Influence of the Material Mechanical Properties on Cutting Surface Quality during Turning
Abstract
1. Introduction
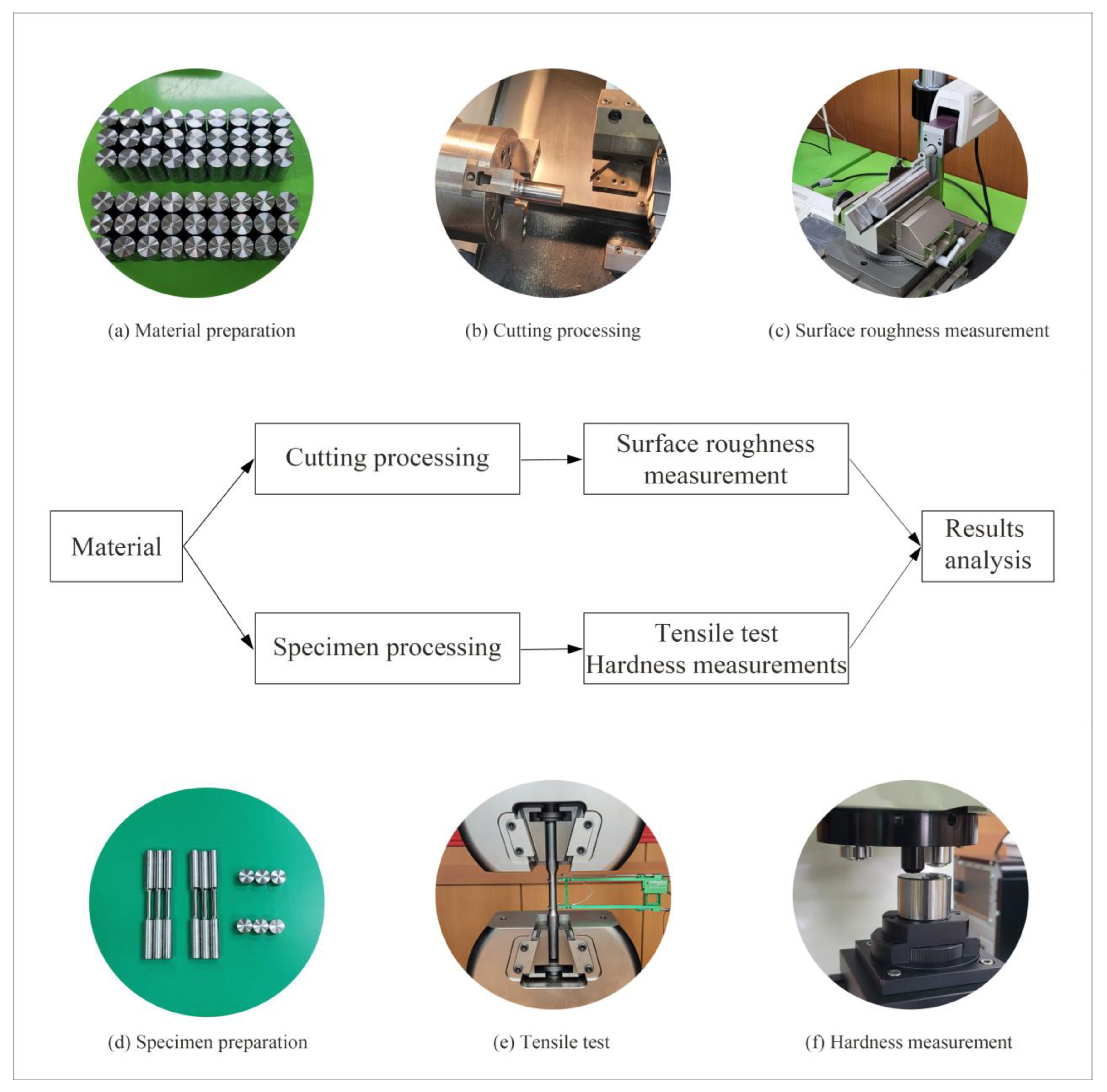
2. Experiment and Methods
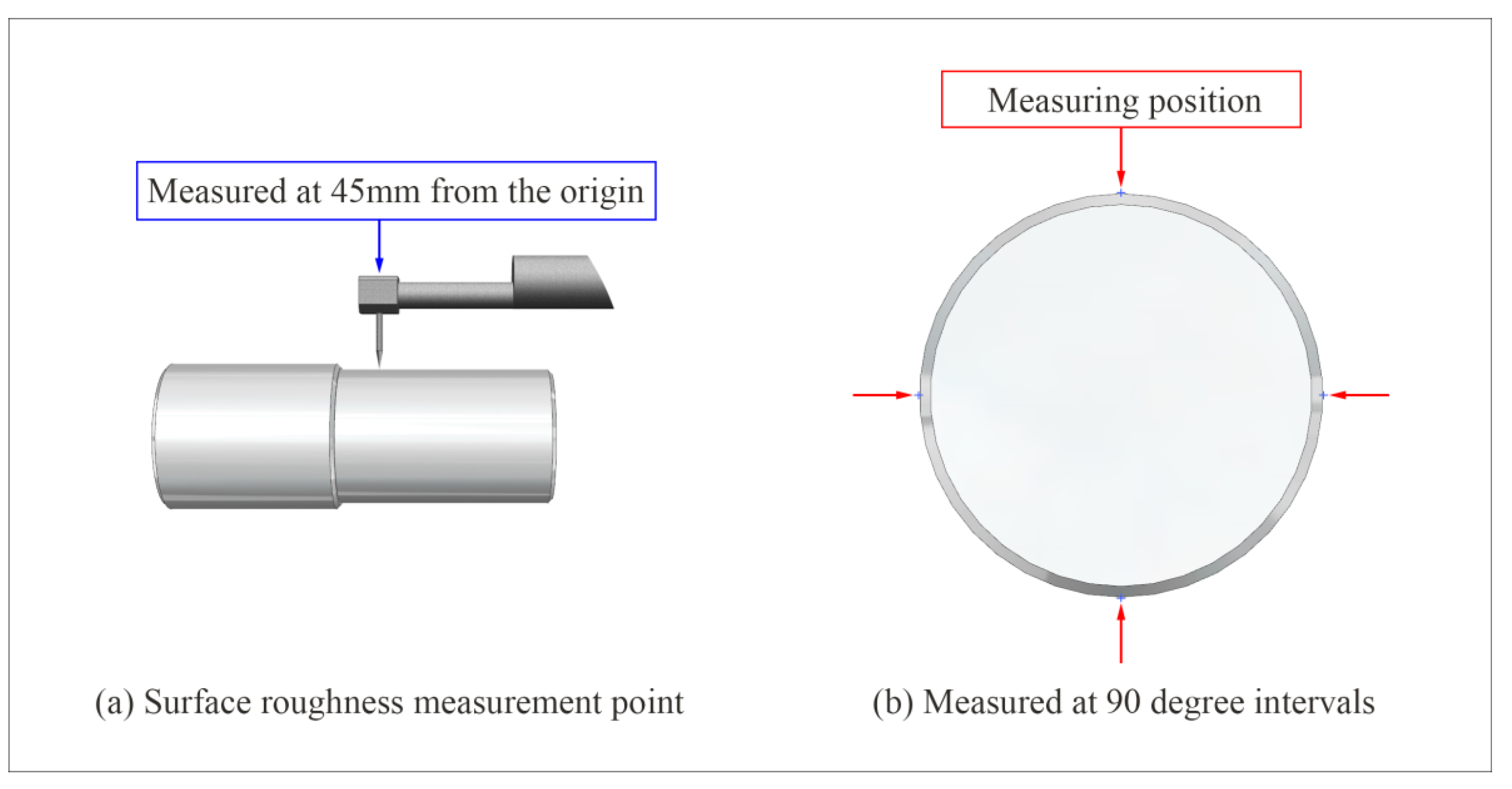
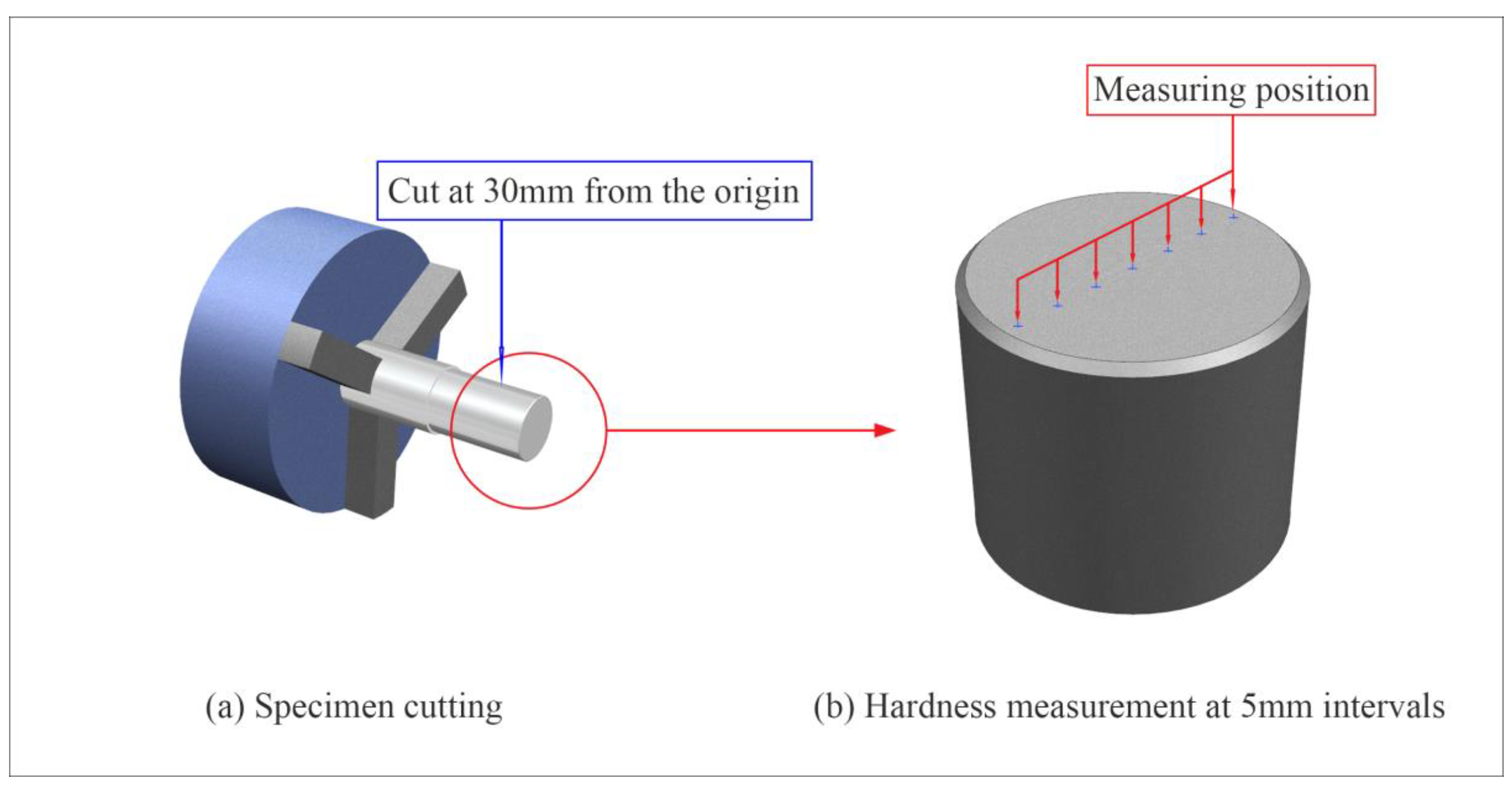
2.1. Workpiece Cutting and Surface Roughness Measurement
2.2. Mechanical Strength and Hardness Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
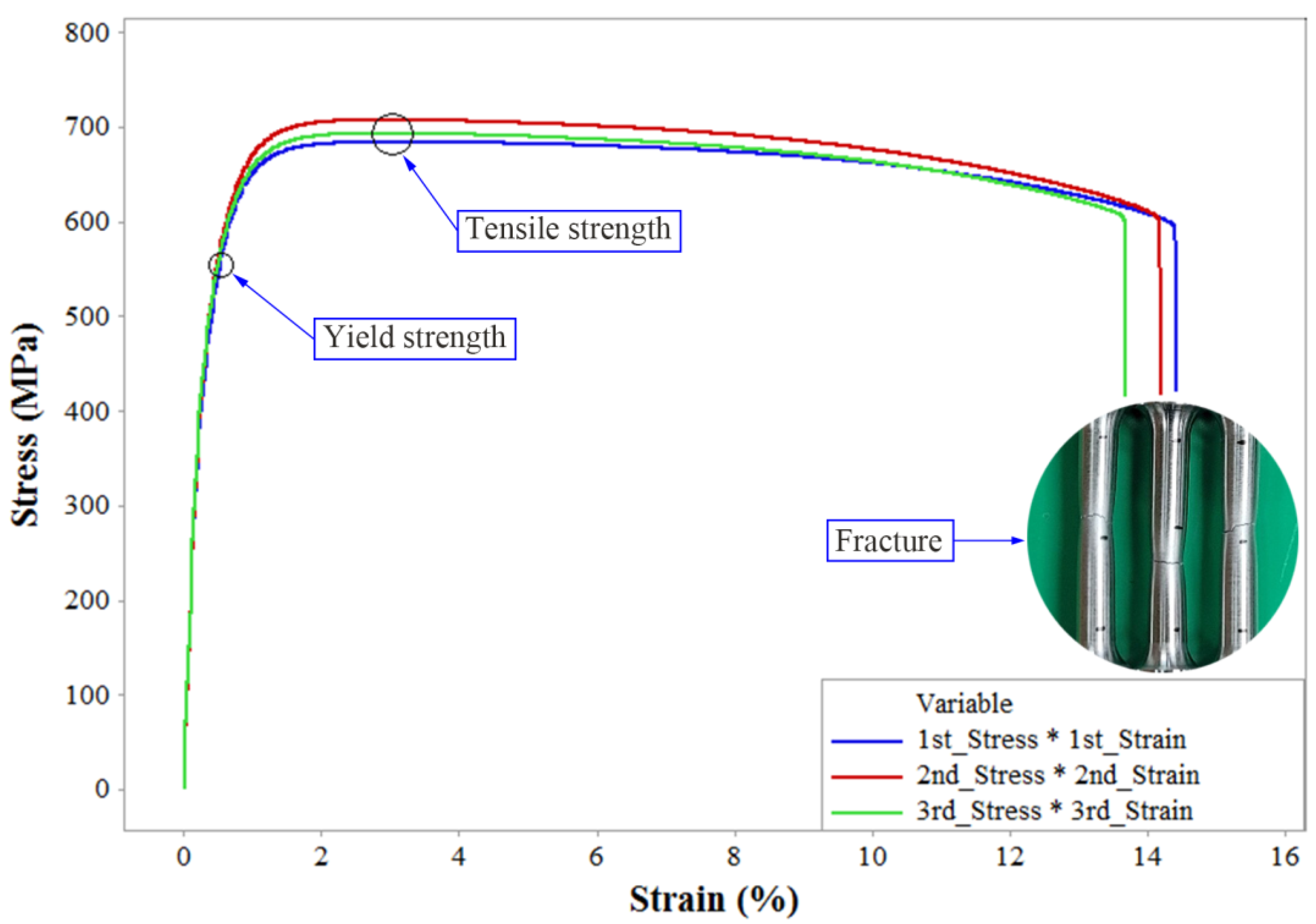
3.1. Analysis of Measured Strength Results
3.2. Analysis of Measured Hardness Results
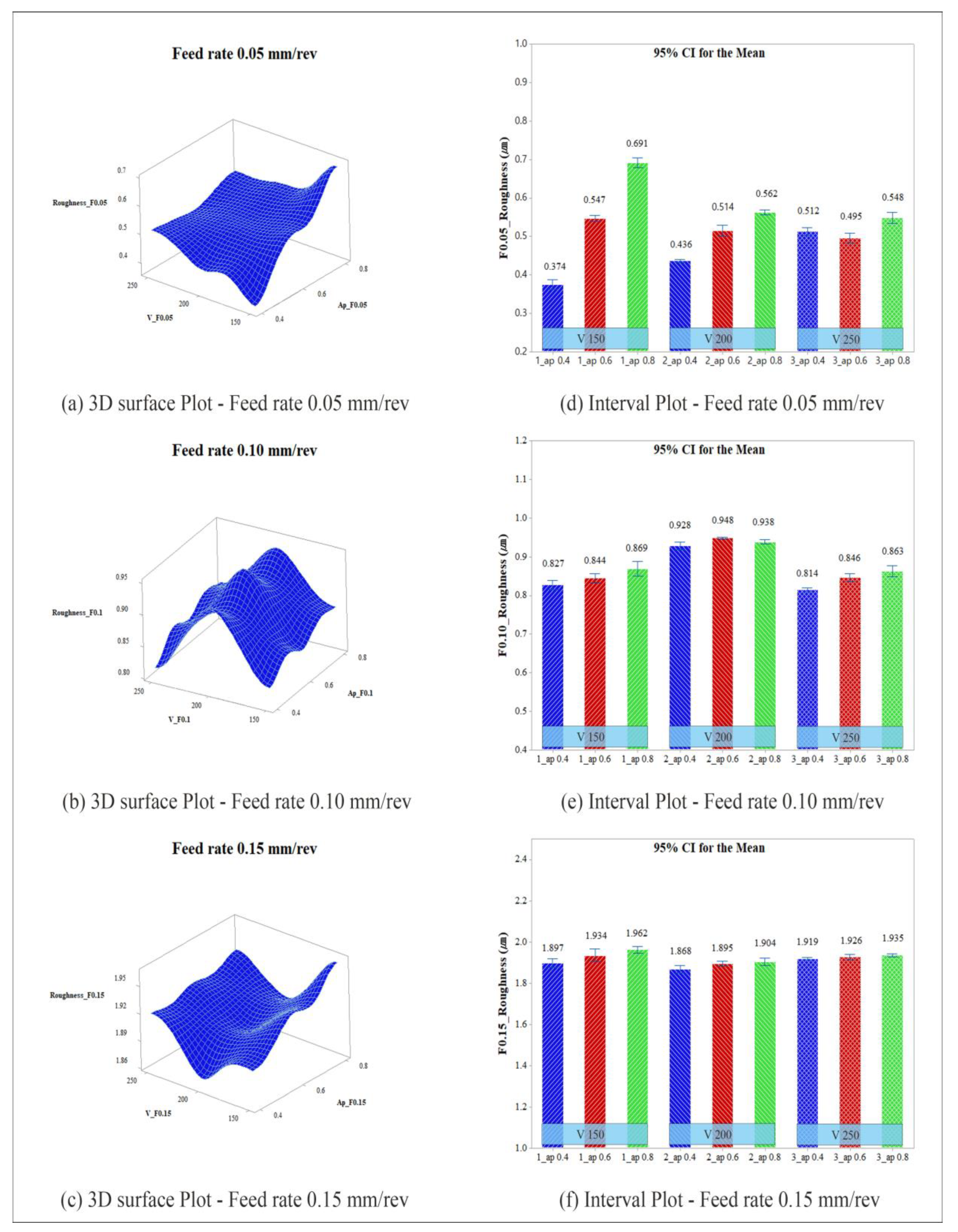
3.3. Analysis of Measured Surface Roughness Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivalingam, V.; Zhou, Q.; Ross, N.S.; Tiwari, S.; Selvam, B.; Sun, J.; Gupta, M.K. Identification of tool wear and surface morphology measurements in sustainable milling of Al 6082 hybrid metal matrix composite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 7570–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, C.; Du, S. Cutting Force Prediction for Trochoid Milling of 300M Ultra-High Strength Steel. Processes 2022, 10, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafanelli, F.; Campatelli, G.; Scippa, A. Effects of cutting conditions on forces and force coefficients in plunge milling operations. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1687814015589547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.H. A study on cutting characteristics in turning operations of titanium alloy used in automobile. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ge, J.C.; Song, J.H. Study on Burr Formation and Tool Wear in Drilling CFRP and Its Hybrid Composites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, P.G. The effect of feed rate and of tool nose radius on the roughness of oblique finish turned surfaces. Wear 1973, 23, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouckry, A.S. The effect of cutting conditions on dimensional accuracy. Wear 1982, 80, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Szczotkarz, N.; Michalski, M.; Arkusz, K.; Wojciechowski, S.; Niesłony, P.; Khanna, N.; Królczyk, G.M. Evaluation of tool wear during turning of Ti6Al4V alloy applying MQL technique with Cu nanoparticles diversified in terms of size. Wear 2023, 532, 205111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, X.; Jiang, F. Experimental Investigation on the Machinability of PCBN Chamfered Tool in Dry Turning of Gray Cast Iron. Processes 2022, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, F.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, D.; Liao, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, B. The study on the effect of various tool wear indicators on the machining of MMCs. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, W.; Kiszka, P.; Kowalczyk, D.; Rech, J.; Claudin, C. Machining of nodular cast iron (PF-NCI) using CBN tools. Procedia CIRP 2012, 1, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksycki, K.; Maruda, R.W.; Feldshtein, E.; Wojciechowski, S.; Habrat, W.; Gupta, M.K.; Królczyk, G.M. Evaluation of tribological interactions and machinability of Ti6Al4V alloy during finish turning under different cooling conditions. Tribol. Int. 2023, 189, 109002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Lee, T.H. Effect of Changing Belt Tension on Machining Surface of CNC Lathe Spindle. Processes 2023, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, L.; Yallese, M.A.; Chaoui, K.; Mabrouki, T.; Boulanouar, L. Mathematical modeling for turning on AISI 420 stainless steel using surface response methodology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manufact. 2015, 229, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Wei, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Tool wear in nickel-based superalloy machining: An overview. Processes 2022, 10, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, Z.; Haddouche, K.; Djellouli, K.; Ghezal, A. An improved thermomechanical modeling for orthogonal cutting of AISI 1045 steel. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombiński, S.; Kossakowska, J.; Jemielniak, K. Detection of accelerated tool wear in turning. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2022, 162, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, D.; Kecibas, G.; Besirova, C.; Chehrehzad, M.R.; Burun, G.; Pehlivan, T.; Uresin, U.; Emekli, E.; Lazoglu, I. Tool flank wear prediction using high-frequency machine data from industrial edge device. Procedia CIRP 2023, 118, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelatta, O.B.; Madl, J. Surface roughness prediction based on cutting parameters and tool vibrations in turning operations. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2001, 118, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyak, M.; Kaner, B. Determination of the actual deflection of the cutting tool ın turning by the Castigliano theorem. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2023, 16, 100744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, G.S.; Kreethi, R.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Lee, K.A. Effects of different HVOF thermal sprayed cermet coatings on tensile and fatigue properties of AISI 1045 steel. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2021, 15, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz, G.D.; Vilchez, J.R.; Dominguez, A. Ultrasonic fatigue on the automotive steels: AISI/SAE 4140T and 1045. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 18, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selçuk, B.; Ipek, R.; Karamış, M.B. A study on friction and wear behaviour of carburized, carbonitrided and borided AISI 1020 and 5115 steels. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2003, 141, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Lee, T.H. Effect of Cutting Conditions on the Cutting Surface when Cutting AISI 1020 CD-Bar. Korean Soc. Mech. Technol. 2023, 25, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Escalona, P.; Cassier, Z. Influence of the critical cutting speed on the surface finish of turned steel. Wear 1998, 218, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-11; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.



| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed | 150 m/min (low speed) 200 m/min (medium speed) 250 m/min (high speed) |
| Depth of cut | 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8 mm |
| Feed rate | 0.05 mm/rev (low speed) 0.1 mm/rev (medium speed) 0.15 mm/rev (high speed) |
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Max. Loading Capacity | 500 kN |
| Resolution | 0.01% |
| Cross Head Speed | 0.01–500.00 mm/min |
| Driving System | AC Servo Motor |
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Test force | 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, 300, 500 and 1000 gf |
| Min. Measuring Unit | 0.03125 µm |
| Max. Height of Specimen | 90 mm |
| Distance of Indenter from Wall | 120 mm |
| Measuring Range | 8~2900 HV |
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Max. Turning Diameter | 320 mm |
| Max. Turning Length | 320 mm |
| Standard chuck size | 20.3 cm (8 inch) |
| Max. Spindle speed | 4000 rpm |
| Max. Spindle power | 11 kw |
| Element | AISI 1020 (wt %) | AISI 1045 (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0.18~0.23 | 0.43~0.50 |
| Mn | 0.30~0.60 | 0.60~0.90 |
| P | 0.040 (Max) | 0.040 (Max) |
| S | 0.050 (Max) | 0.050 (Max) |
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Measuring speed | 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1 mm/s |
| Detector measuring force | 0.75 mN |
| Measuring method | Skidless/skidded |
| Measuring range | 800 µm, 80 µm, 8 µm |
| Traverse | 50 mm |
| Material | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 1045 | 695.31 MPa | 550.51 MPa | 14.1% |
| AISI 1020 | 537.74 MPa | 477.08 MPa | 18.7% |
| Feed Rate [mm/rev] | AISI 1020 [m/min], [mm] | AISI 1045 [m/min], [mm] | Arithmetic Mean of Surface Roughness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1020 [µm] | 1045 [µm] | |||
| 0.05 | V 150, ap 0.8 | V 150, ap 0.4 | 0.383 | 0.374 |
| 0.10 | V 200, ap 0.4 | V 250, ap 0.4 | 0.858 | 0.814 |
| 0.15 | V 250, ap 0.4 | V 250, ap 0.4 | 1.800 | 1.919 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, I.-S.; Lee, T.-H. Influence of the Material Mechanical Properties on Cutting Surface Quality during Turning. Processes 2024, 12, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061171
Kang I-S, Lee T-H. Influence of the Material Mechanical Properties on Cutting Surface Quality during Turning. Processes. 2024; 12(6):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061171
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Il-Seok, and Tae-Ho Lee. 2024. "Influence of the Material Mechanical Properties on Cutting Surface Quality during Turning" Processes 12, no. 6: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061171
APA StyleKang, I.-S., & Lee, T.-H. (2024). Influence of the Material Mechanical Properties on Cutting Surface Quality during Turning. Processes, 12(6), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061171









