Abstract
Due to the time-varying, hysteresis and nonlinear characteristics of fertilizer concentration control in the water–fertilizer ratio control system, common control algorithms such as PID and fuzzy PID cannot obtain the expected control effect. In order to accurately control the cotton field water–fertilizer ratio regulation system drip irrigation process of the water–fertilizer ratio that will be controlled within a reasonable range, it is needed to design a bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID water–fertilizer ratio control strategy, through the use of bat algorithm to find out the optimal expansion factor and the best domain of the current conditions, and then according to the changes in working conditions to automatically adjust the fuzzy control of the domain, through the control of the valve openings to change the fertilizer pump back to the amount of water. Realize the fast and precise control of fertilizer concentration in the water–fertilizer ratio control system. Comparative tests were conducted to verify the traditional PID, fuzzy PID, variable domain fuzzy PID and bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID control algorithms. The results show that: if the water–fertilizer ratio is adjusted to 50:1 from the startup, the adjustment time required to reach the target water–fertilizer ratio under the bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID control is 15.29 s, and the maximum overshooting amount is 16.28%, which is a smaller adjustment time and overshooting amount; if the water–fertilizer ratio is adjusted to 40:1 from 50:1, the advantages of bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID are more obvious, with the best balance of response speed, overshooting amount and optimal control effect. In terms of response speed, overshooting amount and regulation time, the optimal balance is achieved, showing the optimal control effect. It is proved that the performance of the water–fertilizer ratio regulation system in cotton field under bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID control designed in this paper can meet the actual production requirements, and these findings can help to develop precise irrigation technology for cotton cultivation under drip irrigation conditions.
1. Introduction
Water–fertilizer integration technology refers to the scientific irrigation and fertilization technology according to crops’ water and fertilizer needs in different growth periods. In crop drip irrigation fertilization, a reasonable water and fertilizer ratio can avoid excessive irrigation waste, save water and fertilizer, and be more conducive to the growth and development of crop root systems. Reasonable water and fertilizer supply is the guarantee of crop yield [1,2,3]. Cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system fertilizer concentration regulation, if there are serious non-linear, time-varying, and hysteresis problems, will affect the overall operational efficiency of the intelligent drip irrigation system [4]. Presently, domestic and foreign countries mainly use PID control and fuzzy control strategy to realize crop intelligent drip irrigation, achieving a better control effect. In addition, scholars at home and abroad have proposed a large number of intelligent control algorithms to improve the control accuracy of the water–fertilizer ratio [5,6]. Sun G X et al. [7] proposed a segmented predictive control algorithm based on the nutrient dilution model for the fertilization accuracy of multichannel fertilizer applicator, and the study showed that the multichannel water–nutrient mixing ratio obtained under the algorithm had high accuracy, but the system only detects the total conductivity and pH in the fertilizer path, and it cannot obtain the fertilization amount of different fertilizers. Bahat et al. [8] proposed an intelligent control system to control the water–fertilizer ratio, which is a good control strategy. Bahat et al. [8] designed a drip irrigation controller based on a fuzzy logic control algorithm based on summarizing a variety of water–fertilizer machine control methods, and only simulated the simplicity of the fuzzy logic control model in the system design and structure through Simulink. This study lacked the validation in the fertilizer applicator and field trials, and was unable to evaluate its usefulness. Ashraf et al. [9] used a fuzzy decision support algorithm that was used to study the fertilizer application rate in wheat, but it is not universal. Meza-Palacios et al. [10] proposed a decision support system for fertilizer application based on a soil condition model and a nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization model, which can increase crop yield and reduce fertilizer use, but the system focuses on predicting the fertilizer requirement of the crop instead of controlling the amount of fertilizer to be applied. Gómez-Melendez et al. [11] used a fuzzy control algorithm to achieve pH adjustment of a water–fertilizer integrated control system, but the system can only reflect the pH of the water–fertilizer solution, which cannot reflect the amount of each fertilizer applied. Sun F S et al. [12] proposed time-varying nonlinear control algorithms to regulate the concentration of water–fertilizer and achieved a high control accuracy.
In summary, a large number of researchers combine intelligent control algorithms with water–fertilizer integration technology, and some of these algorithms are relatively simple and can realize the control of the water–fertilizer ratio to a certain extent, but there is a low precision of water–fertilizer solution rationing, which is difficult to meet the actual needs of drip irrigation fertilization [13]. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to explore the control strategies for the precise regulation of the water–fertilizer ratio control system in cotton fields, and through the application of these intelligent control algorithms and technologies, the optimal control of water–fertilizer integration technology can be better realized to improve the efficiency and quality of crop production and promote the sustainable development of agriculture [14]. We found that the system has nonlinearity, time-varying and hysteresis problems in the practical application of cotton field water–fertilizer ratio control system, and the common control algorithms, such as PID and fuzzy PID, could not obtain the expected control effect. The variable-theoretic fuzzy PID control strategy can effectively deal with the uncertainty and nonlinearity of the system; however, the variable-theoretic fuzzy PID controller requires a more complex computational process, especially in the real-time control system. The selection of the controller parameters has a great influence on the performance of the system, and inappropriate parameter settings may lead to the degradation of the system performance. The bat optimization algorithm can find out the optimal scaling factor and derive the best thesis domain for the current working condition, and then automatically adjust the thesis domain of fuzzy control according to the change of working condition to solve the over-adjustment phenomenon of the system caused by the variable-domain fuzzy PID controller when the dynamics of cotton field water–fertilizer ratio control system changes rapidly, so as to improve the system’s efficiency and effectiveness. This study aims to combine automation technology and intelligent control algorithms to design a variable-domain fuzzy PID water–fertilizer ratio control system and monitor the changes in the water–fertilizer ratio during drip irrigation in real-time by flow sensors, to provide technical support for the precise control of the water–fertilizer ratio in water–fertilizer integrated drip irrigation.
The Section 1 of this paper analyzes the advantages and challenges of water–fertilizer integration technology and introduces the research progress made by scholars on water–fertilizer ratio control systems. The Section 2 describes the structural composition of the cotton field water–fertilizer ratio control system and the design of various controllers: the conventional PID controller, the fuzzy PID controller, the variable domain fuzzy PID controller, and the bat-optimized variable domain fuzzy PID controller. It also examines the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. In the Section 3, Matlab software (Matlab 2019) is used to establish simulation models for each of the four algorithms for analysis, and a water–fertilizer ratio regulation test bed is constructed for experimental verification. The Section 4 summarizes the conclusions derived from the study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structural Composition of Cotton Field Water and Fertilizer Ratio Control System
The cotton field water–fertilizer ratio control system consists of a water reservoir, fertilizer storage tank, pumping pump, flow meter, peristaltic pump, electronically controlled flow regulating valve, check valve, drip irrigation belt, branch valve, and other parts. Among them, the fertilizer storage tank is part of two chambers, namely, a liquid fertilizer storage chamber and a water–fertilizer mixture mixing chamber. The liquid fertilizer is stored in the liquid fertilizer storage chamber of the cotton field fertilizer storage tank, and a small fertilizer pump is placed inside the chamber, which is responsible for pumping the liquid fertilizer into the water–fertilizer mixture mixing chamber. The cotton field fertilizer storage tank water and fertilizer mixing chamber is equipped with a mixing device, responsible for the irrigation water and liquid fertilizer mixing. The control center selected Siemens small controller S7-1200PLC, used to control the water pump located on the reservoir, is an electronically controlled flow control valve that will pump to the irrigation water tank mixing chamber, and control of the small pumping pump liquid fertilizer pumped to the tank mixing chamber, which through the control of the mixing device will be stirred with the liquid fertilizer mixing, and then control the peristaltic pump that will be stirred with the liquid fertilizer mixing irrigation water evenly injected into the drip irrigation main pipe. To realize the precise regulation of the fertilizer application amount, one electronically controlled flow regulating valve is installed on the return channel, which is controlled by S7-1200 PLC and receives information from the flowmeter sensor, and the control system forms the return flow through this flow regulating valve, and controls the amount of the return water by changing the opening of the flow regulating valve, to realize the indirect adjustment of the actual fertilizer application amount. The cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system corresponds to a drip irrigation system under each fertilizer application equipment. For the drip irrigation system controller selection of wireless electric valve, the use of multiple wireless electric valves decentralized control of the way to build the drip irrigation system. The drip irrigation pipeline is installed on the main voltage regulator to ensure that the pressure of the pipeline is stable during drip irrigation. The outlet is connected to the field drip irrigation belts, and in the main water and fertilizer are installed flow sensors for real-time monitoring of the corresponding pipeline The main water and fertilizer circuit are installed with flow sensors for real-time monitoring of the flow of the corresponding pipeline. Through the corresponding branch valve opening and closing drip irrigation or drip irrigation and fertilization at the same time is achieved. A cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system is a kind of system that can realize the automated control and management of water and fertilizer supply in agricultural production. It can realize the intelligent regulation of water and fertilizer supply to improve the yield and quality of crops and reduce the cost of water and fertilizer [15]. As shown in Figure 1, it is the structure diagram of the cotton field water and fertilizer ratio regulation system.
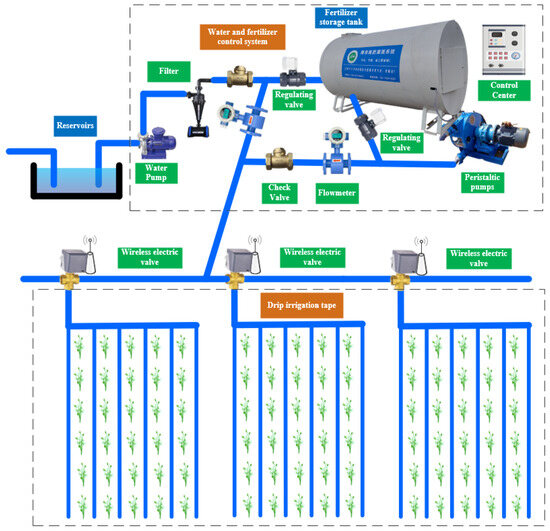
Figure 1.
Structural diagram of cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system.
2.2. Design of Variable-Domain Fuzzy PID Controller
2.2.1. Conventional PID Controller Design
The purpose of the PID controller designed for the cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system is to make the actual output water and fertilizer ratio value of the water and fertilizer ratio control system quickly reach the value set by the user and stabilize it as soon as possible by reasonably controlling the opening degree of the shut-off valve [16]. The structure of the PID controller in this paper is shown in Figure 2.
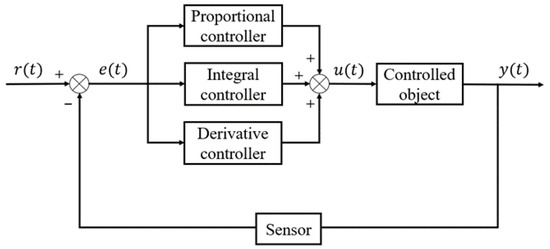
Figure 2.
Conventional PID controller structure.
In the controller, the control quantity u(t) is specified as:
where is the scaling factor.
is the integration time constant and is the differential time constant.
Equation (1) is a continuous expression of the PID control algorithm, and the system output collected by the controller through the timing is a discrete value, so Equation (1) must be discretized [17]. Assuming that the sampling period is T and a total of k samples are taken, it can be obtained:
Equation (2) is the integral component and Equation (3) is the differential component, which, when inserted in Equation (1), gives the PID control algorithm expression:
where u(k) is the output value of this controller; is the proportionality factor, is the integration factor and is the differentiation factor; is the deviation between the current controller input and the set value; is the cumulative sum of the deviation between and the previous controller input and the set value; is the deviation between the previous controller input and the set value [18]. Because the controlled object in this paper has complex nonlinear characteristics, it is difficult to establish an accurate mathematical model, so this paper uses the trial-and-error method to determine the parameters of the PID controller.
However, some key parameters in cotton plant growth are often fuzzy, such as growth rate, nitrogen requirement, and water demand. The traditional PID control method makes it difficult to deal with this ambiguity [19].
2.2.2. Fuzzy PID Controller Design
Fuzzy PID control is a control strategy proposed for the above problems. Compared with the traditional PID control, fuzzy control does not need an exact mathematical model and only needs to summarize the human control experience. The method can simulate the empirical knowledge of human experts by introducing fuzzy logic reasoning and fuzzy set operation, and more accurately describes the growth law of the cotton plant [20]. The fuzzy PID controller consists of two parts: fuzzy controller and PID controller, and its basic block diagram is shown in Figure 3.
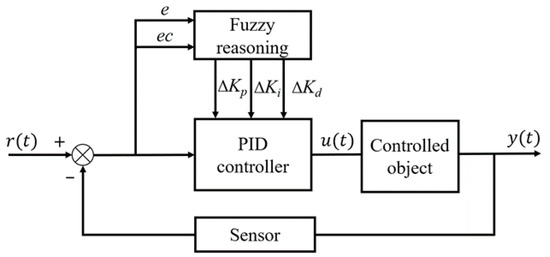
Figure 3.
Fuzzy PID controller structure.
The deviation e and the deviation change rate ec are selected as the two input variables of the fuzzy controller of the water–fertilizer ratio, and the number of pulses u of the control valve is taken as the output variable, and the three control parameter corrections Δ (ratio coefficient correction), Δ (integral coefficient correction) and Δ (differential coefficient correction) of the PID controller are obtained by blurring and fuzzy reasoning to realize the online correction of the three parameters Δ, Δ and Δ of the PID controller. The online correction of the parameters Δ, Δ and Δ of the PID controller is realized, and finally, the number of pulses of the electronically controlled flow control valve is realized to adjust the water–fertilizer ratio [21].
The output of the number of pulses of the electronically controlled flow control valve uses a triangular type of membership function, and the area center of gravity method is selected as the clarity method of the fuzzy controller for the water–fertilizer ratio value. In this paper, the linguistic values of the water–fertilizer ratio deviation e and deviation change rate ec are {NB, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM, PB}, and the fuzzy domains of fuzzy theory are [−3, 3], where NB, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM, and PB denote negative large, negative medium, negative small, 0, positive small, positive medium, and positive large, respectively. Through a large amount of literature and field research to summarize the expert experience of cotton water and fertilizer ratio value, fuzzy control statement selection “If e and ec then u” form, for example, if e is NB and ec is NM then u is PB” implies that when the deviation in the water–fertilizer ratio is significantly negative and the rate of change of the deviation is moderately negative, the number of pulses of the electrically controlled flow regulation valve will increase [22]. The fuzzy control rule table of the number of pulses of the electronically controlled flow regulator valve is shown in Table 1, and its triangular subordinate function diagram is shown in Figure 4.

Table 1.
Fuzzy rule control table for electronically controlled flow control valves.
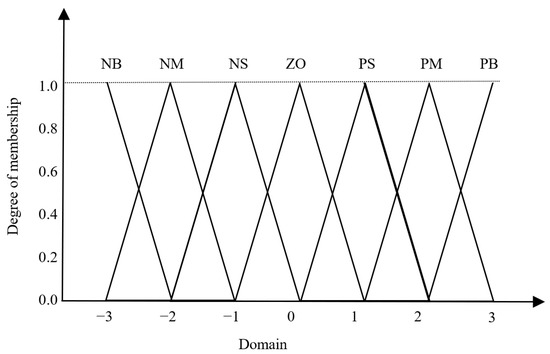
Figure 4.
Triangular affiliation function for the number of pulses of an electronically controlled flow control valve.
Conventional fuzzy PID controllers require a set of fuzzification rules and PID parameters to be determined in advance. However, the setting of these parameters is usually based on experience and subjective judgment. This makes the parameter setting subjective and requires some trial and error and adjustment to achieve better control performance. At the same time, these parameters may need to be readjusted when the system changes, which means that the performance of the controller may not be able to adapt to changes in the operating range of the system or changes in uncertainty, and it is not possible to balance real-time performance and parameter adjustment, and fuzzy PID controllers may not be able to provide optimal control performance when the operating range of the system changes or when there is uncertainty.
2.2.3. Variable-Domain Fuzzy PID Controller Design
Variable-domain fuzzy PID control is a control strategy proposed for the above problems. Variable-domain fuzzy PID control combines fuzzy control with PID control and introduces the variable-domain idea to realize the adaptive control of the change of the water–fertilizer ratio. The controller optimizes the parameters of the PID controller by transforming the change of the water–fertilizer ratio into a certain degree of membership function and using the variable-domain idea and fuzzy reasoning [23]. This can make the controller have strong adaptive ability, anti-interference ability, and high control accuracy. The schematic block diagram of the variable theory domain fuzzy controller is shown in Figure 5. Where r(t) is the set value of the variable-domain fuzzy controller, u(t) is the output value of the controller, y(t) is the feedback value, e is the deviation of the water–fertilizer ratio, ec is the rate of change of the deviation of the water–fertilizer ratio, and , , and are the scaling factors of e, ec, and the controller’s PID parameters under the variable-domain, respectively. By adjusting these parameters, the controller can adjust the water–fertilizer ratio according to the changes in the system, which can automatically adjust the control parameters to adapt to the changes in the controlled process and improve the control performance and reliability to meet the requirements of the control system.
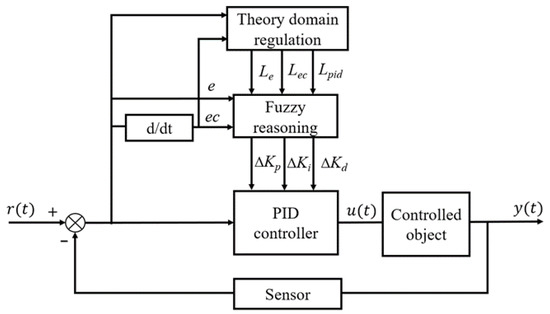
Figure 5.
Variable-domain fuzzy PID Controller Structure.
The deviation e and the rate of change ec of the water–fertilizer ratio are selected as the input variables of the system, and the number of pulses u of the flow control valve is selected as the output variable. The parameters Δ, Δ and Δ of the PID controller are optimized by the variational domain and fuzzy control, so that the output values of the variational domain fuzzy controller are the corrected values of the PID control parameters Δ, Δ and Δ. The fundamental domains of the error e are [−, ]; the fundamental domains of ec are [−, ]; and the fundamental domains of the output values are [−, ]; where , , are the scaling factors corresponding to the range of the variables and their rectification variables are determined by the target values of the water–fertilizer ratios; and is the collective name of Δ, Δ and Δ. Taking the stretch factor as an example, it is solved by the fuzzy ontology construction method. The linguistic value of the variable domain stretch factor is {S,M,Z,B}, and the domain is [0, 1.5], where S, M, Z, and B denote slightly compressed, moderately compressed, basically unchanged, and slightly expanded, respectively. The sub-function of is chosen as the triangular sub-function, as shown in Figure 6.
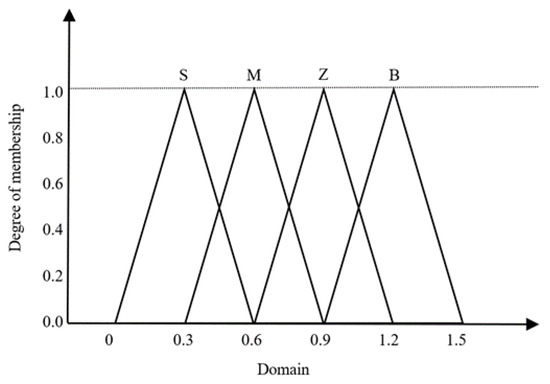
Figure 6.
Triangular membership function of scaling factor αein variable domain.
The fuzzy construction rule can be expressed as follows: if e is and ec is , then is (i = 1, 2, …, n; j = 1, 2, …, m), and the fuzzy rule is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Table of fuzzy control rules of scaling factor in variable domain.
The basic theory range of the fuzzy controller can be changed by the scaling factor, thus correcting the quantization level of the quantization factor and adjusting the size of the scaling factor. The scaling factor can be used to change the range of input or output theories of the fuzzy controller, thus fine-tuning the fuzzy control system. For the quantization factor, changing the scaling factor can affect the quantization of the input variables by the fuzzy controller. By increasing the scaling factor, the quantization level can be made coarser, allowing a wider range of input variables and thus increasing the sensitivity of the system to the input variables [24]. Conversely, by decreasing the scaling factor, the quantization level can be made finer, making the range of input variables narrower and thus improving the system’s fine control of the input variables. For the scaling factor, changing the scaling factor can affect the mapping relationship between the output of the fuzzy controller and the input variables. By increasing the scaling factor, the gain of the fuzzy controller can be increased, making the output variables more sensitive to changes in the input variables [25]. Conversely, by decreasing the scaling factor, the gain of the fuzzy controller can be decreased, making the output variables more moderate to changes in the input variables. In summary, by changing the scaling factor, the fundamental domain of the fuzzy controller can be adjusted, and thus the quantization level of the quantization factor can be corrected, and the size of the scaling factor can be adjusted, so that the fuzzy control system can be flexibly adjusted. The fuzzy sets of both input and output variables are {NB,NM,NS,ZO,PS,PM,PB}, and the thesis domains are [−3, 3], and their membership function diagrams are consistent with the membership function diagrams of fuzzy PIDs in Section 2.2.2, and the fuzzy rules of Δ are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Table of fuzzy control rules of correction value Δ invariable domain.
The deviation e and the deviation change rate ec between the actual value of the water–fertilizer ratio and the set value were calculated, and the scaling factors of e, ec, and were obtained through the variable domain to change the quantization factor and the scaling factor in the fuzzy control, and then the fuzzy, fuzzy reasoning and de-fuzzy processing were performed to obtain the corrected values of Δ, Δ and Δ of the PID parameters, and the corrected values of the PID parameters were as shown in the following equation.
where is the initial value of the proportional coefficient, is the initial value of the integral coefficient, and is the initial value of the differential coefficient.
In the cotton field water–fertilizer ratio regulation system, this control strategy can effectively deal with uncertainty and nonlinear problems and improve the adaptability and robustness of the system. However, despite the many advantages of the variable-domain fuzzy PID controller, the variable-domain fuzzy PID controller requires a more complex computational process, especially in real-time control systems, where the selection of controller parameters has a great impact on the system performance, and inappropriate parameter settings may lead to a degradation of the system performance. In some cases, variable-domain fuzzy PID controllers may cause overregulation phenomena in the system, especially when the system dynamics change rapidly, which may lead to system instability [17].
2.2.4. Design of Bat-Optimized Variable-Domain Fuzzy PID Controller
Bat optimization algorithm is a new bionic meta-inspired search and optimization method which is based on the characteristics of bats that use echoes for localization during flight, and simulates the localization sound waves of bats to find the optimal solution to the optimization problem [23]. The algorithm has the characteristics of fast speed and few parameters and is widely used in various optimization problems. In the bat optimization algorithm, the heuristic search is first started from a random position in the d-dimensional search space, and then the prey is searched at a fixed frequency with different wavelengths and sound intensities. During the search process, bats automatically adjust the wavelength according to the distance to better approach the prey [24]. At the end of the search, the flight speed and spatial position of each bat are updated and the fitness value of the objective function is calculated [26]. The formula for updating the velocity is
where is the pulse frequency of bat individual i at the time of the search; is a random number between [0, 1] and (, ) is the pulse frequency range. After each iteration, the tone intensity and frequency are updated and calculated based on the pulse loudness decay coefficient and pulse frequency increase coefficient.
The update formula for the spatial position is
where
- and —the flight speed of individual bat i at t and t + 1
- and —the position of individual bat i at the time t and t + 1
- —global optimal position
When performing the local search, the optimal solution of the current position is selected for random search, and the bat position is updated in the following way:
where
- —current optimal solution
- —the new solution generated
- —a random number belonging to [−1, 1].
- —average of all bat loudness at time t
As the iteration increases, to better pinpoint the target bats, the loudness will be gradually reduced, while the pulse emissivity will be increased, and the updating mode is
where
- —Loudness attenuation coefficient
- —Pulse emission frequency increase coefficient
- —the maximum pulse emission frequency of the ith bat
When 0 < < 1, > 0, there is , , .
The controller designed in this paper is based on the theory of variable domain, combined with the bat optimization algorithm, according to the difference state between the target value and the actual value of the control objective (e, ec), the bat algorithm is used to find out the optimal scaling factor , which results in the optimal domain for the current working condition, and then the domain of the fuzzy control is automatically adjusted according to the changes in the working condition, which is applied to the control of the speed of the peristaltic pump motor.
The principle of bat optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID (VDFPID) controller is shown in Figure 7, where , are the input and output scaling factors, respectively, and the inputs use the control system’s e, ec. The bat argument domain adjuster yields the optimal scaling factor. The fuzzy controller inputs the scaling factor and the control system deviation, and outputs the corrected values Δ, Δ, and Δ of the three parameters of the PID. The inputs to the corrected values of the three parameters of the PID and the system deviation into the PID controller, and obtains the corrected values of the three parameters , , and .
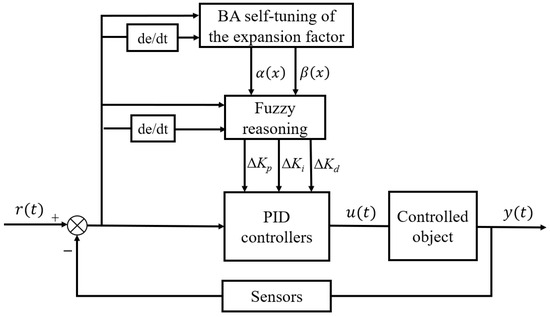
Figure 7.
BA optimization VDFPID control schematic diagram.
In the iterative process, the fitness function is needed to calculate the fitness value of each individual, and then evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of the individual. The Integral of the Time-weighted Absolute Error (ITAE) metric, which has the advantages of fast, smooth, and low overshooting, has been adopted by most of the literatures [27,28,29], therefore, this paper introduces it into the performance evaluation of the precision fertilizer control system, which serves as an important reference index of the controller and as the fitness function of the BA optimization algorithm. The ITAE criterion, i.e., the Time-Multiplied Absolute Error Integral Minimization criterion, can be expressed as follows:
Equation (12) is the mathematical model of the continuous control system, but since the computer uses digital sampling control, the integral part and differential part of Equation (12) are not recognizable and need to be discretized. The sampling moment point is discretized, with T as the sampling period and k as the sampling sequence number. The discrete formula of the ITAE function is
BA uses ITAE as the objective function, samples the current water flow rate and fertilizer path flow rate, and calculates the optimal scaling factor for the current water and fertilizer ratios with inputs e and ec, for a given number of iterations in the variable theory domain, as shown in Figure 8.
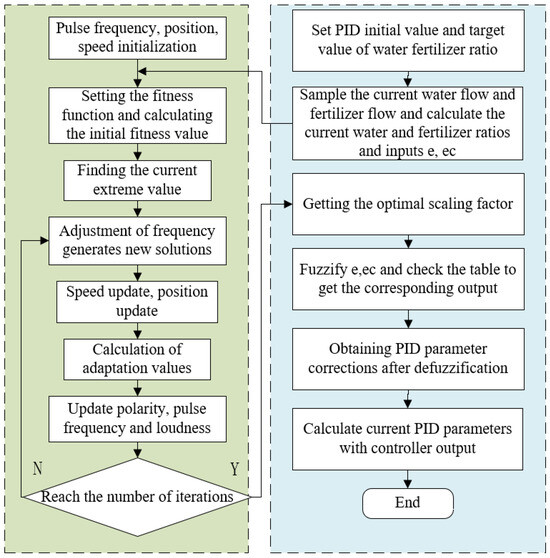
Figure 8.
Bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID water–fertilizer ratio regulation algorithm process.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Simulation Results
In the simulation test, four different control methods were used to simulate the water and fertilizer ratio regulation process in Matlab software (Matlab 2019): conventional PID control, fuzzy PID control (FPID), variable-domain fuzzy PID control (VDFPID), and bat-optimized variable-domain fuzzy PID control (BA-VDFPID). The sampling period was set to 1 ms, and the system delay time was 4 s. In this paper, according to the actual situation simulated the water and fertilizer ratios from the start of the value of 0:0 start regulation to 50:1, and from 50:1 to 40:1 process, the simulation time is 200 s, the control curve of the three control algorithms is shown in Figure 9.
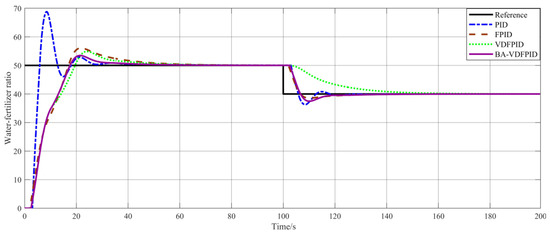
Figure 9.
Comparison of water–fertilizer ratio control effects of three controllers.
From the simulation curves of the four controllers in Figure 9, it can be seen that the water–fertilizer ratio is adjusted from 0:0 at the start to 50:1, and the PID controller is the first one to reach the Reference curve, with the shortest rise time, but its overshooting is the largest and produces large oscillations; the fuzzy PID controller, although its overshooting is smaller than that of the PID controller, has the longest adjustment time in the four controllers. Variable-domain PID controller’s maximum overshoot is smaller than the fuzzy PID controller, but its regulation time is also relatively long, second only to the fuzzy PID controller; BA optimization VDFPID controller produces a certain amount of overshoot, but the smallest of the four controllers in the acceptable range, and the regulation time is much smaller than the fuzzy PID controller and the variable-domain fuzzy PID controller, which can take into account the response to the response to the PID controller and variable-domain fuzzy PID controller. The PID controller can balance the response speed and stability of the control process. The water and fertilizer ratio goes from 50:1 to 40:1 in the process of adjustment, the rise time of the PID controller is basically the same, but its overshooting amount is the largest, the adjustment time is also longer; fuzzy PID controller in the process of superior performance, in addition to the overshooting amount of small, other indicators are the same as the BA optimization of the VDFPID controller; variable-domain fuzzy PID controller in the process of the worst performance, resulting in a long time overshooting, cannot be short-term control process stability. The variable-domain fuzzy PID controller performs the worst in this process, producing a long time of overshooting, and cannot reach the steady state in a short time; the BA-optimized VDFPID controller has a small amount of overshooting and reaches the steady state very quickly, and can also take into account the speed of response and the stability of the control process in this process. In summary, the BA-optimized VDFPID controller can reach the set water–fertilizer ratio value in a short time, and has advantages in response speed, stability and overshooting, which is a controller with better performance. In the next stage, the actual performance of the algorithm will be tested.
3.2. Precision Water–Fertilizer Ratio Control Test
3.2.1. Testing Device and System Design
To compare the control speed, control stability and other characteristics of the four control algorithms in the actual cotton field water and fertilizer ratio control system, and to verify the practical performance of the BA-optimized VDFPID controller, this paper builds the corresponding water and fertilizer ratio control system test platform, and the flowmeter interacts with the computer and the control system through the RS-485 serial bus, to compare and test the different control strategies. The structure of the water–fertilizer ratio control system test platform is shown in Figure 10. In order to verify the effectiveness of the BA-optimized VDFPID controller, a comparative validation test of the water–fertilizer ratio control was conducted on the water–fertilizer ratio control system.
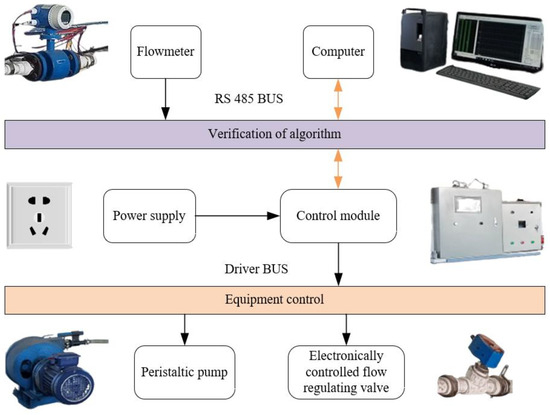
Figure 10.
Structural diagram of test platform for water–fertilizer ratio control system.
To carry out the experiment, 50 L of liquid fertilizer were first prepared, keeping the main pipe outlet flow rate stable at 0.3 m3 per hour. Use the control center to send water and fertilizer regulation information to the water and fertilizer proportioning module to monitor the flow rate of the main and branch roads through the flow sensor, the flow sensor signal is received by the I/O port, calculated by the S7-1200 PLC, and then converted into a variable voltage signal, which is interacted with the computer and the control system through the ModbusRTU communication protocol, to determine the instantaneous flow rate, and real-time uploading of the flow rate of the pipeline to the local end for recording. The number of pulses of the electronically controlled flow regulating valve is adjusted accordingly to ultimately change the fertilizer flow rate of the drip irrigation main line. The water–fertilizer ratio control system test platform used in the experiment is shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
Water and Fertilizer Proportioning Control System Testbed.
3.2.2. Analysis of Test Results
The flow sampling period of the water–fertilizer ratio regulation was set to 1 s, the water–fertilizer ratio adjustment period was 5 s, and the experiment duration was 200 s continuously. Set the water–fertilizer ratio from the start of 0:0 to 50:1 and then adjusted to 40:1, in the S7-1200PLC were written into the traditional PID control algorithm, fuzzy PID control algorithm, variable-domain fuzzy PID control algorithm, and BA optimization VDFPID control algorithm, water–fertilizer ratio control comparison test. Four controller performance indicators are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of experimental results of three algorithms for water and fertilizer ratio regulation.
According to the data in Table 4, the four control algorithms can be specifically analyzed:
PID control algorithm: when the initial water–fertilizer ratio was adjusted from 0:0 to 50:1, the rise time was 5.83 s, the peak time was 8.25 s, the regulation time was 25.42 s, and the maximum overshoot was 58.29%. When adjusting to 40:1, the rise time is 4.86 s, the peak time is 7.72 s, the adjustment time is 12.68 s, and the maximum overshoot is 35.64%. The overall overshoot is large.
Fuzzy PID control algorithm (FPID): when the initial water–fertilizer ratio was adjusted from 0:0 to 50:1, the rise time was 12.43 s, the peak time was 19.62 s, the regulation time was 32.54 s, and the maximum overshoot was 28.83%. When adjusting to 40:1, the rise time was 6.96 s, the peak time was 9.37 s, the regulation time was 10.59 s, and the maximum amount of overshoot was 3.68%. The amount of overshoot is reduced, but the regulation time is longer.
Variable-domain fuzzy PID control algorithm (VDFPID): when the initial water–fertilizer ratio was adjusted from 0:0 to 50:1, the rise time was 16.86 s, the peak time was 21.51 s, the regulation time was 28.79 s, and the maximum overshoot was 22.61%. When adjusting to 40:1, the rise time is 6.86 s, the peak time is 9.29 s, the regulation time is 34.64 s, and the maximum overshoot is 0.76%. The overshooting amount is small, but the regulation time is the longest.
BA-optimized VDFPID control algorithm (BA-VDFPID): when the initial water–fertilizer ratio was adjusted from 0:0 to 50:1, the rise time was 12.61 s, the peak time was 18.68 s, the regulation time was 15.29 s, and the maximum overshooting amount was 16.28%. When adjusting to 40:1, the rise time is 6.97 s, the peak time is 9.86 s, the adjustment time is 10.83 s, and the maximum amount of overshoot is 3.57%. The overshooting amount is the smallest and the regulation time is the shortest.
In summary, compared with the other three control algorithms, the BA-VDFPID control algorithm has the smallest overshoot and the shortest regulation time when regulating the water–fertilizer ratio, and it shows a better comprehensive performance in this experiment, with strong anti-disturbance performance and adaptive ability, which can be adapted to the control of some nonlinear, time-varying, coupling and other complex control objects, and it can meet the precise control requirements of the water–fertilizer ratio in the process of water–fertilizer drip irrigation, reflecting its superiority. It has precise control requirements, reflecting its superiority. The algorithm improves the control effect by optimizing the parameters, realizes fast and accurate regulation, and is more suitable for practical application [30].
4. Conclusions
This paper firstly establishes the structure of a cotton field water–fertilizer ratio control system based on BA optimization VDFPID, to show that the control system is to change the return volume of the fertilizer suction pump to adjust the principle of water–fertilizer solution ratio by controlling the regulating valve; after that, based on the characteristics of the system and the strengths and weaknesses of the controllers, we established the system under control of four kinds of controllers: the conventional PID controller, the fuzzy PID controller, the variable-domain fuzzy PID controller, and the BA optimization VDFPID controller. VDFPID controller; finally, the system under the control of the four controllers was tested in simulation and actual operation effect test experiments, and the effect under BA-VDFPID control was compared with that under conventional PID control, fuzzy PID control and variable-domain fuzzy PID control. The results show that compared with the traditional PID control, fuzzy PID control and variable-domain fuzzy PID control, the regulation time is reduced, and the overshooting and fluctuation amplitude of the system are smaller, which can take into account the response speed and the stability of the control process, improve the accuracy of the water and fertilizer ratio, and effectively deal with the problems of nonlinearity, fuzzy and uncertainty, with obvious advantages.
In summary, the BA-optimized VDFPID control algorithm can automatically adjust the water–fertilizer ratio and control parameters according to the real-time changes of the system by introducing the bat optimization algorithm and the fuzzy logic rules of the variable thesis domain. By monitoring and analyzing the flow rate of the main and branch circuits, the system can provide real-time feedback data, which can then be adjusted according to the preset control strategy, forming an adaptive control strategy that enables the control system to achieve satisfactory control results for control objects under different working conditions. The application of this method in the field of agriculture is promising, and the precise regulation of water and fertilizer ratios will provide a more intelligent and sustainable solution for crop production, and achieve water-saving weight loss and ecologically sustainable development of field crop production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.G. and F.Z.; software design, H.C.; software validation, Z.G., P.Z. and H.C.; resources, H.C.; data curation, Z.G.; writing—original draft, Z.G.; writing—review and editing, F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by 1. Xinjiang Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation General Project (No. 2022D01A05); 2. Xinjiang Institute of Technology High level Talent Research Launch Fund Project (No. XJLG2023G006); 3. Xinjiang “Tianchi Talents” Introduction Program Subsidized Projects (Xinjiang Social Welfare Letter ⟨2023⟩ No. 50).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ahmad, U.; Alvino, A.; Marino, S. Solar Fertigation: A Sustainable and Smart IoT-Based Irrigation and Fertilization System for Efficient Water and Nutrient Management. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, N. Changes of soil water and heat transport and yield of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) in greenhouses with Micro-Sprinkler irrigation under plastic film. Agronomy 2022, 12, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Huang, F.; Li, B. Spatiotemporal patterns of water consumption and irrigation requirements of wheat-maize in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China and options of their reduction. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Hu, K.; Feng, P.; Feng, G.; Gao, Q. Simulating the Effects of Different Textural Soils and N Management on Maize Yield, N Fates, and Water and N Use Efficiencies in Northeast China. Plants 2022, 11, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, U.; Nasirahmadi, A.; Hensel, O.; Marino, S. Technology and Data Fusion Methods to Enhance Site-Specific Crop Monitoring. Agronomy 2022, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, A.; Xu, G.; Levkovitch, I.; Soriano, S.; Bilu, A.; Wallach, R. High fertigation frequency: The effects on uptake of nutrients, water and plant growth. Plant Soil 2003, 253, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.C.; Li, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, T.T. Design and testing of a nutrient mixing machine for greenhouse fertigation. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2015, 8, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, M.; Inbar, G.; Yaniv, O.; Schneider, M. A fuzzy irrigation controller system. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2000, 13, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Akram, M.; Sarwar, M. Fuzzy decision support system for fertilizer. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Palacios, R.; Aguilar-Lasserre, A.A.; Morales-Mendoza, L.F.; Rico-Contreras, J.O.; Sánchez-Medel, L.H.; Fernández-Lambert, G. Decision support system for NPK fertilization: A solution method for minimizing the impact on human health, climate change, ecosystem quality and resources. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 55, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Melendez, D.; Lopez-Lambrano, A.; Herrera-Ruiz, G.; Fuentes, C.; Rico-Garcia, E.; Olvera-Olvera, C.; Alaniz-Lumbrerasc, D.; Fernandez, T.M.; Verlinden, S. Fuzzy irrigation greenhouse control system based on a field programmable gate array. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.S.; Ma, W.S.; Li, H.; Wang, S.H. Research on Water-Fertilizer Integrated Technology Based on Neural Network Prediction and Fuzzy Control. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 032168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Quayle, W.; Scheer, C.; Rowlings, D.; Baldock, J. Effect of soil texture and wheat plants on N2O fluxes: A lysimeter study. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Miao, Y.X.; Feng, G.H.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Khosla, R.; Mulla, D.J.; Zhang, F. Improving nitrogen use efficiency with minimal environmental risks using an active canopy sensor in a wheat-maize cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Tian, M.; Li, J. Control System of Liquid Fertilizer Variable-Rate Fertilization Based on Beetle Antennae Search Algorithm. Processes 2022, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Lei, J.; Du, H.; Yao, B.; Zhu, W.; Hu, X. Proportional-integral-derivative controller optimization by particle swarm optimization and back propagation neural network for a parallel stabilized platform in marine operations. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lv, X.; Zhang, T.; Fan, Z. Research on Temperature Control of Fuel-Cell Cooling System Based on Variable Domain Fuzzy PID. Processes 2022, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, M. Prediction of infiltration behaviors and evaluation of irrigation efficiency in clay loam soil under Moistube® irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.; Aria, M.; Basso, B.; Leone, A.P.; Alvino, A. Use of soil and vegetation spectroradiometry to investigate crop water use efficiency of a drip irrigated tomato. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 59, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Sun, T.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Du, M.; Sheng, T. Modeling long-term water use and economic returns to optimize alfalfa-corn rotation in the corn belt of Northeast China. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Hu, K.L.; Qin, W.; Zuo, Q.; Guo, L.; Tao, Y.Y.; Lin, S. Ground cover rice production system reduces water consumption and nitrogen loss and increases water and nitrogen use efficiencies. Field Crops Res. 2019, 233, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Shao, L.; Wang, Y. Changes in evapotranspiration over irrigated winter wheat and maize in North China Plain over three decades. Agric. Water. Manag. 2011, 98, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.L.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.P.; Chen, D.L.; Wei, Y.P.; Edis, R.; Li, B.G.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.P. Modeling nitrate leaching and optimizing water and nitrogen management under irrigated maize in desert oases in Northwestern China. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzon, J.P.; Sadras, V.O.; Andrade, F.H. Fallow soil evaporation and water storage as affected by stubble in sub-humid (Argentina) and semi-arid (Australia) environments. Field Crops Res. 2006, 98, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Hu, K.L.; Batchelor, W.D.; Qi, Z.M.; Li, B.G. An integrated soil-crop system model used for water and nitrogen management in North China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xing, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Qin, S.; Qi, L.; Huang, F. An Improved Discrete Bat Algorithm for Multi-Objective Partial Parallel Disassembly Line Balancing Problem. Mathematics 2024, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleke, S.; Pydi, B.; Satish, R.; Kotb, H.; Alenezi, M.; Shouran, M. Frequency Stability Enhancement Using Differential-Evolution- and Genetic-Algorithm-Optimized Intelligent Controllers in Multiple Virtual Synchronous Machine Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Rodriguez, M.C.; Carvajal-Mariscal, I.; López-Muñoz, R.; Lopez-Pacheco, M.A.; Tolentino-Eslava, R. Temperature Control of a Chemical Reactor Based on Neuro-Fuzzy Tuned with a Metaheuristic Technique to Improve Biodiesel Production. Energies 2023, 16, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogar, V.N.; Hussain, S.; Gamage, K.A.A. Load Frequency Control Using the Particle Swarm Optimisation Algorithm and PID Controller for Effective Monitoring of Transmission Line. Energies 2023, 16, 5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Niu, W.; Gu, J.; Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhang, R. Effects of moistube depth and density on tomato yield and quality in solar greenhouse. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).