A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Robust Adaptive Control Method for a Class of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
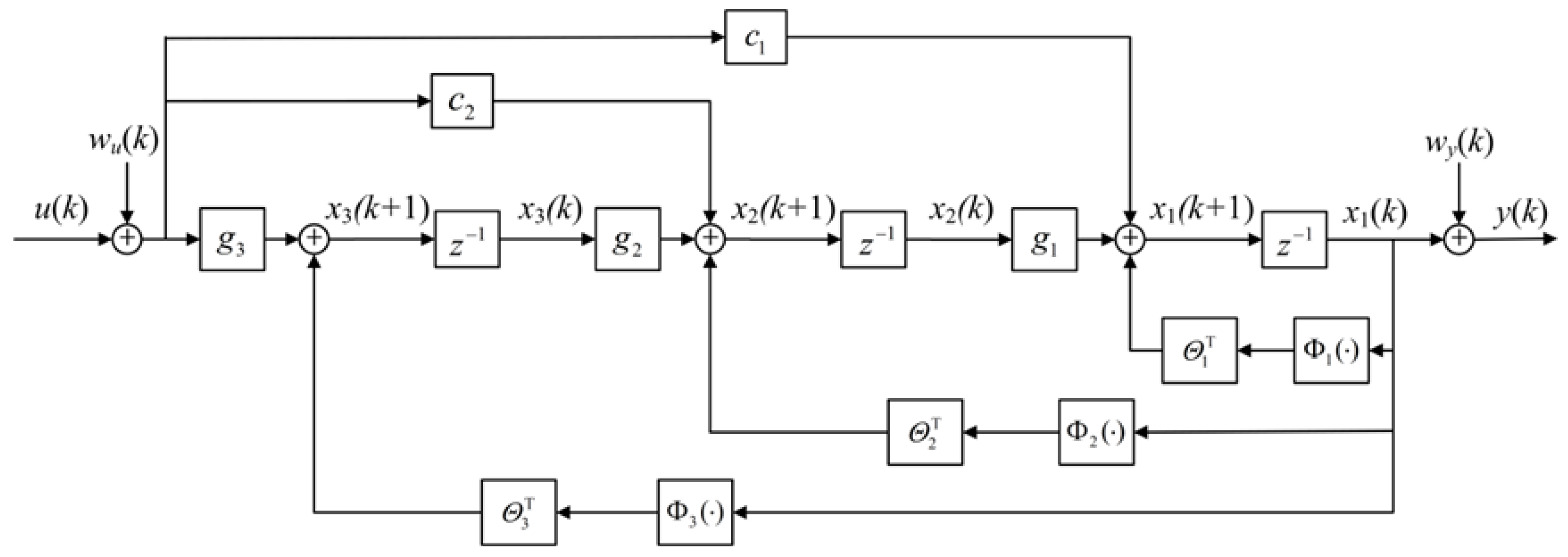
2. System Representation and Transformation
2.1. System Representation
2.2. System Transformation
3. Adaptive Control Design without Disturbance
3.1. Adaptive Control and Parameter Estimation
3.2. Asymptotic Tracking and Stability Analysis
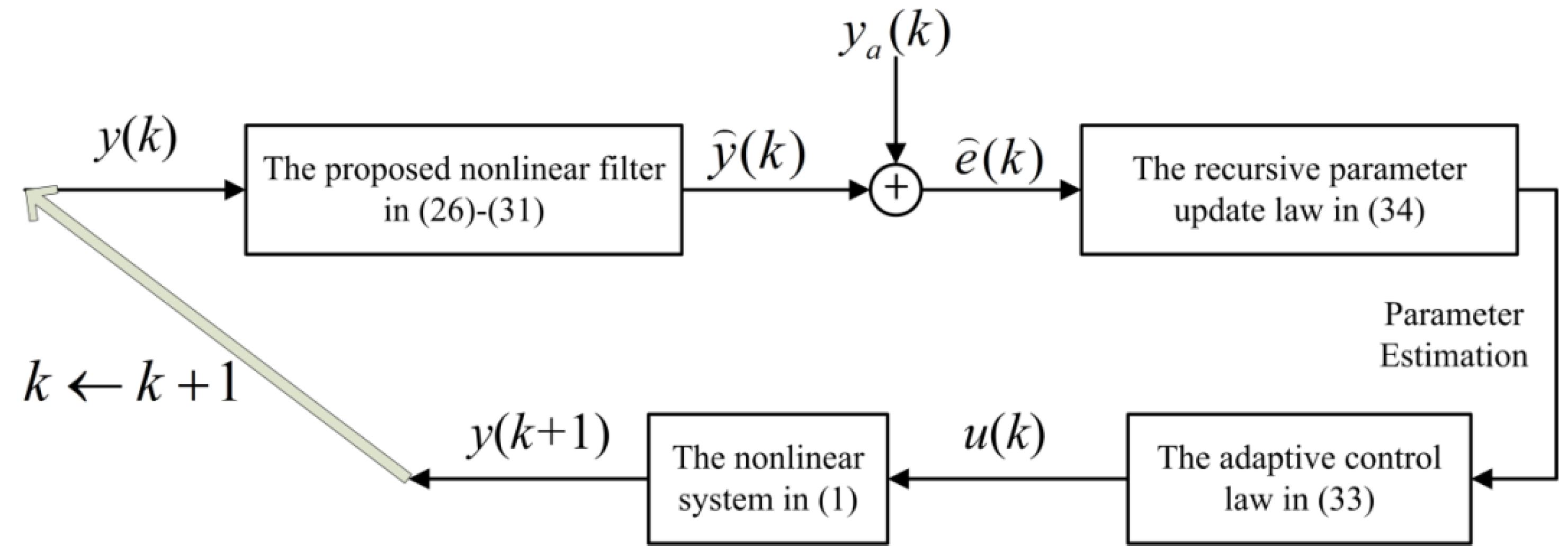
4. A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Adaptive Control Method in the Presence of Disturbances
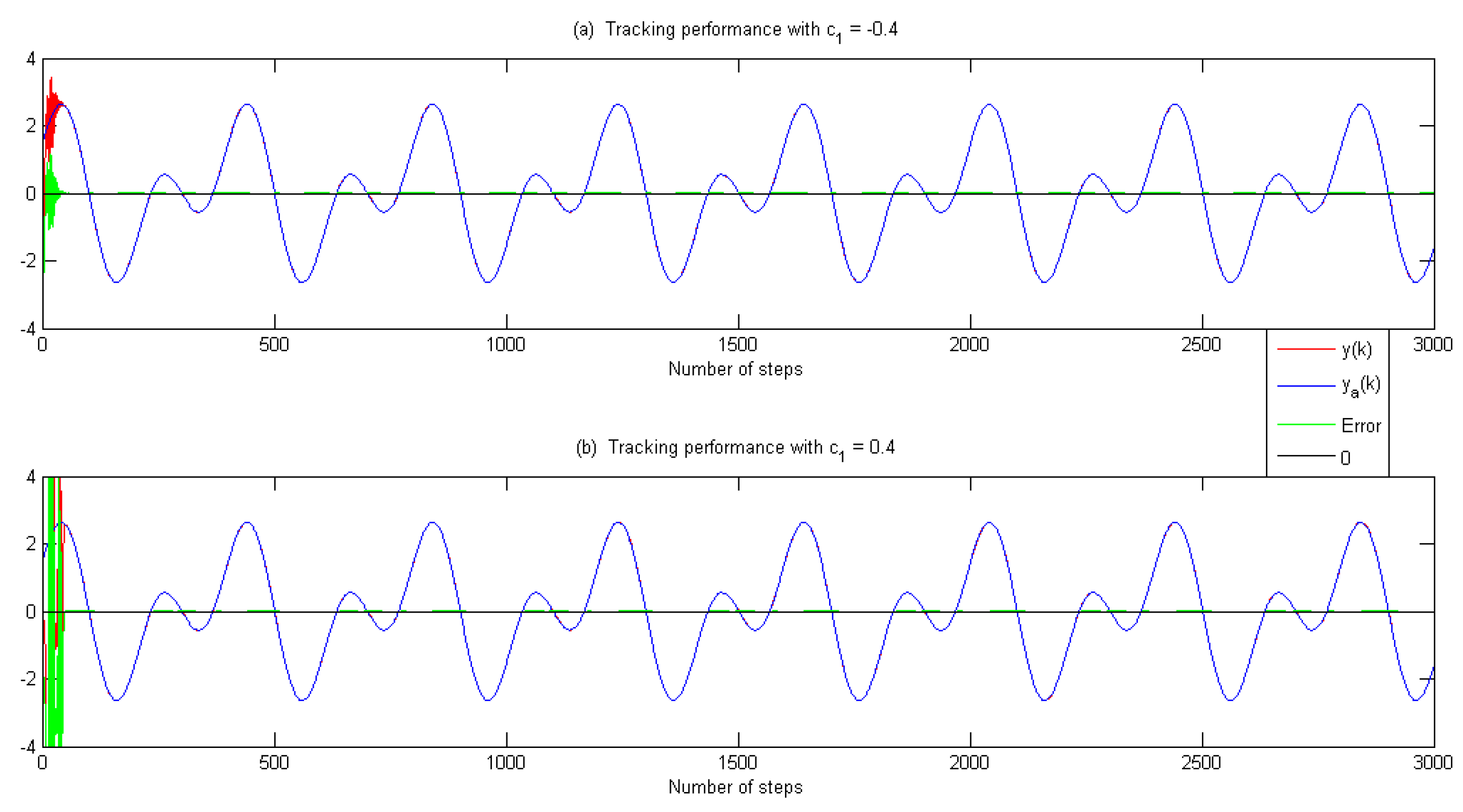
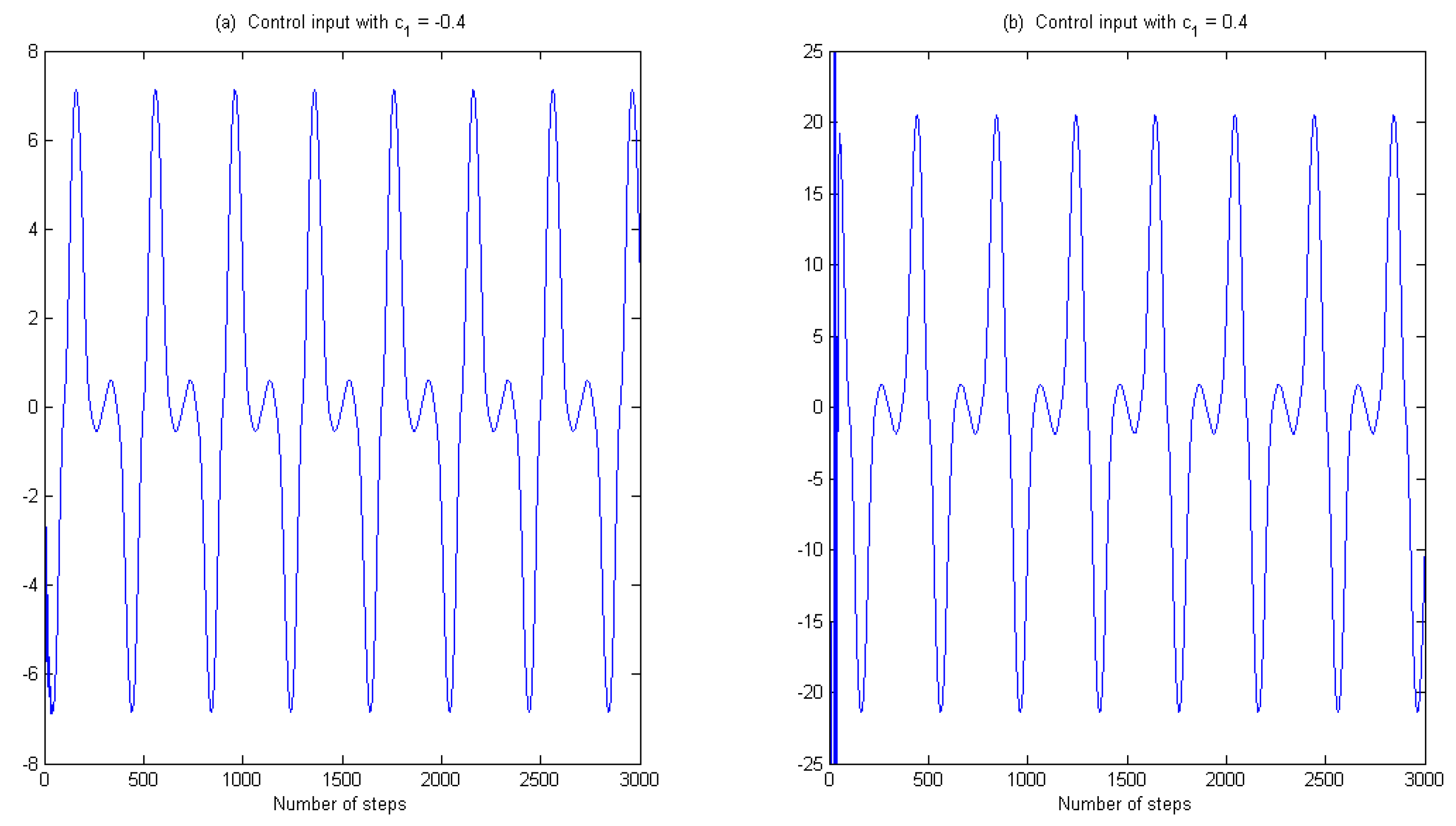
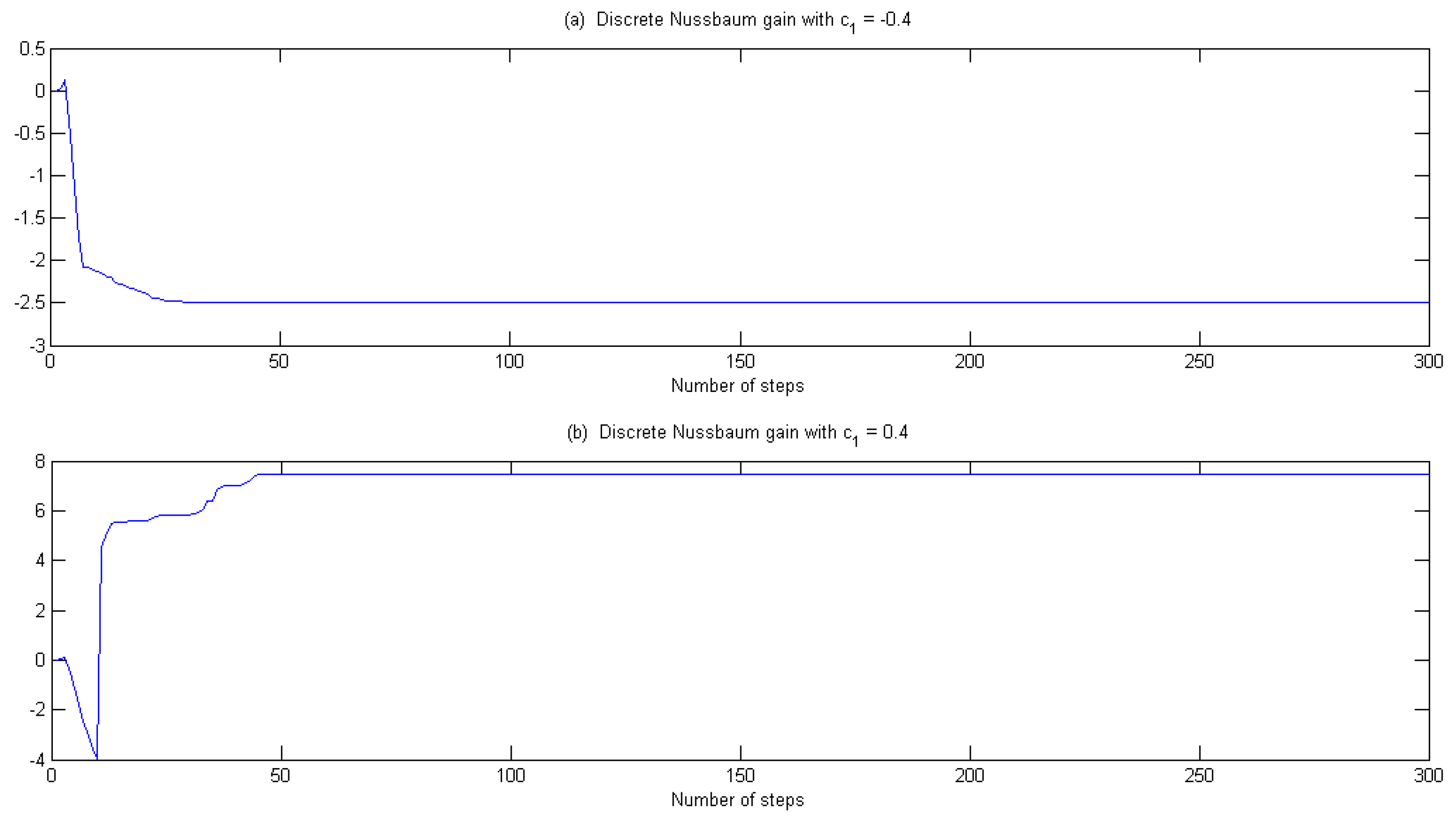
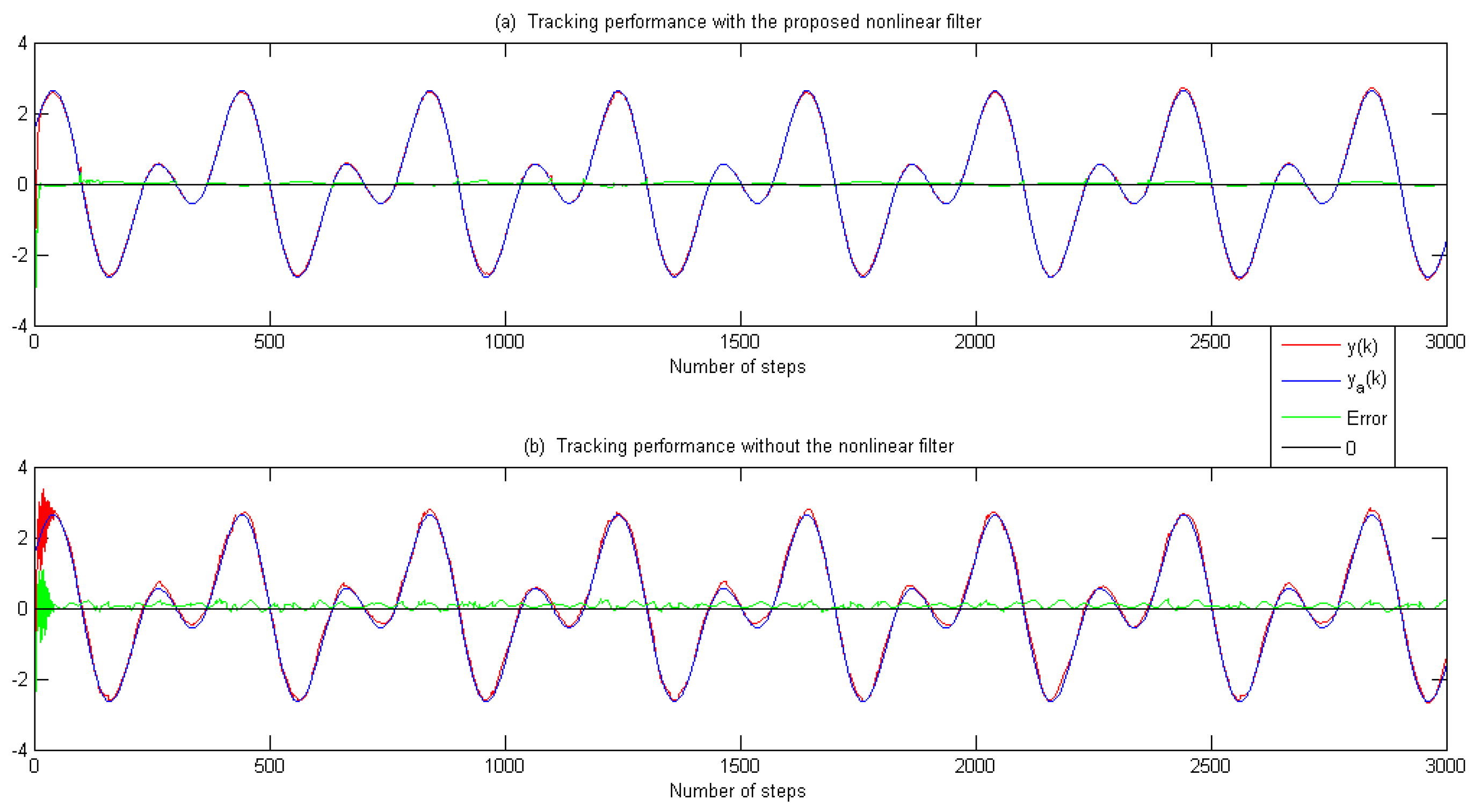
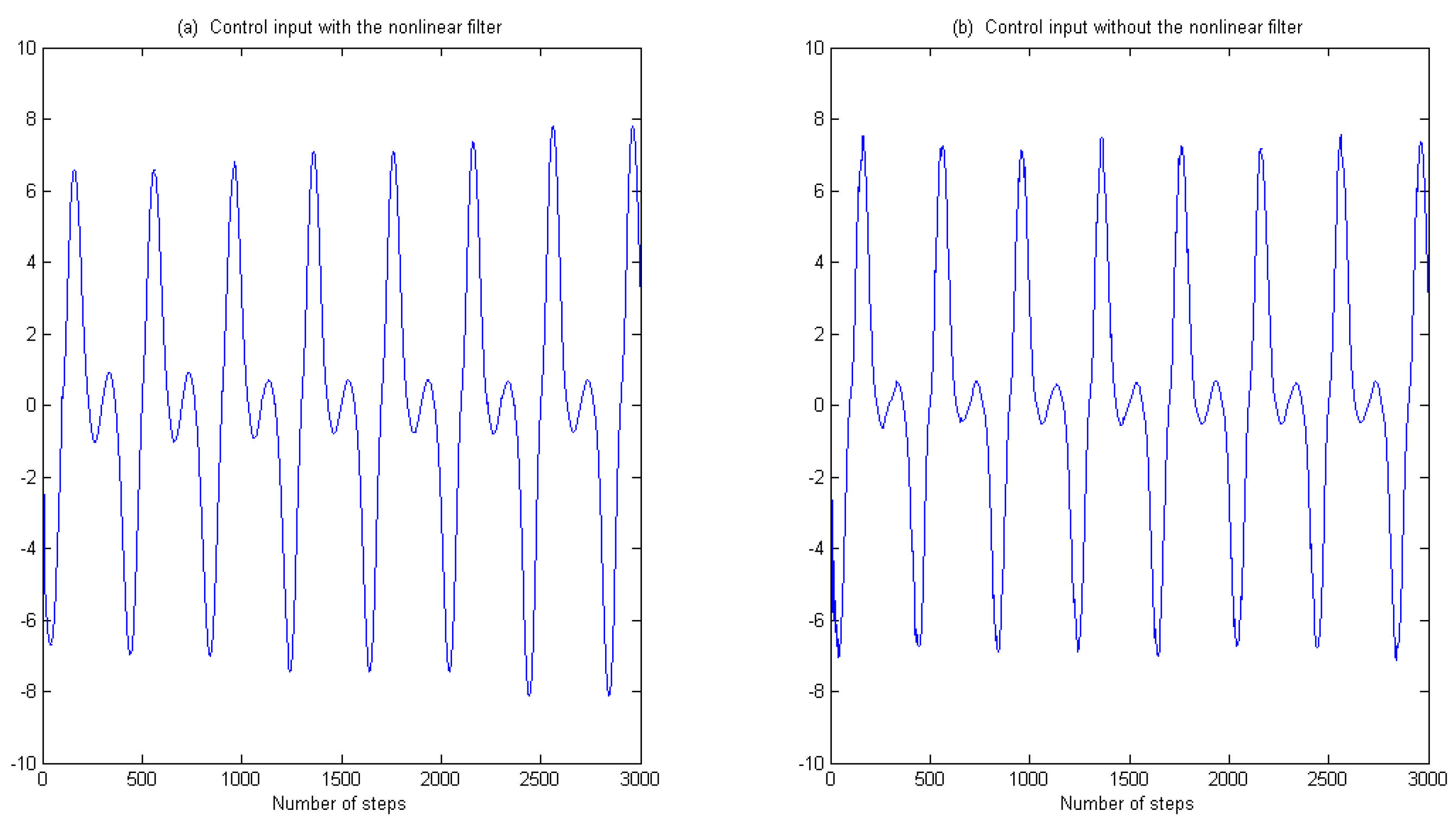
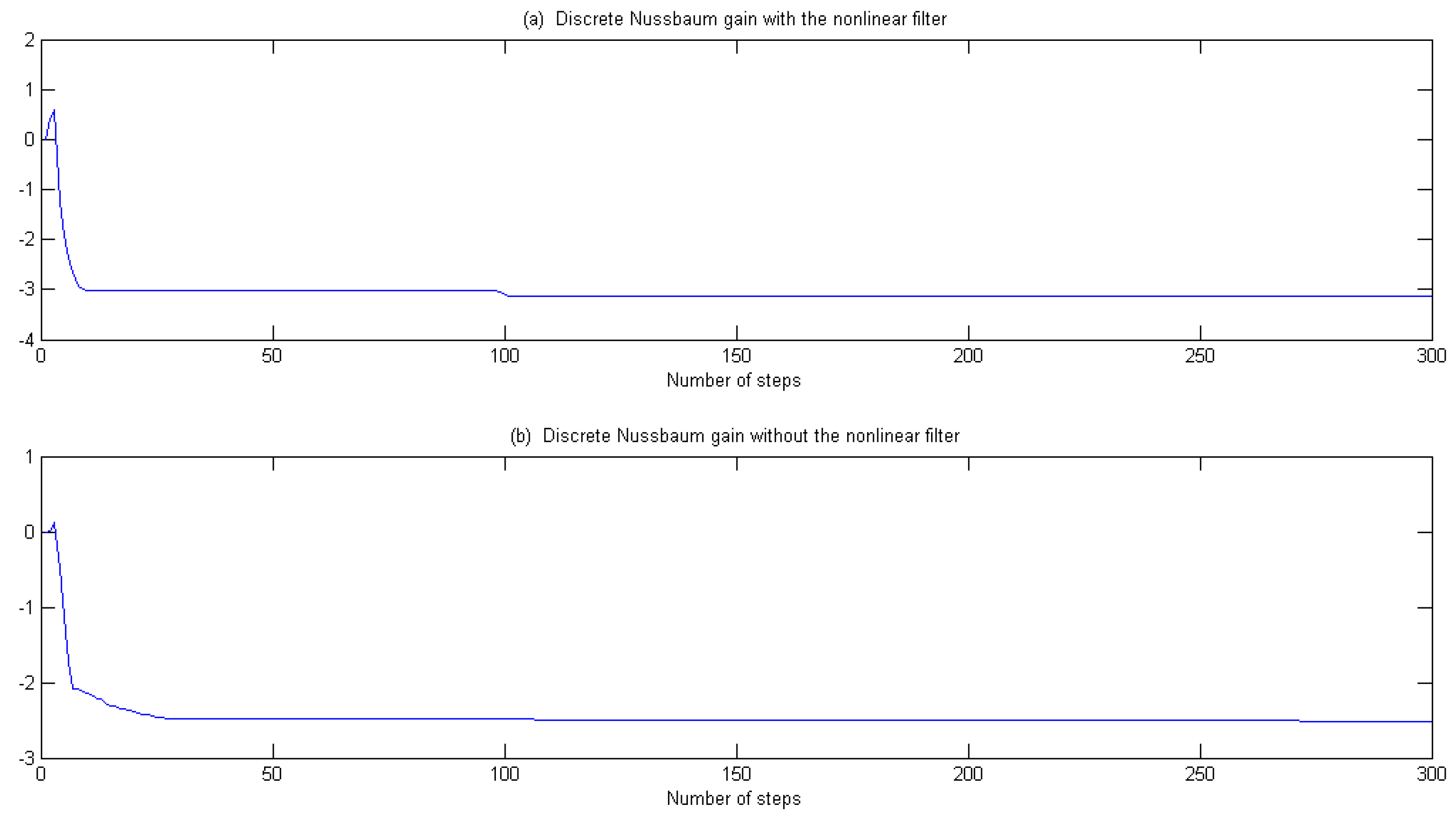
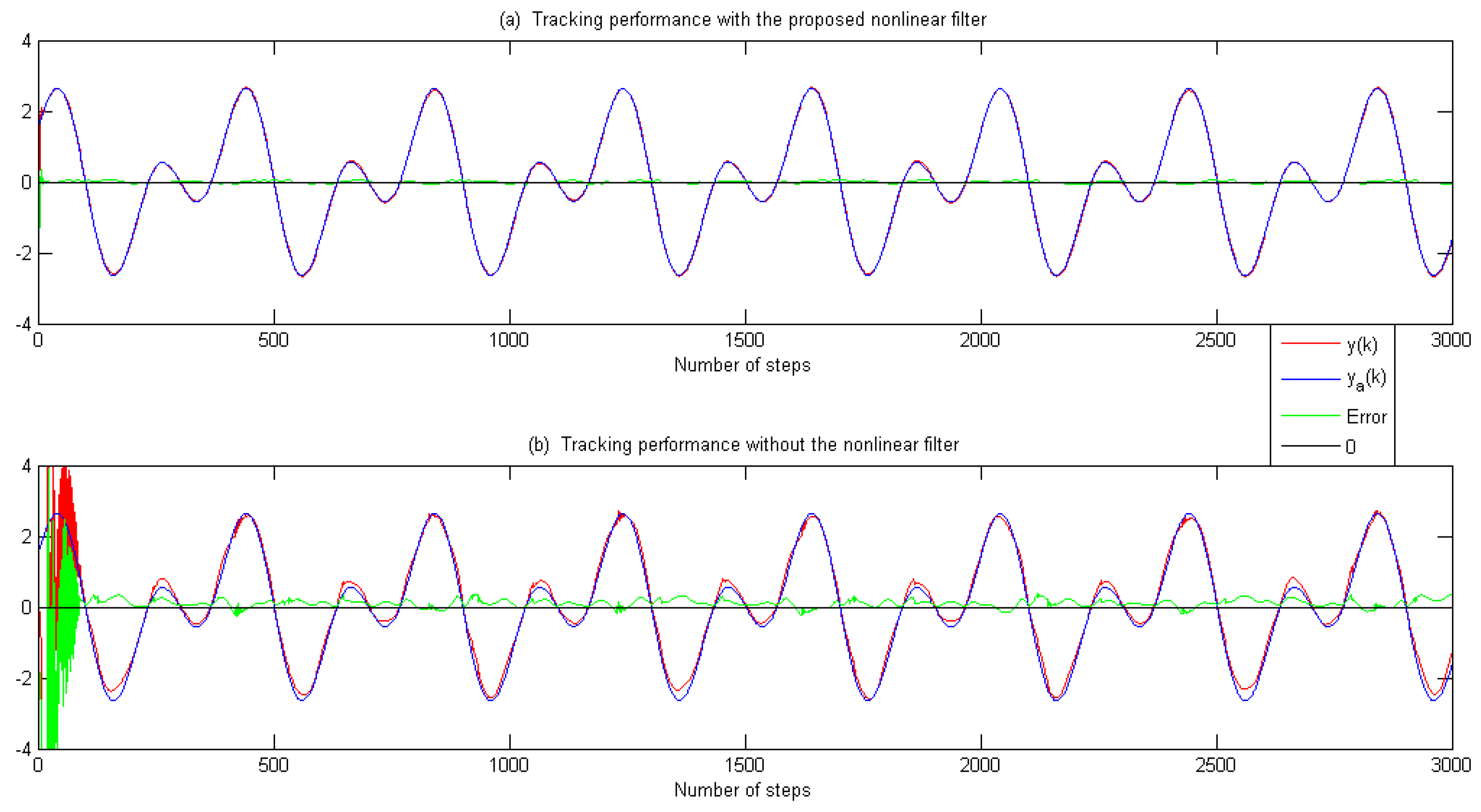
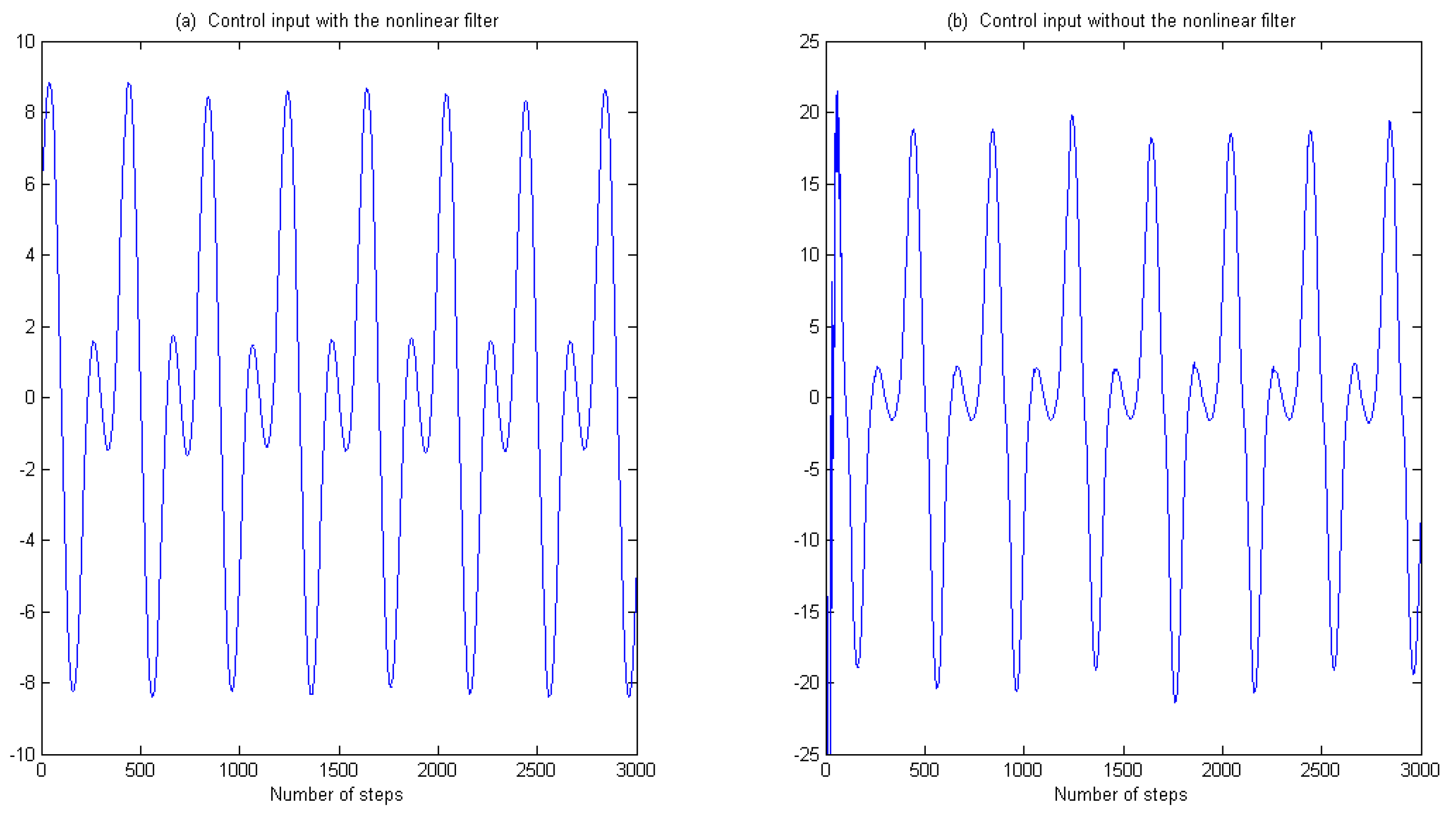
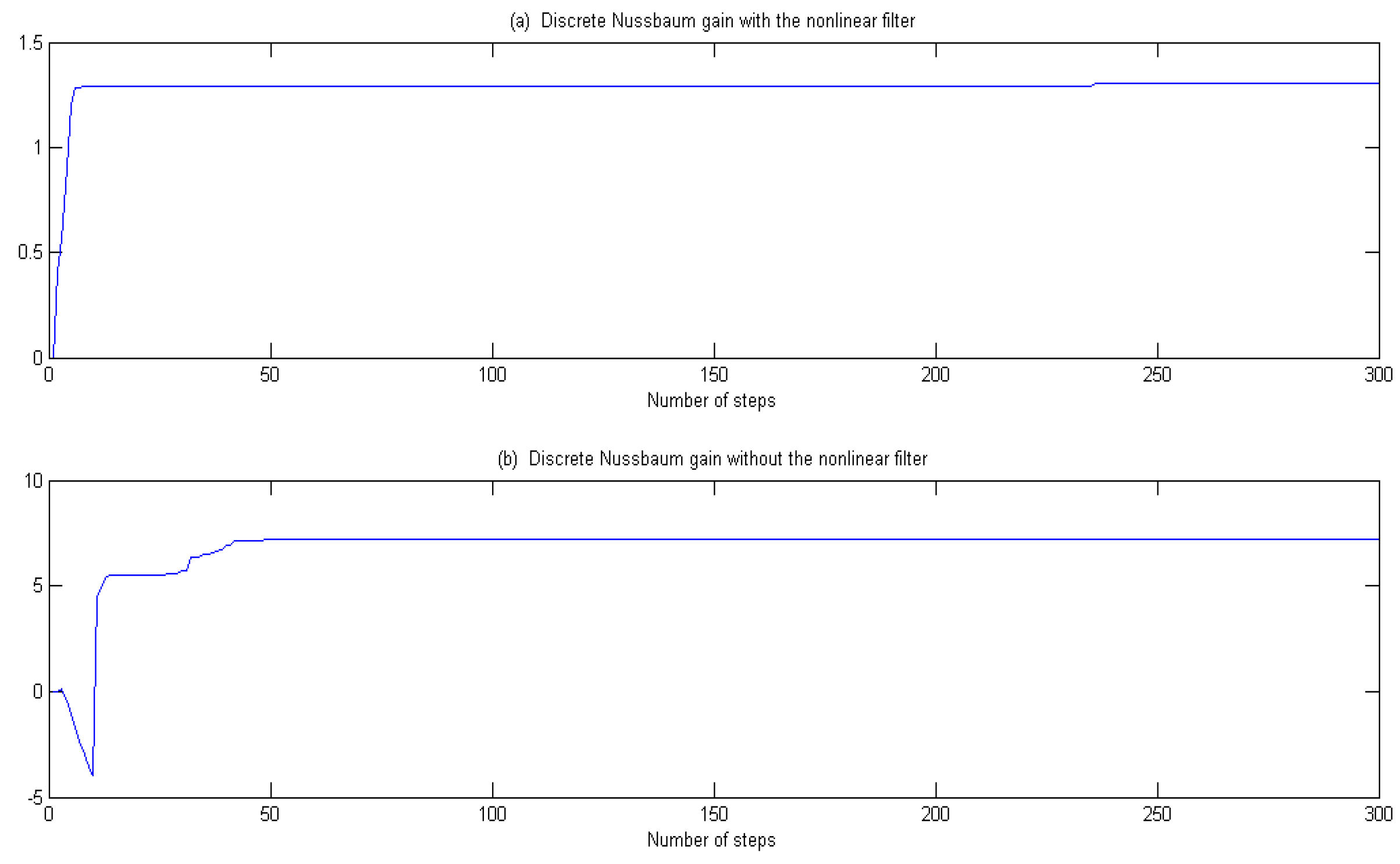
5. Illustrative Examples
- No matter if or , the nonlinear filter-based adaptive control method can show tracking performance more accurately than the general adaptive control scheme;
- In order to track the reference trajectory, both the small overshoot and the short settling time are realized via the nonlinear filter-based adaptive control method;
- The control inputs are bounded in all of the comparative examples;
- Discrete Nussbaum gains, adopted in the proposed identification algorithm, can be designed to detect the direction of model parameters within two direction.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Joint estimation method with multi-innovation unscented Kalman filter based on fractional-order model for state of charge and state of health estimation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmeijer, F. Two-stage least squares as minimum distance. Econom. J. 2019, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, X.; Chiu, M. The identification of neuro-fuzzy based MIMO Hammerstein model with separable input signals. Neurocomputing 2016, 174, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Fan, Z. Iterative Alpha Expansion for estimating gradient-sparse signals from linear measurements. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2021, 83, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ge, S.S.; Hang, C.C. Adaptive neural network control for strict-feedback nonlinear systems using backstepping design. In Proceedings of the 1999 American Control Conference (ACC), San Diego, CA, USA, 2–4 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Jiao, L.; Li, J.; Li, R. Adaptive NN backstepping output-feedback control for stochastic nonlinear strict-feedback systems with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2010, 40, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J. Neural network-based adaptive dynamic surface control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems in strict-feedback form. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2005, 16, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Fuzzy-adaptive decentralized output-feedback control for large-scale nonlinear systems with dynamical uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Tong, S. Adaptive fuzzy output tracking control of MIMO nonlinear uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2007, 15, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, P. Observer-based adaptive fuzzy backstepping output feedback control of uncertain MIMO pure-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ge, S.S.; Voon Ee How, B. Robust adaptive neural network control for a class of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with input nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G.; Ramadge, P.J.; Caines, P.E. Discrete-time multivariable adaptive control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1980, 25, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, K.S.; Lin, Y.H. Stable Discrete Adaptive Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1980, 25, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhai, L.; Ge, S.S.; Chai, T.; Lee, T.H. Adaptive model reference control of a class of MIMO discrete-time systems with compensation of nonparametric uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference (ACC), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–13 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Ji, Y.; Ma, C. Joint two-stage multi-innovation recursive least squares parameter and fractional-order estimation algorithm for the fractional-order input nonlinear output-error autoregressive model. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 1650–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, G. Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2011, 21, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhu, Q. Separable synchronous multi-innovation gradient-based iterative signal modeling from on-line measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 6501313. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Ji, Y. Parameter estimation of fractional-order Hammerstein state space system based on the extended Kalman filter. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, M. Unbiased recursive least squares identification methods for a class of nonlinear systems with irregularly missing data. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 2247–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ding, F. Maximum likelihood based multi-innovation stochastic gradient estimation for controlled autoregressive ARMA systems using the data filtering technique. In Proceeding of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 5993–5998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Two-stage gradient-based iterative algorithms for the fractional-order nonlinear systems by using the hierarchical identification principle. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 1778–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Nouri, H. Identification and U-control of a state-space system with time-delay. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. State filtering and parameter estimation for state space systems with scarce measurements. Signal Process. 2022, 104, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Combined state and least squares parameter estimation algorithms for dynamic systems. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, F.; Ding, F. The modified extended Kalman filter based recursive estimation for Wiener nonlinear systems with process noise and measurement noise. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2020, 34, 1321–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Yang, E. Auxiliary model multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation methods for nonlinear sandwich systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 31, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Auxiliary model-based multi-innovation recursive identification algorithms for an input nonlinear controlled autoregressive moving average system with variable-gain nonlinearity. Int. J. Adapt. Control. Signal Process. 2021, 36, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, J.; Ge, X. Blind deblurring with fractional-order calculus and local minimal pixel prior. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 89, 103645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H. An adaptive fractional-order unscented Kalman filter for Li-ion batteries in the energy storage system. Indian J. Phys. 2022, 96, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, J.; Mojallali, H.; Teshnehlab, M. A multiple-input-single-output fractional-order Hammerstein model identification based on modified neural network. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2018, 41, 6252–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Self-tuning control based on multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation. Syst. Control Lett. 2009, 58, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Chen, T.; Iwai, Z. Adaptive digital control of Hammerstein nonlinear systems with limited output sampling. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2007, 45, 2257–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Least squares parameter estimation and multi-innovation least squares methods for linear fitting problems from noisy data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 426, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Hierarchical gradient- and least-squares-based iterative estimation algorithms for input-nonlinear output-error systems from measurement information by using the over-parameterization. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 34, 1120–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Filtered auxiliary model recursive generalized extended parameter estimation methods for Box Jenkins systems by means of the filtering identification idea. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 33, 5510–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Parameter Estimation for Nonlinear Functions Related to System Responses. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 1780–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Separable newton recursive estimation method through system responses based on dynamically discrete measurements with increasing data length. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Narendra, K.S. Stable discrete adaptive control with unknown high-frequency gain. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1986, 31, 477–479. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Narendra, K.S. Nonlinear adaptive control using neural networks and multiple models. Automatica 2001, 37, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G.C.; Sin, K.S. Adaptive Filtering Prediction and Control; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ge, S.S.; Lee, T.H. Output feedback adaptive control of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown control directions. Automatica 2009, 45, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.S.; Yang, C.; Lee, T.H. Adaptive robust control of a class of nonlinear strict-feedback discrete-time systems with unknown control directions. Syst. Control Lett. 2008, 57, 888–895. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ge, S.S.; Xiang, C.; Chai, T.; Lee, T.H. Output feedback NN control for two classes of discrete-time systems with unknown control directions in a unified approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.C.; Kokotović, P.V. Adaptive control of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Int. J. Control 1995, 62, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, C.; Soh, Y.C. Discrete-time robust backstepping adaptive control for nonlinear time-varying systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2000, 45, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, C.; Soh, Y.C. Robust adaptive control of uncertain discrete-time systems. Automatica 1999, 35, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, C.; Soh, Y.C. Robust adaptive control of nonlinear discrete-time systems by backstepping without over-parameterization. Automatica 2001, 37, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.S.; Yang, C.; Dai, S.L.; Jiao, Z.; Lee, T.H. Robust adaptive control of a class of nonlinear strict-feedback discrete-time systems with exact output tracking. Automatica 2009, 45, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; He, H.B.; Xu, G.C. Adaptively robust filtering for kinematic geodetic positioning. J. Geod. 2001, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatos, G.G. Nonlinear Kalman Filters and Particle Filters for integrated navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2012, 60, 978–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.; Mili, L. Robust Kalman filter based on a generalized maximum-likelihood-type estimator. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2010, 58, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutayeb, M.; Rafaralahy, H.; Darouach, M. Convergence analysis of the extended Kalman filter used as an observer for nonlinear deterministic discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1997, 42, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Robust Adaptive Control Method for a Class of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems. Processes 2024, 12, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010171
Zhao Z, Wang Z, Wang Q. A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Robust Adaptive Control Method for a Class of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems. Processes. 2024; 12(1):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zeyi, Zhu Wang, and Qian Wang. 2024. "A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Robust Adaptive Control Method for a Class of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems" Processes 12, no. 1: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010171
APA StyleZhao, Z., Wang, Z., & Wang, Q. (2024). A Novel Nonlinear Filter-Based Robust Adaptive Control Method for a Class of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems. Processes, 12(1), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010171





