The Mechanism of Channel Opening of Anion Channelrhodopsin GtACR1: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Modeling
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
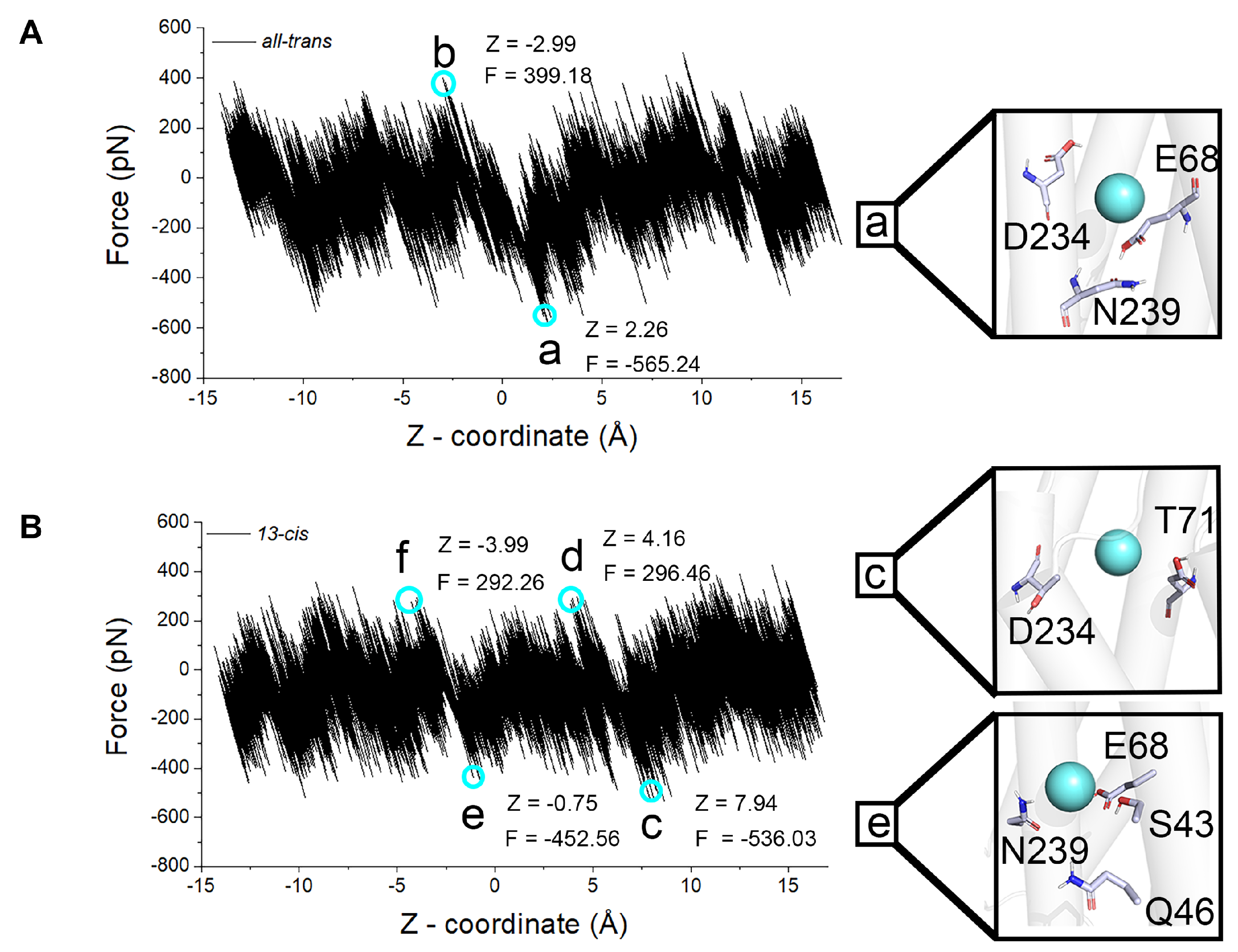
2.3. Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation
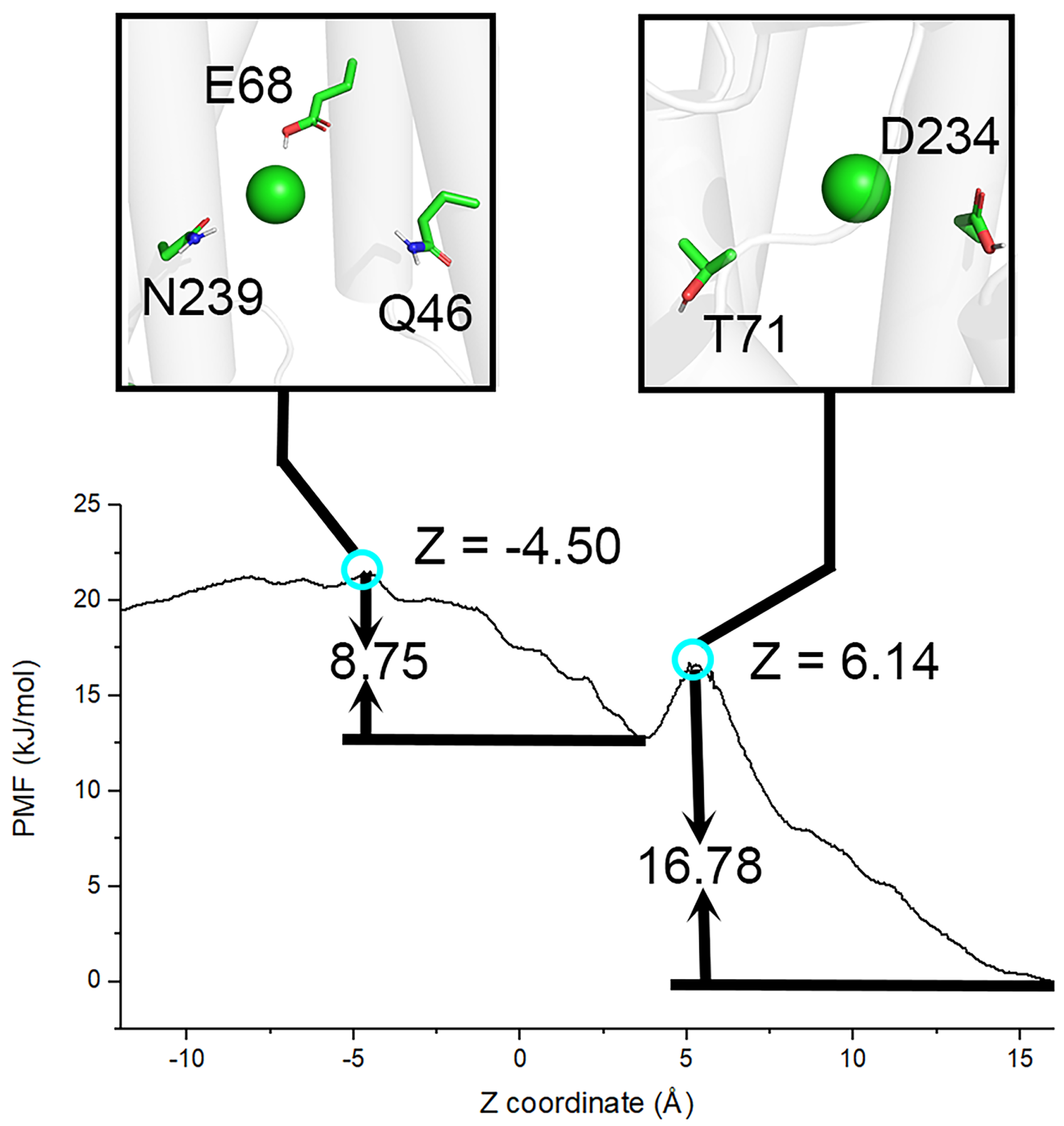
2.4. Umbrella Sampling
3. Results
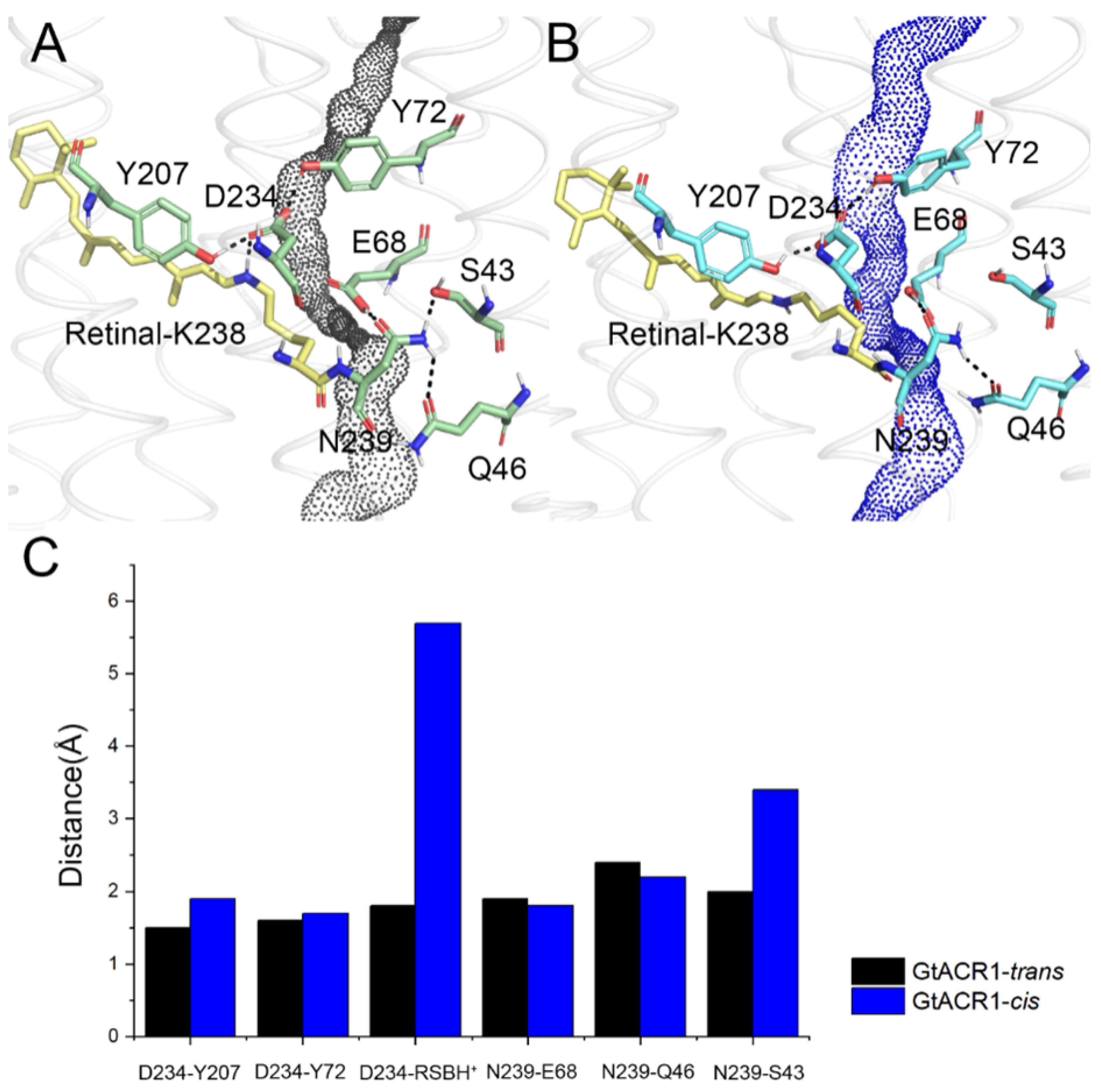
3.1. Conformational Differences between GtACR1-trans and Its 13-cis Isomer
3.2. The Formation of Pre-Opened State (K-like) for GtACR1-cis
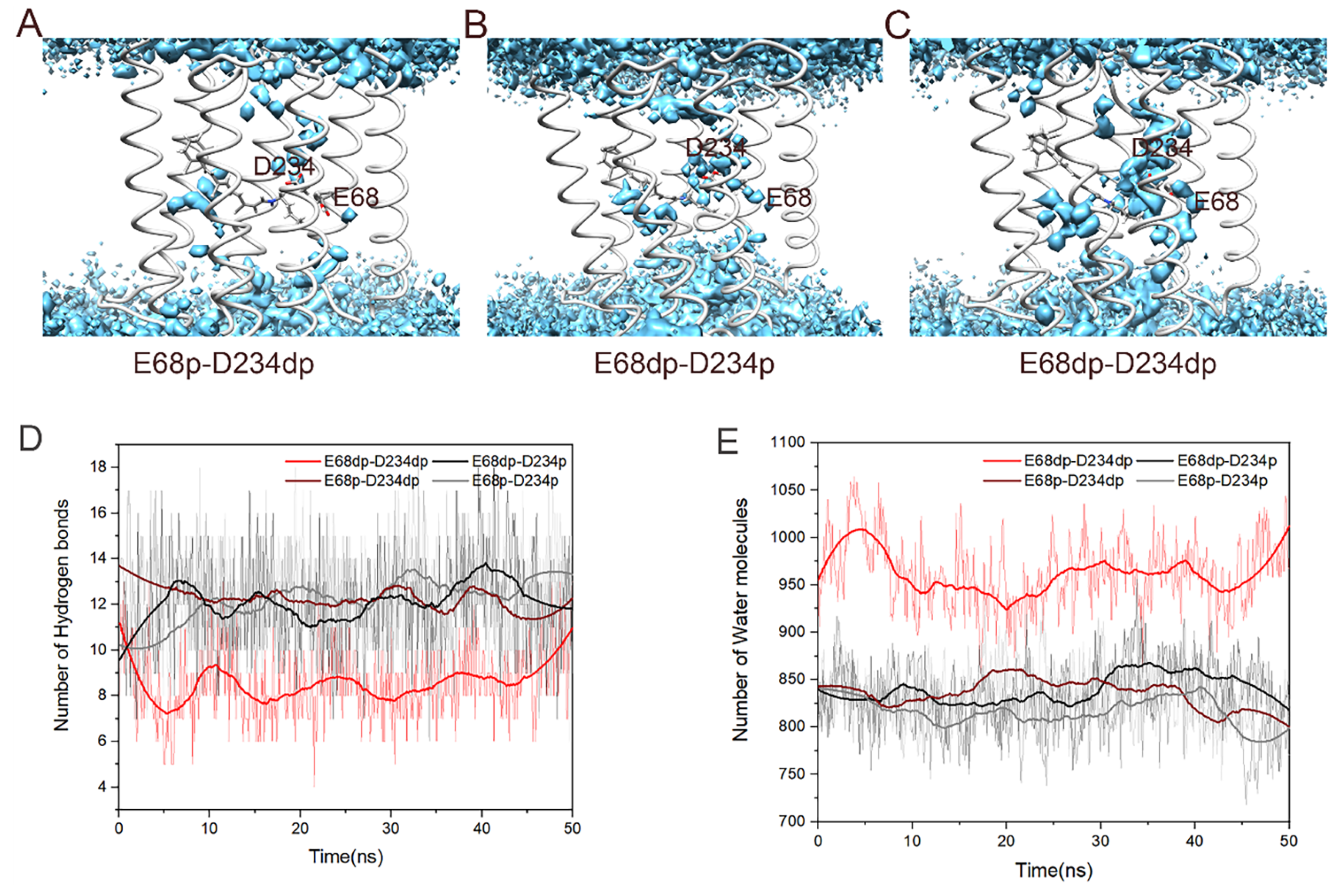
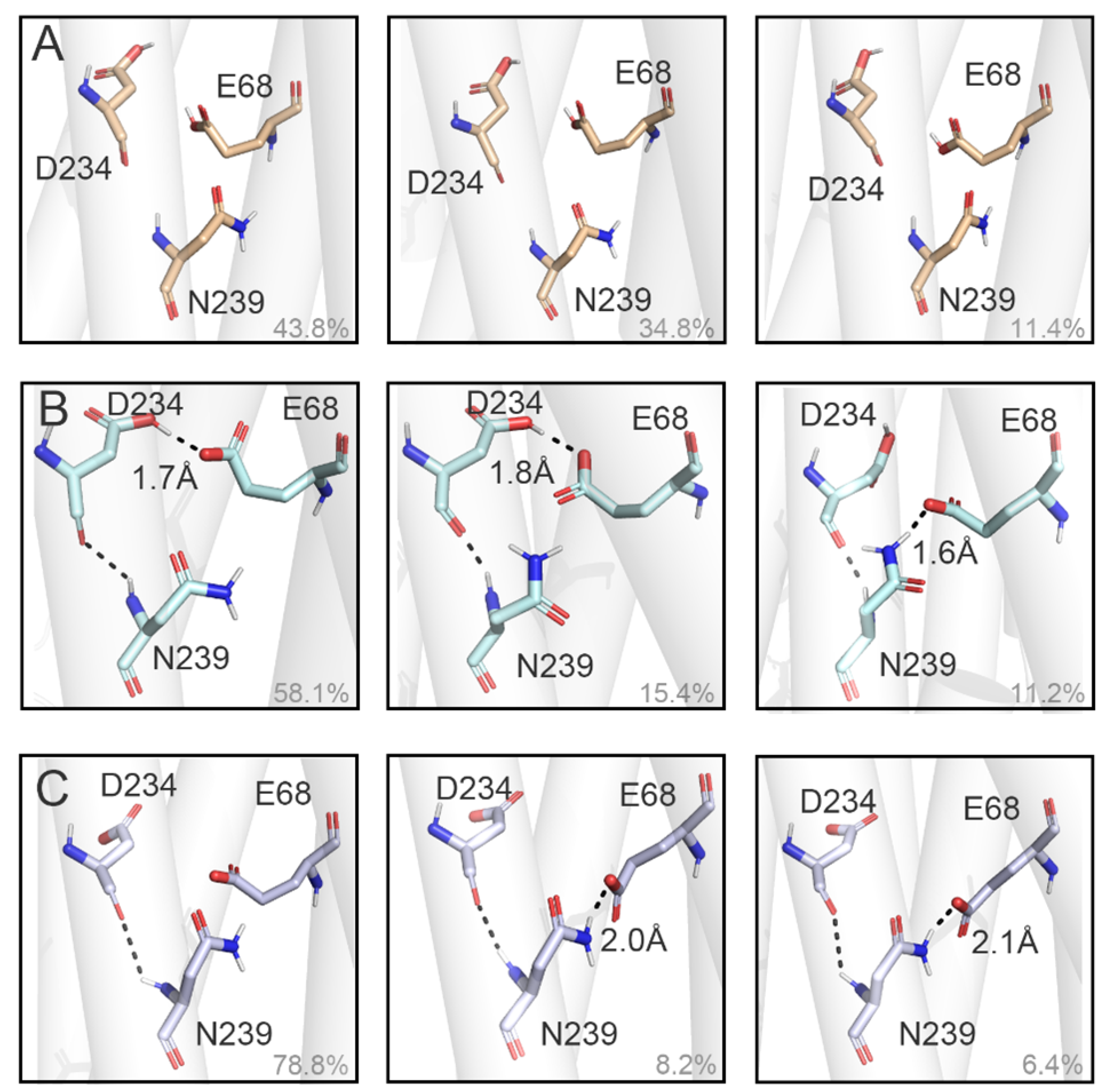
3.3. Binding Sites of Chloride Ions in E68p-D234p (trans) and E68p-D234p (cis)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| GtACR1 | Guillardia theta anion channelrhodopsin 1 |
| ChRs | Channelrhodopsins |
| ACR | Anion channel rhodopsin |
| TM | Transmemebranes |
| EV | Extracellular vestibule |
| CCS | Central constriction site |
| RSBH | Protonated retinal schiff base |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| ChR2 | Channelrhodopsin-2 |
References
- Boyden, E.S.; Zhang, F.; Bamberg, E.; Nagel, G.; Deisseroth, K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisseroth, K.; Feng, G.; Majewska, A.K.; Miesenböck, G.; Ting, A.; Schnitzer, M.J. Next-generation optical technologies for illuminating genetically targeted brain circuits. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10380–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineshchekov, O.A.; Jung, K.H.; Spudich, J.L. Two rhodopsins mediate phototaxis to low-and high-intensity light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8689–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, G.; Ollig, D.; Fuhrmann, M.; Kateriya, S.; Musti, A.M.; Bamberg, E.; Hegemann, P. Channelrhodopsin-1: A light-gated proton channel in green algae. Science 2002, 296, 2395–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, G.; Szellas, T.; Huhn, W.; Kateriya, S.; Adeishvili, N.; Berthold, P.; Ollig, D.; Hegemann, P.; Bamberg, E. Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13940–13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, B.R.; Schneider-Warme, F.; Schmitz, D.; Hegemann, P. Optogenetic tools for subcellular applications in neuroscience. Neuron 2017, 96, 572–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govorunova, E.G.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; Janz, R.; Liu, X.; Spudich, J.L. Natural light-gated anion channels: A family of microbial rhodopsins for advanced optogenetics. Science 2015, 349, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineshchekov, O.A.; Govorunova, E.G.; Li, H.; Spudich, J.L. Gating mechanisms of a natural anion channelrhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14236–14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N. Algae are the best engineers of optogenetic inhibitors. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 806–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Wietek, J.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Steinberg, E.E.; Rashid, A.J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Santoro, A.; Frankland, P.W.; et al. Structural foundations of optogenetics: Determinants of channelrhodopsin ion selectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; Wu, G.; Spudich, J.L. In vitro activity of a purified natural anion channelrhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25319–25325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralvárez-Marín, A.; Garriga, P. Optogenetics Comes of Age: Novel Inhibitory Light-Gated Anionic Channels Allow Efficient Silencing of Neural Function. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sineshchekov, O.A.; Li, H.; Govorunova, E.G.; Spudich, J.L. Photochemical reaction cycle transitions during anion channelrhodopsin gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1993–E2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, A.; Mamaeva, N.; Li, H.; Spudich, J.L.; Rothschild, K.J. Resonance Raman study of an anion channelrhodopsin: Effects of mutations near the retinylidene Schiff base. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yoshizawa, S.; Sudo, Y. An inhibitory role of Arg-84 in anion channelrhodopsin-2 expressed in Escherichia coli . Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, A.; Li, H.; Mamaeva, N.; Fernandez De Cordoba, R.E.; Lugtenburg, J.; DeGrip, W.J.; Spudich, J.L.; Rothschild, K.J. Structural changes in an anion channelrhodopsin: Formation of the K and L intermediates at 80 K. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineshchekov, O.A.; Govorunova, E.G.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Spudich, J.L. Opposite charge movements within the photoactive site modulate two-step channel closing in GtACR1. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Miyoshi, N.; Shibukawa, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Tsujimura, M.; Noji, T.; Ishikita, H.; Yamanaka, A.; Sudo, Y. Green-sensitive, long-lived, step-functional anion channelrhodopsin-2 variant as a high-potential neural silencing tool. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 6214–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kato, H.E.; Yamashita, K.; Ito, S.; Inoue, K.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Fenno, L.E.; Evans, K.E.; Paggi, J.M.; Dror, R.O.; et al. Crystal structure of the natural anion-conducting channelrhodopsin GtACR1. Nature 2018, 561, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, C.Y.; Govorunova, E.G.; Schafer, C.T.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; Spudich, J.L. Crystal structure of a natural light-gated anion channelrhodopsin. Elife 2019, 8, e41741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, M.A.; Althoff, P.; Norahan, M.J.; Tennigkeit, S.A.; El-Mashtoly, S.F.; Lübben, M.; Kötting, C.; Rudack, T.; Gerwert, K. Time-resolved spectroscopic and electrophysiological data reveal insights in the gating mechanism of anion channelrhodopsin. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimura, M.; Noji, T.; Saito, K.; Kojima, K.; Sudo, Y.; Ishikita, H. Mechanism of absorption wavelength shifts in anion channelrhodopsin-1 mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2021, 1862, 148349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, M.; Kojima, K.; Kawanishi, S.; Sudo, Y.; Ishikita, H. Proton transfer pathway in anion channelrhodopsin-1. Elife 2021, 10, e72264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhne, J.; Eisenhauer, K.; Ritter, E.; Hegemann, P.; Gerwert, K.; Bartl, F. Early Formation of the Ion-Conducting Pore in Channelrhodopsin-2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4953–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI input generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM simulations using the CHARMM36 additive force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.L.; Cheng, X.; Jo, S.; Rui, H.; Song, K.C.; Dávila-Contreras, E.M.; Qi, Y.; Lee, J.; Monje-Galvan, V.; Venable, R.M.; et al. CHARMM-GUI membrane builder toward realistic biological membrane simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N· log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammonds, K.D.; Ryckaert, J.P. On the convergence of the SHAKE algorithm. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1991, 62, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinsky, T.J.; Nielsen, J.E.; McCammon, J.A.; Baker, N.A. PDB2PQR: An automated pipeline for the setup of Poisson–Boltzmann electrostatics calculations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W665–W667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isralewitz, B.; Gao, M.; Schulten, K. Steered molecular dynamics and mechanical functions of proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalily Hasani, H.; Ganesan, A.; Ahmed, M.; Barakat, K.H. Effects of protein–protein interactions and ligand binding on the ion permeation in KCNQ1 potassium channel. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücksch, C.; Urbassek, H.M. Accelerating steered molecular dynamics: Toward smaller velocities in forced unfolding simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.S.; Berteotti, A.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Rocchia, W.; Cavalli, A. Steered molecular dynamics simulations for studying protein–ligand interaction in cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, J. Umbrella sampling. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhshi, P.; Wu, G. Umbrella sampling molecular dynamics simulations reveal concerted ion movement through G-quadruplex DNA channels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11017–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Bouzida, D.; Swendsen, R.H.; Kollman, P.A. The weighted histogram analysis method for free-energy calculations on biomolecules. I. The method. J. Comput. Chem. 1992, 13, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, O.; Kovalev, K.; Polovinkin, V.; Borshchevskiy, V.; Bamann, C.; Astashkin, R.; Marin, E.; Popov, A.; Balandin, T.; Willbold, D.; et al. Structural insights into ion conduction by channelrhodopsin 2. Science 2017, 358, eaan8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.E.; Zhang, F.; Yizhar, O.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Nishizawa, T.; Hirata, K.; Ito, J.; Aita, Y.; Tsukazaki, T.; Hayashi, S.; et al. Crystal structure of the channelrhodopsin light-gated cation channel. Nature 2012, 482, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.S.; Kaufmann, J.C.; Kuhne, J.; Vierock, J.; Huber, T.; Sakmar, T.P.; Gerwert, K.; Bartl, F.J.; Hegemann, P. Tracking pore hydration in channelrhodopsin by Site-Directed Infrared-Active azido probes. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lórenz-Fonfría, V.A.; Bamann, C.; Resler, T.; Schlesinger, R.; Bamberg, E.; Heberle, J. Temporal evolution of helix hydration in a light-gated ion channel correlates with ion conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5796–E5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Xin, Q.; Qin, C.; Jiang, M.; Lo, G.V.; Dou, Y.; Yuan, S. The Mechanism of Channel Opening of Anion Channelrhodopsin GtACR1: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Processes 2023, 11, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020510
Liu C, Xin Q, Qin C, Jiang M, Lo GV, Dou Y, Yuan S. The Mechanism of Channel Opening of Anion Channelrhodopsin GtACR1: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Processes. 2023; 11(2):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020510
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunyan, Qi Xin, Cai Qin, Maorui Jiang, Glenn V. Lo, Yusheng Dou, and Shuai Yuan. 2023. "The Mechanism of Channel Opening of Anion Channelrhodopsin GtACR1: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Processes 11, no. 2: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020510
APA StyleLiu, C., Xin, Q., Qin, C., Jiang, M., Lo, G. V., Dou, Y., & Yuan, S. (2023). The Mechanism of Channel Opening of Anion Channelrhodopsin GtACR1: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Processes, 11(2), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020510







