The Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration: A Journey through Electrospun Composites Integrated with Organic and Inorganic Additives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bone Regeneration Techniques
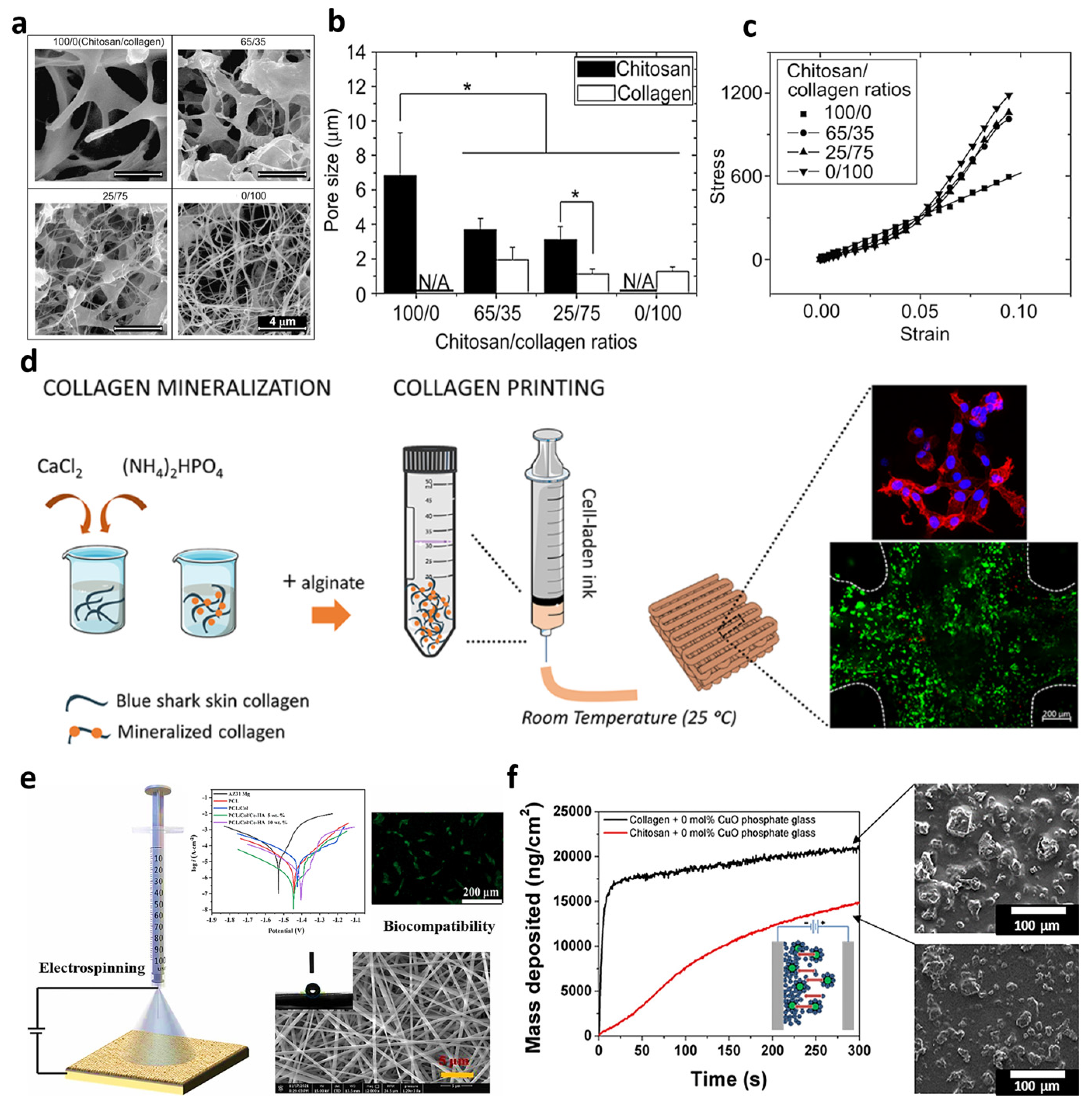
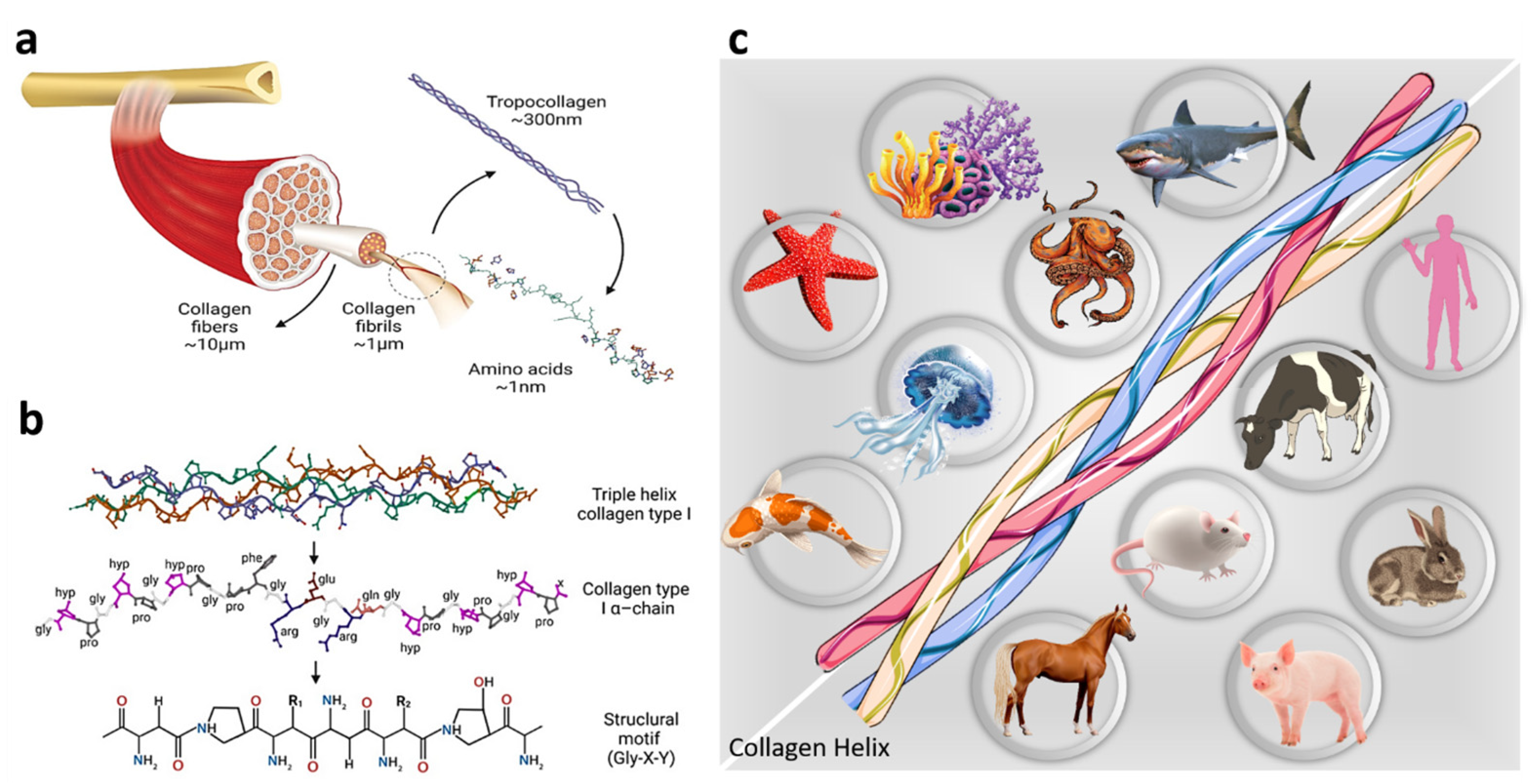
3. Collagen Resources and Electrospun Fiber Formations
4. Collagen-Based Nanofibrous Bone Scaffolds
4.1. Raw Electrospun Collagen Fibers
4.2. Integrated Collagen-Based Electrospun Composites with Organic Materials
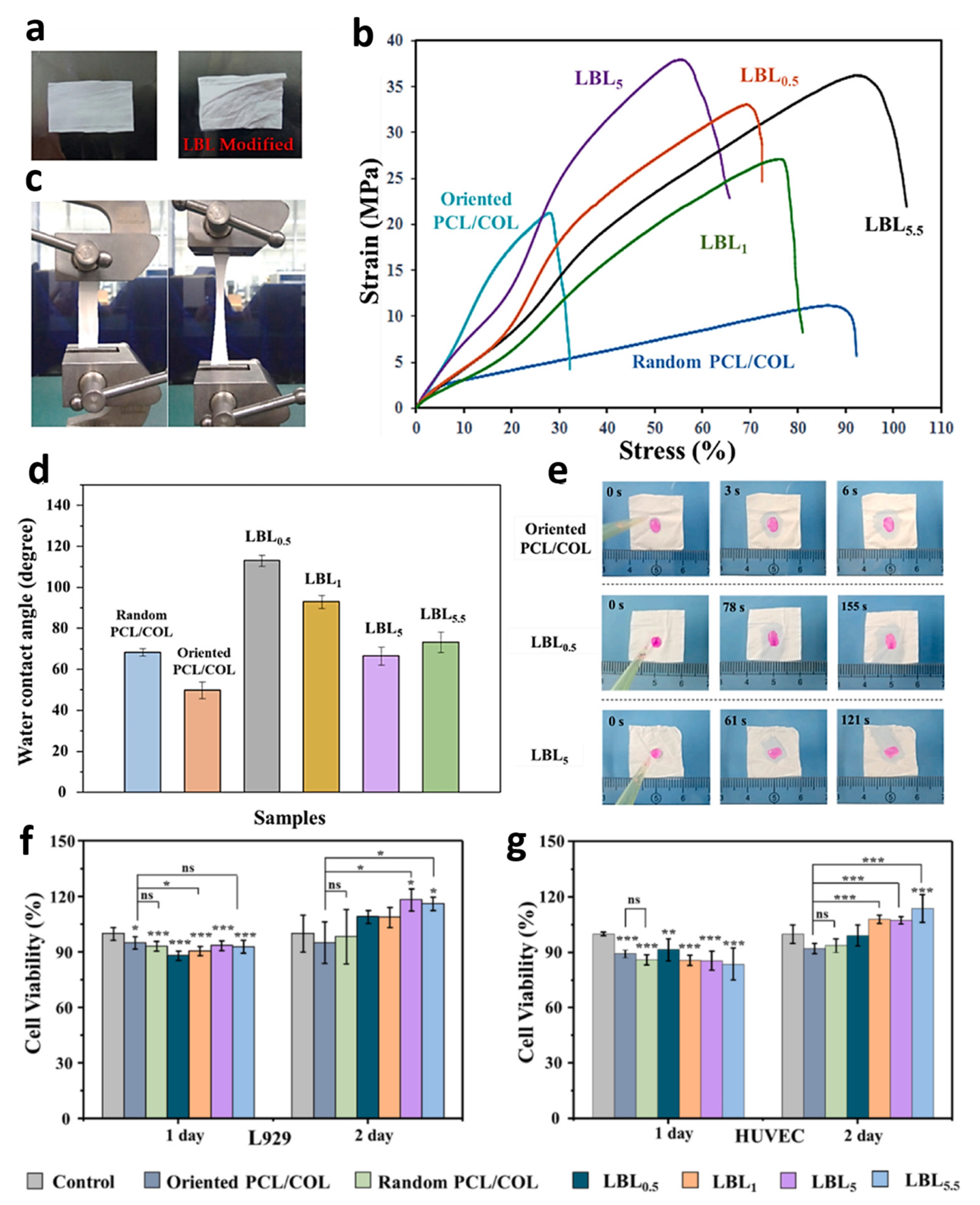
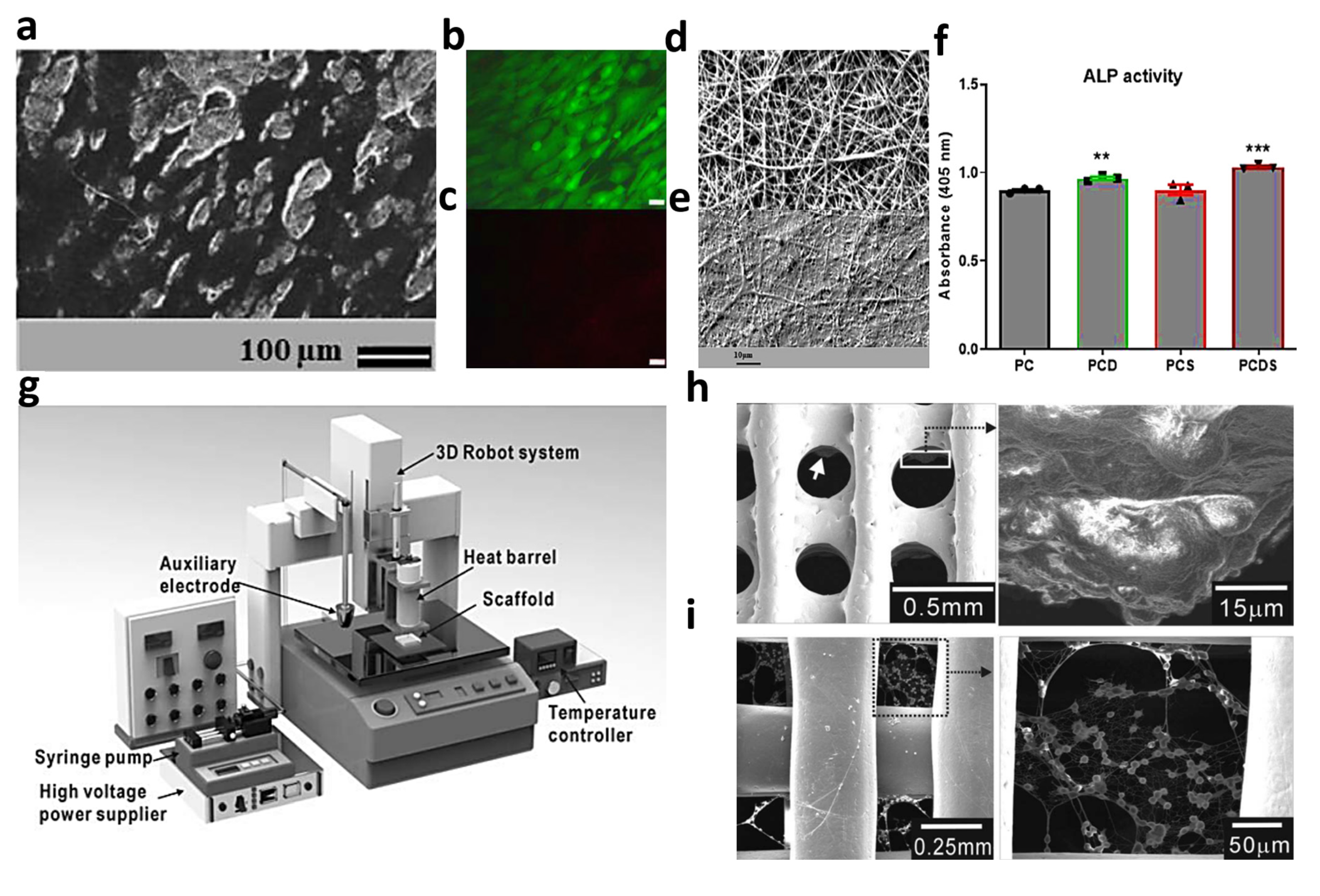
4.3. Electrospun Collagen-Based Fibers Embedded with Inorganic Materials
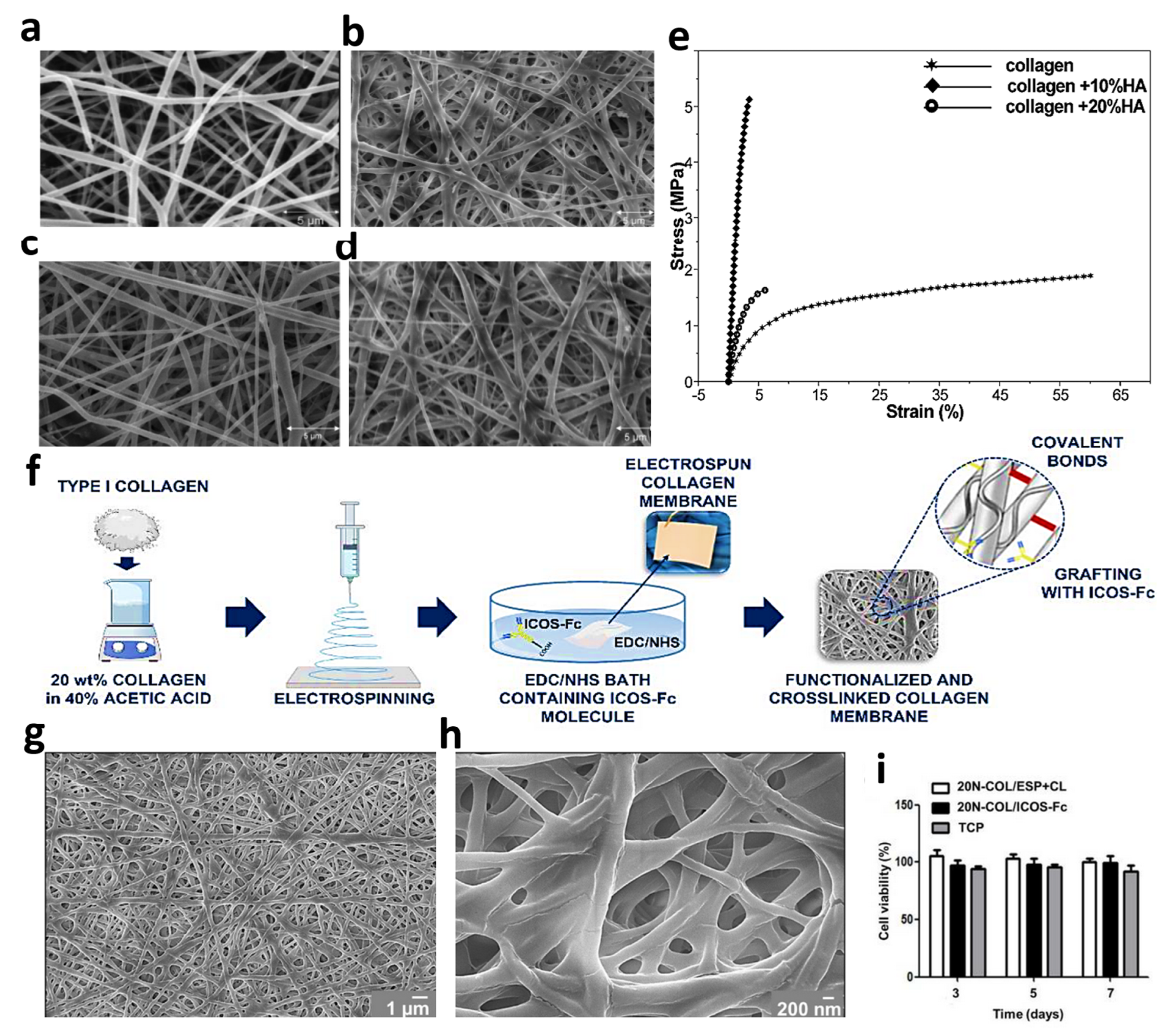
4.4. Electrospun Collagen-Based Composites with Both Organic and Inorganic Materials
5. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y. Collagen tissue engineering: Development of novel biomaterials and applications. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. New approaches and recent results concerning human-tissue collagen synthesis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratzl, P. Collagen: Structure and mechanics, an introduction. In Collagen; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Liu, L. The role of collagen in cancer: From bench to bedside. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterlaken, B.M.; Vena, M.P.; de With, G. In vitro mineralization of collagen. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banitaba, S.N.; Ebadi, S.V.; Salimi, P.; Bagheri, A.; Gupta, A.; Arifeen, W.U.; Chaudhary, V.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kaushik, A.; Mostafavi, E. Biopolymer-based electrospun fibers in electrochemical devices: Versatile platform for energy, environment, and health monitoring. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 2914–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Nourbakhsh, N.; Akbari Kenari, M.; Zare, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Collagen-based biomaterials for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neela, S.; Bandigari, P.; Mayuri, K. Collagen—A Review. YMER 2022, 21, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasari, M.; Poursharifi, N.; Fakhrali, A.; Banitaba, S.N.; Mohammadi, S.; Semnani, D. Fabrication of novel PCL/PGS fibrous scaffold containing HA and GO through simultaneous electrospinning-electrospray technique. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademolqorani, S.; Tavanai, H.; Chronakis, I.; Boisen, A.; Ajalloueian, F. The determinant role of fabrication technique in final characteristics of scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: A focus on silk fibroin-based scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Stegemann, J.P. Thermogelling chitosan and collagen composite hydrogels initiated with β-glycerophosphate for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, G.S.; Marques, C.F.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Cell-laden biomimetically mineralized shark-skin-collagen-based 3D printed hydrogels for the engineering of hard tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3664–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Ying, H.; Yang, W. Electrospinning polycaprolactone/collagen fiber coatings for enhancing the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of AZ31 Mg alloys. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 662, 131041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, I.; Selopal, G.S.; Wang, Z.M.; Rosei, F. Electrophoretic deposition of collagen/chitosan films with copper-doped phosphate glasses for orthopaedic implants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Khan, R.H.; Suman, R. 3D printing applications in bone tissue engineering. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, S118–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Heo, S.-Y.; Oh, G.-W.; Yi, M.; Jung, W.-K. A 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone/Marine Collagen Scaffold Reinforced with Carbonated Hydroxyapatite from Fish Bones for Bone Regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lau, C.-S.; Liang, K.; Wen, F.; Teoh, S.H. Marine collagen scaffolds in tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, C.; Ong, S.T.; Dwivedi, N.; Diaz, S.M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Navaneethan, B.; Fazil, M.H.; Liu, S.; Seitz, V.; Wintermantel, E. Bio-inspired in situ crosslinking and mineralization of electrospun collagen scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademolqorani, S.; Banitaba, N. Application of Electrosprayed Nanoparticles as Targeted Drug Delivery Systems: A Mini Review. J. Appl. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2022, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, B.N.; Gallentine, S.C.; Powell, H.M. Collagen-based electrospun materials for tissue engineering: A systematic review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sionkowska, A.; Skrzyński, S.; Śmiechowski, K.; Kołodziejczak, A. The review of versatile application of collagen. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, Z.; Stylios, G.K. Spinnability of collagen as a biomimetic material: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila Rodríguez, M.I.; Rodríguez Barroso, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, D.T.; Keene, D.R.; Atha, T.; Huang, Y.; Lipman, K.; Li, W.; Chen, M. Injection of recombinant human type VII collagen restores collagen function in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.L.; Hiller, J.; Haston, J.L.; Holmes, D.F.; Kadler, K.E.; Murdoch, A.; Meakin, J.R.; Wess, T.J. Analysis of collagen fibril diameter distribution in connective tissues using small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2005, 1722, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bella, J. A new method for describing the helical conformation of collagen: Dependence of the triple helical twist on amino acid sequence. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 170, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A. Collagen: The organic matrix of bone. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 304, 455–477. [Google Scholar]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.D.; John, A. Collagen: Animal sources and biomedical application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsworth, L.; DeLustro, F.; Brennan, J.; Sawamura, S.; McPherson, J. The human immune response to reconstituted bovine collagen. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herford, A.S.; Akin, L.; Cicciu, M.; Maiorana, C.; Boyne, P.J. Use of a porcine collagen matrix as an alternative to autogenous tissue for grafting oral soft tissue defects. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirrah, I.N.; Lokanathan, Y.; Zulkiflee, I.; Wee, M.M.R.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. A comprehensive review on collagen type I development of biomaterials for tissue engineering: From biosynthesis to bioscaffold. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lew, J.; Premkumar, J.; Poh, C.L.; Win Naing, M. Production of recombinant collagen: State of the art and challenges. Eng. Biol. 2017, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhter, A.B.; Fayzullin, A.L.; Vukolova, M.N.; Rudenko, T.G.; Osipycheva, V.D.; Litvitsky, P.F. Medical applications of collagen and collagen-based materials. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Feng, Q.; Hu, K.; Cui, F. Three-dimensional fibroin/collagen scaffolds derived from aqueous solution and the use for HepG2 culture. Polymer 2005, 46, 12662–12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, C.A.; Olivas-Armendariz, I.; Castro-Carmona, J.S.; García-Casillas, P.E. Scaffolds for tissue engineering via thermally induced phase separation. Adv. Regen. Med. 2011, 35, 275–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, C.J.; Reucroft, I.M.; Grota, M.C.; Shreiber, D.I. Production of highly aligned collagen scaffolds by freeze-drying of self-assembled, fibrillar collagen gels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzana, J.A.; Olvera, D.; Fuller, S.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Graeve, O.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H.A. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, E.D.; Matthews, J.A.; Pawlowski, K.J.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning collagen and elastin: Preliminary vascular tissue engineering. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2004, 9, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meamar, R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Norouzi, M.-R.; Siavash, M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Fesharaki, M. Improved wound healing of diabetic foot ulcers using human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in gelatin electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds plus a platelet-rich plasma gel: A randomized clinical trial. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, M.-R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Itel, F.; Schoeller, J.; Fashandi, H.; Borzi, A.; Neels, A.; Fortunato, G.; Rossi, R.M. Emulsion electrospinning of sodium alginate/poly (ε-caprolactone) core/shell nanofibers for biomedical applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2929–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Mollahosseini, H.; Ajalloueian, F.; Masoudi Rad, M.; Norouzi, M.R.; Sami Jokandan, M.; Khoddami, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Immobilization of silk fibroin on the surface of PCL nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, C.M.; Haugh, M.G.; Liedl, J.; Mulcahy, F.; Hayes, B.; O’Brien, F.J. The effects of collagen concentration and crosslink density on the biological, structural and mechanical properties of collagen-GAG scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.; Moldovan, L.; Constantin, D.; Stanciuc, A.; Boeti, P.S.; Efrimescu, I. Collagen–based scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. J. Med. Life 2011, 4, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Haugh, M.G.; Jaasma, M.J.; O’Brien, F.J. The effect of dehydrothermal treatment on the mechanical and structural properties of collagen-GAG scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2009, 89, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, L.-M.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Xu, N.-W.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Han, H.; Han, L. The effect of different cross-linking conditions of EDC/NHS on type II collagen scaffolds: An in vitro evaluation. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019, 20, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, J.; Sionkowska, A. Effects of different crosslinking methods on the properties of collagen–calcium phosphate composite materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Nagapudi, K.; Apkarian, R.P.; Chaikof, E.L. Engineered collagen–PEO nanofibers and fabrics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mondrinos, M.J.; Gandhi, M.R.; Ko, F.K.; Weiss, A.S.; Lelkes, P.I. Electrospun protein fibers as matrices for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5999–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakuda, Y.; Nishimoto, S.; Suye, S.-I.; Fujita, S. Native collagen hydrogel nanofibres with anisotropic structure using core-shell electrospinning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, K.S.; Jeong, L.; Lee, G.; Seo, B.-M.; Park, Y.J.; Hong, S.-D.; Roh, S.; Cho, J.J.; Park, W.H.; Min, B.-M. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers: Effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulnik, J.; Denis, P.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Kołbuk, D.; Choińska, E. Biodegradation of bicomponent PCL/gelatin and PCL/collagen nanofibers electrospun from alternative solvent system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Arnoult, O.; Smith, M.E.; Wnek, G.E. Electrospinning of collagen nanofiber scaffolds from benign solvents. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Teng, W.K.; Chan, B.P.; Chew, S.Y. Photochemical crosslinked electrospun collagen nanofibers: Synthesis, characterization and neural stem cell interactions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 95, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Roether, J.A.; Schubert, D.W.; Beier, J.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bi-layered porous constructs of PCL-coated 45S5 bioactive glass and electrospun collagen-PCL fibers. J. Porous Mater. 2015, 22, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.R.V.; Chen, C.N.; Tsai, S.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Lee, O.K. Growth of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Electrospun Type I Collagen Nanofibers. Stem. Cells 2006, 24, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.S.; Ayres, C.E.; Bowman, J.R.; Telemeco, T.A.; Sell, S.A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Simpson, D.G. Electrospun Collagen: A Tissue Engineering Scaffold with Unique Functional Properties in a Wide Variety of Applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 348268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.P.; Pemble IV, C.W.; Brand, D.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Cross-linking electrospun type II collagen tissue engineering scaffolds with carbodiimide in ethanol. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Stadler, F.J.; Yang, X.; Deng, F.; Liu, G.; Xia, H. HA-coated collagen nanofibers for urethral regeneration via in situ polarization of M2 macrophages. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.L.; McCoy, M.G.; Grant, S.A. Electrospinning collagen and hyaluronic acid nanofiber meshes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Jia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Gu, G.; Chen, Z. Hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide-collagen mineralized product and aligned nanofibers with enhanced vascularization properties in bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniasadi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Alginate-collagen fibril composite hydrogel. Materials 2015, 8, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-j.; Ahn, S.-H.; Kim, G.H. Three-Dimensional Collagen/Alginate Hybrid Scaffolds Functionalized with a Drug Delivery System (DDS) for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Park, H.N.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Ku, Y.; Rhyu, I.C.; Han, S.B. Biological evaluation of chitosan nanofiber membrane for guided bone regeneration. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Zheng, H.; Du, Y.; Xiang, W.; Deng, H. Applications of chitin and chitosan nanofibers in bone regenerative engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, G.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Mofid, R.; Abbas, F.M.; Ghanavati, F.; Baghban, A.A.; Yavari, S.K.; Pajoumshariati, S. Biological evaluation (in vitro and in vivo) of bilayered collagenous coated (nano electrospun and solid wall) chitosan membrane for periodontal guided bone regeneration. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; He, L.; Yang, R.; Chen, B.; Xie, X.; Jiang, B.; Weidong, T.; Ding, Y. Enhanced effects of electrospun collagen-chitosan nanofiber membranes on guided bone regeneration. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Dai, F.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, H. Chitosan and collagen layer-by-layer assembly modified oriented nanofibers and their biological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, S.; Nivedhitha Sundaram, M.; Deepti Kadavan, J.; Jayakumar, R. Layered chitosan-collagen hydrogel/aligned PLLA nanofiber construct for flexor tendon regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Samimi, A.; Khorram, M.; Abdi, M.M.; Golestaneh, S.I. Fabrication and characterization of conductive polypyrrole/chitosan/collagen electrospun nanofiber scaffold for tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, H.A.; Varghese, J.F.; Dhimmar, B.; Yadav, U.C.S.; Vasita, R. Polycaprolactone-collagen nanofibers loaded with dexamethasone and simvastatin as an osteoinductive and immunocompatible scaffold for bone regeneration applications. Biomater. Biosyst. 2022, 8, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yeo, M.; Ahn, S.; Kang, D.O.; Jang, C.H.; Lee, H.; Park, G.M.; Kim, G.H. Designed hybrid scaffolds consisting of polycaprolactone microstrands and electrospun collagen-nanofibers for bone tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 97, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylan, N.; Bhat, S.; Ditto, M.; Lawrence, J.G.; Lecka-Czernik, B.; Yildirim-Ayan, E. Polycaprolactone nanofiber interspersed collagen type-I scaffold for bone regeneration: A unique injectable osteogenic scaffold. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Christ, G.J.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. The influence of electrospun aligned poly(ɛ-caprolactone)/collagen nanofiber meshes on the formation of self-aligned skeletal muscle myotubes. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, G. Rapid-prototyped collagen scaffolds reinforced with PCL/β-TCP nanofibres to obtain high cell seeding efficiency and enhanced mechanical properties for bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 16880–16889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavimi, M.A.; Negahdari, R.; Bani Shahabadi, A.; Sharifi, S.; Kazeminejad, E.; Shahi, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S. Preparation and study of starch/ collagen/ polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffolds for bone tissue engineering using electrospinning technique. Eurasian Chem. Commun. 2020, 2, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Cui, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. Bilayer membrane composed of mineralized collagen and chitosan cast film coated with berberine-loaded PCL/PVP electrospun nanofiber promotes bone regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 684335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ramos, D.; Lee, P.; Liang, D.; Yu, X.; Kumbar, S.G. Collagen functionalized bioactive nanofiber matrices for osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: Bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Sousa, S.R.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Moroni, L.; Monteiro, F.J. A biocomposite of collagen nanofibers and nanohydroxyapatite for bone regeneration. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Jose, M.V.; Mathew, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Vohra, Y.K. Nanostructured biocomposite scaffolds based on collagen coelectrospun with nanohydroxyapatite. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, H.-E.; Kim, H.-W. Electrospun fibrous web of collagen–apatite precipitated nanocomposite for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Casadiego, D.A.; Maldonado, M.; Sundaram, P.; Almodovar, J. “Green” electrospinning of a collagen/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibrous scaffold. MRS Commun. 2016, 6, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.; Montalbano, G.; Boggio, E.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Dianzani, C.; Dianzani, U.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Fiorilli, S. Electrospun Collagen Scaffold Bio-Functionalized with Recombinant ICOS-Fc: An Advanced Approach to Promote Bone Remodelling. Polymers 2022, 14, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, G.; Tomasina, C.; Fiorilli, S.; Camarero-Espinosa, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Moroni, L. Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation. Materials 2021, 14, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Peng, Z.-X. Nanofibers grafted on titanium alloy: The effects of fiber alignment and density on osteoblast mineralization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez, M.; Montalbano, G.; Gallo-Cordova, A.; Ovejero, J.G.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; González, B.; Tomasina, C.; Moroni, L.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Incorporation of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles into Collagen Formulation for 3D Electrospun Scaffolds. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, D.; Jahandideh, A.; Asghari, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Hesaraki, S. Effect of zeolite and zeolite/collagen nanocomposite scaffolds on healing of segmental femur bone defect in rabbits. Iran. J. Vet. Surg. 2017, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Markel, D.C.; Wang, S.; Shi, T.; Mao, G.; Ren, W. Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol–collagen–hydroxyapatite nanofibers: A biomimetic extracellular matrix for osteoblastic cells. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, M.; Riahinezhad, S.; Sultana, F.; Morris, T.; Wolf, R.; Vaughan, M. Effect of collagen-polycaprolactone nanofibers matrix coating on the in vitro cytocompatibility and in vivo bone responses of titanium. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2018, 38, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngiam, M.; Liao, S.; Patil, A.J.; Cheng, Z.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. The fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite on PLGA and PLGA/collagen nanofibrous composite scaffolds and their effects in osteoblastic behavior for bone tissue engineering. Bone 2009, 45, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J. Fabrication of Biologically Inspired Electrospun Collagen/Silk fibroin/bioactive glass composited nanofibrous scaffold to accelerate the treatment efficiency of bone repair. Regen. Ther. 2022, 21, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, W.; Meng, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Innovative biodegradable poly(L-lactide)/collagen/hydroxyapatite composite fibrous scaffolds promote osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, M. Polycaprolactone, β-tricalcium phosphate, and collagen nanofibers: Fabrication, physical properties, and in vitro cell activity for bone tissue regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, E.; Gaidau, C.; Râpă, M.; Stefan, L.M.; Ditu, L.-M.; Predescu, A.M.; Stanca, M.; Pantilimon, M.C.; Berechet, M.D.; Predescu, C. Sustainable Coated Nanostructures Based on Alginate and Electrospun Collagen Loaded with Antimicrobial Agents. Coatings 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Route | Inorganic Element | Organic Element | Main Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen/PVA nanofibers grafted on titanium alloy | Ti-6Al-4V | PVA | The effects of fiber alignment and density on osteoblast mineralization were investigated. In the first week of cell culturing, the collagen-aligned fibers could induce osteoblasts to elongate along the fiber direction. Meanwhile, it could not be observed in randomly aligned collagen fibers. Also, the cell growth, found on the high-density aligned collagen fibers showed more calcium than it on both high- and low-density collagen random fibers. | Lin and Peng [88] |
| Electrospun PVA/collagen/HA nanofibers | HA | PVA | The designed filled nanofibrous membrane showed in vitro degradability, better mechanical properties, and hydrolytic resistance. Also, excellent adhesion and proliferation of the MC3T3 cells were obtained on the designed scaffold, proposing the capability for an orthopedic prosthetic surface. | Song et al. [91] |
| Electrospinning of Collagen/PCL nanofibers on titanium | Titanium | PCL | The cytocompatibility of titanium was improved through the addition of electrospun Collagen/PCL nanofibers, resulting from the increase in the titanium’s surface roughness. It also influenced the shear strength of titanium implants by facilitating the connective tissue growing on them. | Khandaker et al. [92] |
| Mineralization of n-HA through Ca–P treatment on PLGA/collagen nanofibrous layer | HA | PLGA | Bone-like apatite was shaped on the collagen/PLGA nanofibrous layer and showed the presence of collagen-boosted n-HA nucleation. More n-HA affected the osteoblasts‘ attachment and proliferation. | Ngiam et al. [93] |
| Electrospun Collagen/Silk fibroin/bioactive glass composite | bioactive glass | Silk fibroin | Collagen/Silk fibroin/CaO-SiO2 composite nanofibers were fabricated and the result of the MTT assay corroborated the Saos-2 cell proliferation with no negative effects of a glass substrate. | Wu et al. [94] |
| Electrospinning of PLLA/collagen/HA composite scaffold | HA | PLLA | The osteoblasts MC3T3-E1 cell culturing on PLLA/collagen/HA electrospun scaffold showed enhanced spreading, proliferation, and differentiation as well as mineralization. | Zhou et al. [95] |
| Bi-layered bioactive glass and fibrous layers o Fcollagen/PCL | bioactive glass | PCL | The advantages of collagen composite led to the flattening and attachment of chondrocytes as well as HA formation. | Balasubramanian et al. [57] |
| Melt-plotted PCL/β- tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds combined with collagen nanofibers | β- tricalcium phosphate | PCL | According to SEM images and MTT assay of osteoblast-like cells with (MG63)-seeded scaffolds, the 2.2-times-higher initial attachment in composite–collagen scaffolds was obtained on the composite scaffold, compared to pure collagen nanofibers. Also, the synergistic effects of the collagen nanofibers and β-TCP particles in the scaffold were observed on cell activity. | Yeo et al. [96] |
| Embedding the electrospun collagen filled with the antimicrobial agents into an alginate film | Ag425K antimicrobial agent | Chitosan/Alginate | In vitro, L929 murine fibroblasts cell assay confirmed a proper cytocompatibility for the collagen–alginate scaffold with antibacterial agents. | Matei et al. [97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Banitaba, S.N.; Khademolqorani, S.; Li, J. The Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration: A Journey through Electrospun Composites Integrated with Organic and Inorganic Additives. Processes 2023, 11, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072105
Feng Y, Shi Y, Tian Y, Yang Y, Wang J, Guo H, Banitaba SN, Khademolqorani S, Li J. The Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration: A Journey through Electrospun Composites Integrated with Organic and Inorganic Additives. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072105
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yashan, Yanhong Shi, Yafang Tian, Yongxin Yang, Jun Wang, Haiwei Guo, Seyedeh Nooshin Banitaba, Sanaz Khademolqorani, and Jing’an Li. 2023. "The Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration: A Journey through Electrospun Composites Integrated with Organic and Inorganic Additives" Processes 11, no. 7: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072105
APA StyleFeng, Y., Shi, Y., Tian, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, J., Guo, H., Banitaba, S. N., Khademolqorani, S., & Li, J. (2023). The Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration: A Journey through Electrospun Composites Integrated with Organic and Inorganic Additives. Processes, 11(7), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072105








