Abstract
Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.; AS) is a medicinal plant used in the clinical treatment of cerebrovascular diseases and central nervous system disorders, and it significantly improves blood lipid levels and endothelial cell function in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Isofraxidin, one of the active ingredients of AS, is the core of the plant’s medical effects, and its extraction depends on organic solvents. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are new green solvents synthesized by intermolecular hydrogen bonding between hydrogen bond donors (HBD) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA) which are non-toxic, have a high separation and extraction efficiency, and are environmentally friendly compared to traditional organic solvents. In this paper, DES was used for the extraction of isofraxidin from AS. The primary findings demonstrated that the DES had a viscosity higher than that of ethanol, and even adding a small amount of water (approximately 10%) would trigger solvent redistribution, leading to a considerable reduction in solvent viscosity. In comparison to ethanol, the extraction rate of isofraxidin by DES was 2–3 times higher. Thus, this work developed a new technique for using green extraction of isofraxidin that has some practical implications.
1. Introduction
Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. Maxim.; AS) is a clonal plant species capable of sexual seed reproduction in its native environment. Clone propagation is mainly carried out in northeastern China; it is also practiced in Russia, Korea, and Japan [1].
The active ingredients in AS are mainly polysaccharides, glycosides, terpenoids, lignans, flavonoids, and coumarins. Syringin, also known as Eleutheroside B, is a glycoside and a terpenoid widely found in the leaves of AS. Eleutheroside E is a class of lignan monomers extracted from AS and is mainly found in the fruits of AS. Quercetin is a flavonoid and is widely found in the fruits and leaves of AS [1]. Isofraxidin is a hydroxycoumarin monomeric substance that is widely found in the roots, leaves, and fruits of AS and has a variety of physiological and pharmacological activities. Isofraxidin plays a wide range of pharmacological roles in various diseases such as osteoarthritis [2], cancer [3,4], disorders of lipid metabolism [5], and Alzheimer’s disease [6]. Previous studies have shown that isofraxidin inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by affecting MMP-7 expression. In hepatocellular carcinoma cells, isofraxidin inhibits ERK1/2 phosphorylation and reduces iNOS and COX-2 expression, and isofraxidin also inhibits the formation of TLR4/myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD-2) complexes [7,8]. Isofraxidin can promote immune cells (such as T cells, B cells, NK cells, and M cells) to regulate the immune system more efficiently, mediate interleukin and interferon, stimulate cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, enhance human immunity, and, eventually, execute its anti-tumor activity [9,10]. Isofraxidin also protected mice from acute lung injury by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein expression and decreasing inflammatory cell infiltration into lung tissues [11]. Pretreatment with isofraxidin prior to IL-1 could inhibit IL-1-stimulated expression of iNOS and COX-2, which, in turn, blocked the generation of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 in chondrocytes isolated from osteoarthritis patients (PGE2). Furthermore, matrix metalloproteinases’ mRNA levels and secretions were considerably decreased by isofraxidin (MMPs). It was determined that isofraxidin controlled NF-B signaling to prevent IL-1-induced joint inflammation [12].
The different partition coefficients (KD) of solutes in various solvents are the basis of the separation and extraction process. When the sample volume is large or the KD value is too low, several successive extractions are required to obtain higher recoveries [13]. This method lacks selectivity in the extraction of the desired components, has low extraction efficiency, and uses a large number of organic solvents, which significantly increases the cost of the process. In order to tackle these issues, Abbott et al. introduced the deep eutectic solvent (DES) theory, which calls for the intermolecular synthesis of hydrogen bonds between hydrogen bond donors (HBD) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA). The solvent is non-volatile, has low toxicity, and is eco-friendly [14].
DES is well suited to electrochemical and phytochemical extraction. Due to the high efficiency of DES extraction of flavonoids, lignans, and phenolic glycosides, DES shows great potential in the field of extraction and recovery of phytoactive components [15]. To extract polyphenols, vanillin, and flavonoids, natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) and therapeutic deep eutectic solvents (THEDES) were developed in accordance with this principle [16,17]. To focus on the current challenges of improving drug bioavailability and high-efficiency and high-selectivity phytochemical extraction, this research aimed to develop the separation and extraction of the active components from AS using a new green solvent.
This study used a heating and stirring procedure to create one type of DES. The DES was used to extract the isofraxidin, and then the extracted concentrations were quantified by UHPLC-MS/MS. Finally, the extract’s component was purified using the macroporous resin procedure. This study created a novel method for the green separation and extraction of plant bioactive components, providing a new technological route and potential commercial application for the extraction of isofraxidin from AS. The above advancements followed the development of the concept of green chemistry.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plants Materials
AS samples were collected from Sifeng Mountain, Jiamusi, Heilongjiang Province, and identified by Professor Ximing Zong. The samples were dried at 60 °C until they were a constant weight and then crushed in a high-speed pulverizer (FW100, Tianjin Teste, Tianjin, China) and sieved through an 80-mesh drug sieve. The samples were then vacuum-sealed and stored in vacuum-sealed bags until use.
2.2. Chemicals
Formic acid, methanol, and acetonitrile were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA. Choline chloride and citric acid were purchased from Aladin. Water was purified with the Master Touch-S15 ultrapure water system (HHitech, Shanghai, China). The standard isofraxidin (110837–202009, ≥99.8%) was purchased from the National Institute for Food and Drug Control of China. AB-8 and HPD100C macroporous resin were purchased from Ainuo Technology, China.
2.3. Synthesis of DES
CL-CA-DES was synthesized using citric acid (0.1 mol) as the hydrogen bond donor and choline chloride (0.1 mol) as the hydrogen bond acceptor. The two chemicals were placed into a conical flask and 20 mL of water was added to cause the two phases to infiltrate. The flask was sealed with tinfoil to prevent contamination of the synthesized DES and then placed in a constant-temperature water bath under magnetic stirring. The speed was kept at 500 rpm with heating at a constant temperature of 80 °C. The colorless and clarified CL-CA-DES was obtained after 2 h.
2.4. Viscosity Test
The solution’s viscosity was determined using a digital viscometer (Shanghai Precision Instruments Co., NDG-8S, Shanghai, China). The temperature-controlling equipment had a 0.01 K precision. At a temperature of 23 °C, the viscosity of the DES was measured with an accuracy of 0.001 mPa∙s.
2.5. UHPLC-MS/MS
The chemical components of the samples were separated using Ultimate 3000 high-performance liquid chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The phytochemicals in the samples were detected using a Q Exactive Series UHPLC-MS.
The chromatographic conditions were as follows: formic acid water (0.1%, v/v) and methyl acid acetonitrile (0.1%, v/v) as mobile phases A and B, respectively. The elution gradient programs were as follows: 0~2 min, 5% B; 2~20 min, 5~45% B; 20–21 min, 45–100% B; 21–25 min, 100% B; 25–26 min, 100–5% B; and 26–30 min, 5% B. The gradient flow rate was maintained at 0.3 mL-min−1, the column temperature was 40 °C, and the injection volume was 5 μL.
The high-resolution mass spectrometry parameters were set as follows: sheath gas pressure, 40 psi; auxiliary gas pressure, 20 psi; purge gas pressure, 10 psi; capillary voltage, 3 kV; ion transport tube temperature, 320 °C; AUG gas heating temperature, 350 °C; collision gas: nitrogen; normalized collision energies, 20, 40, and 60 eV; and RF lens amplitude field strength (s-lens), 60. This was combined with the selection of primary mass spectrometry, using the full-scan automatically triggered secondary mass spectrometry scan mode (Fullms-ddms2). The resolution parameters were as follows: primary and secondary high-resolution mass spectrometer resolution, 70,000 FWHM/17,500 FWHM, respectively; ion scan range, m/z 50−1500; cycle count, 3 times; four-level isolation window, 1.5 m/z; and dynamic exclusion time of 5 s.
2.6. Extraction of Specific Components from AS
In this experiment, isofraxidin was extracted from AS using ethanol, 70%, 50%, and 30% ethanol aqueous solution (v/v) water, and DES. The same ratio of extraction medium was used for different solvents for all the sample preparation processes to determine the isofraxidin concentrations of different solvent extracts. The AS powder that was filtered through 80 mesh was dried at 80 °C. A total of 20 mL of solvent (1:20 w/v) was used to extract 1.0 g of the powder. Prior to UHPLC/MS analysis, the water and ethanol extract was diluted 10 times, and the DES extract was diluted 20 times with methanol and filtered using an organic membrane syringe filter with a 0.22 μm pore size. The DES was extracted isofraxidin from AS at a temperature of 80 °C for 2 h.
2.7. Analysis Methodology Validation
2.7.1. Specific Test
A total of 5 μL of DES solution, isofraxidin solution (0.01 mg/mL), 70% ethanol, and blank control water solution were measured precisely and analyzed under UHPLC-MS/MS conditions for the specificity test.
2.7.2. Linear Regression Test
A total of 2 mg of isofraxidin was diluted and fixed in methanol to five reference standard solutions of 0.007 mg/mL, 0.005 mg/mL, 0.003 mg/mL, 0.002 mg/mL, and 0.001 mg/mL concentrations. The concentrations of the standard solutions of isofraxidin were measured according to the UHPLC-MS/MS conditions, and the linear range and regression equation were obtained by the least squares method.
2.7.3. Quantitative Limit
Isofraxidin was detected several times according to the UHPLC-MS/MS conditions, and a standard curve was established to determine the standard deviation of the peak area S. After obtaining the deviation of the response value S and the slope of the standard curve K, the limits of quantification were calculated separately.
Quantitation limit = 10 S/K
2.7.4. Precision Test
Six standard sample solutions of 0.002, 0.01, and 0.1 mg/mL were measured precisely and applied following the assay method described above. The above concentrations were calculated using the standard curve developed on the same date, and then the data were analyzed to calculate the RSD%.
2.7.5. Accuracy Test
The precision of the approach was examined using the analysis results of the standard sample recovery experiment. A volume of 10 mL of DES was added to 0.5 mL of isofraxidin (0.2 μg/mL) standard solution. The peak areas were measured by UHPLC. Six simultaneous treatments were performed for each sample. The established regression equations were used to determine the isofraxidin concentrations and blank DES recoveries. In addition, to accurately quantify the concentration of isofraxidin, 10 mL of each AS-DES extract was measured, and the sample extraction recovery was calculated by adding the standard solution, applied as described above.
2.7.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8.00 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA), and Student t-tests were used to compare the two groups of independent samples.
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and Physical Characterization of DES
3.1.1. The Stability of DES
The DES that was synthesized in this research is shown in Supplementary Materials Figure S1A,B. No component precipitation was detected in the DES; this shows that the solvents’ hydrogen bonds with other solvents were not disrupted and that they remained relatively stable at 4 °C for 3 months.
3.1.2. Viscosity Test
An essential solvent property parameter is viscosity. The high viscosity of nonionic common organic solvents increases mass transfer resistance during extraction, lowering the extraction efficiency [14]. The viscosity of DES has less effect on the extraction efficiency than that of nonionic solvents, but the high viscosity of DES still reduces the extraction efficiency.
This study investigated the viscosity of a single type of DES. The results showed that the initial viscosity of DES was significantly greater than that of common organic chemical solvents. Water had a major influence on both the stability of the hydrogen bond system and the viscosity of DES. As shown in Figure 1, the water concentration had a significant relationship with the DES viscosity, and the viscosity of DES was dramatically reduced by the addition of water.
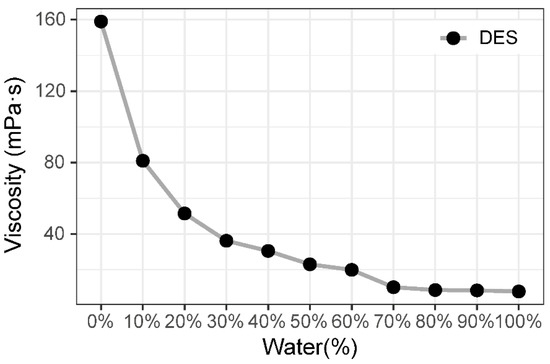
Figure 1.
The viscosity of DES was related to the water content.
Adding water significantly reduced the DES viscosity. For DES containing 10% water, the viscosity was reduced by 49.06%, and the DES viscosity decreased by 68.03% when the DES contained 20% water. At 50% water, the viscosity decreased slowly until the hydrogen bonding network of the DES system was destroyed, and the properties were seriously affected by the water. Therefore, the water content of DES is typically less than 30% in multiple applications, considering the effect of viscosity on the performance of natural product extraction, the effect of the solvent on the chromatographic system, and the stability of the solvent system [13,14].
The DES exhibited a higher viscosity than traditional solvents, and this viscosity improved as the quantity of active neutral hydroxyl groups from the hydrogen-bonded donors increased. Water plays a crucial role in determining the solvent’s viscosity. After DES production, small quantities of water can considerably lower the solvent’s viscosity. In the extraction test of natural plant chemical components, the amount of water used should not exceed 20% so as to ensure the physical and chemical qualities of the DES.
3.2. DES Separation and Extraction of Pharmacologically Active Compounds from AS
3.2.1. Identification of Isofraxidin from AS
Isofraxidin has the chemical formula C11H10O5 and the excimer ion [M + H]+ (m/z: 223.05977). Figure 2 shows the chromatograms of isofraxidin extracted using different solvents. Figure 2A–C shows the water, ethanol, and DES chromatograms as blank solvents. The chromatogram peaks are spurious at the same mass-to-charge ratio [M + H]+ (m/z: 223.05977) as isofraxidin, and the signal response intensity is relatively low (104) and can be ignored. These results indicate that the blank solvent chromatogram has a stable baseline with no interfering peaks from other components in 0–20 min. The incubation time of the isofraxidin standard reference samples shown in Figure 2D was 11.17 min, and the retention times of the chromatographic peaks of the 70% ethanol (Figure 2E) and DES (Figure 2F) extracts were the same. This demonstrated the separation and extraction of isofraxidin from AS with 70% ethanol and DES.
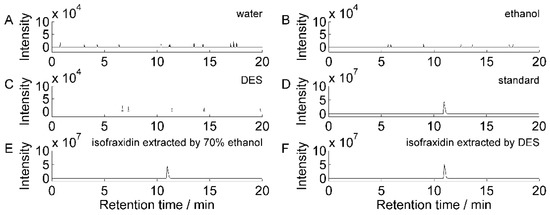
Figure 2.
Chromatogram of extracted ions of isofraxidin [M + H]+ (m/z: 223.05977). (A) Chromatogram of the aqueous solution as a blank solvent; (B) chromatogram of the ethanol blank solvent; (C) chromatogram of the DES blank solvent; (D) chromatogram of the reference standard samples of isofraxidin; (E) chromatogram of 70% ethanol-extracted isofraxidin; (F) chromatogram of DES-extracted isofraxidin.
3.2.2. The Capacity to Extract Isofraxidin from Different Solvents
The most frequently utilized solvents for recovering natural chemicals are water and ethanol. Figure 3 compares the capacities of solvents commonly used to extract isofraxidin from AS using excimer ion [M + H]+ (m/z: 223.05977) chromatograms of isofraxidin extracted using different solvents. This analysis demonstrated that 70% ethanol outperforms water and other ethanol concentrations in terms of extraction performance. DES is more capable than 70% ethanol.
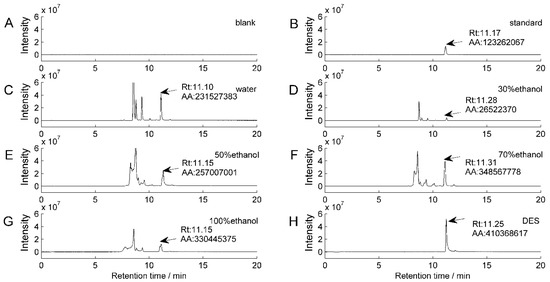
Figure 3.
Chromatograms of isofraxidin-extracted ions [M + H]+ (m/z: 223.05977) extracted using various solvents. (A) Chromatogram of the aqueous solution as the blank solvent; (B) chromatogram of isofraxidin reference standard samples; (C) chromatogram of isofraxidin extracted from water solution; (D) isofraxidin chromatogram extracted with 30% ethanol; (E) isofraxidin chromatogram extracted with 50% ethanol; (F) isofraxidin chromatogram extracted with 70% ethanol; (G) isofraxidin chromatogram extracted with 100% ethanol; (H) isofraxidin chromatogram extracted with DES.
3.3. Methodology Validation
3.3.1. Specific Test
Figure 2A–C show the extraction ion chromatograms in the blank solvents of water, ethanol, and DES. No additional component interference peaks negatively impacted these findings within 0–20 min, as indicated in the figures, and the baseline of the blank solvent chromatogram was stable.
3.3.2. Linear Regression Test
The standard curve of isofraxidin was measured, and the results showed that the regression equation fit well for isofraxidin concentrations in the 0.1–20 ug/mL range. The linear regression equation was as follows:
Peak area = 1.006 × 1011 × Concentration + 1.998 × 107
The correlation coefficient R2 was 0.9812.
3.3.3. Quantitative Limit
The limit of quantification for isofraxidin was determined to be 0.27 μg/mL by establishing the equation for the UHPLC-MS/MS data analysis.
3.3.4. Precision Test
The precision test was performed to determine the precision of the procedure. The test result data are shown in Table 1. According to these data, the RSD% of the isofraxidin is less than 2.11%, and the system error had no impact on the results.

Table 1.
Precision test results (n = 6).
3.3.5. Accuracy Test
The accuracy of the procedure was determined using the results of the recovery tests. The recovery rates were 93.1% (low concentration: 1 g/mL, RSD: 1.93%), 82.1% (medium concentration: 100 g/mL, RSD: 1.47%), and 80.7% (high concentration: 200 g/mL, RSD: 2.11%).
3.3.6. The Highest Content of DES Solvent Extraction Isofraxidin
Different DES-extracted isofraxidin concentrations were quantified using UHPLC-MS/MS. As shown in Figure 4, there were significant differences in the efficiency of different solvents for extracting isofraxidin from AS. DES displayed the highest isofraxidin extraction efficiency among all the test solvents. The concentration was 1.56 mg/g, which was 2–3 times higher than the values of the other solvents.
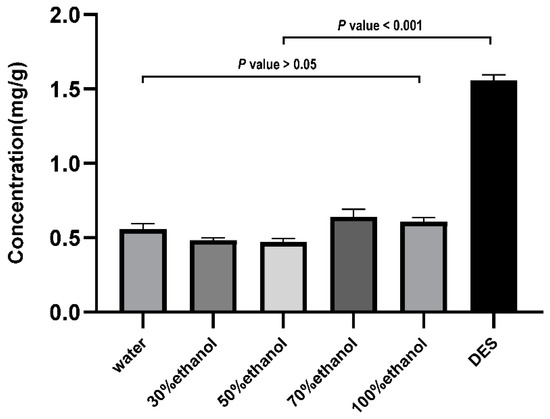
Figure 4.
The efficiency of different solvents for the extraction of isofraxidin.
4. Discussion
AS is a medicinal plant in the family of Araliaceae. Previous studies have shown that the active ingredients of AS can significantly improve blood lipid levels and endothelial cell function in patients with acute cerebral infarction, promote the proliferation of neural stem cells in ischemic brain tissue, and have therapeutic effects on cerebrovascular diseases such as hypertension and cerebral infarction [18,19,20]. In addition, AS has a sedative effect on the central nervous system, which can improve anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and other symptoms, and is commonly used for the clinical treatment of abnormal affective disorders and neurological disorders [21,22]. As a result, it is critical to efficiently extract the active components in AS. Traditional organic solvent extraction of active compounds from plants has several limitations, including the higher cost of organic solvents used in traditional extraction processes, difficulty in controlling the extraction parameters such as temperature and pH, the potential for toxicity due to the use of hazardous organic solvents, and an inability to extract polar compounds due to the non-polar nature of the organic solvents. Based on the concept of upholding safety and environmental protection, more green extraction solvents have emerged. As early as 2003, a researcher discovered that mixing choline chloride and urea under certain conditions can form a transparent liquid through hydrogen bonding called DES, which is highly efficient, degradable, non-polluting and can dissolve a variety of substances, including polysaccharides, alkaloids, flavonoids, etc. Therefore, DES has received the attention of many researchers and has been applied to the extraction of plant active components. The extraction of isofraxidin from AS using DES has great advantages compared to methods used in previous studies, including low melting points. The melting point of the deep eutectic solvents produced from choline chloride and citric acid is much lower than that of traditional solvents, making them easier to use and handle. The deep eutectic solvents produced from choline chloride and citric acid also have high solubility for a wide range of substances, making them ideal for a variety of applications; are much less toxic than traditional solvents, making them safer to use; and are much cheaper than traditional solvents, making them a cost-effective choice for synthesizing deep eutectic solvents.
Previous studies have found that using liquid–liquid extraction methods purified 90 mg of isofraxidin from 80 g dried ethyl acetate extract of Chloranthus japonicus root, and the extraction rate was 1.12 mg/g [23]. In this study, we used DES synthesized by choline chloride and citric acid, for the first time, as an extraction solvent for the extraction of isofraxidin from AS. The extraction rate of DES was 2–3 times higher than that obtained using conventional solvents.
Upon the initiation of isofraxidin extraction, it is crucial to choose a stable and efficient DES. In this study, we described only one DES synthesized from choline chloride and citric acid, but in the pre-experiments, we synthesized five DESs including DES synthesized from choline chloride and citric acid, DES synthesized from choline chloride and L-ascorbic acid, betaine and proline, betaine and maleic acid, and betaine and xylitol.
Previous studies have used the above-mentioned DESs to extract other active ingredients, but it is worth noting that almost all the previous studies synthesized DESs and used them directly to extract active ingredients or for other purposes. For example, Tsvetov et al. used choline chloride and organic acids (malonic, malic, tartaric, and citric acids) to synthesize NADES in order to extract bioactive components from chamaenerion angustifolium and found that a mixture of NADES, choline chloride, and citric acid are more effective for the extraction of bioactive components [24]. Luo et al. used choline chloride and L-ascorbic acid to synthesize DES in order to extract secondary metabolites from eucommia ulmoides leaves [25], and Zhang et al. used glycerol and levulinic acid to synthesize DES for extracting flavonoids from Acanthopanax senticosus [26]. Other functions include the synthesis of DES and the removal of copper corrosion products using choline chloride and L-ascorbic acid, as performed by Akiko Tsurumaki et al. [27]. There are also a few studies that have performed the short-term storage of newly synthesized DES. For example, Andrew J Maneffa et al. used choline chloride and other compounds to synthesize DESs. After 7 days of storage, it was found that some DESs had crystallized, indicating that the eutectic state of these DESs had changed [28].
In practical industry application, the stability of DES is also a concern. Therefore, in this study, the newly synthesized DES was stored in the dark at 4 °C for 100 days. We found that choline-chloride- and L-ascorbic-acid-synthesized DES (Figure S1E), betaine- and proline-synthesized DES (Figure S1F), and betaine and maleic acid DES (Figure S1G) showed very obvious crystallization. Similarly, betaine and xylitol DES (Figure S1H) showed partial crystallization; however, the DES from choline chloride and citric acid was still stable (Figure S1C,D). As such, we may infer that this composition is the closest to the eutectic composition of the choline chloride and citric acid mixtures, which can be used to synthesize DES. Moreover, the DES molecular formula can be accurately detected based on the advantages of high sensitivity and high resolution of mass spectrometry. The molar ratio of the hydrogen bond donor and acceptor may not be a critical factor in the molecular composition of DES, and most DES are synthesized in a 1:1 molar ratio of hydrogen bond donor and hydrogen bond acceptor. We therefore chose a molar ratio of 1:1. In addition, the viscosity of DES is a key factor in the extraction rate.
The viscosity of DES is mainly determined by van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding, and the solvent viscosity can influence the extraction efficiency of chemical components. The viscosity of DES is usually greater at room temperature, which may be caused by van der Waals forces or electrostatic interactions between ions [1]. Some research results found that temperature also has an effect on the viscosity of DES, with a higher temperature corresponding to a lower viscosity. Therefore, the viscosity of the solvent can be changed by heating. There is a strong hydrogen bonding interaction between the two constituents of DES, and an appropriate water content can reduce the viscosity of the solvent, thus increasing its solubility for the extract. This increase in solubility can lead to an increase in the conductivity of some DESs [29]. However, the interaction between hydrogen bonds gradually decreases when the water content reaches 50%; thus so the effect of the water content of DES should be considered when extracting chemical components.
The high-resolution Q Exactive Plus hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometer is a new type of mass spectrometry analyzer which has the advantages of a faster speed and higher resolution compared to time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The combination of UHPLC can greatly shorten the sample analysis time and improve the efficiency of chemical composition identification. For this reason, it has become a powerful tool for the analysis of complex samples in recent years and has been widely used in basic research on the pharmacodynamic components of various Chinese medicines. This technique was used to establish a rapid method for the analysis of isofraxidin in AS. An in-depth study of its chemical composition and further clarification of its material basis will be of great significance for the elucidation of the mechanism of the medicinal effect of AS.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we created a novel green isofraxidin extraction technique with practical implications. The novel green DES plays a vital role in the investigation of the separation and extraction of phytochemical components of AS, and it may be employed in the future as a green solvent, instead of organic reagents such as ethanol, for the separation and extraction of active components of AS. Following the development concept of green chemistry, the DES synthesized in this work was applied to the green separation and extraction of chemical components of medicinal plants, providing a new technological pathway for the optimal exploitation of active medicinal components of AS and showing its potential for commercial industrial applications in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr11030943/s1, Figure S1: Static stability of DES.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-h.S. and J.-h.H.; methodology, J.-h.H.; software, J.-h.H.; validation, C.-h.S., J.-h.H. and S.-y.S.; formal analysis, J.-h.H.; investigation, S.-y.S.; resources, Y.Z.; data curation, J.-h.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-h.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z.; visualization, X.-r.Z.; supervi-sion, L.-t.M.; project administration, X.-r.Z.; funding acquisition, L.-t.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, grant number [YQ2022E042], the Basic Research Project of Heilongjiang Province, grant number [2020-KYYWF-0243], the Special Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Jiamusi University, grant number [JMSUBZ2021-09], the Special Discipline Construction Project of the North Medicine and Functional Food, Jiamusi University, grant number [JDXKTD-2019005], and the Key Laboratory of New Drug Development and Pharmacodynamic Toxicological Evaluation in Heilongjiang Province, grant number [kfkt2021-02].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Nisibe, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Takeda, H.; Okano, G. Phenolic Compounds from Stem Bark of Acanthopanax senticosus and Their Pharmacological Effect in Chronic Swimming Stressed Rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.; Chen, K.W.; Cheng, I.S.; Tsai, P.H.; Lu, Y.J.; Lee, N.Y. The effect of eight weeks of supplementation with Eleutherococcus senticosus on endurance capacity and metabolism in human. Chin. J. Physiol. 2010, 53, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Ren, F.; Huang, W.; Ding, R.T.; Zhou, Q.S.; Liu, X.W. Anti-fatigue activity of extracts of stem bark from Acanthopanax senticosus. Molecules 2010, 16, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Park, J.; Yoon, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, H. Neuroprotective effects of Eleutherococcus senticosus bark on transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; You, J.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; Jin, L.; Xu, Y. Protective effects of aqueous extract from Acanthopanax senticosus against corticosterone-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, B.; Nebe, C.T.; Birr, C. Flow-cytometric studies with eleutherococcus senticosus extract as an immunomodulatory agent. Arzneimittelforschung 1987, 37, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Song, X.; Lin, D.; Xu, P. Isofraxidin Alleviates Myocardial Infarction Through NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition. Inflammation 2020, 43, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, X. Syringaresinol-di-O-β-D-glucoside, a phenolic compound from Polygonatum sibiricum, exhibits an antidiabetic and antioxidative effect on a streptozotocin-induced mouse model of diabetes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5511–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Tokiwa, T. Isofraxidin, a coumarin component from Acanthopanax senticosus, inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression and cell invasion of human hepatoma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yu, X.; Hu, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhong, X.; Xu, J.; Shang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Isofraxidin targets the TLR4/MD-2 axis to prevent osteoarthritis development. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.L.; Zhai, S.K.; Chen, H.L.; Luo, Y.D.; Tu, G.R.; Ou, D.W. Immunomopharmacological effects of polysaccharides from Acanthopanax senticosus on experimental animals. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1991, 13, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.B.; Yoon, Y.D.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.W.; Yoon, W.K.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M. Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of B cells and macrophages by polysaccharide isolated from cell culture of Acanthopanax senticosus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Insights into the relationships between physicochemical properties, solvent performance, and applications of deep eutectic solvents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 35537–35563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Feng, C.; Hu, L.; Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, M.; Xie, W. Exploration of a ternary deep eutectic solvent for the efficient extraction of plantamajoside, acteoside, quercetin and kaempferol from Plantago asiatica L. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osamede Airouyuwa, J.; Mostafa, H.; Riaz, A.; Maqsood, S. Utilization of natural deep eutectic solvents and ultrasound-assisted extraction as green extraction technique for the recovery of bioactive compounds from date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seeds: An investigation into optimization of process parameters. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 91, 106233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Cheng, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; He, L. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Assisted Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides from Paecilomyces hepiali. Molecules 2022, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Li, S.; Duan, F.; Liu, M.; Shan, S.; Ju, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W. The Therapeutic Effect of Acanthopanax senticosus Components on Radiation-Induced Brain Injury Based on the Pharmacokinetics and Neurotransmitters. Molecules 2022, 27, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, W. Image Effect Observation of Acanthopanax senticosus on Antifatigue Activity after Exercise. Scanning 2022, 2022, 7588680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiokawa, Y.; Miyauchi-Wakuda, S.; Kagota, S.; Maruyama-Fumoto, K.; Yamada, S.; Shinozuka, K. Acanthopanax senticosus Induces Vasorelaxation via Endothelial Nitric Oxide-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, S.N.; Yang, Z.M.; Wang, K.X.; Lu, F.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Acanthopanax senticosus Protects Structure and Function of Mesencephalic Mitochondria in A Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Tang, S.Q.; Huang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Yook, C.S.; Whang, W.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Liu, X.Q. Acanthopanax henryi: Review of Botany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Molecules 2021, 26, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majnooni, M.B.; Fakhri, S.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Mojarrab, M.; Kazemi-Afrakoti, S.; Farzaei, M.H. Isofraxidin: Synthesis, Biosynthesis, Isolation, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacological Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetov, N.; Pasichnik, E.; Korovkina, A.; Gosteva, A. Extraction of Bioactive Components from Chamaenerion angustifolium (L.) Scop. with Choline Chloride and Organic Acids Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Ren, X.; Shi, X.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. Study on enhanced extraction and seasonal variation of secondary metabolites in Eucommia ulmoides leaves using deep eutectic solvents. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, X. A Green Method of Extracting and Recovering Flavonoids from Acanthopanax senticosus Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumaki, A.; Chiarucci, C.; Khaire, S.; Dal Bosco, C.; Gentili, A.; Navarra, M.A. Removal of Copper Corrosion Products by Using Green Deep Eutectic Solvent and Bio-Derivative Cellulose Membrane. Polymers 2022, 14, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneffa, A.J.; Harrison, A.B.; Radford, S.J.; Whitehouse, A.S.; Clark, J.H.; Matharu, A.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Natural Ascorbic Acid Analogues and Choline Chloride. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).