Investigation of Pressure Variations in Hose Pumps under Different Flow Regimes Using Bidirectional Fluid–Structure Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simplified Model and Numerical Computational Methods
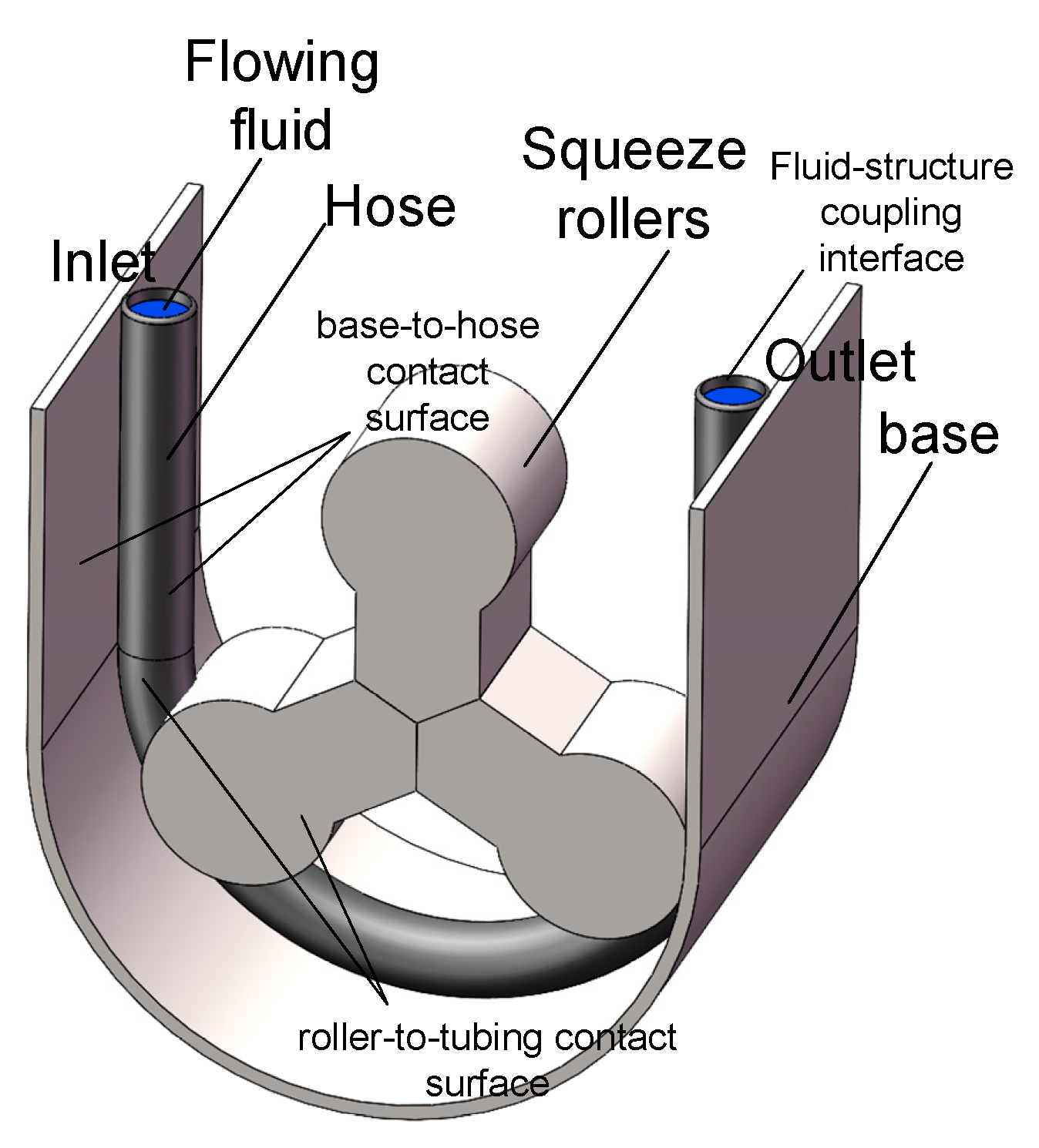
2.1. Geometric Model
2.2. Mesh Generation
2.3. Simulation Model Establishment
2.4. Contact Settings
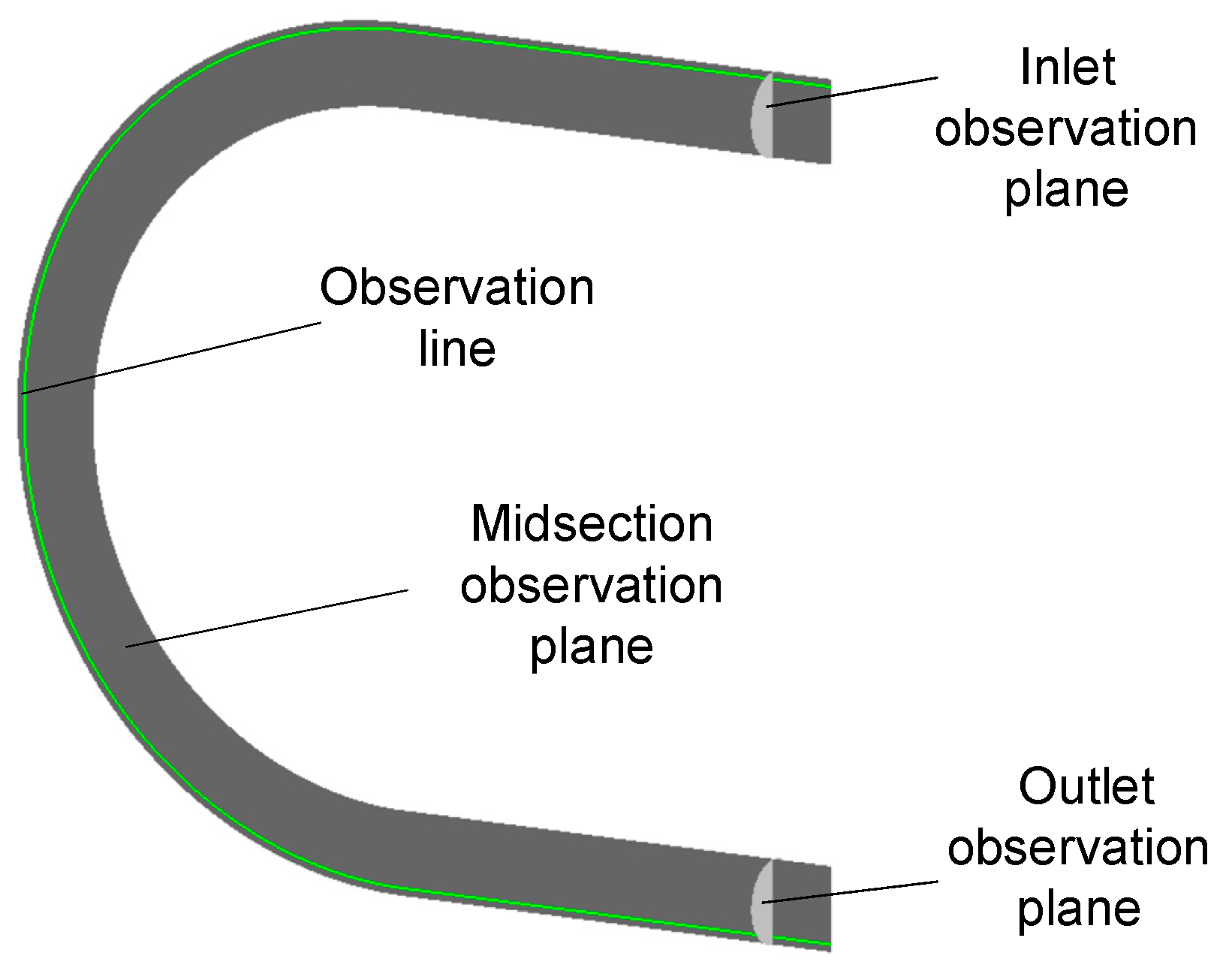
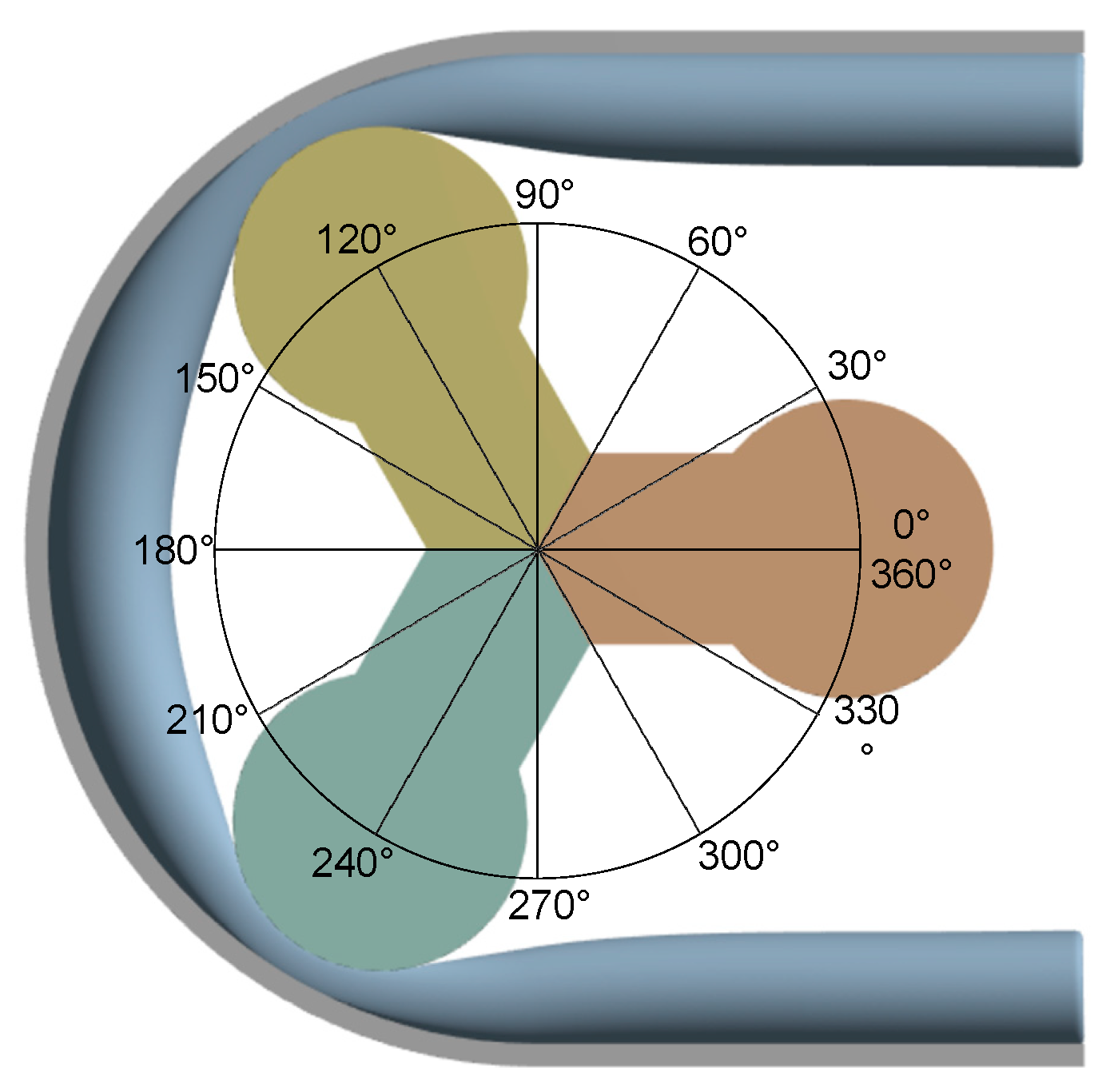
2.5. Observation Surface Settings
3. Experimental Setup
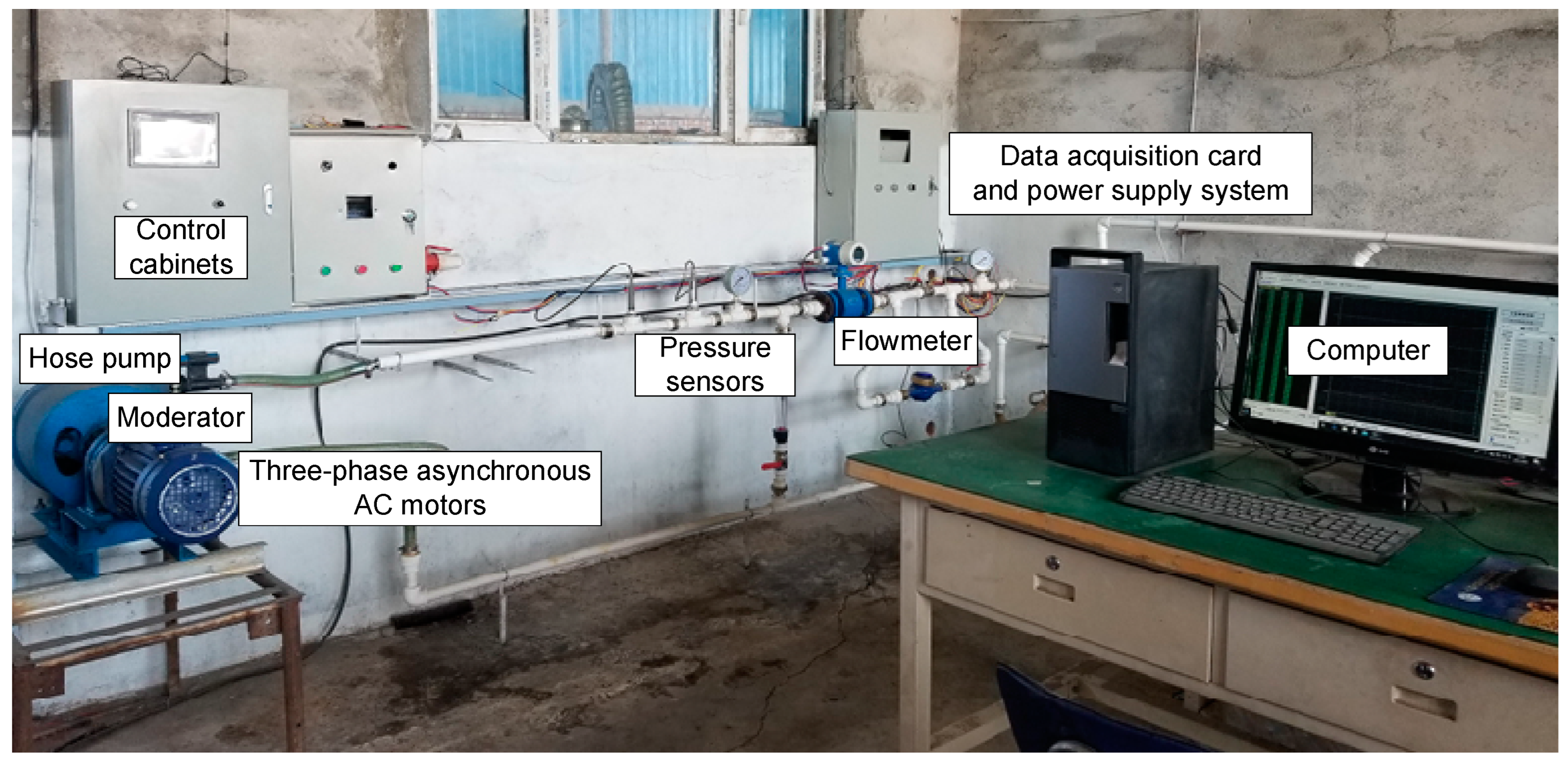
Description of the Experimental Rig
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Result Validation
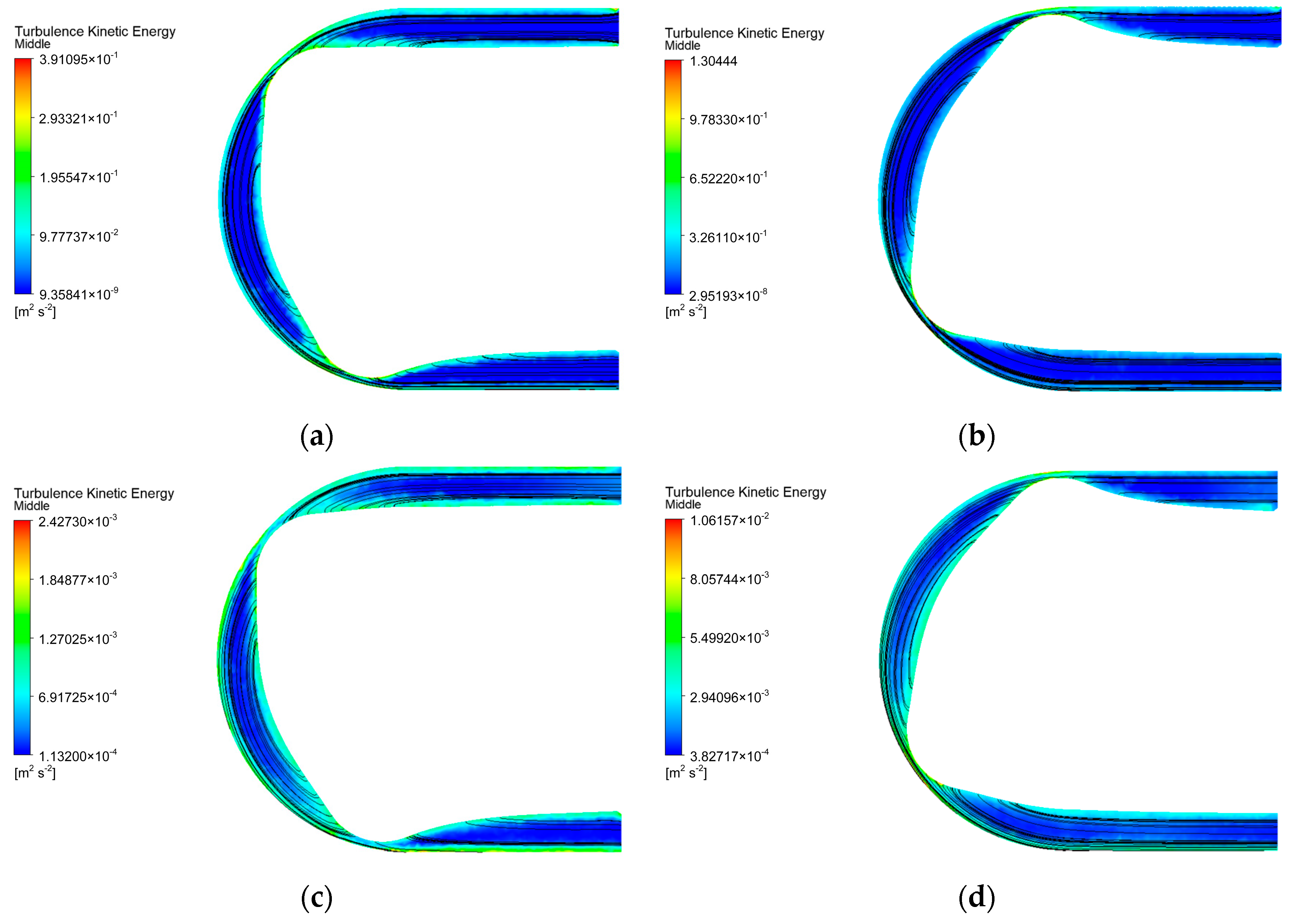
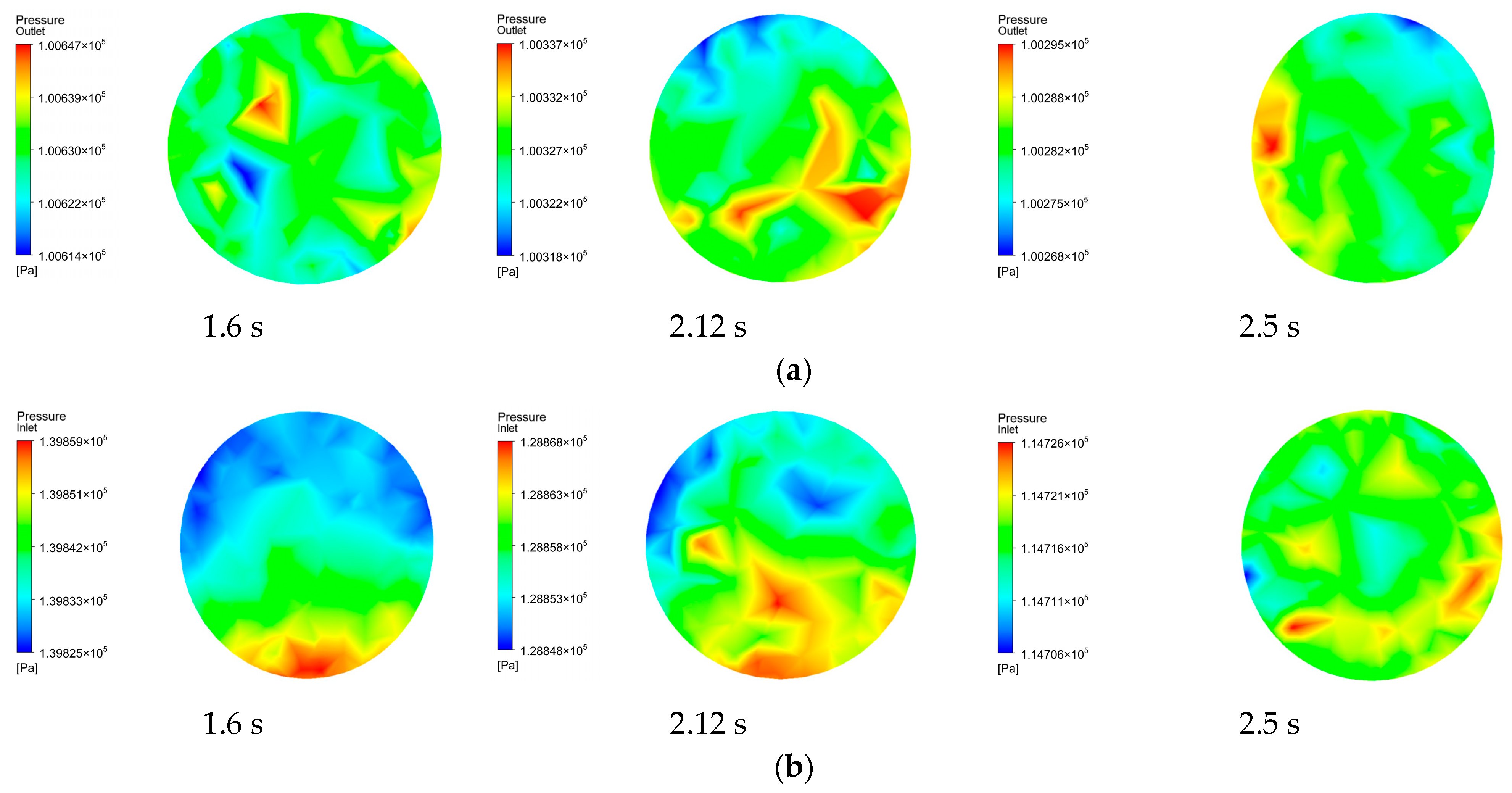
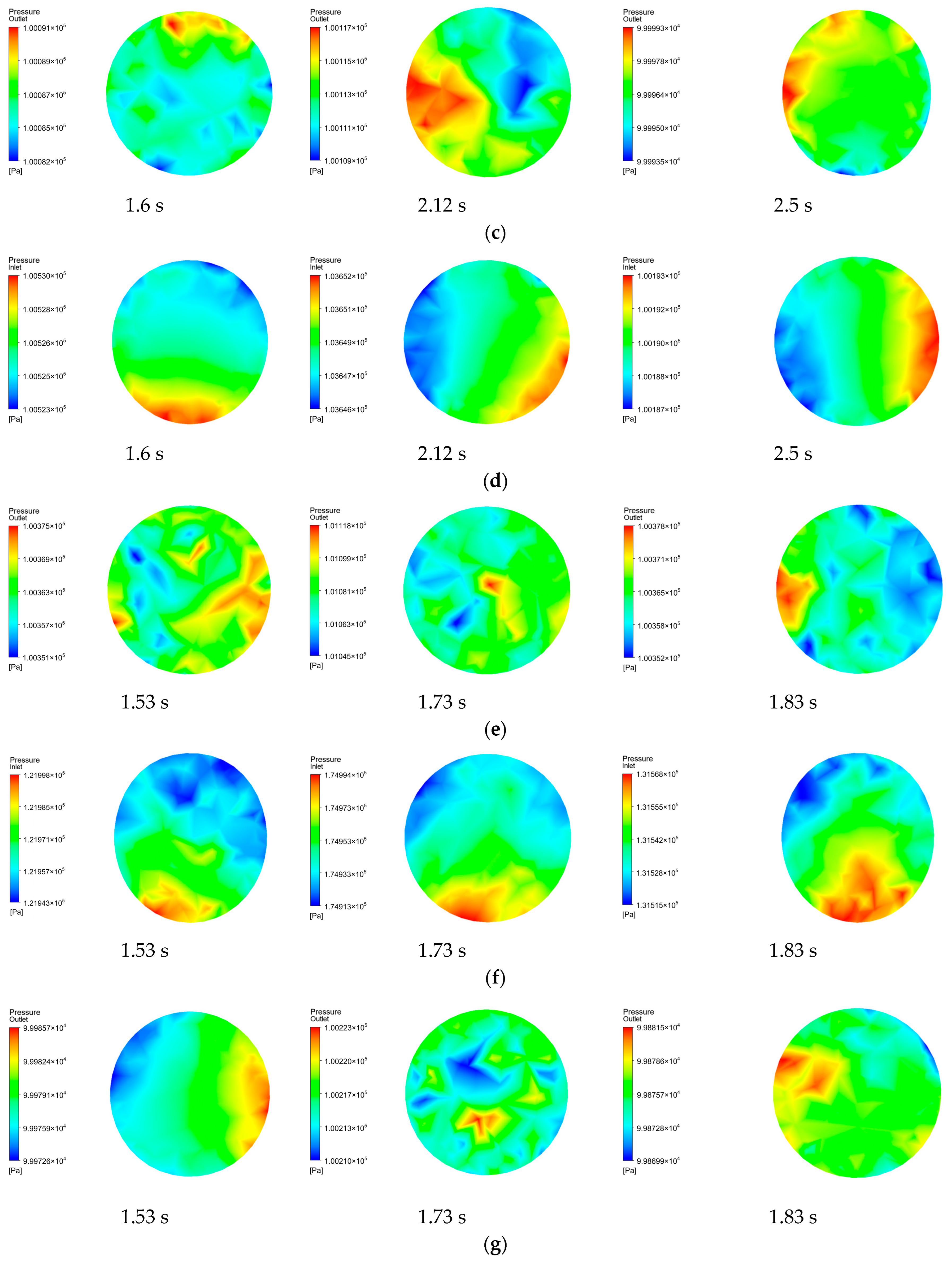
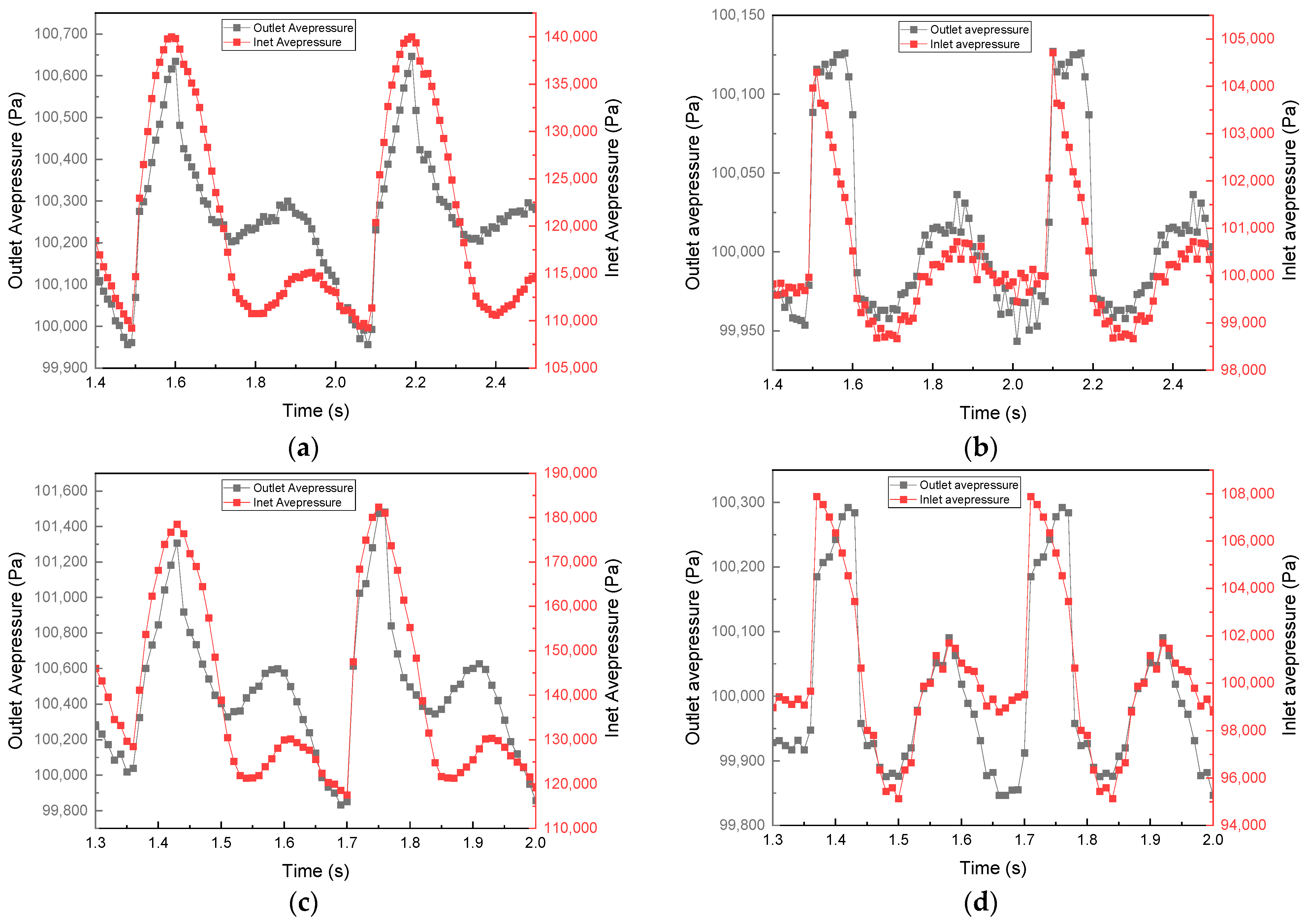
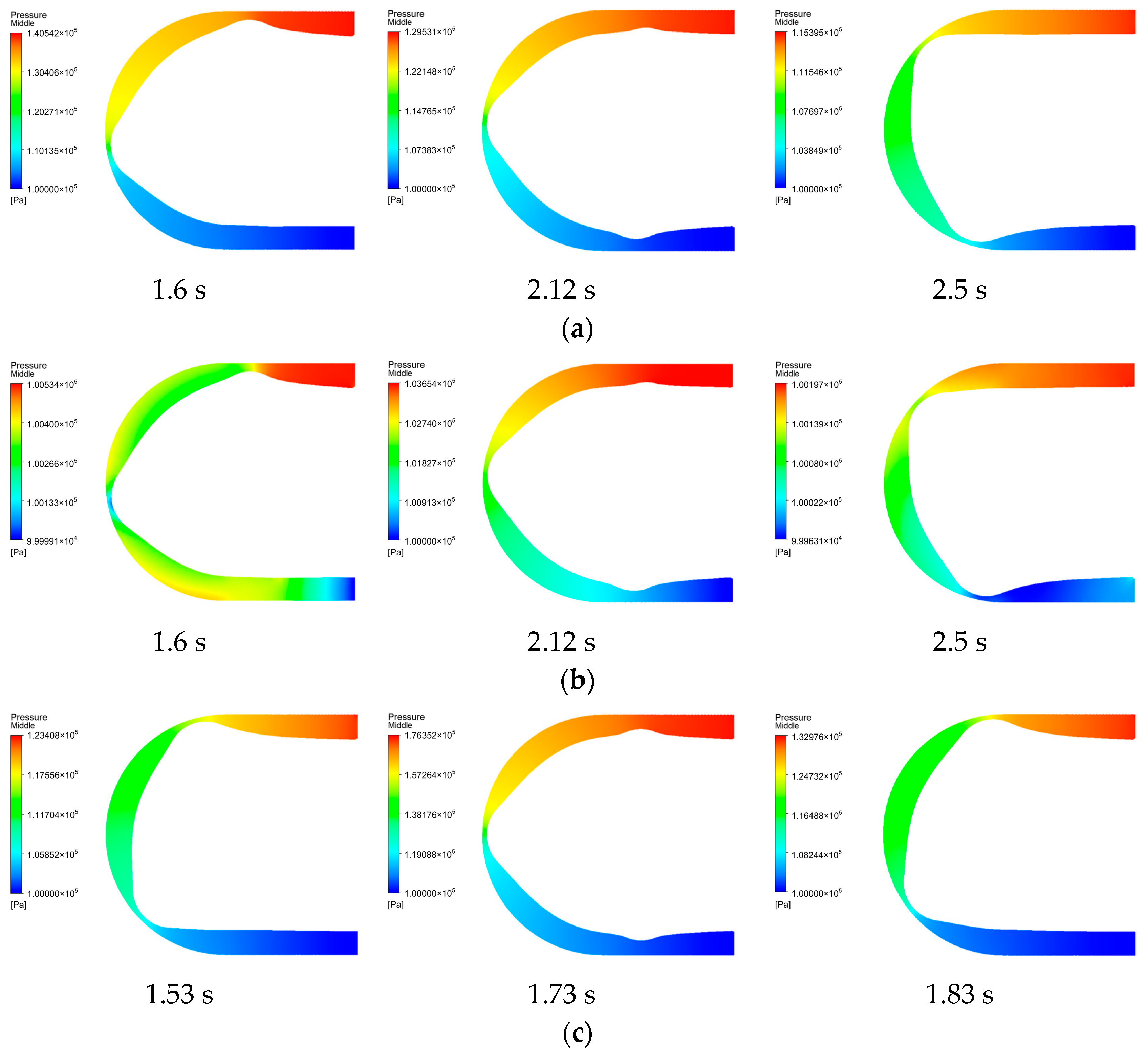
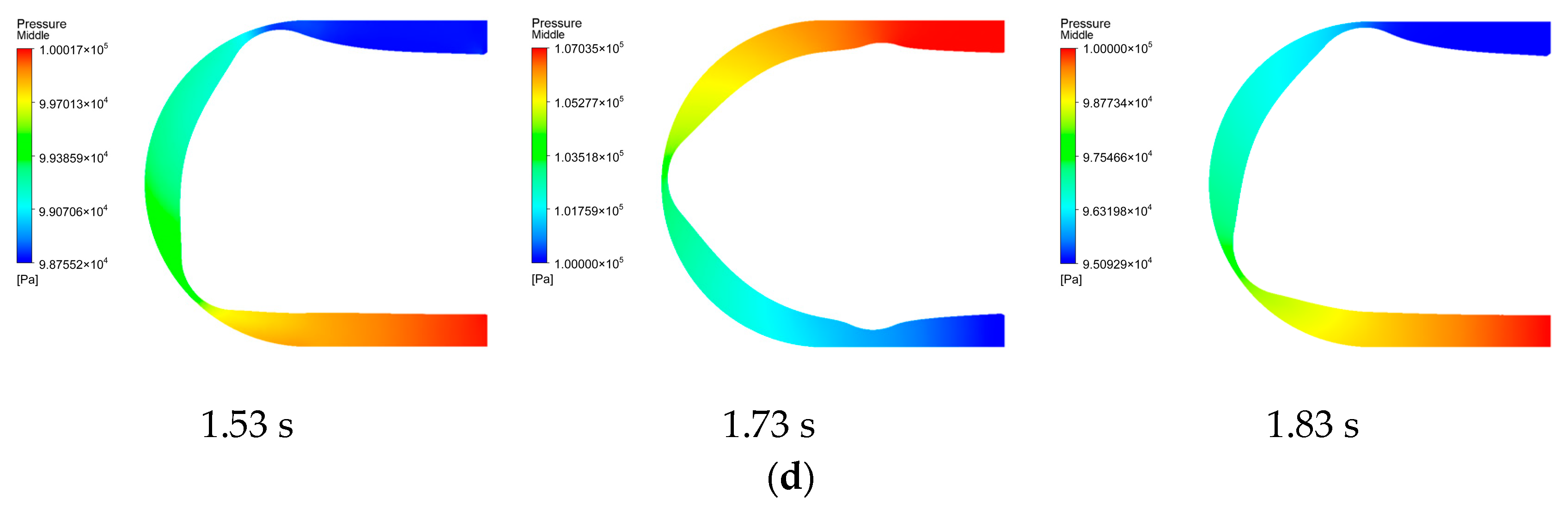
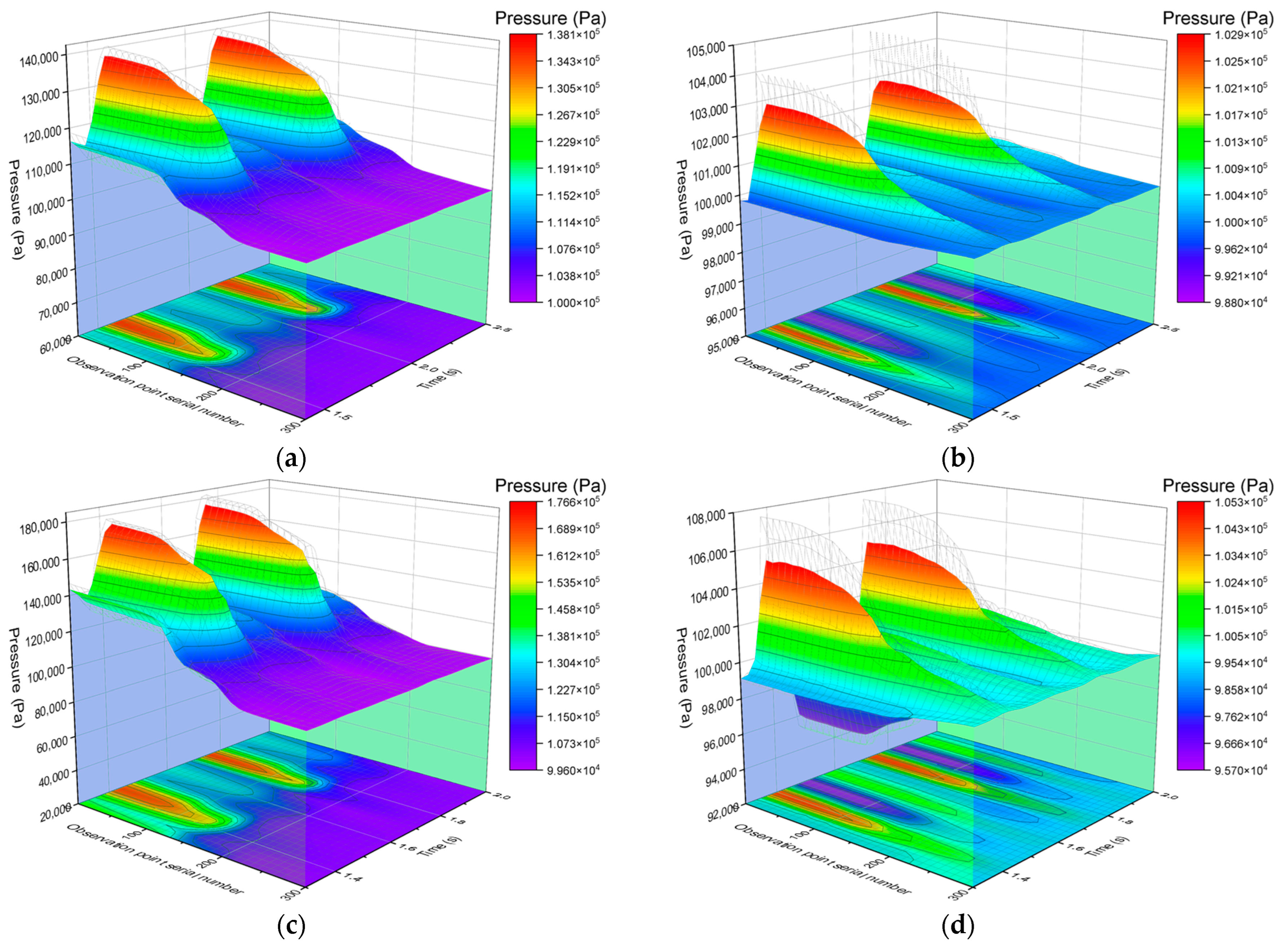
4.2. Simulation Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Du, C. The shell shape optimization and fluid–structure interaction simulation of hose pump in water-fertilizer integrated fertilizer application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cui, Q.Z. Structure Analyses and Flow Rate Model of Peristaltic Pump of Cement Foaming Machine. In Advanced Engineering Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bach, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 852–855. [Google Scholar]
- Busono, P.; Iswahyudi, A.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Fitrianto, A. Design of Embedded Microcontroller for Controlling and Monitoring Blood Pump. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, T.; Achten, E. High-pressure peristaltic pumps tackle petrochemicals. World Pumps 2005, 2005, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashchenko, V.I.; Emelianova, I.A.; Chaika, D.O. Features of the Use of a Universal Hose Concrete Pump in the Construction Site. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Postma, T. Bredel Hose Pumps invests in advanced grinding machinery. World Pumps 2002, 2002, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitavade, E.N.; Patil, S.D.; Kadam, A.N.; Mulla, T.S. An overview of peristaltic pump suitable for handling of various slurries and liquids. J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2012, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Tan, R. Research on peristaltic pump design based on patent analysis. J. Eng. Des. 2013, 20, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Shamanskiy, A.; Simeon, B. Mesh deformation techniques in fluid-structure interaction: Robustness, accumulated distortion and computational efficiency. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.14051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.N.; Le Touze, D.; Oger, G.; Zhang, A.M. An accurate FSI-SPH modeling of challenging fluid-structure interaction problems in two and three dimensions. Ocean Eng. 2021, 221, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, G. Deep neural network based reduced-order model for fluid–structure interaction system. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 073610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.T.; Min, C.; Gibou, F. An efficient fluid–Solid coupling algorithm for single-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2009, 228, 8807–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Kamran, A.; Siddiqui, M.Z.; Farhan, M. Mechanical Characterization and FE Modelling of a Hyperelastic Material. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosiak, M.; Karpenko, M.; Prentkovskis, O.; Deptuła, A.; Skačkauskas, P. Research of vibrations effect on hydraulic valves in military vehicles. Def. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formato, G.; Romano, R.; Formato, A.; Sorvari, J.; Koiranen, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Villecco, F. Fluid–Structure Interaction Modeling Applied to Peristaltic Pump Flow Simulations. Machines 2019, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinaro, G.; Frosina, E.; Senatore, A. A Numerical Analysis of an Innovative Flow Ripple Reduction Method for External Gear Pumps. Energies 2021, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y. The research on flow pulsation characteristics of axial piston pump. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering, Nanjing, China, 17–18 September 2017; Volume 10322, pp. 888–892. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, M.P.; van Schoor, G.; Uren, K.R.; Kloppers, C.P. Modelling the pulsatile flow rate and pressure response of a roller-type peristaltic pump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 325, 112708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, M.; Prentkovskis, O.; Šukevičius, Š. Research on high-pressure hose with repairing fitting and influence on energy parameter of the hydraulic drive. Eksploatacja Niezawodność 2022, 24, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Hu, Z.; Yan, Y. Experimental and numerical simulation study of pressure pulsations during hose pump operation. Processes 2021, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X. Flow Pulsation Optimization of Peristaltic Pump Based on Surrogate Model. In International Joint Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Hirata, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Okano, K.; Katoh, K. Model-based design of tube pumps with ultra-low flow rate pulsation. SICE J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2022, 15, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, F.; Masselter, T.; Speck, T. Silent Pumpers: A Comparative Topical Overview of the Peristaltic Pumping Principle in Living Nature, Engineering, and Biomimetics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheed, R.; Mohammadian, A.; Kheirkhah Gildeh, H. A comparison of standard k–ε and realizable k–ε turbulence models in curved and confluent channels. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.; Park, H.; Yeom, S.; Park, S.H. A comparison among Neo-Hookean model, Mooney-Rivlin model, and Ogden model for chloroprene rubber. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yao, L.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X. Theoretical research prospects for hose pumps of guest soil sprayers for greening. For. Mach. Woodwork. Equip. 2006, 34, 19–22. [Google Scholar]


| Power Supply Frequency (Hz) | Number of Rollers | Drum Diameter (mm) | Outer Circle Diameter (mm) | Hose Inlet Diameter (mm) | Hose Outer Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35/65 | 3 | 69 | 260 | 25 | 25 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Dynamic Viscosity (kg/(m s)) | |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Fertilizer | 1300 | 0.7 |
| Water | 998.2 | 0.001003 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Material Constant C10 | Material Constant C01 |
|---|---|---|
| 1100 | 5.2 × 107 | 1.3 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Chao, X. Investigation of Pressure Variations in Hose Pumps under Different Flow Regimes Using Bidirectional Fluid–Structure Interaction. Processes 2023, 11, 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113079
Wang M, Zhang L, Wang W, Ma X, Hu X, Zhao J, Chao X. Investigation of Pressure Variations in Hose Pumps under Different Flow Regimes Using Bidirectional Fluid–Structure Interaction. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113079
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengfan, Lixin Zhang, Wendong Wang, Xiao Ma, Xue Hu, Jiawei Zhao, and Xuewei Chao. 2023. "Investigation of Pressure Variations in Hose Pumps under Different Flow Regimes Using Bidirectional Fluid–Structure Interaction" Processes 11, no. 11: 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113079
APA StyleWang, M., Zhang, L., Wang, W., Ma, X., Hu, X., Zhao, J., & Chao, X. (2023). Investigation of Pressure Variations in Hose Pumps under Different Flow Regimes Using Bidirectional Fluid–Structure Interaction. Processes, 11(11), 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113079







