Physical and Numerical Simulation Study on Structure Optimization of the Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting of Molten Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Simulation Research
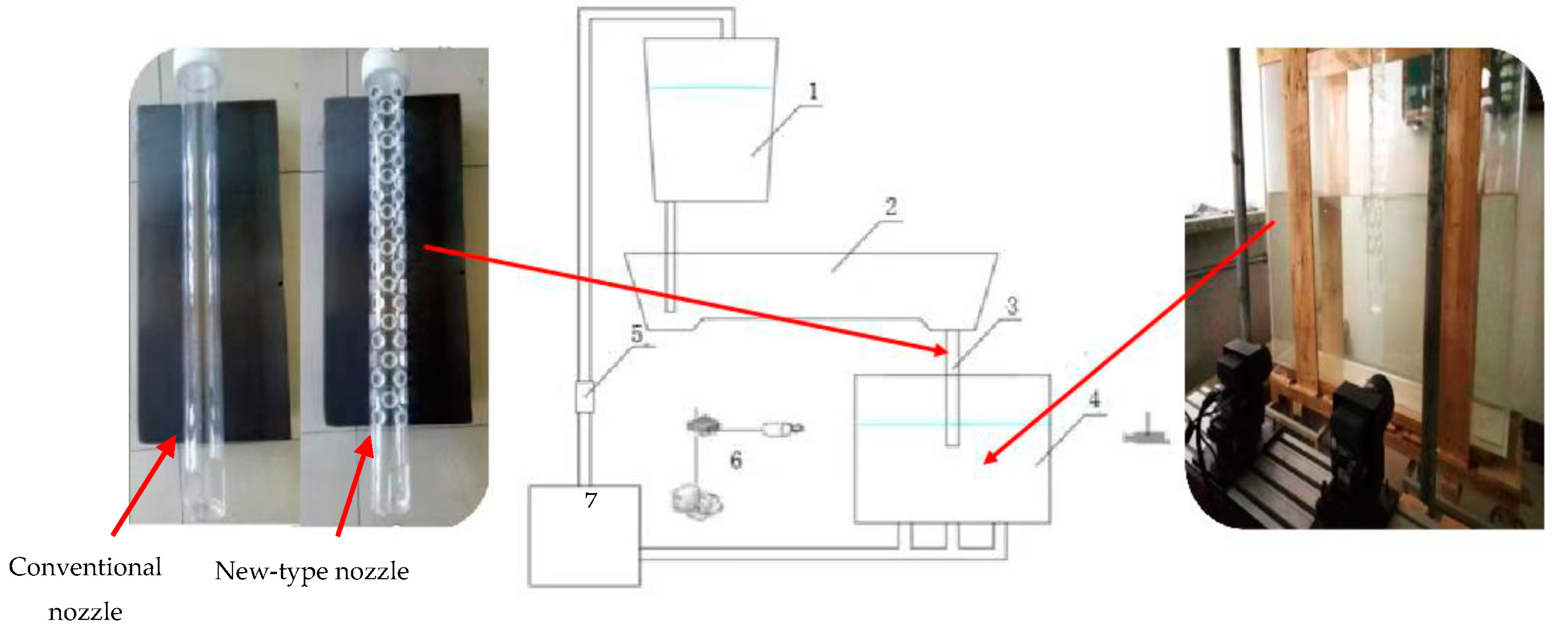
2.1. Experimental Device and Principle
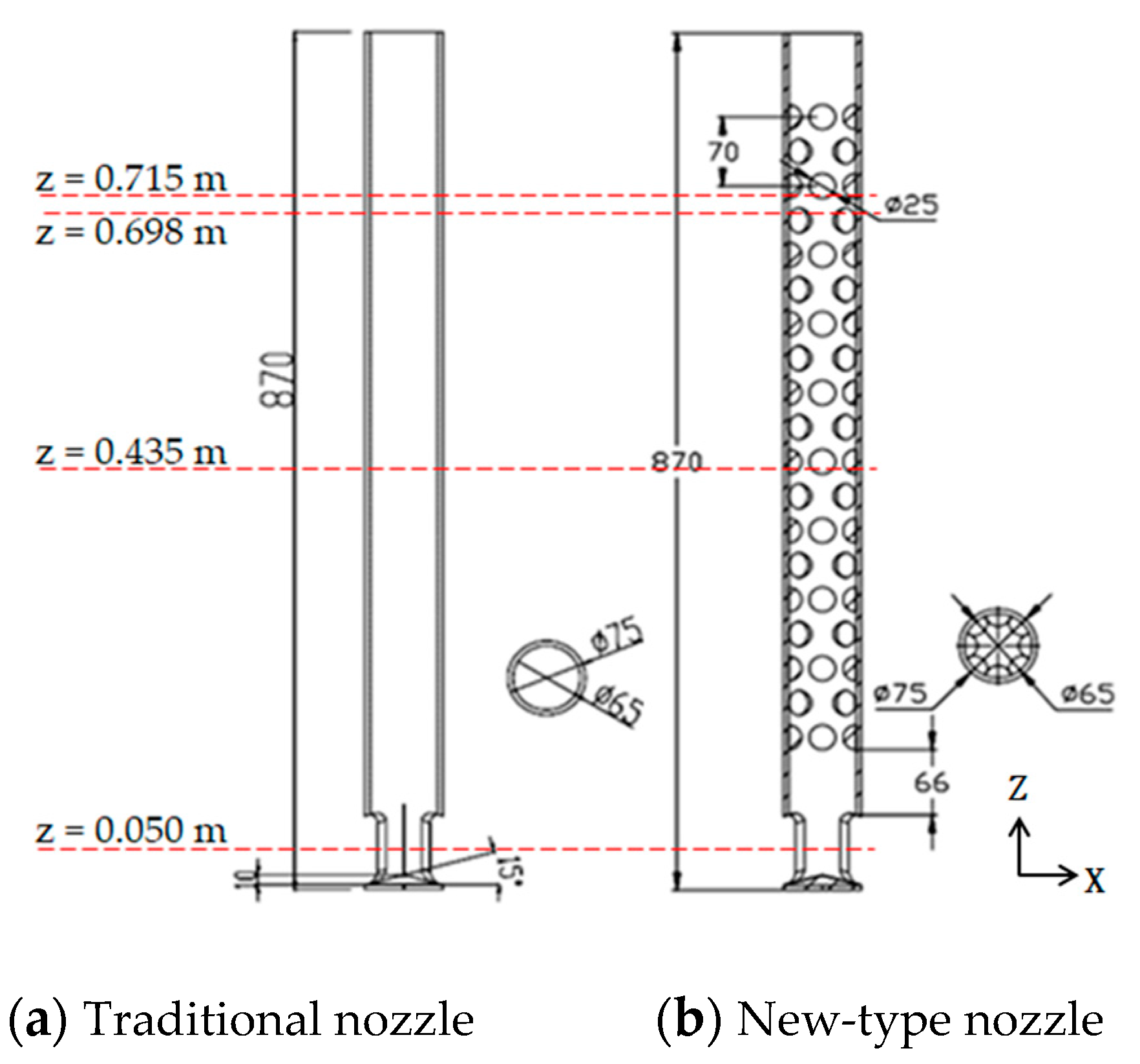
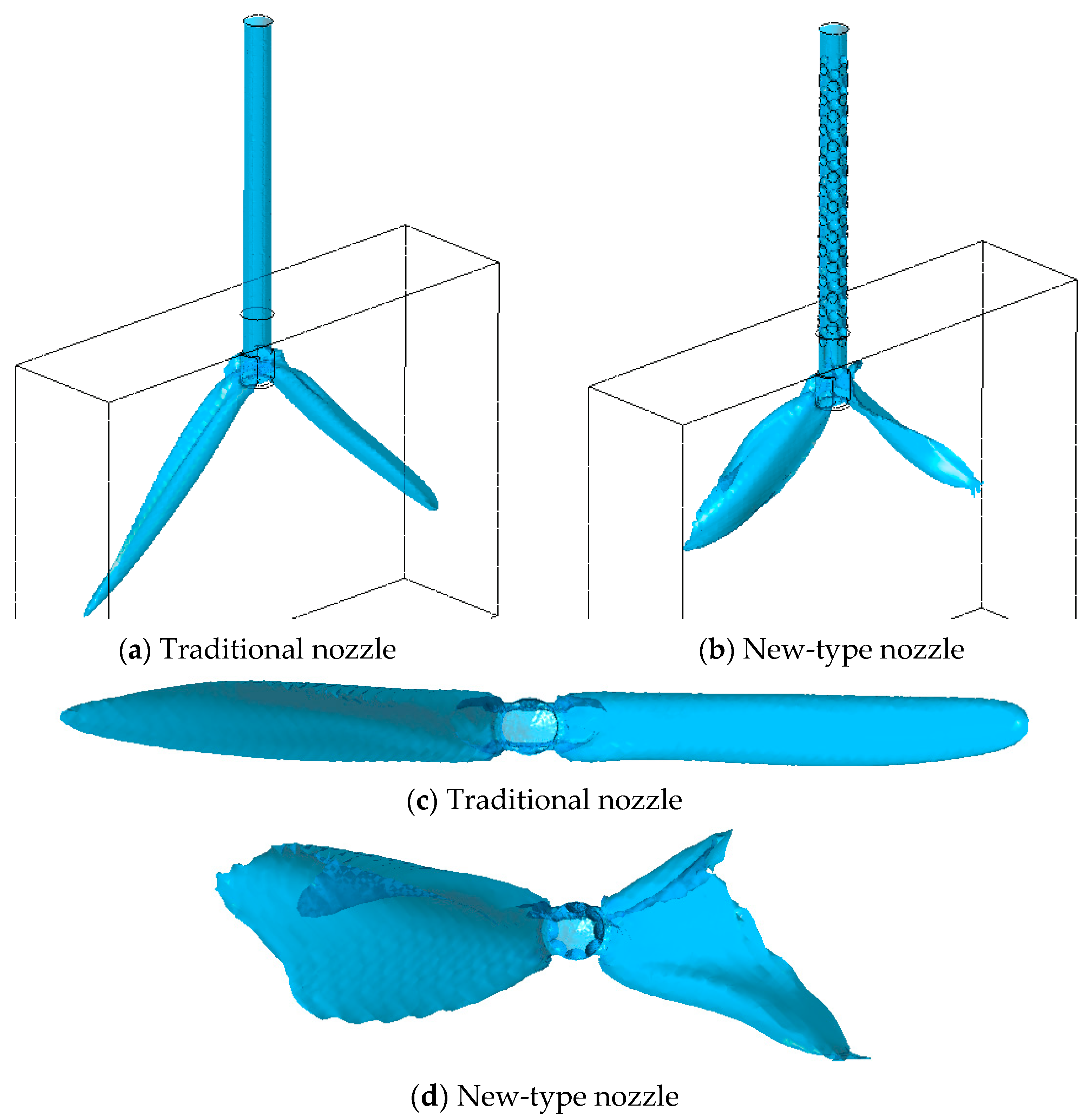
2.2. Structure of Traditional and New-Type Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting
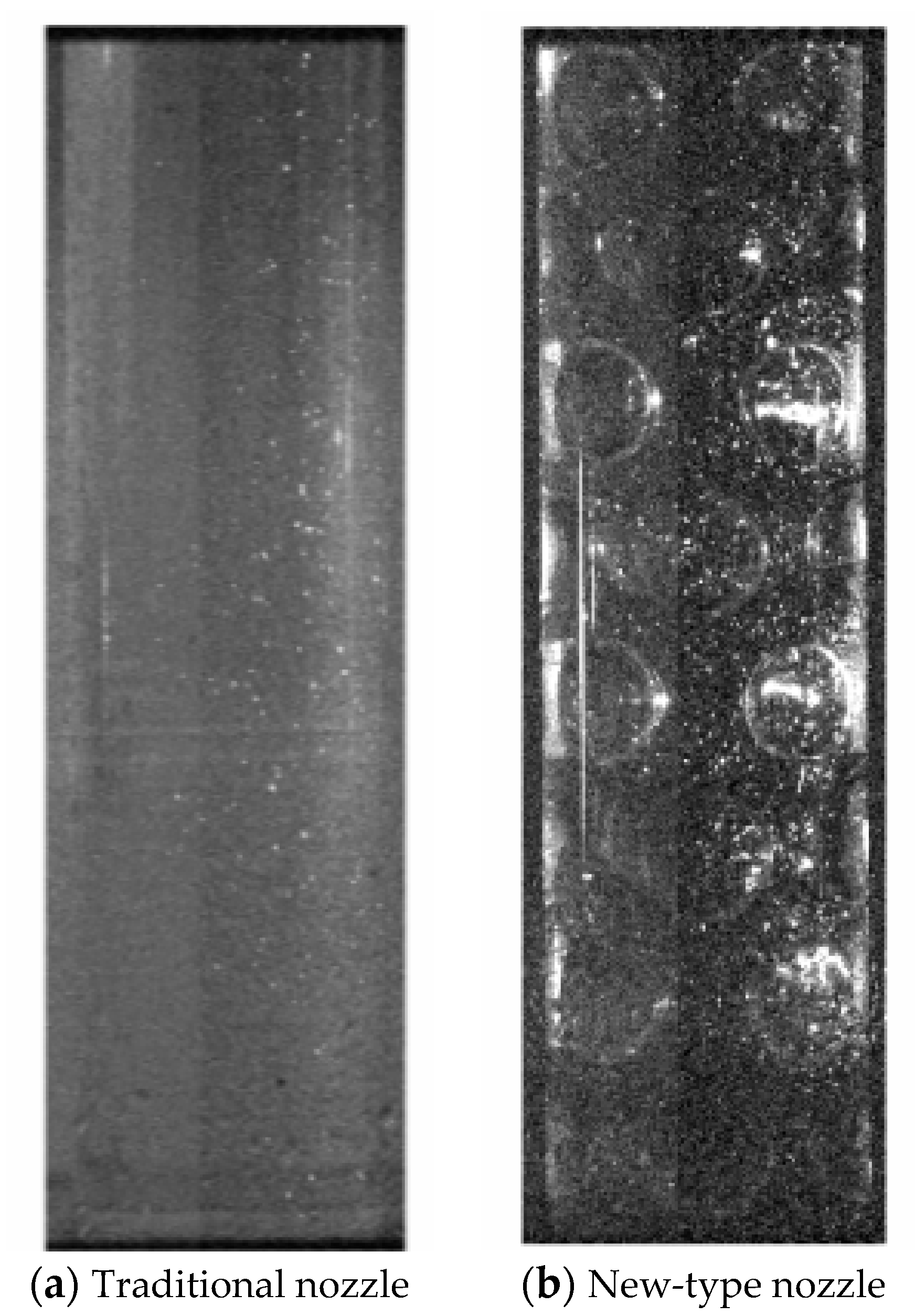
2.3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3. Numerical Simulation Research
3.1. General Assumptions of the Numerical Model
3.2. Governing Equations
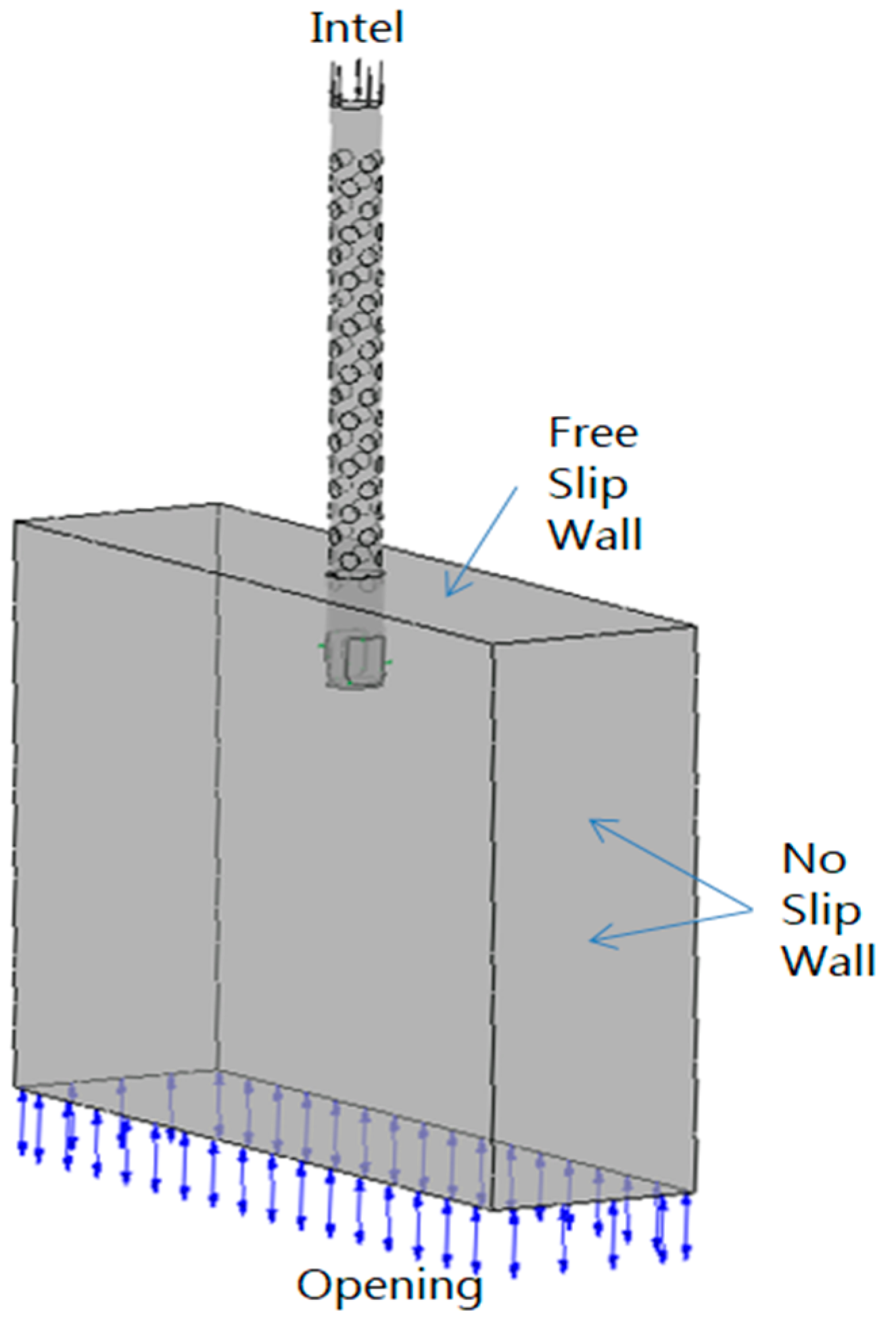
3.3. Boundary Conditions and Computation Initialization
3.4. Numerical Simulation Results and Analysis
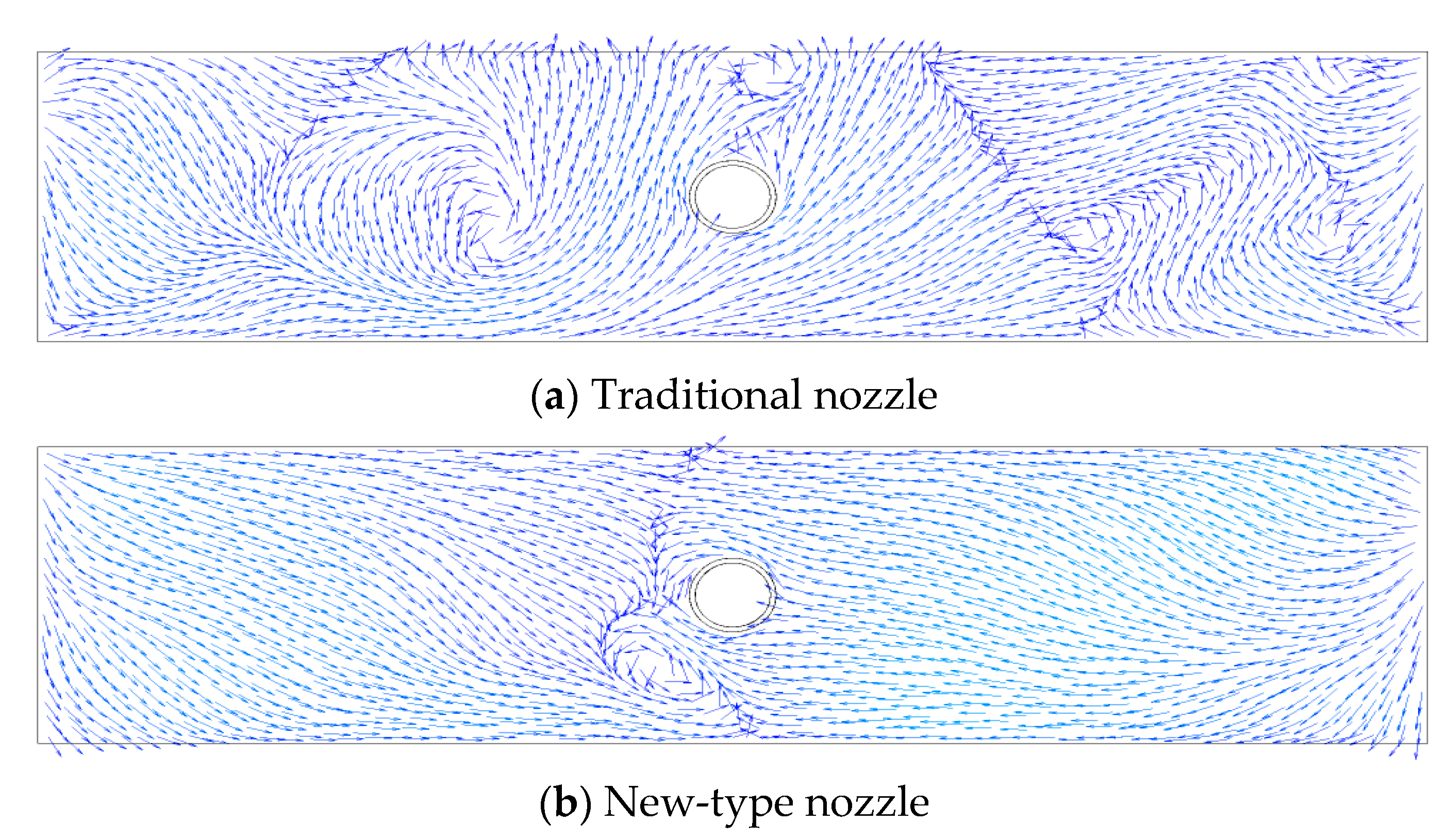
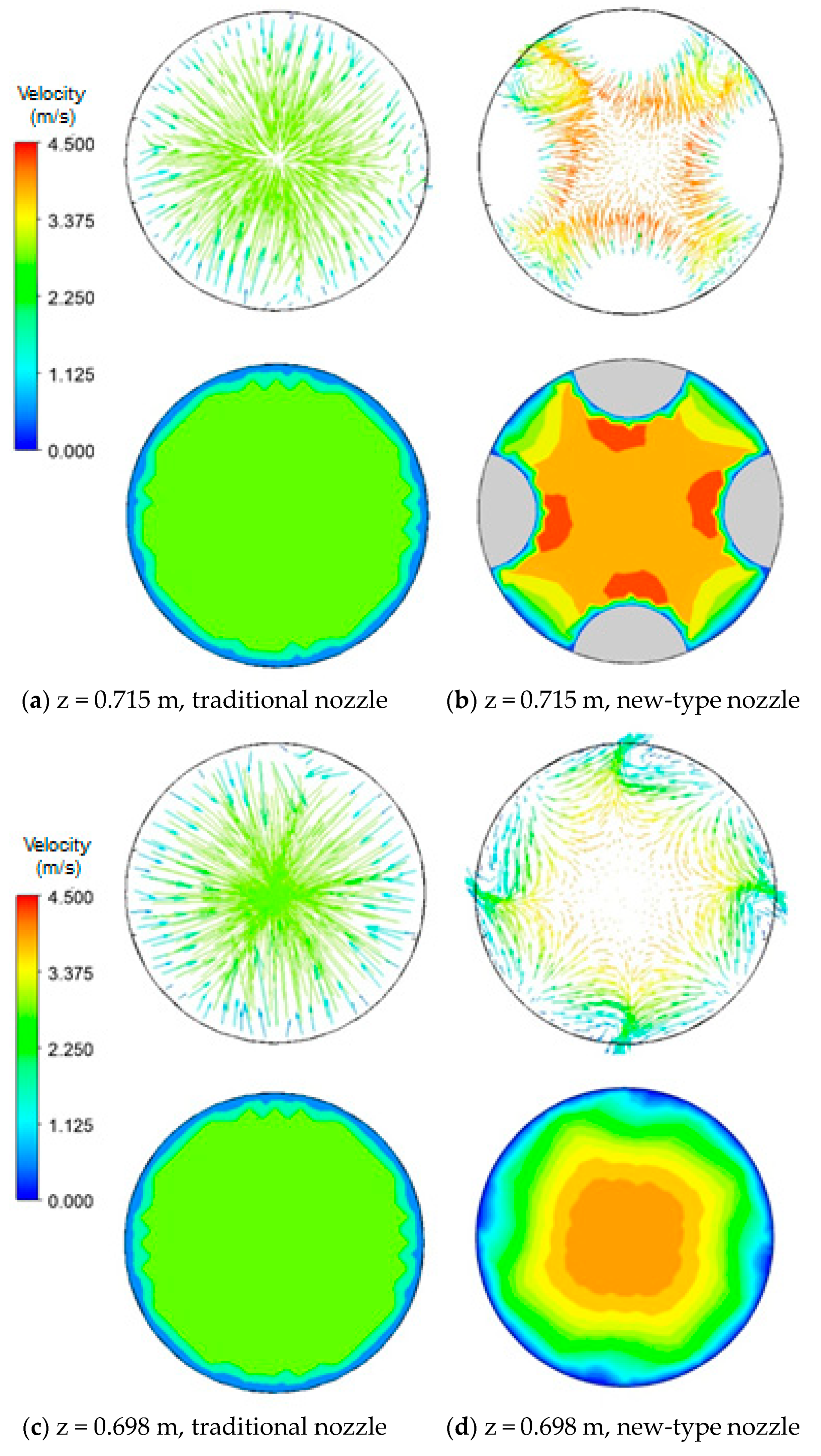
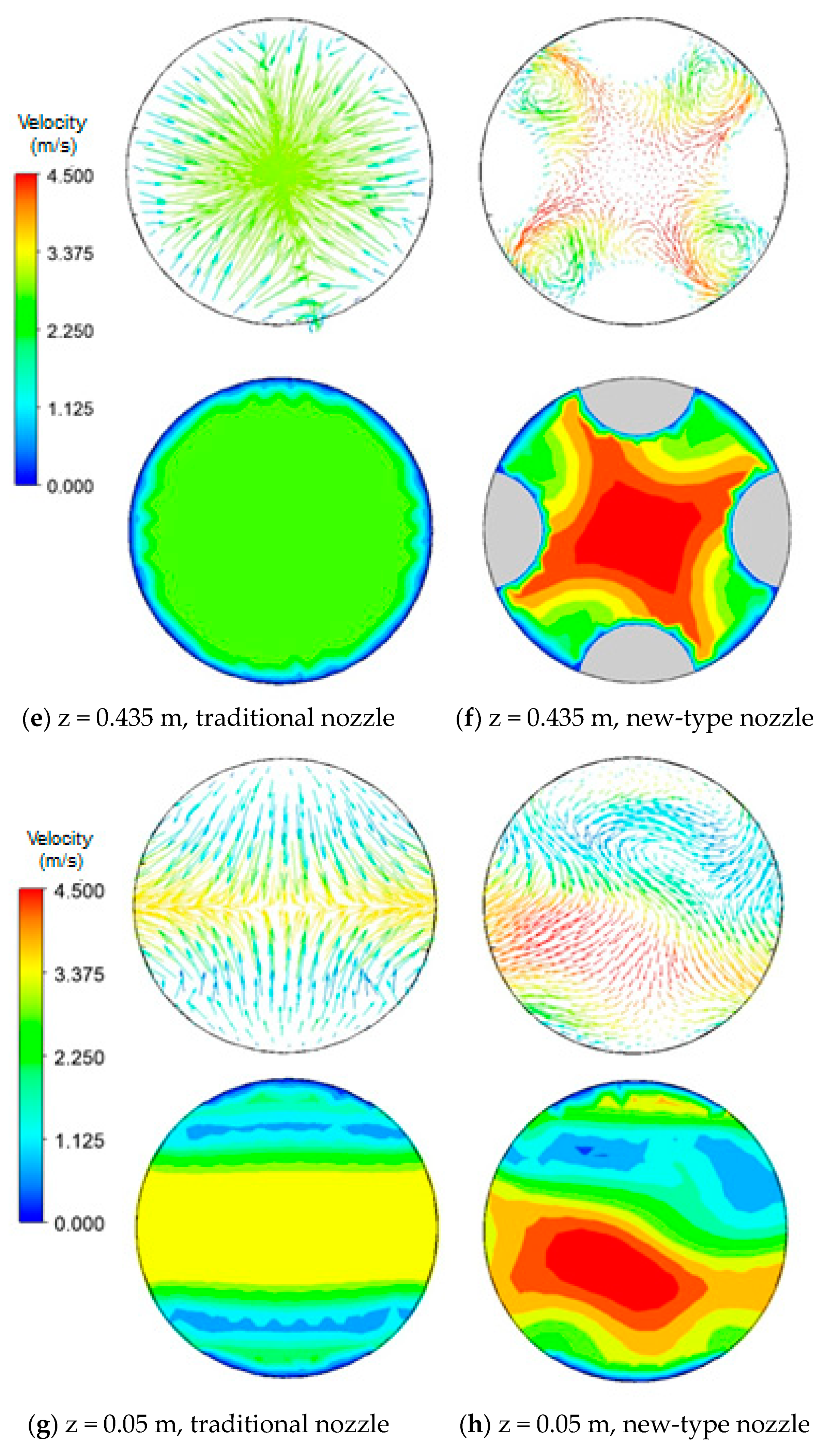
3.4.1. Influence of Nozzle Type on Flow Field
3.4.2. Effect of Nozzle Type on the Nozzle Outlet Jet
4. Conclusions
- (1)
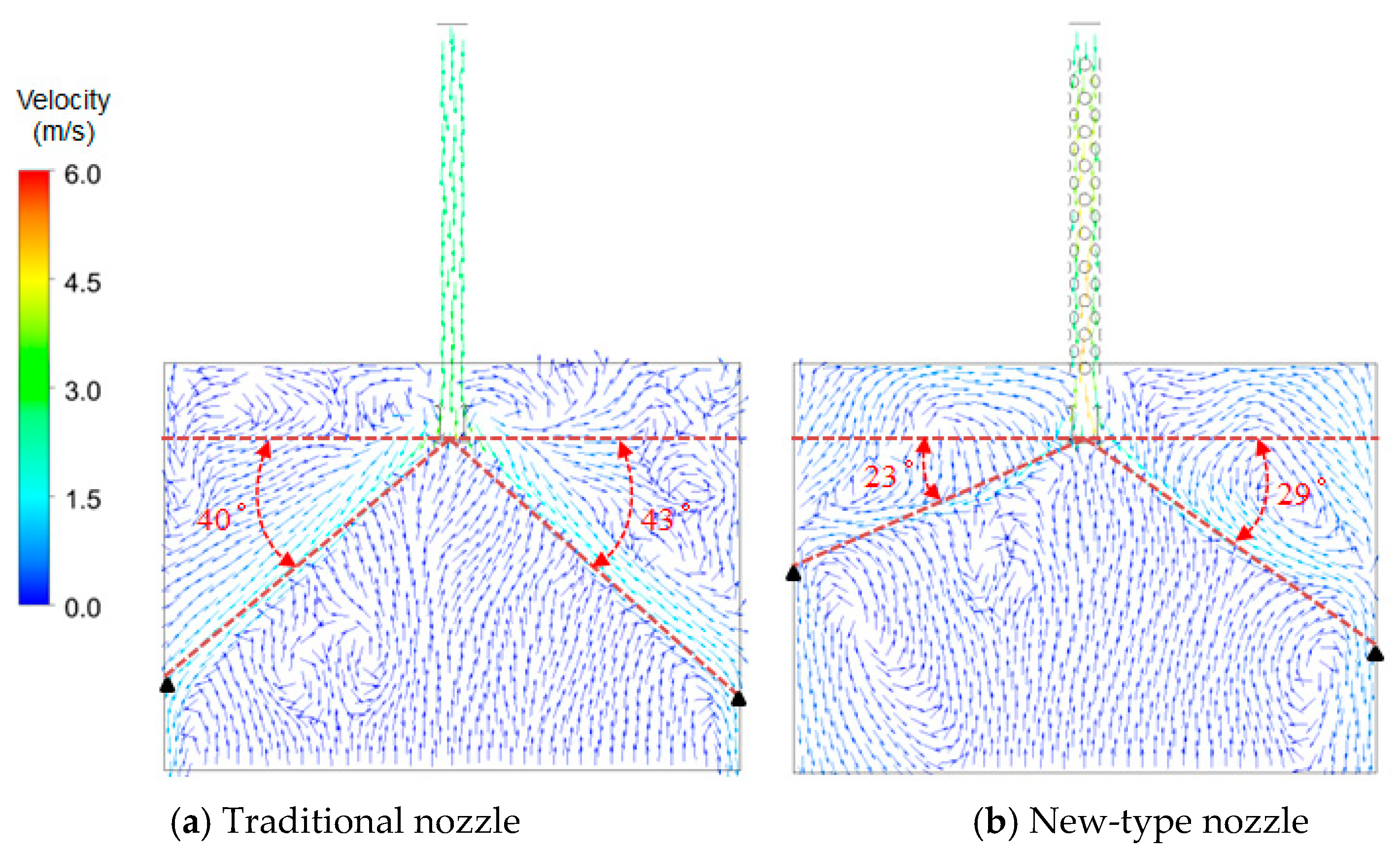
- Compared with the traditional nozzle, the new-type nozzle with internal hemispherical crowns has a shallower molten steel jet impact depth, the impact depth is between 26.5 and 33.61 cm, and the impact angle is between 23 and 29 degrees, and the position of the circuiting zone is closer to the molten steel free surface, which is more conducive to the floating of inclusions. The probability of occurrence of entrapment of top slag is small.
- (2)
- The longitudinal velocity distribution inside the traditional nozzle is uniform. Inside the new-type nozzle, however, transverse velocity components are generated due to the existence of the hemispherical crowns, forming swirl jets at the nozzle outlets with reduced velocity. Therefore, different from the traditional nozzle, the outlet flow from the new-type nozzle is a rotating jet with weaker impact, which is beneficial for using higher casting speed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Trejo, J.; Real-Ramírez, C.; Miranda-Tello, J.R.; Gabbasov, R.; Carvajal-Mariscal, I.; Sanchez-Silva, F.; Cervantes-De-La-Torre, F. Influence of the Submerged Entry Nozzle’s Bottom Well on the Characteristics of Its Exit Jets. Metals 2021, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.L.; Gong, Z.J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, J.W. Experimental study of PIV used in slab continuous casting mold flow field. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2009, 9, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoya, S.; Westoff, R.; Asako, Y.; Hara, S.; Szekely, J. Numerical Study of Immersion Nozzle Outlet Flow Pattern with Swirling Flow in Continuous Casting. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Shen, M.G.; Ji, K.F.; Zhang, Z.S.; Liu, Y.J. Research on the Influence of the Inner Wall Structure of the Continuous Casting Submerged Nozzle on the Stream of Molten Steel. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G. Continuous Casting. Mater. Eng. 2002, 19, 1075–8577. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, M.; Chen, M. Optimal Design of the Submerged Entry Nozzle for Thin Slab Continuous Casting Molds. Metals 2021, 11, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, N.; Ichikawa, K.; Iida, E.; Morita, A.; Inoue, J. Improvement of Submerged Nozzle Design Based on Water Model Examination of Tundish Slide Gate. In Proceedings of the 74th ISS Steelmaking Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 14–17 April 1991; Volume 74, pp. 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.F.; Shi, W.G. Research and application of tundish bottle nozzle in continuous casting. Steelmaking 1992, 8, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukaguchi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Kurimoto, H.; Yokoya, S.; Marukawa, K.; Tanaka, T. Development of Swirling-flow Submerged Entry Nozzles for Slab Casting. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Tomoichi, T.; Shinichiro, Y. Design of Swirl Blade for Slab Casting: Development of Swirling Flow Immersion Nozzle for Slab Casting-2. CAMP-ISIJ 2002, 15, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, C.S. Numerical Simulation and Experimental study of Spin Stirring of molten Steel in Mold. J. Taiyuan Heavy Mach. Inst. 2002, 23, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.W.; Su, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Fan, W. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and temperature field of slab under composite magnetic field. J. Mater. Metall. 2021, 20, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.F.; Wang, F.P.; Qiao, J.L.; Luo, L.H. Continuous casting tundish nozzle clogging mechanism and preventive measures. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2016, 7, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Su, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Marukawa, K.; He, J. Effects of Electromagnetic Swirling Flow in Submerged Entry Nozzle on Square Billet Continuous Casting of Steel Process. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fluid Media | Density (kg/m3) | Dynamic Viscosity (kg/(m·s)) | Kinematic Viscosity (m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molten steel | 7020 | 6.2 × 10−3 | 0.95 × 10−6 |
| Water | 1000 | 1 × 10−3 | 1 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, C.; Zhao, M.; Shen, M.; Pan, Y.; Deng, X.; Shi, C. Physical and Numerical Simulation Study on Structure Optimization of the Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting of Molten Steel. Processes 2023, 11, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113237
Cai C, Zhao M, Shen M, Pan Y, Deng X, Shi C. Physical and Numerical Simulation Study on Structure Optimization of the Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting of Molten Steel. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113237
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Changyou, Ming Zhao, Minggang Shen, Yuhua Pan, Xin Deng, and Chunyang Shi. 2023. "Physical and Numerical Simulation Study on Structure Optimization of the Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting of Molten Steel" Processes 11, no. 11: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113237
APA StyleCai, C., Zhao, M., Shen, M., Pan, Y., Deng, X., & Shi, C. (2023). Physical and Numerical Simulation Study on Structure Optimization of the Inner Wall of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Continuous Casting of Molten Steel. Processes, 11(11), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113237








