CFD-DEM Simulation of Slugging and Non-Slugging Fast Fluidization of Fine Particles in a Micro Riser
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Models
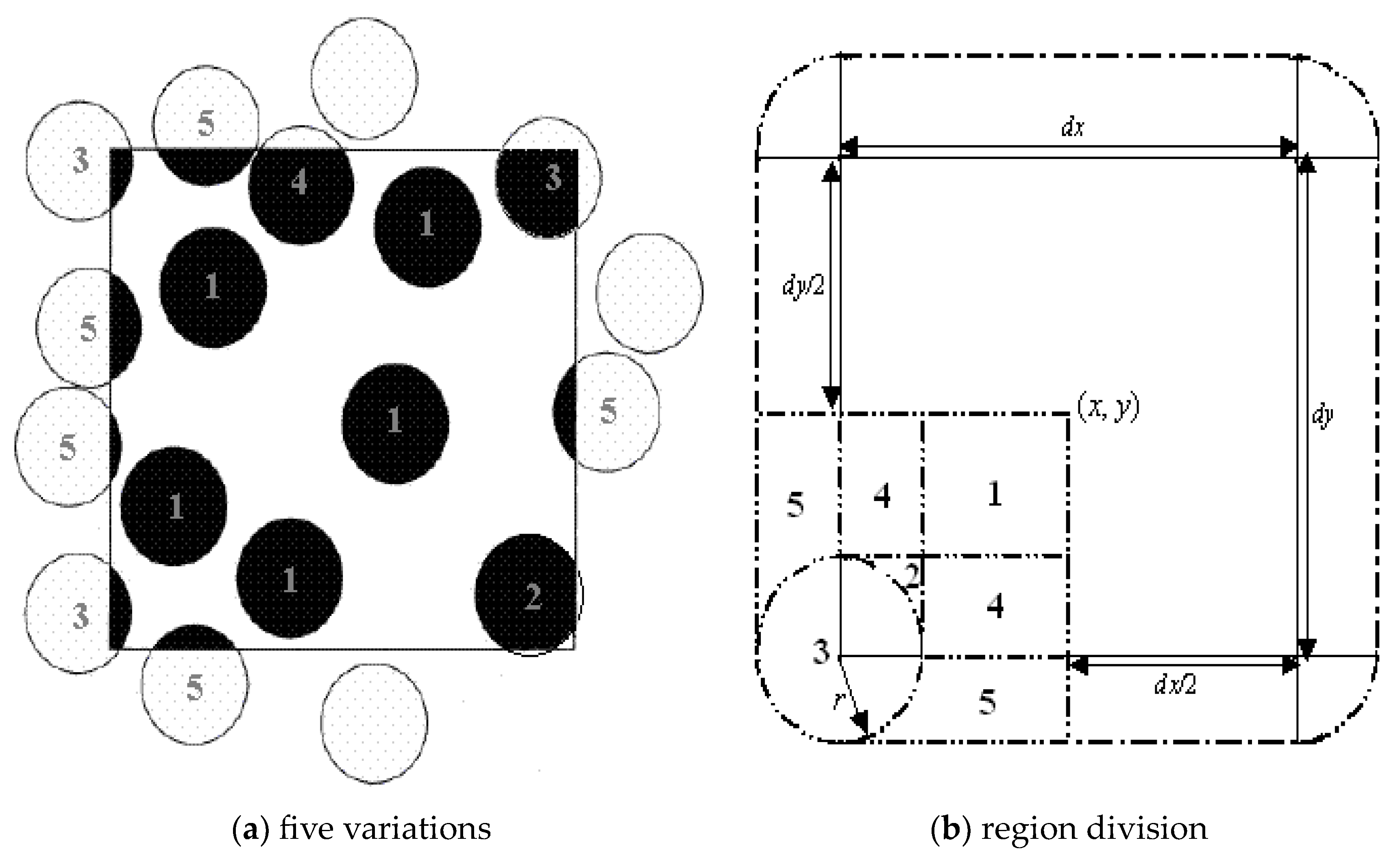
2.1. Precise Area Fraction Model
2.2. Drag Model
3. Simulation Method
4. Results and Discussion
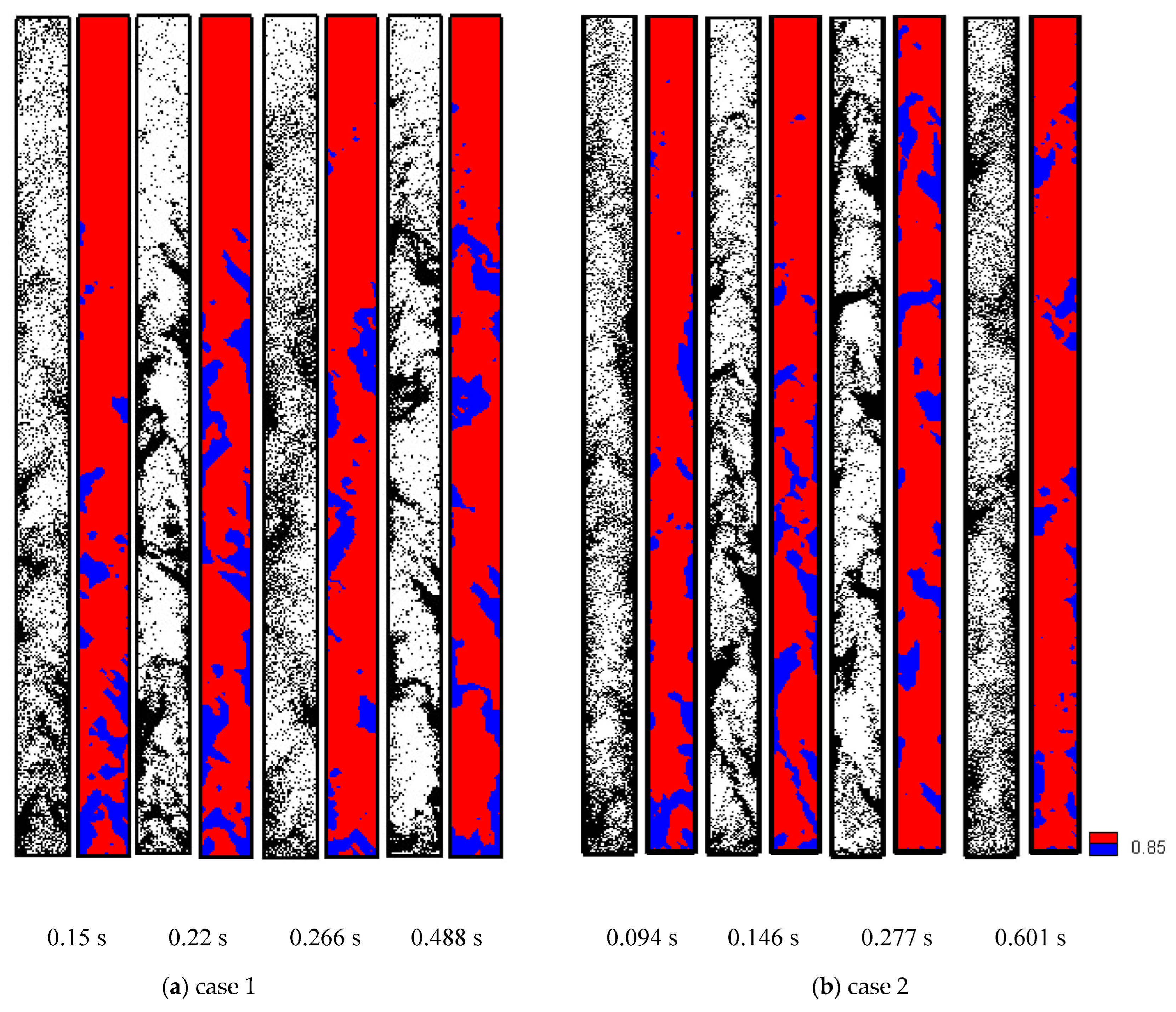
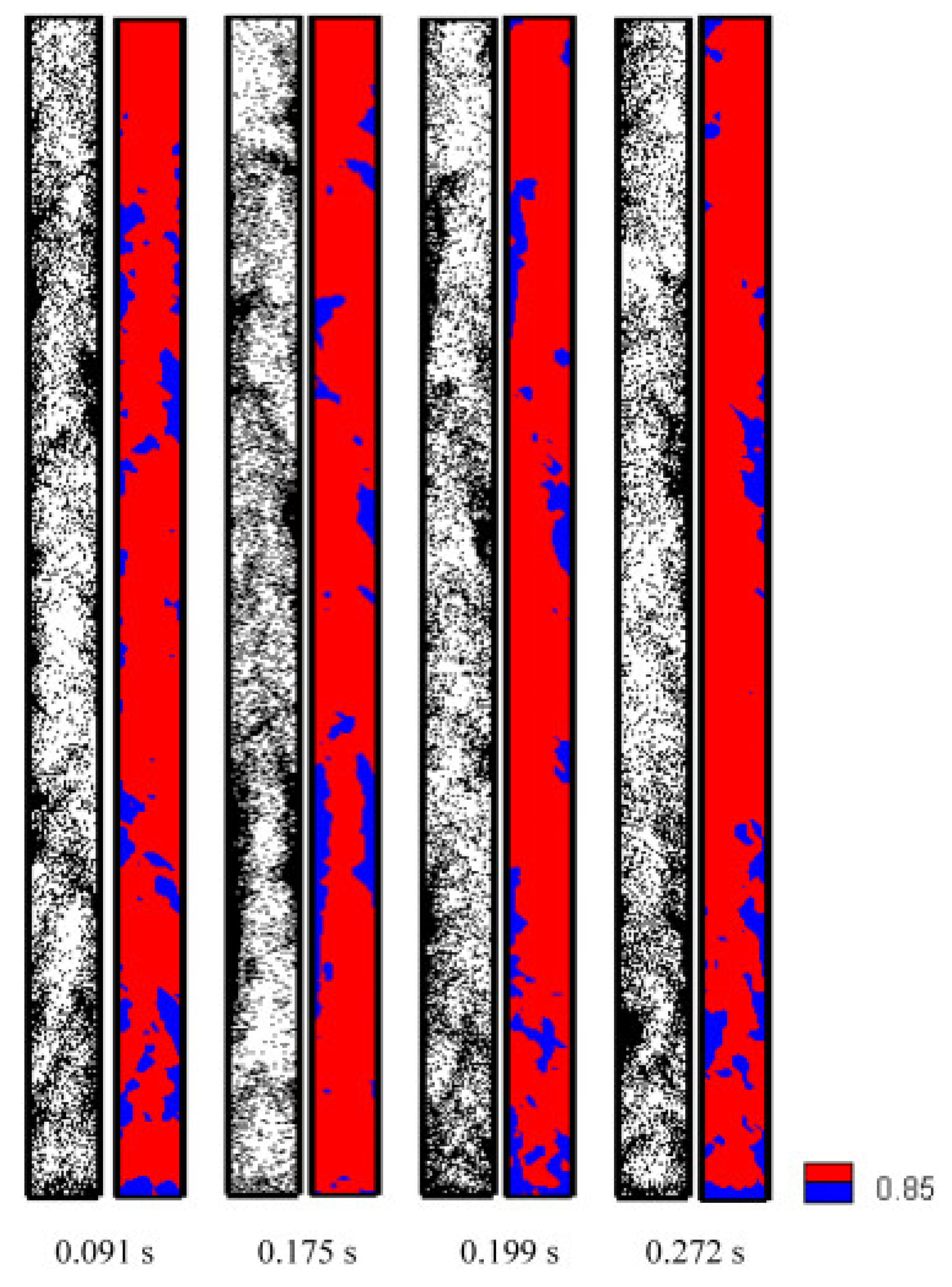
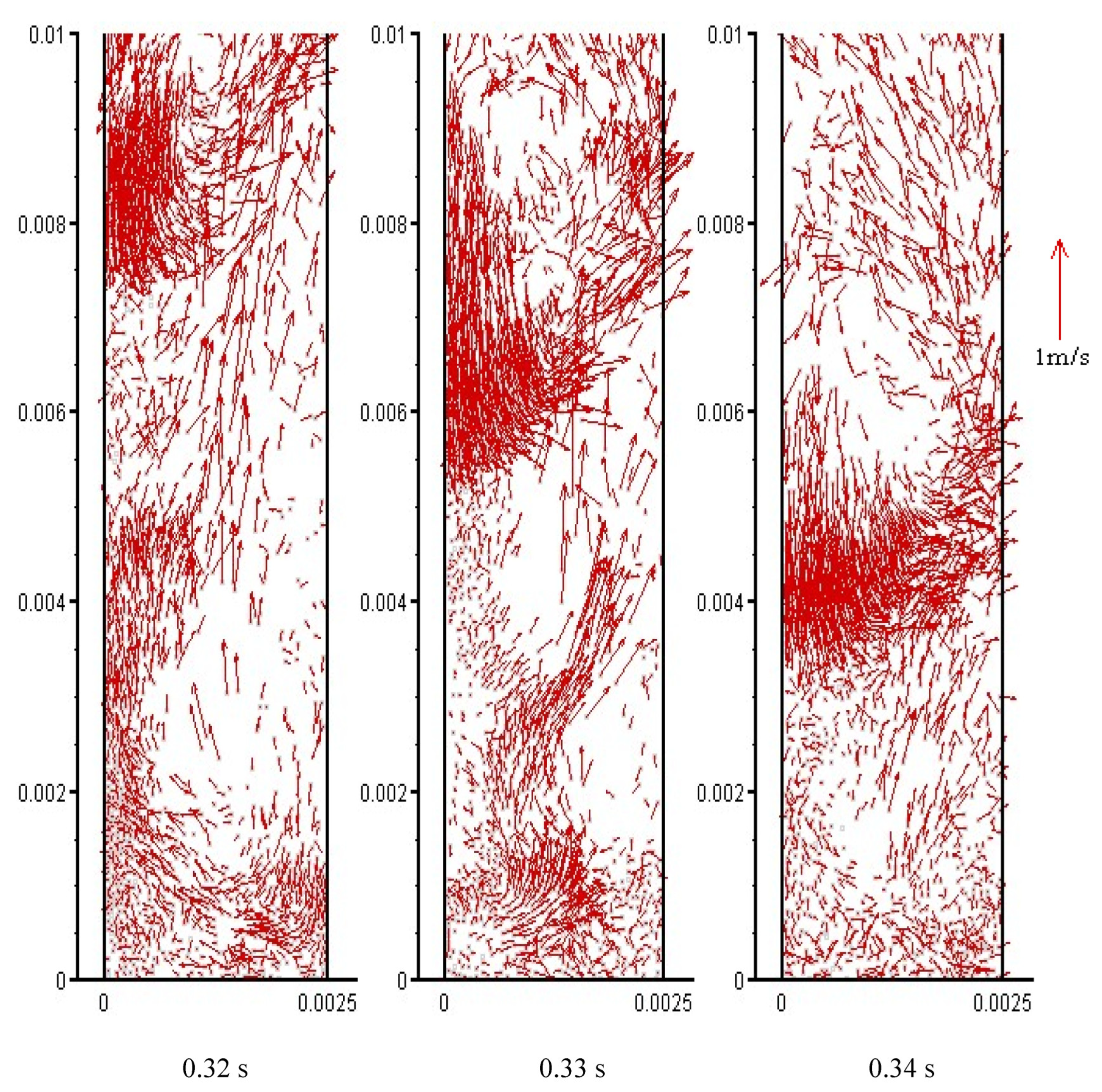
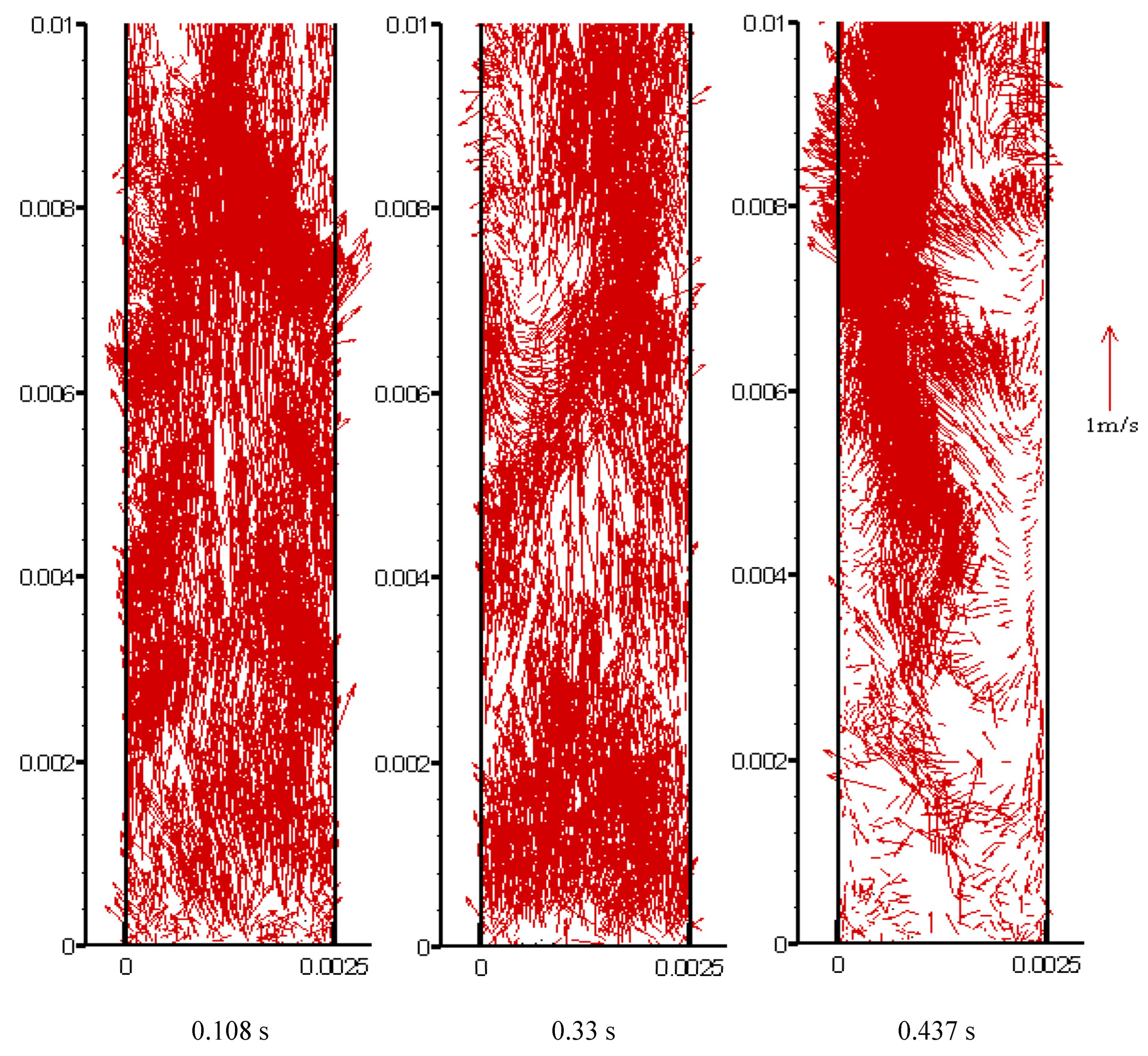
4.1. Clustering
4.2. Particle Backmixing
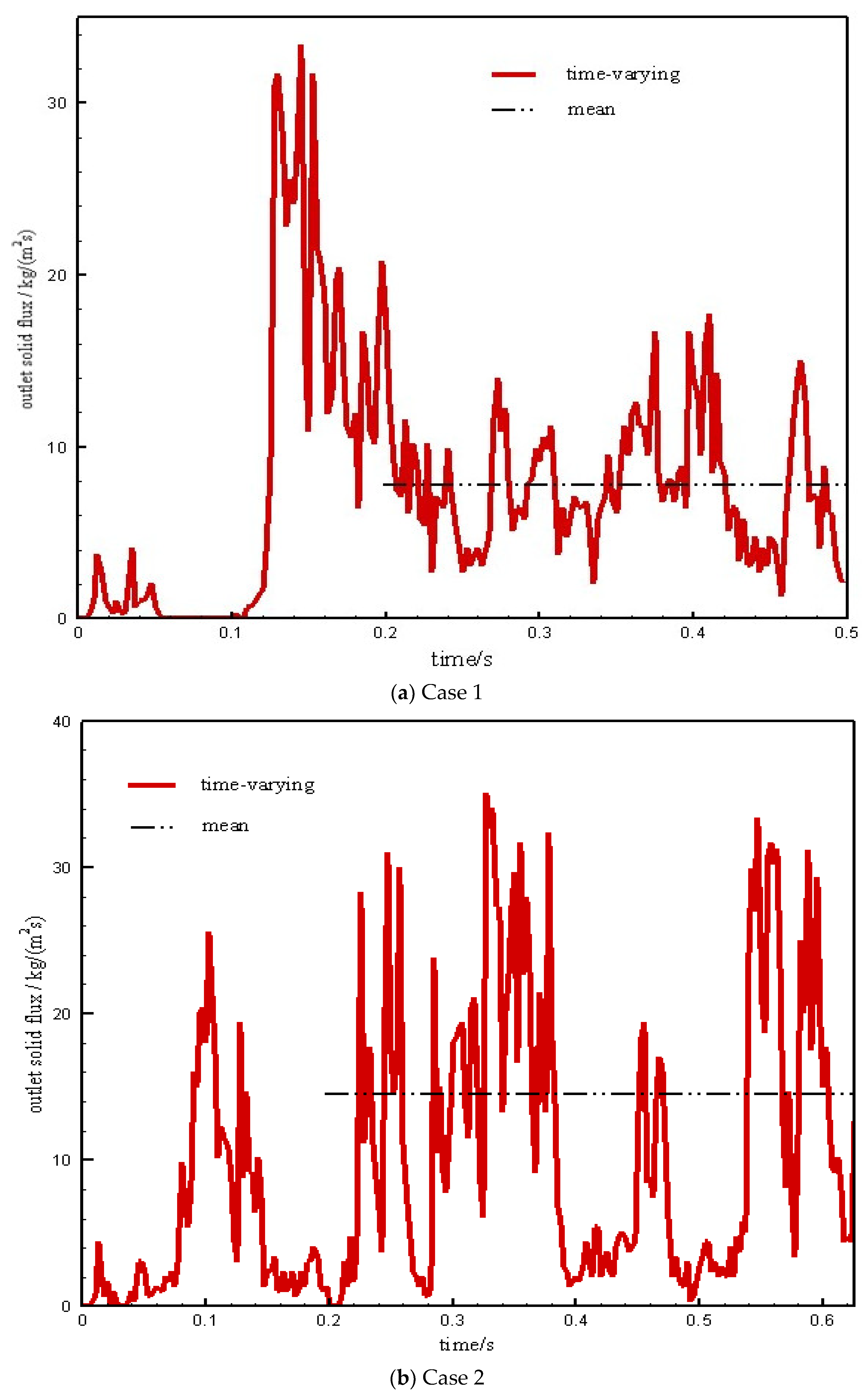
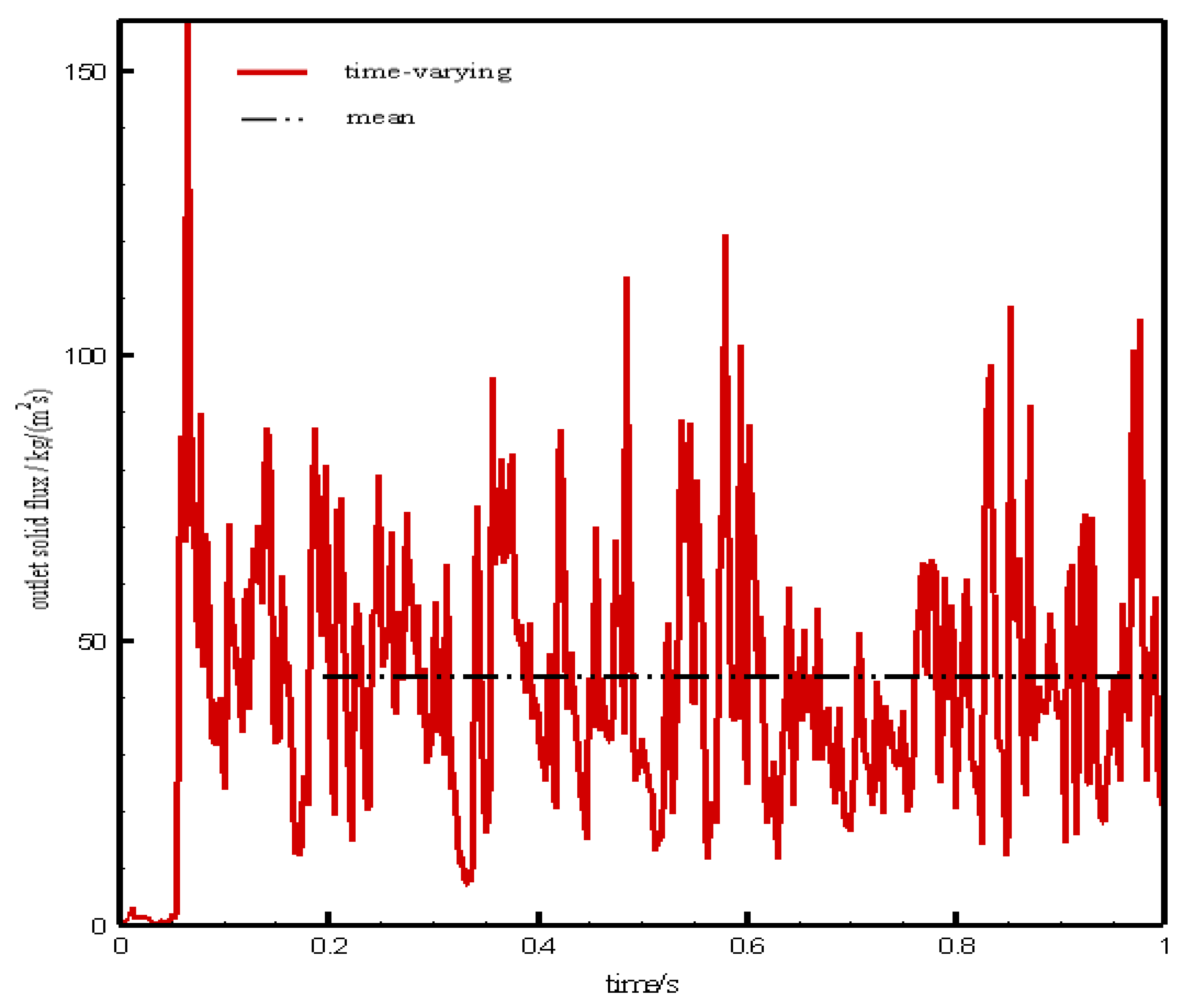
4.3. Outlet Solid Flux
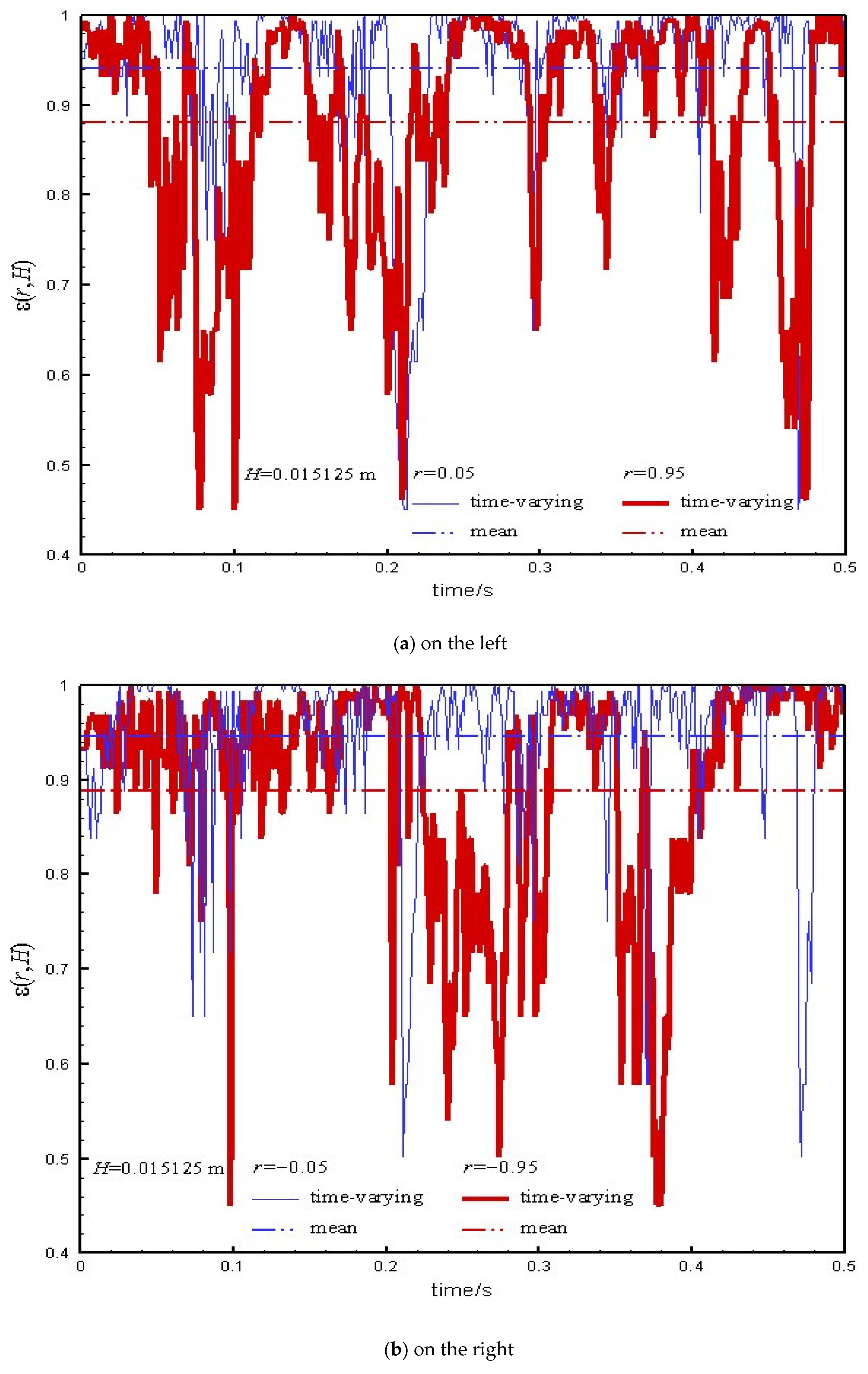
4.4. Core-Annular Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | area, m2 |
| Ar | Archimedes number |
| C | drag coefficient |
| D | bed diameter, m |
| d | particle diameter or distance between particles, m |
| e | unit vector |
| F | force on particle, N |
| f | grid area fraction occupied by particle |
| Fr | Fred number |
| G | outlet solid flux, kg·m−2·s−1 |
| g | gravity acceleration, m·s−2 |
| h | smooth length, m |
| H | height in bed, m |
| Ha | Hamaker constant, N·m |
| H0 | truncation distance, m |
| I | inertia moment of particle as spherical, kg·m2 |
| i, j, k | particle or grid index |
| N | number of particles |
| p | pressure, Pa |
| R | particle radius, m |
| r | particle position vector |
| r | dimensionless bed radius, m |
| Sp | momentum exchange source term |
| T | torque, N·m |
| t | time, s |
| u0 | inlet gas velocity, m·s−1 |
| u | gas velocity, m·s−1 |
| ut | particle terminal speed |
| V | volume, m3 |
| v | particle velocity, m·s−1 |
| X, Y | particle centriod coordinate component, m |
| x, y | grid node coordinate component, m |
| porosity | |
| cross-sectional porosity | |
| solid volume fraction at bottom of bed | |
| stiffness coefficient, N·m−1 | |
| solid volume fraction multiplier | |
| viscosity, N·s·m−2 | |
| density, kg·m−3 | |
| viscocous stress tensor, Pa | |
| particle angular velocity, s−1 | |
| restitution coefficient | |
| subscript | |
| 2D | two dimension |
| 3D | three dimension |
| c | contact |
| d | drag |
| g | gas |
| i, j, k | particle or grid index |
| mf | minimal fluidized state |
| p | particle |
| s | solid |
| t | total |
| v | van der Waals |
| w | bed wall |
References
- Li, J.; Ouyang, J.; Gao, S.; Ge, W.; Yang, N.; Song, W. Multi-Scale Simulation of Particle-Fluid Complex Systems; Sience Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Wang, Z.W.; Yu, Z.Q. Fluidization Engineering Principles; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, C.T. Multiphase Flow Handbook; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Yue, J.; Geng, S.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; Bello Suleiman, S.; Cui, Y.; Bai, D.; Xu, G. State-of-the-art hydrodynamics of gas-solid micro fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 232, 116345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanake, T. Discrete particle simulation of two-dimensional fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 1993, 77, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoomans, B.P.B.; Kuipers, J.A.M.; Briels, W.J.; Van Swaaij, W.P.M. Discrete particle simulation of bubble and slug formation in a two-dimensional gas-fluidised bed: A hard-sphere approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B. Numerical simulation of the gas-solid flow in a fluidized bed by combing discrete particle method with computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 2785–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, J.H. Particle-motion-resolved discrete model for simulating gas-solid fluidization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.B.; Xu, B.H. Particle-scale modelling of gas–solid flow in fluidisation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; van der Hoef, M.; Kuipers, J. A numerical study of fluidization behavior of Geldart A particles using a discrete particle model. Powder Technol. 2004, 139, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potic, B.; Kersten, S.R.A.; Ye, M.; van der Hoef, M.A.; Kuipers, J.A.M.; van Swaaij, W.P.M. Fluidization with hot compressed water in micro-reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 54, 5982–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Bordbar, A.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Xu, S. A CFD-DEM study of the solid-like and fluid-like states in the homogeneous fluidization regime of Geldart A particles. AIChE J. 2022, 68, e17420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Direct comparison of CFD-DEM simulation and experimental measurement of Geldart A particles in a micro-fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 64, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.L.; Zhao, Y.Z. Discrete element method and its applications in fluidizatio. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 2520–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.F.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yu, A.B. Micromechanical modeling and analysis of different flow regimes in gas fluidization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Van der Hoef, M.A.; Kuipers, J.A.M. CFD study of the minimum bubbling velocity of Geldart A particles in gas-fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 3772–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Van der Hoef, M.A.; Kuipers, J.A.M. Why the two-fluid model fails to predict the bed expansion characteristics of Geldart A particles in gas-fluidized beds: A tentative answer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Rabha, S.; Verma, V.; Dietiker, J.F.; Xu, Y.; Lu, L.; Rogers, W.; Gopalan, B.; Breault, G.; Tucker, J.; et al. Experimental study and discrete element method simulation of Geldart Group A particles in a small-scale fluidized bed. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.R.; Ouyang, J. Fine grid DEM simulation of bed layer height in bubbling fluidized-bed. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.Y.; Yu, Y.H. Mechanics of fluidization. Chem. Eng. Progr. Symp. Ser. 1966, 62, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, V.L.; Naumann, A. Uber die grundlegenden berechnungen bei der schwerkraftaufbereitung. Z. Ver. Dtsch. Ing. 1993, 77, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Ge, W.; Li, J.H. A discrete particle model for particle–fluid flow with considerations of sub-grid structures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.R.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Q. Revised drag calculation method for coarse grid Lagrangian-Eulerian simulation of gas-solid bubbling fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, T.V. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers, J.A.M.; van Uuin, K.J.; van Beckum, F.P.H.; van Swaaij, W.P.M. A numerical model of gas-fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.M.; Guo, Y.C.; Chan, C.K. Cluster-based drag coefficient model for simulating gas-solid flow in a fast-fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, R.; Lan, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. CPFD simulation of solids residence time and back-mixing in CFB risers. Powder Technol. 2015, 271, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.R.; Zuo, Z.F.; Li, Y.G.; Israr, M. Improvement of relative DEM time step range in fast fluidization simulation of Type-A FCC particles. Processes 2023, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kwauk, M. Particle-Fluid Two-Phase Flow: The Energy-Minimization Multi-Scale Method; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Wang, W.; Ge, W.; Li, J.H. CFD simulation of concurrent-up gas-fluid flow in circulating fluidized beds with structure-dependent drag coefficient. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 96, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Bobek, M.; Breault, R.; Mei, J.; Shadle, L. Investigation of core-annular flow in an industrial scale circulating fluidized bed riser with electrical capacitance volume tomography (ECVT). Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensler, T.; Firsching, M.; Bonilla, J.S.G.; Wörlein, T.; Uhlmann, N.; Wirth, K.E. Non-invasive investigation of the cross-sectional solids distribution in CFB risers by X-ray computed tomography. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
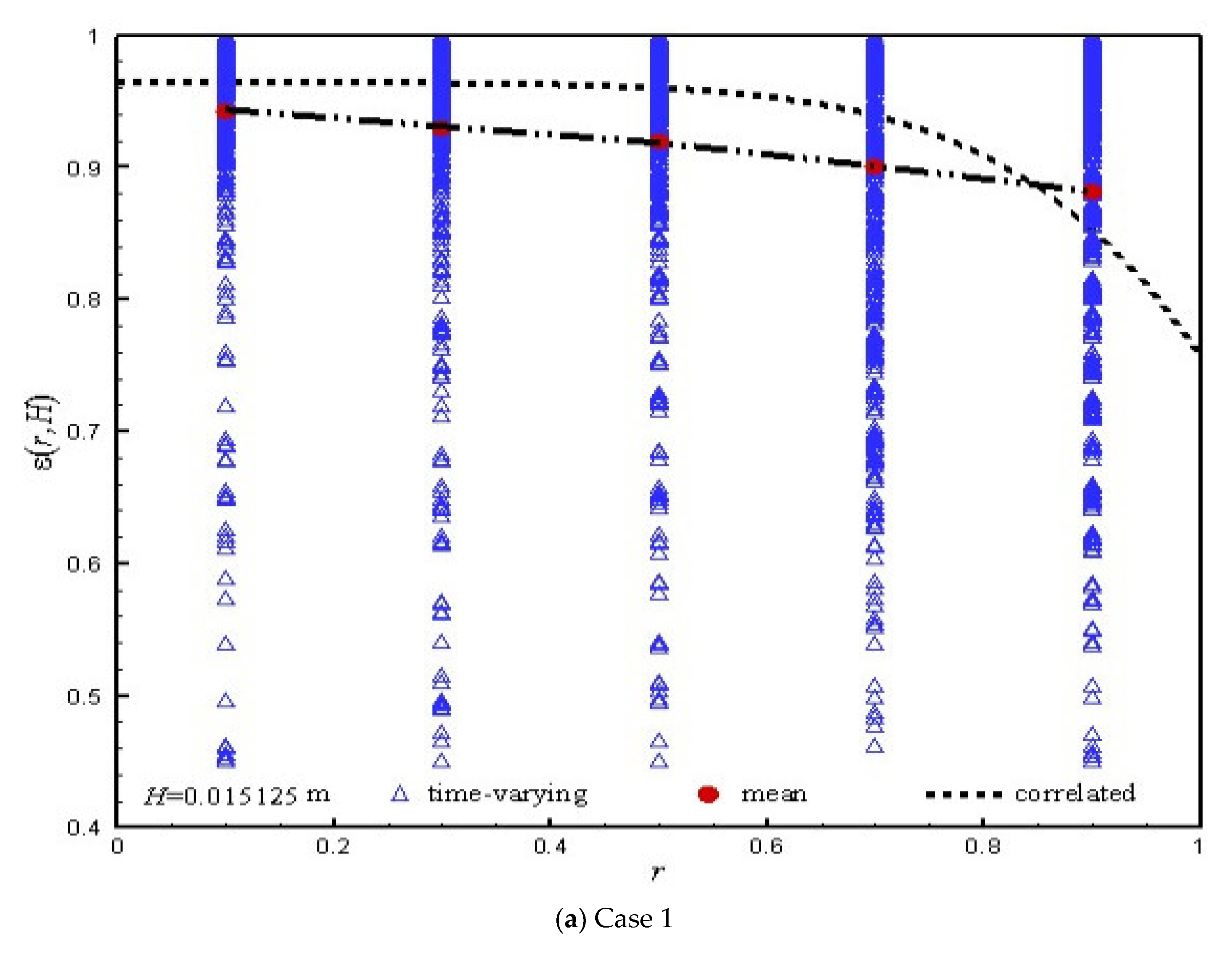
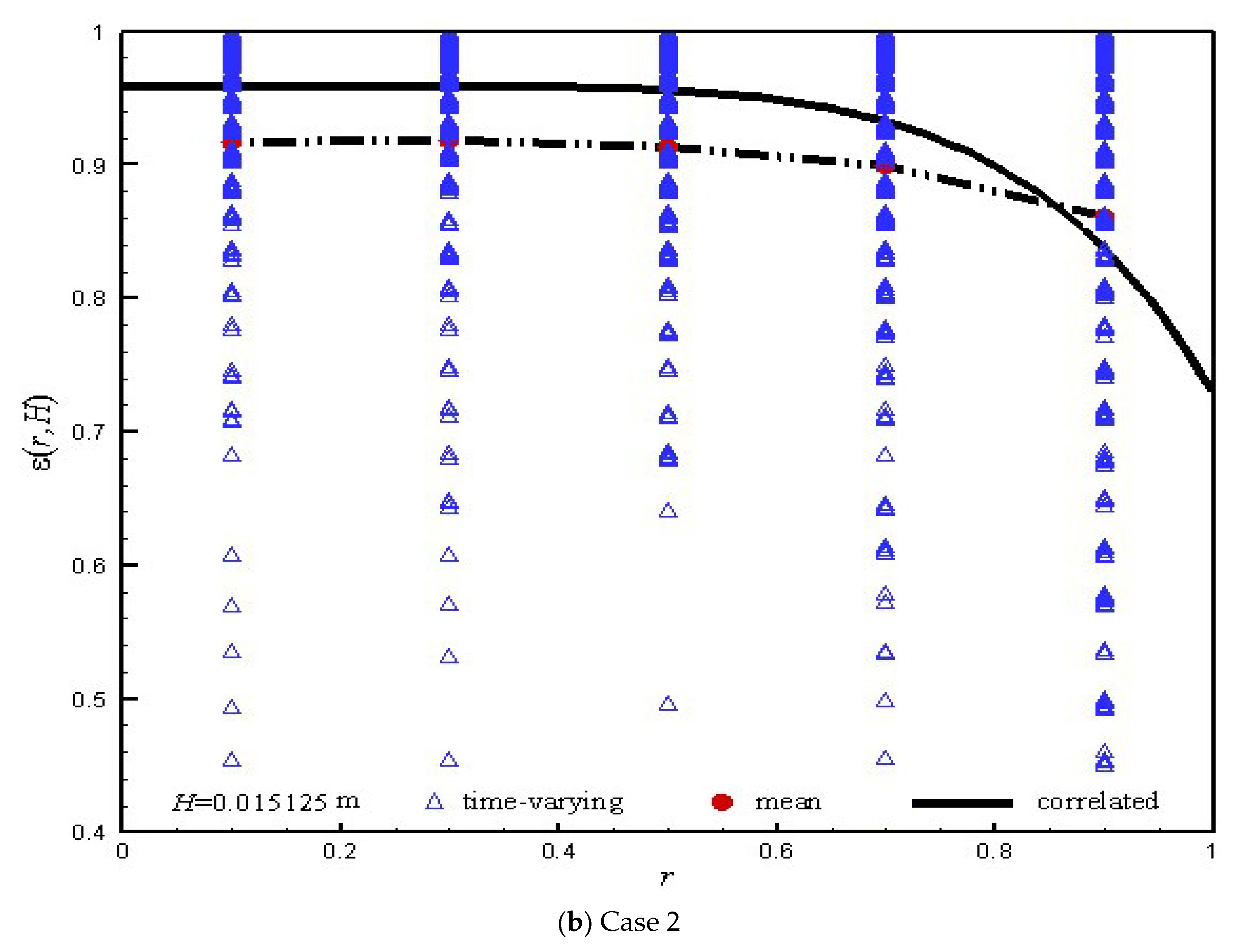
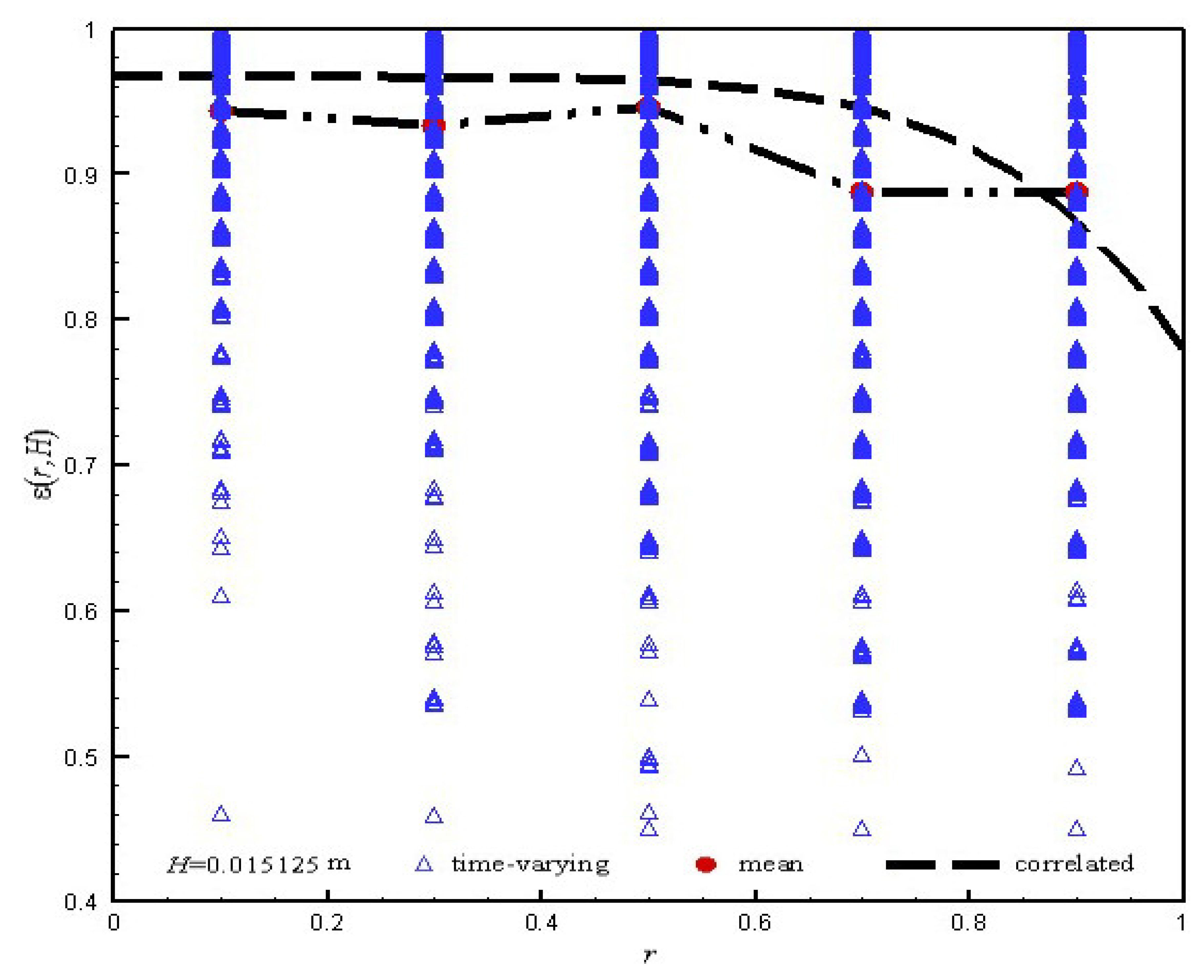
| Particle | Gas |
|---|---|
| Density ρp = 930 kg·m−3 | Viscosity μg = 1.7 × 10−5 N·s·m−2 |
| Particle diameter dp = 54 μm | Density ρg = 1.28 kg·m−3 |
| Minimum porosity εmf = 0.45 | CFD time step Δtg = 2 × 10−6 s |
| Stiffness Coef. κ = 10 N·m−1 | |
| Restitution Coef. ξ = 0.9 | |
| Friction Coef. f = 0.3 | |
| Smooth length = 2.5 dp | |
| Cutoff distance = 0.4 nm | |
| DEM time step Δtp = 2.5 × 10−7 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Li, Y. CFD-DEM Simulation of Slugging and Non-Slugging Fast Fluidization of Fine Particles in a Micro Riser. Processes 2023, 11, 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11102977
Wu G, Li Y. CFD-DEM Simulation of Slugging and Non-Slugging Fast Fluidization of Fine Particles in a Micro Riser. Processes. 2023; 11(10):2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11102977
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guorong, and Yanggui Li. 2023. "CFD-DEM Simulation of Slugging and Non-Slugging Fast Fluidization of Fine Particles in a Micro Riser" Processes 11, no. 10: 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11102977
APA StyleWu, G., & Li, Y. (2023). CFD-DEM Simulation of Slugging and Non-Slugging Fast Fluidization of Fine Particles in a Micro Riser. Processes, 11(10), 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11102977










