Novel Iterative Feedback Tuning Method Based on Overshoot and Settling Time with Fuzzy Logic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. PID Controller
2.2. PID Controller Behavior
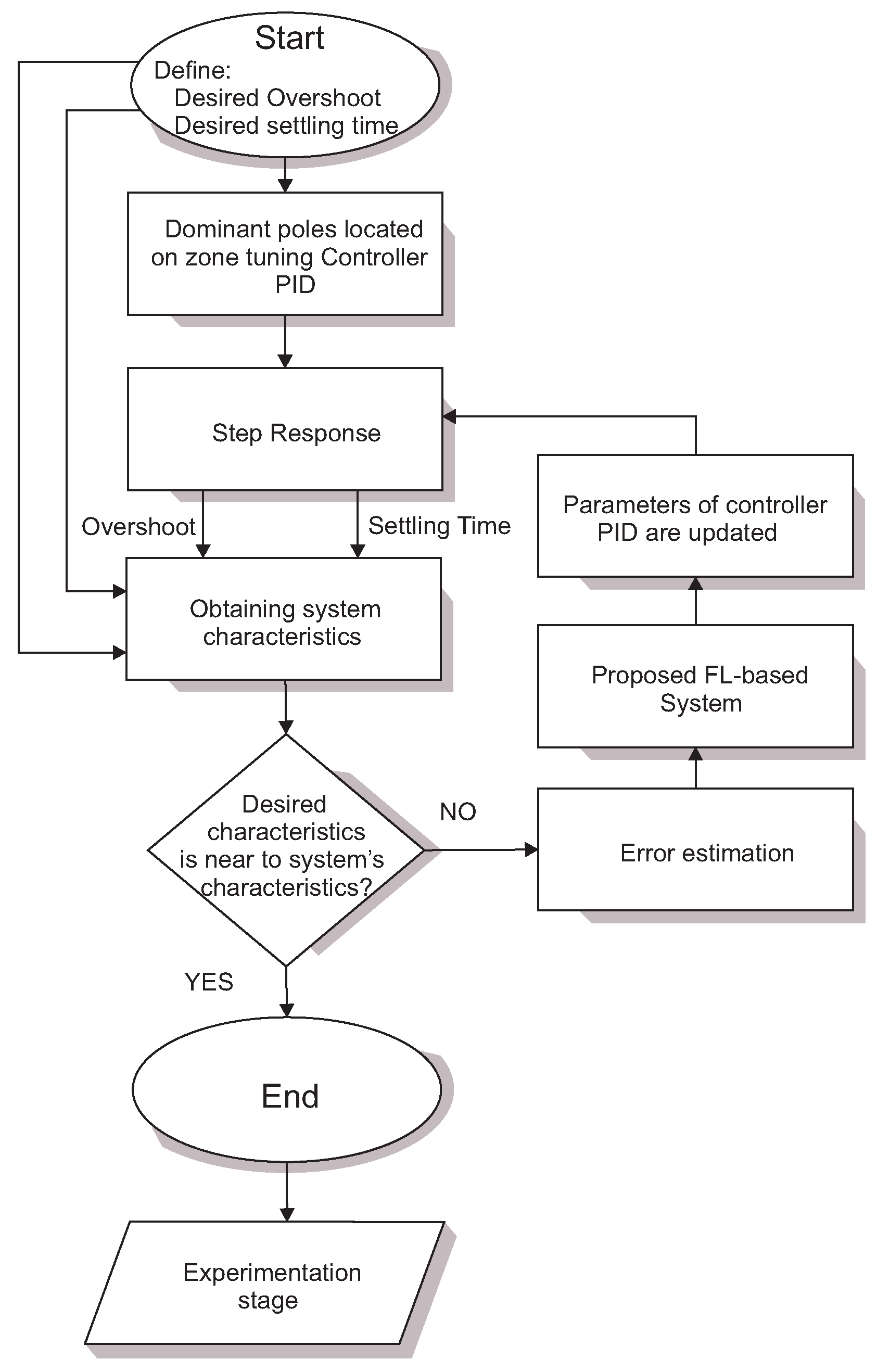
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Proposed Methodology
- Step 1:
- The user proposes the desired overshoot and settling time characteristics of the system to be tuned.
- Step 2:
- The parameters of overshoot and settling time of the plant are obtained to estimate the dominant poles and position them in the semicircle that crosses the tuning zone as described above and with which the initial gains of the PID controller are obtained.
- Step 3:
- The system step response is obtained with the controller to estimate the actual values of overshoot and settling time.
- Step 4:
- The errors between the desired parameters and the actual parameters are calculated.
- Step 5:
- If the errors are small enough, PID adjustment is finished (step 8); otherwise, the estimated errors are used to calculate the new PID gains.
- Step 6:
- From the errors obtained in step 4 and with the proposed system based on FL, the new PID gains are estimated.
- Step 7:
- The PID gains are updated, and the process is repeated from step 3.
- Step 8:
- The tuning process is finished and continues with the implementation of the controller.
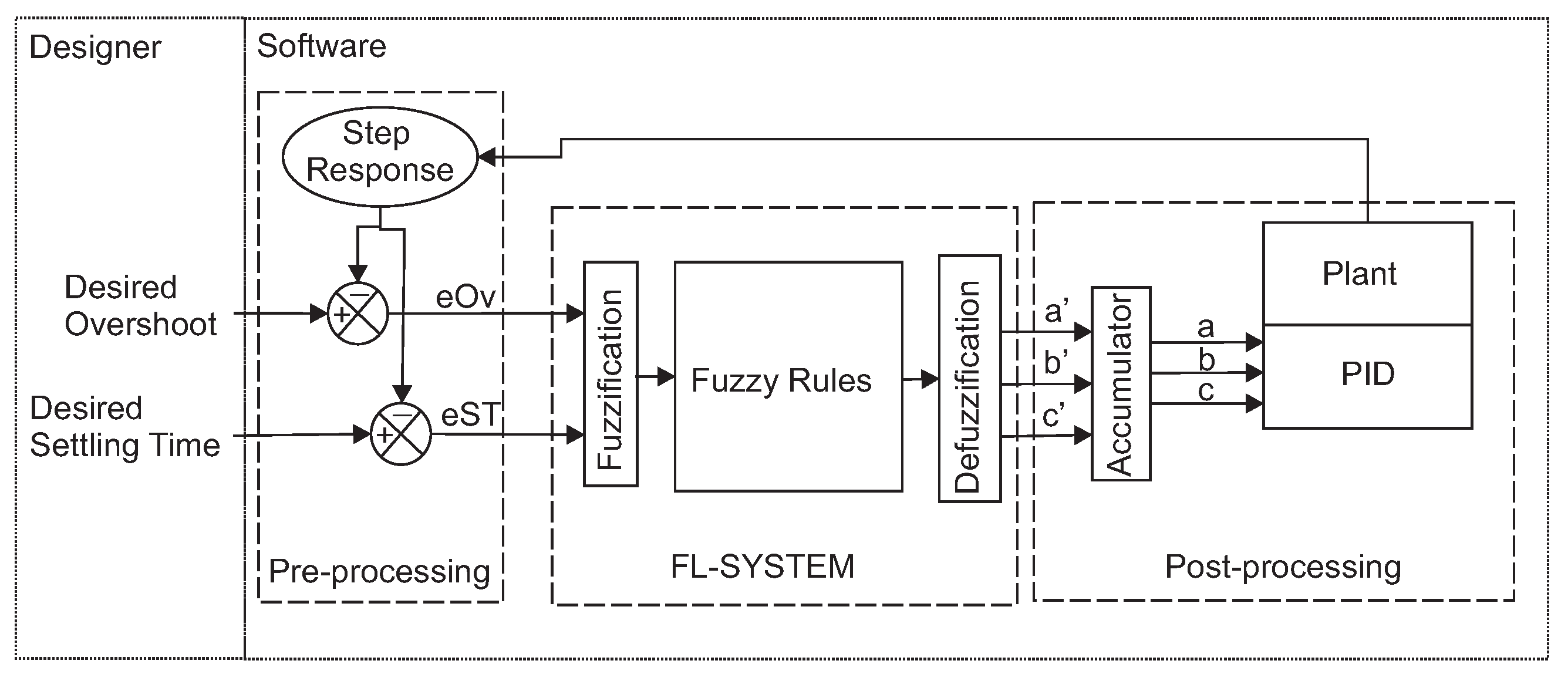
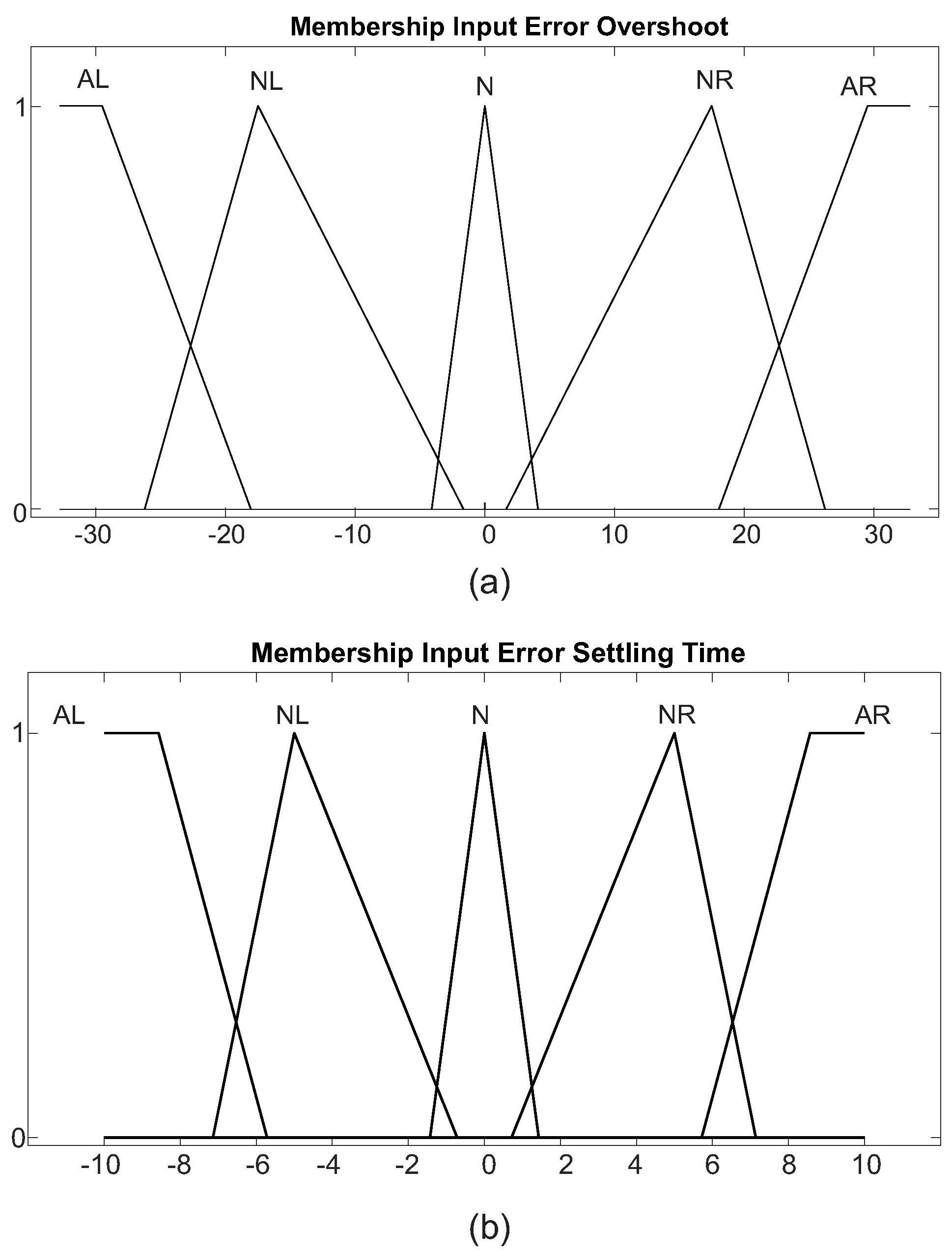
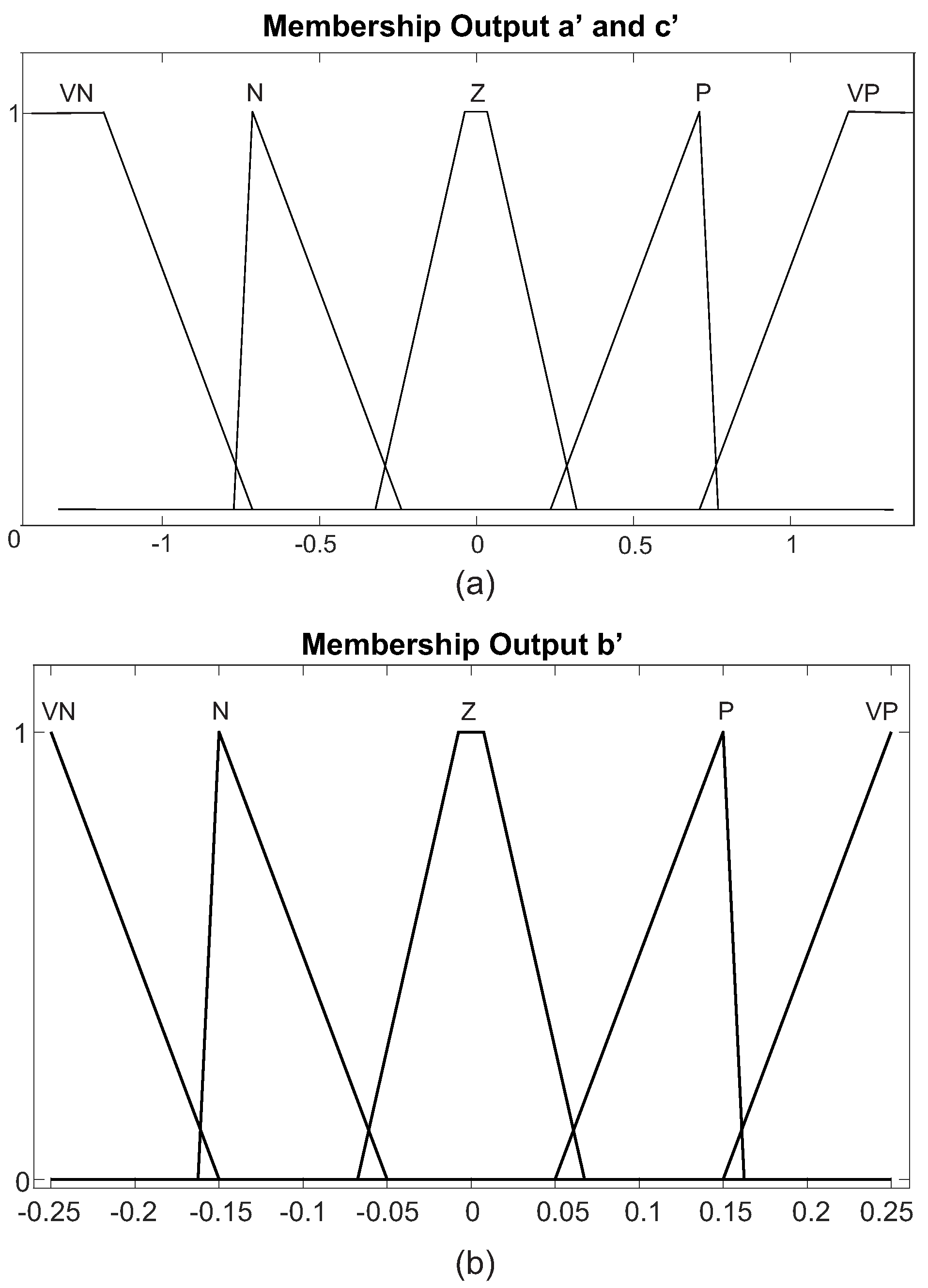
3.2. Implementation of FL-Based System
4. Results
4.1. Simulation
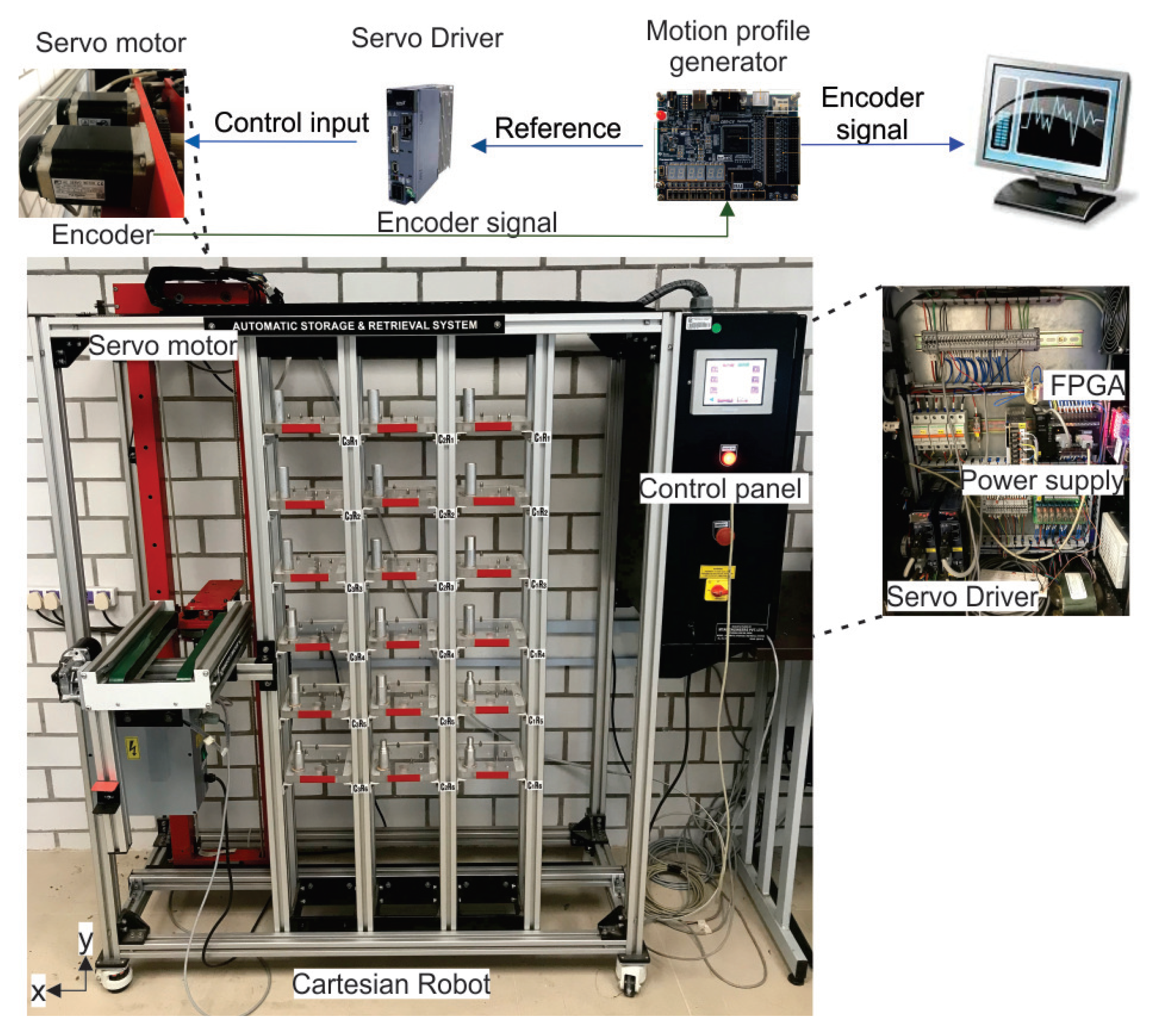
4.2. Experimental Validation
4.3. Result Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PID | Proportional–integral–derivative |
| FL | Fuzzy logic |
| IFT | Iterative feedback tuning |
| MF | Membership functions |
References
- Chen, P.; Luo, Y. A Two-Degree-of-Freedom Controller Design Satisfying Separation Principle with Fractional Order PD and Generalized ESO. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 27, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Perez, R.; Guerrero, M.; Dzul, A. Nonlinear PID-type controller for quadrotor trajectory tracking. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 23, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.S. A self-tuning PI controller for the speed control of electrical motor drives. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 119, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, P. Fuzzy-model-based sampled-data control of chaotic systems: A fuzzy time-dependent Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 25, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyetkin, M.M.; Onat, C.; Tan, N. PID tuning method for integrating processes having time delay and inverse response. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, L. Theory and design of PID controller for nonlinear uncertain systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2019, 3, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, W.L.; Araujo, I.B.; Filho, J.B.M.; Junior, A.G.C. Mathematical modeling and PID controller parameter tuning in a didactic thermal plant. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2017, 15, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Yang, G.H. Data-driven approach to accommodating multiple simultaneous sensor faults in variable-gain PID systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 66, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. NARX prediction-based parameters online tuning method of intelligent PID system. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130922–130936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Tan, W. Analysis and tuning of general linear active disturbance rejection controllers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5497–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, B.; Padhy, P.K. Optimal PID controller design with adjustable maximum sensitivity. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, P. Overshoot and settling time assignment with PID for first-order and second-order systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, K.J.; Hägglund, T.; Hang, C.C.; Ho, W.K. Automatic tuning and adaptation for PID controllers-a survey. Control Eng. Pract. 1993, 1, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddahi, A.; Sepehri, N.; Kinsner, W. Fractional-order control of hydraulically powered actuators: Controller design and experimental validation. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, S.; Ganguly, A.; Chatterjee, R.; Basak, B.; Sheet, D.; Ganguly, A. A review on tuning methods for PID controller. Asian J. Converg. Technol. (AJCT) 2019, 5, 818–827. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cluett, W.R. Tuning PID controllers for integrating processes. IEEE Proc. Control Theor. Appl. 1997, 144, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrančić, D.; Huba, M.; Oliveira, P.M. PID controller tuning for integrating processes. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atic, S.; Cokmez, E.; Peker, F.; Kaya, I. PID controller design for controlling integrating processes with dead time using generalized stability boundary locus. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazanella, A.S.; Pereira, L.F.A.; Parraga, A. A new method for PID tuning including plants without ultimate frequency. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 25, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, N.; Nizam, H.; Shahida, N.; Abdullah, Q.; Ibrahim, Z.; Binti, J.; Jidin, A. A Novel Self-Tuning Fuzzy Logic Controller Based Induction Motor Drive System: An Experimental Approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 68172–68184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Lucena, C.; Cardoso, A.; Palma, L.B. Gain tuning of fuzzy PID controllers for MIMO systems: A performance-driven approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, S.; Merazchiev, D.; Jain, L. A two-variable fuzzy control design with application to an air-conditioning system. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramabadi, S.S.; Bakhshai, A. Critic-based self-tuning PI structure for active and reactive power control of VSCs in microgrid systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, R.E.; David, R.C.; Petriu, E.M. Grey wolf optimizer algorithm-based tuning of fuzzy control systems with reduced parametric sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinski, C.; Leandro, G.V.; da Costa Oliveira, G.H. Fuzzy PID controller design for LFC in electric power systems. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2019, 17, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Mohamed, A.; Abdolrasol, M.G. Fuzzy logic speed controller optimization approach for induction motor drive using backtracking search algorithm. Measurement 2015, 78, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.G.M.; Uchida, K.; Kofuji, K.; Jintsugawa, T.; Nakazawa, C. An automatic-tuning scheme based on fuzzy logic for active power filter in wind farms. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, C.; Xu, W. Adaptive fuzzy logic control of fuel-cell-battery hybrid systems for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbasar, T. Robust stability analysis and systematic design of single-input interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 675–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.H.; Javadi, S.; Reza, S.N. DC motor speed control by self-tuning fuzzy PID algorithm. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2014, 37, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, H.; Gunnarsson, S.; Gevers, M. A convergent iterative restricted complexity control design scheme. In Proceedings of the 1994 33rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 14–16 December 1994; pp. 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, H.; Gevers, M.; Gunnarsson, S.; Lequin, O. Iterative feedback tuning: Theory and applications. IEEE CS-M 1988, 18, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, M.C.; Lecchini, A.; Savaresi, S.M. Virtual reference feedback tuning: A direct method for the design of feedback controllers. Automatica 2002, 38, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, S.; Kaneko, O.; Fujii, T. A new approach to parameter tuning of controllers by using one-shot experimental data—A proposal of fictitious reference iterative tuning. Trans. ISCIE 2004, 17, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, O.; Soma, S.; Fujii, T. Fictitious reference iterative tuning in the two-degree of freedom control scheme and its application to a facile closed loop system identification. Trans. ISCIE 2006, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Tasaka, K.; Ogawa, M.; Takinami, A.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshii, S. Extended fictitious reference iterative tuning and its application to chemical processes. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Advanced Control of Industrial Processes (ADCONIP), Hangzhou, China, 23–26 May 2011; pp. 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, S. Iterative Controller Parameters Tuning Using Gradient Estimate of Variance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems (ICAMechS), Kusatsu, Japan, 26–28 August 2019; pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcel, F.H.; Bart, V.V. Constrained iterative feedback tuning for robust control of a wafer stage system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, R.E.; Preitl, Z.; Preitl, S. Iterative feedback tuning approach to development of PI-fuzzy controllers. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Fuzzy Systems Conference, London, UK, 23–26 July 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, R.E.; Radac, M.B.; Tomescu, M.; Petriu, E.M.; Pretil, S. Stable and convergent iterative feedback tuning of fuzzy controllers for discrete-time SISO systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 40, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, S.; Peng, Q.; Asif, A.; Yasir, M.; Inam, A. A Simple Tuning Algorithm of Augmented Fuzzy Membership Functions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 35805–35814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarif, B.M.; Kumar, V.A.; Rao, V.G. Comparison Study of PID Controller Tuning using Classical/Analytical Methods. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 5618–5625. [Google Scholar]
 central semicircle;
central semicircle;  semicircle at −0.5;
semicircle at −0.5;  semicircle at −0.25;
semicircle at −0.25;  semicircle at 0.25;
semicircle at 0.25;  semicircle at 0.5. (d) Tuning plane on straight line, (e) overshoot behavior on straight line, and (f) settling time behavior on straight line:
semicircle at 0.5. (d) Tuning plane on straight line, (e) overshoot behavior on straight line, and (f) settling time behavior on straight line:  central line;
central line;  bottom line (near real axis);
bottom line (near real axis);  line between central line and bottom line;
line between central line and bottom line;  line between central and top line;
line between central and top line;  top line (near imaginary axis).
top line (near imaginary axis).
 central semicircle;
central semicircle;  semicircle at −0.5;
semicircle at −0.5;  semicircle at −0.25;
semicircle at −0.25;  semicircle at 0.25;
semicircle at 0.25;  semicircle at 0.5. (d) Tuning plane on straight line, (e) overshoot behavior on straight line, and (f) settling time behavior on straight line:
semicircle at 0.5. (d) Tuning plane on straight line, (e) overshoot behavior on straight line, and (f) settling time behavior on straight line:  central line;
central line;  bottom line (near real axis);
bottom line (near real axis);  line between central line and bottom line;
line between central line and bottom line;  line between central and top line;
line between central and top line;  top line (near imaginary axis).
top line (near imaginary axis).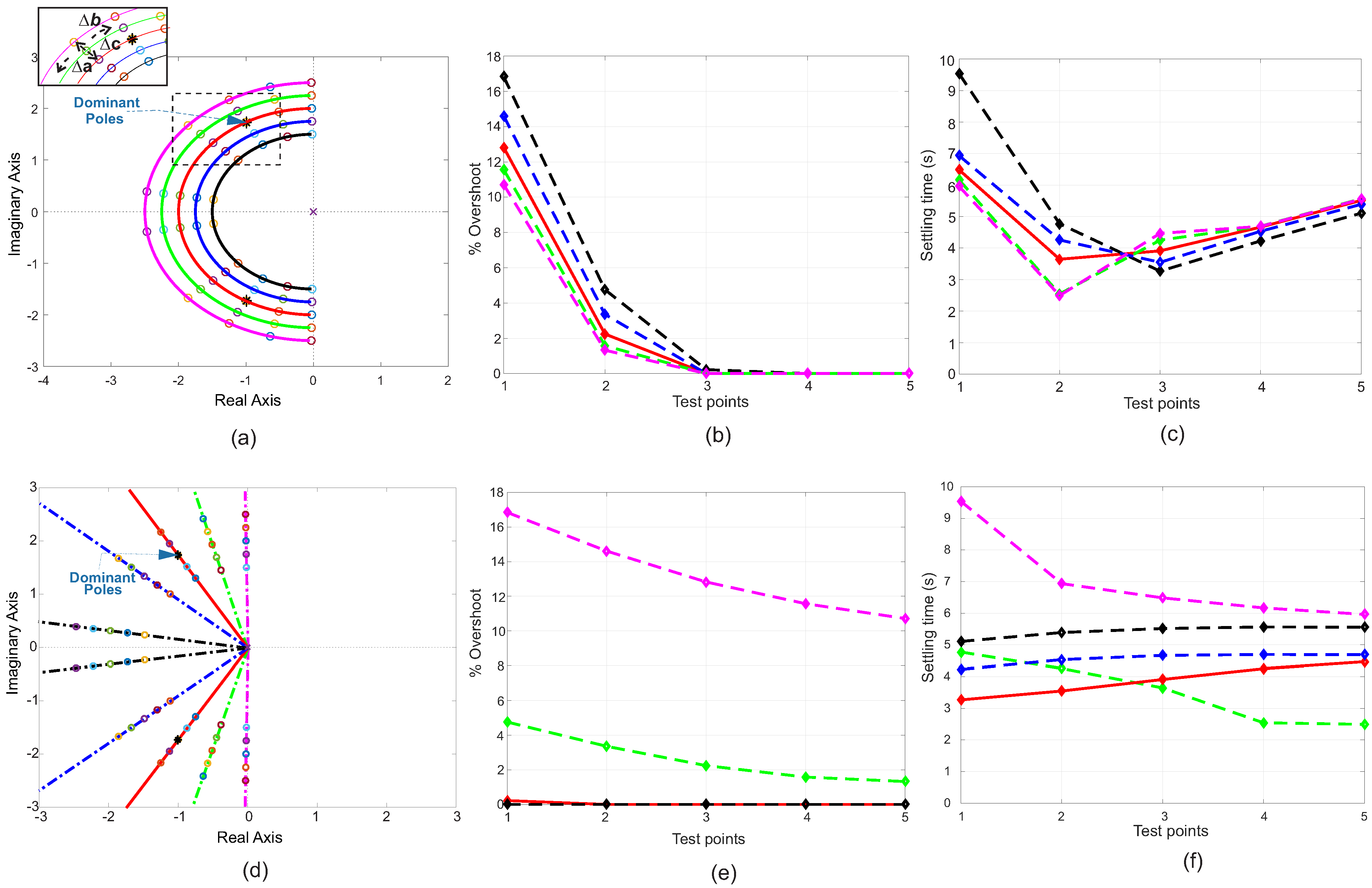
 final controller tuning and
final controller tuning and  initial controller tuning.
initial controller tuning.
 final controller tuning and
final controller tuning and  initial controller tuning.
initial controller tuning.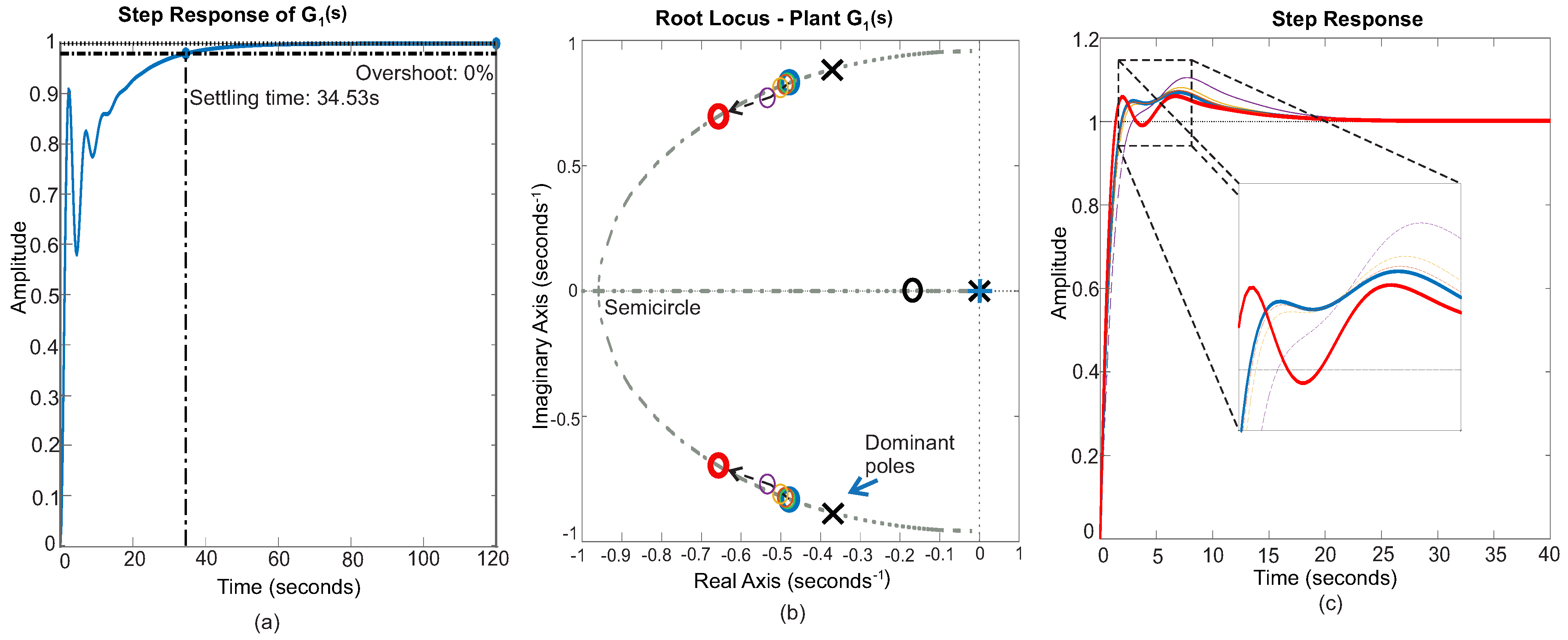
 proposed tuning method and
proposed tuning method and  PI/PID tuning method [19].
PI/PID tuning method [19].
 proposed tuning method and
proposed tuning method and  PI/PID tuning method [19].
PI/PID tuning method [19].
 tuned system response with proposed method and
tuned system response with proposed method and  reference signal.
reference signal.
 tuned system response with proposed method and
tuned system response with proposed method and  reference signal.
reference signal.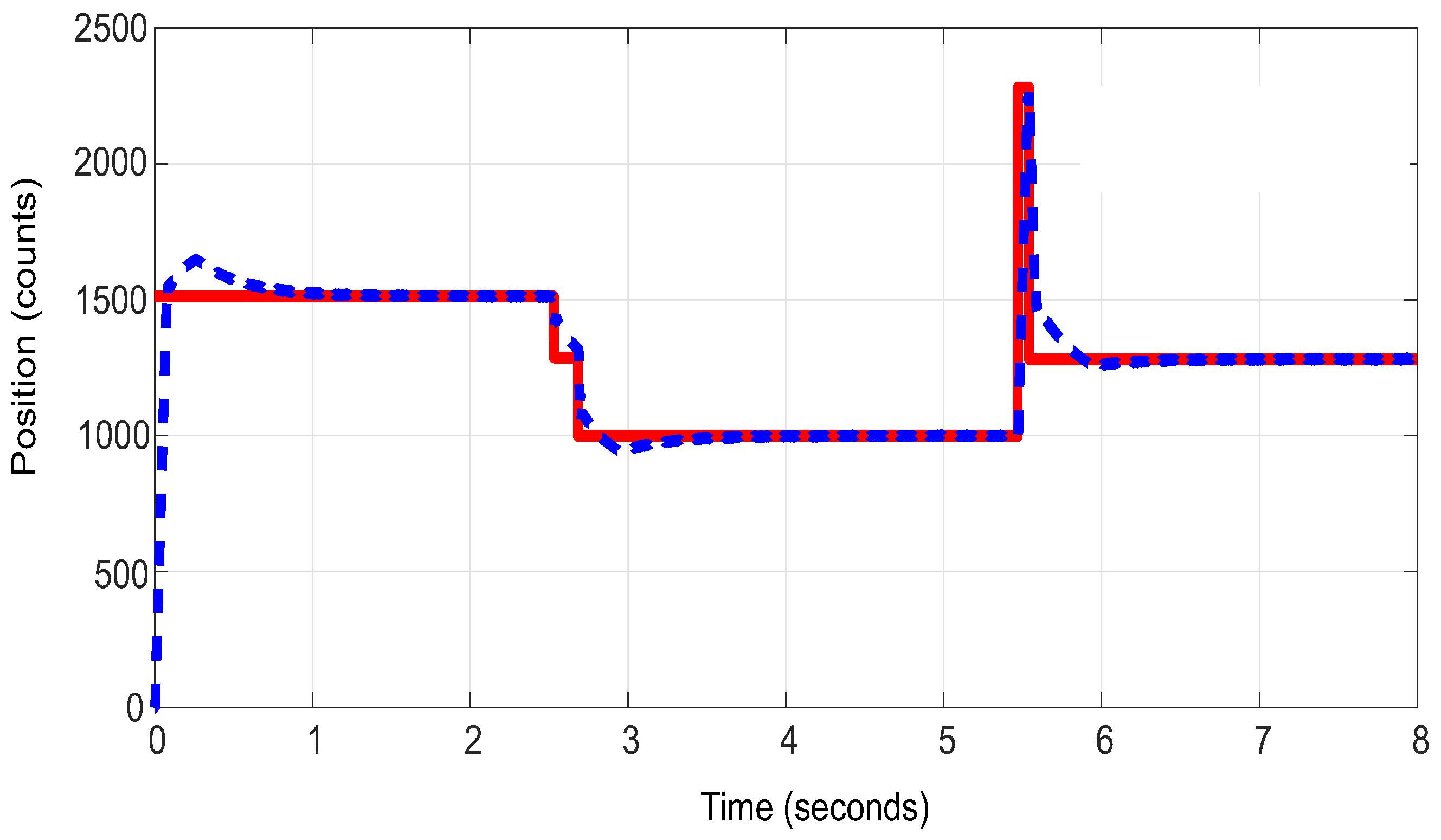
| e(Ov) | AL | NL | N | NR | AR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e(ST) | ||||||
| AL | VP | P | Z | N | VN | |
| NL | P | P | Z | N | VN | |
| N | P | Z | Z | N | N | |
| NR | N | N | Z | N | N | |
| AR | VN | N | Z | P | VP | |
| e(Ov) | AL | NL | N | NR | AR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e(ST) | ||||||
| AL | VN | N | Z | P | VP | |
| NL | VP | P | Z | N | VN | |
| N | P | Z | Z | Z | P | |
| NR | VN | N | Z | P | P | |
| AR | VN | N | Z | P | VP | |
| Tuning Method | PID Parameter | Dynamic Performance Specification | ISE | IAE | ITSE | ITAE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | ||||||||||
| [16] | 1.6 | 3.2 | 0.061 | 15.1 | 27.7 | 2.57 | 6.51 | 10.39 | 24.15 | 132.2 |
| Proposed | 4.4006 | 2.6139 | 0.0906 | 7.14 | 10.9 | 0.633 | 5.27 | 6.14 | 9.97 | 24.79 |
| [17] | 0.567 | 0.49 | 0.0766 | 1.97 | 22.8 | 64 | 3.84 | 6.37 | 14.26 | 36.62 |
| Proposed | 0.725 | 0.38 | 0.055 | 2.13 | 30 | 31.6 | 2.92 | 5.87 | 9.30 | 41.70 |
| [17] | 0.279 | 0.493 | 0.0235 | 3.49 | 26.6 | 54.3 | 5.48 | 9.02 | 29.26 | 70.26 |
| Proposed | 0.3086 | 0.4993 | 0.0022 | 3.52 | 44.2 | 32.7 | 4.08 | 6.81 | 12.26 | 46.11 |
| [17] | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.0233 | 1.88 | 23 | 53.7 | 6.58 | 8.98 | 24.26 | 59.68 |
| Proposed | 0.2344 | 0.1822 | 0.0007 | 2.93 | 14.7 | 22.4 | 5.23 | 6.46 | 12.02 | 28.50 |
| [18] | 1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.679 | 10.6 | 48.5 | 1.66 | 2.6698 | 1.85 | 6.88 |
| Proposed | 0.9566 | 1.3564 | 0.2301 | 0.616 | 10.4 | 47.2 | 1.62 | 2.6607 | 1.79 | 7.31 |
| [18] | 1.106 | 1.1856 | 0.1558 | 1.4 | 15.6 | 10.5 | 0.694 | 1.837 | 0.739 | 8.797 |
| Proposed | 2.425 | 1.74 | 0.395 | 0.471 | 11 | 8.69 | 0.4636 | 1.1 | 0.306 | 3.746 |
| [18] | 0.569 | 0.4995 | 0.081 | 1.77 | 11.2 | 47.3 | 2.51 | 4.31 | 6.14 | 17.32 |
| Proposed | 0.6053 | 0.6771 | 0.1135 | 1.56 | 11.3 | 47.3 | 2.35 | 4.15 | 5.49 | 16.5 |
| [19] | 0.75 | 0.12 | 0.1488 | 5.9 | 35.6 | 11.7 | 1.18 | 4.12 | 4.62 | 50.36 |
| Proposed | 1.4565 | 1.124 | 1.044 | 0.982 | 13.5 | 6.07 | 0.33 | 1.026 | 0.22 | 4.86 |
| [19] | 3.11 | 0.41 | 17.083 | 0.167 | 0.288 | 0 | 0.021 | 0.058 | 8.6 | 0.005 |
| Proposed | 1 | 1044 | 1.09 | 4.37 | 7.67 | 0.072 | 9.9 | 1.9 | 9.9 | 3.8 |
| [39] | 0.0027 | 0 | 1.09 | 0.115 | 0.312 | 3.64 | 0.055 | 0.084 | 0.0020 | 0.0053 |
| Proposed | 1 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 1.57 | 2.8 | 0 | 3.6 | 7.2 | 1.3 | 5.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Villagomez, J.; Rodriguez-Donate, C.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Mata-Chavez, R.I.; Palillero-Sandoval, O. Novel Iterative Feedback Tuning Method Based on Overshoot and Settling Time with Fuzzy Logic. Processes 2023, 11, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030694
Gonzalez-Villagomez J, Rodriguez-Donate C, Lopez-Ramirez M, Mata-Chavez RI, Palillero-Sandoval O. Novel Iterative Feedback Tuning Method Based on Overshoot and Settling Time with Fuzzy Logic. Processes. 2023; 11(3):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030694
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Villagomez, Jacob, Carlos Rodriguez-Donate, Misael Lopez-Ramirez, Ruth I. Mata-Chavez, and Omar Palillero-Sandoval. 2023. "Novel Iterative Feedback Tuning Method Based on Overshoot and Settling Time with Fuzzy Logic" Processes 11, no. 3: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030694
APA StyleGonzalez-Villagomez, J., Rodriguez-Donate, C., Lopez-Ramirez, M., Mata-Chavez, R. I., & Palillero-Sandoval, O. (2023). Novel Iterative Feedback Tuning Method Based on Overshoot and Settling Time with Fuzzy Logic. Processes, 11(3), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030694








