Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting Based on Similar Segment Importance in the Process Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methodologies
3.1. Long Short-Term Memory Network
3.2. Patch Squeeze and Excitation Module
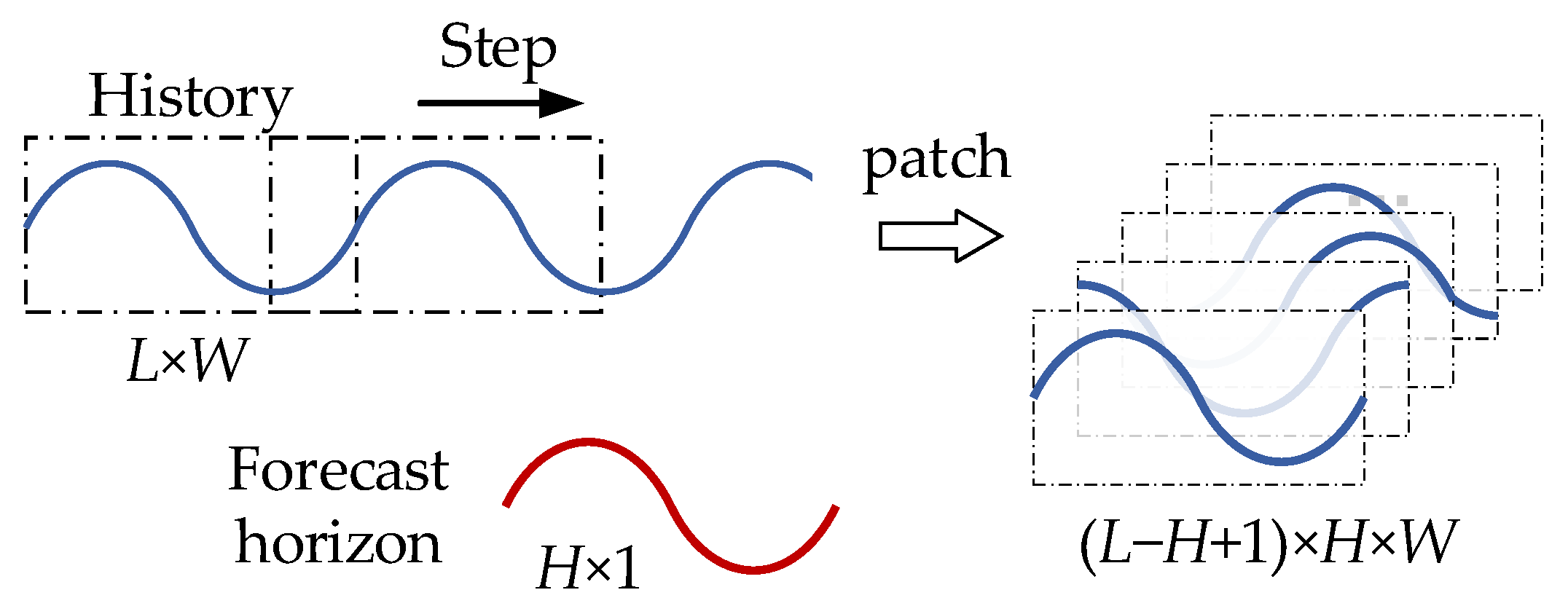
3.3. Algorithm Implementation
3.4. Probabilistic Forecasting
3.4.1. Parametric Approach
3.4.2. Non-Parametric Approach
4. Experimental Setup and Results
4.1. Data Preparation
4.1.1. Data Description
4.1.2. Data Preprocessing
4.1.3. Performance Metrics
4.2. Comparison Experiments
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, I.; Salzer, S.; Stein, S.; Olusanya, T.O.O.; Thiel, O.F.; Kockmann, N. AI-Based Integrated Smart Process Sensor for Emulsion Control in Industrial Application. Processes 2024, 12, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Papageorgiou, L.G. Multiobjective optimisation of production, distribution and capacity planning of global supply chains in the process industry. Omega 2013, 41, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; He, H.; Niu, Z. Frequency-domain MLPs are more effective learners in time series forecasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 76656–76679. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.Q.; Wu, C.; Si, Y.-W. LSTM with particle Swam optimization for sales forecasting. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2022, 51, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Yu, C. A new feature based deep attention sales forecasting model for enterprise sustainable development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Ding, J. A holistic feature selection method for enhanced short-term load forecasting of power system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2500911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X. Short-term offshore wind power forecasting-A hybrid model based on Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (SARIMA), and deep-learning-based Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). Renew. Energy 2022, 185, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; He, F. Multistep speed prediction on traffic networks: A deep learning approach considering spatio-temporal dependencies. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 105, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Li, X.; Law, R. Tourism demand forecasting using tourist-generated online review data. Tour Manag. 2022, 90, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croston, J.D. Forecasting and Stock Control for Intermittent Demands. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1972, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syntetos, A.A.; Boylan, J.E. On the bias of intermittent demand estimates. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 71, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunter, R.H.; Syntetos, A.A.; Zied Babai, M. Intermittent demand: Linking forecasting to inventory obsolescence. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 214, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, C. The Holt-winters forecasting procedure. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1978, 27, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Lama, A.; Mishra, P.; Biswas, T.; Das, S.S.; Gurung, B. An ARIMA-LSTM model for predicting volatile agricultural price series with random forest technique. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 149, 110939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmanini, C.; Sarma, N.; Gezegin, C.; Ozgonenel, O. Short term load forecasting based on ARIMA and ANN approaches. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, I.; Kushchazli, A.; Burtseva, S.; Gorshenin, A. Short-term mobile network traffic forecasting using seasonal ARIMA and holt-winters models. Future Internet 2023, 15, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Feng, Z. Short-term offshore wind speed forecast by seasonal ARIMA-A comparison against GRU and LSTM. Energy 2021, 227, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.-W.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Daily tourism volume forecasting for tourist attractions. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 83, 102923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, D.; Zhao, J.; Cai, D.; Hu, W.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Q. A novel hybrid short-term load forecasting method of smart grid using MLR and LSTM neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.A.C.G.; Cunha, C.B. Disaggregated retail forecasting: A gradient boosting approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 141, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Dang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. An optimized nonlinear time-varying grey Bernoulli model and its application in forecasting the stock and sales of electric vehicles. Energy 2023, 263, 125871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fildes, R. Retail sales forecasting with meta-learning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 288, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, A.; Caramia, P.; De Falco, P.; Hong, T. Multivariate quantile regression for short-term probabilistic load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 35, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic water demand forecasting using quantile regression algorithms. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, B.; Lu, H. A novel ensemble probabilistic forecasting system for uncertainty in wind speed. Appl. Energy 2022, 313, 118796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M. Nonparametric probabilistic forecasting for wind power generation using quadratic spline quantile function and autoregressive recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, V.; Bianchi, F.M.; Anfinsen, S.N. Ensemble conformalized quantile regression for probabilistic time series forecasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 9014–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Dong, J.; Kong, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Short-Term Probabilistic Load Forecasting Using Quantile Regression Neural Network with Accumulated Hidden Layer Connection Structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics. 2024, 20, 5818–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Yu, Y. Quantile-mixer: A novel deep learning approach for probabilistic short-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2024, 15, 2237–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H. Probabilistic wind power forecasting resilient to missing values: An adaptive quantile regression approach. Energy 2024, 300, 131544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Xiao, J.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, Y. Hybrid model based on similar power extraction and improved temporal convolutional network for probabilistic wind power forecasting. Energy 2024, 304, 131966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecov, P.; Prasanna, A.N.; Ackermann, K.; Campbell, S.; Scott, D.; Lubman, D.I.; Bergmeir, C. Probabilistic causal effect estimation with global neural network forecasting models. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 4999–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, D.; Flunkert, V.; Gasthaus, J.; Januschowski, T. DeepAR: Probabilistic forecasting with autoregressive recurrent networks. Int. J. Forecast. 2020, 36, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Probabilistic forecasting with temporal convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 2020, 399, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Feng, C.; Zhang, J. Multi-distribution ensemble probabilistic wind power forecasting. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, K.G.; Meetei, O.N.; Ma, R.; Reddy, R.; Cao, M.; Dicker, L. Probabilistic hierarchical forecasting with deep poisson mixtures. Int. J. Forecast. 2024, 40, 470–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rügamer, D.; Baumann, P.F.M.; Kneib, T.; Hothorn, T. Probabilistic time series forecasts with autoregressive transformation models. Stat. Comput. 2023, 33, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Gao, H.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K. Reservoir Porosity Construction Based on BiTCN-BiLSTM-AM Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Processes 2024, 12, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Sillanpää, V.; Liesiö, J. Forecasting replenishment orders in retail: Value of modelling low and intermittent consumer demand with distributions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 4168–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, L.R.; Helman, P.; West, M. Probabilistic forecasting of heterogeneous consumer transaction–sales time series. Int. J. Forecast. 2020, 36, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, A. ElectricityLoadDiagrams20112014. 2015. UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/321/electricityloaddiagrams20112014 (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Hanifi, S.; Cammarono, A.; Zare-Behtash, H. Advanced hyperparameter optimization of deep learning models for wind power prediction. Renew. Energy 2024, 221, 119700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calik, N.; Güneş, F.; Koziel, S.; Pietrenko-Dabrowska, A.; Belen, M.A.; Mahouti, P. Deep-learning-based precise characterization of microwave transistors using fully-automated regression surrogates. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Paper | Field | Category | Differences with Our Work |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bracale et al. [23] | Electricity load forecasting | Quantile-based | Focus on predicting multiple power loads concurrently. |
| Luo et al. [28] | Electricity load forecasting | Quantile-based | Refining the model to enhance prediction accuracy. |
| Ryu et al. [29] | Electricity load forecasting | Quantile-based | Using advanced model structure to enhance prediction accuracy. |
| Wen et al. [30] | Wind power forecasting | Quantile-based | Focus on adaptively handling missing data. |
| Salinas et al. [33] | Time series forecasting | Distribution-based | Generate recursively multi-step probabilistic forecasts using recurrent networks. |
| Chen et al. [34] | Time series forecasting | Distribution-based | Generate directly multi-step probabilistic forecasts using TCN. |
| Sun et al. [35] | Wind power forecasting | Distribution-based | Perform ensemble predictions based on multiple distribution assumptions. |
| ours | Time series forecasting | Both quantile-based and distribution-based | Focus on the importance of various segments of historical data. |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| # of time series | 370 |
| granularity | per 15 min |
| time scope | 1 January 2011 00:15:00 to 1 January 2015 00:00:00 |
| backtracking history | 192 |
| forecast horizon | 24, 48 |
| domain |
| Hidden Node | Hidden Layer | Learning Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 128 | 2 | 0.01 |
| LSTM-Gaussian | 128 | 2 | 0.001 |
| LSTM-quantile | 128 | 2 | 0.01 |
| DeepAR-Gaussian | 40 | 2 | 0.001 |
| PSE-LSTM-Gaussian | 128 | 2 | 0.001 |
| PSE-LSTM-quantile | 128 | 2 | 0.01 |
| Forecast Horizon | 24 | 48 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Metric | PICP↑ | PINAW↓ | ND↓ | sMAPE↓ | PICP↑ | PINAW↓ | ND↓ | sMAPE↓ |
| LSTM | - | - | 0.117 | 0.167 | - | - | 0.118 | 0.174 | |
| LSTM-Gaussian | 0.971 | 1.931 | 0.120 | 0.163 | 0.974 | 1.567 | 0.121 | 0.168 | |
| LSTM-quantile | 0.795 | 0.770 | 0.115 | 0.154 | 0.792 | 0.499 | 0.106 | 0.144 | |
| DeepAR-Gaussian | 0.974 | 2.221 | 0.128 | 0.183 | 0.964 | 1.542 | 0.142 | 0.188 | |
| PSE-LSTM-Gaussian | 0.980 | 1.166 | 0.082 | 0.120 | 0.978 | 0.938 | 0.093 | 0.133 | |
| PSE-LSTM-quantile | 0.786 | 0.423 | 0.082 | 0.121 | 0.768 | 0.331 | 0.088 | 0.125 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, Q. Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting Based on Similar Segment Importance in the Process Industry. Processes 2024, 12, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122700
Yan X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Miao Q. Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting Based on Similar Segment Importance in the Process Industry. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122700
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xingyou, Heng Zhang, Zhigang Wang, and Qiang Miao. 2024. "Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting Based on Similar Segment Importance in the Process Industry" Processes 12, no. 12: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122700
APA StyleYan, X., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., & Miao, Q. (2024). Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting Based on Similar Segment Importance in the Process Industry. Processes, 12(12), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122700






