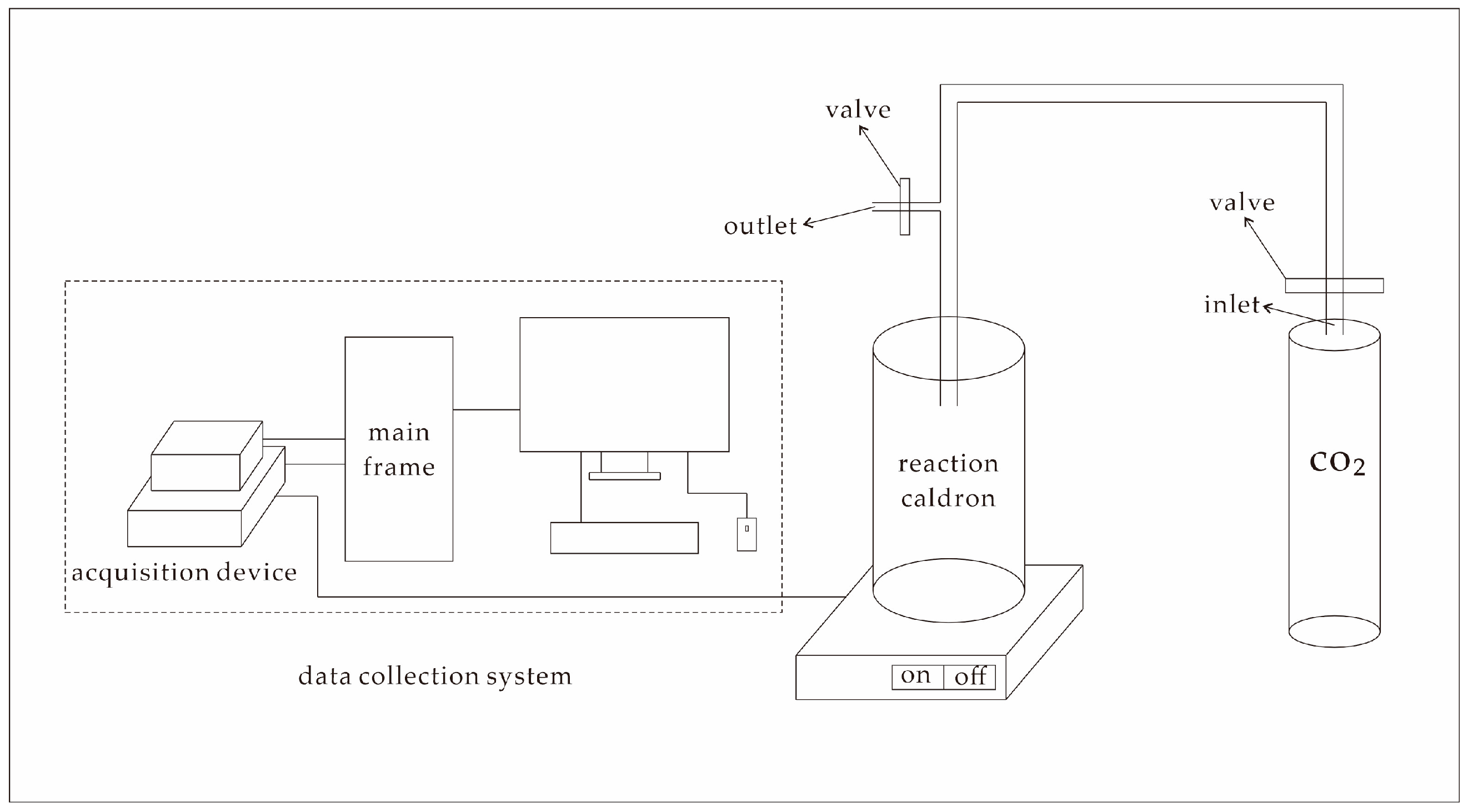
The heat released by coal in the process of adsorbing gas is called adsorption heat. The coal sample was ground to about 20 mesh and placed in a 60 °C drying oven. After drying for 48 h, remove the sample and store it in a sealed plastic bag for later use. The adsorption heat of coal samples during CO2 adsorption was determined using the C80 Calvet Calorimeter (Figure 1) produced by SETARAM located in Caluire-et-Cuire, France. Each sample weighed 1 g, and the test pressures were set to 1 MPa, 2 MPa, 3 MPa, and 4 MPa, with test temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C, 80 °C, and 100 °C. The curves of adsorption heat versus adsorption pressure (Figure 2) and adsorption heat versus temperature (Figure 3) during the CO2 adsorption process were obtained by fitting Equation (1) [20] and a two-order equation, respectively.

Figure 1.
C80 Calvet Calorimeter.
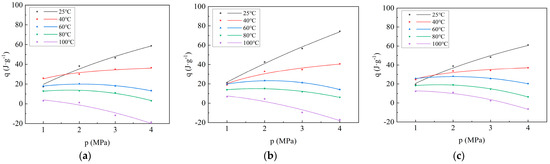
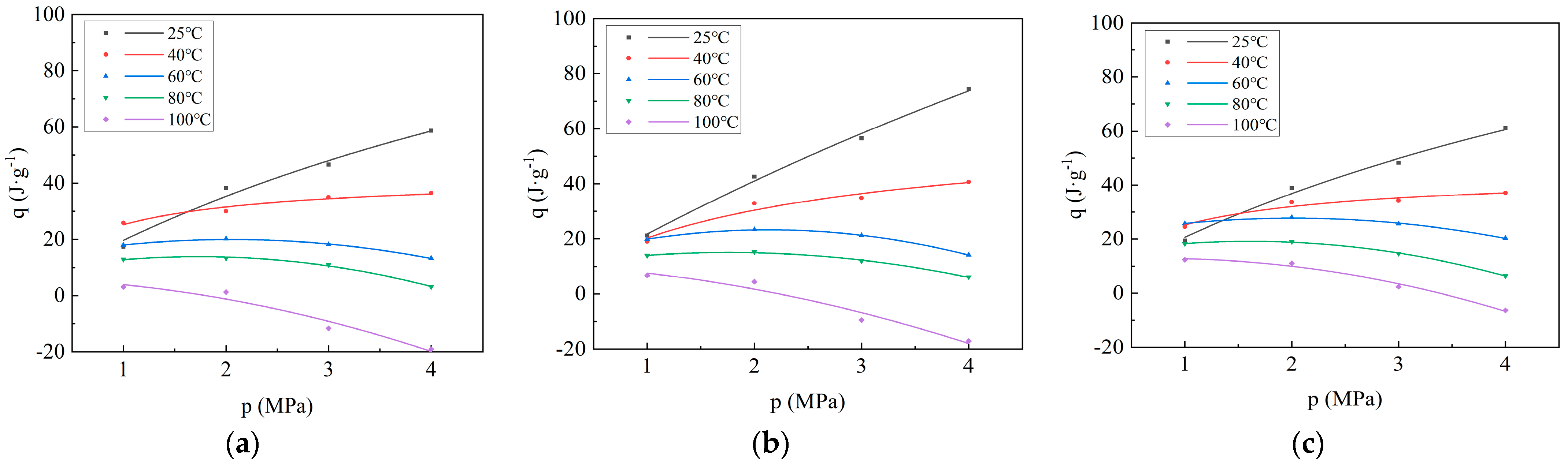
Figure 2.
Curves of adsorption heat versus adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption on coal: (a) Xinjiang; (b) Liulin; and (c) Zhaozhuang.
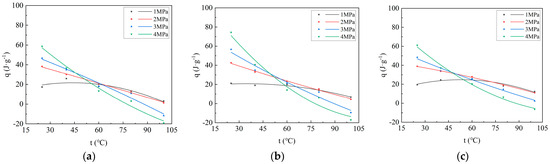
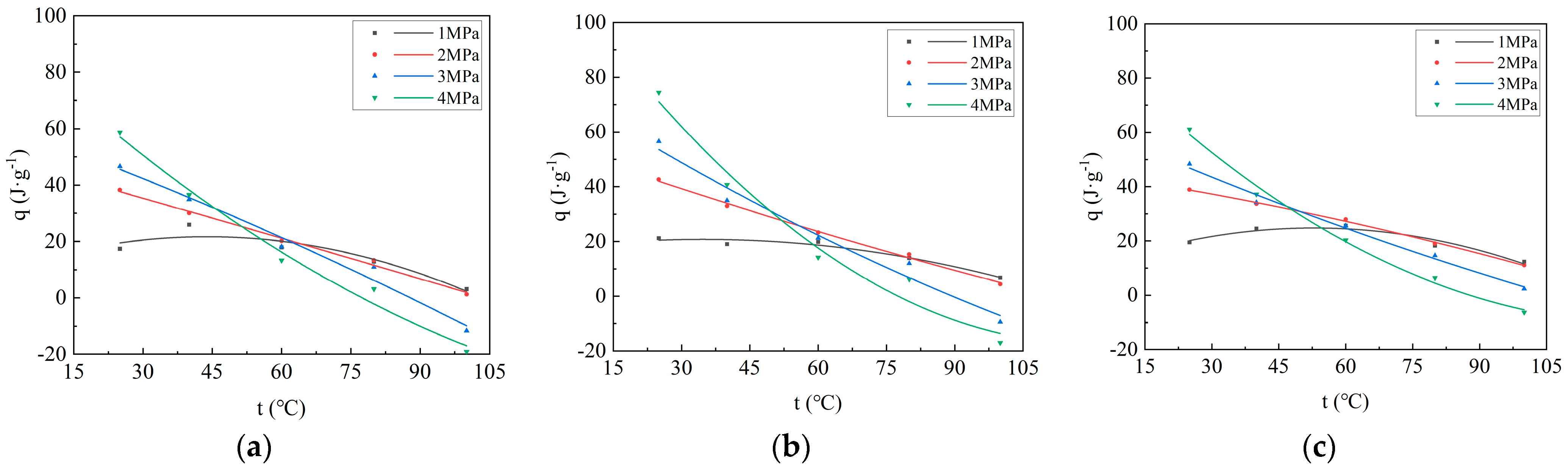
Figure 3.
Curves of adsorption heat versus adsorption temperature during CO2 adsorption on coal: (a) Xinjiang; (b) Liulin; and (c) Zhaozhuang.
Here, q denotes the adsorption heat in J/g. p denotes the pressure in MPa. qL denotes the maximum value of adsorption heat in J/g. pL denotes the pressure at which the adsorption heat reaches 50% of the maximum adsorption heat in MPa.
3. The Adsorption Thermal Expansion Characteristics of Coal
3.1. Adsorption Heat
As depicted in Figure 2, at 25 °C and 40 °C, the adsorption heat generated by the adsorption of CO2 by coal samples increases rapidly with the increase in adsorption pressure, and then gradually stabilizes, which is consistent with the Langmuir equation. The measured adsorption heat is the integral heat of adsorption, defined as the heat released by the solid adsorbing a certain amount of gas. Therefore, the greater the adsorption capacity, the greater the adsorption heat. Considering that the adsorption capacity and adsorption pressure of coal adsorbing CO2 follow the Langmuir equation, the relationship between adsorption heat and pressure also follows the Langmuir equation. The numerical value of adsorption heat is affected by temperature and pressure. The increase in temperature is not conducive to adsorption, so the adsorption heat decreases. The increase in pressure is conducive to adsorption; thus, the adsorption heat increases. It can be seen from Figure 2 that, at 25 °C and 40 °C, the adsorption heat increases with increasing pressure, indicating that pressure is the main factor affecting the adsorption heat at this time. At 60 °C and 80 °C, before 2 Mpa, the adsorption heat increases with increasing pressure, and beyond 2 Mpa, the adsorption heat decreases with increasing pressure, indicating that before 2 Mpa, pressure is still the main factor affecting the adsorption heat, and beyond 2 Mpa, temperature is the main factor affecting the adsorption heat. Under the condition of 100 °C, the adsorption heat decreases with the increase in pressure, indicating that temperature is the main factor affecting the adsorption heat. At 60 °C, the adsorption heat first increases and then decreases with the increase in adsorption pressure. The relationship between adsorption heat and pressure no longer follows the Langmuir equation but instead conforms to a second-order equation. At 80 °C, the adsorption heat also increases first and then decreases with increasing adsorption pressure. At 100 °C, the adsorption heat decreases with increasing pressure. In summary, from 25 °C to 100 °C, the adsorption heat showed an obvious stage variation with increasing adsorption pressure. At 25 °C and 40 °C, the adsorption heat increases rapidly at first and then stabilizes with increasing pressure. At 60 °C and 80 °C, the adsorption heat first increases and then decreases with increasing pressure. At 100 °C, the adsorption heat decreases with increasing pressure. According to the fitting curve and equation (Table 3), at 25 °C, the adsorption heat of the coal samples follows the order: Liulin > Zhaozhuang > Xinjiang. The order corresponds to the porosity of the coal samples: Liulin > Zhaozhuang > Xinjiang (Table 1). Under the same conditions, the adsorption capacity also follows the order: Liulin > Zhaozhuang > Xinjiang. Considering that greater adsorption capacity results in more heat being released, the adsorption heat capacity is stronger. At 40 °C, the relationship of adsorption heat among the three coal samples does not show consistency under the same conditions. After 60 °C, the adsorption heat follows the order: Zhaozhuang > Liulin > Xinjiang; the relationship of adsorption heat among the three coal samples becomes consistent. This indicates that 40 °C is a transition period where temperature begins to exert a major influence on adsorption heat. After 60 °C, temperature has completely become the main factor influencing adsorption heat. Figure 3 illustrates that the adsorption heat decreases with increasing temperature, indicating that a higher temperature is not conducive to gas adsorption. As temperature increases, molecular thermal motion intensifies, and intermolecular van der Waals forces decrease, which facilitates gas desorption. Additionally, at 100 °C, the adsorption heat at 3 MPa and 4 MPa is negative, indicating an endothermic reaction. This occurs because, under high pressure, the pore size of the porous medium decreases to a certain extent, making it more difficult for adsorption molecules to enter the pores owing to the higher barrier and reduced diffusion caused by smaller pore size. This phenomenon leads to instability after adsorption and an increase in energy, resulting in a positive enthalpy change greater than 0, characterizing an endothermic reaction [21]. Additionally, with increasing temperature, the rate of reduction in adsorption heat varies under different pressures. The higher the pressure, the stronger the inhibitory effect of temperature on adsorption heat. Because under high-pressure conditions, the forementioned endothermic situation occurs, and the higher the pressure, the earlier this phenomenon arises during heating. Therefore, the inhibitory effect on adsorption heat becomes more pronounced. Consequently, the higher the pressure, the more significant the inhibitory effect of temperature on adsorption heat.

Table 3.
Fitting equation of adsorption heat with adsorption pressure during the CO2 adsorption process on coal.
3.2. Effect of Adsorption Heat on Coal Temperature
The heat released from CO2 adsorption by coal alters the coal temperature. If the adsorption system is considered an isolated system with no energy exchange with the surroundings, the temperature change in a unit mass of coal after the release of heat from CO2 adsorption can be calculated using the specific heat formula (Formulas (2) and (3)). This temperature change (Formula (4)) of coal is directly proportional to the adsorption heat and inversely proportional to the thermal capacity.
Here, Q is the heat absorbed/released by the increase/decrease in the object’s temperature, measured in joules (J); q is the adsorption heat, measured in joules per gram (J/g); c is the thermal capacity of the object, measured in joules per gram per degree Celsius (J/(g·K)); m is the mass of the object, measured in grams (g); ΔT is the temperature variation in the object, measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
The temperature variation during the CO2 adsorption process of coal samples (Table 4) is calculated using Formula (4) and the thermal capacity test results of coal samples (Table 2). Owing to the abundance of data, only the maximum temperature variation in CO2 adsorption for coal samples under each temperature condition is listed in the table (Table 4).

Table 4.
Adsorption heat and temperature variation in coal samples during the CO2 adsorption process.
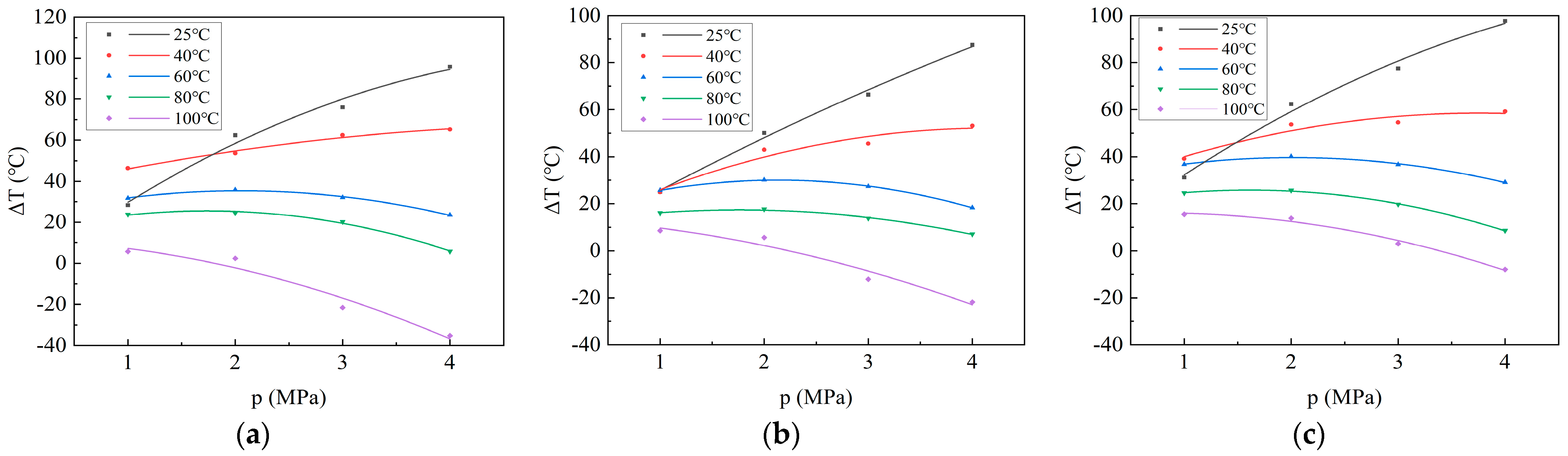
According to the above, the relationship between adsorption heat and adsorption pressure conforms to the Langmuir equation. Similarly, according to Formula (4), the relationship between cΔT and adsorption pressure also conforms to the Langmuir equation. Therefore, mathematically, the relationship between temperature variation and adsorption pressure does not follow the Langmuir equation. However, the trend of the relationship between the temperature variation and pressure and the trend of adsorption heat with pressure should be similar. Hence, it is more appropriate to fit a second-order equation to the temperature variation. The curve of temperature variation with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption on coal samples is obtained through fitting (Figure 4). The pattern of temperature variation with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption on coal samples is similar to that of adsorption heat with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption. Specifically, at 25 °C and 40 °C, the temperature variation increases rapidly with the increase in adsorption pressure and then gradually stabilizes. At 60 °C and 80 °C, the temperature change initially increases and then decreases with the increase in adsorption pressure. At 100 °C, the initial temperature variation decreases with the increase in adsorption pressure. At 4 MPa, the temperatures of Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples increased by 95.767 °C, 87.463 °C, and 97.8 °C, respectively, after CO2 adsorption (Table 4). This aspect has not been recognized in previous studies. During the adsorption/desorption process of coal reservoirs under in situ conditions, the environment cannot be considered an independent energy system; it must exchange energy with the surrounding environment. The temperature change in the coal may not be severe, but there will be changes. However, owing to the influence of terrestrial heat flow, the temperature will quickly return to the original reservoir temperature. Consequently, the change in reservoir temperature caused by this adsorption heat is not significant.
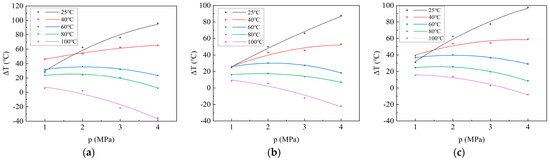
Figure 4.
Curves illustrating temperature variation in coal samples with adsorption pressure during the CO2 adsorption process: (a) Xinjiang; (b) Liulin; and (c) Zhaozhuang.
3.3. Thermal Expansion Rates
Coal is a material composed of organic matter, and like any material, it exhibits thermal expansion and contraction. Anthracite, in particular, which shares some characteristics with metals, demonstrates more pronounced thermal expansion and contraction phenomena. The results of the linear expansion coefficient tests for coal samples (Table 2) are utilized in Formula (5) to determine the volume expansion coefficient of coal (Table 5). By substituting the volume expansion coefficient and temperature variation in coal (Table 4) into Formula (6), the thermal expansion rate of coal samples can be derived (Table 5). Owing to the abundance of data, only the maximum thermal expansion rate of CO2 adsorbed by coal samples at each temperature condition is listed in the table (Table 5).

Table 5.
Volume expansion coefficient and thermal expansion rate of coal samples during CO2 adsorption.
Here, γ denotes the volume expansion coefficient, measured in K−1; α is the linear expansion coefficient, measured in K−1; η is the thermal expansion rate, measured in %.
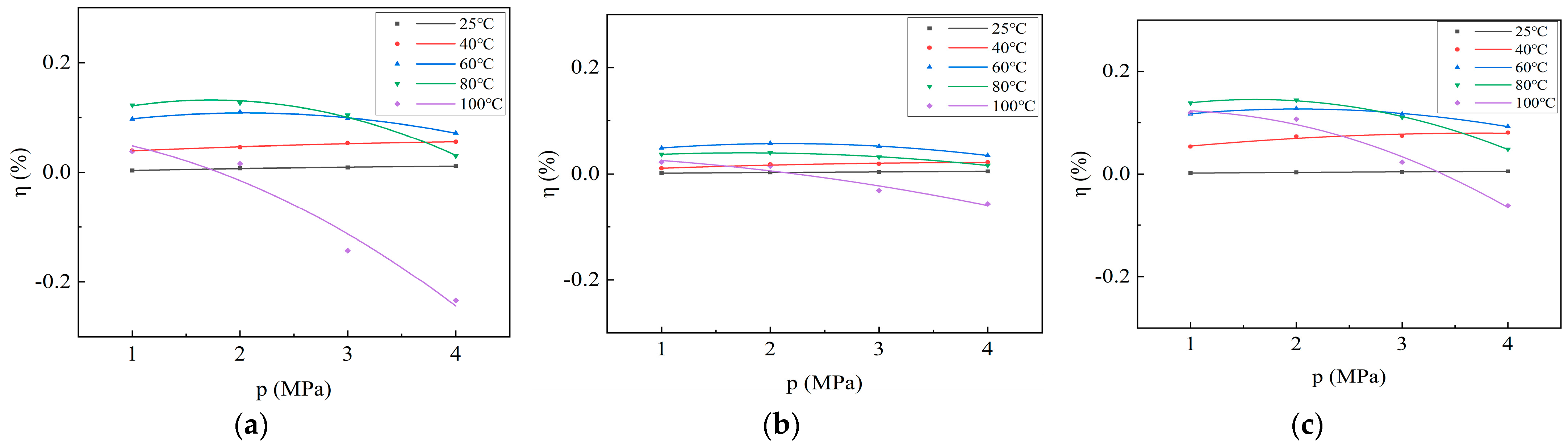
Equation (6) illustrates that the thermal expansion rate is directly proportional to the temperature variation, which, in turn, is proportional to the adsorption heat. Consequently, the thermal expansion rate is also directly proportional to the adsorption heat. Although the relationship between temperature variation and adsorption pressure does not adhere to the Langmuir equation, the relationship between thermal expansion rate and adsorption pressure is likely to exhibit a similar trend to that of the adsorption heat pressure curve. A second-order equation is fitted to the thermal expansion rate data to obtain the curve describing the thermal expansion rate with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption by coal samples (Figure 5). At 25 °C and 40 °C, the thermal expansion rates of the three coal samples increase rapidly and then stabilize with increasing adsorption pressure. At 60 °C and 80 °C, they initially increase before decreasing with increasing pressure, while at 100 °C, they decrease with increasing pressure. Moreover, the maximum thermal expansion rates of CO2 adsorption by Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples reach 12.66%, 5.74%, and 14.37%, respectively (Table 5). These significant changes in coal matrix volume resulting from the release of adsorption heat indicate that thermal expansion is the primary driver of coal adsorption expansion in actual coal reservoirs.
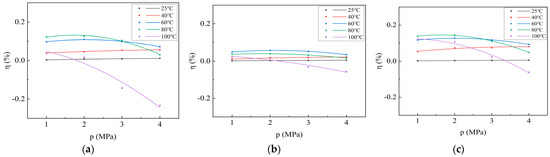
Figure 5.
Curve depicting the variation in thermal expansion rate with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption on coal samples: (a) Xinjiang; (b) Liulin; and (c) Zhaozhuang.
3.4. Effect of Thermal Expansion on Coal Permeability
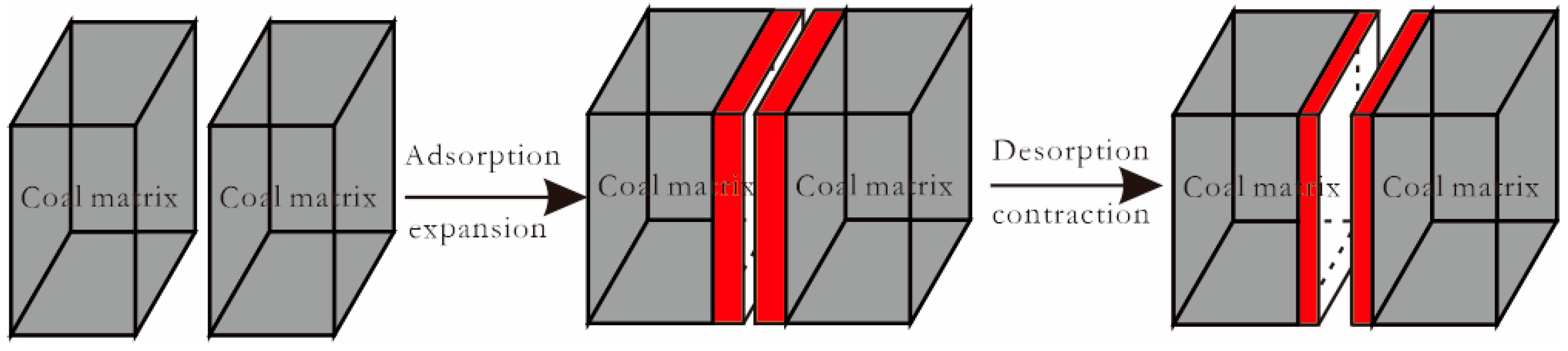
The coal matrix releases heat during CO2 adsorption, leading to thermal expansion, and absorbs heat and contracts during CO2 desorption, resulting in a change in fracture width (Figure 6).
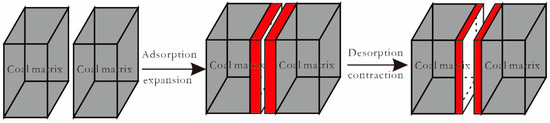
Figure 6.
Change in fracture width before and after expansion of the coal matrix.
To characterize the relationship between fracture width and permeability, the cubic law [22] can be utilized to depict the seepage behavior within a single fracture. The fracture is abstracted as a parallel plate with a certain opening. Under the influence of a stable equilibrium pressure gradient, the cubic law expression derived from the Navier–Stokes equations is as follows:
Here, Qv is the flow rate, measured in m3/s. b is the fracture opening, measured in m. p is pressure, measured in Pa. l is the length of the parallel plate, measured in m. μ is the dynamic viscosity coefficient of the fluid, measured in mPa·s.
Fracture porosity is expressed as follows:
Here, φf is fracture porosity, expressed as a%. A is the sectional area of the sample, measured in m2.
By substituting Formula (8) into Formula (7), we obtain the following:
Here, assuming that the effective permeability of the fracture model is kf, Darcy’s law is given as follows:
where kf is the effective permeability of the fracture model, measured in m2.
Through the combination of Formulas (9) and (10), the relationship between permeability and fracture width can be obtained (note: for a single fracture, A = bl, so the single fracture porosity is 1):
Then, the permeability per unit fracture width is expressed as follows:
After the thermal expansion of the adsorbed gas, the permeability per unit fracture width is expressed as follows:
Here, k′f is the permeability per unit fracture width after thermal expansion, measured in m2, and α is the linear expansion coefficient, measured in K−1.
By combining Formulas (12) and (13), we obtain the following:
Here, Δk is the permeability loss rate after the thermal expansion of the adsorbed gas, expressed as a%.
Through the substitution of the linear expansion coefficient (Table 2) and temperature variation (Table 4) of coal samples into Formula (14), the permeability loss rate of coal after thermal expansion can be obtained (Table 6). Owing to the abundance of data, only the maximum permeability loss rate of CO2 adsorbed by coal samples at each temperature condition is listed in the table (Table 6).

Table 6.
Permeability loss rate of coal samples during CO2 adsorption.
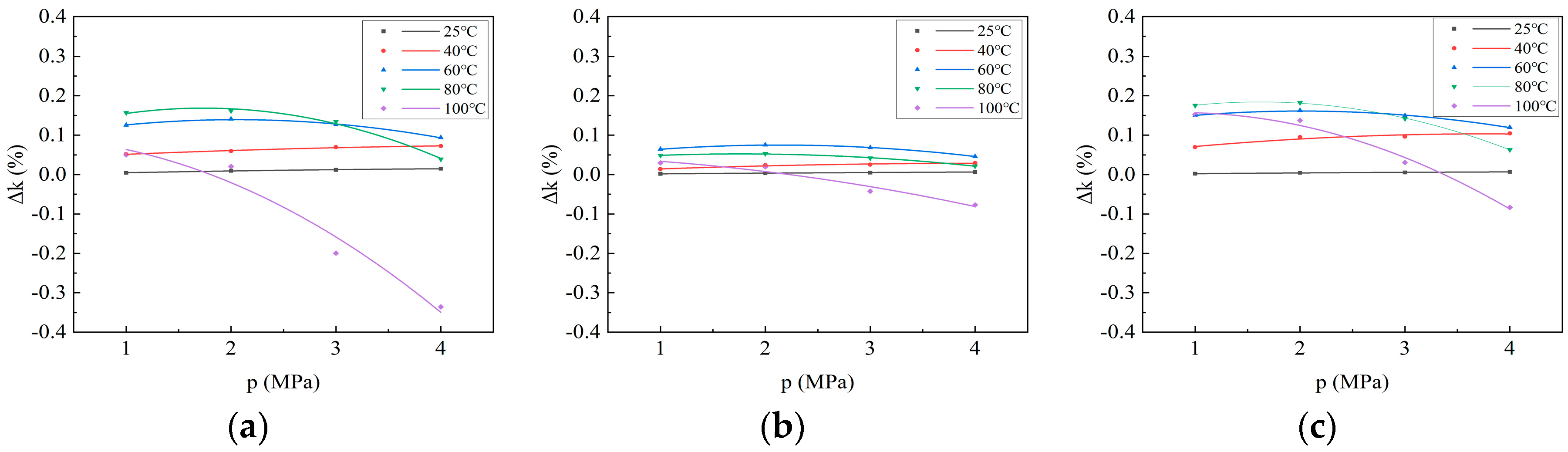
As depicted in Formula (14), the permeability loss rate is not directly proportional to the temperature change; therefore, the relationship between the permeability loss rate and the adsorption pressure may not conform to the Langmuir equation. The permeability loss rate is fitted using a second-order equation to obtain the curve illustrating the change in permeability loss rate with adsorption pressure during the CO2 adsorption process of the coal samples (Figure 7). The correlation coefficient R2 exceeds 0.9, indicating a good fit to the second-order equation. Additionally, as depicted in Figure 6, the change in permeability loss rate with adsorption pressure is similar to the change in adsorption heat with adsorption pressure. At 25 °C and 40 °C, the permeability loss rate increases rapidly with increasing adsorption pressure and then stabilizes. At 60 °C and 80 °C, the permeability loss rate first increases and then decreases with increasing adsorption pressure. At 100 °C, it decreases with the increase in adsorption pressure.
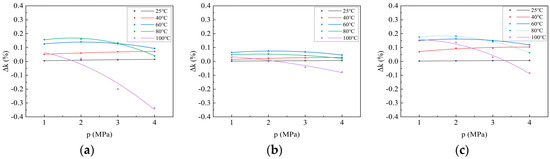
Figure 7.
Variation curve of permeability loss rate with adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption on coal samples: (a) Xinjiang; (b) Liulin; and (c) Zhaozhuang.
In addition, the maximum permeability loss rates of CO2 adsorbed by Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples reached 16.16%, 7.51%, and 18.24%, respectively (Table 6). This indicates that the coal expands owing to heating, which reduces the fracture opening between the coal matrix blocks. Consequently, the channels for coalbed methane migration become smaller, reducing the permeability of the coal reservoir.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under the same conditions, the adsorption heat increases with increasing pressure and decreases with increasing temperature. The relationship between adsorption heat and adsorption pressure conforms to the Langmuir equation up to 40 °C. Beyond 40 °C, the relationship conforms to a second-order equation, and at 100 °C, the adsorption heat during CO2 adsorption is more affected by temperature. The relationship between temperature variation, thermal expansion rate, permeability loss rate, and adsorption pressure during CO2 adsorption conforms to a second-order equation, and the change trends of these parameters with pressure are similar to the change trend of adsorption heat with pressure.
- (2)
- At 4 MPa, the temperatures of Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples increased by 95.767 °C, 87.463 °C, and 97.8 °C, respectively, after CO2 adsorption. Under the in situ condition of the coal reservoir, owing to energy exchange with the surrounding environment, the temperature variation in the coal is not severe.
- (3)
- The maximum thermal expansion rates of Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples reach 12.66%, 5.74%, and 14.37%, respectively, after CO2 adsorption. Under the in situ condition of the coal reservoir, the change in coal matrix volume caused by the heat released by adsorbed CO2 is considerable, indicating that thermal expansion is the main reason for coal adsorption expansion.
- (4)
- The thermal expansion of coal samples during the CO2 adsorption process leads to a decrease in coal reservoir permeability, with the maximum permeability loss rates of Xinjiang, Liulin, and Zhaozhuang coal samples reaching 16.16%, 7.51%, and 18.24%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.; Methodology, Y.S.; Writing—original draft, Y.S.; Writing—review & editing, Y.L.; Project administration, Y.L.; Funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (no. 242300420222), the Key scientific and technological projects of Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (no. 232102321139), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 42230804), The “Double First Class” Discipline Creation Project of the Department of Safety and Energy Engineering at Henan Polytechnic University (no. AQ20230715), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (no. NSFRF240811).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [author initials], upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lyu, Q.; Shi, J.; Gamage, R.P. Effects of testing method, lithology and fluid-rock interactions on shale permeability: A review of laboratory measurements. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 78, 103302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Huo, J.; Li, S.; Li, X. Modeling study on supercritical CO2 fracturing applicability and capacity to stimulate reservoirs with different permeabilities. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 213, 110427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lian, H.; Li, L. Fracturing in coals with different fluids: An experimental comparison between water, liquid CO2, and supercritical CO2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 110427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Q.; Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. CO2 adsorption and swelling of coal under constrained conditions and their stage-change relationship. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 76, 103205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Du, Z.; Wang, G.G.; Heng, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, J. CO2 and N2 adsorption/desorption effects and thermodynamic characteristics in confined coal. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath KH, S.M.; Perera MS, A.; Matthai, S.K.; Ranjith, P.G.; Dong-yin, L. Modelling of fully-coupled CO2 diffusion and adsorption-induced coal matrix swelling. Fuel 2020, 262, 116486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-wei, C.; Lin, W.; Tian-hong, Y.; Hong-min, Y. Deformation and swelling of coal induced from competitive adsorption of CH4/CO2/N2. Fuel 2021, 286, 119356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, H. Insight into the Adsorption of Methane on Gas Shales and the Induced Shale Swelling. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31508–31517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Niu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Weng, H.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Du, Z. CO2 Adsorption/Desorption, Induced Deformation Behavior, and Permeability Characteristics of Different Rank Coals: Application for CO2-Enhanced Coalbed Methane Recovery. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 5709–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; He, H.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Hou, Q.; Liu, L.; Cheng, N. Anisotropic strain of anthracite induced by different phase CO2 injection and its effect on permeability. Energy 2023, 284, 128619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Elsworth, D.; Fu, X.; Liang, S.; Chen, H. Contribution of thermal expansion on gas adsorption to coal sorption-induced swelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Masum, S.; Sadasivam, S.; Thomas, H. Modelling anisotropic adsorption-induced coal swelling and stress-dependent anisotropic permeability. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 153, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhao, K.; Lei, C.; Wen, H.; Ma, L.; Shu, C.M. Deformation mechanism and displacement ability during CO2 displacing CH4 in coal seam under different temperatures. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 108, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.J.; Wang, C.P.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, J.; Tian, Y.; Song, J.J.; Chen, X.-J.; Sun, G.F. Thermal properties of coal during low temperature oxidation using a grey correlation method. Fuel 2020, 260, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Zhai, C.; Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Tang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, J. Study on typical temperature effect mechanism of multi-component coal during low-temperature thermal expansion. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 43, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Feng, Z.; Cai, T.; Shen, Y. Coal Permeability Variation during the Heating Process considering Thermal Expansion and Desorption Shrinkage. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7848388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Su, X.; Yu, S.; Su, L.; Hou, J.; Wang, Q. Experimental Investigation of the Thermal Expansion Characteristics of Anthracite Coal Induced by Gas Adsorption. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2023, 5201794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, L. Permeability Evolution of Naturally Fractured Coal Injected with High-Temperature Nitrogen: Experimental Observations. Processes 2021, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, Q.; Kang, J.; Cheng, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S. A Comparative Investigation of the Adsorption Characteristics of CO2, O2 and N2 in Different Ranks of Coal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 40, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.A.; Liu, J.; Thallapally, P.K.; Strachan, D.M. Switching Kr/Xe Selectivity with Temperature in a Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9046–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Shang, X.; He, P. A Connectivity Metrics-Based Approach for the Prediction of Stress-Dependent Fracture Permeability. Water 2024, 16, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).