In Situ Remediation of Combined Ammonia and Nitrate Nitrogen Contamination Using Zero-Valent Iron-Enhanced Microorganisms in Acidic Groundwater: A Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
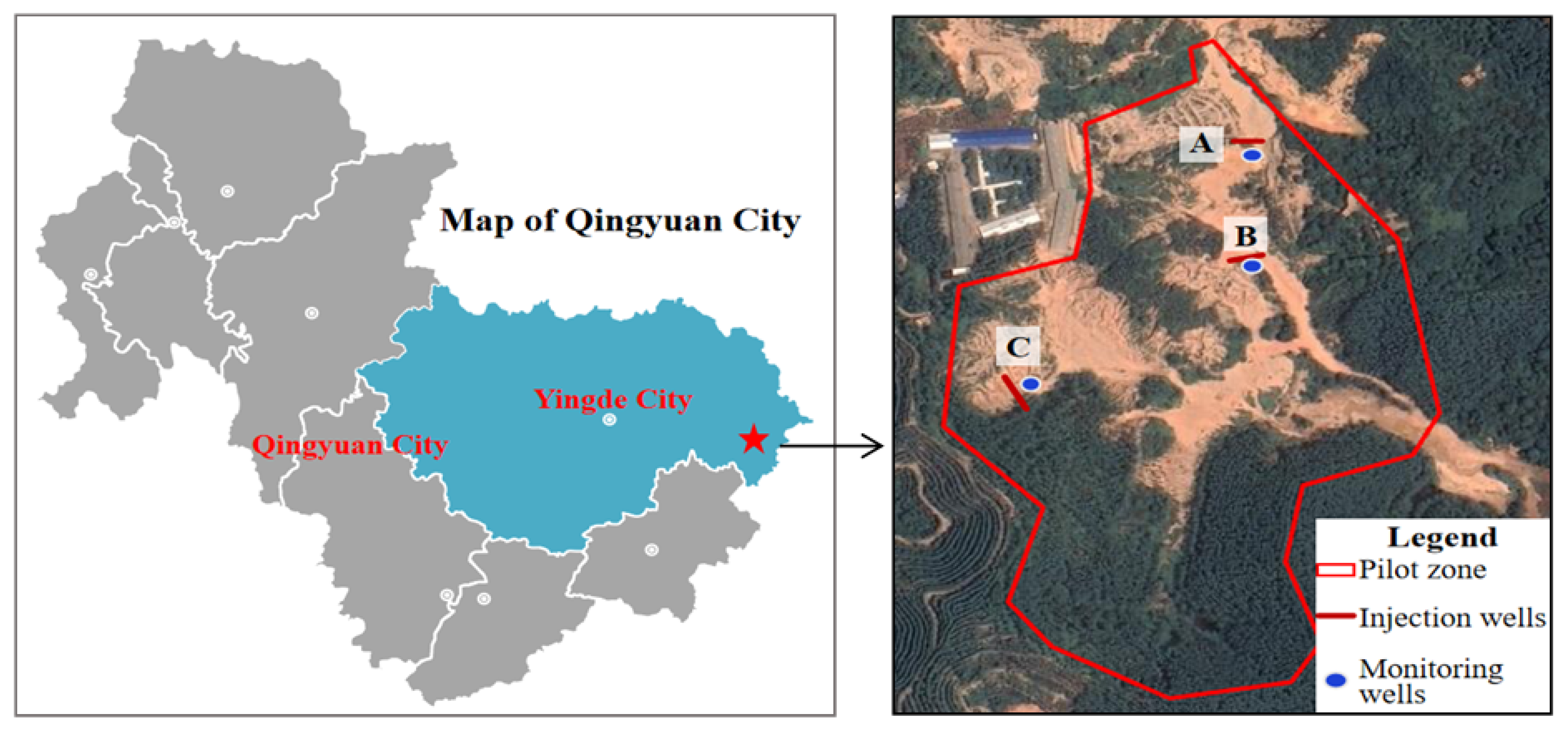
2. Research Area and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Reaction Column Experiment in Laboratory
2.3. Hydrogeological and Climatic Characteristics of the Study Area
2.4. Groundwater Pollution Characteristics
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Column Experiment Results
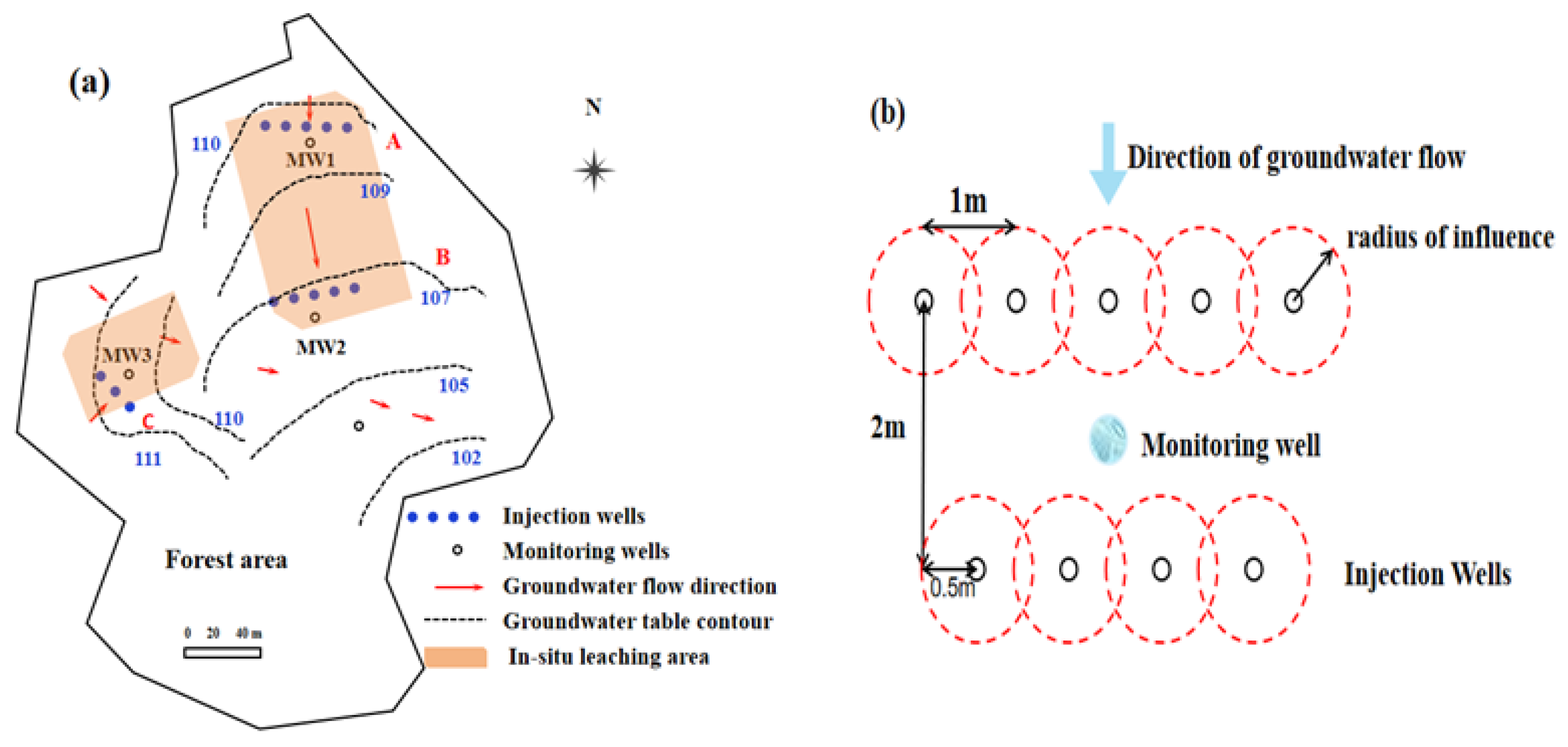
3.2. The Pilot Study for the Assessment of NH4+-N and NO3−-N Combined Contaminations
3.3. Experimental Results of Pilot Site
3.3.1. Monitoring Results of Total Iron Concentration in Groundwater
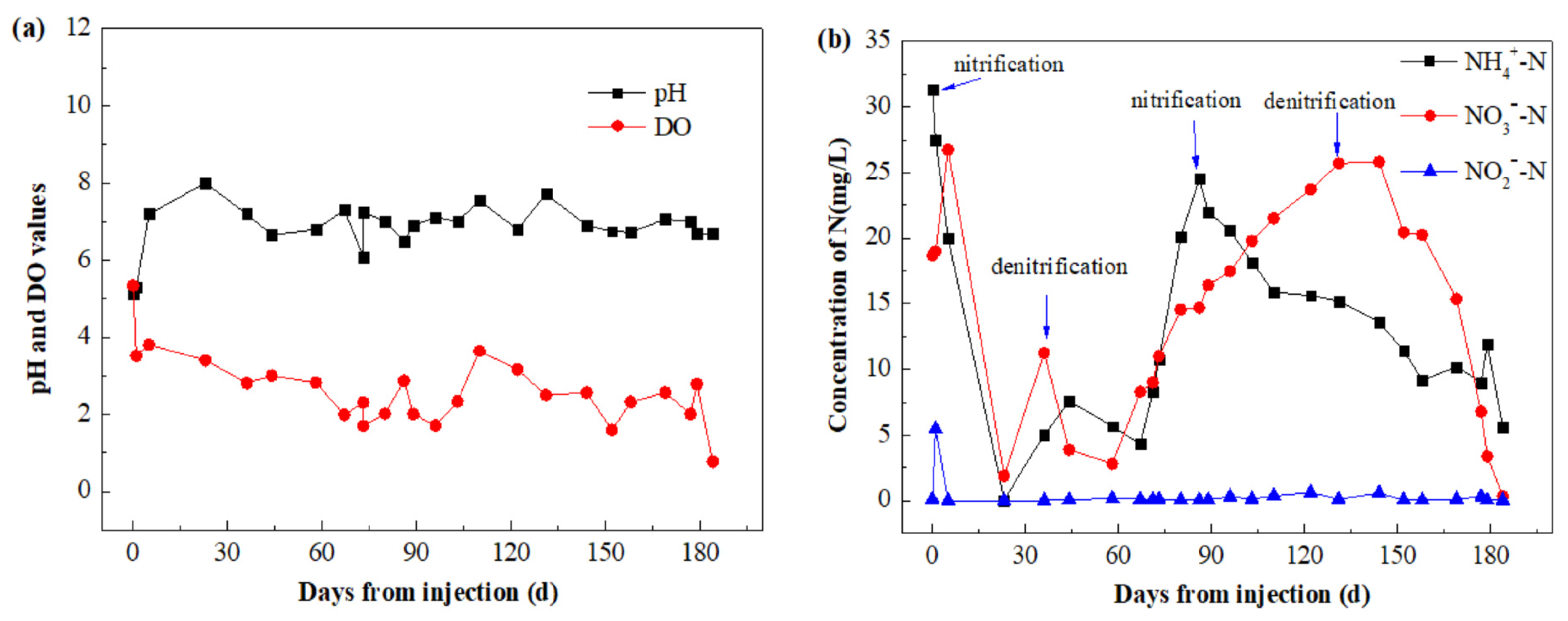
3.3.2. Monitoring Results of Injection Point A
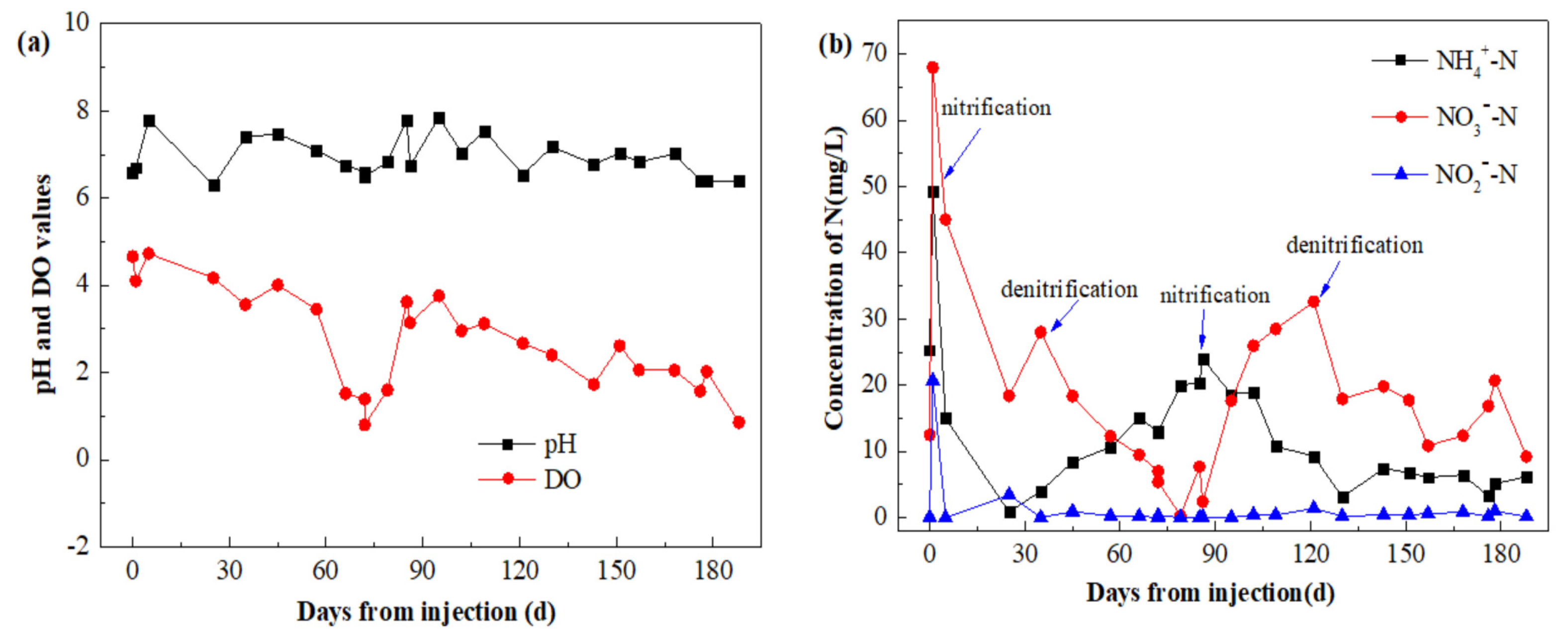
3.3.3. Monitoring Results of Injection Point B
3.3.4. Monitoring Results at Injection Point C
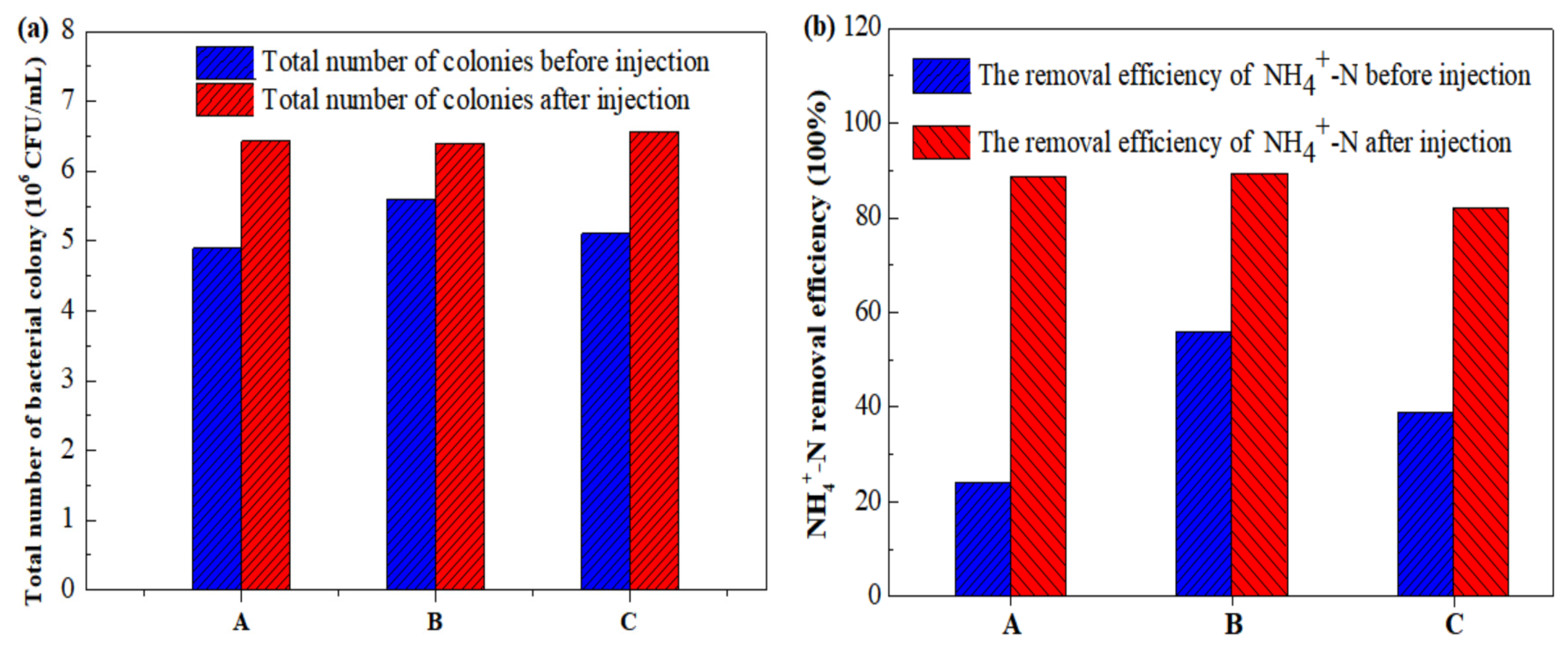
3.3.5. Total Number of Colonies and NH4+-N Removal Efficiency
3.3.6. Site Management and Operational Experience
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The laboratory experiments showed that nitrifying bacteria could increase the removal efficiency for 50 mg/L of NH4+-N to over 99% within 5 days. DO concentration emerged as a crucial factor influencing nitrification efficiency, with higher DO levels significantly enhancing the nitrification process. The introduction of ZVI in the reaction columns reduced the denitrification-driven NO3−-N remediation cycle from 15 days to approximately 10 days. This improvement was mainly attributed to ZVI elevating pH levels and facilitating the reduction of NO3−-N, thereby promoting denitrification through microbial activity synergistically.
- (2)
- The pilot-scale experiments demonstrated that the combination of ZVI with microbial agents substantially boosted the removal efficiency for NH4+-N and NO3−-N combined contamination in groundwater. The injection of ZVI and microbial agents increased the removal efficiency for NH4+-N and NO3−-N contaminants to above 80%. However, the presence of complex hydrogeological interactions, such as those between soil and groundwater and the existence of low-permeability layers, hindered the removal efficiency for N-pollutants. Adjusting the process parameters, including the remediation agent injection frequency and aeration frequency, is essential to meet the remediation requirements for NH4+-N and NO3−-N combined contamination.
- (3)
- In practical engineering applications, enhancing monitoring and remediation agent injection is critical. Locations with inadequate remediation outcomes require increased injection frequency. Addressing issues like sludge accumulation in well bottoms, voids around injection wells, and solid alkali precipitation necessitates improved maintenance of in situ injection wells. Strategies to enhance overall remediation efficiency involve supplementing filling materials, reinforcing injection wells, regular well maintenance, and optimizing alkali dosing levels.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Qian, H. Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: A special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ma, T.; Du, Y. Temporal variations in groundwater nitrogen under intensive groundwater/surface-water interaction. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Niu, J. Degradation and detoxification mechanisms of organophosphorus flame retardant tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) during electrochemical oxidation process. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Du, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Contrasting sources and fate of nitrogen compounds in different groundwater systems in the Central Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.J.; Cao, Q.; Connell, D.W. An overall risk probability-based method for quantification of synergistic and antagonistic effects in health risk assessment for mixtures: Theoretical concepts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2011, 19, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Douglas, G.B.; Pu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, W.; Luo, B.; Hong, W.; Cui, L.; Ye, Z. Zero-valent iron-facilitated reduction of nitrate: Chemical kinetics and reaction pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, F.; Li, F.; Chen, G.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Du, K.; Liu, S.; Li, Z. Ammonia nitrogen sources and pollution along soil profiles in an in-situ leaching rare earth ore. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 15449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Effective recovery of the nitritation process through hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 28404–28417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, A.K.; Mori, K.; Toyama, T. Nitrogen removal ability and characteristics of the laboratory-scale tidal flow constructed wetlands for treating ammonium-nitrogen contaminated groundwater. Water 2020, 12, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powlson, D.S.; Addiscott, T.M.; Benjamin, N.; Cassman, K.G.; Kok, T.M.; Grinsven, H.; L’hirondel, J.L.; Avery, A.A.; Kessel, C. When does nitrate become a risk for humans? J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Hosono, T.; Onodera, S.; Siringan, F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R.; Yoshimizu, C.; Tayasu, I.; Nagata, T.; Taniguchi, M. Sources of nitrate and ammonium contamination in groundwater under developing Asian megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. The analysis of groundwater nitrate pollution and health risk assessment in rural areas of Yantai, China. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S. Analysis of microbial community structure and degradation of ammonia nitrogen in groundwater in cold regions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44137–44147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajta, A.; Bhatia, R.; Setia, H.; Pathania, P. Role of heterotrophic aerobic denitrifying bacteria in nitrate removal from wastewater. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisante, E.; Muzuka, A.N.N. Assessment of sources and transformation of nitrate in groundwater on the slopes of Mount Meru, Tanzania. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ying, X.; Zhao, N.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Interspecies electron transfer between Geobacter and denitrifying bacteria for nitrogen removal in bioelectrochemical system. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 1385–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ling, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Cai, S. Treatment of Ammonium-Nitrogen–Contaminated Groundwater by Tidal Flow Constructed Wetlands Using Different Substrates: Evaluation of Performance and Microbial Nitrogen Removal Pathways. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.M.; Eldon, R.R.; Hullebusch, E.D.; Annachhatre, A.P. Nitrate removal from groundwater: A review of natural and engineered processes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2018, 67, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, K.M.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Cole, I.; Marney, D. Critical review: Microbially influenced corrosion of buried carbon steel pipes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 93, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Jeen, S.-W.; Gui, L.; Gillham, R.W. Nitrate reduction and its effects on trichloroethylene degradation by granular iron. Water Res. 2017, 112, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, A.; Miao, L.; Wu, J.; Xing, B. The role of nitrate in simultaneous removal of nitrate and trichloroethylene by sulfidated zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Reduction of nitrate by zero valent iron (ZVI)-based materials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.P.; Guo, Z.; Yin, H.; Yu, Y.; Dang, Z. Removal of heavy metal ions and polybrominated biphenyl ethers by sulfurized nanoscale zerovalent iron: Compound effects and removal mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gao, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Xue, M.; Zha, M.; Gong, B. The rapid adsorption-microbial reduction of perchlorate from aqueous solution by novel amine-crosslinked magnetic biopolymer resin. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 240, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Douglas, G.B.; Anna, H.; Cui, L.; Ye, Z. Microbial reduction of nitrate in the presence of zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B. Influence of rapid rural-urban population migration on riverine nitrogen pollution: Perspective from ammonia-nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27201–27214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climate Bulletin of Qingyuan City of 2023. Available online: http://www.gdqy.gov.cn/jjqy/ljqy/jrfc/qyqh/content/post_1841096.html (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Lin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Determination of ammonia nitrogen in natural waters: Recent advances and applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 24, e00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Detection methods of ammonia nitrogen in water: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, O.R.; Stephen, R.B.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Chrystina, D.B. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Dong, W.; Su, X.; Shen, X.; Yi, X.; Chen, Y. Effects of magnetite on microbially driven nitrate reduction processes in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 15895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pu, Y.; Qi, W.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wan, P.; Adrian, F. Chemical removal of nitrate from water by aluminum-iron alloys. Chemosphere 2016, 166, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutvonen, H.; Rajala, P.; Carpén, L.; Malin, B. Nitrate and ammonia as nitrogen sources for deep subsurface microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Du, Y. Nitrogen Removal and N2O Accumulation during Hydrogenotrophic Denitrification: Influence of Environmental Factors and Microbial Community Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhai, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiao, L. Research Advances in the Analysis of Nitrate Pollution Sources in a Freshwater Environment Using δ15 N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3−. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.T.; Wu, S.C.; Chou, C.M.; Che, C.H.; Tsai, S.M.; Lien, H.L. Influence of nanoscale zero-valent iron on geochemical properties of groundwater and vinyl chloride degradation: A field case study. Water Res. 2010, 44, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Long, Q.; Li, R.; Lu, C. Ammonia nitrogen adsorption by different aquifer media: An experimental trial for nitrogen removal from groundwater. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xia, X.; Liu, S.; Mou, X.; Qiu, Y. Acceleration of Denitrification in Turbid Rivers Due to Denitrification Occurring on Suspended Sediment in Oxic Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4053–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wayne, S.A. Novel Membrane Inlet Mass Spectrometer Method to Measure 15 NH4+ for Isotope-Enrichment Experiments in Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9555–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Zhao, A.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Anaerobic ferrous oxidation by heterotrophic denitrifying enriched culture. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Song, F.; Gu, T. Laboratory investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of C1018 carbon steel by nitrate reducing bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Ye, Z.; Paul, K. Treatment of heavy oil wastewater by a conventional activated sludge process coupled with an immobilized biological filter. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 84, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X. Change in microbial community in landfill refuse contaminated with antibiotics facilitates denitrification more than the increase in ARG over long-term. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves da Silva, D. Nitrosomonas Eutropha D23—An In Vitro, Evaluation of Its Metabolic Phenotype and Evidence for Its Bio-Activity. Doctoral Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2019; p. 272. Available online: http://eprints.soton.ac.uk/id/eprint/437367 (accessed on 28 November 2024).


| Sites | NH4+-N (mg/L) | NO3−-N (mg/L) | NO2−-N (mg/L) | Total Nitrogen (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 31.3 | 18.7 | 0.105 | 50.105 |
| B | 25.3 | 12.5 | 0.049 | 37.849 |
| C | 34.9 | 51.35 | 0.045 | 86.295 |
| Injection Wells | Number of Rows | Number of Wells Per Row | Total Number of Injection Wells | Depth (m) | Actual Top Tube Length (m) | Length of Bobbin (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 11 | 6.8 |
| B | 1 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 9 | 8.8 |
| C | 2 | 7 | 14 | 10.5 | 3.5 | 6.8 |
| Monitoring Well Number | Length of Upper Solid Pipe (m) | The Length of the Screen (m) | Settling Tube Length (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MW1 | 9 | 10 | 1 |
| MW2 | 7 | 12.3 | 1 |
| MW3 | 3 | 20 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Fan, H.; Wei, X. In Situ Remediation of Combined Ammonia and Nitrate Nitrogen Contamination Using Zero-Valent Iron-Enhanced Microorganisms in Acidic Groundwater: A Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Study. Processes 2024, 12, 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122768
Chen J, Luo Y, Zhang J, Lu Z, Han Y, Chen X, Li M, Fan H, Wei X. In Situ Remediation of Combined Ammonia and Nitrate Nitrogen Contamination Using Zero-Valent Iron-Enhanced Microorganisms in Acidic Groundwater: A Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Study. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122768
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junyi, Yuchi Luo, Junda Zhang, Zexuan Lu, Yitong Han, Xiangxin Chen, Mingkui Li, Hanyun Fan, and Xipeng Wei. 2024. "In Situ Remediation of Combined Ammonia and Nitrate Nitrogen Contamination Using Zero-Valent Iron-Enhanced Microorganisms in Acidic Groundwater: A Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Study" Processes 12, no. 12: 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122768
APA StyleChen, J., Luo, Y., Zhang, J., Lu, Z., Han, Y., Chen, X., Li, M., Fan, H., & Wei, X. (2024). In Situ Remediation of Combined Ammonia and Nitrate Nitrogen Contamination Using Zero-Valent Iron-Enhanced Microorganisms in Acidic Groundwater: A Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Study. Processes, 12(12), 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122768






