Complex Agent for Phosphate Sequestration from Digested Sludge Liquor: Performances and Economic Cost Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Complex Agent and DSL Characteristics
2.2. Adsorption and Clarification Batch Experiments
2.3. Desorption and Regeneration Experiments
2.4. Chemicals
2.5. Method of Calculation on Dosing Cost
3. Results
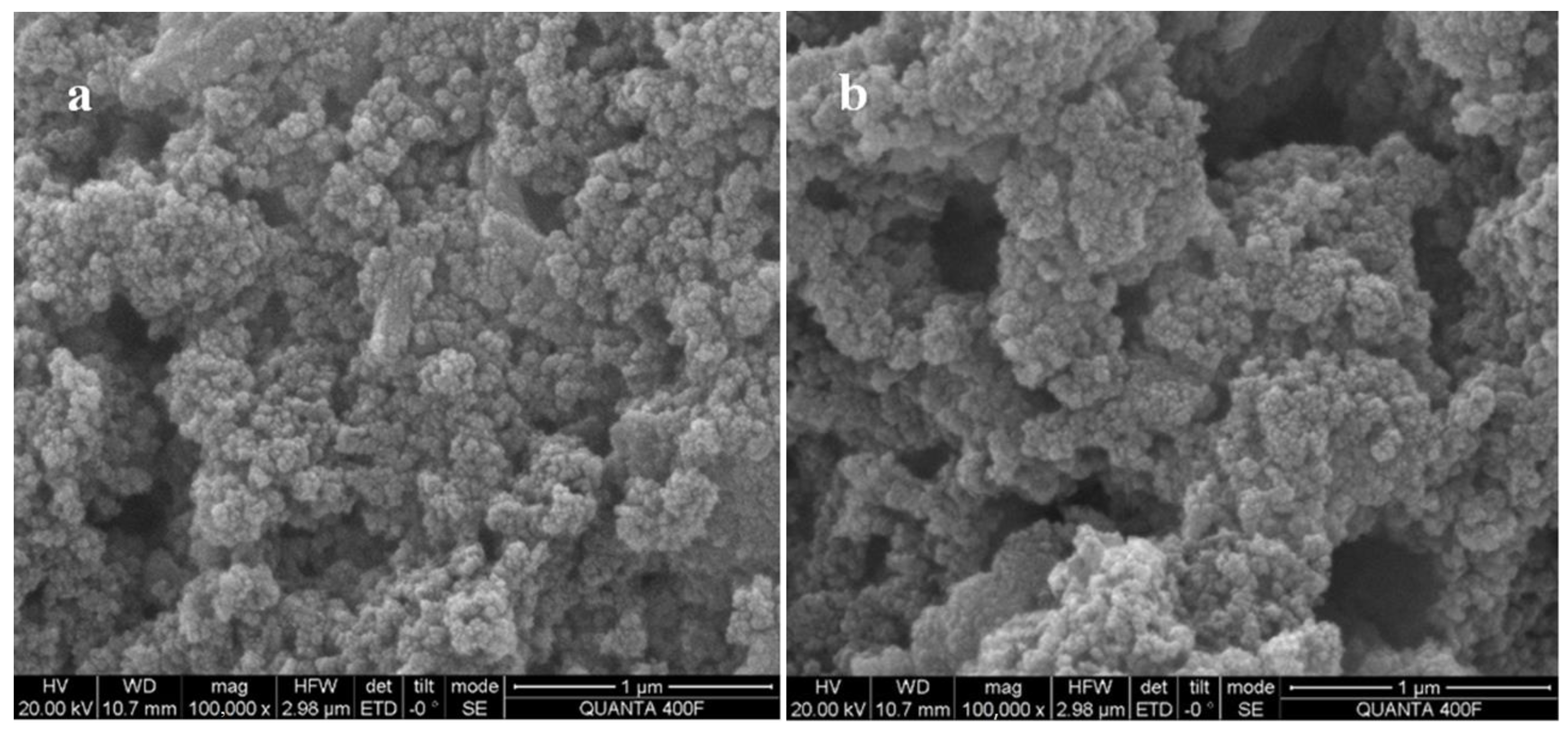
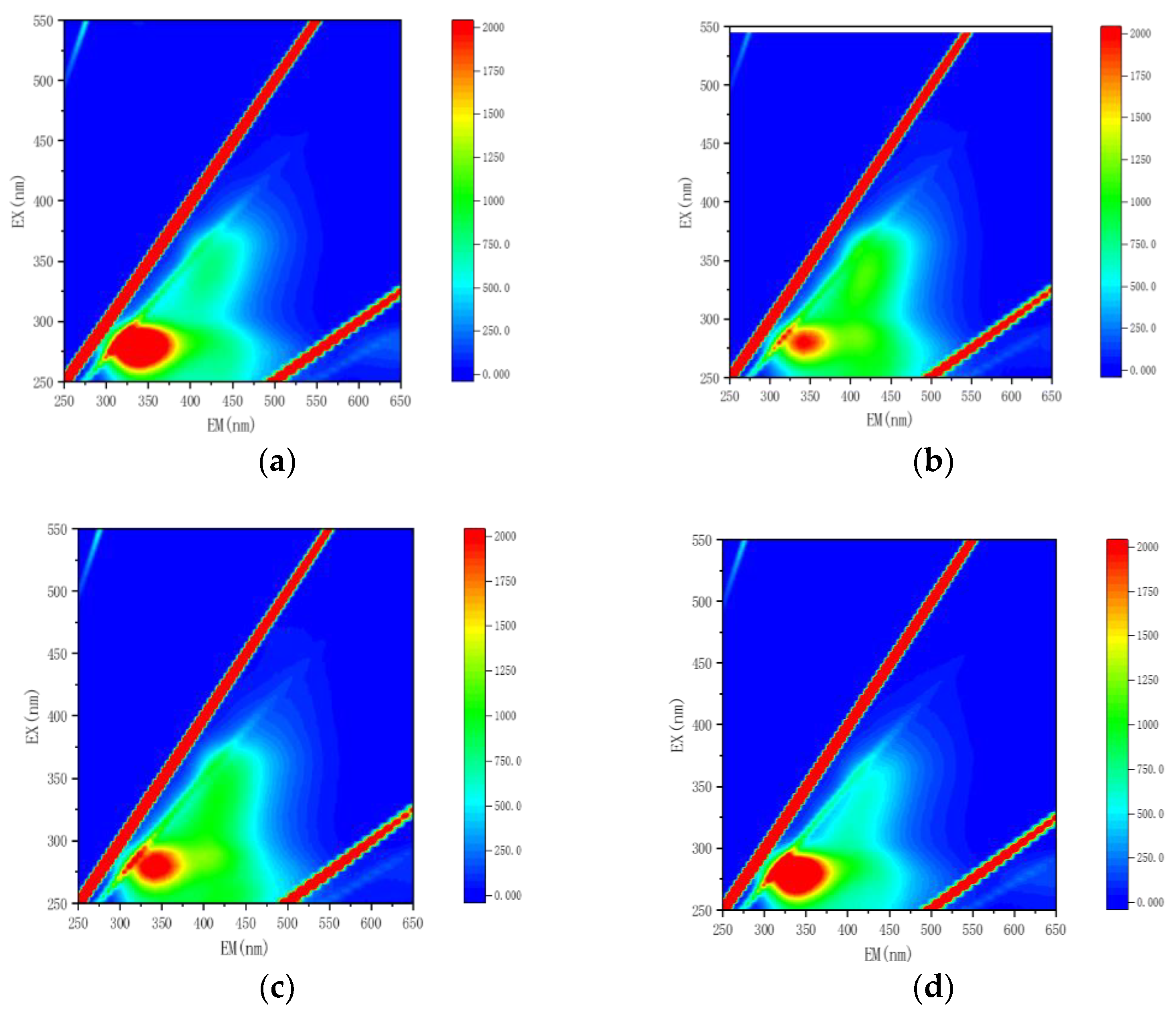
3.1. Structural Characterizations of the Complex Agent
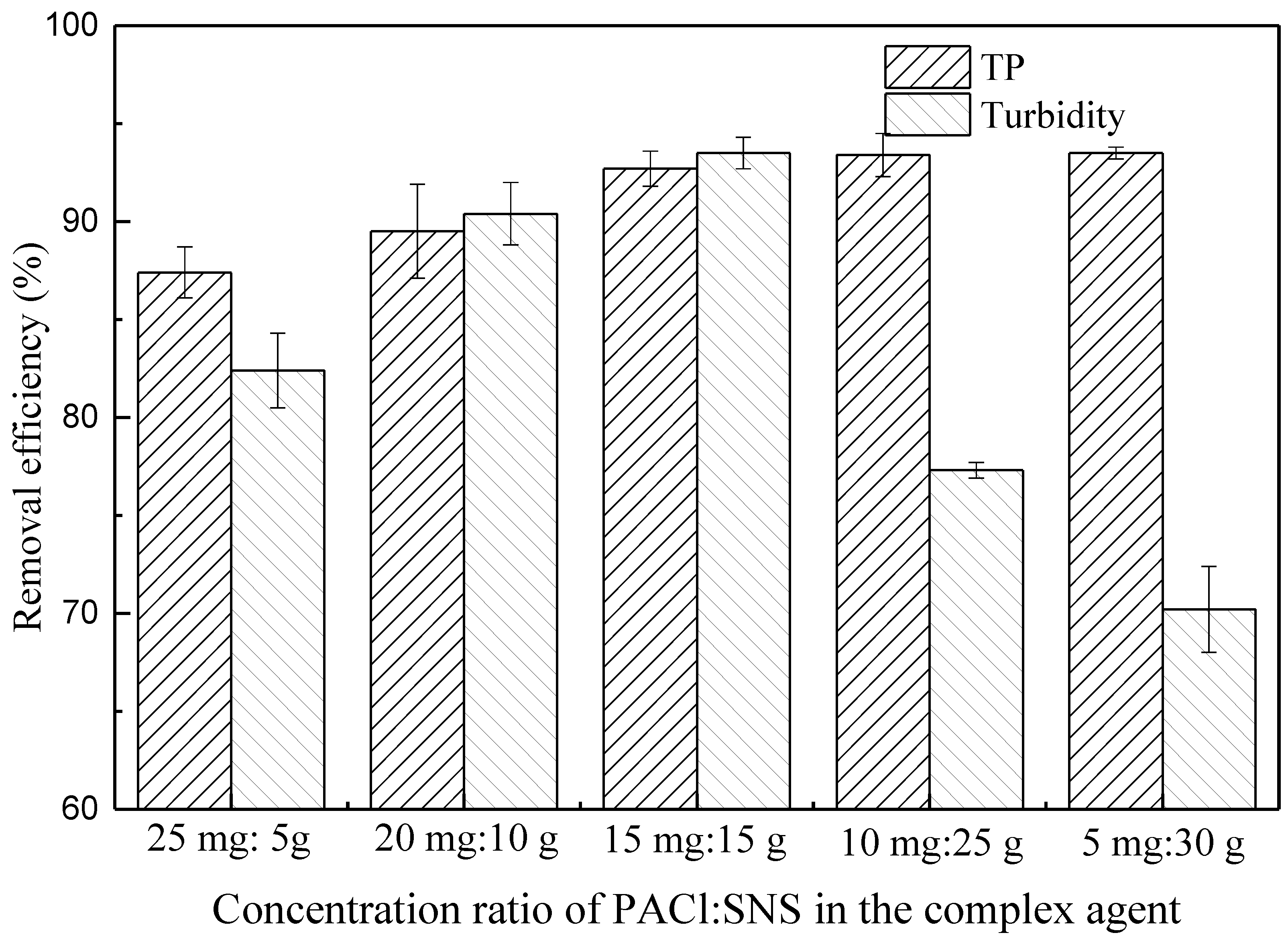
3.2. TP and Turbidity Removal Performance by Complex Agent
3.3. Reusability of Complex Agent
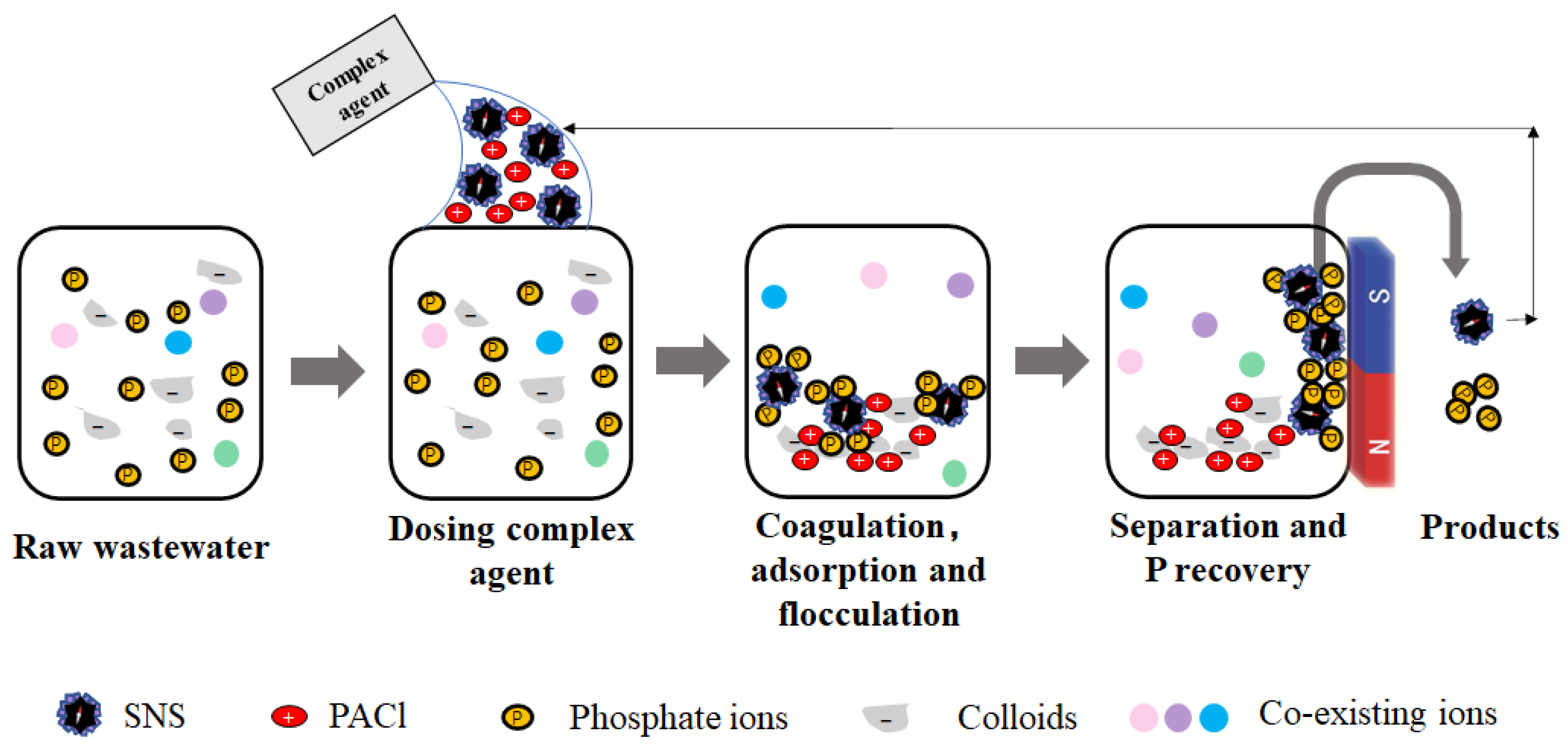
3.4. Mechanism
3.5. Economic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAO | anaerobic–anoxic–oxic |
| DOM | dissolved organic matter |
| EEM | dimensional excitation-emission matrix |
| PFC | polyferric chloride |
| SNS | superparamagnetic nano-sorbent |
| WWTPs | wastewater treatment plants |
| CaP | hydroxyapatite |
| DSL | digested sludge liquor |
| PACl | polyaluminum chloride |
| P | phosphorus |
| TP | total phosphorus |
References
- Bareha, Y.; Saoudi, M.; Santellani, A.-C.; Le Bihan, A.; Picard, S.; Mebarki, C.; Cunha, M.; Daumer, M.-L. Use of fermentation processes for improving the dissolution of phosphorus and its recovery from waste activated sludge. Environ. Technol. 2020, 43, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y. Energy self-sufficient biological municipal wastewater reclamation: Present status, challenges and solutions forward. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monea, M.C.; Löhr, D.K.; Meyer, C.; Preyl, V.; Xiao, J.; Steinmetz, H.; Schönberger, H.; Drenkova-Tuhtan, A. Comparing the leaching behavior of phosphorus, aluminum and iron from post-precipitated tertiary sludge and anaerobically digested sewage sludge aiming at phosphorus recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, D. Magnetite/Lanthanum hydroxide for phosphate sequestration and recovery from lake and the attenuation effects of sediment particles. Water Res. 2018, 130, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Boiarkina, I.; Yu, W.; Huang, H.M.; Munir, T.; Wang, G.Q.; Young, B.R. Phosphorous recovery through struvite crystallization: Challenges for future design. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzet, S.; Peplinski, B.; Cornel, P. On wet chemical phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash by acidic or alkaline leaching and an optimized combination of both. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadie, A.; Belay, A.; Liu, W.; Yesigat, A.; Hao, X.; Wang, A. Rift Valley Lake as a potential magnesium source to recover phosphorus from urine. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, C.E.; Herman, K. Treatment of supernatant sludge liquor by coagulation and sedimentation. Sew. Work. J. 1940, 12, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Peng, F.; Gong, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K. Ammonia removal from low-strength municipal wastewater by powdered resin combined with simultaneous recovery as struvite. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.G.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, X.W.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, K.F.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Zhao, W.X.; Meng, S.J.; Mu, R.M. Preparation of a novel hafnium-loaded Fe3O4@SiO2 superparamagnetic nanoparticles and its adsorption performance for phosphate in water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 216, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.F.; Song, H.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Tian, F.Y.; Meng, S.J.; Zhang, K.F.; Wang, N.; Mu, R.M.; et al. Mechanism of phosphate adsorption on superparamagnetic microparticles modified with transitional elements: Experimental observation and computational modelling. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenkova-Tuhtan, A.; Schneider, M.; Franzreb, M.; Meyer, C.; Gellermann, C.; Sextl, G.; Mandel, K.; Steinmetz, H. Pilot-scale removal and recovery of dissolved phosphate from secondary wastewater effluents with reusable ZnFeZr adsorbent@ Fe3O4/SiO2 particles with magnetic harvesting. Water Res. 2017, 109, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sui, Q.; Yu, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, M.; Ritigala, T.; Wei, Y. Development of a Short-Cut Combined Magnetic Coagulation-Sequence Batch Membrane Bioreactor for Swine Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, T.R.T.; Mateus, G.A.P.; Silva, M.F.; Miyashiro, C.S.; Nishi, L.; de Andrade, M.B.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Gomes, R.G.; Bergamasco., R. Evaluation of Magnetic Coagulant (α-Fe2O3-MO) and its reuse in textile wastewater treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.H.M.; Azli, M.F.Z.M.; Ngadi, N.; Inuwa, I.M.; Opotu, L.A.; Mohamed, M. Optimization of sonication-assisted synthesis of magnetic Moringa oleifera as an efficient coagulant for palm oil wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, K.; Shan, R.R.; Yan, T.; Wei, J.; Yu, S.J.; Yu, H.Q.; Du, B. Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations of phosphate adsorption onto core–shell Fe3O4@ LDHs composites with easy magnetic separation assistance. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, Z.; Wei, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, G. Performance of magnetic zirconium-iron oxide nanoparticle in the removal of phosphate from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tian, J.Z.; Zhang, K.F.; Wang, H.B.; Li, M.; Meng, S.J.; Mu, R.M.; Liu, L.; Yin, M.M.; Li, J.J.; et al. Phosphate recovery from the P-enriched brine of AnMBR-RO-IE treating municipal wastewater via an innovated phosphorus recovery batch reactor with nano-sorbents. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunkjær, K.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, P.H. Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Logan, B.E.; van der Hoek, J.P.; Sun, M.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y. Magnetic seeding coagulation: Effect of Al species and magnetic particles on coagulation efficiency, residual Al, and floc properties. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Application of a green coagulant with PACl in efficient purification of turbid water and its mechanism study. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 81, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, R.; Rajarao, G.K. Effective water content reduction in sewage wastewater sludge using magnetic nanoparticles. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 153, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triques, C.C.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Suzaki, P.Y.R.; Mateus, G.A.P.; Wernke, G.; Bergamasco, R.; Rodrigues, M.L.F. Influence evaluation of the functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with a natural extract coagulant in the primary treatment of a dairy cleaning-in-place wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, D.; Liu, X. Intermolecular interactions of polysaccharides in membrane fouling during microfiltration. Water Res. 2018, 143, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, H.; Liang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y. Transparent exopolymer particles (TEPs)-associated protobiofilm: A neglected contributor to biofouling during membrane filtration. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, C.; Fan, X.L.; Lu, B.H.; Tian, X.; Jin, W.; He, X.X.; Guo, W.Z. Toxicity of three crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles in activated sludge: Bacterial cell death modes differentially weaken sludge dewaterability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4542–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.N.; Honda, R.; Noguchi, M.; Ito, T. Optimum selection of extraction methods of extracellular polymeric substances in activated sludge for effective extraction of the target components. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 127, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, D.R.; Cecilia, J.A.; Santos, S.O.; Rodrigues, T.N.B.; Aguiar, J.E.; Vilarrasa-Garcia, E.; Rodriguez-Castellon, E.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Silva, I.J., Jr. Influence of buffer solutions in the adsorption of human serum proteins onto layered double hydroxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouhi, M.; Torabian, A.; Bozorg, A.; Mehrdadi, N. A novel convenient approach toward the fouling alleviation in membrane bioreactors using the combined methods of oxidation and coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Barbeau, B. Selection of media for the design of ballasted flocculation processes. Water Res. 2018, 147, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Term | DSL |
|---|---|
| Total dissolved P (mg/L) | 22.6 ± 1.4 |
| Orthophosphate (mg/L) | 20.3 ± 0.9 |
| HCO3− (mg CaCO3/L) | 57.2 ± 0.7 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 47.6 ± 2.8 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 5.2 ± 0.3 |
| SS (mg/L) | 135 ± 18 |
| Zn2+ (mg/L) | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| Extracellular protein (mg/L) | 20.5 ± 1.3 |
| Polysaccharide (mg/L) | 28.4 ± 0.7 |
| pH | 6.4 ± 0.2 |
| Magnetic Seeding Coagulation | Complex Agent | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost (EUR/m3) | 0.015 | 1.54 |
| Profit (EUR/m3) | 0 | 1.46 |
| Net cost (EUR/m3) | 0.015 | 0.08 |
| Environmental benefit | Low | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Nie, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Q. Complex Agent for Phosphate Sequestration from Digested Sludge Liquor: Performances and Economic Cost Analysis. Processes 2023, 11, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072050
Yan S, Nie L, Ren J, Wang W, Xu J, Wang N, Zhao Q. Complex Agent for Phosphate Sequestration from Digested Sludge Liquor: Performances and Economic Cost Analysis. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072050
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shi, Li Nie, Juan Ren, Wei Wang, Jingtao Xu, Ning Wang, and Qian Zhao. 2023. "Complex Agent for Phosphate Sequestration from Digested Sludge Liquor: Performances and Economic Cost Analysis" Processes 11, no. 7: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072050
APA StyleYan, S., Nie, L., Ren, J., Wang, W., Xu, J., Wang, N., & Zhao, Q. (2023). Complex Agent for Phosphate Sequestration from Digested Sludge Liquor: Performances and Economic Cost Analysis. Processes, 11(7), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072050






