The Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Surface Roughness on Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
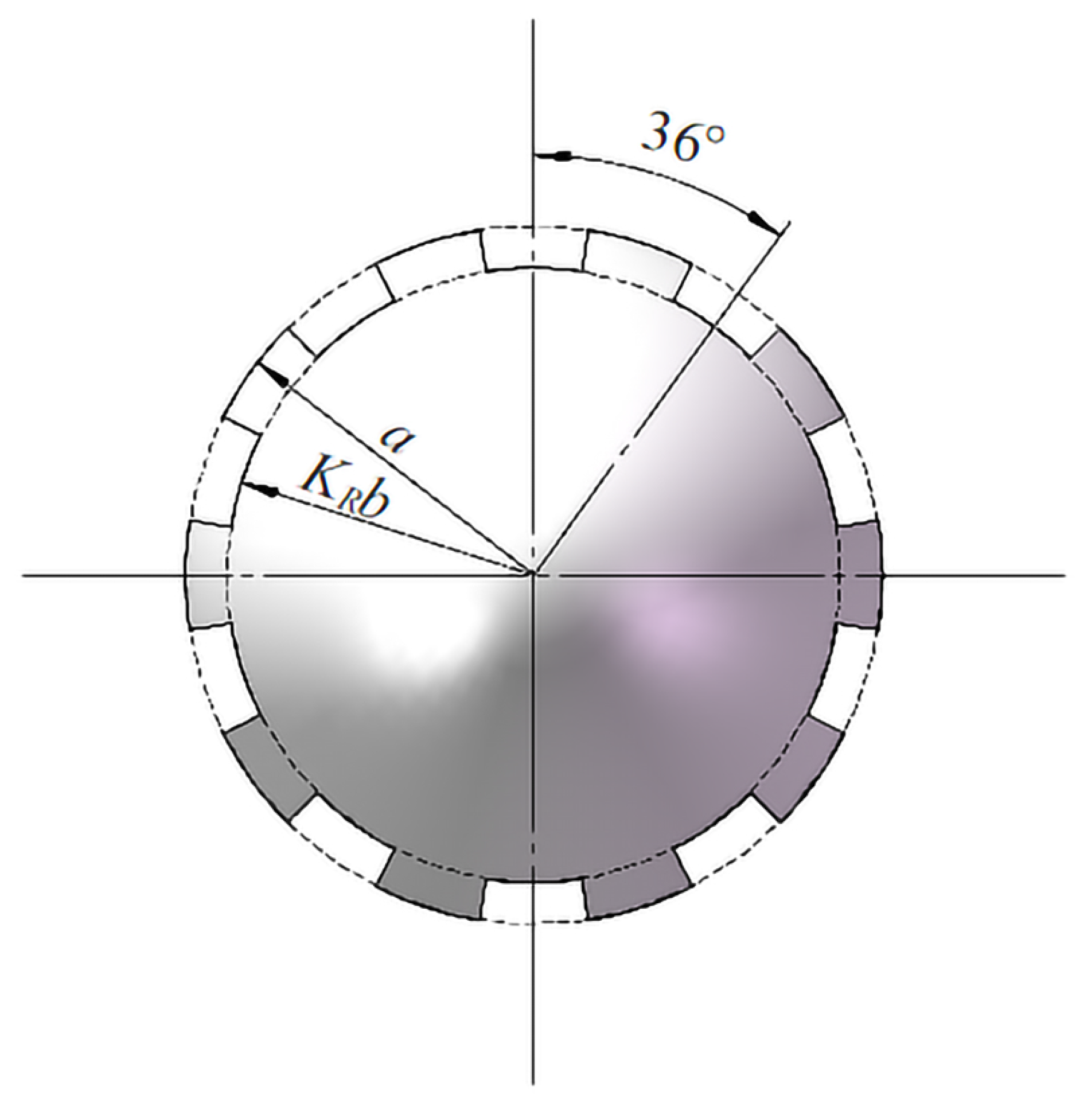
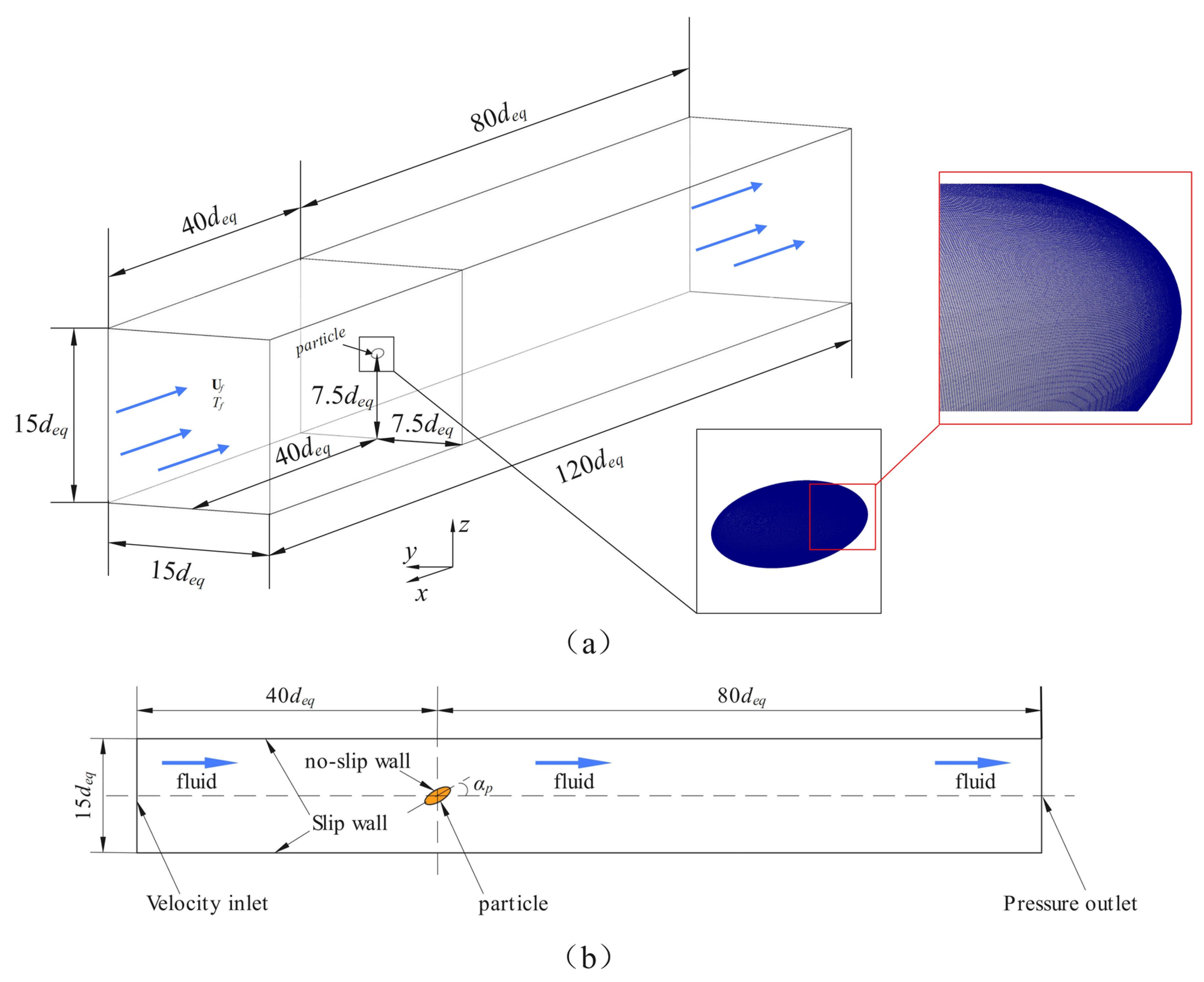
2. Conservation Equations and Simulation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
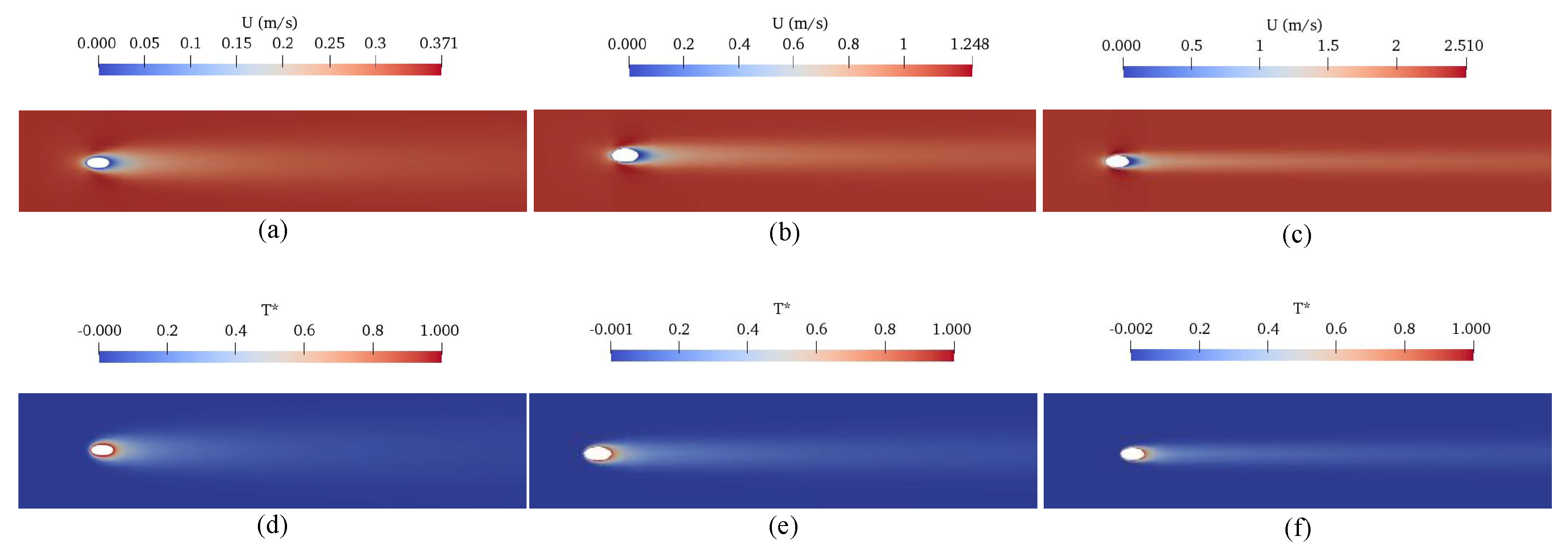
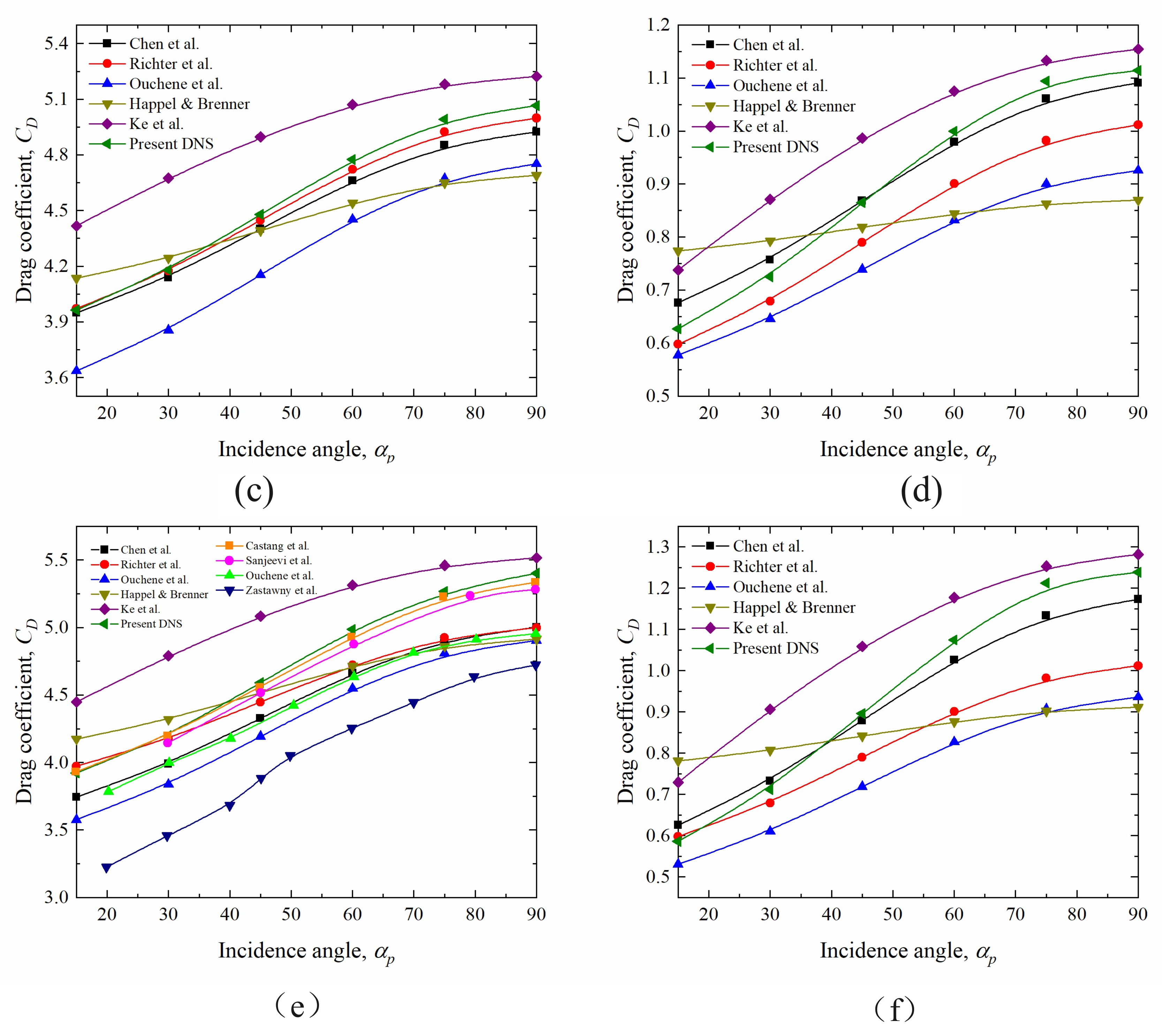
3.1. Validation of Results
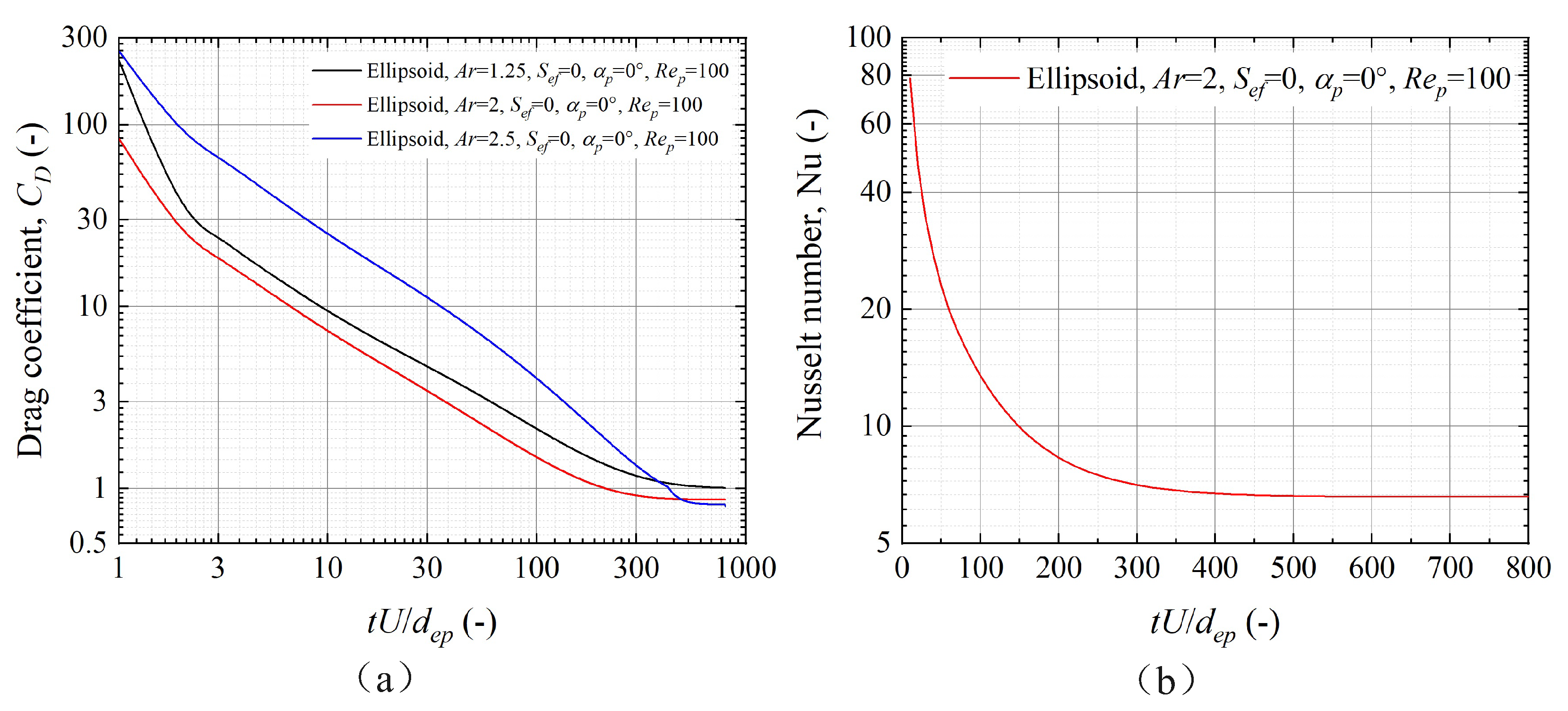
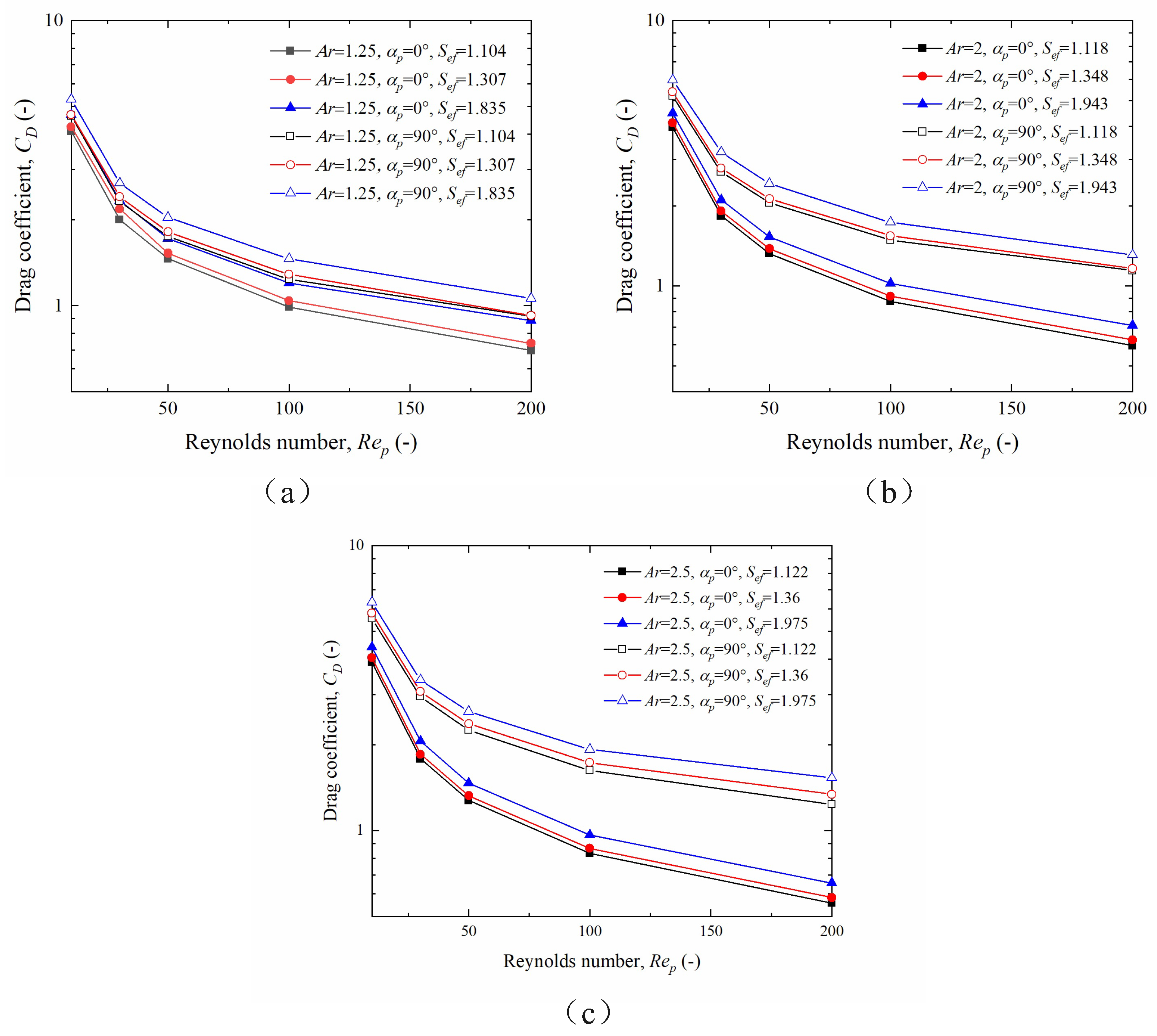
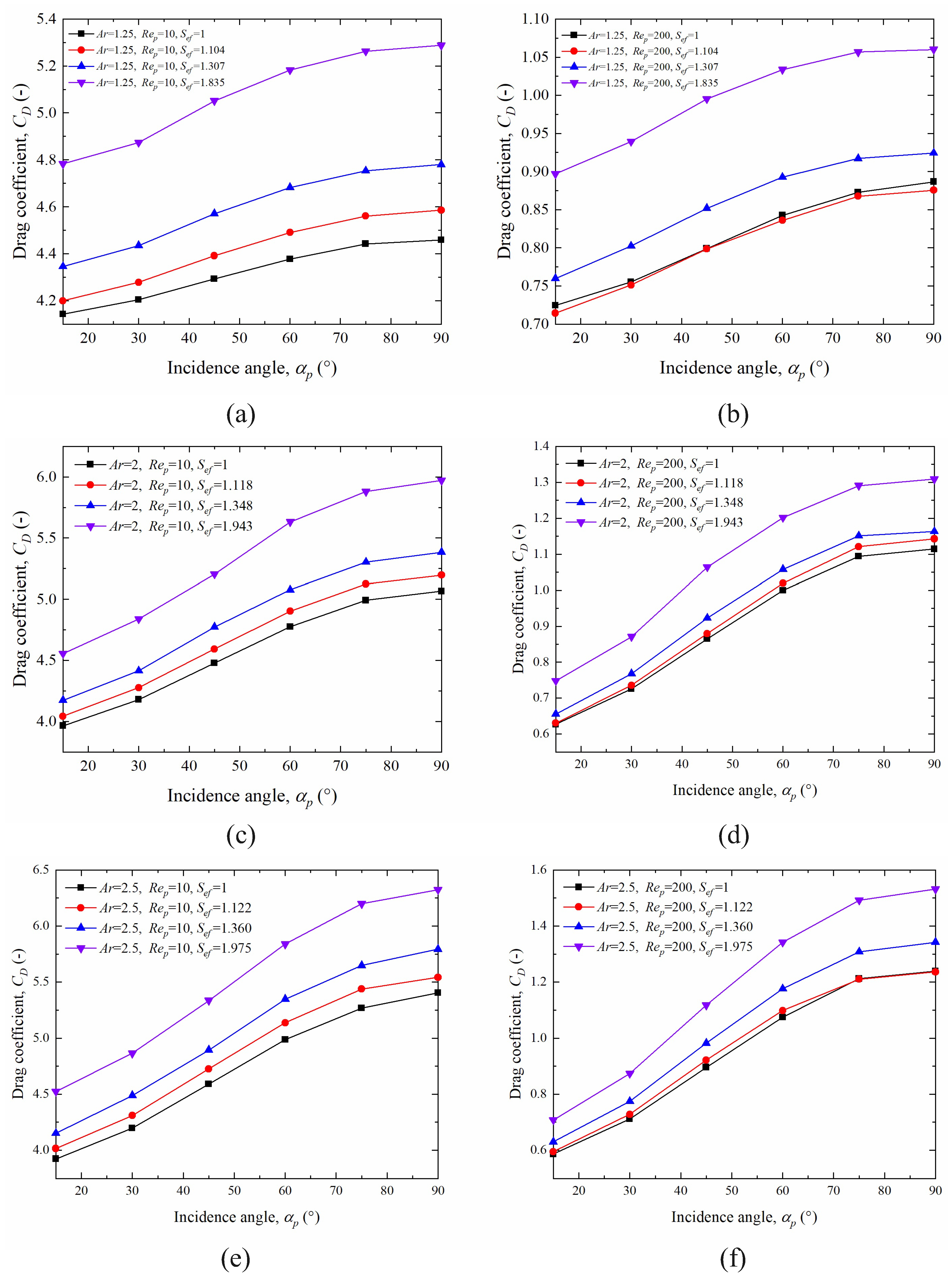
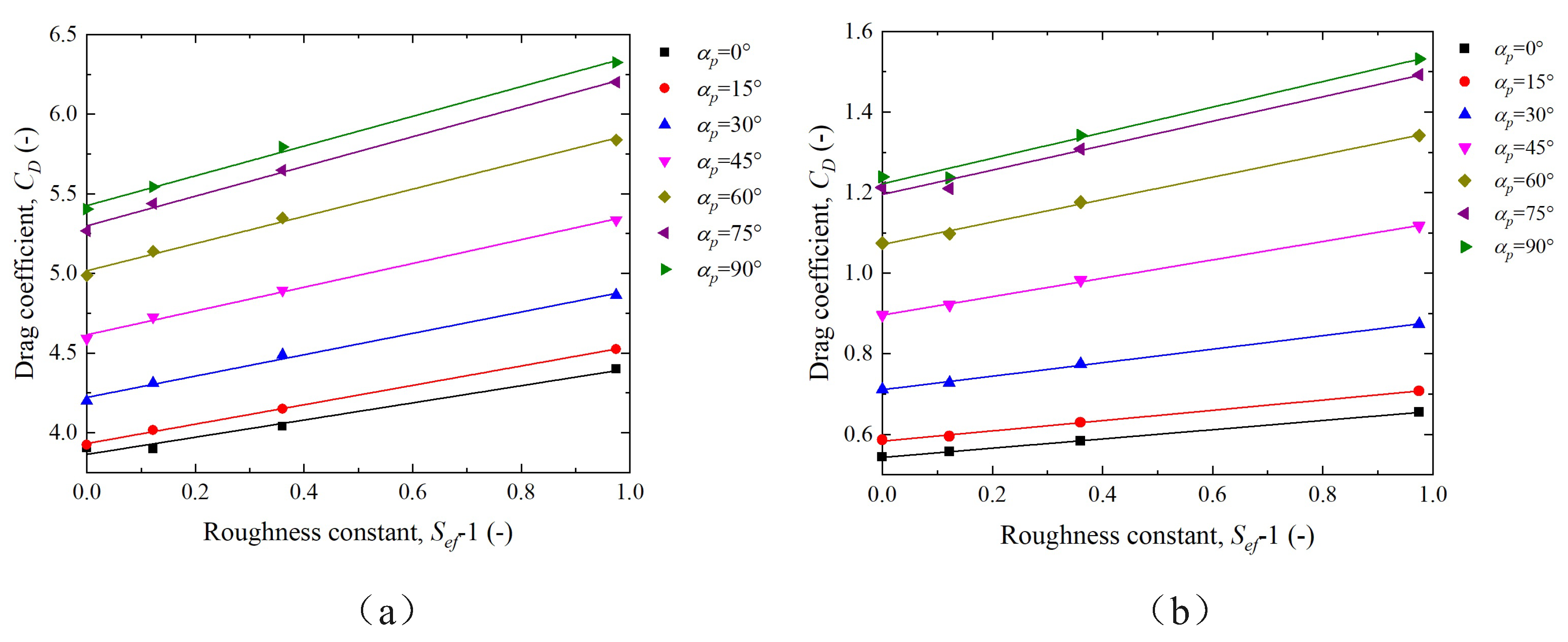
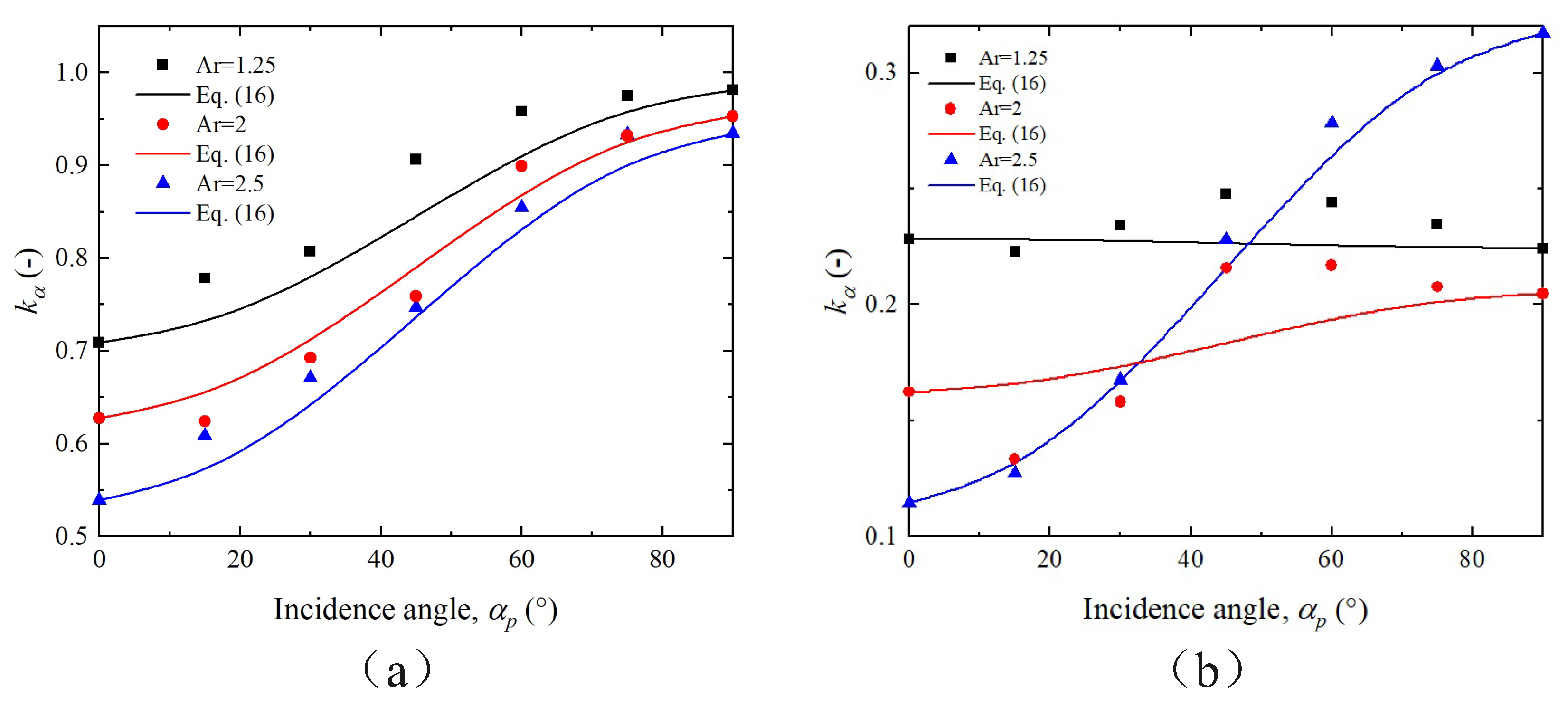
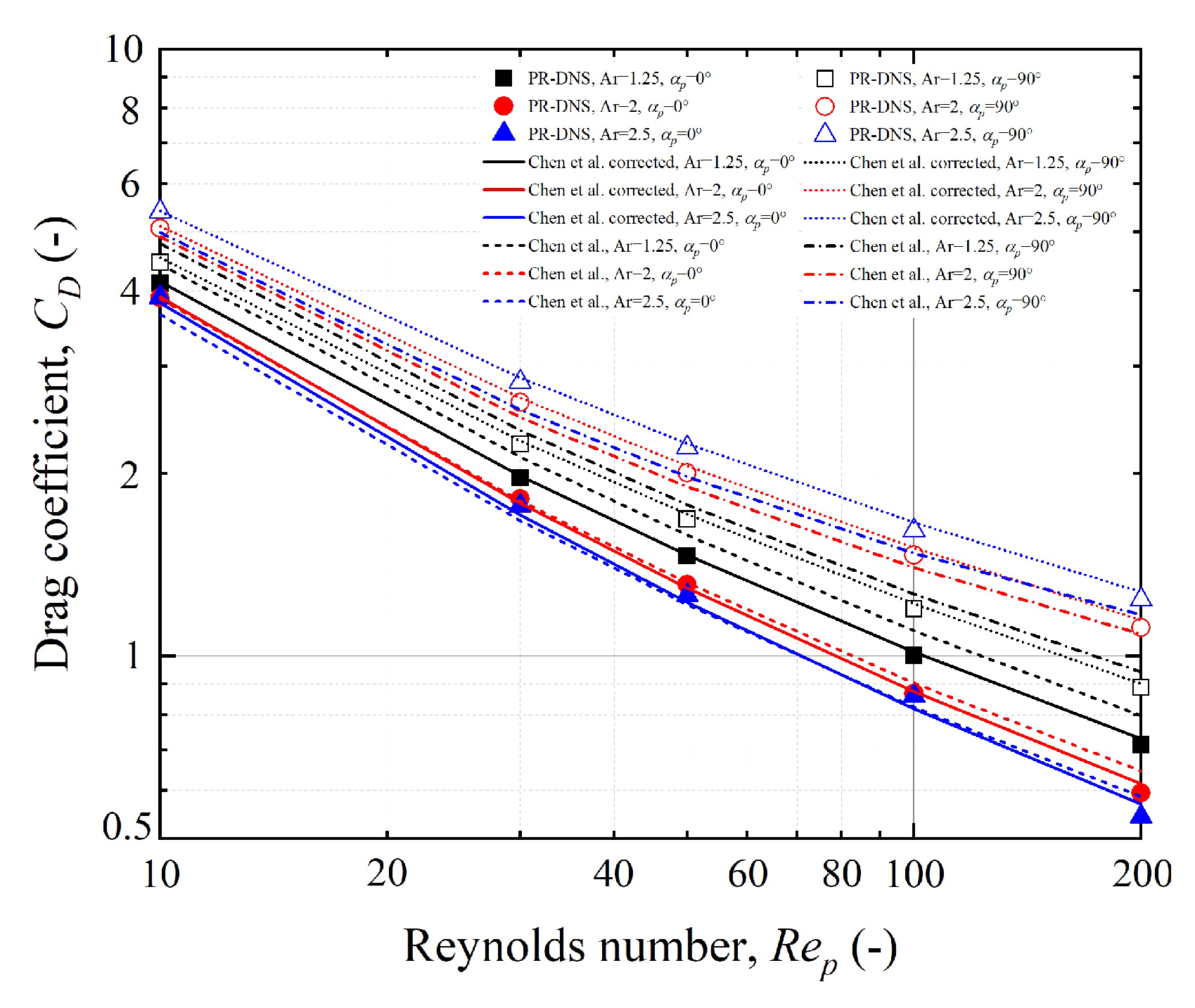
3.2. Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Roughness on the Drag Coefficient
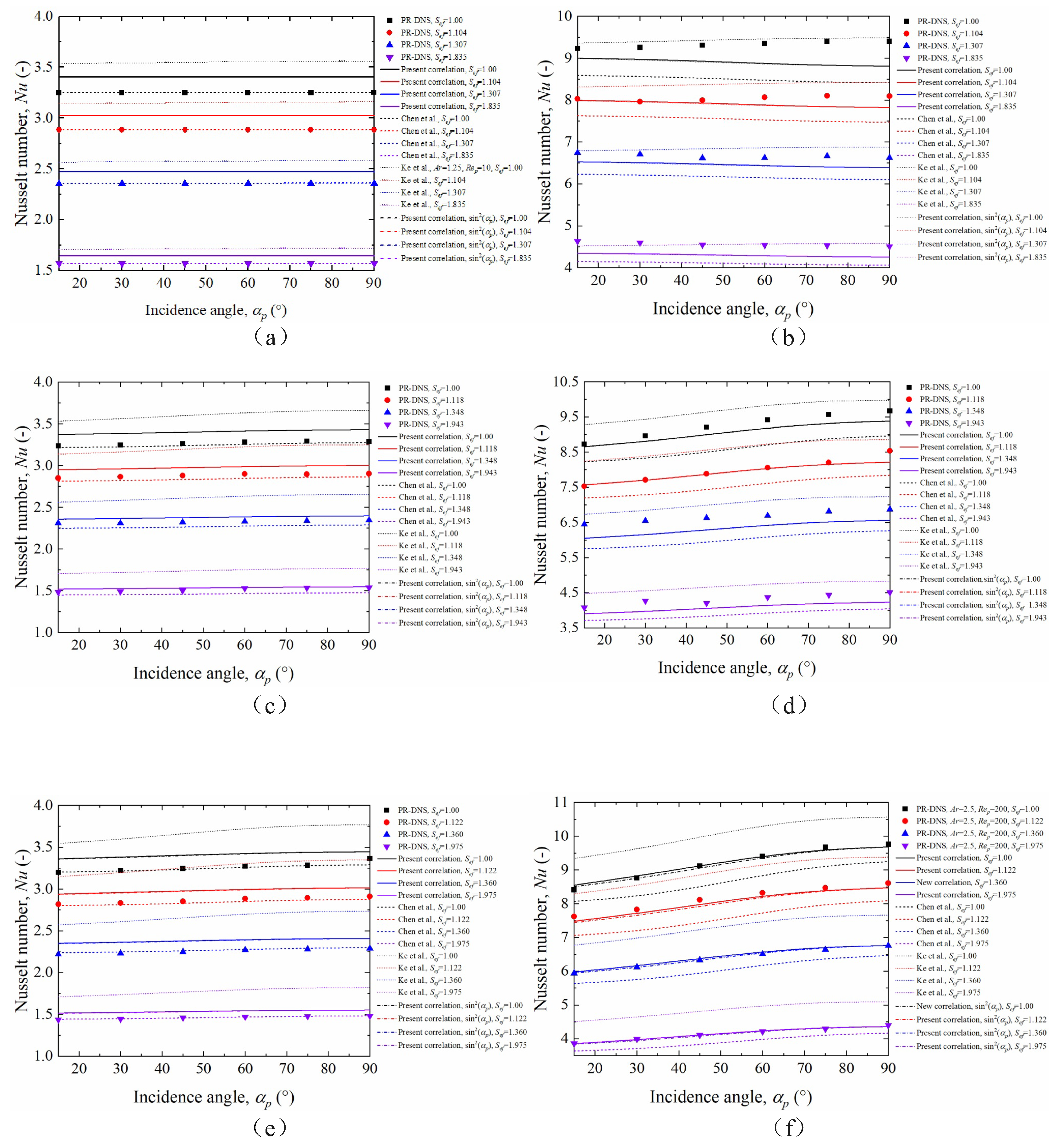
3.3. Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Roughness on the Nusselt Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols: | |
| aspect ratio, - | |
| a, b and c | axis lengths of the ellipsoid, |
| specific heat capacity, /( · ) | |
| drag coefficient, - | |
| drag coefficient of a particle at , - | |
| drag coefficient of smooth particles, - | |
| drag coefficient of spherical particles, - | |
| volume equivalent diameter, | |
| heat transfer efficiency factor, - | |
| correction factor, - | |
| correction factor, - | |
| k | correction factor, - |
| thermal conductivity, /( · ) | |
| roughness coefficient, - | |
| correction factor, - | |
| Nusselt number, - | |
| surface-averaged Nusselt number for the particle with zero roughness, - | |
| p | normal stress, |
| Prandtl number, - | |
| average roughness factor, - | |
| particle Reynolds number, - | |
| roughness coefficient, - | |
| particle surface area, m2 | |
| geometric surface area of the particle without roughness, μm2 | |
| geometric surface area of the particle with roughness, μm2 | |
| T | temperature, |
| cylinder surface temperature, | |
| free stream temperature, | |
| undisturbed temperature of the fluid, | |
| computation time, - | |
| particle drag force, | |
| unit vector normal to the particle surface, - | |
| fluid velocity, / | |
| inlet fluid velocity, / | |
| volume of the particle, μm3 | |
| x, y and z | coordinate positions of a point on the surface of the ellipsoid, μm |
| Greek Symbols: | |
| incidence angle, ° | |
| dynamic viscosity, | |
| fluid density, / |
References
- Vijayan, A.; Joy, B.; Annabattula, R.K. Fluid Flow Assisted Mixing of Binary Granular Beds Using CFD-DEM. Powder Technol. 2021, 383, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Xiong, T.; Wei, W.; Fang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wang, B. Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients for Axisymmetric Nonspherical Particles: A LBM Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.S.; Faia, P.M.; Garcia, F.a.P.; Rasteiro, M.G. Experimental and Simulated Studies of Oil/Water Fully Dispersed Flow in a Horizontal Pipe. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Park, H.C.; Choi, H.S. Multiphase Fluid Dynamics Coupled Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass in a Rectangular Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor: Process Intensification. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2018, 128, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pedraza, C.; de Lasa, H. Hybrid Particle Cluster CPFD Simulation in the Acceleration and Stabilized Sections of a Downflow Circulating Fluidized Bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 20325–20336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, F.; Wang, W.; Li, J. A Sub-Grid EMMS Drag for Multiphase Particle-in-Cell Simulation of Fluidization. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, W.; He, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. A Dynamic Particle Scale-Driven Interphase Force Model for Water-Sand Two-Phase Flow in Hydraulic Machinery and Systems. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2022, 95, 108974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Meng, X.; Deng, J.; Wu, J. Theoretical Modeling of the Drag Reduction Influenced by Film Boiling Heat Transfer on a Spherical Body. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 134, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, M.; Gerhardter, H.; Prieler, R.; Muehlboeck, M.; Tomazic, P.; Hochenauer, C. Particle Classification and Drag Coefficients of Irregularly-Shaped Combustion Residues with Various Size and Shape. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castang, C.; Lain, S.; Sommerfeld, M. Pressure Center Determination for Regularly Shaped Non-Spherical Particles at Intermediate Reynolds Number Range. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2021, 137, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castang, C.; Lain, S.; Garcia, D.; Sommerfeld, M. Aerodynamic Coefficients of Irregular Non-Spherical Particles at Intermediate Reynolds Numbers. Powder Technol. 2022, 402, 117341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchene, R.; Khalij, M.; Arcen, B.; Taniere, A. A New Set of Correlations of Drag, Lift and Torque Coefficients for Non-Spherical Particles and Large Reynolds Numbers. Powder Technol. 2016, 303, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.B.; Carrano, A.L.; Kandlikar, S.G. Characterization of the Effect of Surface Roughness and Texture on Fluid Flow—Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2006, 45, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierich, F.; Nikrityuk, P.A. A Numerical Study of the Impact of Surface Roughness on Heat and Fluid Flow Past a Cylindrical Particle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 65, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Alame, K.; Mahesh, K. Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Channel Flow over Random Rough Surfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 908, A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Chan, H.K.; Raper, J.A. Prediction of Aerodynamic Diameter of Particles with Rough Surfaces. Powder Technol. 2004, 147, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierich, F.; Nikrityuk, P.A. A Numerical Study of the Influence of Surface Roughness on the Convective Heat Transfer in a Gas Flow. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2010, 64, 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Nikku, M.; Jalali, P.; Ritvanen, J.; Hyppanen, T. Characterization Method of Average Gas-Solid Drag for Regular and Irregular Particle Groups. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiong, B.; An, X.; Ke, C.; Chen, J. Numerical prediction on the drag force and heat transfer of non-spherical particles in supercritical water. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Nikrityuk, P.A. New correlations for heat and fluid flow past ellipsoidal and cubic particles at different angles of attack. Powder Technol. 2013, 249, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Shu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.; Yang, D. On the drag coefficient and averaged Nusselt number of an ellipsoidal particle in a fluid. Powder Technol. 2018, 325, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Nikrityuk, P.A. Drag forces and heat transfer coefficients for spherical, cuboidal and ellipsoidal particles in cross flow at sub-critical Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, P.; Wen, C. Particle-resolved simulation on viscous flow past random and ordered arrays of hot ellipsoidal particles. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2021, 142, 103736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roostaee, A.; Vaezi, M. Developing a standard platform to predict the drag coefficient of irregular shape particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 314–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, C. Modeling total drag force exerted on particles in dense swarm from experimental measurements using an inline image-based method. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Singh, A.K. Augmentation of heat transfer from a solid cylinder wrapped with a porous layer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Pang, Z.; Zhu, Z. A new model for predicting drag coefficient and settling velocity of spherical and non-spherical particle in Newtonian fluid. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeevi, S.K.; Kuipers, J.A.M.; Padding, J.T. Drag, lift and torque correlations for non-spherical particles from Stokes limit to high Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 106, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhu, X. Numerical simulation of force and seperation on plusing airflow. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 162–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zastawny, M.; Mallouppas, G.; Zhao, F.; van Wachem, B. Derivation of drag and lift force and torque coefficients for non-spherical particles in flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2012, 39, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzer, A.; Sommerfeld, M. New simple correlation formula for the drag coefficient of non-spherical particles. Powder Technol. 2008, 184, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Levenspiel, O. Drag coefficient and terminal velocity of spherical and nonspherical particles. Powder Technol. 1989, 58, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Xie, W.; Wei, N.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Drag Coefficients for Elongated/Flattened Irregular Particles Based on Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation. Powder Technol. 2023, 418, 118290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Figure | Figure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 1722.617 | 1.25 | 1.000 | 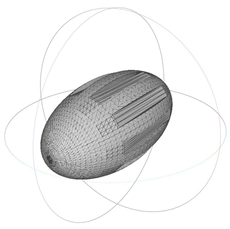 | 1195.409 | 2.00 | 1.348 |
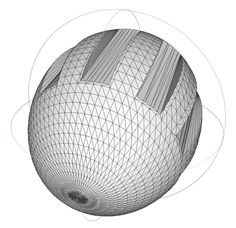 | 1691.286 | 1.25 | 1.104 | 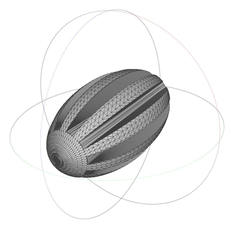 | 1104.852 | 2.00 | 1.943 |
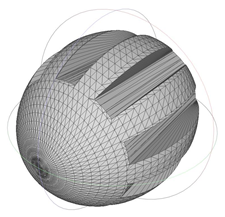 | 1635.158 | 1.25 | 1.307 |  | 1085.568 | 2.50 | 1.000 |
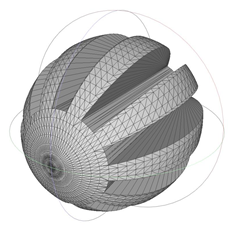 | 1511.248 | 1.25 | 1.835 |  | 1065.815 | 2.50 | 1.122 |
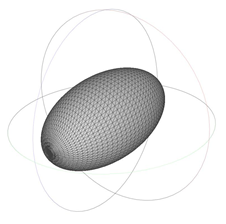 | 1259.411 | 2.00 | 1.000 |  | 1030.485 | 2.50 | 1.360 |
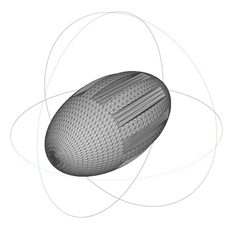 | 1236.473 | 2.00 | 1.118 |  | 952.482 | 2.50 | 1.975 |
| Equations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| Happel and Brenner [12] | ||
| Chen et al. [2] | Prolate ellipsoids Oblate ellipsoids | |
| Richter et al. [22] | Prolate ellipsoids | |
| Ke et al. [21] | Prolate ellipsoids | |
| Ouchene et al. [12] | Prolate ellipsoids |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, H.; Zhang, F.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, J.; Yang, C. The Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Surface Roughness on Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation. Processes 2024, 12, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112473
Luo H, Zhang F, Huang H, Huang Y, Liu Z, Yan J, Yang C. The Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Surface Roughness on Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112473
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Heng, Fengbin Zhang, Haibo Huang, Yong Huang, Zhendong Liu, Jianxi Yan, and Chicheng Yang. 2024. "The Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Surface Roughness on Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation" Processes 12, no. 11: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112473
APA StyleLuo, H., Zhang, F., Huang, H., Huang, Y., Liu, Z., Yan, J., & Yang, C. (2024). The Effect of Ellipsoidal Particle Surface Roughness on Drag and Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Particle-Resolved Direct Numerical Simulation. Processes, 12(11), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112473





