Comparison of the Bacterial Inactivation Efficiency of Water Activated by a Plasma Jet Source and a Pin-to-Pin Electrode Configuration Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
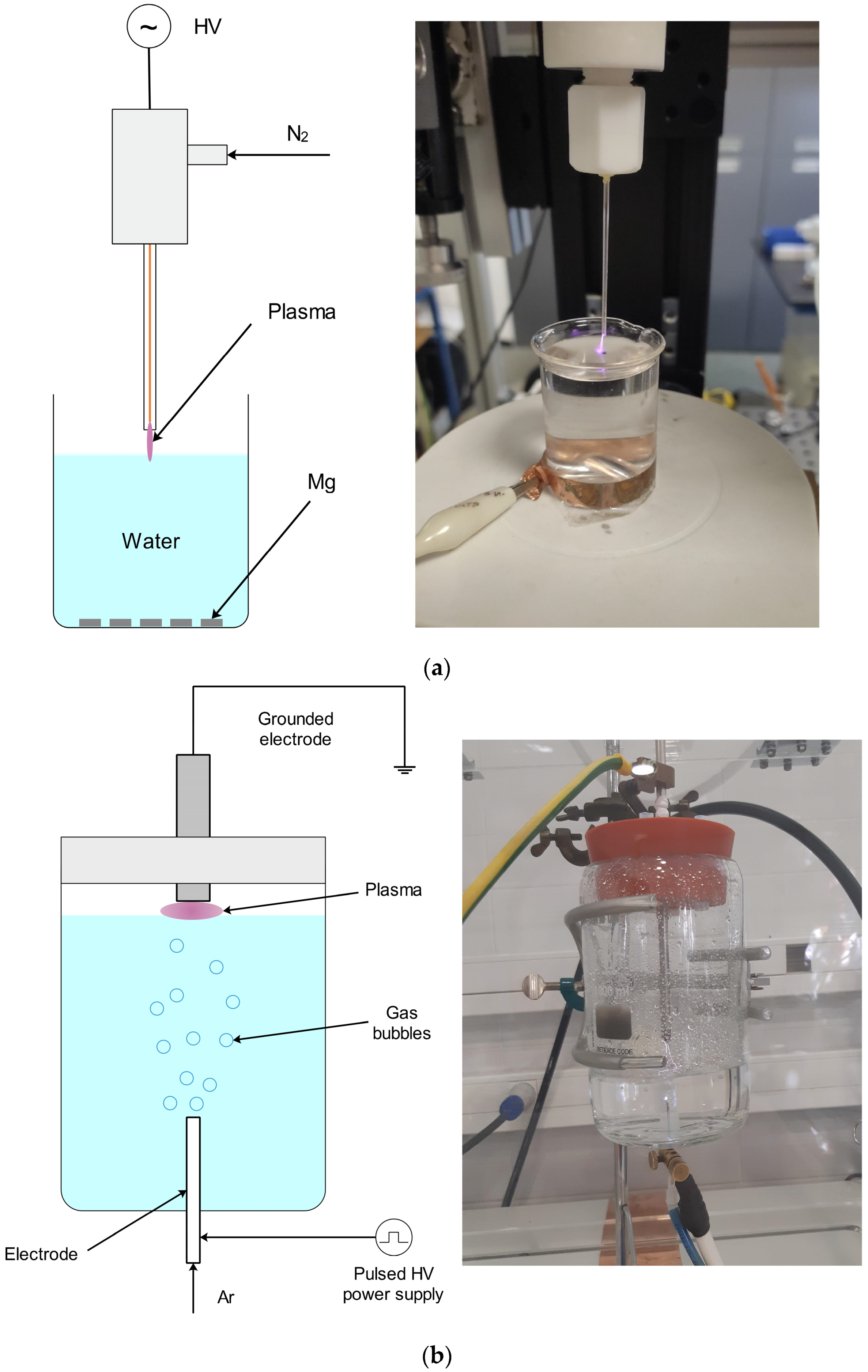
2.1. Generation of Plasma-Activated Water
2.1.1. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet
2.1.2. Hybrid Plasma Reactor
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of PAW
2.3. Planktonic Bacterial Suspension Preparation of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
2.4. Influence of Different Exposure Times
2.5. Microbiological Analysis
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Imaging
2.7. PAW Microbial Inactivation Kinetics
3. Results
3.1. Inactivation Efficacy of PAW
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Images
3.3. Physicochemical Properties and Aging of PAW
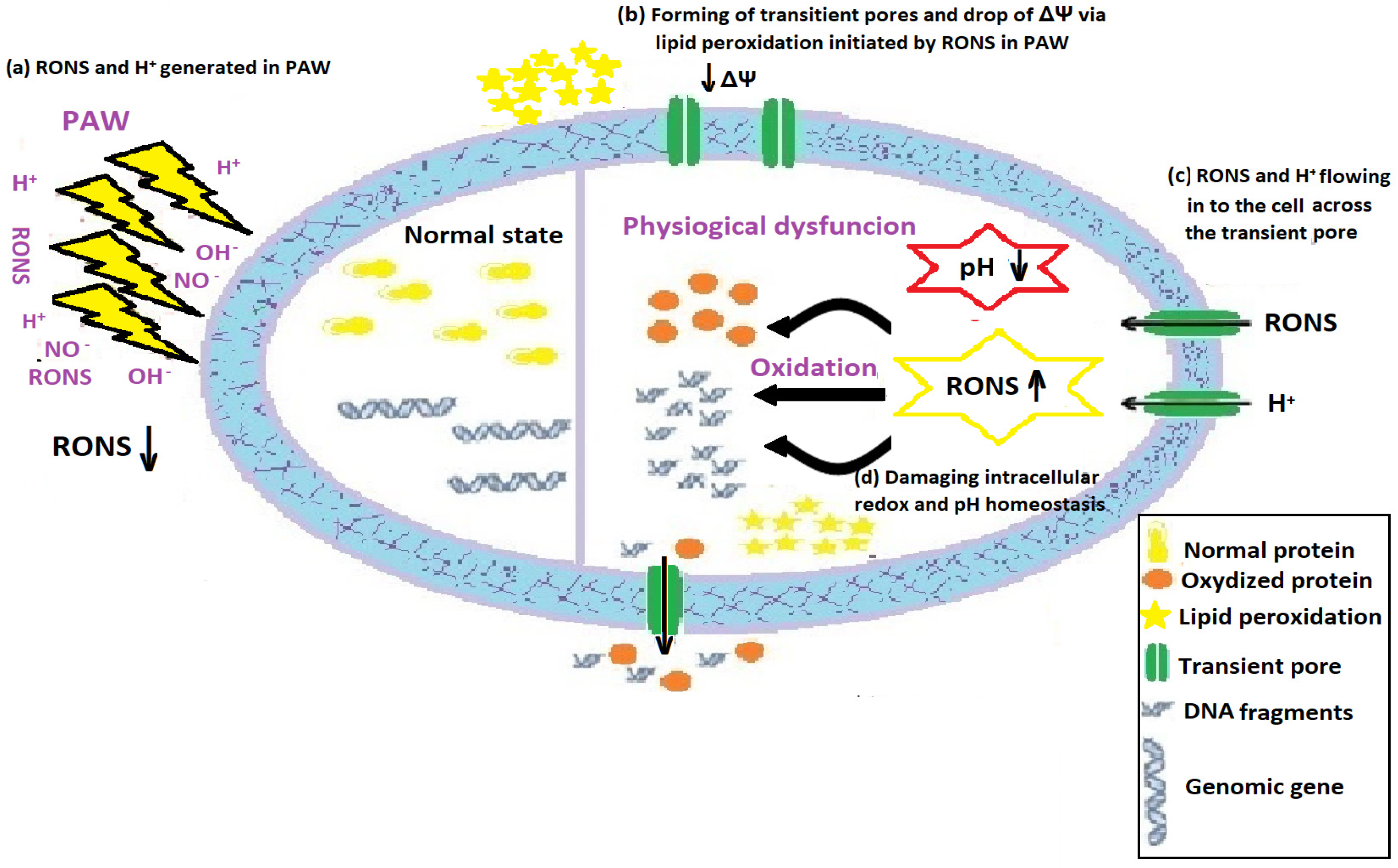
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amit, S.K.; Uddin, M.M.; Rahman, R.; Islam, S.M.R.; Khan, M.S. A Review on Mechanisms and Commercial Aspects of Food Preservation and Processing. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C.D. Foodborne Diseases: Overview of Biological Hazards and Foodborne Diseases. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.E.D. Challenges, Trends and Opportunities in Food Processing. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 35, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, H.M.; Moreno-Vilet, L.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, S.J. Current Status of Emerging Food Processing Technologies in Latin America: Novel Non-Thermal Processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 58, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konchekov, E.M.; Gusein-zade, N.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Kolik, L.V.; Dorokhov, A.S.; Izmailov, A.Y.; Shokri, B.; Gudkov, S.V. Advancements in Plasma Agriculture: A Review of Recent Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemira, B.A. Cold Plasma Decontamination of Foods *. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Schlüter, O.; Cullen, P.J. Plasma in Food and Agriculture. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Kothakota, A.; Annapure, U.; Siliveru, K.; Blundell, R.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V.P. Plasma Activated Water (PAW): Chemistry, Physico-Chemical Properties, Applications in Food and Agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Non-Thermal Plasma-Activated Water Inactivation of Food-Borne Pathogen on Fresh Produce. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutasi, K.; Popović, D.; Krstulović, N.; Milošević, S. Tuning the Composition of Plasma-Activated Water by a Surface-Wave Microwave Discharge and a KHz Plasma Jet. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 095010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, C.; Li, D.; Yang, A.J.; Rong, M.Z.; Chen, H.L.; Kong, M.G. Physicochemical Processes in the Indirect Interaction between Surface Air Plasma and Deionized Water. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 495201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrikov, K.K.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Lu, X.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-Activated Water: Generation, Origin of Reactive Species and Biological Applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Physics. 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, K.; Krstulović, N.; Jurov, A.; Salamon, K.; Popović, D.; Milošević, S. Controlling: The Composition of Plasma-Activated Water by Cu Ions. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2021, 30, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y.; Su, B.; Wang, K.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Sterilization Efficiency of a Novel Electrochemical Disinfectant against Staphylococcus Aureus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3184–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Ghimire, B.; Li, Y.; Adhikari, M.; Veerana, M.; Kaushik, N.; Jha, N.; Adhikari, B.; Lee, S.J.; Masur, K.; et al. Biological and Medical Applications of Plasmaactivated. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, J.F.; Mohamed, A.A.H.; Price, R.O.; Swanson, R.J.; Bowman, A.; Chiavarini, R.L.; Stacey, M.; Schoenbach, K.H. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Air Plasma Jet for Medical Applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 241501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sun, K.; Liang, Y.; Sun, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Fang, J.; Becker, K.H. Cold Plasma Therapy of a Tooth Root Canal Infected with Enterococcus Faecalis Biofilms in Vitro. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Bactericidal Effects against S. Aureus and Physicochemical Properties of Plasma Activated Water Stored at Different Temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Salvi, D. Evaluation of Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) as a Novel Disinfectant: Effectiveness on Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua, Physicochemical Properties, and Storage Stability. LWT 2021, 149, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Ojha, S.; Burgess, C.M.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B.K. Inactivation Efficacy and Mechanisms of Plasma Activated Water on Bacteria in Planktonic State. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Xu, R.; Gou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G.; Guo, C.L. Mechanism of Virus Inactivation by Cold Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma and Plasma-Activated Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Patange, A.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B. Plasma-Activated Water: Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Inactivation Mechanisms, Factors Influencing Antimicrobial Effectiveness, and Applications in the Food Industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3951–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, V.; Pazlarova, J.; Souskova, H.; Khun, J.; Julak, J. Nonthermal Plasma—A Tool for Decontamination and Disinfection. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Jiang, A.; Guan, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Hao, K.; Hu, W. The Effects of Cold Plasma-Activated Water Treatment on the Microbial Growth and Antioxidant Properties of Fresh-Cut Pears. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2019, 12, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Jiang, A.; Sun, X.; Guan, Q.; Hu, W. Effects of Plasma-Activated Water on Microbial Growth and Storage Quality of Fresh-Cut Apple. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Niu, J.; Xia, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y. Effect of Nonthermal Plasma-Activated Water on Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Fresh-Cut Kiwifruit. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 4811–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royintarat, T.; Choi, E.H.; Boonyawan, D.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Wattanutchariya, W. Chemical-Free and Synergistic Interaction of Ultrasound Combined with Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) to Enhance Microbial Inactivation in Chicken Meat and Skin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, T. Application of Atmospheric Cold Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) Ice for Preservation of Shrimps (Metapenaeus ensis). Food Control 2018, 94, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaka, M.R.; Sone, I.; Álvarez, R.G.; Walsh, J.L.; Prabhu, L.; Sivertsvik, M.; Fernández, E.N. Towards the Next-Generation Disinfectant: Composition, Storability and Preservation Potential of Plasma Activated Water on Baby Spinach Leaves. Foods 2019, 8, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Chu, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.P.; Wu, J.S.; Hsieh, C.W.; Hou, C.Y. The Optimization of Plasma-Activated Water Treatments to Inactivate Salmonella Enteritidis (ATCC 13076) on Shell Eggs. Foods 2019, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Tian, E.; Liu, D.; Niu, J.; Wang, W.; Qi, Z.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Z. Plasma-Activated Water Treatment of Fresh Beef: Bacterial Inactivation and Effects on Quality Attributes. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020, 4, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; He, X.; Shao, H.; Dong, Y. Effects of Cold Plasma Treatment on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Soybean. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.P.; Davis, K.; Gilani, S.; Alonzo, C.A.; Dobrynin, D.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Rabinovich, A.; Fridman, G. Reactive Nitrogen Species Produced in Water by Non-Equilibrium Plasma Increase Plant Growth Rate and Nutritional Yield. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13 (Suppl. 1), S19–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplotnik, R.; Kregar, Z.; Bišćan, M.; Vesel, A.; Cvelbar, U.; Mozetič, M.; Milošević, S. Multiple vs. Single Harmonics AC-Driven Atmospheric Plasma Jet. Europhys. Lett. 2014, 106, 25001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplotnik, R.; Bišćan, M.; Kregar, Z.; Cvelbar, U.; Mozetič, M.; Milošević, S. Influence of a Sample Surface on Single Electrode Atmospheric Plasma Jet Parameters. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2015, 103–104, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierczik, K.; Vukušić, T.; Kovács, L.; Székely, A.; Szalai, G.; Milošević, S.; Kocsy, G.; Kutasi, K.; Galiba, G. Plasma-Activated Water to Improve the Stress Tolerance of Barley. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 1900123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanjek Fajdetić, N.; Benković-Lačić, T.; Mirosavljević, K.; Antunović, S.; Benković, R.; Rakić, M.; Milošević, S.; Japundžić-Palenkić, B. Influence of Seed Treated by Plasma Activated Water on the Growth of Lactuca sativa L. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, K.; Bencs, L.; Tóth, Z.; Milošević, S. The Role of Metals in the Deposition of Long-Lived Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species into the Plasma-Activated Liquids. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, 20, 2200143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmigen, K.; Hähnel, M.; Brandenburg, R.; Wilke, C.; Weltmann, K.D.; Von Woedtke, T. The Role of Acidification for Antimicrobial Activity of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Liquids. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Dolezalova, E.; Sisrova, I.; Clupek, M. Aqueous-Phase Chemistry and Bactericidal Effects from an Air Discharge Plasma in Contact with Water: Evidence for the Formation of Peroxynitrite through a Pseudo-Second-Order Post-Discharge Reaction of H2O2 and HNO2. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 015019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Wei, J.; Lan, Y.; Ni, G.; Sun, Q.; Qian, S.; Zhang, H.; Xia, W.; et al. Bactericidal Effects of Plasma Induced Reactive Species in Dielectric Barrier Gas–Liquid Discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2017, 37, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, M.A.C.; Mann, M.; Weltmann, K.D.; Von Woedtke, T. Analysis of Antibacterial Efficacy of Plasma-Treated Sodium Chloride Solutions. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 454001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Method 6020A; Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. U.S. EPA Office of Solid Waste (OSW) Methods Team: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Erkmen, O.; Bozoglu, T.F. Food Microbiology: Principles into Practice; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2016; pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Khlyustova, A.; Labay, C.; Machala, Z.; Ginebra, M.P.; Canal, C. Important Parameters in Plasma Jets for the Production of RONS in Liquids for Plasma Medicine: A Brief Review. In Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Brocks, G.; Bieberle-Hütter, A. Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) Mechanism under Alkaline and Acidic Conditions. J. Phys. Energy 2021, 3, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.N.; Feng, H.Q.; Liang, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Su, B.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. An Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Leads to Apoptosis in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae by Accumulating Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and Calcium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 285401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, J.K. DNA Damage and Mitochondria Dysfunction in Cell Apoptosis Induced by Nonthermal Air Plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 021502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, J.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Interaction of Atmospheric-Pressure Air Microplasmas with Amino Acids as Fundamental Processes in Aqueous Solution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezalova, E.; Lukes, P. Membrane Damage and Active but Nonculturable State in Liquid Cultures of Escherichia Coli Treated with an Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 103, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Locke, B.R.; Brisset, J.-L. 7 Aqueous-Phase Chemistry of Electrical Discharge Plasma in Water and in Gas-Liquid Environments. Plasma Chem. Catal. Gases Liq. 2012, 1, 243–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma-Liquid Interactions: A Review and Roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, G.; Sanz, P.D.; Pré Stamo, G. Response to High-Pressure, Low-Temperature Treatment in Vegetables: Determination of Survival Rates of Microbial Populations Using Flow Cytometry and Detection of Peroxidase Activity Using Confocal Microscopy. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Ojha, S.; Burgess, C.M.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B.K. Inactivation Efficacy of Plasma-Activated Water: Influence of Plasma Treatment Time, Exposure Time and Bacterial Species. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M.; Mendis, D.A.; Rosenberg, M. Plasma Interaction with Microbes. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang-Youbi, G.; Herry, J.M.; Meylheuc, T.; Brisset, J.L.; Bellon-Fontaine, M.N.; Doubla, A.; Naïtali, M. Microbial Inactivation Using Plasma-Activated Water Obtained by Gliding Electric Discharges. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, U.K.; Smith, J.; Ji, H.F.; Brooks, A.D.; Joshi, S.G. Chemical Changes in Nonthermal Plasma-Treated N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Solution and Their Contribution to Bacterial Inactivation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursache, M.; Moraru, R.; Hnatiuc, E.; Nastase, V.; Mares, M. Comparative Assessment of the Relation between Energy Consumption and Bacterial Burden Reduction Using Plasma Activated Water. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Cheile Gradistei, Romania, 22–24 May 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, P.; Bai, N.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Becker, K.; et al. Inactivation of Bacteria in an Aqueous Environment by a Direct-Current, Cold-Atmospheric-Pressure Air Plasma Microjet. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Shim, G.B.; Uhm, H.S.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Effects of Background Fluid on the Efficiency of Inactivating Yeast with Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Kang, C.; Niu, L.; Zhao, D.; Li, K.; Bai, Y. Antibacterial Activity and a Membrane Damage Mechanism of Plasma-Activated Water against Pseudomonas Deceptionensis CM2. LWT 2018, 96, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Borghesi, D.; Lucchiari, M.; Pelizzetti, E. New Processes in the Environmental Chemistry of Nitrite. 2. The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bacteria | Exposure Time (h) | NT | PAW-Jet | Log10 Reduction | PAW-Hybrid | Log10 Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Listeria monocytogenes | 0 | 9.28 ± 0.01 | 9.28 ± 0.01 | 0.00 | 9.28 ± 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 0.5 | 8.29 ± 0.01 | 0.99 | 8.31 ± 0.00 | 0.97 | ||
| 1 | 8.21 ± 0.02 | 1.07 | 8.23 ± 0.04 | 1.05 | ||
| 3 | 8.15 ± 0.02 | 1.13 | 8.10 ± 0.03 | 1.18 | ||
| 5 | 8.07 ± 0.01 | 1.21 | 8.00 ± 0.01 | 1.28 | ||
| 10 | 7.17 ± 0.02 | 2.11 | 6.65 ± 0.03 | 2.63 | ||
| 24 | 4.09 ± 0.13 | 5.19 | 3.88 ± 0.05 | 5.40 | ||
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 | 0 | 9.34 ± 0.04 | 9.34 ± 0.04 | 0.00 | 9.34 ± 0.04 | 0.00 |
| 0.5 | 7.82 ± 0.07 | 1.52 | 7.78 ± 0.08 | 1.56 | ||
| 1 | 7.81 ± 0.03 | 1.53 | 7.66 ± 0.03 | 1.68 | ||
| 3 | 7.61 ± 0.03 | 1.73 | 7.45 ± 0.04 | 1.89 | ||
| 5 | 7.43 ± 0.08 | 1.91 | 7.27 ± 0.03 | 2.07 | ||
| 10 | 6.11 ± 0.04 | 3.23 | 6.16 ± 0.02 | 3.18 | ||
| 24 | 3.54 ± 0.06 | 5.80 | 3.63 ± 0.11 | 5.65 | ||
| Salmonella enteritidis | 0 | 9.16 ± 0.03 | 9.15 ± 0.06 | 0.01 | 9.15 ± 0.06 | 0.01 |
| 0.5 | 8.04 ± 0.02 | 1.12 | 8.01 ± 0.01 | 1.15 | ||
| 1 | 7.98 ± 0.02 | 1.18 | 7.99 ± 0.02 | 1.17 | ||
| 3 | 7.82 ± 0.05 | 1.34 | 7.82 ± 0.05 | 1.34 | ||
| 5 | 7.66 ± 0.04 | 1.50 | 7.09 ± 0.05 | 2.07 | ||
| 10 | 6.24 ± 0.03 | 2.92 | 6.14 ± 0.01 | 3.02 | ||
| 24 | 4.15 ± 0.03 | 5.01 | 3.90 ± 0.04 | 5.26 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 8.71 ± 0.03 | 8.71 ± 0.03 | 0.00 | 8.71 ± 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 0.5 | 7.68 ± 0.00 | 1.03 | 7.65 ± 0.02 | 1.06 | ||
| 1 | 7.52 ± 0.06 | 1.19 | 7.50 ± 0.02 | 1.21 | ||
| 3 | 7.42 ± 0.06 | 1.29 | 7.40 ± 0.07 | 1.31 | ||
| 5 | 7.16 ± 0.03 | 1.55 | 7.11 ± 0.02 | 1.60 | ||
| 10 | 5.90 ± 0.04 | 2.81 | 6.00 ± 0.03 | 2.71 | ||
| 24 | 3.67 ± 0.03 | 5.04 | 3.71 ± 0.11 | 5.00 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 0 | 8.62 ± 0.02 | 8.62 ± 0.03 | 0.00 | 8.62 ± 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 0.5 | 7.44 ± 0.06 | 1.18 | 7.62 ± 0.02 | 1.00 | ||
| 1 | 7.38 ± 0.08 | 1.24 | 7.49 ± 0.04 | 1.13 | ||
| 3 | 7.00 ± 0.01 | 1.62 | 7.35 ± 0.04 | 1.27 | ||
| 5 | 6.80 ± 0.06 | 1.82 | 6.07 ± 0.03 | 2.55 | ||
| 10 | 6.26 ± 0.04 | 2.36 | 5.71 ± 0.02 | 2.91 | ||
| 24 | 3.59 ± 0.05 | 5.03 | 3.55 ± 0.05 | 5.07 | ||
| Bacillus cereus | 0 | 7.42 ± 0.03 | 7.42 ± 0.03 | 0.00 | 7.42 ± 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 0.5 | 6.55 ± 0.09 | 0.87 | 6.73 ± 0.07 | 0.69 | ||
| 1 | 6.34 ± 0.02 | 1.08 | 6.31 ± 0.02 | 1.11 | ||
| 3 | 6.11 ± 0.03 | 1.31 | 6.12 ± 0.02 | 1.30 | ||
| 5 | 5.65 ± 0.10 | 1.77 | 5.58 ± 0.03 | 1.77 | ||
| 10 | 4.52 ± 0.07 | 2.90 | 5.21 ± 0.04 | 2.21 | ||
| 24 | 3.15 ± 0.08 | 4.27 | 2.80 ± 0.05 | 4.62 |
| PAW-Jet | Listeria monocytogenes | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | Salmonella enteritidis | Staphylococcus aureus | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Bacillus cereus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0 | 1.92 × 109 | 2.28 × 109 | 1.40 × 109 | 5.27 × 108 | 4.18 × 108 | 2.68 × 107 |
| k | −4.3 ± 0.8 | −6.9 ± 0.9 | −4.8 ± 0.8 | −4.6 ± 0.6 | −5.3 ± 0.5 | −3.8 ± 0.4 |
| Reduced Chi-Sqr | 8.92 × 1015 | 1.04 × 1015 | 2.32 × 1015 | 2.78 × 1014 | 5.37 × 1013 | 7.73 × 1011 |
| R-Square (COD) | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| PAW-Hybrid | Listeria monocytogenes | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | Salmonella enteritidis | Staphylococcus aureus | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Bacillus cereus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0 | 1.92 × 109 | 2.28 × 109 | 1.40 × 109 | 5.27 × 108 | 4.18 × 108 | 2.68 × 107 |
| k | −4.2 ± 0.7 | −7.2 ± 0.7 | −4.8 ± 0.7 | −4.6 ± 0.6 | −4.4 ± 0.6 | −3.1 ± 0.2 |
| Reduced Chi-Sqr | 7.43 × 1015 | 5.17 × 1014 | 2.07 × 1015 | 2.78 × 1014 | 2.00 × 1014 | 4.44 × 1011 |
| R-Square (COD) | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Element (µg/L) | PAW-Jet | PAW-Hybrid |
|---|---|---|
| Ni | <1 | 87.9 ± 0.7 |
| Pb | 3.637 ± 0.009 | 4.21 ± 0.04 |
| Fe | 39.3 ± 0.9 | 429 ± 3 |
| Sn | 2.48 ± 0.07 | 1.0 ± 0.4 |
| Na | 1326 ± 7 | 1345 ± 12 |
| Hg | <1 | <1 |
| Mn | <1 | 14.9 ± 0.4 |
| Ca | 1160 ± 34 | 3093 ± 13 |
| B | 10.9 ± 0.3 | 81.50 ± 0.06 |
| Al | 93.5 ± 0.5 | 30 ± 1 |
| Se | NQ | <1 |
| Ba | 6.73 ± 0.03 | 8.2 ± 0.05 |
| Mg | 1882 ± 5 | 559 ± 4 |
| Mo | <1 | 3.9 ± 0.4 |
| As | 91.2 ± 0.2 | 73.6 ± 0.5 |
| K | 5299 ± 4 | 6383 ± 32 |
| Cr | 7.28 ± 0.02 | 133 ± 6 |
| Cd | <1 | <1 |
| Co | <1 | 2.7 ± 0.2 |
| Zn | 51.3 ± 0.3 | 80.0 ± 0.2 |
| Sb | <1 | <1 |
| Cu | 5.11 ± 0.09 | 19.9 ± 0.1 |
| Be | <1 | <1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čobanović, R.; Maletić, D.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Čabarkapa, I.; Kokić, B.; Kojić, P.; Milošević, S.; Stulić, V.; Pavičić, T.V.; Vukić, M. Comparison of the Bacterial Inactivation Efficiency of Water Activated by a Plasma Jet Source and a Pin-to-Pin Electrode Configuration Source. Processes 2023, 11, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123286
Čobanović R, Maletić D, Kocić-Tanackov S, Čabarkapa I, Kokić B, Kojić P, Milošević S, Stulić V, Pavičić TV, Vukić M. Comparison of the Bacterial Inactivation Efficiency of Water Activated by a Plasma Jet Source and a Pin-to-Pin Electrode Configuration Source. Processes. 2023; 11(12):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123286
Chicago/Turabian StyleČobanović, Radovan, Dejan Maletić, Sunčica Kocić-Tanackov, Ivana Čabarkapa, Bojana Kokić, Predrag Kojić, Slobodan Milošević, Višnja Stulić, Tomislava Vukušić Pavičić, and Milan Vukić. 2023. "Comparison of the Bacterial Inactivation Efficiency of Water Activated by a Plasma Jet Source and a Pin-to-Pin Electrode Configuration Source" Processes 11, no. 12: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123286
APA StyleČobanović, R., Maletić, D., Kocić-Tanackov, S., Čabarkapa, I., Kokić, B., Kojić, P., Milošević, S., Stulić, V., Pavičić, T. V., & Vukić, M. (2023). Comparison of the Bacterial Inactivation Efficiency of Water Activated by a Plasma Jet Source and a Pin-to-Pin Electrode Configuration Source. Processes, 11(12), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123286










