Hydrocarbon Generation History of the Eocene Source Rocks in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea: Insights from a Basin Modeling Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
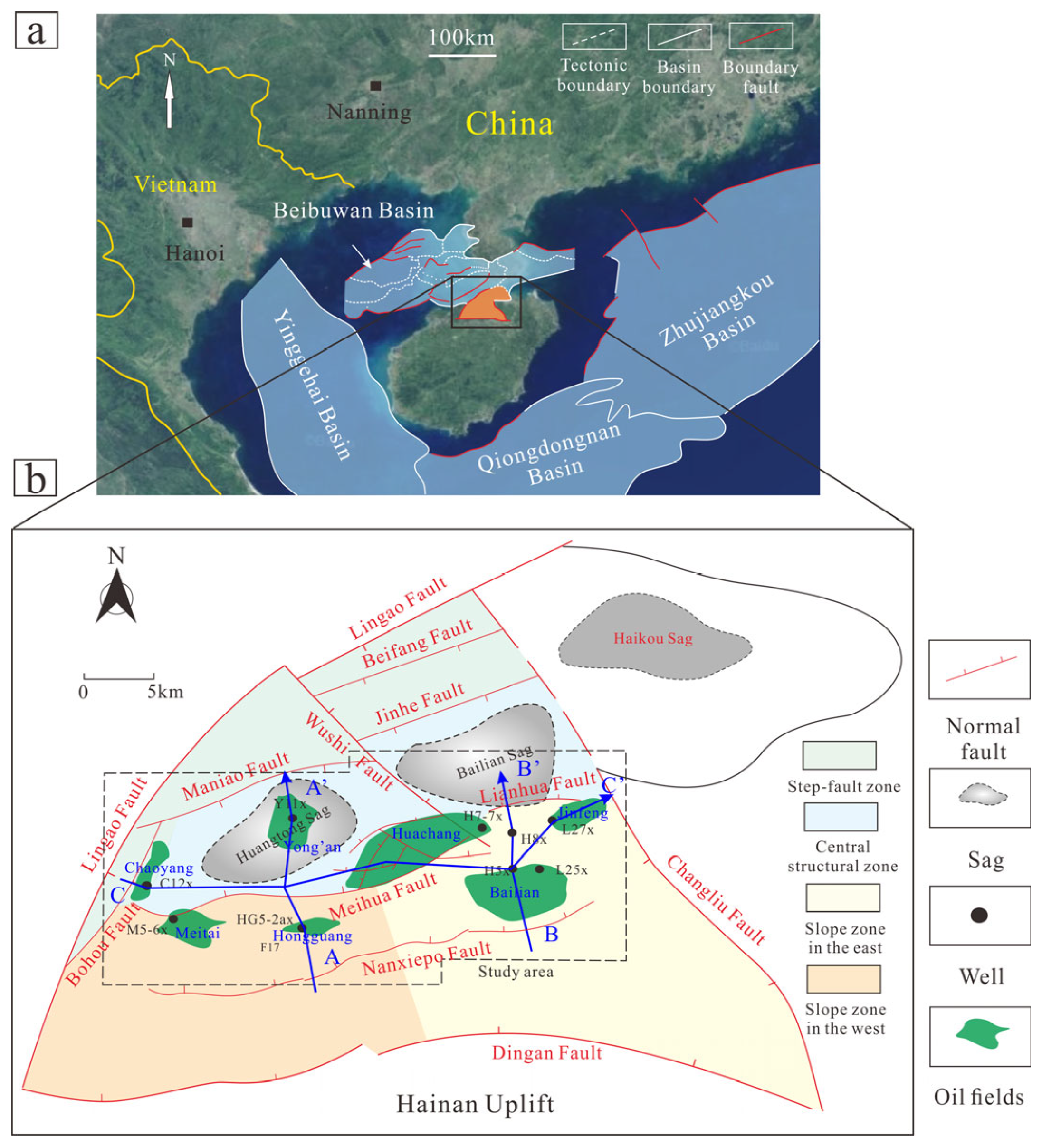
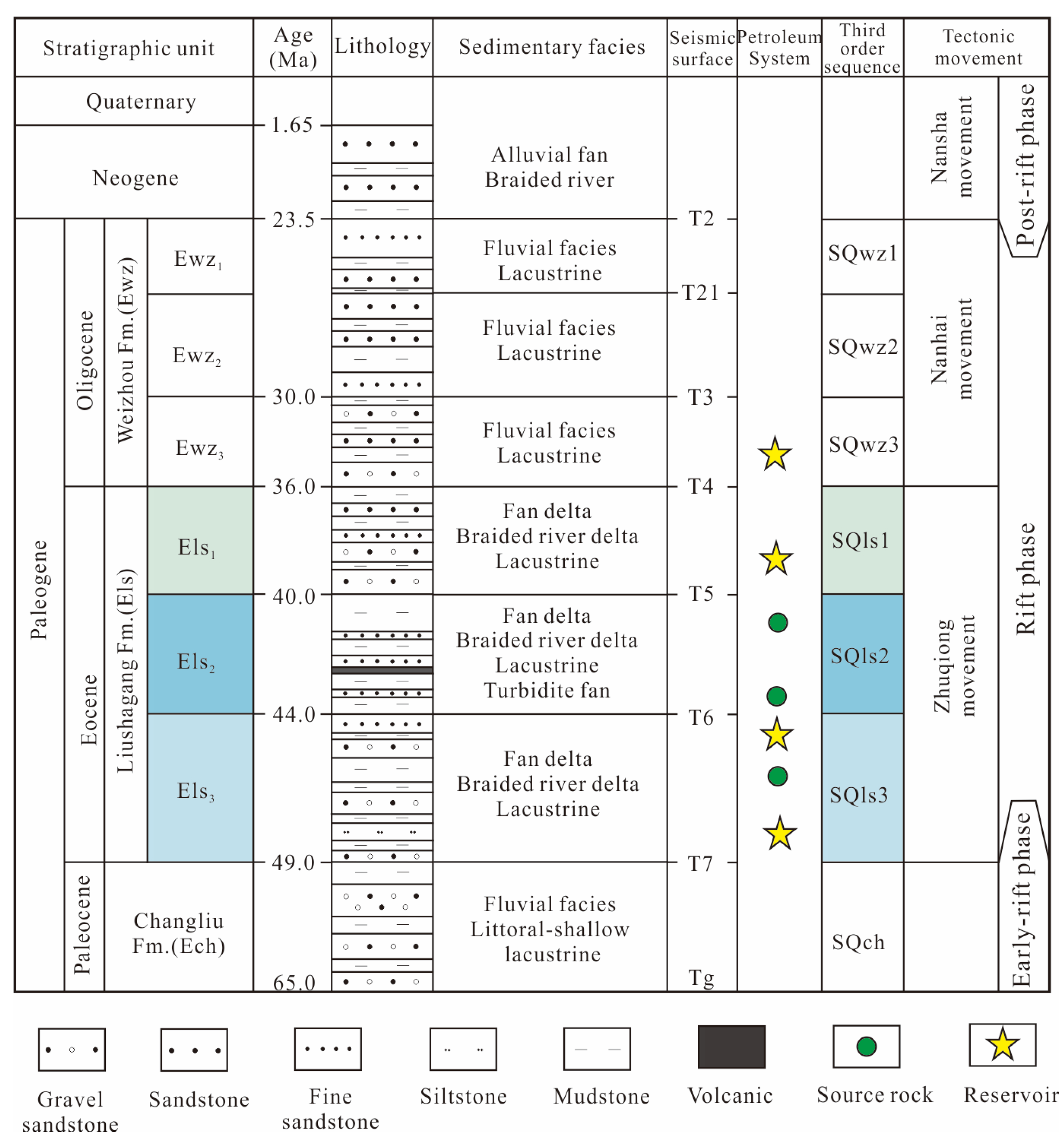
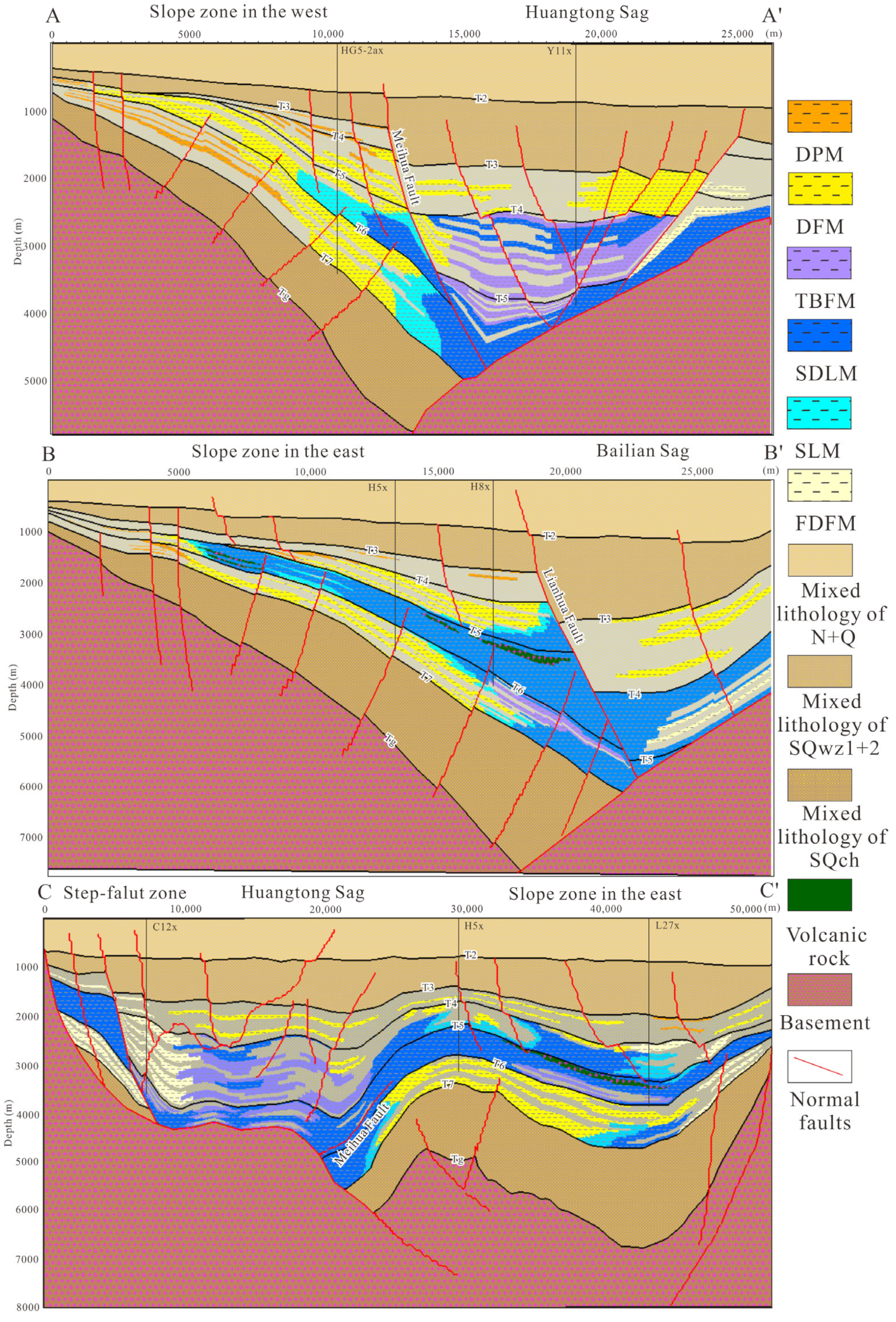
2. Geological Setting
3. Data and Methods
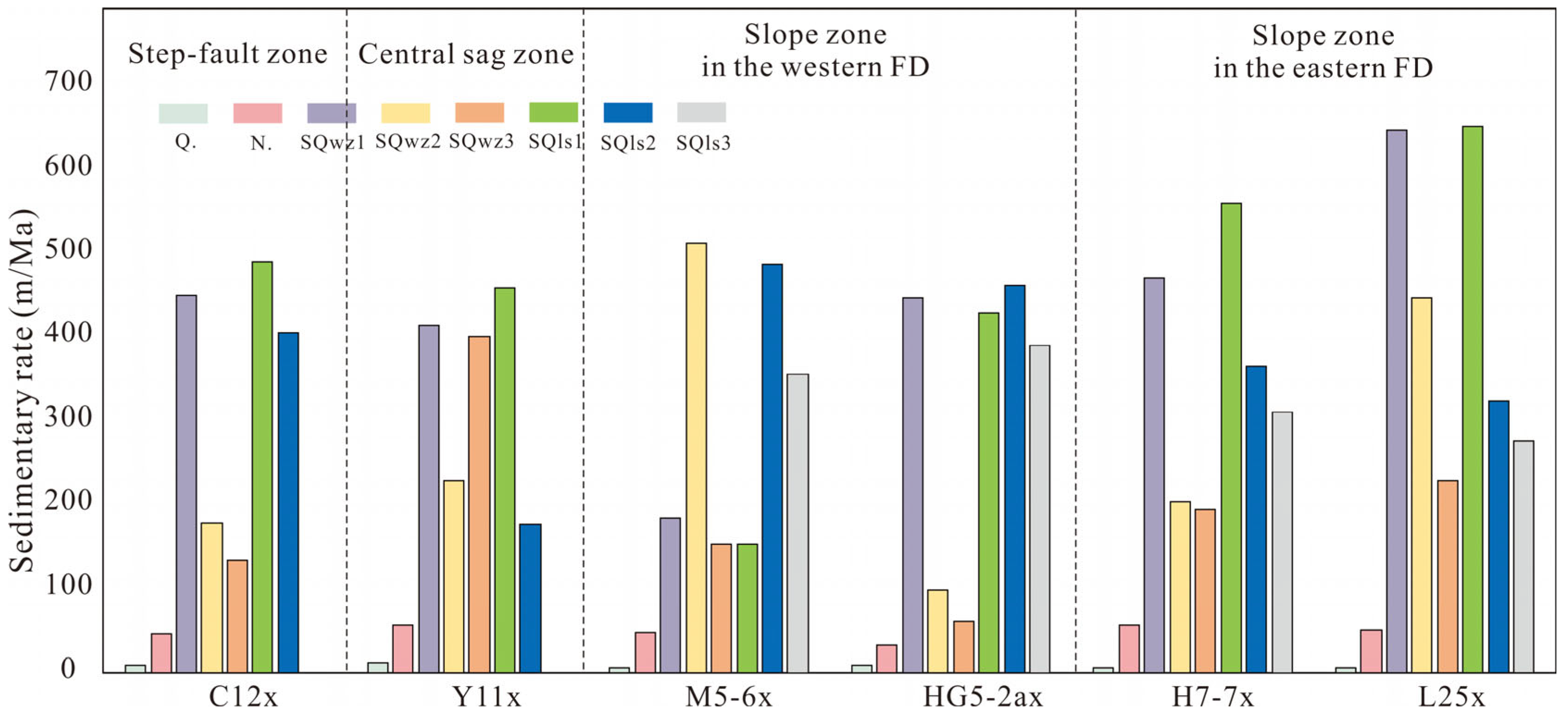
3.1. Data Base
3.2. Methods
4. Results
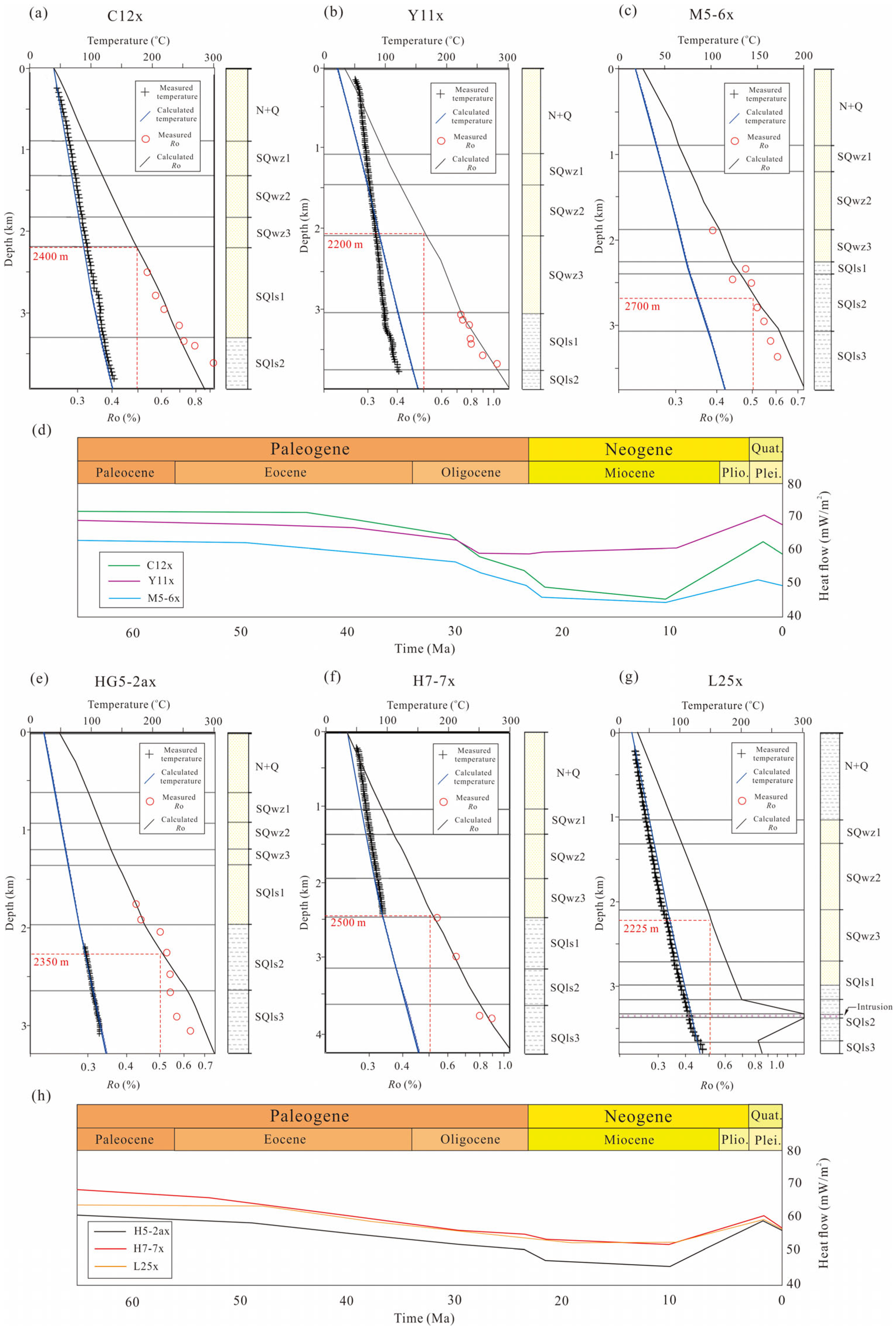
4.1. Burial History of 1D Basin Modeling
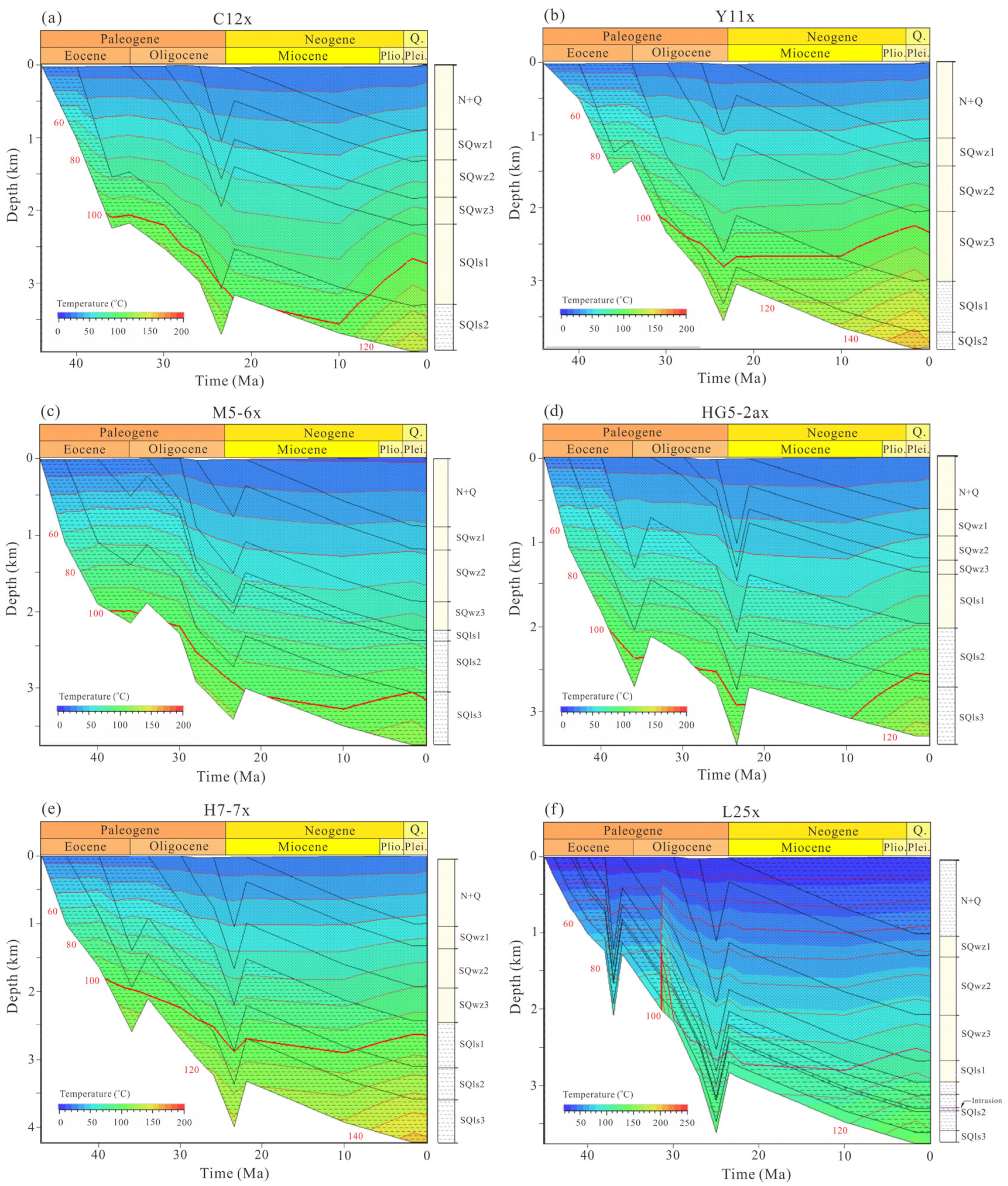
4.2. Thermal History of 1D Basin Modeling
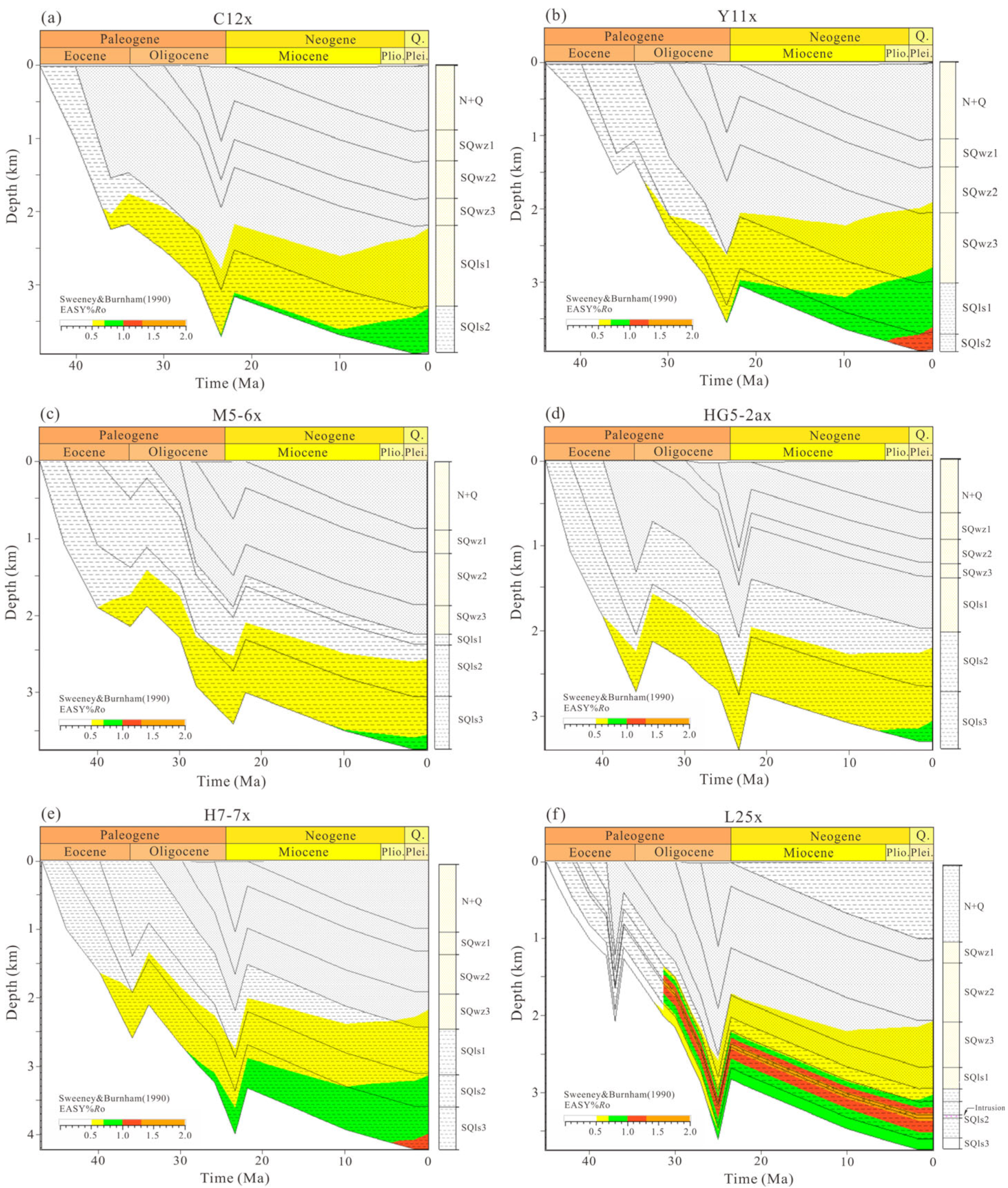
4.3. Maturity History of 1D Basin Modeling
5. Discussion
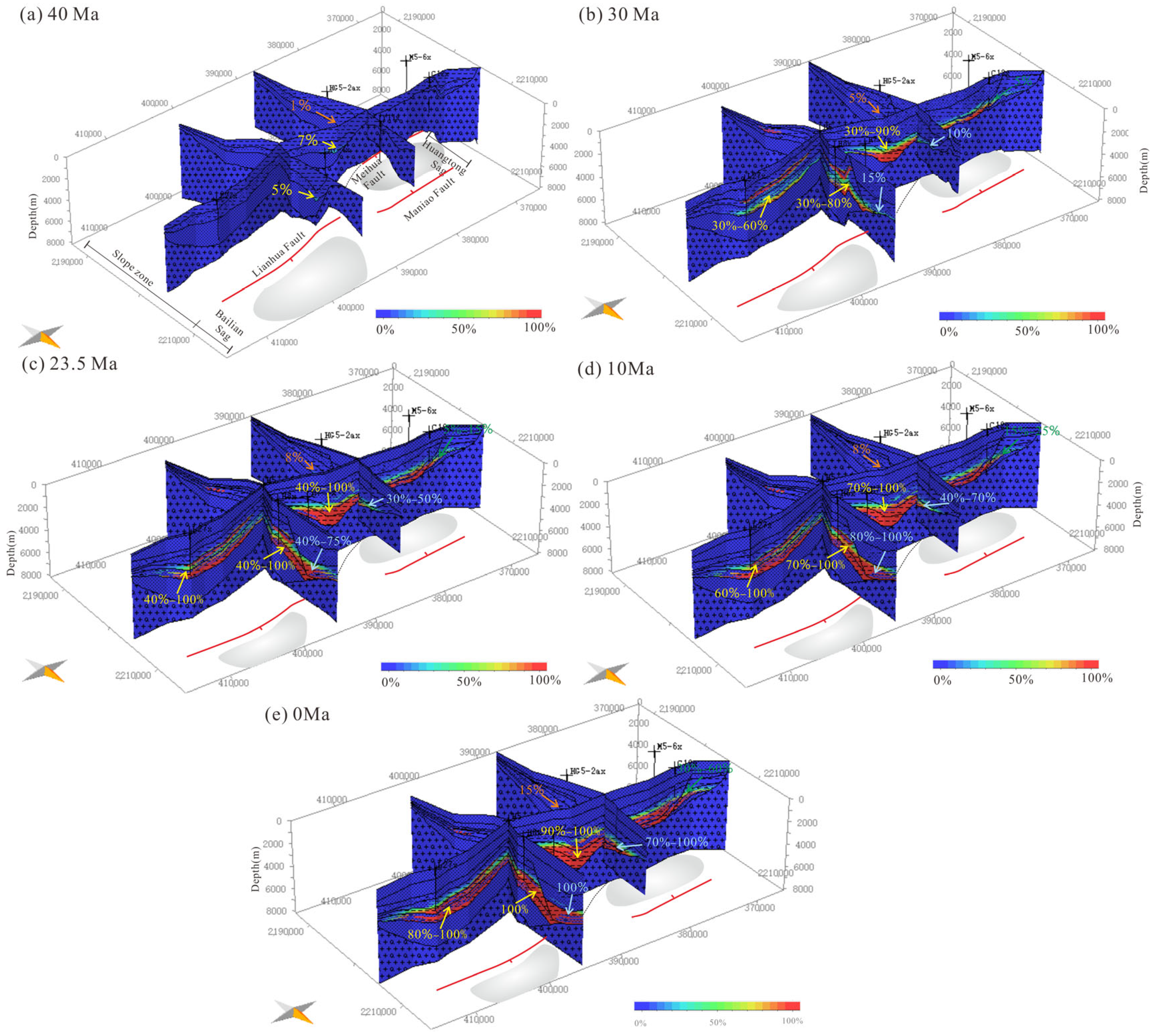
5.1. Hydrocarbon Generation History
5.2. Critical Moment for the Petroleum System
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karahanoǧlu, N.; Erler, A. Mathematical approach to hydrocarbon generation history and source rock potential in the Thrace Basin, Turkey. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1995, 12, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeen, Y.M.; Abdullah, W.H.; Pearson, M.J.; Hakimi, M.H.; Ayinla, H.A.; Elhassan, O.M.A.; Abas, A.M. History of hydrocarbon generation, migration and accumulation in the Fula sub-basin, Muglad Basin, Sudan: Implications of a 2D basin modeling study. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.H.; Al-Matary, A.M.; Hersi, O.S. Burial and thermal history reconstruction of the Mukalla-Sayhut Basin in the Gulf of Aden, Yemen: Implications for hydrocarbon generation from Paleocene potential source rock. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 144, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawad, E.A.A.E.; Ghanem, M.F.; Lotfy, M.M.; Mousa, D.A.; Temraz, M.G.; Shehata, A.M. Burial and thermal history simulation of the subsurface Paleozoic source rocks in Faghur basin, north Western Desert, Egypt: Implication for hydrocarbon generation and expulsion history. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 28, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; Wang, T.G.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Wu, W.Q.; Gao, L.H. Occurrence and origin of carbon dioxide in the Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2008, 25, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.J.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Q.L.; Liu, E.T.; Yan, D.T.; Pan, Z.J. Geochemical characteristics and genetic origin of crude oil in the Fushan sag, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 112, 104114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Zeng, B.; Wang, F.; Ran, Z. Petroleum Charging History of the Paleogene Sandstone Reservoirs in the Huangtong Sag of the Fushan Depression, South China Sea. Energies 2022, 15, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Zhao, S.E.; Liao, Y.T.; Lin, Z.L. Sequence architectures of Paleogene Liushagang Formation and its significance in Fushan Sag of the Beibuwan Basin. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37, 667–678. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.T.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Leonard, N.D.; Lin, Z.L.; Ma, Q.L. Sedimentary characteristics and tectonic setting of sublacustrine fans in a half-graben rift depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 52, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.T.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Leonard, N.D.; Feng, Y.X.; Pan, S.Q.; Xia, C.Y. Relative role of accommodation zones in controlling stratal architectural variability and facies distribution: Insights from the Fushan Depression, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 68, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, E.T.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.X.; Pan, S.Q.; Jing, Z.H.; Ma, Q.L.; Gan, H.J.; Zhao, J.X. Sedimentary architecture and provenance analysis of a sublacustrine fan system in a half-graben rift depression of the South China Sea. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 409, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Luo, D. Depositional setting analysis using seismic sedimentology: Example from the Paleogene Liushagang sequence in the Fushan depression, South China Sea. Geod. Geodyn. 2017, 8, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.D.; Wang, H.; Cao, H.Y.; Gan, H.J.; Chen, S.B. Lake-type controls on sedimentary infill and petroleum source rocks in the Palaeogene Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China. Geol. J. 2019, 55, 3936–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.J.; Gong, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ma, Q.L.; Liu, K.X.; Lv, Z.H. Geochemical characteristics of inclusion oils and charge history in the Fushan Sag, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 150, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Li, M.J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.Z.; Gong, C.L.; Lai, J.; Shi, Y. Source rock evaluation within a sequence stratigraphic framework of the Palaeogene Liushagang Formation in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 2409–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Li, M.J.; Wang, N.; Shi, Y.; Wang, F.Z.; Wang, X. Geochemistry and heterogeneous accumulation of organic matter in lacustrine basins: A case study of the Eocene Liushagang Formation in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 2533–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Gan, H.J.; Xia, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.D.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, X. History Simulation of Thermal Evolution and Hydrocarbon Generation of Source Rocks in Bailian Sub-Sag, Fushan Sag, Beibuwan Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2014, 35, 672–677. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; Wang, T.G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.Z.; Lu, H.; Ma, Q.L.; Gao, L.H. A discussion on hydrocarbon accumulation dating determined by homogenization temperature and burial history of fluid inclusio—An example from the Fushan depression, Beibuwan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2007, 28, 151–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.L.; Wang, H.; Li, H.J.; Ma, Q.L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.E. Genetic mechanism of double-layer structure in Paleogene of Fushan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin. Earth Sci. 2015, 40, 169–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E. Tectonic Geothermal History and Hydrocarbon Enrichment Rules in the Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E.; Kacewicz, M.; Curry, D.J. An overview of basin and petroleum system modeling: Definitions and concepts. In Basin Modeling: New Horizons in Research and Applications; AAPG Hedberg Series; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012; Volume 4, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zeinalzadeh, A.; Moussavi-Harami, R.; Mahboubi, A.; Sajjadian, V.A. Basin and petroleum system modeling of the Cretaceous and Jurassic source rocks of the gas and oil reservoirs in Darquain field, south west Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 26, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gan, H.; Zhu, C.; Tian, J. Study on subsidence history of Weixinan Depression in Beibuwan Basin. J. Xinjiang Pet. Inst. 2002, 14, 12–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wygrala, B. Integrated Study of an Oil Field in the Southern Po Basin, Northern Italy; Kernforschungsanlage Jülich GmbH.: Jülich, Germany, 1989; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenbruch, A. Crustal temperature and heat productivity: Implications of the linear heat flow relation. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.A.; Allen, J.R. Basin Analysis Principles and Applications; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 1–642. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, Y.M.; Michael, J.P.; William, A.A.; James, E.I.; Arthur, J.W. Modeling petroleum generation in the southern Muglad rift basin, Sudan. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1999, 83, 1943–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Welte, D.H.; Yukler, A. Petroleum origin and accumulation in basin evolution a quantitative model. Am. Assoc. Petr. Geol. Bull. 1981, 65, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Hakimi, M.H.; Abdullah, W.H.; Shalaby, M.R. Organic geochemistry, burial history and hydrocarbon generation modeling of the upper Jurassic Madbi Formation, Masila basin, Yemen. J. Pet. Geol. 2010, 33, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.P.; Welte, D.H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hantschel, T.; Kaurauf, A.I. Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; p. 476. [Google Scholar]
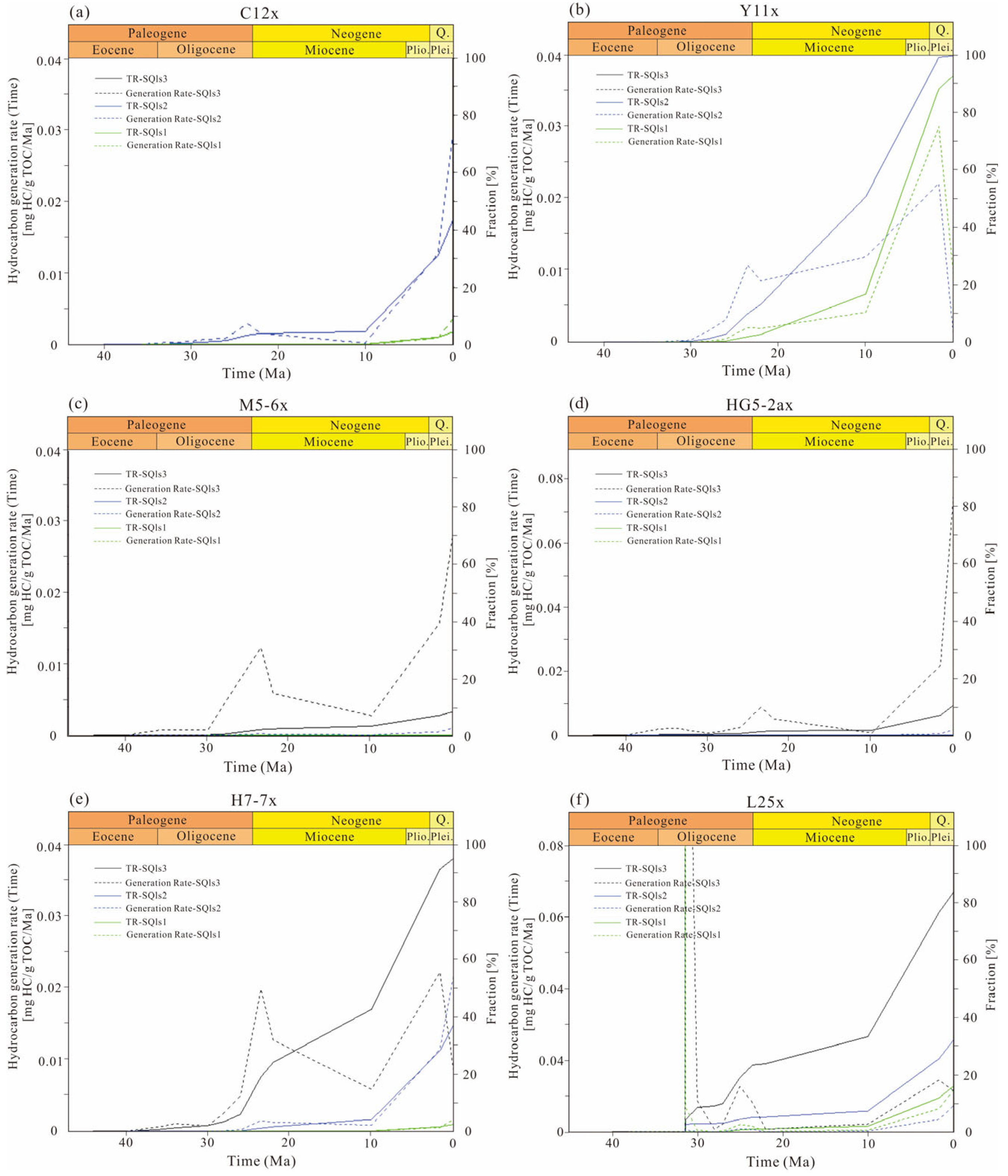
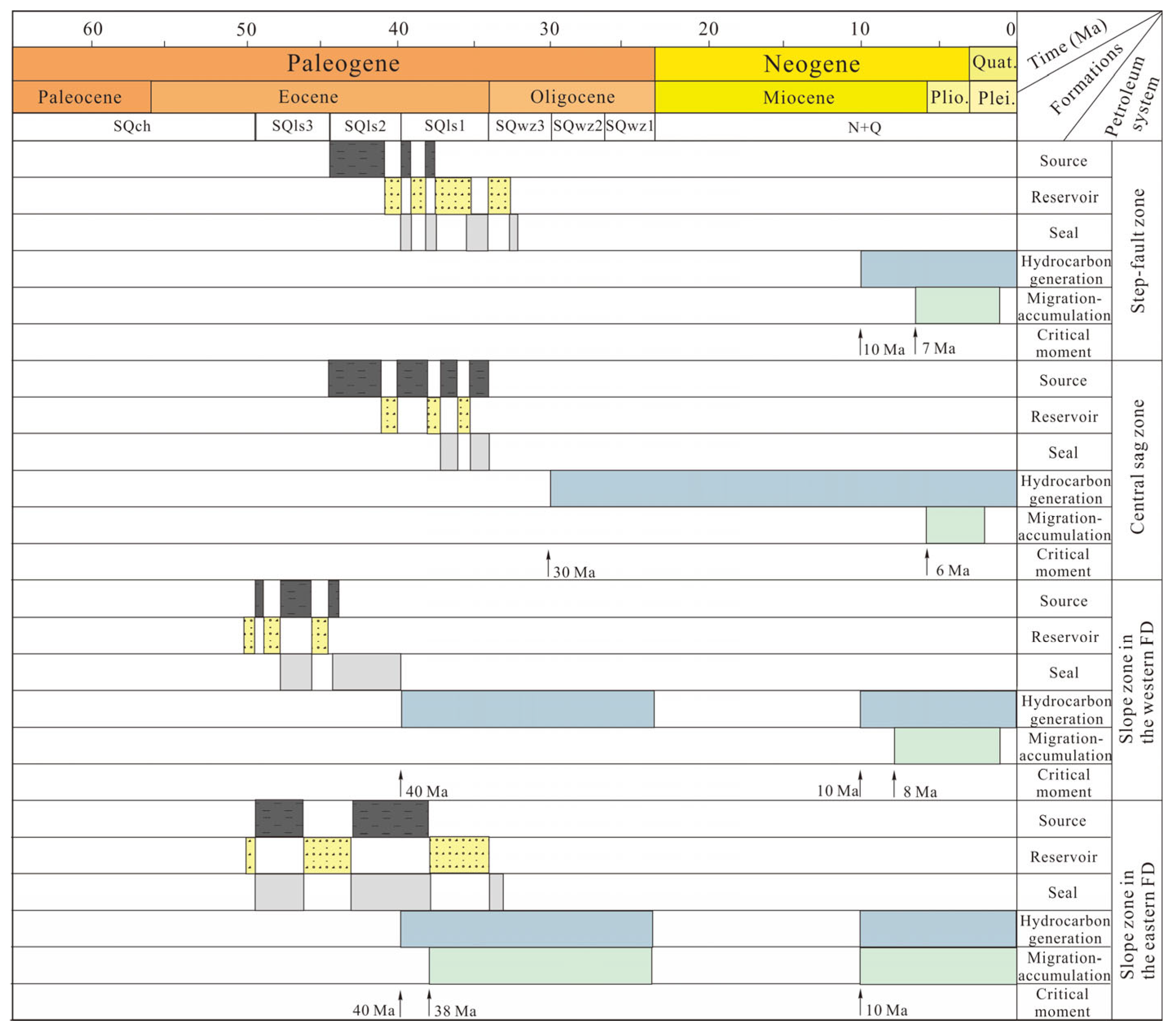
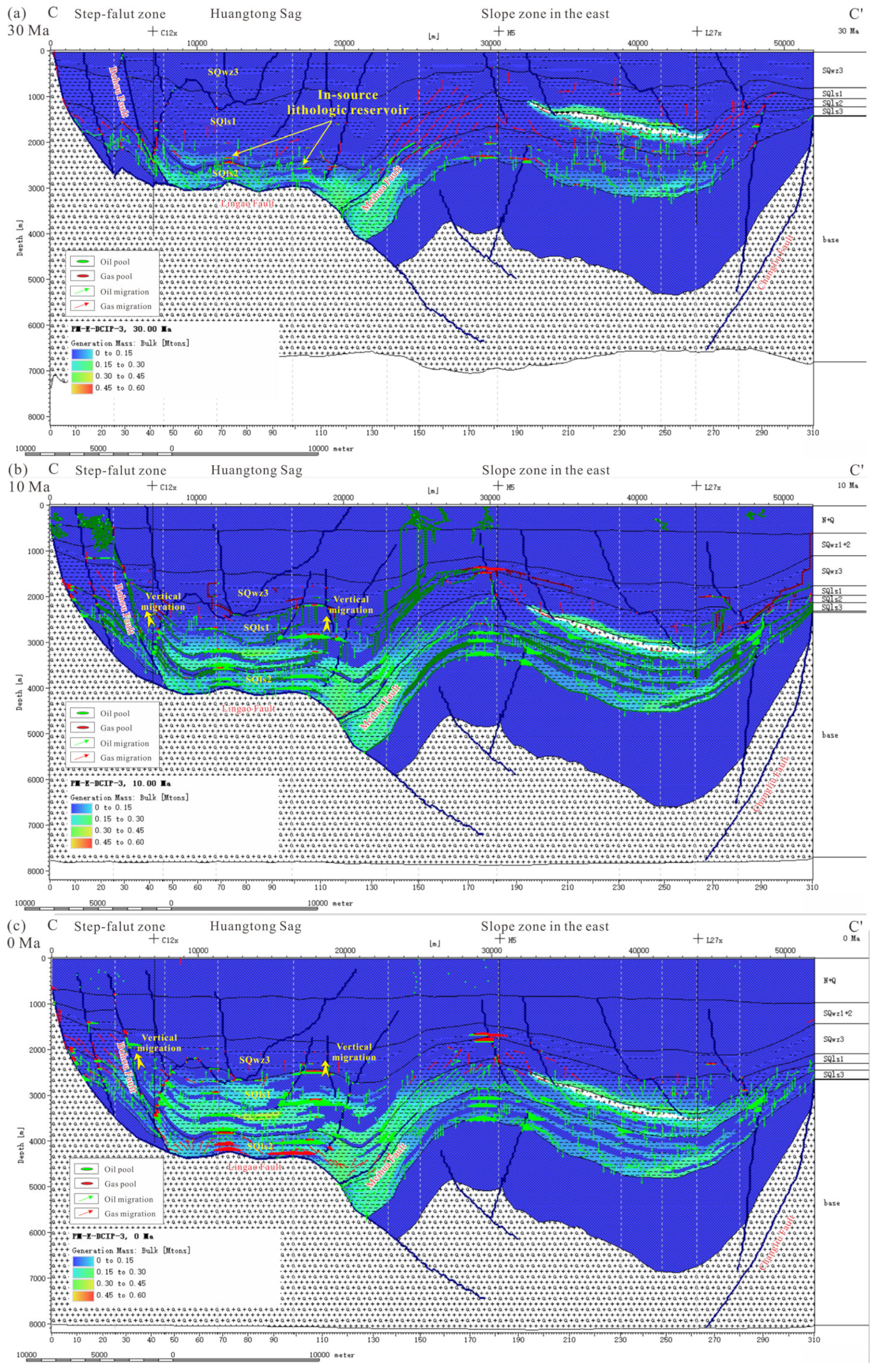
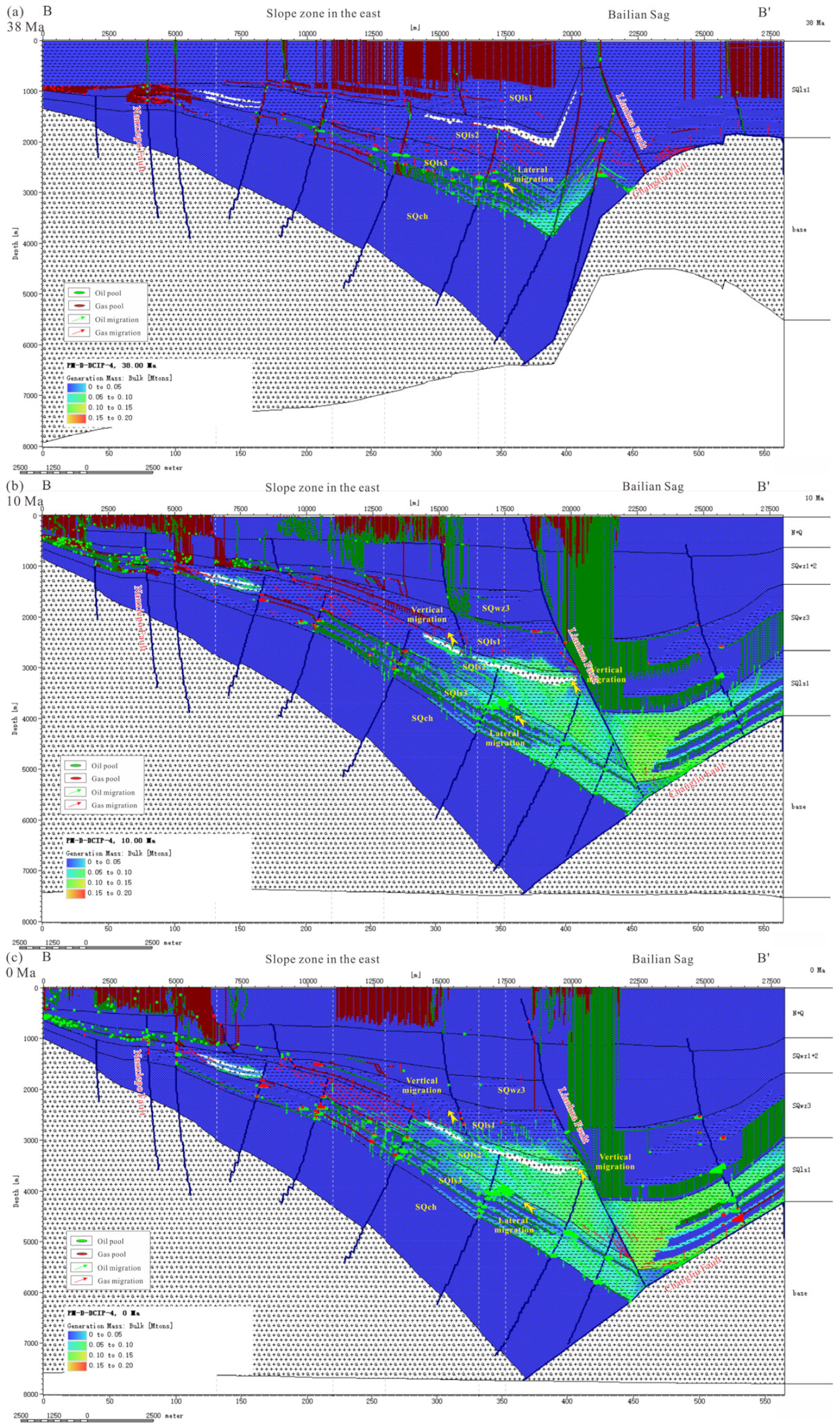
| Formation | Age (Ma) | C12x Well | Y11x Well | |||||
| /Event | From | To | Top | Thickness | Lithology | Top | Thickness | Lithology |
| (m) | /Erosion (m) | (m) | /Erosion (m) | |||||
| Quaternary S. | 1.65 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ST(90%) + C(10%) | 0 | 20 | ST(98%) + C(2%) |
| Neogene S. | 23.5 | 1.65 | 15 | 883 | ST(92%) + C(8%) | 20 | 1038 | ST(95%) + C(5%) |
| Erosion-T2 | 24.5 | 23.5 | 898 | −500 | - | 1058 | −450 | - |
| SQwz1 | 27 | 24.5 | 898 | 420 | ST(95%) + SH(5%) | 1058 | 381 | ST(90%) + SH(10%) |
| SQwz2 | 30 | 27 | 1318 | 506 | ST(80%) + SH(20%) | 1439 | 626 | ST(77%) + SH(23%) |
| SQwz3 | 34 | 30 | 1824 | 368 | ST(85%) + SH(15%) | 2065 | 953 | ST(69%) + SH(31%) |
| Erosion-T4 | 36 | 34 | 2192 | −50 | - | 3018 | −100 | - |
| SQls1 | 40 | 36 | 2192 | 1105 | ST(70%) + SH(30%) | 3018 | 699 | ST(35%) + SH(65%) |
| SQls2 | 44 | 40 | 3297 | 623 | ST(25%) + SH(75%) | 3717 | 233 | ST(5%) + SH(95%) |
| SQls3 | 49 | 44 | 3920 | - | - | 3950 | - | - |
| SQch | 65 | 49 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Formation | Age (Ma) | M5-6x Well | HG5-2ax Well | |||||
| /Event | From | To | Top | Thickness | Lithology | Top | Thickness | Lithology |
| (m) | /Erosion (m) | (m) | /Erosion (m) | |||||
| Quaternary S. | 1.65 | 0 | 0 | 10 | ST(93%) + C(7%) | 0 | 15 | ST(90%) + C(10%) |
| Neogene S. | 23.5 | 1.65 | 10 | 889 | ST(95%) + C(5%) | 15 | 603 | ST(96%) + SH(4%) |
| Erosion-T2 | 24.5 | 23.5 | 899 | −350 | - | 618 | −650 | - |
| SQwz1 | 27 | 24.5 | 899 | 300 | ST(85%) + SH(15%) | 618 | 307 | ST(95%) + SH(5%) |
| SQwz2 | 30 | 27 | 1199 | 679 | ST(71%) + SH(29%) | 925 | 276 | ST(72%) + SH(28%) |
| SQwz3 | 34 | 30 | 1878 | 382 | ST(75%) + SH(25%) | 1201 | 163 | ST(70%) + SH(30%) |
| Erosion-T4 | 36 | 34 | 2260 | −150 | - | 1364 | −450 | - |
| SQls1 | 40 | 36 | 2260 | 132 | ST(37%) + SH(63%) | 1364 | 609 | ST(65%) + SH(35%) |
| SQls2 | 44 | 40 | 2392 | 678 | ST(5%) + SH(95%) | 1973 | 678 | ST(10%) + SH(90%) |
| SQls3 | 49 | 44 | 3070 | 680 | ST(28%) + SH(72%) | 2651 | 649 | ST(8%) + SH(92%) |
| SQch | 65 | 49 | 3750 | - | - | 3300 | - | - |
| Formation | Age (Ma) | H7-7x Well | L25x Well | |||||
| /Event | From | To | Top | Thickness | Lithology | Top | Thickness | Lithology |
| (m) | /Erosion (m) | (m) | /Erosion (m) | |||||
| Quaternary S. | 1.65 | 0 | 0 | 10 | ST(98%) + SH(2%) | 0 | 10 | ST(91%) + C(9%) |
| Neogene S. | 23.5 | 1.65 | 10 | 999 | ST(90%) + SH(10%) | 10 | 1012 | ST(88%) + SH(12%) |
| Erosion-T2 | 24.5 | 23.5 | 1009 | −600 | - | 1022 | −700 | - |
| SQwz1 | 27 | 24.5 | 1009 | 326 | ST(90%) + SH(10%) | 1022 | 278 | ST(70%) + SH(30%) |
| SQwz2 | 30 | 27 | 1335 | 591 | ST(86%) + SH(14%) | 1300 | 778 | ST(48%) + SH(52%) |
| SQwz3 | 34 | 30 | 1926 | 510 | ST(80%) + SH(20%) | 2078 | 603 | ST(26%) + SH(74%) |
| Erosion-T4 | 36 | 34 | 2436 | −300 | - | 2681 | −550 | - |
| SQls1 | 40 | 36 | 2436 | 669 | ST(31%) + SH(69%) | 2681 | 455 | ST(8%) + SH(92%) |
| SQls2 | 44 | 40 | 3105 | 485 | ST(2%) + SH(98%) | 3136 | 510 | ST(11%) + SH(86%) + G(3%) |
| SQls3 | 49 | 44 | 3590 | 630 | ST(25%) + SH(75%) | 3646 | 116 | ST(43%) + SH(57%) |
| SQch | 65 | 49 | 4220 | - | - | 3762 | - | - |
| Formation | TOC | HI | Kerogen Type | Kinetic Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (mg HC/g TOC) | |||
| SQls1 | 1.18 | 180 | Type II | (Burnham, 1989 T-II) |
| SQls2 | 1.78 | 243 | Type II | (Burnham, 1989 T-II) |
| SQls3 | 1.62 | 248 | Type II | (Burnham, 1989 T-II) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Lu, Z.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Liao, F.; Li, M. Hydrocarbon Generation History of the Eocene Source Rocks in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea: Insights from a Basin Modeling Study. Processes 2023, 11, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072051
Zeng B, Lu Z, Yang T, Shi Y, Guo H, Wang X, Liao F, Li M. Hydrocarbon Generation History of the Eocene Source Rocks in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea: Insights from a Basin Modeling Study. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072051
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Bang, Zhenghuan Lu, Taotao Yang, Yang Shi, Hao Guo, Xin Wang, Feiyan Liao, and Meijun Li. 2023. "Hydrocarbon Generation History of the Eocene Source Rocks in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea: Insights from a Basin Modeling Study" Processes 11, no. 7: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072051
APA StyleZeng, B., Lu, Z., Yang, T., Shi, Y., Guo, H., Wang, X., Liao, F., & Li, M. (2023). Hydrocarbon Generation History of the Eocene Source Rocks in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea: Insights from a Basin Modeling Study. Processes, 11(7), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072051





