Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe–Mn–Ni System and Diffusion Mobility of Its Face-Centered Cubic Phase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Thermodynamics
2.2. Diffusion Mobility
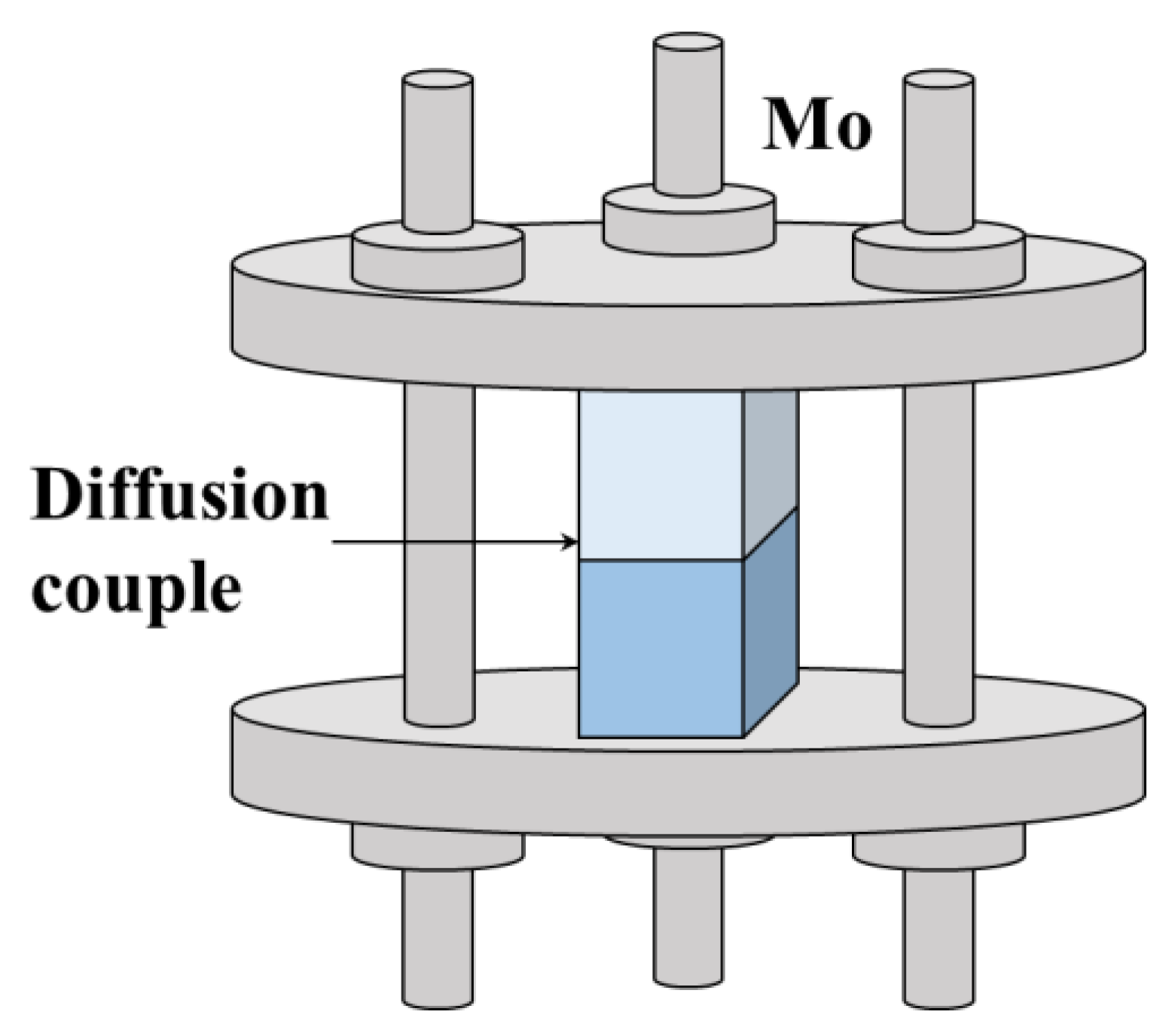
3. Experiments
4. Modeling
4.1. Thermodynamic Models
4.2. Diffusion Mobility Modeling
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Thermodynamic Assessment
5.2. Diffusion Mobility Optimization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersson, J.O.; Helander, T.; Höglund, L.; Shi, P.; Sundman, B. Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science. Calphad 2002, 26, 273–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Dupin, N.; Zhou, H.; Tang, C. Phase equilibria and thermal analysis in the Fe–Mn–Ni system. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 100, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. An assessment of the Fe-Mn system. Calphad 1989, 13, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, C.; Sundman, B.; Lyon, O. Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Fe-Ni system. Calphad 2001, 25, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Order-Disorder Phase Transition, Phase Diagram Topological Relationship and Its Application in Solidification Process of Aluminum Alloy. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Thermodynamic and Diffusion Kinetic Studies of Key Phases in the Co-Al-Fe-Ni System. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Yu, D.; Liang, D. Atomic mobilities, uphill diffusion and proeutectic ferrite growth in Fe–Mn–C alloys. Calphad 2009, 33, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Xu, X.; Lu, X.-G.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H. Experimental and computational study of diffusion mobilities for fcc Ni–Cu–Mn alloys. Calphad 2016, 54, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L. Coupled phase diagrams and thermochemical data for transition metal binary systems-III. Calphad 1978, 2, 117–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. An assessment of the Fe-Mn system. Calphad 1987, 11, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-J.; Lee, D.N. A thermodynamic study on the Mn-C and Fe-Mn systems. Calphad 1989, 13, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Witusiewicz, V.T.; Sommer, F.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Reevaluation of the Fe-Mn phase diagram. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2004, 25, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witusiewicz, V.T.; Sommer, F.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Enthalpy of formation and heat capacity of Fe-Mn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, J.; Jacques, P.J. Effects of the thermodynamic parameters of the hcp phase on the stacking fault energy calculations in the Fe-Mn and Fe-Mn-C systems. Calphad 2010, 34, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurovic, D.; Hallstedt, B.; Von Appen, J.; Dronskowski, R. Thermodynamic assessment of the Fe-Mn-C system. Calphad 2011, 35, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotes, S.M.; Guillermet, A.F.; Sade, M. Fcc/hcp martensitic transformation in the Fe-Mn system: Part II. Driving force and thermodynamics of the nucleation process. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeong-Joo, L. Revision of thermodynamic descriptions of the Fe-Cr and Fe-Ni liquid phases. Calphad 1993, 17, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.S.; Gohil, D.D.; Dinsdale, A.T.; Chart, T. National Physical Laboratory DMA (A) 103; National Physical Laboratory: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciamani, G.; Dinsdale, A.; Palumbo, M.; Pasturel, A. The Fe-Ni system: Thermodynamic modelling assisted by atomistic calculations. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, P.; Seifert, H.J. The influence of magnetic and chemical ordering on the phase diagram of Cr–Fe–Ni. Calphad 2011, 35, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, I.; Shimenouchi, S.; Omori, T.; Ishida, K.; Kainuma, R. Experimental determination and thermodynamic evaluation of low-temperature phase equilibria in the Fe–Ni binary system. Calphad 2019, 67, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J. Thermodynamic solution phase data for binary Mn-based systems. Calphad 2001, 25, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Du, Z. Thermodynamic optimization of the Mn-Ni system. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, P. An assessment of the ordered phases in Mn-Ni using two- and four-sublattice models. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 98, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L. Experimental Investigation of Phase Equilibria and Interdiffusion Coefficients in Ni-Mn System: A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of. Master of Science. Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.S.; Yu, J.H.; Lee, B.-J.; Lee, H.M. Assessment of the mobility of Mn in the Fe-Mn and Ni-Mn binary system. Z. Met. 2000, 91, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, B. Mobilities in Fe-Ni alloys—Assessment of the mobilities of Fe and Ni in fcc Fe-Ni alloys. Scand. J. Metall. 1994, 23, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.-H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Lu, X.-G.; Zhang, L. Thermodynamic assessment of the Co–Fe–Ni system and diffusion study of its fcc phase. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, L. Atomic mobility, diffusivity and diffusion growth simulation for fcc Cu–Mn–Ni alloys. Calphad 2011, 35, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, M. The compound energy formalism. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 320, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, A.T. SGTE data for pure elements. Calphad 1991, 15, 317–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Ågren, J. Models for numerical treatment of multicomponent diffusion in simple phases. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, B. On ferromagnetic ordering and lattice diffusion—A simple model. Z. Met. 1992, 83, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, O.; Kister, A.T. Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and the Classification of Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1948, 40, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrat, D.M. Phase relationships in the Fe-Cr-Mn-Ni-C system at solidification temperatures. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1986, 17, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parravano, N. Ternary alloys of iron-nickel-manganese, nickel-manganese-copper, and iron-manganese-copper. Z. Met. 1913, 4, 171–201. [Google Scholar]
- Whittle, D.; Green, A. The measurement of diffusion coefficients in ternary systems. Scr. Metall. 1974, 8, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Tölle, V. Monovacancy and divacancy contributions to self-diffusion in face-centred cubic metals reanalysis for copper, silver, gold, nickel and platinum. Philos. Mag. A 1986, 54, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Alloy | Composition (wt.%) | Temperature (K) | Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe–4Mn–4Ni | 923 | 70 |
| 973 | 60 | ||
| 2 | Fe–8Mn–2Ni | 923 | 70 |
| 3 | Fe–2Mn–2Ni | 973 | 60 |
| 1023 | 50 | ||
| 4 | Fe–2Mn–4Ni | 973 | 70 |
| Diffusion Couple | Composition (at.%) | Temperature (K) | Time (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Fe/Fe–15.42Mn–83.04Ni | 1373 | 96 |
| F2 | Fe/Fe–15.36Mn–14.09Ni | 1373 | 96 |
| F3 | Fe–14.46Mn/Fe–18.26Ni | 1373 | 96 |
| F4 | Fe–14.50Mn/Fe–49.33Ni | 1373 | 96 |
| N1 | Ni/Fe–14.52Mn | 1373 | 96 |
| N2 | Ni–21.35Fe/Ni–15.74Mn | 1373 | 96 |
| N3 | Ni–49.85Fe/Ni–16.46Mn | 1373 | 96 |
| Alloy | Temperature (K) | Phase Composition (wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCC | FCC | ||||
| Mn | Ni | Mn | Ni | ||
| 1 | 923 | 2.07 | 2.08 | 4.72 | 4.96 |
| 973 | 1.35 | 1.88 | 4.09 | 4.15 | |
| 2 | 923 | 2.61 | 0.91 | 7.82 | 1.96 |
| 3 | 973 | 1.41 | 1.72 | 4.10 | 3.90 |
| 1023 | 1.10 | 1.24 | 2.52 | 2.72 | |
| 4 | 973 | 1.02 | 2.31 | 2.87 | 5.34 |
| Phase | Thermodynamic Parameters | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid | [3] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | [3] | |
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| BCC | [3] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | [3] | |
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| FCC | [3] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | [3] | |
| [3] | ||
| [3] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| αMn | [3] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | [5] | |
| [5] | ||
| βMn | [3] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | This work | |
| [5] | ||
| HCP | [15] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)1 | [15] | |
| B2 | This work | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)0.5(Fe,Mn,Ni)0.5 | [6] | |
| [5] | ||
| L12 | [6] | |
| (Fe,Mn,Ni)0.75(Fe,Mn,Ni)0.25 | [6] | |
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [6] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| L10 | [5] | |
| (Mn,Ni)0.5(Mn,Ni)0.5 | [5] | |
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [5] | ||
| MnNi2 | [5] | |
| (Mn,Ni)1(Ni)2 | [5] | |
| [5] |
| Diffusion Couple | Composition (at%) | Interdiffusion Coefficients (×10−15 m2/s) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Mn | Ni | |||||||||
| F1/F3 | 81.15 | 0.83 | 18.02 | 3.59 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 2.09 | 2.77 | −0.15 | −0.01 | 3.87 |
| F1/F4 | 51.26 | 2.43 | 46.31 | 12.11 | −0.71 | −4.77 | 6.56 | 5.02 | −1.21 | 0.60 | 13.07 |
| F2/F3 | 89.15 | 7.05 | 3.80 | 2.63 | −0.08 | −0.11 | 0.46 | −0.05 | −3.43 | −0.12 | 2.08 |
| F2/F4 | 84.45 | 8.59 | 6.96 | 2.90 | −0.31 | −1.24 | 1.08 | 0.60 | −1.44 | 0.53 | 3.91 |
| F2/N1 | 83.45 | 8.94 | 7.61 | 2.60 | −0.25 | −1.61 | 1.46 | 1.11 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 3.56 |
| N1/F1 | 36.86 | 4.64 | 58.50 | 19.70 | −3.11 | −4.78 | 12.51 | 10.62 | −7.04 | 3.84 | 25.74 |
| N1/N3 | 28.16 | 4.80 | 67.05 | 17.37 | −5.11 | −20.42 | 18.39 | 12.16 | 15.64 | 4.61 | 22.11 |
| N1/N2 | 15.29 | 4.87 | 79.84 | 12.08 | −4.60 | −4.53 | 14.58 | 11.72 | 6.31 | 5.10 | 18.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Fan, G.; Ma, C.; Mei, Y.; Luo, T.; Zheng, W.; Wang, J. Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe–Mn–Ni System and Diffusion Mobility of Its Face-Centered Cubic Phase. Processes 2023, 11, 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113216
Wang M, Fan G, Ma C, Mei Y, Luo T, Zheng W, Wang J. Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe–Mn–Ni System and Diffusion Mobility of Its Face-Centered Cubic Phase. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113216
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Guodong Fan, Chengyang Ma, Yu Mei, Tao Luo, Weisen Zheng, and Jiang Wang. 2023. "Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe–Mn–Ni System and Diffusion Mobility of Its Face-Centered Cubic Phase" Processes 11, no. 11: 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113216
APA StyleWang, M., Fan, G., Ma, C., Mei, Y., Luo, T., Zheng, W., & Wang, J. (2023). Thermodynamic Assessment of the Fe–Mn–Ni System and Diffusion Mobility of Its Face-Centered Cubic Phase. Processes, 11(11), 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113216









