Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Activated Fly Ash–Cement Paste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of AFCP Specimens and Curing Conditions
2.3. Analysis Methods and Apparatus
3. Results and Discussion
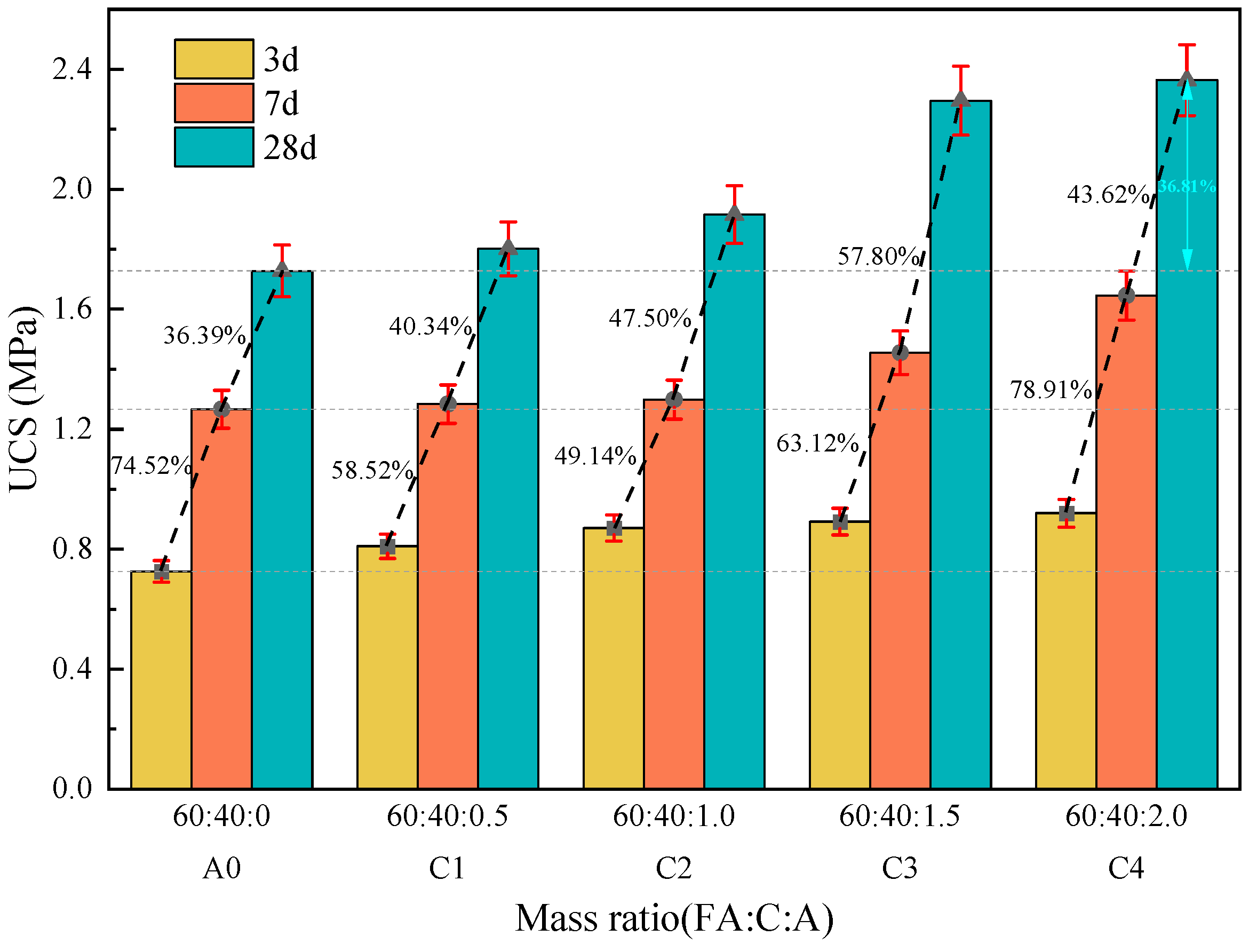
3.1. Compressive Strength Test
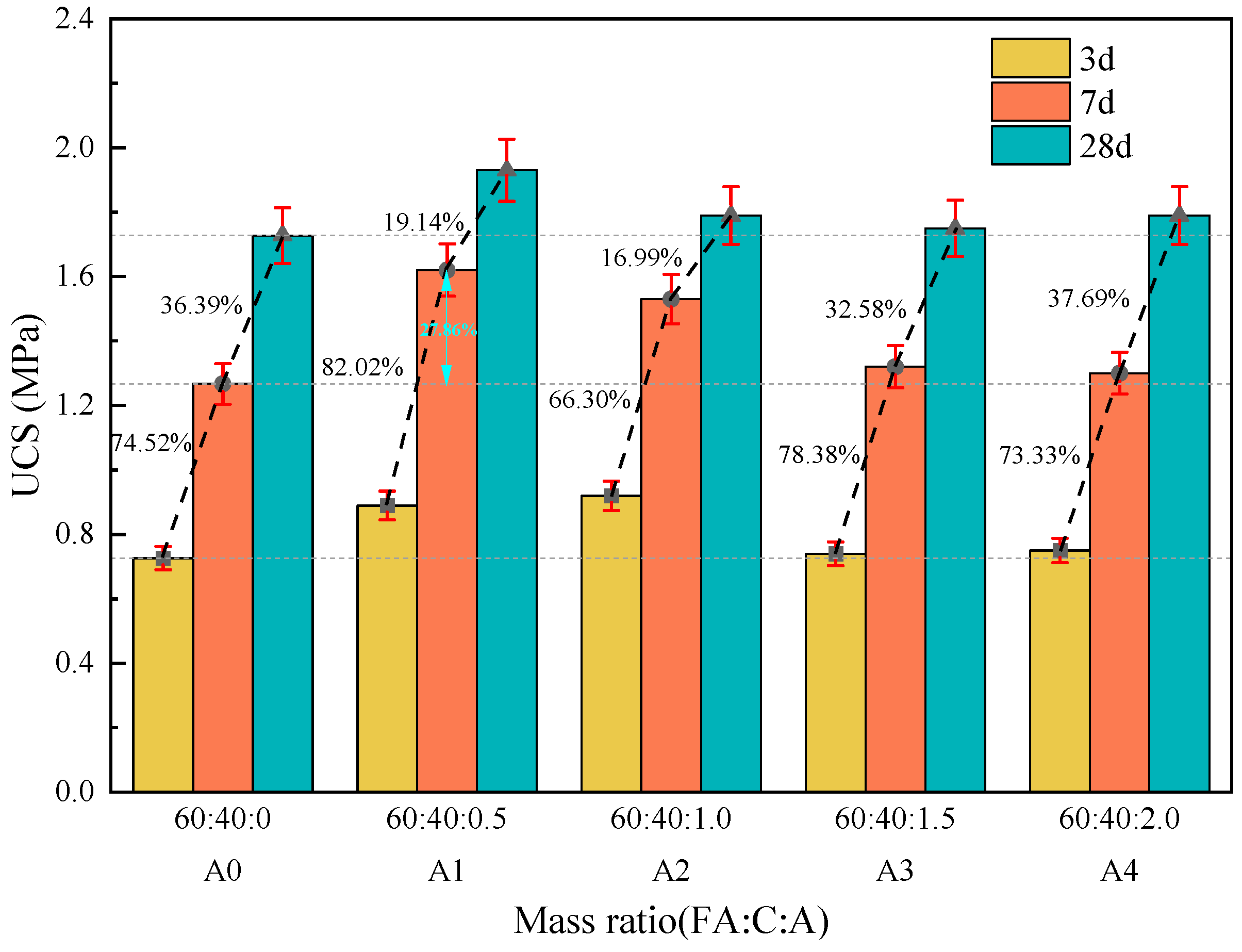
3.1.1. The Effect of Na2SO4 on the Strength of Fly Ash–Cement Paste
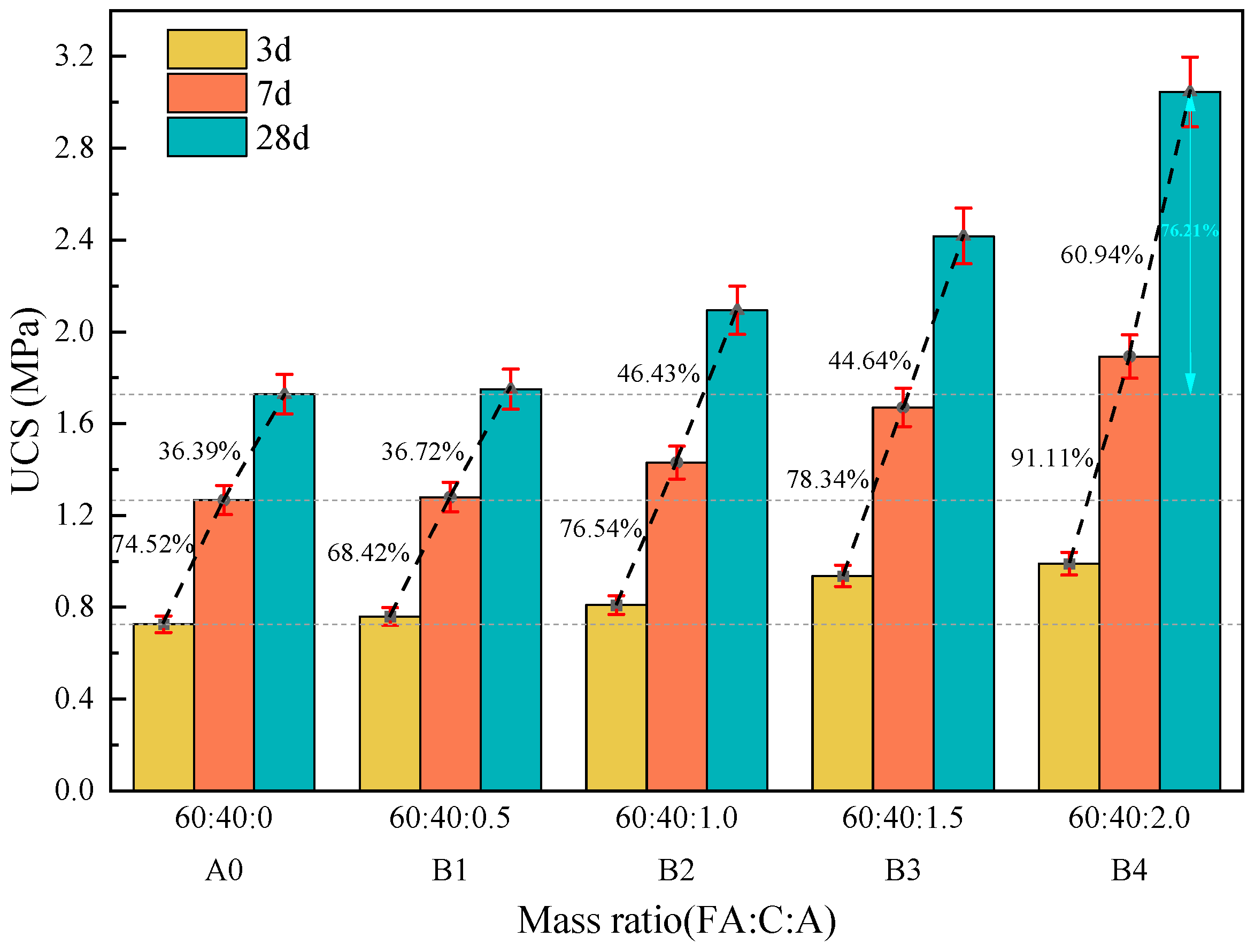
3.1.2. The Effect of Ca(OH)2 on the Strength of Fly Ash–Cement Paste
3.1.3. The Effect of Composite Activator on the Strength of Fly Ash–Cement Paste
3.2. Microscopic Test
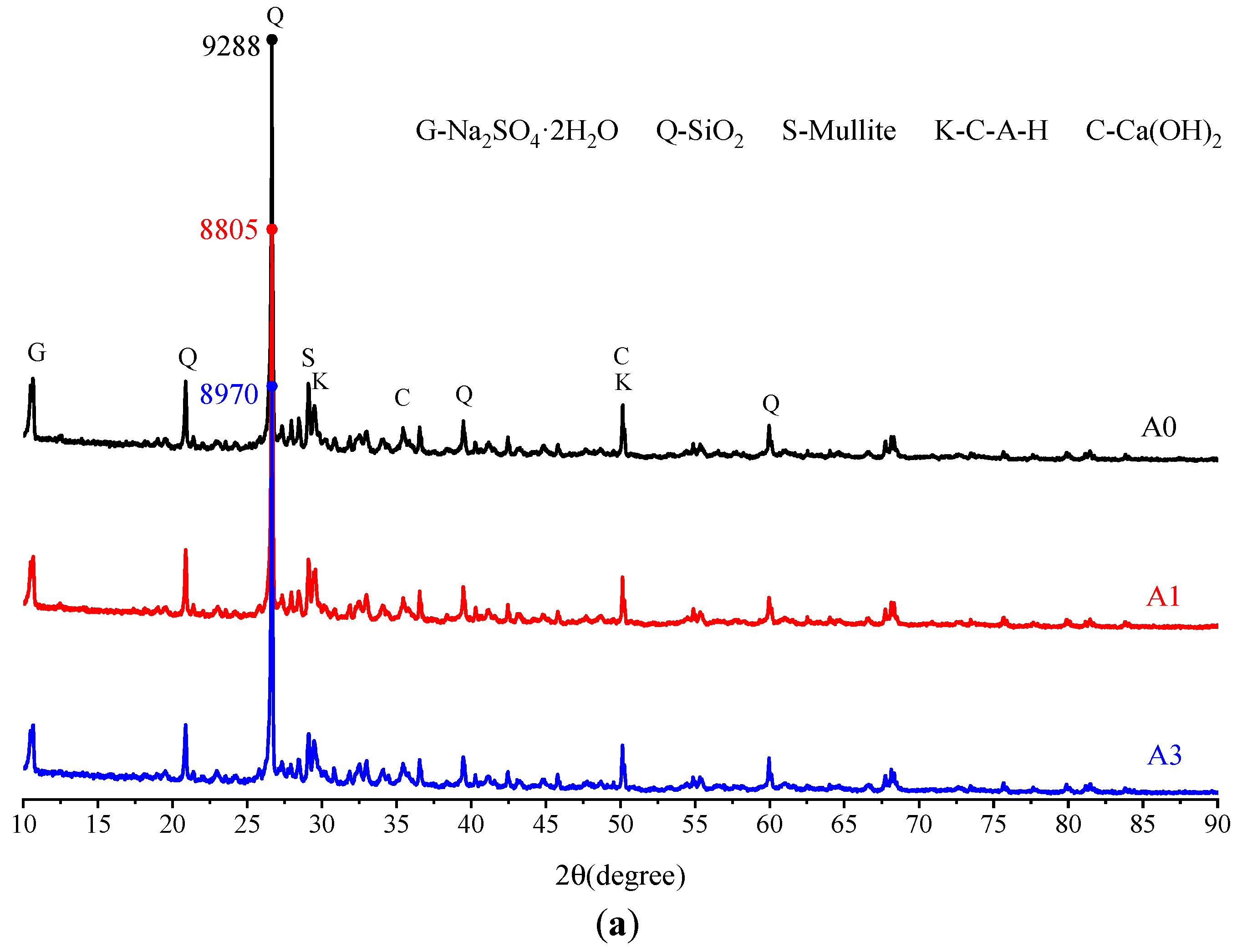
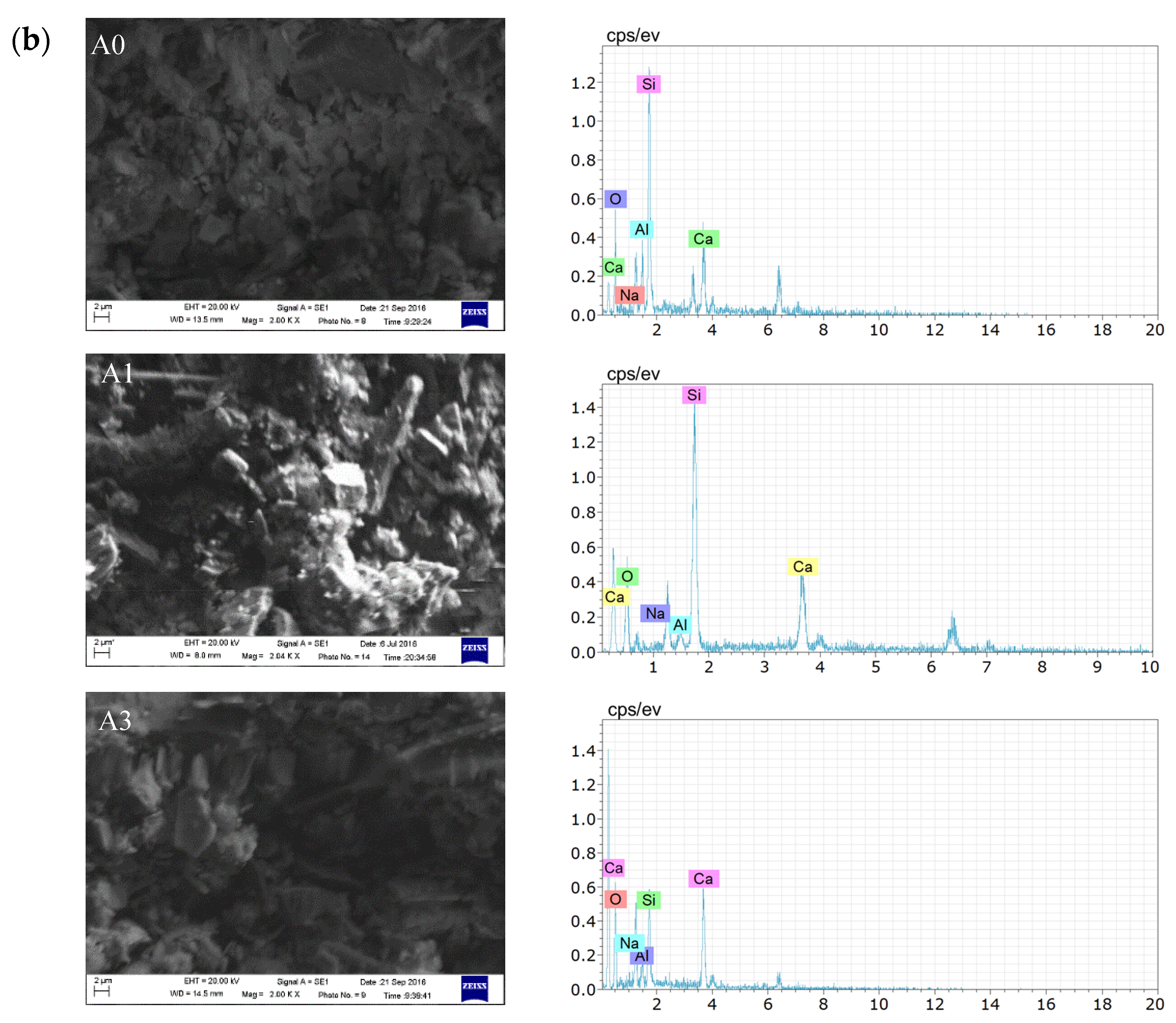
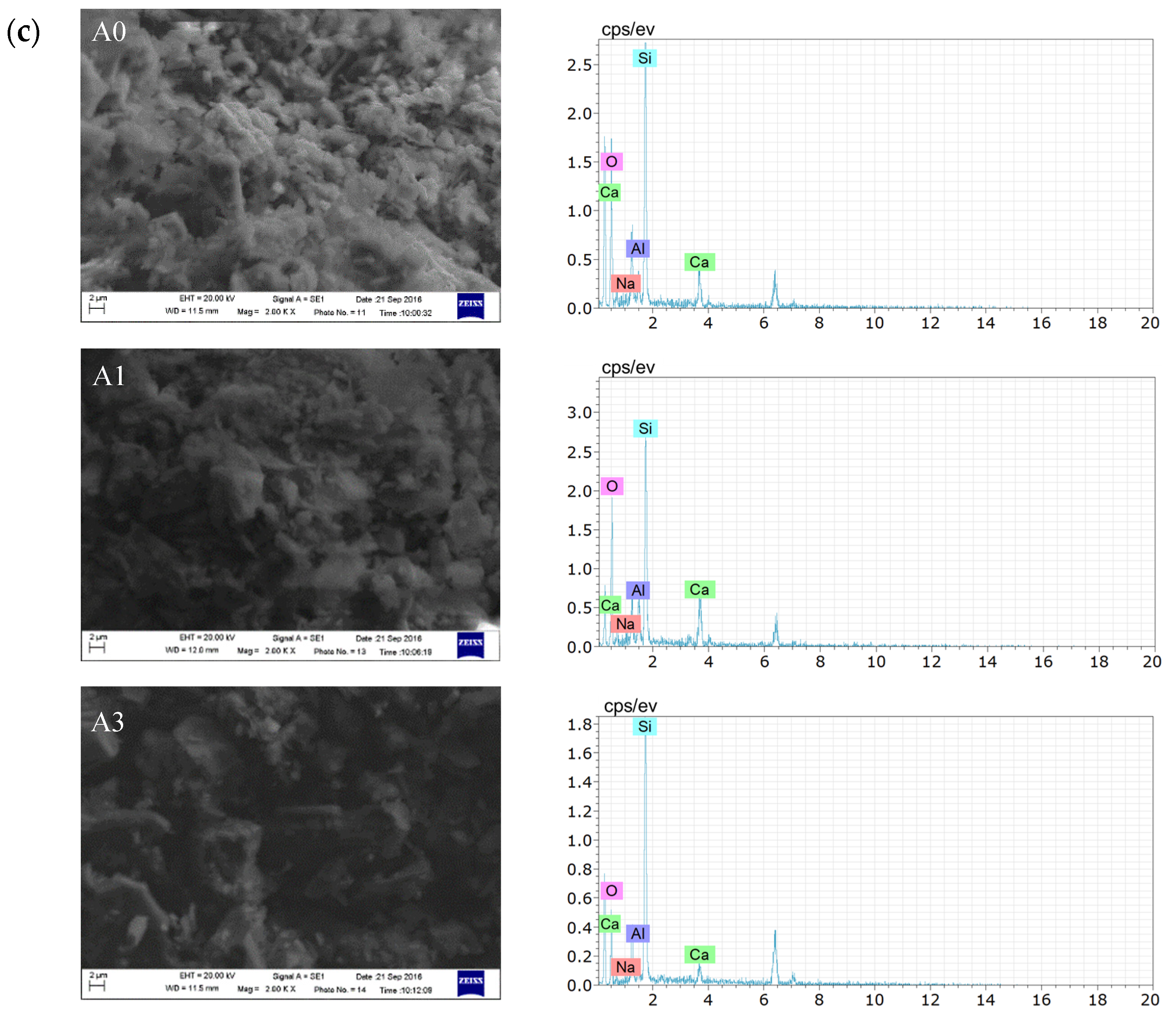
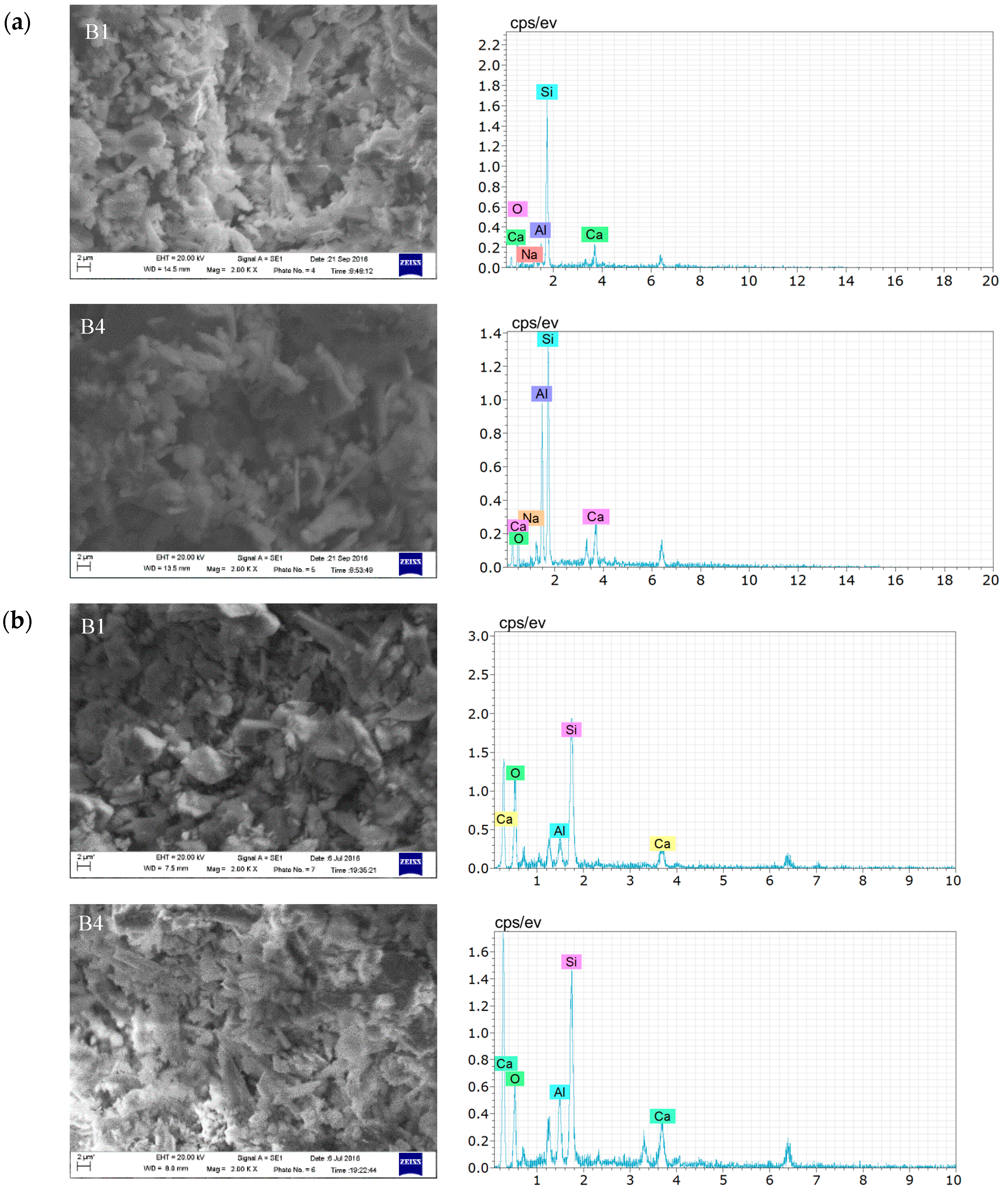
3.2.1. Microscopic Analysis of Filling Bodies Activated by Na2SO4
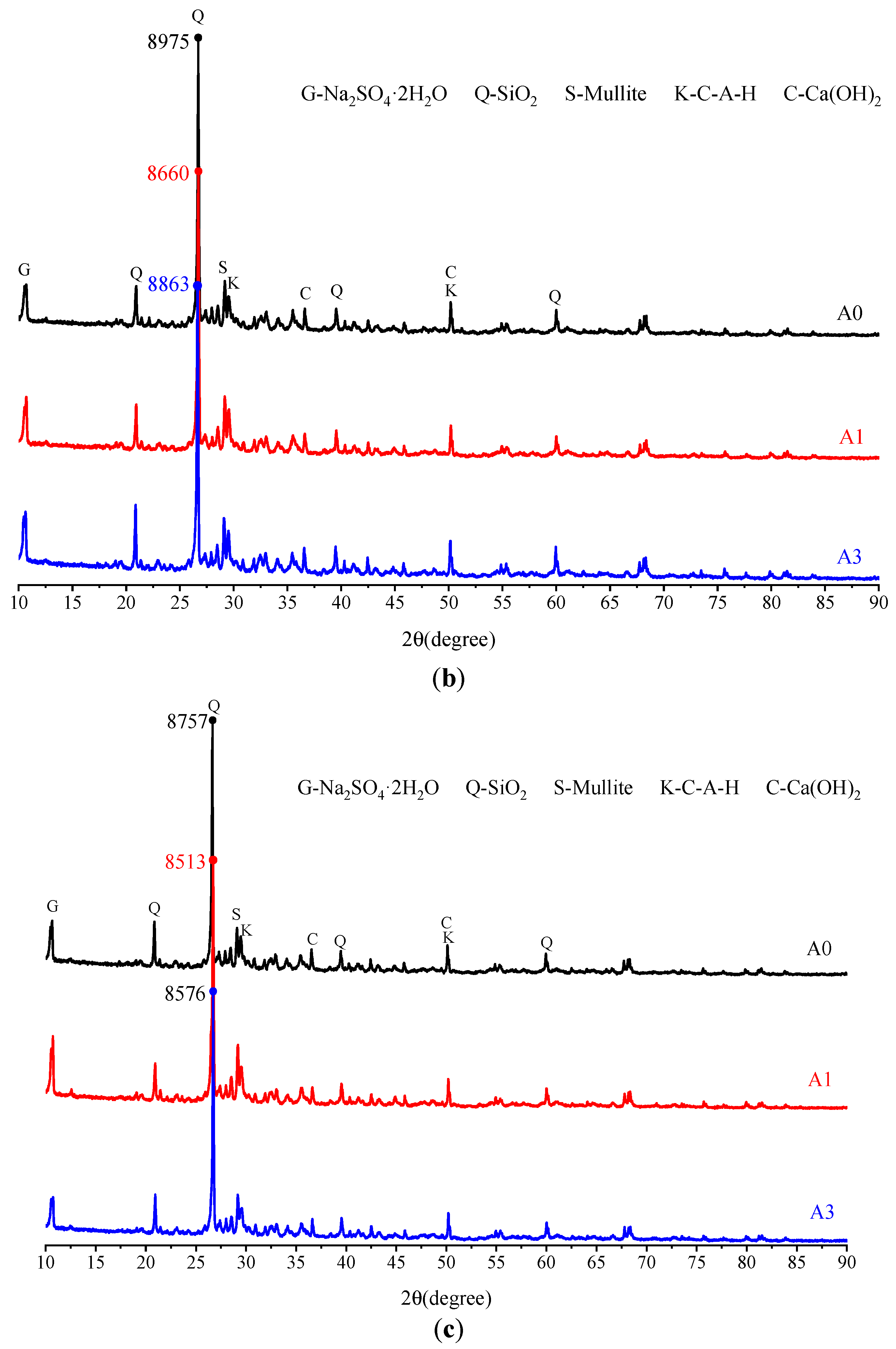
3.2.2. Microscopic Analysis of Filling Bodies Activated by Ca(OH)2
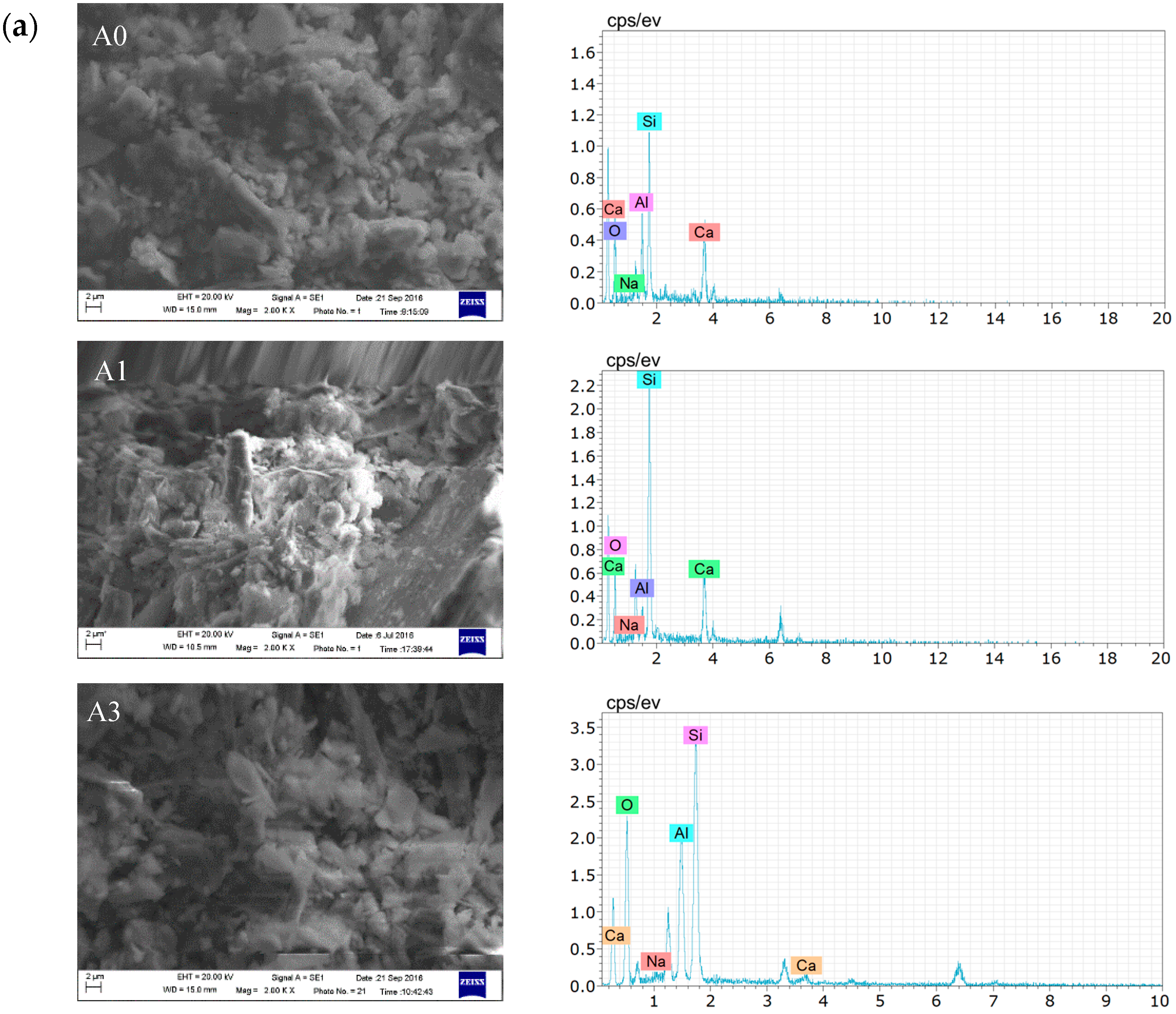
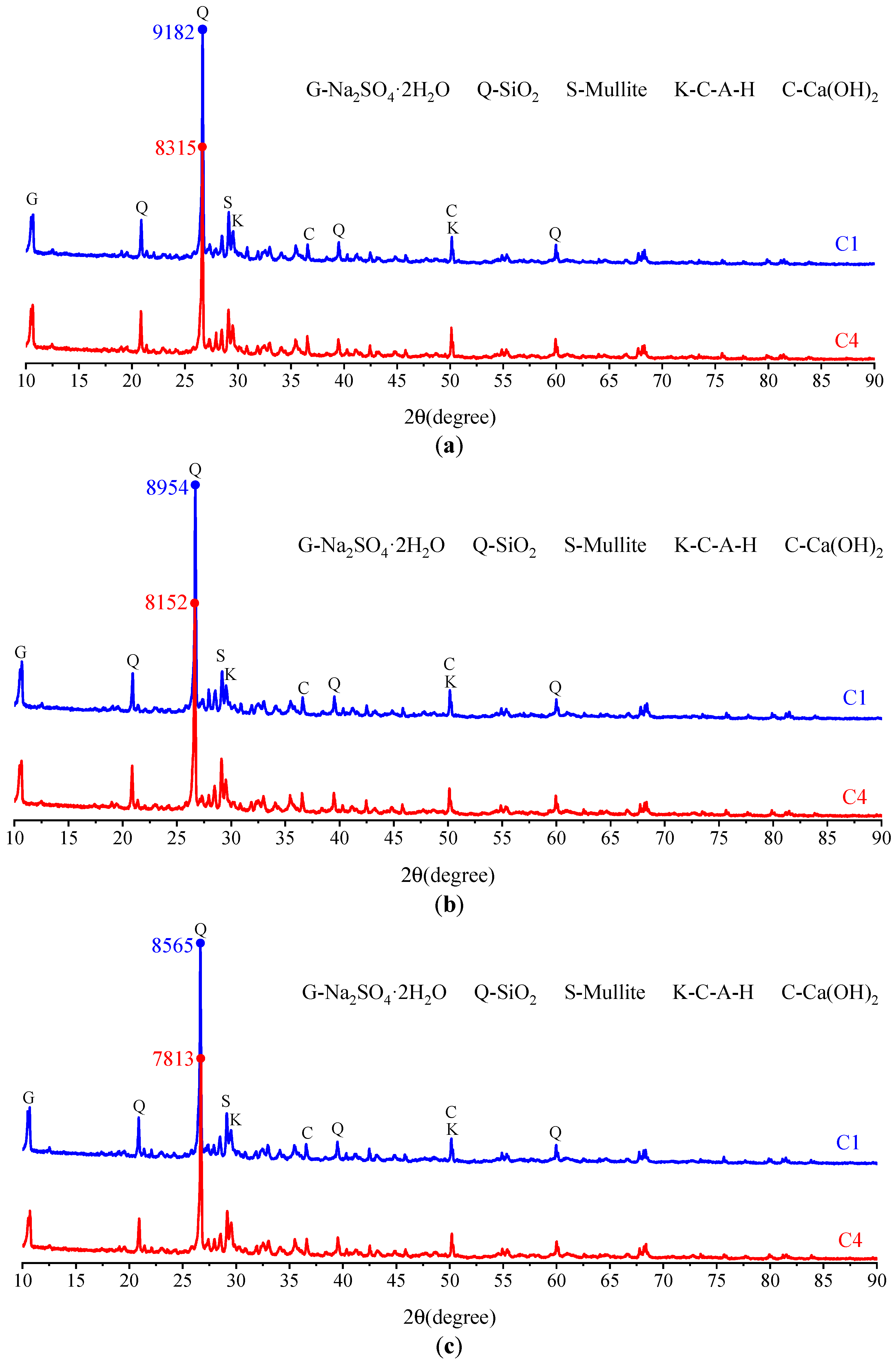
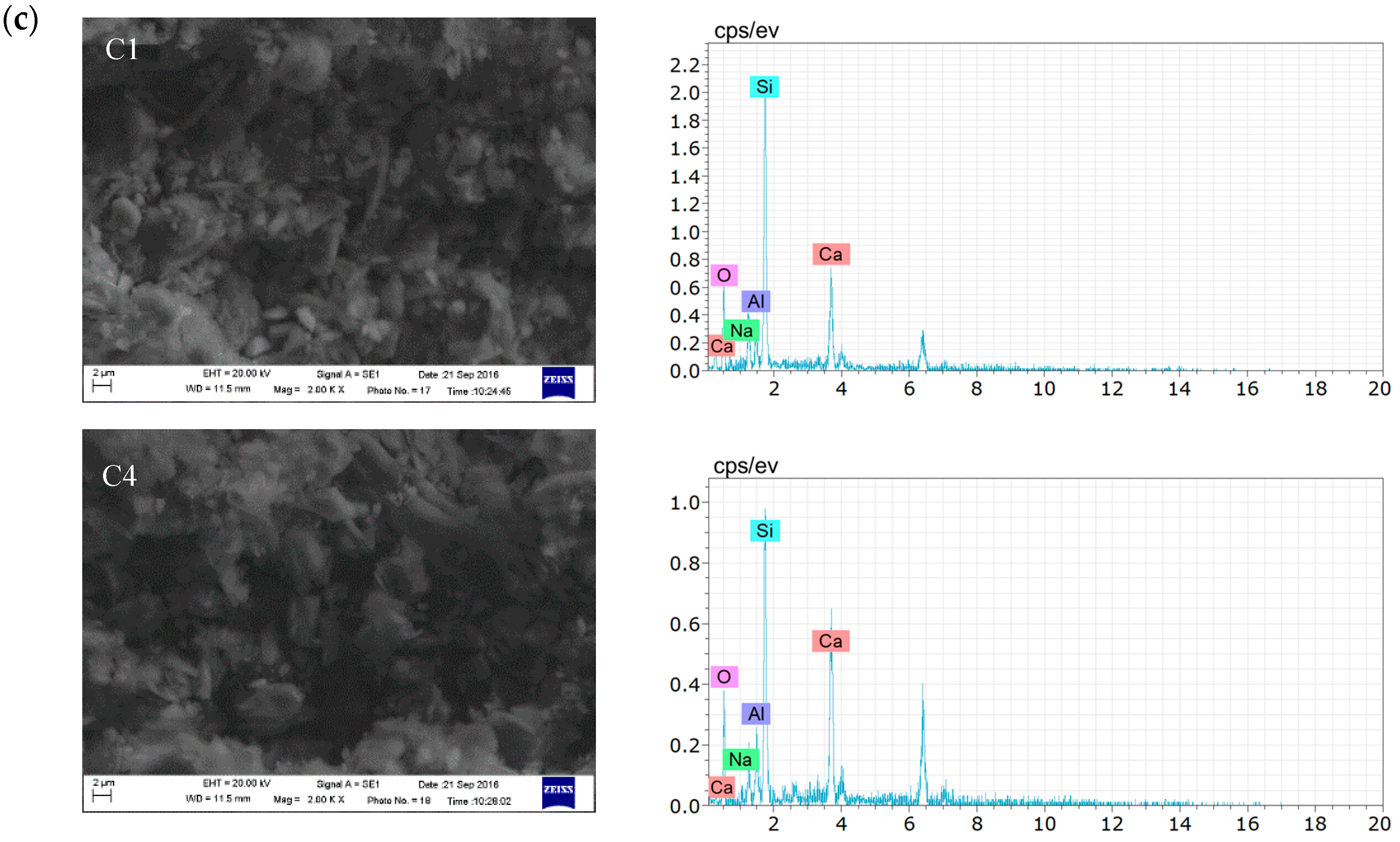
3.2.3. Microscopic Analysis of Filling Bodies Activated by the Composite Activators
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Activators enhanced the strength of fly ash–cement composites compared to the control group, with their effectiveness ranking as Ca(OH)2 > composite activator > Na2SO4. The efficacy of activators diminishes with curing time.
- (2)
- The activation mechanisms of Na2SO4 enhanced the fly ash–cement system by facilitating the formation of AFt, which promoted Ca2⁺ diffusion and reaction with SiO2 and Al2O3.
- (3)
- Ca(OH)2 increased alkalinity, aiding bond cleavage and the formation of reactive oligomers. These interactions led to the production of C-S-H and C-A-H gel products, significantly improving early strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Han, Y. A Numerical Investigation on Kick Control with the Displacement Kill Method during a Well Test in a Deep-Water Gas Reservoir: A Case Study. Processes 2024, 12, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. The Carrying Behavior of Water-Based Fracturing Fluid in Shale Reservoir Fractures and Molecular Dynamics of Sand-Carrying Mechanism. Processes 2024, 12, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.C.; Bouzalakos, S.; Dudeney, A.W.L. Integrated Waste and Water Management in Mining and Metallurgical Industries. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.G.; Stacey, T.R.; Genske, D.D. Mining Subsidence and Its Effect in the Environment: Some Differing Examples. Environ. Geol. 2000, 40, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.; Han, Y. Status and Prospects of Paste Technology in China. Chin. J. Eng. 2018, 40, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Ruan, Z.; Bürger, R.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Optimization of Flocculation and Settling Parameters of Tailings Slurry by Response Surface Methodology. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Transportability and Pressure Drop of Fresh Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill (CGFB) Slurry in Pipe Loop. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. Cemented Paste Backfill for Mineral Tailings Management: Review and Future Perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2019, 144, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarizadeh, A.; Lim, H. The Benefit of Delithiated Beta Spodumene to Reduce the Carbon Footprint of Cemented Paste Backfill. In Proceedings of the Paste 2023: 25th International Conference on Paste, Thickened and Filtered Tailings, Banff, AB, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2023; pp. 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuaguluchi, O.; Eren, Ö. Durability-Related Properties of Mortar and Concrete Containing Copper Tailings as a Cement Replacement Material. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 64, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Mazumdar, S.; Dutt, K.B. Stabilization Characteristics of Copper Mine Tailings through Its Utilization as a Partial Substitute for Cement in Concrete: Preliminary Investigations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniuk, N.; McFarlane, L.; Hariharan, N. Development of Slag Alternatives for Paste Backfill Operations. In Proceedings of the Paste 2024—26th International Conference on Paste, Thickened and Filtered Tailings, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 16–18 April 2024; pp. 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingliang, Z.; Zhengyu, M.; Jingping, Q.; Xiaogang, S.; Xiaowei, G. Experimental Study on the Utilization of Steel Slag for Cemented Ultra-Fine Tailings Backfill. Powder Technol. 2020, 375, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Fractal Features and Dynamical Characters of the Microstructure of Paste Backfill Prepared from Fly Ash Based Binder. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2016, 35, 4241–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q. Analysis of Development Prospects and Status Quo of Comprehensive Utilization of Fly Ash at Home and Abroad. China Well Rock Salt 2011, 42, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Du, C.; He, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.J.; Zheng, Z.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y. Enhancement of Compressive Strength of High-Volume Fly Ash Cement Paste by Wet Grinded Cement: Towards Low Carbon Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nguyen, T.H.Y. Enhancing the Effectiveness of Steam Curing for Cement Paste Incorporating Fly Ash Based on Long-Term Compressive Strength and Reaction Degree of Fly Ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Mishra, D.P.; Singh, P.; Mishra, K.; Mandal, S.K.; Ghosh, C.N.; Kumar, R.; Mandal, P.K. Utilization of Mill Tailings, Fly Ash and Slag as Mine Paste Backfill Material: Review and Future Perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuaguluchi, O.; Ratu, R.; Banthia, N. Effect of Sodium Sulfate Activation on the Early-Age Matrix Strength and Steel Fiber Bond in High Volume Fly Ash (HVFA) Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qin, W.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Leaching and Kinetic of Lithium Element from Waste Coal Fly Ash. Hydrometall. China. 2024. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3012.TF.20240625.1525.008 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Yang, J. Research Progress of Coal Fly Ash for CO2 Mineralization Process. Clean Coal Technol. 2024, 30, 300–315. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, K.; Budiea, A.M.A.; Azhar, N.W.; Jaafar, M.S.; Mohsin, S.M.S.; Arifin, N.F.; Mat Yahaya, F. Durability Properties of Oil Palm Shell Lightweight Aggregate Concrete Containing Fly Ash as Partial Cement Replacement. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 41, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, K.M. Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Chemically Activated Fly Ash–Cement Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.W. Hydration Properties of Cement Pastes Containing High-Volume Mineral Admixtures. Comput. Concr. 2010, 7, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmluk, M.; Nawa, T. Effect of Fly Ash on the Kinetics of Portland Cement Hydration at Different Curing Temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, E.; Miyahara, S.; Ohsawa, S.; Lee, S.H.; Daimon, M. Hydration of Fly Ash Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Choi, Y.C. Effects of Fineness and Chemical Activators on the Hydration and Physical Properties of High-Volume Fly-Ash Cement Pastes. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengdeng, Z.; Tao, J.I.; Canqiang, W.; Wenyuan, Z.; Kejia, C.; Xujian, L.I.N. Effect of Alkali-Activator on Compression Strength of Alkali-Activated Slag Cement Mortar. J. Fuzhou Univ. Sci. Ed. 2016, 44, 593–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wilińska, I.; Pacewska, B.; Ostrowski, A. Investigation of Different Ways of Activation of Fly Ash–Cement Mixtures: Part 1. Chemical Activation by Na2SO4 and Ca(OH)2. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 4203–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, H.; Kong, X.; Song, C.; Hu, Y. Effects of Compound Activators on the Early Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortar Incorporating Large Volume off Fly Ash. Concrete 2010, 2010, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB175-2007; General Portland Cement. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB/T 17671-1999; Method of Testing Cements—Determination of Strength. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Gonzalez-Panicello, L.; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Puertas, F.; Palacios, M. Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses. Materials 2022, 15, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, X. Quantification of the Reaction Degree of Fly Ash in Blended Cement Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 167, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Lin, Z.; Kou, S.; Pan, Z. Influence of Chemical Activators on the Pozzolanic Property of Reject Fly Ash. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2004, 26, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Y. Research on the Stabilizer for the Soil with Higher Water Content. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 1998, 20, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Tian, X.; Hou, Y.; Wei, S.; Yue, R.; Fan, P.; Zhu, S.; Yin, T. Experimental Study on the Pore and Strength Properties of Cemented Unclassified during the Consolidation Process. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade Neto, J.S.; Rodríguez, E.D.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; De la Torre, A.G.; Kirchheim, A.P. Hydration of C3S and Al-Doped C3S in the Presence of Gypsum. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 152, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Nie, R.; Zhou, S.; Lu, S.; Qing, Z. Effect of Sulfate-Containing Wastewater on the Properties of Phosphogypsum-Based Cemented Paste Backfill. Gold Sci. Technol. 2024, 32, 416–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, W.; Zheng, K.; Chen, H.; Qin, H.; Liu, J. Influence of Fly Ash Proportion on Creep Characteristics of High-Performance Concrete and Its Mechanism. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 34, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohit, M.; Ranjbar, A.; Sharifi, Y. Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Mortars Incorporating Ceramic Waste Powder Exposed to the Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lai, J.; Ruan, S.; Qian, X.; Qian, K. Effect of Composite Early Strength Agent on Strength and Hydration of Mortar with Limestone Powder. Mater. Rep. 2025, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lan, W.; Liu, C. Effect of Compound Activator on Copper Slag Activity and Preparation of Filling Materials. Chin. J. Eng. 2017, 39, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
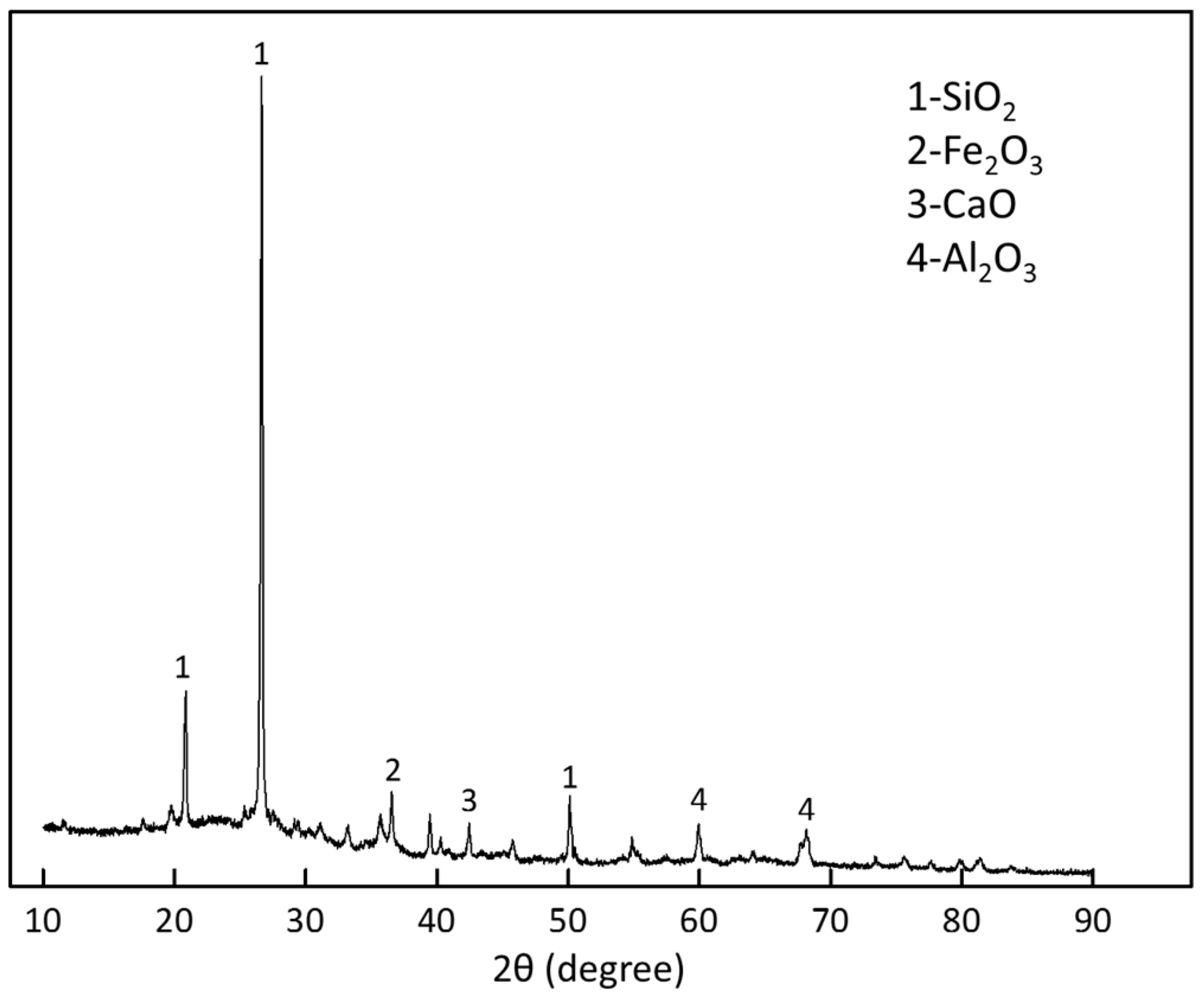
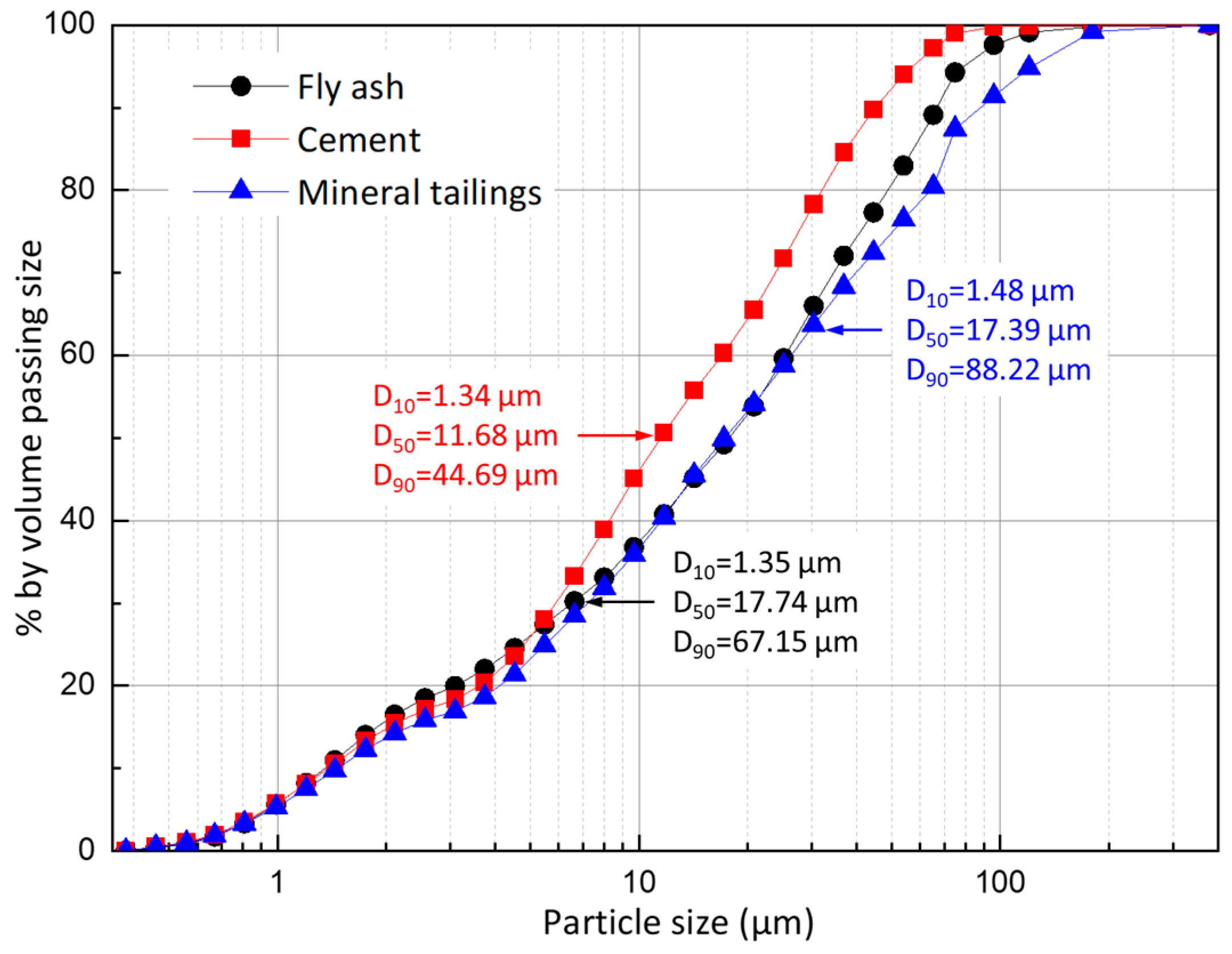



| Compositions | Mineral Tailings | Fly Ash | Cement |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 50.63 | 53.57 | 22.60 |
| Al2O3 | 2.72 | 7.25 | 5.74 |
| Fe2O3 | 25.54 | 8.43 | 3.48 |
| K2O | - | 3.88 | 0.79 |
| MgO | 5.62 | 3.46 | 2.01 |
| CaO | 9.39 | 9.37 | 60.56 |
| SO3 | 1.92 | 6.55 | 2.79 |
| Samples | FA/C | W/C | T/C | A/(C+FA) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-I/(C+FA) | A-II/(C+FA) | ||||
| A0 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| A1 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0.5 | 0 |
| A2 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 1 | 0 |
| A3 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 1.5 | 0 |
| A4 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 2 | 0 |
| B1 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0 | 0.5 |
| B2 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| B3 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0 | 1.5 |
| B4 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0 | 2 |
| C1 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| C2 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| C3 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| C4 | 1.5 | 4.39 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Wu, A.; Xiao, B.; Ruan, Z. Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Activated Fly Ash–Cement Paste. Processes 2024, 12, 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112356
Wang J, Guo R, Wu A, Xiao B, Ruan Z. Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Activated Fly Ash–Cement Paste. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112356
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiandong, Ruiming Guo, Aixiang Wu, Bolin Xiao, and Zhuen Ruan. 2024. "Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Activated Fly Ash–Cement Paste" Processes 12, no. 11: 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112356
APA StyleWang, J., Guo, R., Wu, A., Xiao, B., & Ruan, Z. (2024). Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Activated Fly Ash–Cement Paste. Processes, 12(11), 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112356







