Abstract
Hydrophobic eutectic solvents (HES) show significant promise as extractants for metal ions. At their current stage of development, however, they have many disadvantages, such as high costs, limited data on reusability and, often, lower extraction efficiency when compared with traditional extraction systems. This study investigates the physico-chemical properties of five HES formulations based on 1-octanol in combination with camphor, 2′-hydroxypropiophenone, menthol, 1-octanoic acid, and thymol. The 1-octanol/camphor HES exhibited substantially higher extraction efficiency for Fe(III) ions than a solution of 1-octanol in toluene at the same concentration. Furthermore, it showed stability when used in a mixer-settler type extractor. The 1-octanol/camphor HES achieved a rapid extraction and re-extraction rate, with phase contact time reduced to just 2 min, without loss of extraction efficiency. Using the supported liquid membrane method, the proposed Oct/Cam HES enabled a threefold concentration of iron ions in the raffinate phase under continuous operation, confirming its potential for reusability.
1. Introduction
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) have attracted substantial interest in academic research [1], particularly following their recognition as a distinct system type [2] and classification by Abbott [3]. DES have since been investigated in the context of various applications, including as leaching agents for metal oxides [4,5], in analytical chemistry [6,7,8], for extracting organic compounds [9,10,11,12], for cellulose extraction [13,14], and as solvents or catalysts in organic synthesis [15,16,17]. In 2015, Dannie van Osch introduced “hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents” (HDES), demonstrating the use of these solvents as extractants for organic substances and for extracting metal ions from aqueous solutions [18]. Tereshatov et al.’s 2016 study on metal extraction from aqueous phases further established HDES as a leading research focus in liquid metal extraction [19]. In [20,21,22,23], the problems associated with the use of traditional solvents related to their fire hazard and toxicity are noted. The use of HDES may be more feasible due to the low volatility, non-flammability, non-toxicity, and biodegradability of these solvents. These advantages are attractive for modern industries.
HDES owe their popularity to the diverse range of compounds used in their preparation, enabling tailored extractant properties. Notable HDES components with extraction capabilities include alkylphosphine [24] and alkylphosphoric acids [25,26], trioctylphosphine oxide [27,28,29], quaternary ammonium bases [30,31], diketones [32], and fatty acids [33]. Type V HDES are widely used in particular due to their favorable viscosity levels, which are attributable to their non-ionic components, as noted by Abranches [34]. However, with the emergence of new DES classes, the criteria and the definition of DES itself were also refined, since many works appeared in which various binary mixtures were positioned as deep eutectic solvents, although they were ordinary eutectic mixtures (ES or HES in the case of hydrophobic eutectic solvent) [35]. However, despite the misconception in terms, HES are also a very notable class for use as extractants. Indeed, from a chemical engineering point of view, both HDES and HES type V have a number of important advantages, such as low vapor pressure and low volatility, [36], a broad operating temperature range, and optimal viscosity [37,38,39]. Many properties essential for efficient, continuous extraction processes, however, such as chemical stability and reusability, are often insufficiently studied [40,41]. HDES systems may also exhibit reduced extraction efficiency due to decreased solvation capacity when organic molecules replace traditional solvents, although in some cases selectivity is enhanced [42]. Systems containing oxygen acceptor atoms, such as trioctylphosphine oxide, may experience reduced ion complexation due to hydrogen bonding networks involving oxygen atoms [43].
One significant challenge in developing these extraction systems is the lack of pilot-scale testing, as operational conditions in pilot equipment are often more rigorous than in laboratory setups. In academic settings, emulsification typically occurs by shaking, while continuous extractors with mechanical mixing produce finer emulsions, which may separate more slowly in the sump chamber. Thus, advancing HDES as industrial extractants requires a more targeted selection of components.
The most widespread method for the extraction and separation of metals from aqueous media is countercurrent extraction in a cascade of mixer-settler extractors due to the technologically and economically attractive design that allows achieving high process efficiency [44,45,46]. In [47], the performance of agitated column and mixer-settler extractors cascade for the separation of Ni/Co pair using Cyanex 272 was compared. The results showed that efficient Co(II) extraction and metal pair separation were equally achievable using both types of apparatuses. However, it is noted that a more complex design is required in stirred column operation, as the operation of the sections affect each other significantly. In the operation of non-sectional columns, time and effort are required to ensure chemical and hydrodynamic equilibrium, which causes difficulties in restarting the unit after shutdown. Although methods for scaling processes with conventional solvents are widely presented [48,49,50,51], there are few studies where HDES have been applied to pilot equipment. The scaling of an extraction process with DES was carried out in [52]. In this work, DES choline chloride/ethylene glycol (1:2) was used as an alternative to an aqueous solution of Fe, Zn, and Pb. Extraction was performed using Aliquat 336 and Cyanex 923 on a mixer-settler extractor. It is noted that during stripping in a mixer-settler extractor, relatively high viscosities of the solutions led to long delamination of the phases, which hindered the process. This is a typical example that shows the reasons for the low number of publications on process scaling and points to the need to search for HDES extraction systems with favorable characteristics. Such an approach was used to scale up the denitrification process of light hydrocarbon fractions presented earlier by the authors [53]. It was shown that natural DES based on malic acid, citric acid, and xylitol can be applied as an alternative to conventional extractants. Denitrification to a solution nitrogen content <1 ppm was achieved in six steps of countercurrent extraction. In another study [54], a centrifugal extractor was used for the kinetic separation of quinoline, pyridine, and indole, which were separated 6000-fold by repeatedly increasing the volume flow rate of the solutions, thus under-achieving thermodynamic equilibrium for indole. When using DES in the apparatuses in these studies, there were no persistent emulsions or phase entrainment, and the systems operated in a stable hydrodynamic regime. The development of extraction technologies is not limited to the search for alternative solvents. Thus, increasing the environmental friendliness and economic efficiency of extraction systems became possible by using the supported liquid membrane method (multistage three-phase extraction) [55]. In this method, the extractant is introduced once into a system of pairwise connected mixer-settler extractors and circulates between the extraction/stripping units, forming a closed cycle regime. Thus, because the organic phase is not removed from the circuit, this process saves reagents, protecting the environment and reducing production costs. The second incomparable advantage of these systems is the possibility of controlling the efficiency and selectivity of the process and also allows the concentration of components from dilute solutions [56,57]. The application of this method for scaling up extraction systems with HDES is a promising direction.
This study explores the potential of five HES formulations based on 1-octanol, combined with camphor, 2′-hydroxypropiophenone, menthol, 1-octanoic acid, and thymol. These HES, previously synthesized and characterized using IR spectroscopy and solid-liquid phase diagrams, were evaluated for their Fe(III) ion extraction efficiency, which is a model system due to iron’s prevalence in complex separable mixtures. The HES exhibited high extraction efficiency and selectivity, indicating promise for chemical and technological applications. Moreover, the extraction properties were tunable based on the HES components [58]. This work extends the authors’ prior research, focusing on the suitability of 1-octanol-based HES for continuous extraction processes.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physical Properties of HESs
The density and dynamic viscosity of the extractant are crucial physical properties influencing phase separation rates, emulsion formation, and extraction kinetics. To ensure efficient operation, the density ratio between the aqueous and organic phases should not exceed 0.95. Lower density ratios enhance emulsion stratification, whether through centrifugal forces or gravity. The most effective extraction systems maintain viscosities below 100 MPa. Staying within this viscosity threshold helps prevent extractant loss due to entrainment with the aqueous phase in emulsion form.
The study of the density and dynamic viscosity of HES depending on temperature was carried out in the range of 15 to 60 °C (Figure 1). It can be seen from the graphs obtained that with an increase in temperature, the density and viscosity of the HES studied decreased. At room temperature, the density of the HES did not exceed 0.89 g × cm−3, and the dynamic viscosity did not exceed 11.34 MPa×s. These indicators meet set criteria and allow the use of HES data on laboratory and industrial extraction equipment.
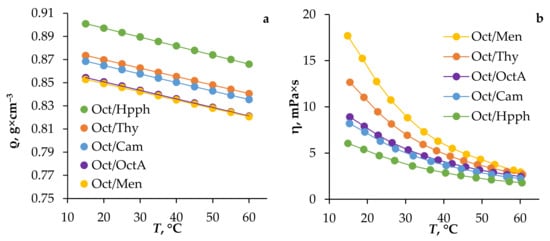
Figure 1.
Density (a) and dynamic viscosity (b) of HES based on 1-octanol, depending on temperature.
2.2. Laboratory Extraction Experiment
In a prior study by the authors [58] on the physico-chemical and extraction properties of the HES used in this work, a hydrochloric acid medium was used. Increasing the chloride ion concentration with HCl and LiCl was shown to enhance metal extraction efficiency. However, high concentrations of HCl pose challenges that impact both the environmental and safety profiles of the process, as well as the durability of the equipment. Conversely, the absence of HCl reduces extraction efficiency, as hydrogen protons play a key role in the extraction mechanism and aid the formation of the extracted compound. In this study, HCl concentration was reduced to 2 mol/L, and LiCl was substituted with CaCl2 to raise chloride ion levels in the system. CaCl2 offers a clear cost advantage over LiCl. Consequently, metal extraction experiments were conducted using a 2 mol/L HCl solution with individualized CaCl2 additions for each HES.
2.2.1. Effect of Phase Contact Time on Extraction Efficiency
In extraction systems, achieving thermodynamic equilibrium quickly is essential for optimizing process efficiency. Aliphatic alcohols are known to facilitate rapid extraction kinetics for metals. In the current study, however, 1-octanol, a component in HES, has been shown to decelerate the formation rate of the extracted compound due to hydrogen bonding and van der Waals interactions among the HES components.
The efficiency of Fe(III) ion extraction from acidic solutions in HES-based systems with 1-octanol was assessed over a time interval ranging from 0.5 to 60 min (see Figure 2). The graph clearly shows that thermodynamic equilibrium in this extraction system was nearly instantaneous. This rapid equilibrium attainment underscores the suitability of this extraction system for real-world extraction equipment applications.
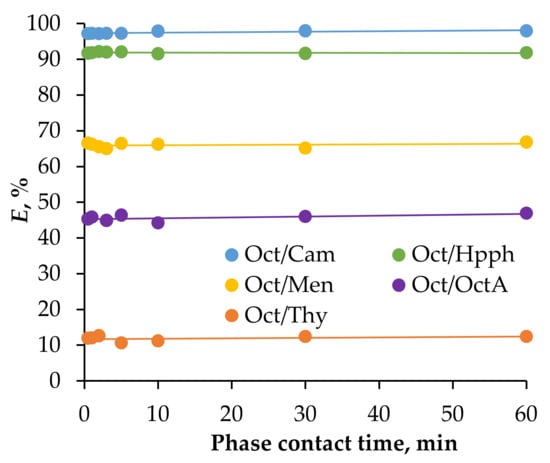
Figure 2.
The extraction efficiency of Fe(III) ions was evaluated as a function of phase contact time in a solution containing 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl, and 2 mol/L CaCl2; Vaq/VHES = 1/1, T = 25 °C.
2.2.2. Influence of the Precipitator
As outlined above, this study investigates the impact of CaCl₂ on the extraction efficiency of Fe(III) ions from hydrochloric acid solutions in systems with HES based on 1-octanol. The concentration of CaCl₂ was varied, from 0 to 3.7 mol/L. Extraction efficiencies in these HES systems were compared with those obtained using 1-octanol dissolved in toluene at an equivalent concentration to that in HES. The results (Figure 3) demonstrate that the addition of Cam, Hpph, and Men positively influenced the extraction properties of Oct, whereas OctA and Thy additions had a negative effect. This trend aligns with findings from the authors’ previous work.
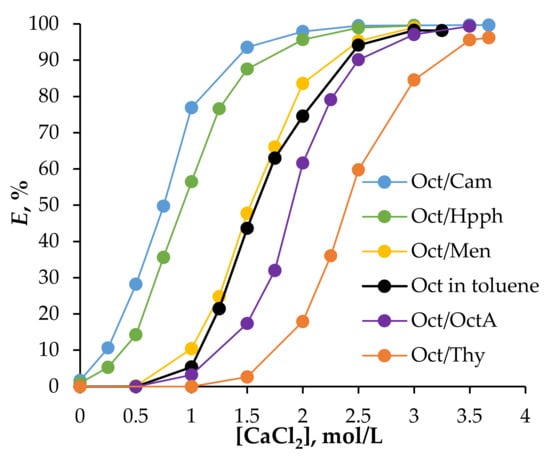
Figure 3.
Dependence of the degree of extraction of Fe(III) ions from 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl solution on the initial concentration of CaCl2 in the aqueous phase; Vaq/VHES = 1/1, T = 25 °C, phase contact time = 5 min.
The results further indicate that adding CaCl₂ to the system enhanced Fe(III) extraction efficiency due to the increased concentration of chloride ions, which promoted the formation of the anionic iron complex [FeCl₄]⁻. This complex readily bound with 1-octanol, resulting in an extractable compound [59]. In addition, CaCl₂ was shown to increase the Fe(III) reduction rate more efficiently than LiCl at equivalent concentrations. This difference is due to the fact that CaCl₂ provides two chloride ions per molecule while LiCl provides only one, making CaCl₂ more efficient, requiring a lesser amount to achieve the same effect. CaCl₂ also has a cost advantage over LiCl, making it a more economical choice. The addition of CaCl2 increases the density of the solution to a greater extent than LiCl, leading to faster delamination, which is enabled by the lower phase ratio. Thus, the inclusion of CaCl₂ allows reducing the HCl concentration without compromising the Fe(III) extraction efficiency.
2.2.3. Influence of the Ratio of Water and Organic Phases
Before scaling up the extraction process, it is crucial to investigate the impact of the phase volume ratio on extraction efficiency. The dependence of Fe(III) ion extraction efficiency on the volume ratio of aqueous to organic phases was examined, with ratios ranging from 0.5 to 5 (Figure 4).
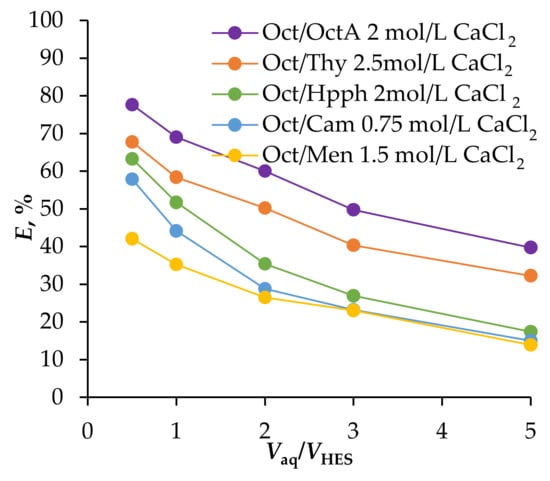
Figure 4.
Dependence of the degree of extraction of Fe(III) ions from 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl solution on the ratio of aqueous and organic phases; T = 25 °C, phase contact time = 5 min.
The results show that as the volume of the organic phase increased, Fe(III) ion extraction efficiency improved. This enhancement is probably due to an increase in the relative excess of the extractant compared with Fe(III) ions, shifting the equilibrium toward the formation of the extractable compound. However, the efficiency gain diminished when the extractant volume was increased tenfold. This reduced effect can be attributed to the concurrent extraction of hydrochloric acid into the HES phase, which inhibits the formation of the Fe(III) extractable compound.
Therefore, a 1:1 ratio of aqueous to organic phases is optimal, offering sufficient extraction efficiency without excessive HES consumption.
2.2.4. Effect of Phase Contact Time on Re-Extraction Efficiency
It is well established that aliphatic alcohols in HES systems can be regenerated using distilled water after metal ion extraction. In this study, distilled water was employed as the re-extractant. Figure 5 presents the relationship between Fe(III) re-extraction efficiency from the HES phase and phase contact time. The data indicate that, while thermodynamic equilibrium was achieved within approximately 2 min, the re-extraction process proceeded at a slower rate than the extraction process. This relatively slow re-extraction could pose challenges for maintaining efficiency when implementing the system using extraction equipment.
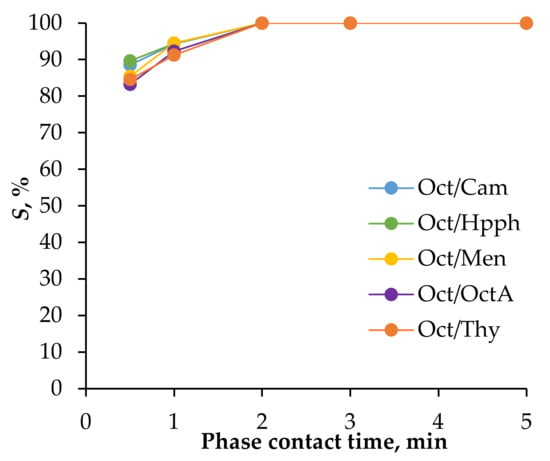
Figure 5.
Dependence of the degree of stripping of Fe(III) ions from the phase of HES (obtained by extraction of Fe(III) from solution 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl, and 2 mol/L CaCl2) by distilled water on the time of phase contact: VHES/Vwater = 1/1, T = 25 °C.
2.2.5. Chemical Resistance and Reusability of HES
The reusability of HES is crucial for their application in closed-loop systems. Any decline in extraction performance due to the chemical non-inertness of HES can significantly reduce the process’s efficiency. Additionally, low HES stability, particularly through water solubility, not only leads to extractant loss but also contributes to wastewater contamination and environmental pollution. Therefore, the ability of an extractant to be reused without compromising its extraction efficiency is essential for industrial use.
Water absorption by the extractant can negatively impact its extraction capabilities. To evaluate the water-dissolving capacity of HES, samples were mixed with distilled water in a 1:1 volume ratio and left to interact for 24 h. Following centrifugation and phase separation, the water content in the HES phase was determined using Karl Fischer titration. The results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Results of K. Fisher HES titration before and after contact with water for 24 h.
Table 1 indicates that the average water content in the HES tested remained largely unchanged after water contact, although it did increase by approximately 2.94 wt%. While this increase is not critical, it could potentially reduce Fe(III) ion extraction efficiency when the HES are reused.
A study of the extraction efficiency of 1-octanol-based HES over repeated cycles was conducted, encompassing seven extraction/re-extraction cycles. Figure 6 presents the results for Fe(III) ion extraction, with each re-extraction consistently performed using distilled water for quantitative recovery.
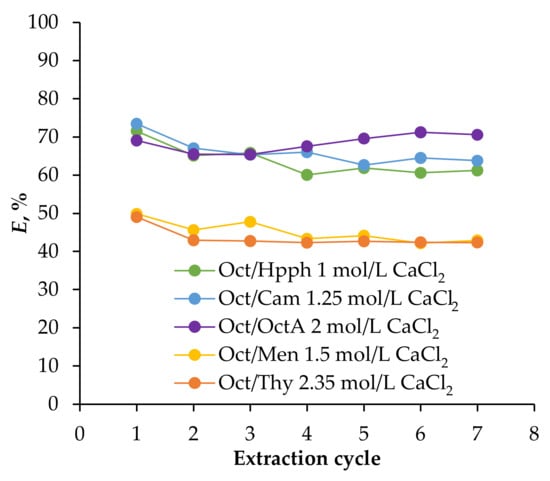
Figure 6.
Dependence of the degree of extraction of Fe(III) ions from 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl solution, Vaq/VHES = 1/1, T = 25 °C, phase contact time = 5 min, depending on the extraction/stripping cycle.
The data obtained indicate that all hydrophobic extractants, with the exception of Oct/OctA, exhibited a slight decrease in their ability to extract Fe(III) ions during the first 2–4 cycles, after which their extraction capacity stabilized. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that the HES absorb a small amount of water upon contact with the aqueous phase owing to their solubility (as shown in Table 1). Once the extractant becomes saturated with water, extraction efficiency remains consistent in subsequent extraction and re-extraction cycles. Consequently, overall water absorption by the HES does not significantly impact their extraction properties during prolonged use.
In addition, the infrared (IR) spectra of the HES were recorded before and after the extraction and re-extraction cycles, as illustrated in Figure 7.
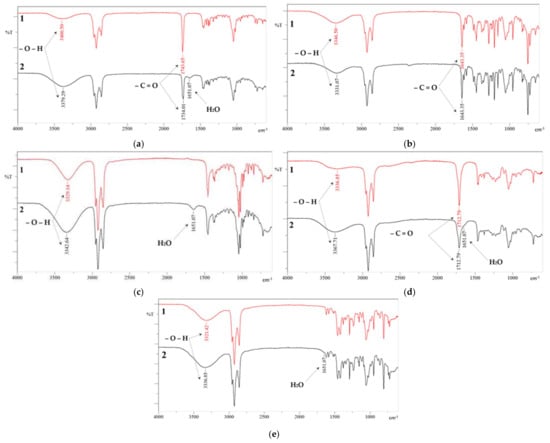
Figure 7.
IR spectra before (1) and after (2) extraction/re-extraction cycles. HES: (a) Oct/Cam, (b) Oct/Hpph, (c) Oct/Men, (d) Oct/OctA, (e) Oct/Thy.
It can be seen from the spectra obtained that the peak of the valence oscillation of the OH group on all spectra after the extraction/re-extraction cycles decreased (~3350 cm−1). The reason for this is the water absorbed by the extractant, which also had a peak of the valence oscillation of the OH group in the same region. It can also be seen that at 1651.07 cm−1, after extraction/re-extraction cycles, there is a new peak in all HES, with the exception of Oct/Hpph, in whose spectrum this peak apparently overlaps with the peak of the valence oscillation of the C=O group Hpph. The reason for this is dissolved water, which has a scissoring peak of H-O-H at a given frequency. Also, there are no other peaks on the spectra obtained before and after the extraction/re-extraction cycles that might indicate the occurrence of any additional chemical reactions. The peaks of the functional groups of HES components that appeared originally could still be observed.
Overall, the results obtained suggest that the HES studied are stable during their long-term use, with no loss of physico-chemical or extraction properties.
2.2.6. The Rate of Phase Delamination
A low rate of phase delamination can lead to the unintentional removal of the extractant along with the aqueous phase; the loss of the extractant negatively impacts the economics of the process. In addition, contamination of the aqueous phase with the extractant can adversely affect the quality of the final product. It is important to note that, in academic studies involving hydrophobic extractants, samples are often mixed using a rotary shaker rather than being emulsified with a mechanical stirrer, as is common with settling mixers. In this investigation, a mechanical agitator was employed to ensure reliable results. The duration of phase delamination in systems containing the HES studied is summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
The rate of phase delamination in HES systems based on 1-octanol.
Based on the results obtained, it can be concluded that the hydrophobic extractant Oct/Cam not only exhibits the best extraction properties in the series but also demonstrates the fastest delamination rate. Under the continuous extraction conditions employed in this study, the optimal delamination time is 1.5 min, which was achieved by this HES. In contrast, the use of octanoic acid resulted in the formation of a stable emulsion at the phase interface, leading to the longest phase delamination time observed.
2.2.7. HCl Extraction
The results indicate that all five proposed hydrophobic extractants are sufficiently stable for use in closed-loop technology. When scaling the process to extraction equipment, however, the extractant HES Oct/Cam is recommended due to its superior effectiveness in extracting Fe(III) ions from hydrochloric acid media (as shown in Figure 3). Furthermore, this HES demonstrated a technological suitability comparable with that of the other candidates.
As previously noted, aliphatic alcohols are capable of extracting HCl, which can negatively impact the extraction process when applied in an extractor cascade. Acid extraction not only lowers the efficiency of Fe(III) ion extraction but may also cause shifts in the volume of the aqueous and organic phases. To investigate this, the extraction of HCl was examined across a concentration range of 2 to 8 mol/L of the initial acid concentration within the system using the chosen HES Oct/Cam (see Figure 8).
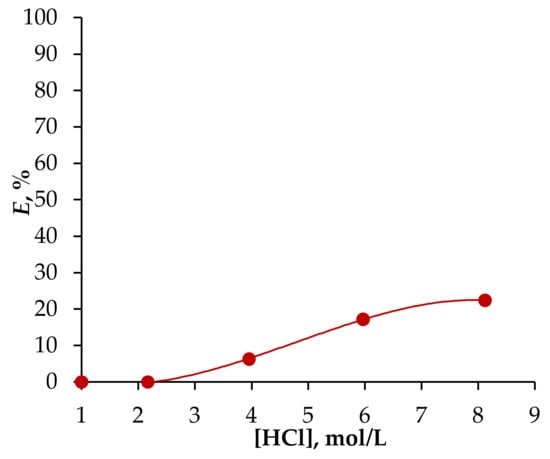
Figure 8.
The dependence of the degree of HCl extraction on its initial concentration using HES Oct/Cam. Vaq/VHES = 1/1, T = 25 °C, phase contact time = 60 min.
The data indicate that as the concentration of HCl increased, so did the degree of its extraction. Notably, when the acid concentration exceeded 4 mol/L, an expansion in the volume of the organic phase was observed. However, at an initial HCl concentration of 2 mol/L, no changes occurred in either the volume of the phases or the extraction of HCl. This study therefore confirms that the HCl concentration selected will not disrupt the extraction process when applied to extraction equipment.
2.3. Continuous Extraction Experiment on Mixer-Settlers
Preliminary optimization of the plant’s operation on a single extraction cell was achieved by adjusting agitator rotation speeds, volume flow rates, and the height of the phase interface. It was determined that the optimal process parameters were an agitator rotation speed of 750 to 900 rpm and a phase ratio of 1:1.5 to 1:2 (Vaq/VHES) in the sump under maximum operating conditions. With these parameters, the installation achieved an efficiency of 99%.
To enable repeated use of the extractant, it was necessary to assess the amount of extractant entrained with the aqueous phase and determine the maximum number of extraction/re-extraction cycles for which it retained its properties. The extractant’s stability is illustrated in Figure 9. The unit was operated using the defined process parameters, with both phases maintained at an equal flow rate of 250 mL/h. After adjusting the liquid levels, a raffinate sample was immediately collected. As shown in the figure, after 15 min, the extraction rate had reached 20%, indicating that a stable hydrodynamic regime had not yet been established. Maximum extraction efficiency was achieved at 33 min, equivalent to circulating a solution volume approximately five times that of the apparatus through the extraction cell reaching 42%, after which it remained stable for 3.3 h.
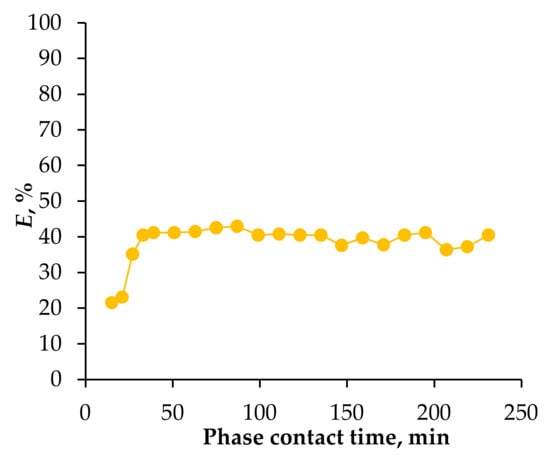
Figure 9.
Dependence of the degree of Fe(III) extraction from 0.01 mol/L Fe(III), 2 mol/L HCl, and 0.75 mol/L CaCl2 solution, T = 25 °C, stripping by distilled water, on the operating time of the installation, with equal volume flow rates of phases—250 mL/h when using the HES Oct/Cam in the supported liquid membrane method.
Thus, it was determined that the extractant can withstand more than 33 extraction/re-extraction cycles without a loss in efficiency, which is a satisfactory result. This processed 825 mL of aqueous Fe(III) solution using about 50 mL of extractant throughout the process. The total HES volume loss at the conclusion of the experiment was less than 1% by volume.
To verify the establishment of thermodynamic equilibrium across the full range of operating volume flow rates, the process was conducted using a single extraction cell with equal flow rates for both phases. The results, presented in Figure 10, show that the extraction efficiency of Fe(III) ions and re-extraction efficiency were largely unaffected by variations in flow rate. This indicates that kinetic factors do not influence the efficiency of HES extraction, allowing for a substantial increase in extraction throughput without compromising performance.
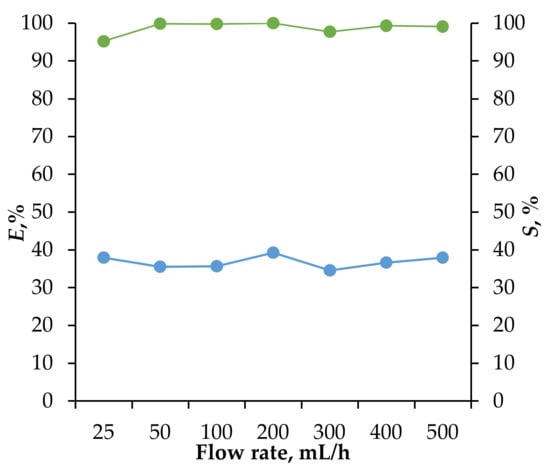
Figure 10.
The dependence of the degree of extraction of Fe(III) (blue dots) and the degree of stripping (green dots) on the total volume flow per extraction cell when using HES Oct/Cam.
After conducting preliminary studies to determine the stability conditions of the new extraction system when working in a laboratory installation, the effect of the number of extraction/re-extraction cycles, and the thermodynamic equilibrium, Fe(III) was extracted and concentrated using the supported liquid membrane method with HES. This technique enables control of the extraction capacity with varying phase flow rates. According to the equations of the material balance, an increase in circulation rate will lead to an increase in the degree of extraction, and a decrease in the volume flow of the extractant phase will lead to the concentration of Fe(III) in the re-extraction phase, while at the same time reducing the degree of extraction. Thus, for multiple concentrations, while maintaining the degree of extraction, it is necessary to vary all parameters simultaneously. To increase and maintain the degree of extraction of Fe(III), the W/V1 ratio was set to 2. To concentrate Fe3+ in the re-extraction phase, the V1/V2 ratio was gradually increased. The results of the experiment are shown in Figure 11. It can be seen from the results obtained that the experimental data are in good agreement with the calculated data. It is shown that an increase in the V1/V2 ratio led to an increase in the concentration of Fe(III) in the raffinate, and, accordingly, to a decrease in the degree of extraction by 10%; at the same time, there was a threefold increase in the concentration of Fe(III) in the re-extraction phase, compared with the regime that had an equal volume ratio of phases.
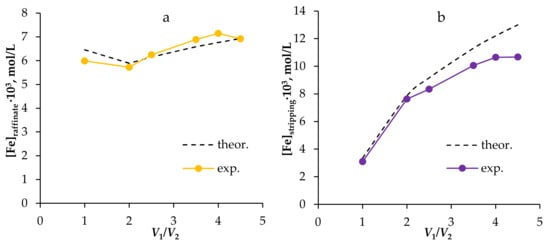
Figure 11.
The concentration of Fe(III) in the raffinate (a) and re-extraction (b) phases depends on the V1/V2 ratio at W/V1 = 2 when using HES Oct/Cam in the supported liquid membrane method.
Thus, it has been shown that hydrophobic eutectic solvents based on alcohols are effective extractants that are suitable for further study of their use in chemical and technological processes. The supported liquid membrane method is a technologically attractive tool for performing extraction processes using a limited amount of extractant.
Thus, it has been shown that the proposed HES are an alternative substitute for conventional solvents, which show their effectiveness in the pilot setting. It should be noted that these solvents can be applied to a wide range of processes, such as the recovery of metals from ores, brines, and wastewater, as well as for the processing of leaching solutions for electronic products.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
Information on the reagents used in the experiments is presented in Table 3. All chemicals were used in the form in which they were received from the supplier without additional purification.

Table 3.
Reagents.
3.2. Preparation of HES
All HDES mixtures were prepared by combining 1-octanol with a second component, camphor, 2′-hydroxypropiophenone, menthol, 1-octanoic acid, or thymol, in a molar ratio of 7:3. The components were blended in a thermostatically controlled Enviro-Genie SI-1202 shaker (Scientific Industries Inc., Bohemia, NY, USA) at 60.0 °C for 10 min. After preparation, the mixture was slowly cooled to room temperature and stored in screw-capped test tubes in air until use.
3.3. Characterization of HES
The IR spectra of the HES were recorded using an IRTracer-100 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with an NIP attachment, covering a range of 4000 to 600 cm−1. The densities of the HES were measured over a temperature range of 15 to 60 °C using an Anton Paar DMA 1001 densitometer (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) with an accuracy of ±0.0001 g × cm−3. The viscosity of the HDES was studied by rotational rheometry on a Physica MCR301 (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) rheometer; a cone-plane measuring unit was used, with a cone diameter of 50 mm and a cone angle of 1°. Titration of the HES samples was performed using the coulometric method before contact with water and subsequently using the volumetric method.
3.4. HES Extraction Experiment
The initial Fe(III) solution was prepared by dissolving a precisely weighed sample of FeCl₃ × ₂O in distilled water. Similarly, the CaCl₂ solution was prepared by dissolving a weighed sample of CaCl₂ × 2H₂O in distilled water. The concentration of CaCl₂ in the solutions was verified by argentometric titration using an AgNO₃ solution with K₂CrO₄ as the indicator. All extraction experiments were conducted in graduated centrifuge tubes at room temperature and atmospheric pressure (~100 kPa), with an organic-to-aqueous phase volume ratio (VHES/Vaq) of 1:1. Fe(III) ions were extracted from a 0.01 mol/L FeCl₃ solution by mixing HES with the Fe(III) aqueous solution in varying CaCl₂ concentrations and a 2 mol/L HCl solution.
Re-extraction involved mixing the Fe(III)-enriched HES phase with distilled water. The test tubes were shaken using an IKA Trayster digital shaker at 45 rpm for 5 min. Following mixing, samples were centrifuged on an SM-6MT centrifuge (SIA ELMI, Latvia) at 2500 rpm for 5 min to achieve complete phase separation. The separated phases were then transferred to separation funnels, and the aqueous phase was analyzed. The concentration of Fe(III) ions was measured by spectrophotometry at 420 nm using sulfosalicylic acid as the indicator, with water as a reference. The Fe(III) ion concentration in the organic phase post-extraction was calculated using the material balance equation.
The degree of extraction (E, %) was determined using Equation (1):
where nin and naq are the number of Fe(III) ions in the initial solution and aqueous solution after extraction, respectively.
Re-extraction degree (S, %) was calculated according to Equation (2):
where naq is the amount of Fe(III) ion in aqueous phase after re-extraction and nHES are the amount of Fe(III) ions in HES phase prior to re-extraction.
Extraction data were measured three times, and the values were averaged, with a relative standard deviation of less than 5%.
3.5. Investigation of the Phase Delamination Rate
A mixture of 50 mL of HES and 50 mL of distilled water was added to a 250 mL measuring cylinder with a diameter of 38 mm. The two phases were then vigorously mixed using an overhead mechanical stirrer at a rotation speed of 1500 rpm for 5 min. The phase separation time was recorded from the moment mixing stopped until a clear boundary formed between the aqueous and organic phases.
3.6. Process Scaling
To scale the extraction processes with new deep eutectic solvents, a laboratory setup was used that comprised mixer-settler SOLVEX 8.04 extractors (Solvex, Moscow, Russia) constructed from polypropylene and polytetrafluoroethylene. Each cell had a volume of 50 mL and a maximum capacity of 1000 mL/h (Figure 12). This setup was used to assess the extractant’s stability over multiple extraction/stripping cycles, evaluate the extraction efficiency as a function of phase flow rates, and examine the influence of Fe(III) concentration in the stripping phase using the supported liquid membrane method.
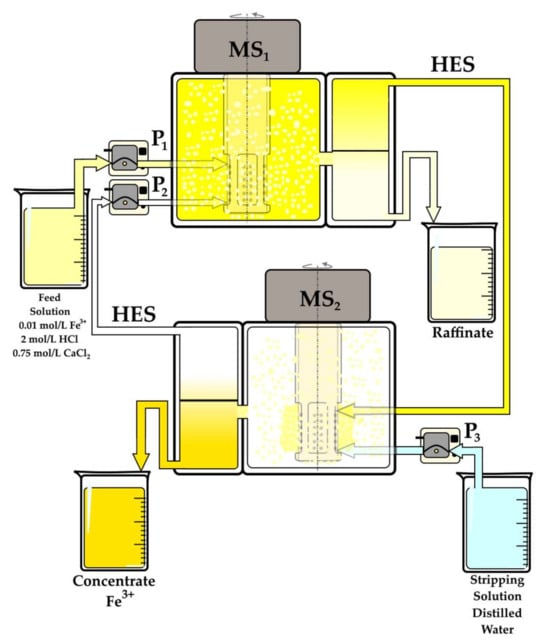
Figure 12.
The scheme of a lab prototype, which works using the supported liquid membrane method. MS—mixer-settler extractor, P—peristatic pump.
Initially, the installation was validated on a standard reactive extraction test system (Zn2⁺/di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid) recommended by the European Federation of Chemical Engineering, achieving an efficiency of over 99%. Subsequently, the system’s operation with HES Oct/Cam and distilled water in a single extraction cell was optimized to identify the optimal process parameters (agitator rotation speed, phase flow rate, and phase interface height) for stable hydrodynamic performance. The same optimization procedure was applied for using the supported liquid membrane method.
This installation differs fundamentally from conventional extraction systems in that the extractant is introduced into the system only once before startup, and it then circulates continuously between the extraction (MS1) and re-extraction (MS2) cells. The system uses a P2 pump to maintain the desired volume flow, allowing control over process efficiency and enabling the concentration of components from dilute solutions without the need for buffer tanks for the extractant, which minimizes extractant volume.
The setup comprises two mixer-settler extractors: MS1 (extraction unit) and MS2 (re-extraction unit). The initial feed is an aqueous solution containing 0.01 mol/L Fe(III) in 2 mol/L HCl, which is supplied via a peristaltic pump (P1 BT 100M, Shenchen Pump, Baoding, China) fitted with a YZ2515X pump head and Shenchen Silicon Tubing (15 size, internal diameter 4.8 mm, wall thickness 2.4 mm), supporting flow rates of 0.17 to 1020 mL/min. Distilled water, serving as the stripping solution, is supplied to MS2 by a P3 BT 100M peristaltic pump (Shenchen Pump) with an AMC series pump head, using tubing with an internal diameter of 3 mm and a wall thickness of 1 mm, supporting flow rates of 0.03 to 45.4 mL/min. The extractant, Oct/Cam, circulates between MS1 and MS2 using a P2 BT 100M peristaltic pump (Shenchen Pump), with the same pump head and tubing specifications as P3.
In operation, iron-saturated HES flowed into MS2 by gravity, aided by the vacuum generated in MS2’s mixing chamber when the agitator was in motion. Before startup, the cells were prefilled to half their volume with their respective aqueous solutions, and 50 mL of HES was evenly introduced into the system. Once the system started, the phase volumes redistributed across the extraction cells, soon reaching full volume capacity and establishing a stable hydrodynamic regime.
Sampling of the raffinate and Fe(III) concentrate during re-extraction for analysis was performed using the heavy phase discharges of MS1 and MS2. Samples were collected three times during each operational mode, with intervals corresponding to the passage of a volume of solutions equal to the apparatus volume. Changes in experimental mode were made after obtaining consistent analytical results from three consecutive samples. For all experiments, the HDES extraction system volume was maintained at 100 mL.
Equations (4) and (5) were used to calculate the output concentrations of Fe(III) in both the raffinate and concentrate. These equations were derived from the material balance Equation (3) and were based on the schematic layout shown in Figure 13. By applying these formulas, the Fe(III) concentration in each phase could be accurately calculated, enabling an assessment of extraction and re-extraction efficiencies under the process conditions set, as follows:
where xi′ represents the concentration of Fe(III) in the ith flow of the aqueous phase as it enters the apparatus, xi” denotes the concentration of Fe(III) in the ith flow of the aqueous phase as it exits the apparatus, and yij corresponds to the concentration of Fe(III) in the phase of the HES flow moving from block i to block j.
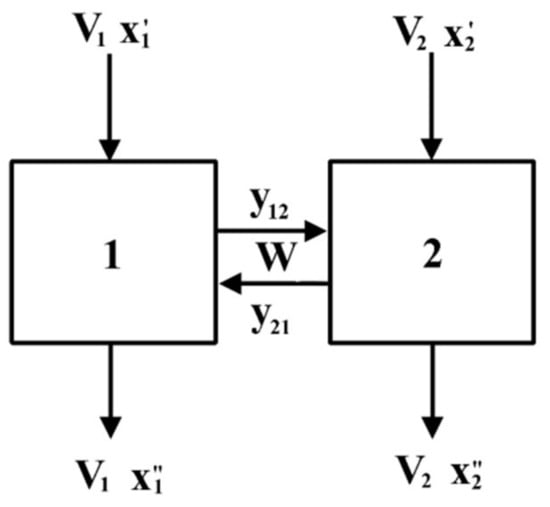
Figure 13.
Scheme of supported liquid membrane extraction: 1—extraction block, 2—stripping block, V1—feed solution (0.01 mol/L FeCl3 in 2 mol/L HCl) flow rate, V2—stripping solution (distilled water) flow rate, W—HES flow rate.
4. Conclusions
This article explores the technological suitability of hydrophobic eutectic solvents as extractants for isolating iron(III) from hydrochloric acid solutions. This study investigated several HES, namely Oct/Cam, Oct/Hpph, Oct/Men, Oct/OctA, and Oct/Thy, as potential candidates. Laboratory tests confirmed that these solvents possess favorable physical and extraction properties, with density and viscosity values not exceeding 0.893 g × cm−3 and 10.74 MPa × s at room temperature, respectively. The extraction efficiency for iron(III) from model solutions reached an impressive >99.9% in a single step. Additionally, the HES exhibited substantial chemical stability, maintaining performance over seven extraction/re-extraction cycles.
Based on extraction efficacy and phase separation speed, HES Oct/Cam emerged as the most technologically promising solvent. Subsequent continuous operation experiments on a laboratory extraction system validated the extractant’s stability and high extraction/re-extraction efficiency, even with increased flow rates of up to 500 mL/h. To enhance HES usage, a finite-extractant experiment using the supported liquid membrane method achieved a more than threefold iron(III) concentration increase. It is shown that the existing drawbacks of the extraction system, such as water and HCl solubility, are insignificant and do not affect the thermodynamic and hydrodynamic equilibrium or the degree of extraction. The findings indicate that the proposed HES meets all key technological requirements and is suitable for future application in real solution extraction processes.
The results obtained are promising for the creation of environmentally friendly and safe closed-cycle extraction technologies. Further research can be aimed at scaling up the processes of metal separation in wastewater, leaching solutions of spent lithium-ion batteries and other electronic products, and for the separation of metals from brines and ores.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V.K., N.A.M., and A.A.V.; methodology, D.V.L.; software, I.S.F.; validation, Y.A.Z.; formal analysis, Y.A.Z. and I.S.F.; investigation, A.V.K., D.V.L., and N.A.M.; data curation, A.V.K. and Y.A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V.K., D.V.L., and N.A.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.A.Z. and A.A.V.; visualization, A.V.K.; supervision, Y.A.Z.; project administration, A.A.V.; funding acquisition, A.A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This article was prepared within the project “The ‘Clean Water’ project as the most important component of cooperation between the Russian Federation and the countries of the Global South: socio-economic and technological dimensions”, which was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation program for research projects in priority areas of scientific and technological development (Agreement No. 075-15-2024-546).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mu, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, C.; Lv, S. Research Progress on Deep Eutectic Solvents and Recent Applications. Processes 2023, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-Based Ionic Liquids with Metal-Containing Anions and Cations. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical Recovery of Cobalt from Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials Using Deep-Eutectic Solvents. Green. Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ortiz, W.; Aldana-González, J.; Le Manh, T.; Romero-Romo, M.; Mejía-Caballero, I.; Ramírez-Silva, M.T.; Arce-Estrada, E.M.; Mugica-Álvarez, V.; Palomar-Pardavé, M. A Deep Eutectic Solvent as Leaching Agent and Electrolytic Bath for Silver Recovery from Spent Silver Oxide Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 016508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, S.; Esfandiari, Z.; Khodadadi, M.; Dehaghani, M.S.T. Simultaneous Analysis of Benzoic and Sorbic Acids in Orange Juice Using Thymol/Water Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and DLLME Method Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 6285–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Gerasimov, A.; Nechaeva, D.; Volodina, N.; Bessonova, E.; Bulatov, A. An Effervescence-Assisted Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent Decomposition: Determination of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac in Liver. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Israelyan, D.; Bulatov, A. Automated Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Chromatomembrane Microextraction: Separation and Preconcentration of Bisphenols from Aqueous Samples. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338, 126480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannuchi, N.; Braga, A.R.C.; De Rosso, V.V. High-Performance Extraction Process of Anthocyanins from Jussara (Euterpe Edulis) Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Processes 2022, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Rubio, C.; Rafikova, K.; Mutelet, F. Desulfurization and Denitrogenation Using Betaine-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2024, 69, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Liu, G.; Xu, Q. Study on Extraction Desulfurization of Road-Paving Asphalt by Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, S1226086X24006166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxim, C.; Blaga, A.C.; Tataru-Farmus, R.-E.; Suteu, D. Acmella Oleracea Metabolite Extraction Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Processes 2024, 12, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.Y.; Hoo, D.Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Manickam, S.; Yu, L.J.; Tan, K.W. One-Pot Extraction of Nanocellulose from Raw Durian Husk Fiber Using Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent with in Situ Ultrasound Assistance. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 106, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ge, H.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Xu, H. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Cellulose and Aromatic Compounds from Rose Petals Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokesh Kumar, S.; Tabassum, S.; Govindaraju, S. Novel Deep Eutectic Solvent Catalysed Single-Pot Open Flask Synthesis of Tetrasubstituted-1H-Pyrroles. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparella, A.N.; Stallone, M.; Pulpito, M.; Perna, F.M.; Capriati, V.; Vitale, P. An Enhanced Stereoselective Synthesis of α,β-Unsaturated Esters through the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons Reaction in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Sarrafi, Y.; Maleki, B. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent as a Green Catalyst for the One-Pot Synthesis of Chromene and 4H-Pyran Derivatives. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2024, 56, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Water-Immiscible Extractants. Green. Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshatov, E.E.; Boltoeva, M.Y.; Folden, C.M. First Evidence of Metal Transfer into Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic and Low-Transition-Temperature Mixtures: Indium Extraction from Hydrochloric and Oxalic Acids. Green. Chem. 2016, 18, 4616–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Banjare, M.; Behera, K.; Satnami, M.L.; Pandey, S.; Ghosh, K.K. Self-Assembly of a Short-Chain Ionic Liquid within Deep Eutectic Solvents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7969–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulcova, A.; Russ, A.; Jablonsky, M.; Sima, J. The pH Behavior of Seventeen Deep Eutectic Solvents. BioResources 2018, 13, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. New Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent Based on Bis(2,4,4-Trimethylpentyl)Phosphinic Acid and Menthol: Properties and Application. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37(1), 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Al(III) with the Deep Eutectic Solvent D2EHPA/Menthol. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Lobovich, D.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zinov’eva, I.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. The Use of Organophosphorus Extractants as a Component of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDES) for the Processing of Spent Lithium-iron Phosphate Batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 228, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milevskii, N.A.; Zinov’eva, I.V.; Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Sm/Co Magnetic Materials: A Recycling Strategy Using Modifiable Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Trioctylphosphine Oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.; McCourt, É.N.; Connolly, F.; Nockemann, P.; Swadźba-Kwaśny, M.; Holbrey, J.D. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Incorporating Trioctylphosphine Oxide: Advanced Liquid Extractants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 17323–17332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Su, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhi, H.; Sun, X. A Cleaner Strategy for Comprehensive Recovery of Waste SmCo Magnets Based on Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milevsky, N.A.; Zinovieva, I.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extractive Separation of Co/Ni Pair With the Deep Eutectic Solvent Aliquat 336/Timol. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, K.; Fan, J. Highly Efficient Extraction/Separation of Cr (VI) by a New Family of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Ji, L.; Li, L. Separation of Lithium from Alkaline Solutions with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on β-Diketone. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zante, G.; Braun, A.; Masmoudi, A.; Barillon, R.; Trébouet, D.; Boltoeva, M. Solvent Extraction Fractionation of Manganese, Cobalt, Nickel and Lithium Using Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Type V Deep Eutectic Solvents: Design and Applications. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 35, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Everything You Wanted to Know about Deep Eutectic Solvents but Were Afraid to Be Told. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2023, 14, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Roghair, I.; Gallucci, F.; Van Sint Annaland, M. Total Vapor Pressure of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Experiments and Modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From Phase Change Materials to Green Solvents: Hydrophobic Low Viscous Fatty Acid–Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Influence of the Molecular Structure of Constituents and Liquid Phase Non-Ideality on the Viscosity of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Ionic Liquids and Deep-Eutectic Solvents in Extractive Metallurgy: Mismatch Between Academic Research and Industrial Applicability. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Hayyan, M. Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis: The Missing Piece in the Puzzle of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshatov, E.E.; Volia, M.F.; Folden Iii, C.M. Menthol-Based Eutectic Solvent for Indium and Thallium Partition from Hydrochloric Acid Media. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.J.R.; Pérez-Sánchez, G.; Schaeffer, N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Solvent Extraction in Extended Hydrogen Bonded Fluids—Separation of Pt(iv) from Pd(ii) Using TOPO-Based Type V DES. Green. Chem. 2021, 23, 4540–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewulf, B.; Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Heavy Rare-Earth Elements by Non-Aqueous Solvent Extraction: Flowsheet Development and Mixer-Settler Tests. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Petranikova, M.; Ekberg, C.; Steenari, B.-M. Mixer-Settler System for the Recovery of Copper and Zinc from MSWI Fly Ash Leachates: An Evaluation of a Hydrometallurgical Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, R.-Z.; Hou, Z.-A.; Li, Z.-L. Investigation of the Extraction Kinetics of Cobalt and Nickel and the Optimization of Operation Parameters in a Mixer-Settler for the Extraction of Cobalt. Hydrometallurgy 1987, 18, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.R.; Deferm, C.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Separation of Cobalt and Nickel via Solvent Extraction with Cyanex-272: Batch Experiments and Comparison of Mixer-Settlers and an Agitated Column as Contactors for Continuous Counter-Current Extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Huang, Y.; Yahagi, T.; Hossain, M.K.; Sato, Y.; Narita, H. Solvent Extraction Recovery of Nickel from Spent Electroless Nickel Plating Baths by a Mixer-Settler Extractor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.M.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Otero, A. Dynamic Modelling of Copper Solvent Extraction Mixer–Settler Units. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiev, D.; Paulo, J.B.A. Extraction Separation in Mixer–Settlers Based on Phase Inversion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 43, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, B.; Sampath, M.; Sivakumar, D.; Kamachi Mudali, U.; Natarajan, R. Development of a Micro-Mixer-Settler for Nuclear Solvent Extraction. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 291, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathariotis, S.; Peeters, N.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Separation of Iron(Iii), Zinc(Ii) and Lead(Ii) from a Choline Chloride–Ethylene Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvent by Solvent Extraction. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33161–33170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobovich, D.V.; Solov’eva, S.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Denitrogenation of Light Hydrocarbon Fractions with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Commercial Extraction Equipment. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2023, 57, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobovich, D.V.; Zinov’eva, I.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Kostanyan, A.E.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction Kinetics of Pyridine, Quinoline, and Indole from the Organic Phase with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Separation Study Using a Centrifugal Extractor. Processes 2024, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.-M. A New Liquid Membrane Technology—Electrostatic Pseudo Liquid Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostanyan, A.; Safiulina, A.; Tananaev, I.; Myasoedov, B. Multiphase Extraction: Design of Single- and Multistage Separation Using Liquid Pseudomembranes. Dokl. Chem. 2005, 404, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostanyan, A.E.; Belova, V.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Copper from Sulfuric Acid Solutions Based on Pseudo-Liquid Membrane Technology. Membranes 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Uvarova, E.S.; Maltseva, V.E.; Ananyev, I.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Fedulov, I.S.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Design of Eutectic Solvents with Specified Extraction Properties Based on Intermolecular Interaction Energy. Molecules 2024, 29, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.; Valeev, D.; Kasikov, A. Solvent Extraction of Iron(III) from Al Chloride Solution of Bauxite HCl Leaching by Mixture of Aliphatic Alcohol and Ketone. Metals 2021, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).