Response and Mechanism of Coal Fine Production to Differential Fluid Action in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
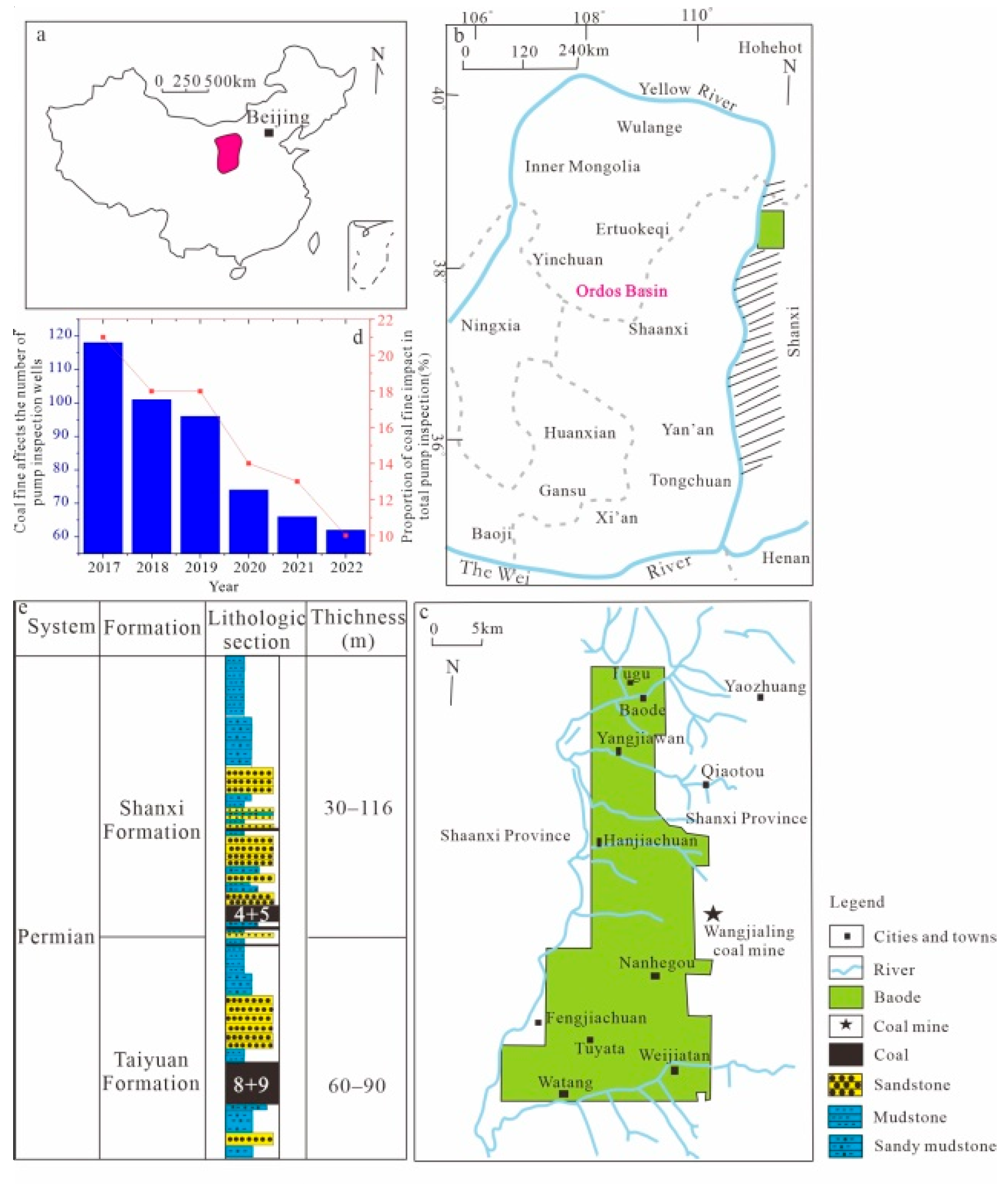
2. Geological Background
3. Samples and Methodology
3.1. Sample Basic Test
3.2. Physical Simulation Experiment of Coal Fine Production
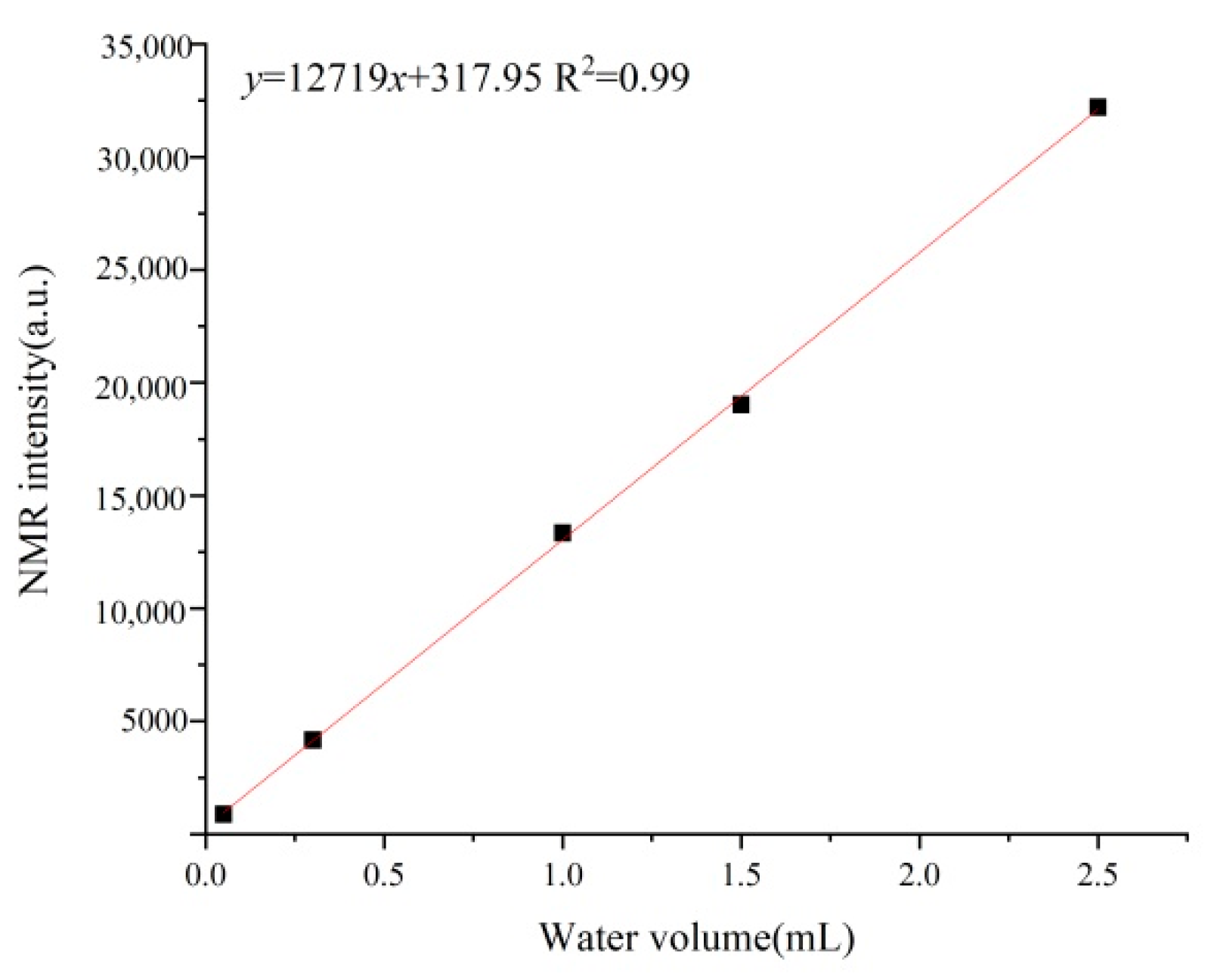
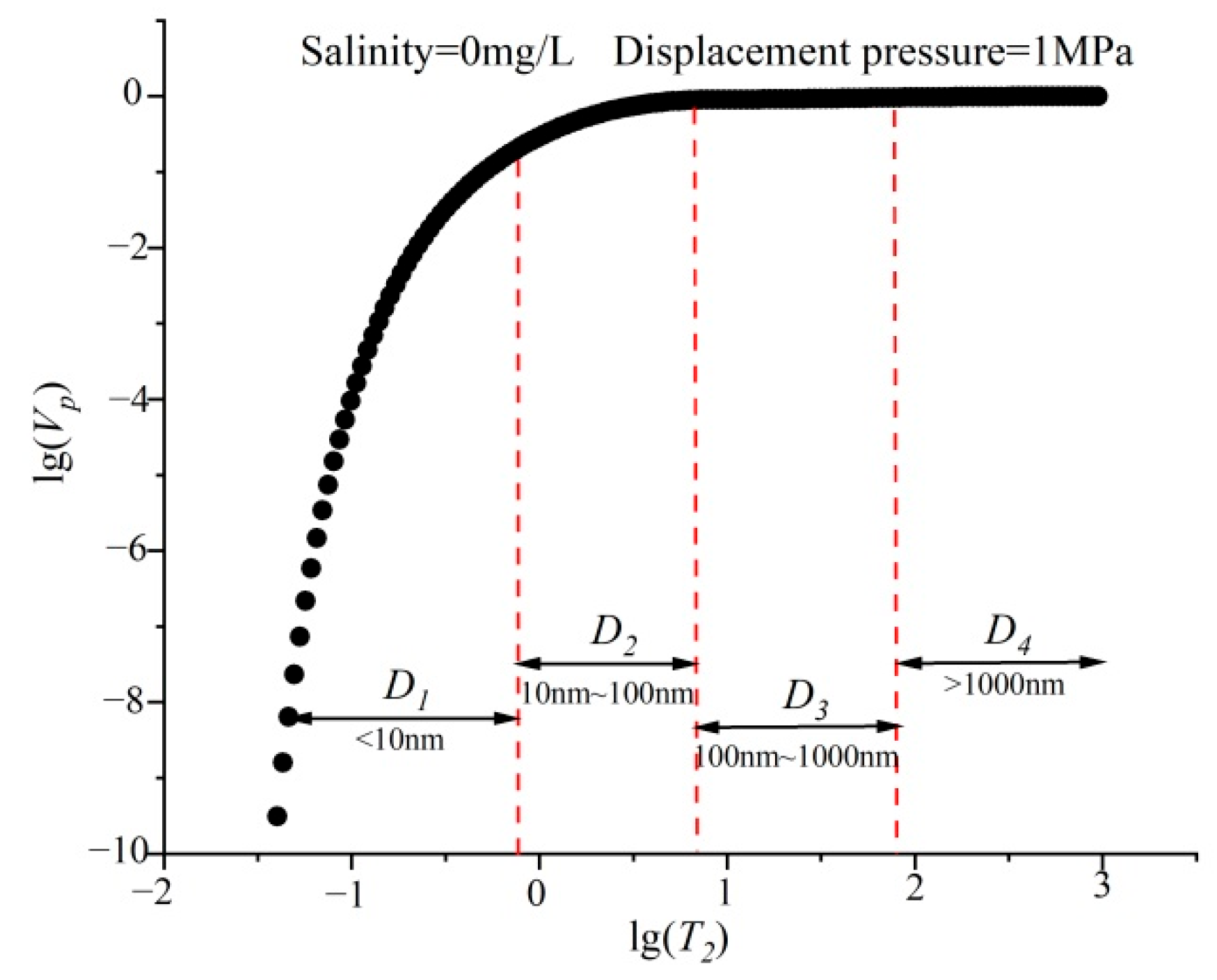
3.3. Data Processing Methods
- (1)
- NMR pore size conversion combined with high-pressure mercury intrusion data
- (2)
- Fractal dimension calculation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Basic Characteristics of the Sample
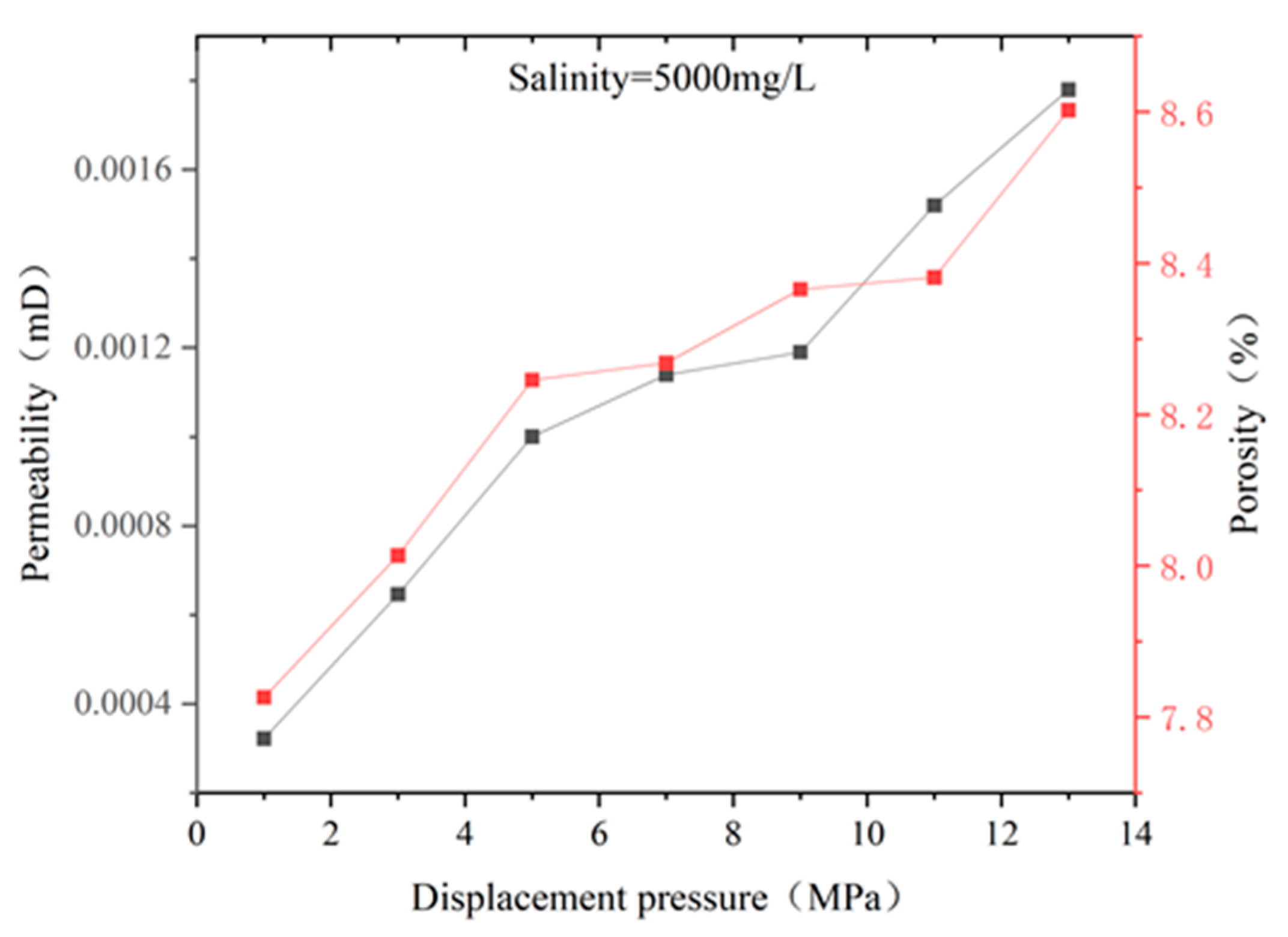
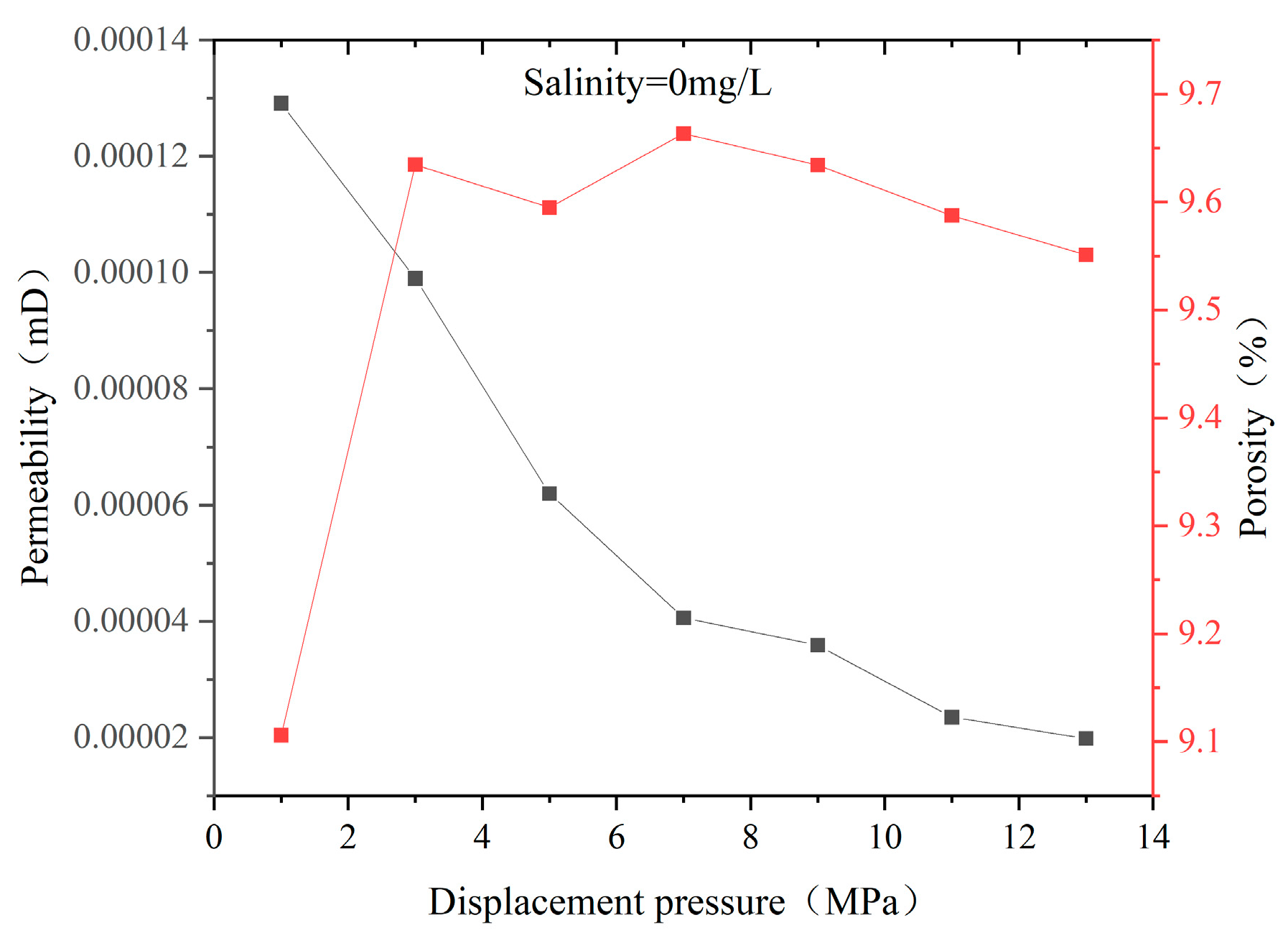
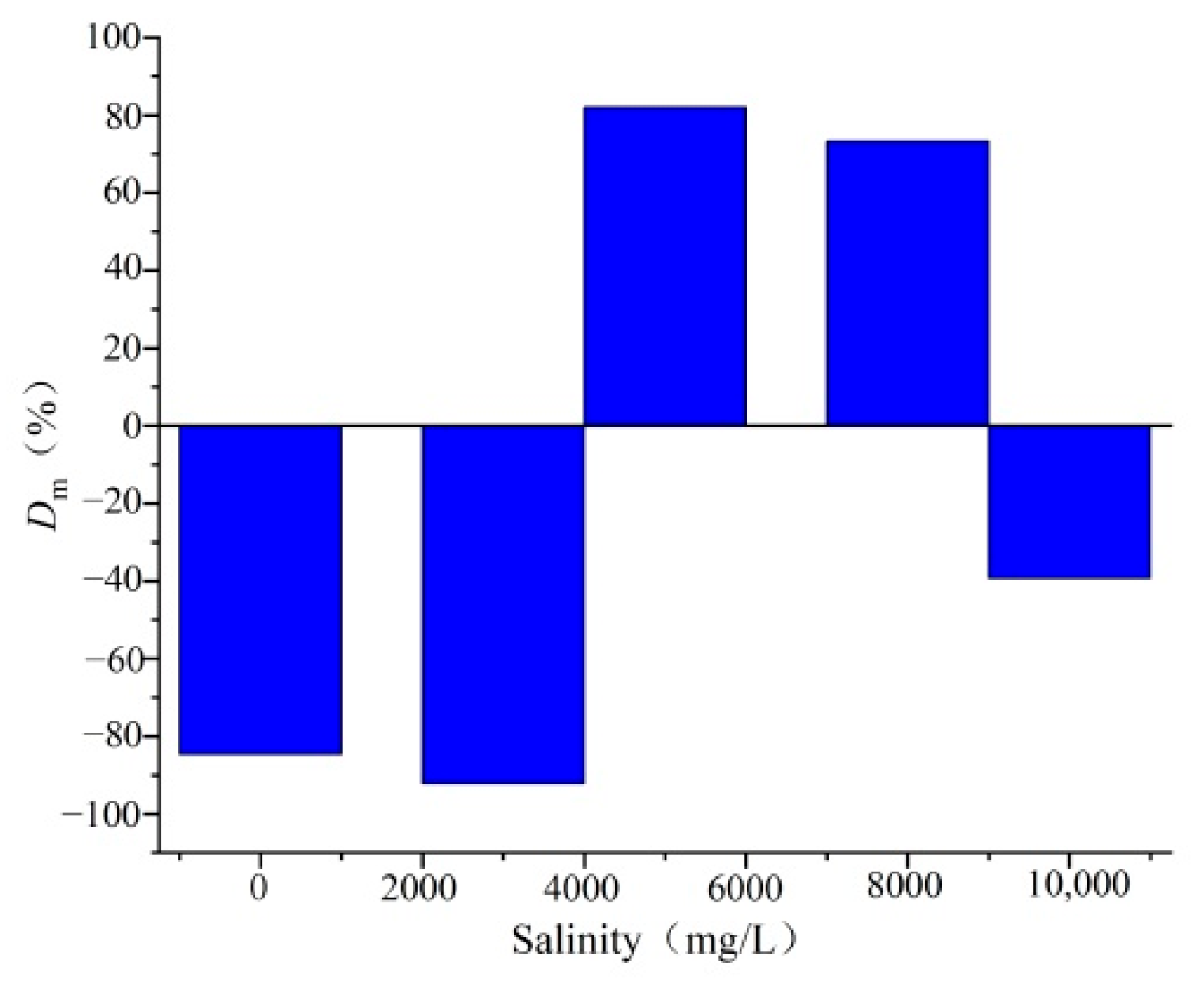
4.2. Changes in Macro–Micro Physical Properties of Coal Reservoirs under Different Fluid Conditions
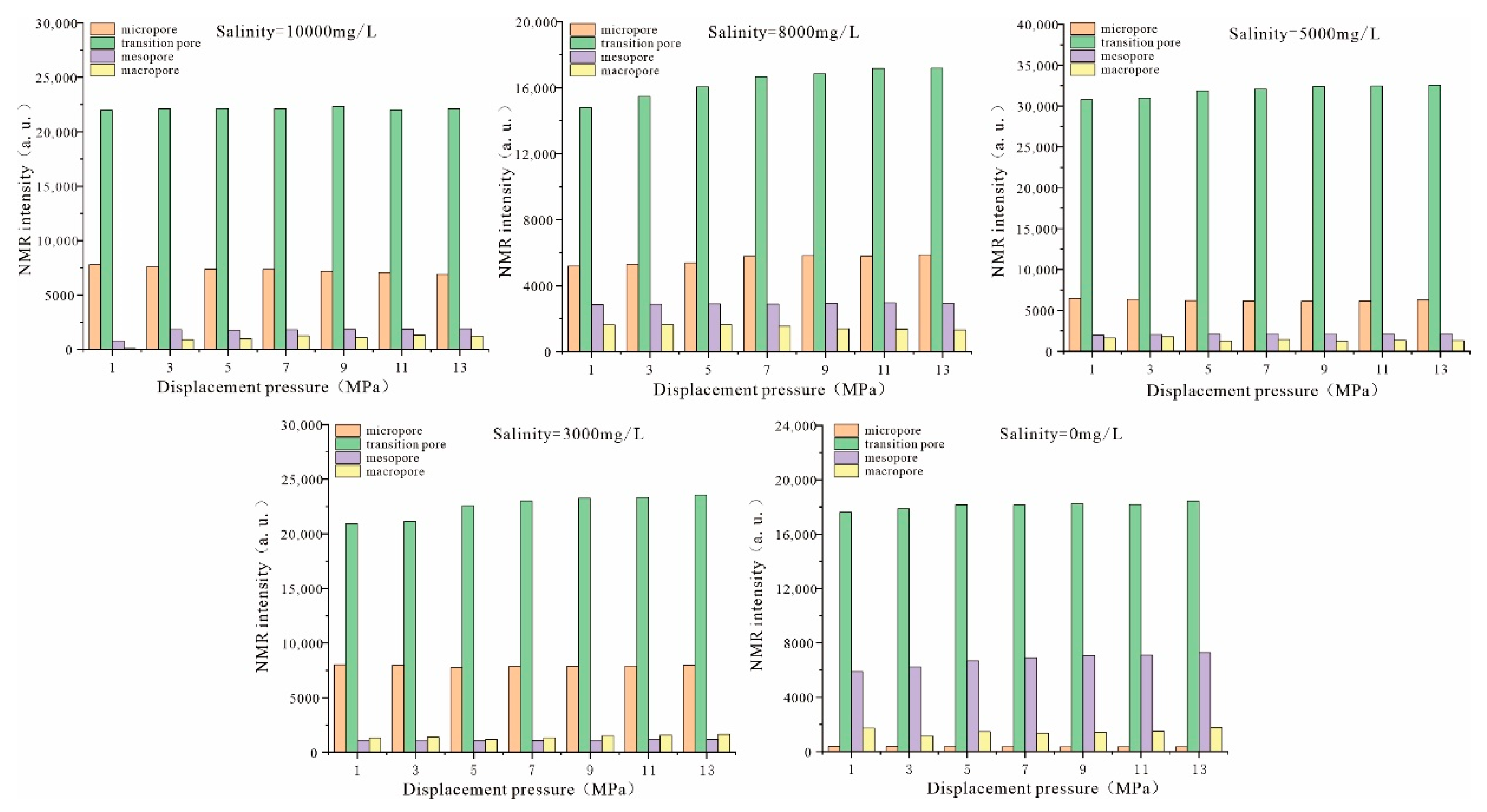
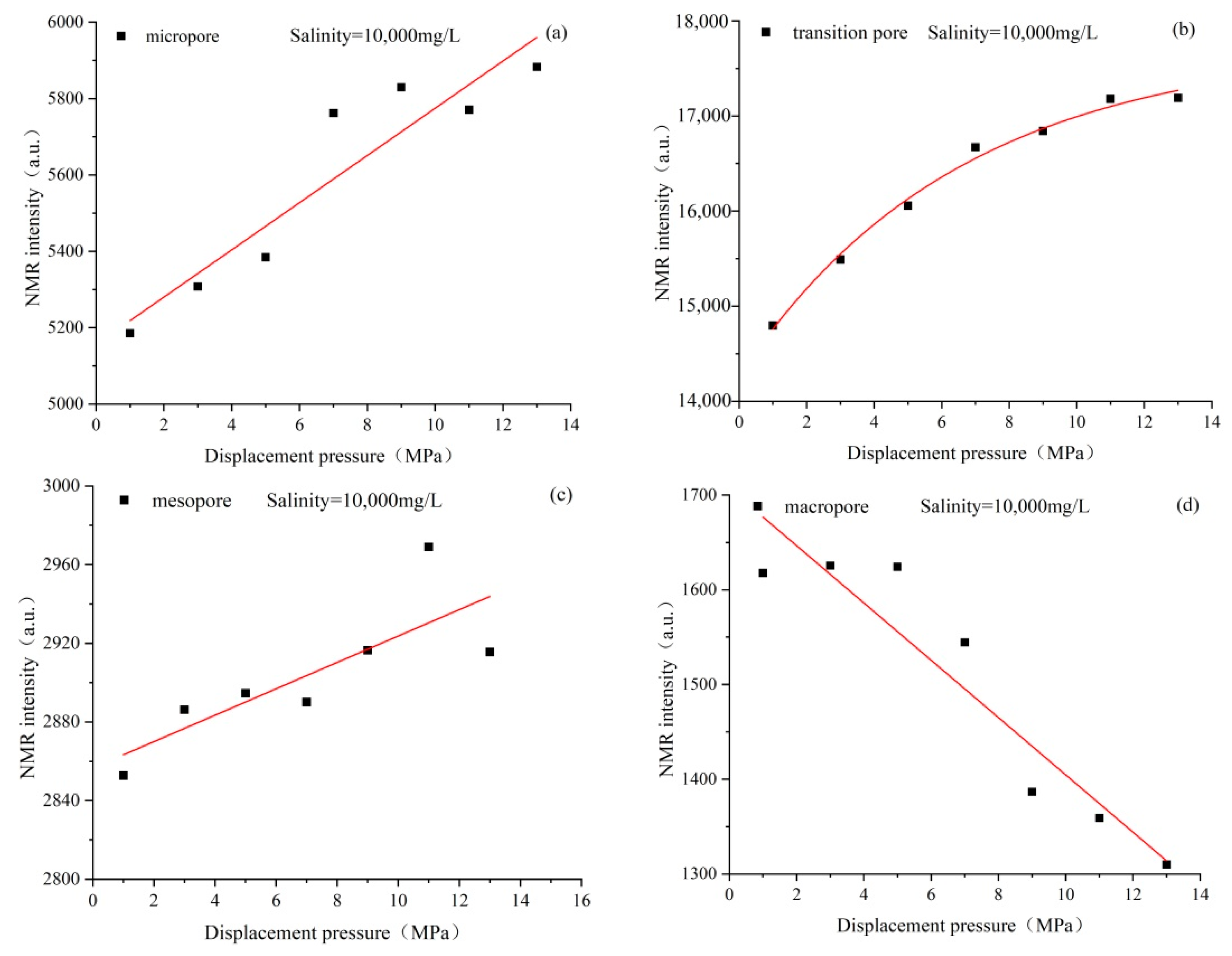
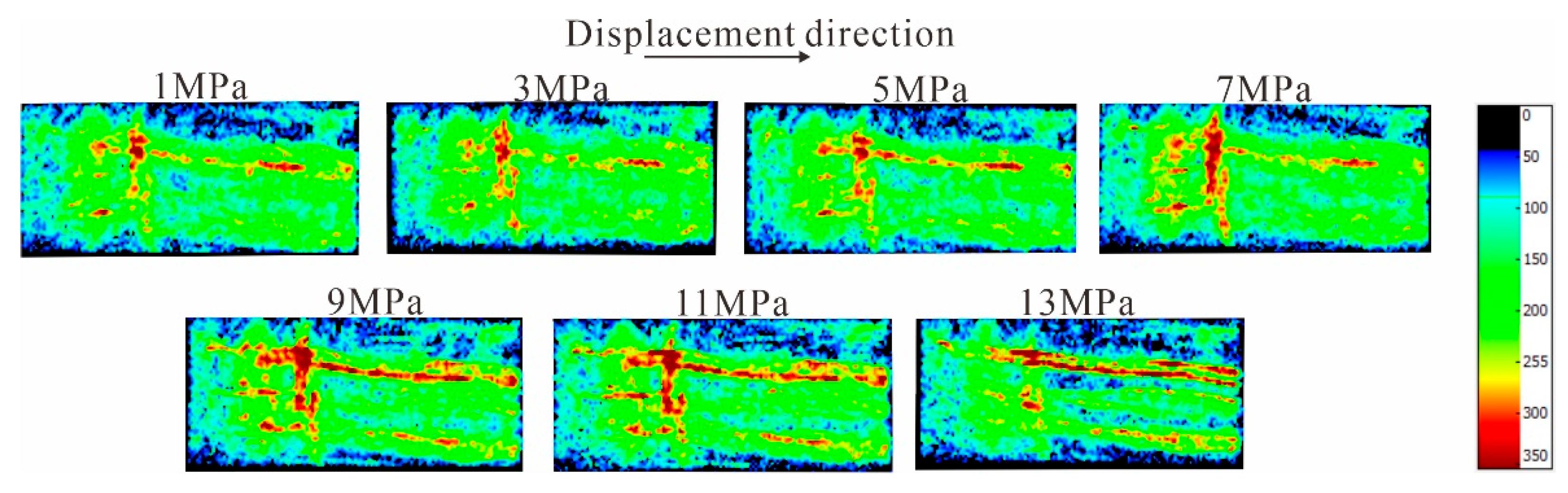
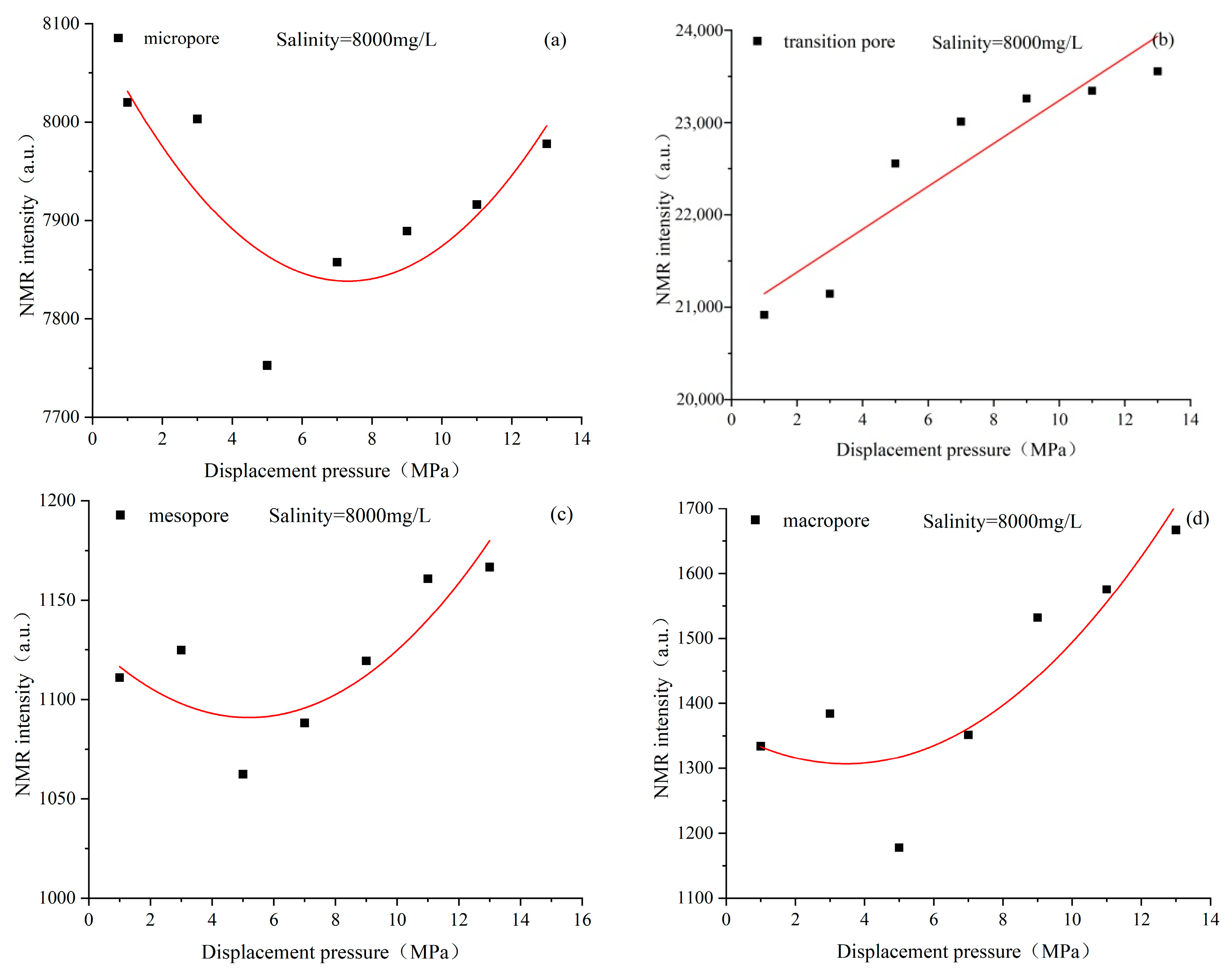
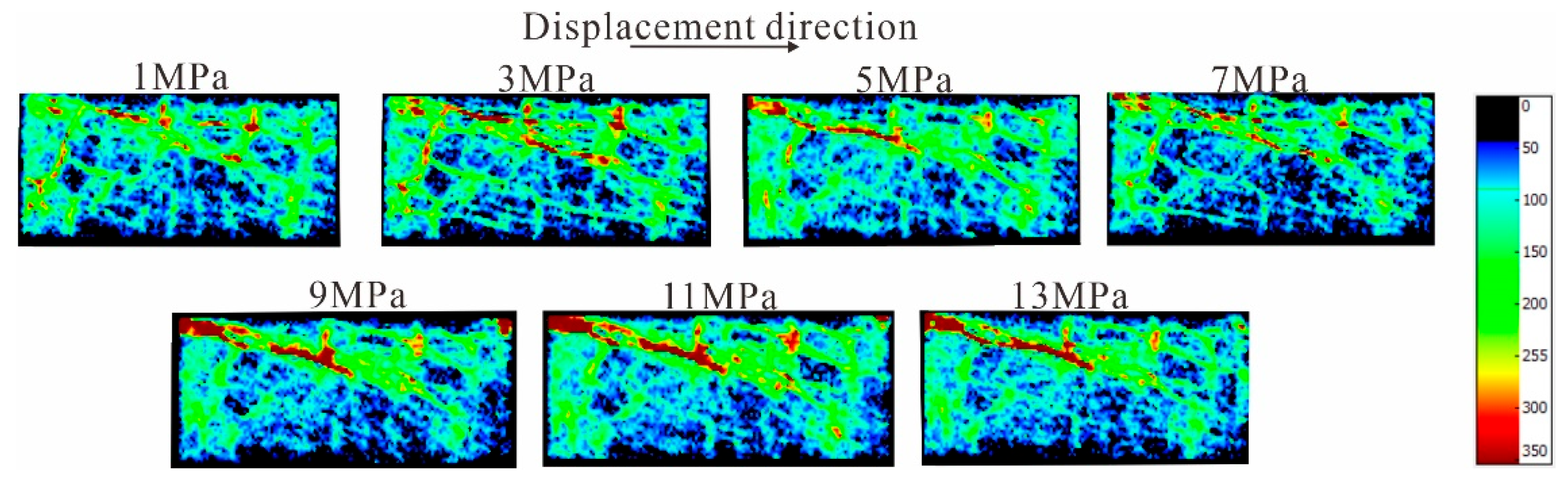
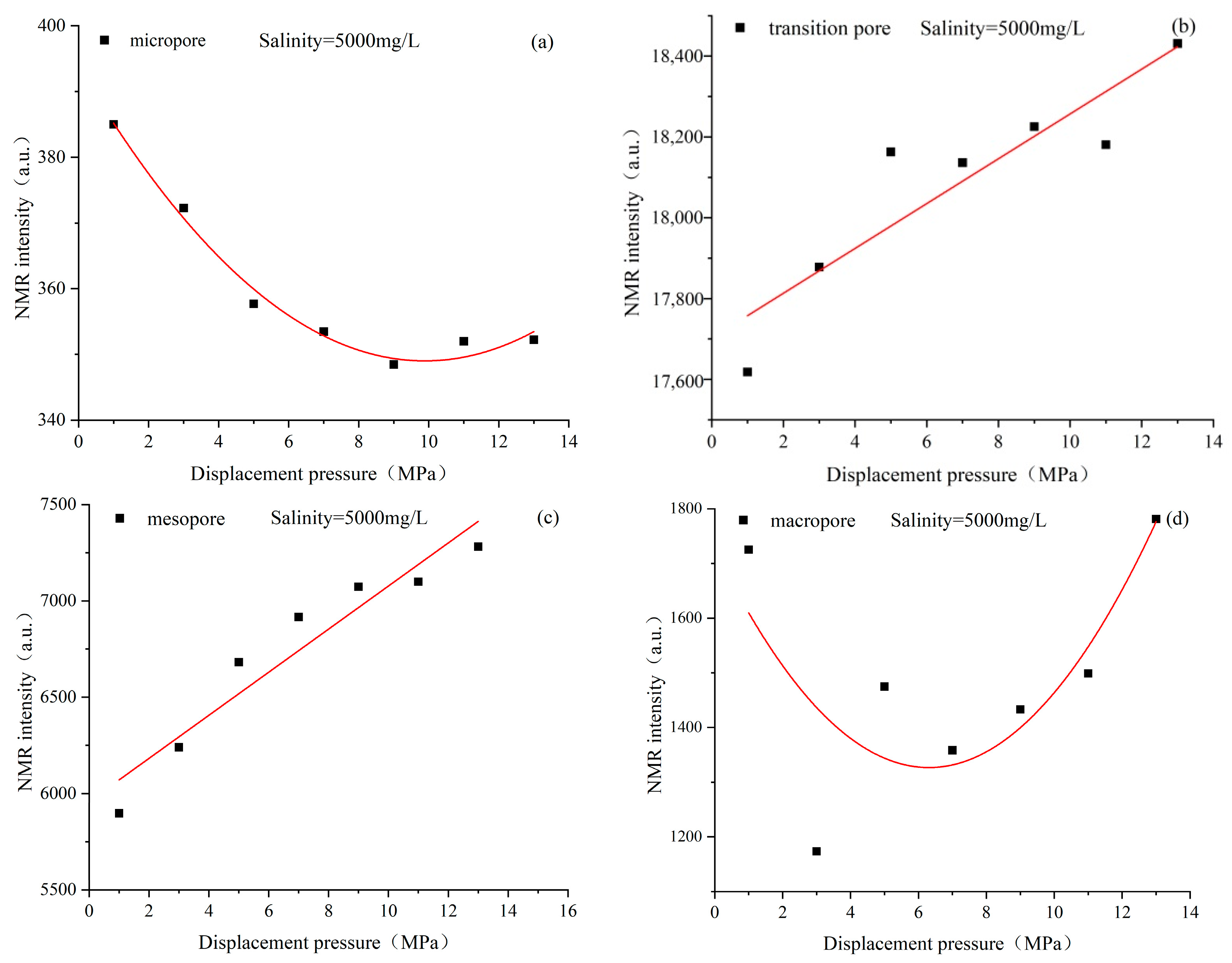
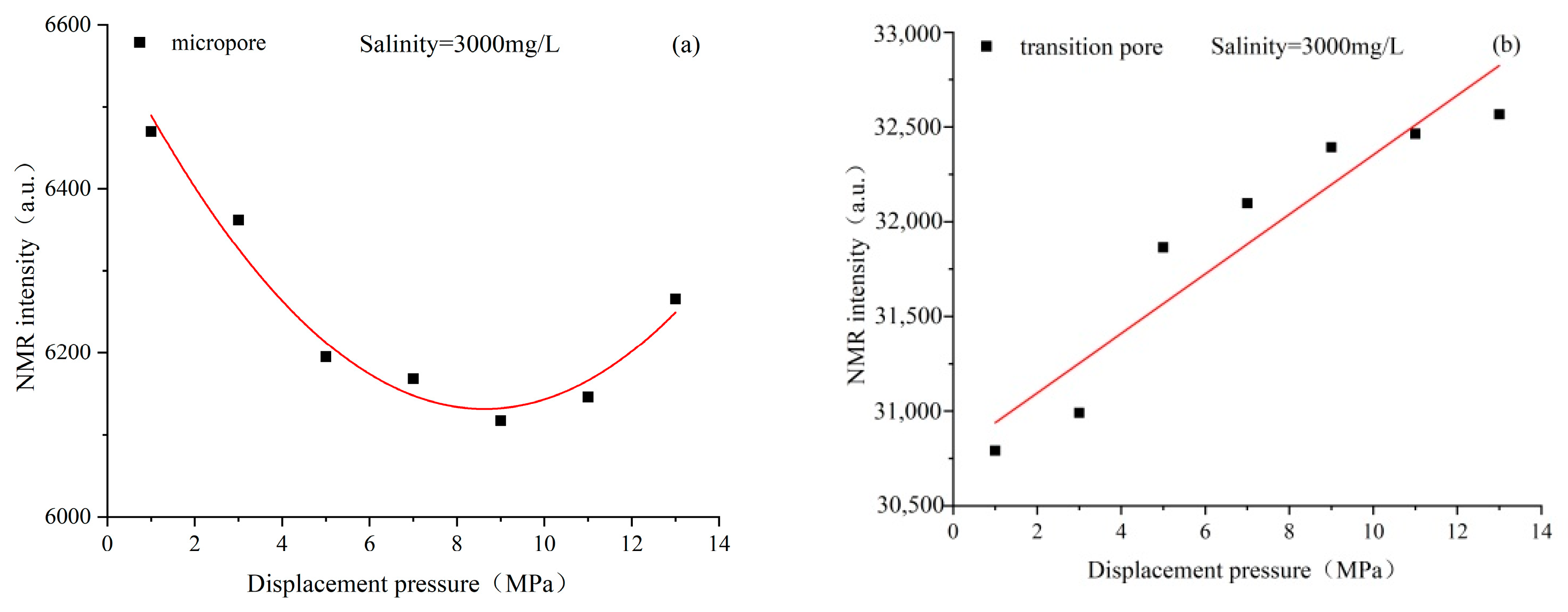
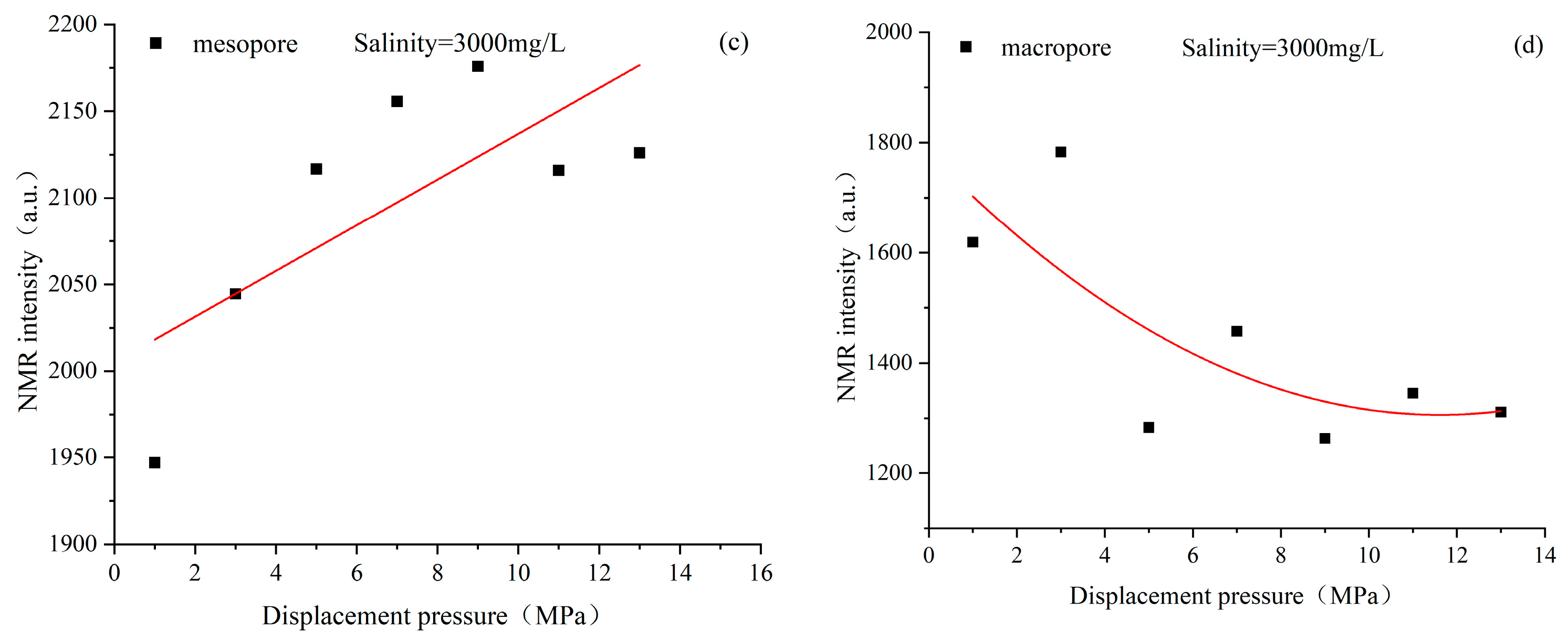
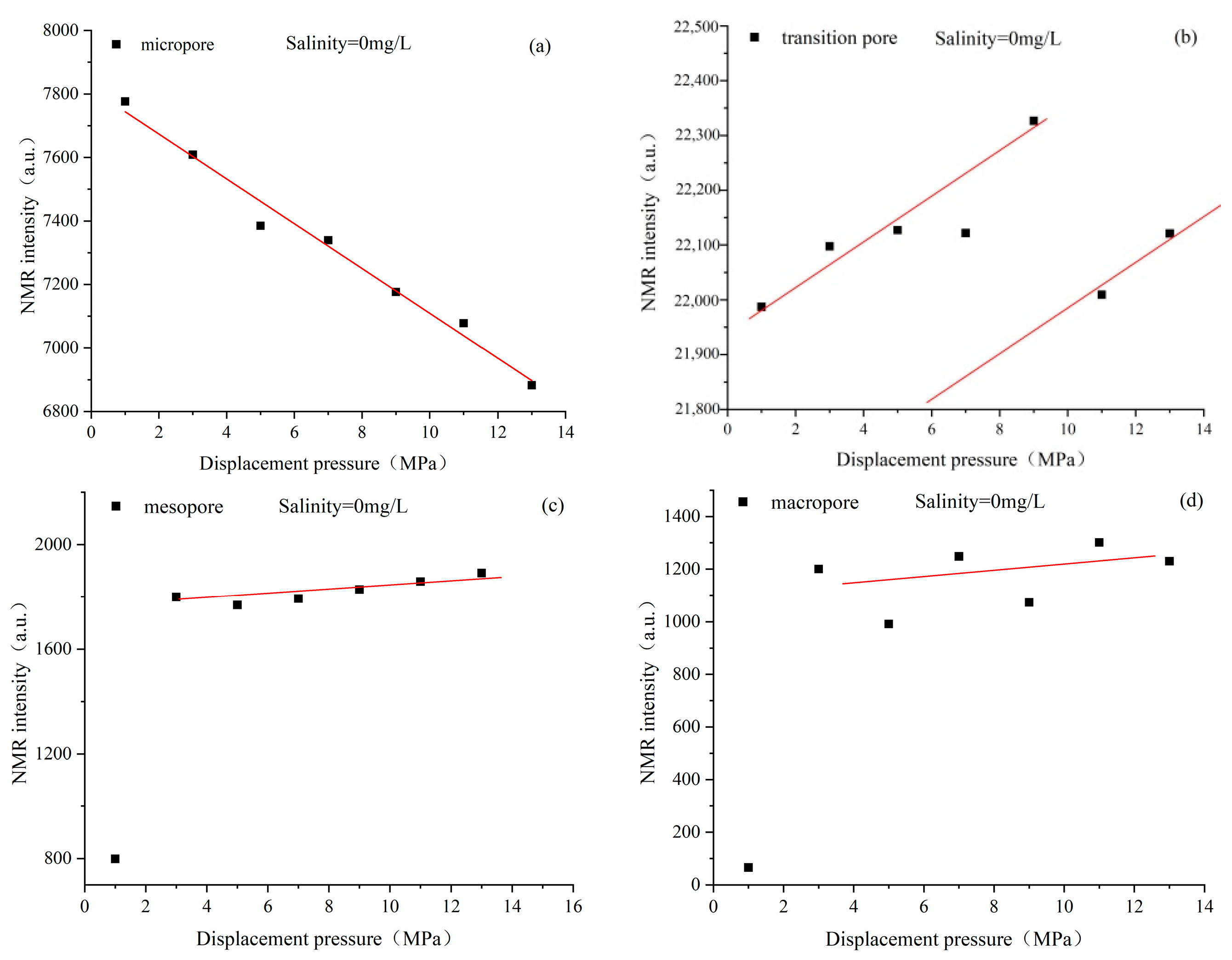
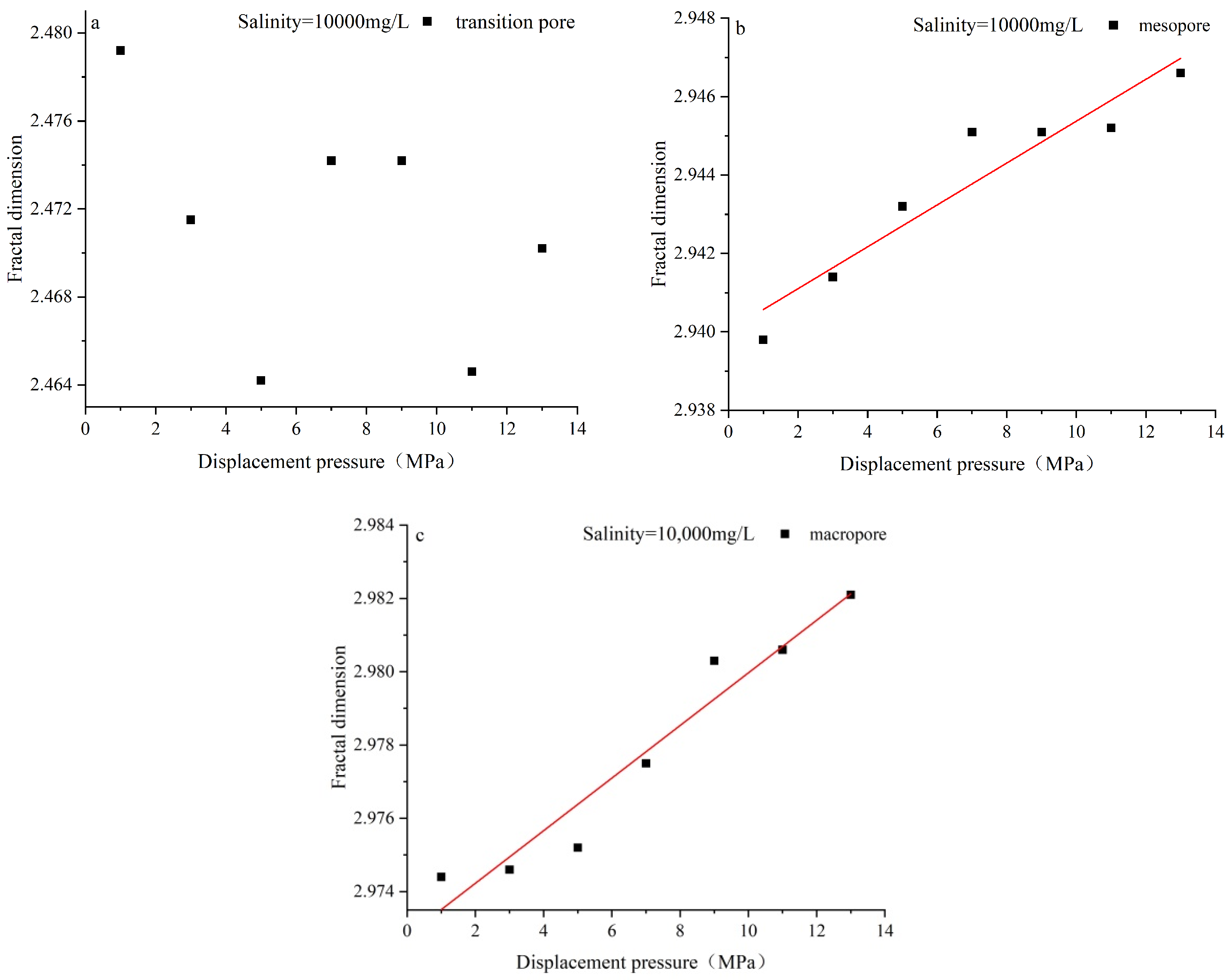
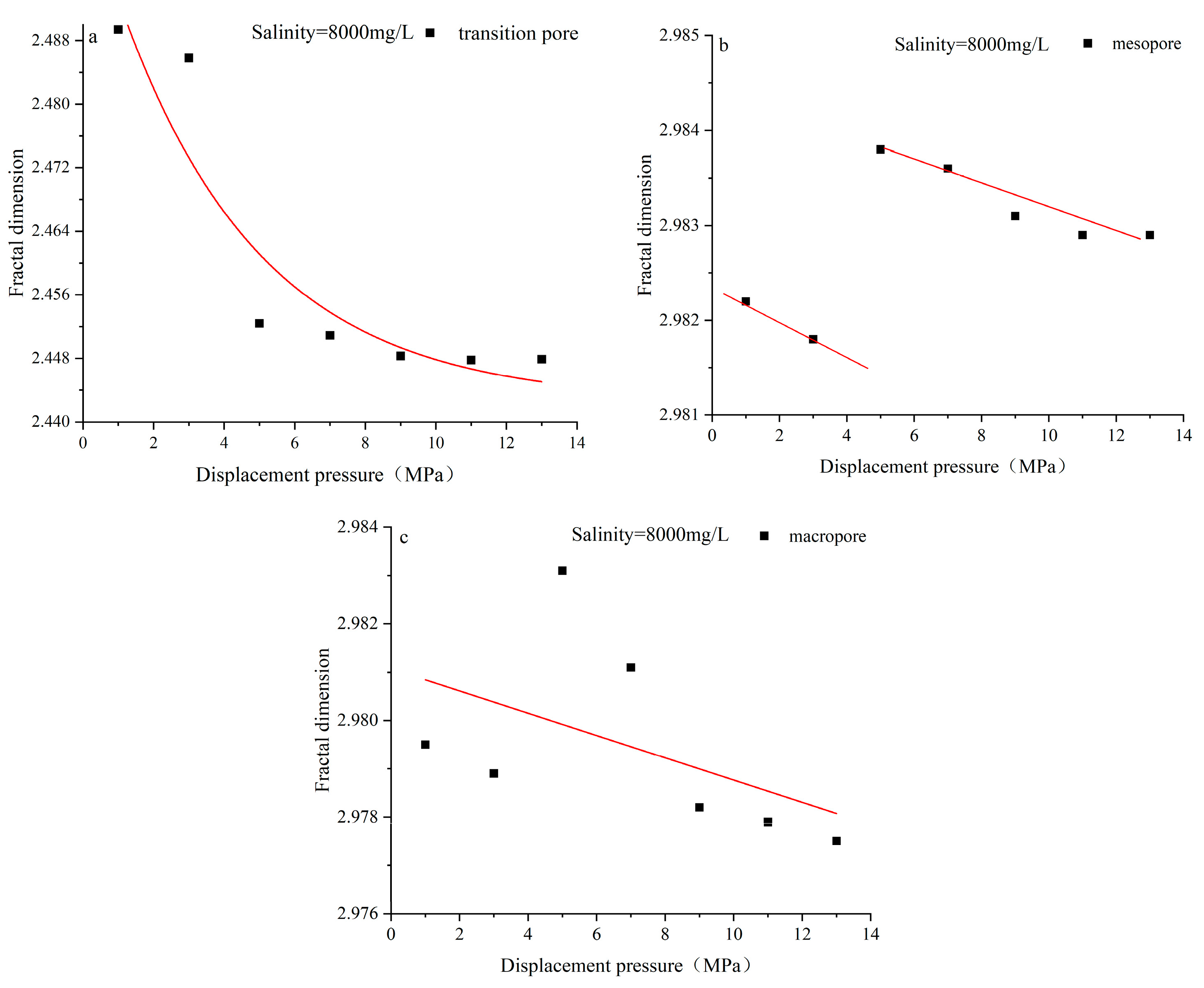
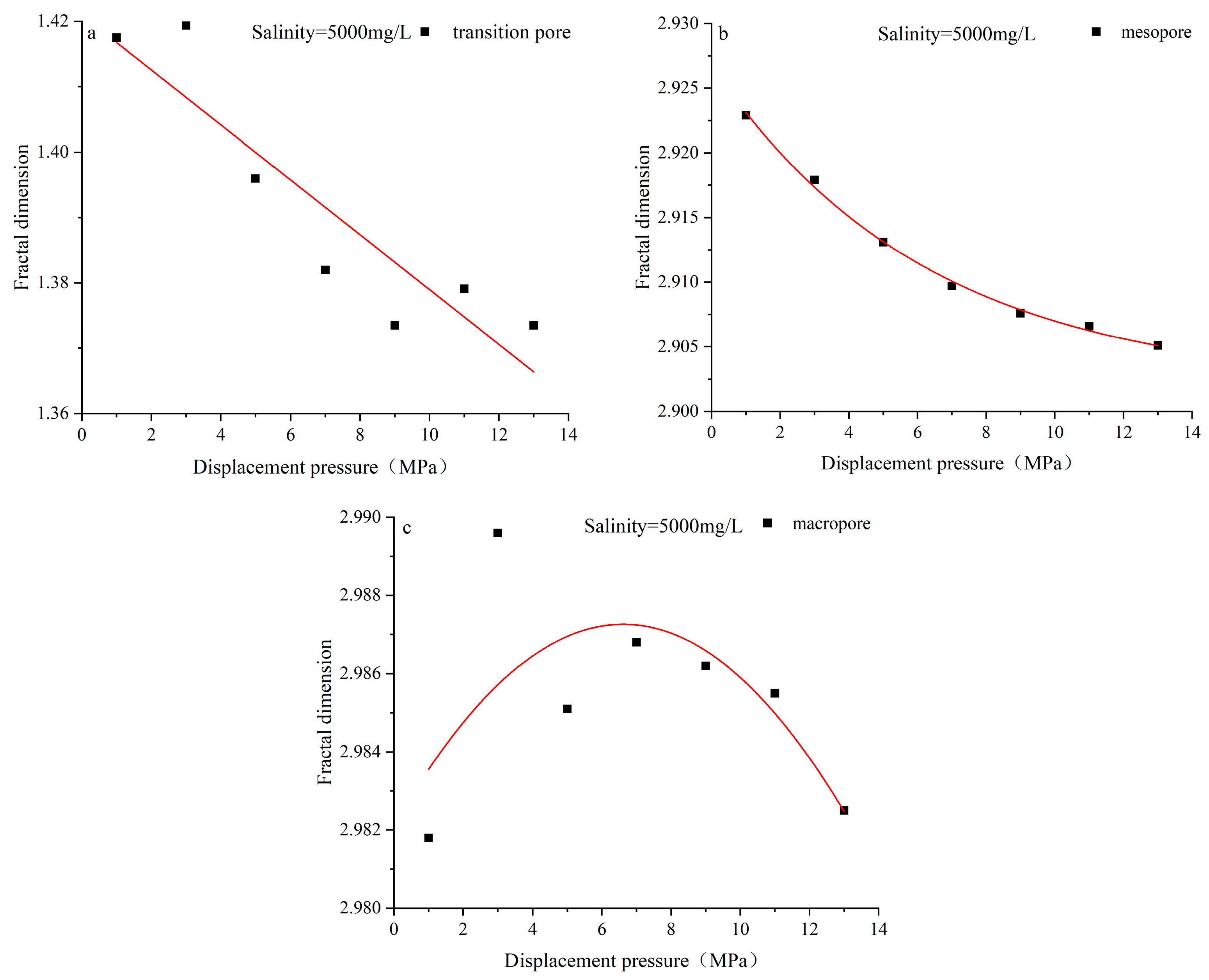
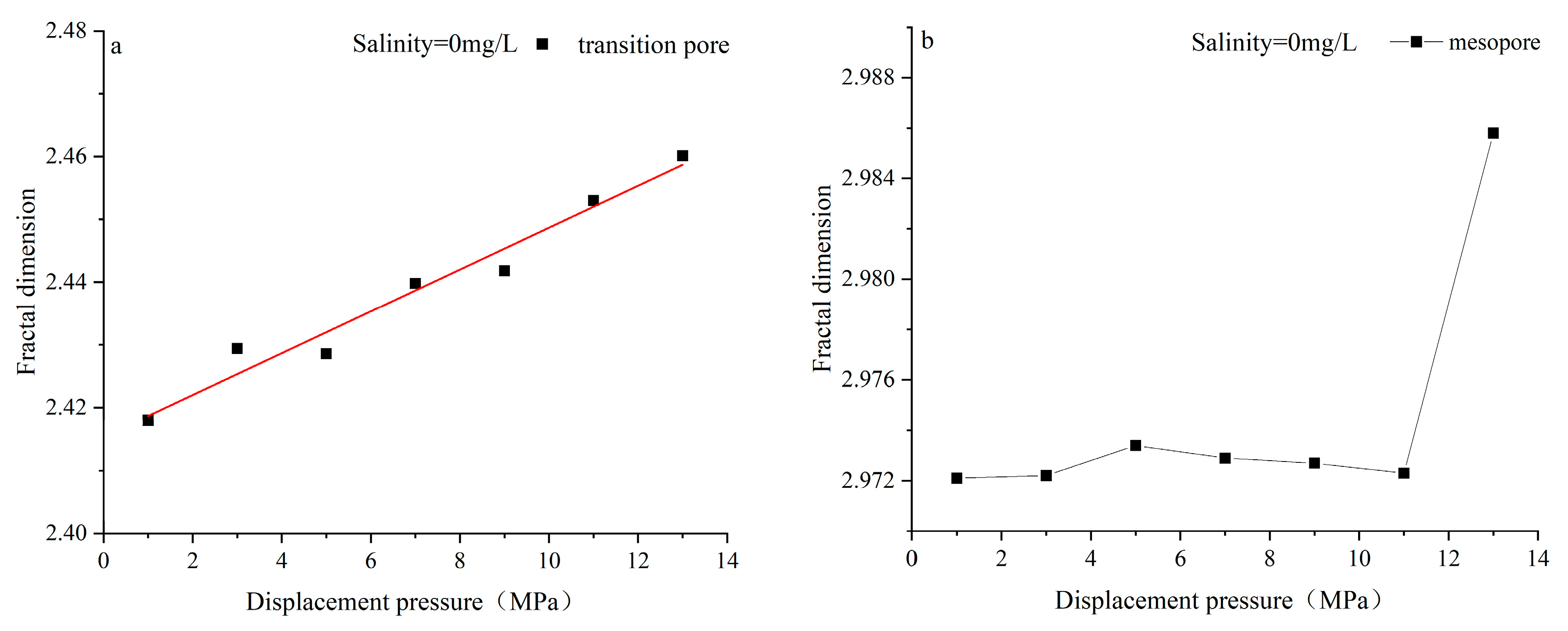
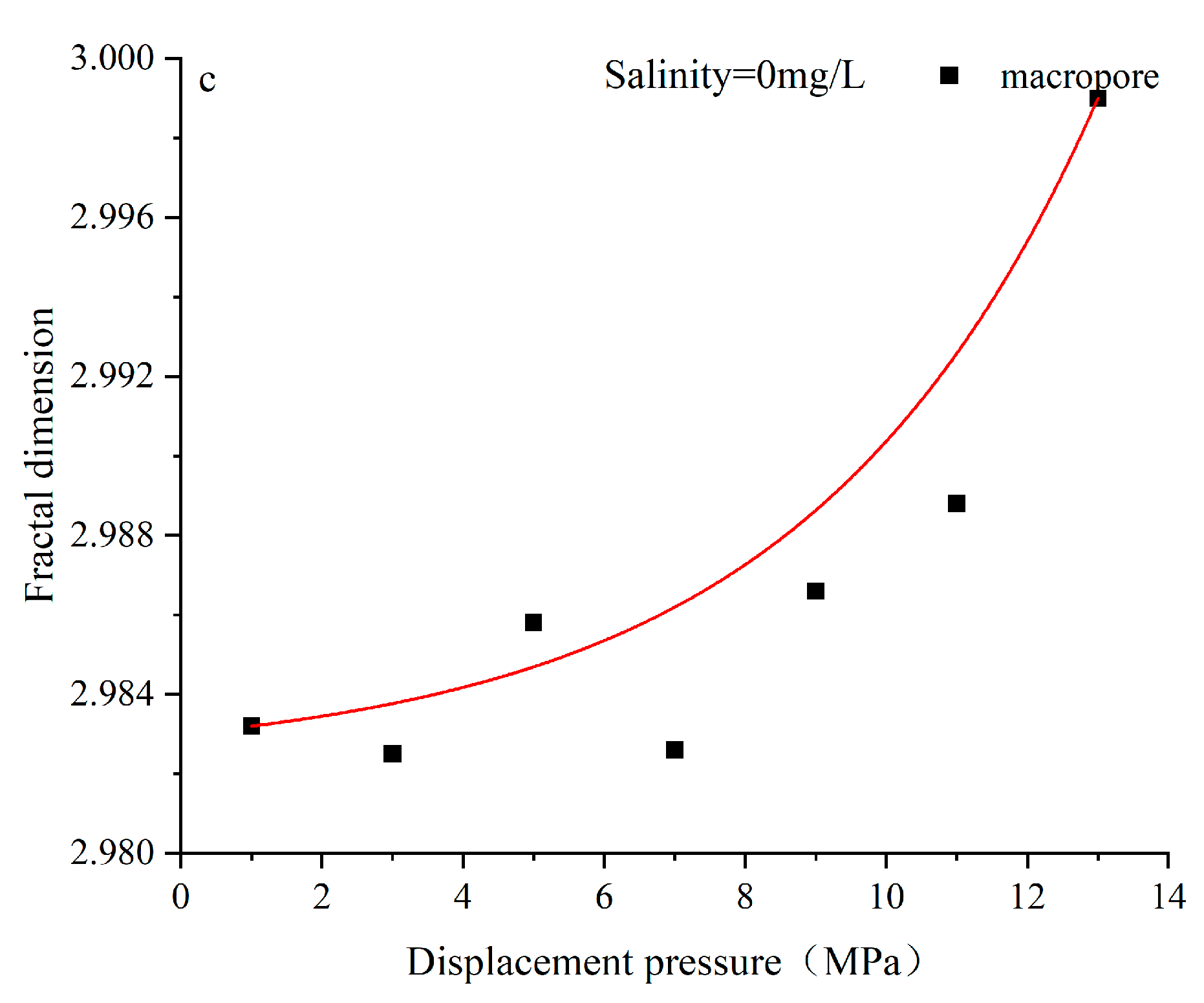
4.3. Characteristics of Pore Structure Changes in Coal Reservoirs under Different Fluid Conditions
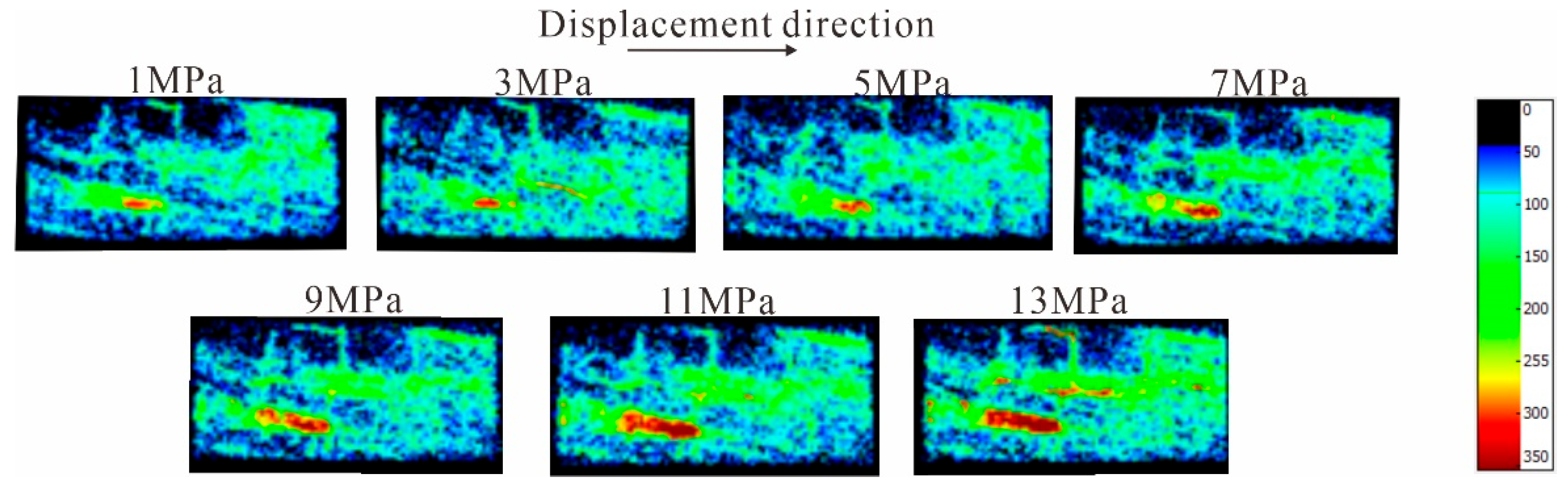
4.4. Response Mechanism of Coal Fine Migration-Induced Reservoir Damage under Different Fluid Action
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Zhang, A.; Yao, Z.; Xiong, X. The output mechanism and control measures of the pulverized coal in coalbed methane development. Coal Geol. Explor. 2018, 46, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, F.; Arif, M.; Iglauer, S.; Keshavarz, A. Coal fines migration: A holistic review of influencing factors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 301, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Cai, X. Experimental study on coal fines migration and effects on conductivity of hydraulic fracture during entire coalbed methane production period. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cao, D.; Wei, Y.; Rufford, T.E. Characterization of fines produced during drainage of coalbed methane reservoirs in the Linfen block, Ordos Basin. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2020, 38, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, F.; Ji, Y.; Peng, T. Characteristics of the Coal Fines Produced from Low-Rank Coal Reservoirs and Their Wettability and Settleability in the Binchang Area, South Ordos Basin, China. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 5560634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Hou, Q. Experimental research on stress sensitivity of coal reservoir and its influencing factors. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Cao, D.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X. Study on Influencing Factors of Coal Fines Produced by CBM Wells in Hancheng block, Shaanxi Province, China. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 295–298, 3228–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Li, R. Migration and control of coal powder in CBM well. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Magill, D.; Ramurthy, M.; Jordan, R.; Nguyen, P. Controlling coal-fines production in massively cavitated openhole coalbed-methane wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 18–20 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Massarotto, P.; Iyer, R.S.; Elma, M.; Nicholson, T. An experimental study on characterizing coal bed methane (CBM) fines production and migration of mineral matter in coal beds. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Vu, P.N.H.; Hussain, F. A laboratory study of the effect of creep and fines migration on coal permeability during single-phase flow. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 200, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.U.R.; Keshavarz, A.; Akhondzadeh, H.; Nosrati, A.; Al-Anssari, S.; Iglauer, S. Optimizing the dispersion of coal fines using sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 18–19 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Kang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, G.; Mao, D.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, T. Low coal rank coalbed methane accumulation model and exploration direction. Acta Pet. Sin. 2019, 40, 786–797. [Google Scholar]
- Badalyan, A.; Beasley, T.; Nguyen, D.; Keshavarz, A.; Schacht, U.; Carageorgos, T.; You, Z.; Bedrikovetsky, P.; Hurter, S.; Troth, I. Laboratory and mathematical modelling of fines production from CSG interburden rocks. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, 25–27 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Hamilton, C.; Ferbina, T.R.; Rudolph, V.; Rufford, T.E. Smart, porous polymer coatings to bind clay minerals in coal bed methane wells. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 14–16 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Cui, B.; Xiang, X. Effect of pulverized coal dispersant on coal in the CBM well-washing technology. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Kang, N.; Le-Hussain, F. An NMR-assisted laboratory investigation of coal fines migration in fracture proppants during single-phase water production. Fuel 2023, 343, 127926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Sang, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y. Characteristics and generation mechanisms of coal fines in coalbed methane wells in the southern Qinshui Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wu, X.; Han, G.; Li, C.; He, L.; Xiong, X.; Wang, S. Experimental investigation on particle transport of coal fines in unsteady terrain slug flow. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 166, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, A.; Xiang, X. New Progress on the Coal Fines Affecting the Development of Coalbed Methane. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. 2018, 92, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Experimental Method to Simulate Coal Fines Migration and Coal Fines Aggregation Prevention in the Hydraulic Fracture. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 101, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Chen, Z.; Aminossadati, S.; Pan, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Characterization of coal fines generation: A micro-scale investigation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, M.; Wang, L. An experimental study of the agglomeration of coal fines in suspensions: Inspiration for controlling fines in coal reservoirs. Fuel 2018, 211, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Chen, Z.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Rufford, T.E.; Li, L. Experimental investigation on the impact of coal fines generation and migration on coal permeability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Kang, Y.; You, Z.; You, L.; Xu, C. Critical conditions for massive fines detachment induced by single-phase flow in coalbed methane reservoirs: Modeling and experiments. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 6782–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Hao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Feng, G.; Li, G.; Guan, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Experimental study of the effects of fine retention on fracturing proppant permeability in coalbed methane reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 83, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hou, W.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, S.; et al. Coalbed methane reservoir description and enhanced recovery technologies in Baode block, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2023, 43, 96–112. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, S.; Meng, Q.; Kou, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Fluid velocity sensitivity of coal reservoir and its effect on coalbed methane well productivity: A case of Baode Block, northeastern Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 152, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Tao, S.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Ma, L. Mechanical behavior of low-rank bituminous coal under compression: An experimental and numerical study. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 66, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tian, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, S. Genesis of Coalbed Methane and Its Storage and Seepage Space in Baode Block, Eastern Ordos Basin. Energies 2022, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mao, J.; Lin, W.; Hao, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Exploration History and Enlightenment of Coalbed Methane in Baode Block. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2021, 42, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 8899-1998; Determination of Maceral Group Composition and Minerals in Coal. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1998; 8p. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 6948-1998; Microscopical Determination of the Reflectance of Vitrinite in Coal. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1998; 11p. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 212-2001; Proximate Analysis of Coal. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2001; 9p. (In Chinese)
- SY/T 6385-2016; Porosity and Permeability Measurement under Overburden Pressure. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016; 9p. (In Chinese)
- Yan, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Analysis of the Drainage and Production Effect of High Yield Water Wells in the Coalbed Methane Enrichment Area of Baode Block, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Indus. 2018, S1, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Wen, S.; Nei, Z.; Sun, W. Re-recognition of geological factors affecting coalbed methane development effect. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2020, 27, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T5358-2010; Formation Damage Evaluation via Flow Test. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010; 32p. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 42035-2022; Determination of Pore Size Distribution of Coal and Rock Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022; 13p. (In Chinese)
- Qin, L.; Zhai, C.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Dong, R. Fractal dimensions of low rank coal subjected to liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw based on nuclear magnetic resonance applied for coalbed methane recovery. Powder Technol. 2018, 325, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Ning, L.; Zhao, H.; Bi, J. Pore and fracture development in coal under stress conditions based on nuclear magnetic resonance and fractal theory. Fuel 2022, 309, 122112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Dong, C.; You, Z.; Shang, X. Detachment of coal fines deposited in proppant packs induced by single-phase water flow: Theoretical and experimental analyses. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2021, 239, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, A.; Cao, D. Physical simulation experiment of the effect of hydrochemical properties on the migration of coal fines in propped fractures. J. China Coal Soc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qin, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M. Experimental study on water sensitivity and salt sensitivity of lignite reservoir under different pH. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 172, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Peng, X.; Wang, P.; Zhao, N.; Chu, S.; Wang, X.; Kong, L. Water-sensitive damage mechanism and the injection water source optimization of low permeability sandy conglomerate reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Qu, R.; Li, Y.; Zheng, A.; Liu, T.; Dong, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, F.; She, Y.; Sun, S. Mechanism of microorganisms to relieve reservoir water sensitivity damage. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Dong, Z. Study on Fractal Characteristics of Pore Structure of Pyrolysis Coal by Nuclear Magnetic Resource Technology. Min. Res. Dev. 2021, 41, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Ling, K.; Wu, H.; Gao, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, M. An experimental study of coal-fines migration in Coalbed-methane production wells. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, D. Experimental Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fines Migration on Coal Core Water Flooding. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Cao, D.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Experimental analysis on the effect of tectonically deformed coal types on fines generation characteristics. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chequer, L.; Vaz, A.; Bedrikovetsky, P. Injectivity decline during low-salinity water flooding due to fines migration. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 1054–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Moghanloo, R. Analytical model of well injectivity improvement using nanofluid preflush. Fuel 2017, 202, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbrand, E.; Haugwitz, C.; Jacobsen, P.; Kjoller, C.; Fabricius, I. The effect of hot water injection on sandstone permeability. Geothermics 2014, 50, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, A.; Cao, D. Experiment on the Effect of Water with Different Hydrochemistry on the Coal Fines Aggregation. Coal Geol. China 2023, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, A.; Yang, Y.; Badalyan, A.; Johnson, R.; Bedrikovetsky, P. Laboratory-based mathematical modelling of graded proppant injection in CBM reservoirs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 136, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample Number | Salinity (mg/L) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Single Velocity Sensitive Experimental Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| BD-1-1 | 0 | 8 | Table 2 for details |
| BD-1-2 | 3000 | 8 | |
| BD-1-3 | 5000 | 8 | |
| BD-1-4 | 8000 | 8 | |
| BD-1-5 | 10,000 | 8 |
| Injection Pressure (MPa) | Confining Pressure (MPa) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Single Displacement Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.5 | 8 | Displace until the fluid state is nearly stable and connect 500 mL of the produced liquid with a measuring cylinder. |
| 3 | 9.5 | 8 | |
| 5 | 10.5 | 8 | |
| 7 | 11.5 | 8 | |
| 9 | 12.5 | 8 | |
| 11 | 13.5 | 8 | |
| 13 | 14.5 | 8 |
| Industry analysis and Ro,max test | Mad (%) | Ad (%) | Vdaf (%) | FCd (%) | Ro (%) |
| 1.98 | 9.65 | 35.59 | 59.62 | 0.68 | |
| Maceral with mineral matter | Vitrinite (%) | Inertinite (%) | Liptinite (%) | Mineral matter (%) | |
| 56.2 | 30.5 | 2.5 | 10.8 | ||
| Sample Number | Length (cm) | Diameter (cm) | Porosity (%) | Permeability (mD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD-1-1 | 5.031 | 2.575 | 5.353 | 0.45929 |
| BD-1-2 | 5.104 | 2.479 | 6.343 | 0.33752 |
| BD-1-3 | 5.025 | 2.585 | 6.082 | 0.41539 |
| BD-1-4 | 5.031 | 2.457 | 4.333 | 0.30313 |
| BD-1-5 | 5.115 | 2.543 | 3.195 | 0.31189 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, L. Response and Mechanism of Coal Fine Production to Differential Fluid Action in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin. Processes 2023, 11, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082476
Wang B, Cui Y, Li J, Zhang J, Bai L, Wang L. Response and Mechanism of Coal Fine Production to Differential Fluid Action in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin. Processes. 2023; 11(8):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082476
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Boyang, Yunfei Cui, Jingjing Li, Junjian Zhang, Longhui Bai, and Liu Wang. 2023. "Response and Mechanism of Coal Fine Production to Differential Fluid Action in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin" Processes 11, no. 8: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082476
APA StyleWang, B., Cui, Y., Li, J., Zhang, J., Bai, L., & Wang, L. (2023). Response and Mechanism of Coal Fine Production to Differential Fluid Action in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin. Processes, 11(8), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082476






