Abstract
The magnesium nanosized ferrite powder with formula MgFe2O4 was synthesized via a pyrochemical sol–gel glycine–nitrate method and annealed consistently at temperatures of up to 1300 °C. The MgFe2O4 ferrite samples’ microstructure was studied by SEM and XRD methods. According to the results of the studies, the increase in MgFe2O4 nanoparticles size from about 15 nm to micron-sized particles was observed when increasing annealing temperatures. The DC electrical conductivity of MgFe2O4 also clearly shows the change in conduction behavior of samples with increased calcination temperatures. The electromagnetic microwave properties of micron-sized particles of MgFe2O4 ferrite powder for a 1200 °C annealing temperature were studied for composites in paraffin matrix with produced magnetic filler mass concentration at 40% and 50%. The filament composites of polymer polylactic acid with MgFe2O4 ferrite powder samples were prepared by the FDM 3D-printing process and their microwave-absorbing properties were investigated. The application of developed PLA–MgFe2O4 ferrite filament for fabricating magnetic microwave-absorbing components also was demonstrated.
1. Introduction
Magnesium spinel ferrite MgFe2O4 is a unique ferrite species with low toxicity and tunable moderate magnetic properties [1,2,3] performing the random distribution of cations over the available tetrahedral (A) and octahedral [B] sites in the general structure of spinel MeFe2O4 (Me = two-charged metal ions) ferrites. The degree of inversion in MgFe2O4 samples and their magnetic properties depends on synthesis methods [4] and sintering temperature [5]. The electromagnetic properties of MgFe2O4 ferrite samples prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method are different from each other because of their particle size and porosity [2,3,6,7,8,9,10]. The MgFe2O4 used for constructed miniaturization of microstrip patch antennas used magnetodielectric substrate reduces the size and weight and gives an upgraded S11 parameter, bandwidth and directivity as contrasted with planar substrate antennas [11].
Additive manufacturing in fused deposition modelling (FDM) mode, which is a widely used 3D printing low-budget method, is a versatile fabrication method for fast prototyping with the primary goal to decrease the design cycle in a typical R&D process. However, the FDM typically employs only common thermoplastic materials with low glass transition temperature Tg or high dielectric loss at high frequencies, hence limiting their applications to low-power or low-performance microwave devices. Three-D FDM printing is an interesting direction for fabrication of RF and microwave components by utilizing the advantages of the design flexibility, compactness, and fast manufacturing of the next generation of high-performance 3D-printed RF/microwave devices and antennas operating at RF-wave frequencies [12]. The proposed range of functional microwave devices that might be realized by 3D printing is limited by the current range of developed FDM filament materials. The development of a magnetic composite based on polymer-ferrite composite fiber filaments that are compatible with FDM is a prospective direction. An FDM 3D-printing process with PLA-nanosized Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (35% (wt.)) ferrite-based composite filament for fabricating magnetic and microwave absorption components was demonstrated recently by us [13]. Further, the investigation of 3D-printed NiZn ferrite-ABS composite [14], Li0.44Zn0.2Fe2.36O4/polylactic acid composites [15], Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4/polylactic acid [16], and Fe-Ni alloy/polylactic acid composites [17] was published.
To understand the effect of MgFe2O4 particle size on their microwave electromagnetic properties of a comparative study of the annealing effect on microstructure and microwave absorption properties of MgFe2O4 powders, a prepared sol–gel glycine–nitrate auto combustion method was performed. The glycine–nitrate sol–gel method, followed by calcination of the MgFe2O4 samples at different temperatures, was proposed as a suitable simple method for the synthesis of spinel nanoferrite powders.
The aim of this work is to evaluate the application of MgFe2O4 powders produced by glycine–nitrate sol–gel method as magneto-dielectric filler to developed polylactic acid (PLA)-based composites for filament production for FDM 3D-printing. Polylmerized lactic acid or polylactide polymer, which is a readily available engineering modeling plastic, was chosen as the suitable matrix polymer in our investigation due to its well-known ease of printing, low cost, nontoxicity, appropriate biodegradable properties and wide commercial availability. Magnesium ferrite MgFe2O4 was chosen as magnetic microwave absorption filler due to its well-known ease of production with low cost, nontoxicity, close to ideal ecological properties and good microwave-absorbing properties.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, polycrystalline nano- and microsized MgFe2O4 powder samples were prepared in laboratory conditions using a sol–gel glycine–nitrate autocombustion technique. The materials used as precursors were magnesium nitrate hexahydrate Mg(NO3)2×6H2O, iron nitrate nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3×9H2O and glycine (all these were purchased from Vecton Ltd., Russian Federation). All of them were of high purity: Mg(NO3)2×6H2O as «pure for analysis» 99%, Fe(NO3)3×9H2O and glycine as «chemically pure grade» with 99.5% and 99.9% purity, respectively. It was known that glycine possesses a high heat of combustion in an oxidized environment [4,18] and its metal-complexing composition provides a suitable sol–gel formation substance for pyrochemical reactions during the course of combustion. Initially the solid magnesium nitrate hexahydrate, iron nitrate nonahydrate and glycine are taken in raw materials in the proposed molar proportion 1:2:6, respectively. The reagent and methods flow chart to synthesize MgFe2O4 nanosized powder is presented in Figure 1.
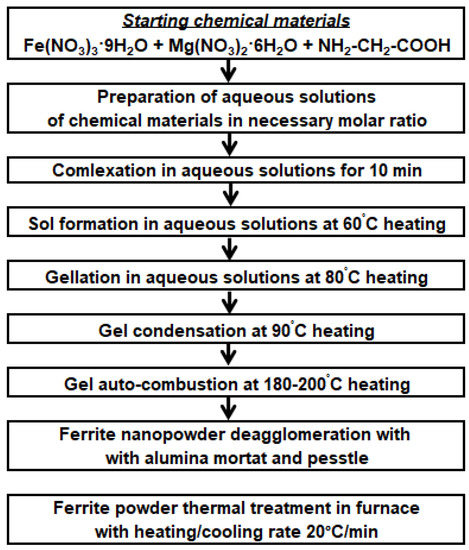
Figure 1.
Flow chart to synthesize MgFe2O4 nanopowder.
Starting chemical materials (both nitrate crystallohydrates as oxidizers and glycine as complexing gelating agent and organic fuel) were carefully dissolved in a beaker with bidistillated water with slow stirring by using a glass rod, and a clear orange solution was obtained. Then they formed a solution that was evaporated on a hot plate in the temperature range of 60 °C to 90 °C, resulting in a thick gel. The gel was kept on a ceramic hot plate for auto combustion and heated in the temperature range of 180 °C to 200 °C so that the resulting gel was self-igniting. The ultradisperse nanocrystalline yellowish-brown MgFe2O4 powder was formed within a few minutes and after reaction completed and subsequently cooled; the ferrite sample powder was crushed in a ceramic mortar for 5 min. Then, to remove residual impurities, possibly incompletely unreacted starting materials, and increase phase purity and crystallinity, the resulting synthesized powder was then calcined at about 500 °C to 1300 °C with temperature step 100 °C for about 1 h at a heating rate of 20 °C/min in a “Nabertherm Top 16/R + B400” common furnace in an oxygen-containing air medium to produce from light reddish-yellow hue to brown color shining powder of well-crystallized MgFe2O4. After the cooling, the calcined magnesium ferrite powder was additionally crushed in a ceramic alumina mortar for 10 min until a homogeneous micro-powder was obtained.
Phase evolution of produced MgFe2O4 powder samples was analyzed by a Shimadzu XRD-7000 X-ray diffractometer (Japan) using monochromatic Cu-Ka radiation (λ = 0.154056 nm) at room temperature in Bragg–Brentano geometry in the range of angles 2θ from 20° to 70° with a scanning step—0.05° and a spectrum acquisition time of 1 sec per point to obtain diffractograms. The average nanocrystallite size in the samples was also calculated from the width of all observed XRD peaks using Scherrer’s equation:
where Dhkl is the average crystallite size, the coefficient k is 0.9 (for a cubic structure of spinel ferrite), λ is the X-ray wavelength used, βhkl is the intrinsic full width at half maximum of the diffraction line profile, and θ is the position of the principal diffraction peak. The identification of diffraction reflections and the search for crystalline phases in the samples were carried out using the computer program Profex 4.0.0 (Nicola Döbelin, Solothurn, Switzerland) and XPowderX software (ver 2018) (J. Daniel Martín-Islán, Granada, Spain). The density of produced MgFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles was determined by the X-ray diffraction method by analyzing the obtained data structural parameters, including the crystal lattice volume.
Dhkl = kλ/βhklcosθ
The morphological features and microstructure of the nanoparticles in produced MgFe2O4 powder samples depending on the annealing temperature conditions were observed by scanning electron microscope with a Jeol JSM-7500F (Jeol, Tokyo, Japan). The elemental composition of MgFe2O4 was investigated using the energy-dispersive analysis method using the INCA X-Sight energy dispersive microanalysis system (Oxford Instruments, Abington, UK) on a scanning electron microscope. Determination of the elemental ratio of MgFe2O4 samples was performed by collecting statistical data with subsequent averaging and determining the error of measurements.
The DC conductivity of produced MgFe2O4 powder samples was measured by a two-probe method in plastic tubes with a length of 5.0 mm and an internal diameter of 2.0 mm for a stuffed sample at ~1 ton/cm2 using a digital resistance meter UT-601 (UNI-T, Dongguan, China) with averaging over 5 measurements.
The electromagnetic characteristics of produced MgFe2O4 powder samples were investigated by vector network analysis using the Deepace KC901V device (Deepace technology, Dongguan, PRC) in a 10 cm HP-11566A coaxial transmission airline probe (HP, Palo Alto, USA) by the standard method in the form of a composite with concentration 40% and 50% (weight) in paraffin in the form of a pressed toroid with dimensions 3.05 × 7 mm and 5 mm thickness. The choice of the concentration of the investigated MgFe2O4-paraffin samples and paraffin as a matrix is due to the convenience of comparison with the known data on the previously investigated different types of microwave-absorbing fillers. Calculation of the electromagnetic characteristics (complex permeability μ = μ′ + iμ″ and permittivity ε = ε′ + iε″) of the samples from the measured scattering parameters S11 and S21 were carried out by the Nicolson–Ross–Weir method [19].
The MgFe2O4 with polylactic acid (FDplast Company, Moscow, Russian Federation) composite filament was prepared by ball milling mixing in an alumina jar and balls and subsequent melt extrusion (Wellzoom Desktop Extruder Line II, Shanghai, China) with control of the nozzle temperature in the range 200–210 °C. Approximately, the self-made 2–3 m of MgFe2O4-PLA composite filament of 1.75 mm diameter with standard deviation of 0.02–0.03 mm was made with different samples of calcined MgFe2O4 powders. The MgFe2O4–PLA composites were prepared by fused deposition modeling by the FlashForge Creator Pro 3D printer (Zhejiang Flashforge 3D Technology Co., Jinhua, China) using concentric rings print style with 100% filling factor with the corresponding settings: 200 °C titanium alloy nozzle temperature and 80 °C printed bed temperature.
The DSC analysis of prepared MgFe2O4-PLA samples allowed investigating the transition temperatures for melting and crystallization, as well as glass-transition temperatures. The heat-flux DSC 204 F1 Phoenix (NETZSCH-Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany) setups were used. Microwave absorption performances of the 3D-printed MgFe2O4–PLA sample were evaluated based on the measured reflection loss (RL) values data for a 3.05 × 7 mm composite toroid with thickness of 10 mm in an HP-11566A coaxial transmission airline probe.
3. Results
3.1. Electron Microscopy
In order to study the effect of calcination temperature on the morphology of MgFe2O4 particles in their powder samples, the scanning electron microscopy investigation was carried out. The morphologies of MgFe2O4 specimens calcined at temperatures from 500 °C to 1300 °C are shown in Figure 2.
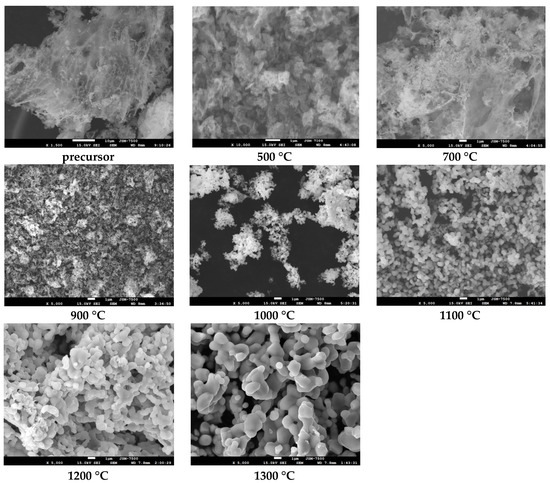
Figure 2.
SEM images of the MgFe2O4 powders calcined at the various temperatures.
3.2. XRD Analysis
The XRD patterns of the calcined MgFe2O4 samples (Figure 3) show that as the calcination temperature increases, the associated diffraction peaks become sharper and more intense, indicating an improvement in crystalline quality of produced ferrite with calcination temperature increase.
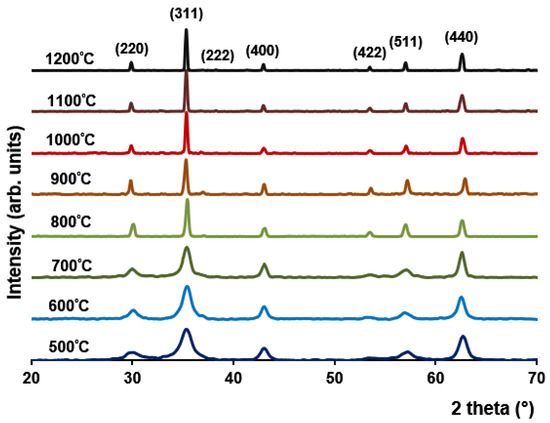
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction results for the MgFe2O4 samples following calcination at the various temperatures.
3.3. DC Electrical Conductivity
Figure 4 shows a graph of the dependence of the annealing temperature on electrical conductivity of MgFe2O4 powders for direct current condition.
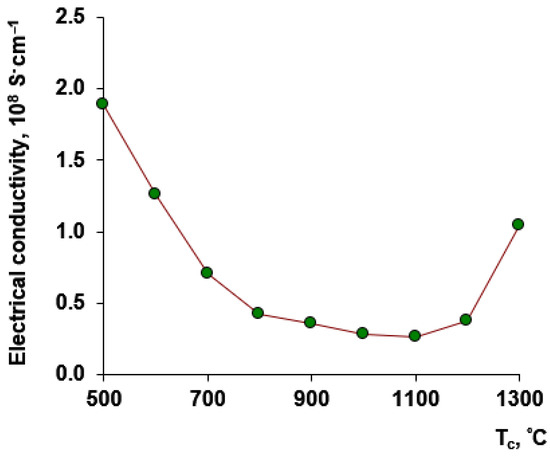
Figure 4.
DC electrical conductivity of MgFe2O4 powders for samples calcined at different temperatures.
3.4. EDX Analysis
Figure 5 shows the results of energy-dispersive X-ray elemental microanalysis of MgFe2O4 powder calcined at 1200 °C.
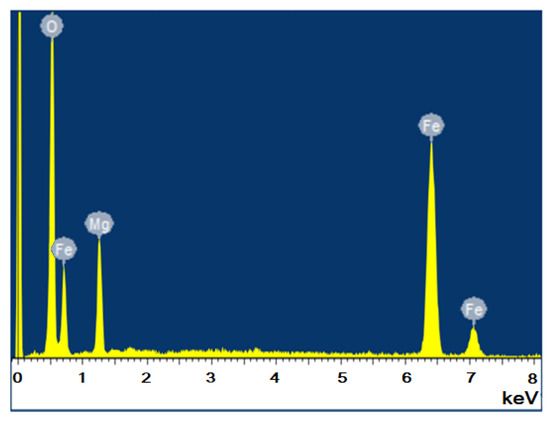
Figure 5.
EDX spectrum of MgFe2O4 sample calcined at 1200 °C.
3.5. VNA Measurement MgFe2O4–Paraffin Composites
The electromagnetic characteristics of the manufactured MgFe2O4–paraffin composites with a mass concentration of magnesium ferrite particles of 40% and 50% were investigated by the VNA method. The EM frequency dependence of calculated complex permeability and permittivity with corresponding loss tangents for MgFe2O4–parrafin composite and parrafin and PLA polymer matrix are in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
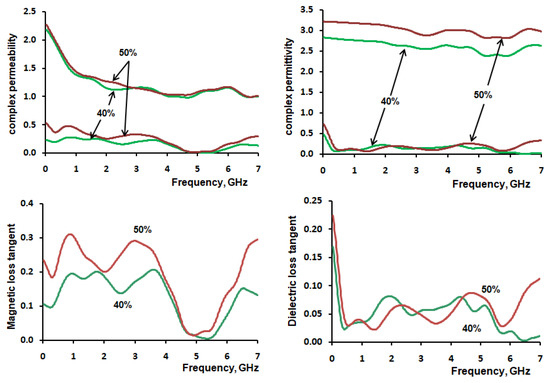
Figure 6.
The complex permeability, complex permittivity, magnetic loss and dielectric loss tangent of MgFe2O4–paraffin composite.
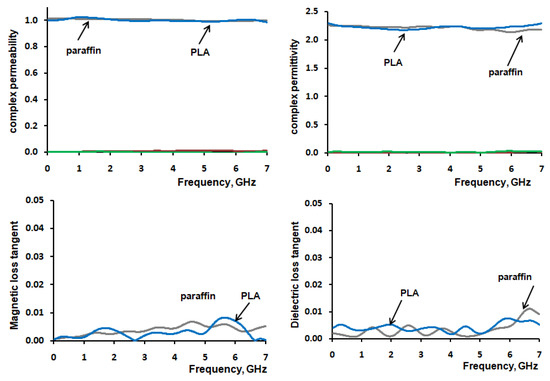
Figure 7.
The complex permeability, complex permittivity, magnetic loss and dielectric loss tangent of paraffin and PLA polymer.
3.6. 3D FDM Printing MgFe2O4–PLA
Two samples of composite materials were made based on the obtained MgFe2O4 micro-powder at an annealing temperature of 1200 °C and PLA polylactide with a concentration of magnetic filler particles of 40% and 50%, respectively. The choice of MgFe2O4 powder at an annealing temperature of 1200 °C as a filler is due to the suitable shape and size of its microparticles, without a large number of agglomerates that can significantly complicate the 3D printing process due to the strong friction and wear in the heated extrusion nozzle. The DSC data for investigated MgFe2O4–PLA composites are shown in Figure 8 and Table 1.
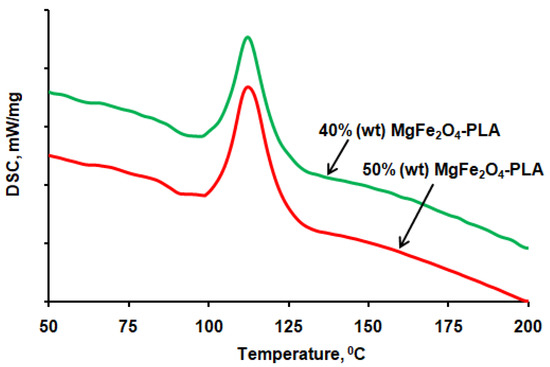
Figure 8.
DSC thermograms of MgFe2O4–PLA composites.

Table 1.
DSC data of MgFe2O4-PLA composites.
According the data from Table 1, low printing temperature and practically observed good observed layer adhesion make the developed MgFe2O4–PLA composites suitable good material for 3D FDM printing.
It was obvious that the ferrite fraction in plastic composites for 3D printing is desired to be as high as possible to provide the highest magnetic permeability across a printed component. However, the MgFe2O4 fraction in PLA plastic must be low enough so as to enable the material to exit the heated extrusion nozzle of common 3D printers. We carried out optimization between composite filament extrusion production, printing parameters, and reliable operation in the FDM 3D-printing process of MgFe2O4–PLA composite filament. The suitable maximum fraction is 40% weight MgFe2O4 ferrite. The COMPO micro-image of the PLA–40% weight MgFe2O4 composite microstructure in Figure 9 reflects the relative homogeneous distribution of MgFe2O4 microparticles in PLA polymer matrix.
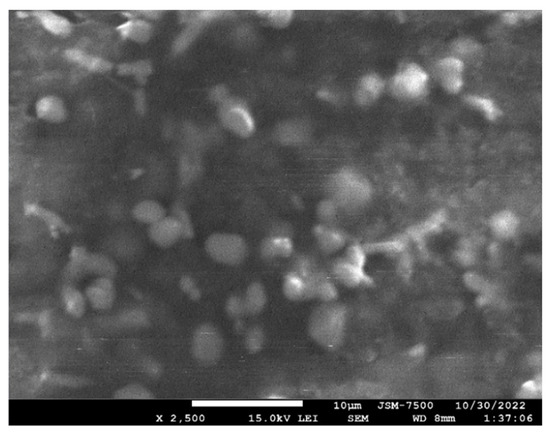
Figure 9.
COMPO image of the PLA–40% weight MgFe2O4 composite.
We make note that at higher ferrite micropowder fractions, the filament tends towards brittle behavior in feeding and becomes difficult to print [13]. The printability of the composite filament was assessed by printing simple blocks using the FDM process. The composite filament is driven by a stepper motor into a temperature-controlled nozzle, and molten material is extruded and deposited onto the build platform in a layer according to the pre-programmed pattern.
3.7. VNA Measurement MgFe2O4–PLA Composites
The measured reflection losses for a 3D-printed sample of the composition of 40% (wt.) MgFe2O4–PLA and pure PLA polymer at a thickness of 10 mm are shown in Figure 10.
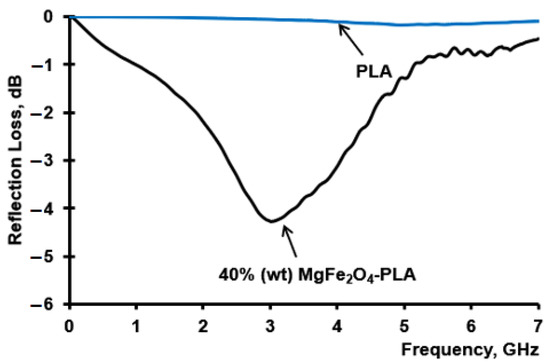
Figure 10.
The measured reflection loss of 40% (wt.) MgFe2O4–PLA and pure PLA polymer FDM 3D-printed samples.
4. Discussion
SEM images show that the non-calcined samples (precursor) of MgFe2O4 consist of very small particles with average grain size of 15 ± 5 nm. It should be noted that the main morphological changes in studied MgFe2O4 samples were observed at temperatures above 700 °C, with a change in the shape of particles from an amorphous loose network to close-to-spherical nanoparticles. In the course of our research, it was found that highly ordered MgFe2O4 nanoparticles with an average size of 50–60 nm are formed at 700–800 °C. As can be seen from the presented data, a change in the treatment temperature leads to a change in the morphological features of nanoparticles related primarily to their enlargement and formation of large agglomerates at high temperatures (above 900 °C) resulting from the sintering of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles. The MgFe2O4 specimen sintered at 1100 °C (Figure 2) exhibits small equiaxed particles with average size of about 400 ±100 nm, although larger agglomerates are also seen. Meanwhile, pronounced grain growth of MgFe2O4 particles is seen at the sintering temperatures of 1200 °C and 1300 °C (Figure 2). The MgFe2O4 specimen sintered at 1300 °C is composed of uniform coarse structure with a well-clear crystalline microstructure having very small numbers of small particles. The average grain size for the MgFe2O4 powder specimen calcined at 1200 °C was about 1.1 ± 0.5 μm. An average grain size at 1300 °C of 2.1 ± 0.7 μm was obtained for the MgFe2O4 sample calcined at 1300 °C. An increase in grain size, followed by the formation of agglomerates, leads to a decrease in the specific surface area of MgFe2O4 powders, which may positively affect the mixing characteristics of ferrite powders with polymer matrix.
All the observed diffraction peaks for the MgFe2O4 samples (Figure 3) were compared with standard diffraction lines of magnesium spinel ferrite, JCPDS Card No. 88-1943. The most prominent diffraction peak is centered at 2θ = 35.3–35.4° and corresponds to crystal plane (311), which is a characteristic peak of MgFe2O4 spinel structure. The other peaks are also assigned to spinel cubic structure (Figure 3) with Miller indices of (111), (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511) and (440). It is established that all the produced MgFe2O4 samples correspond to cubic phase with symmetry group Fd3 ̅m. The lattice parameter (a) of the MgFe2O4 sample sintered at 1000 °C was found to be 8.4004 Å with corresponding X-ray density about 4.52 g/cm3, consistent with the literature. The a value for stoichiometric MgFe2O4 usually ranges between 8.38–8.40 Å [20,21] and is consistent with our value.
The XRD graphs for investigated MgFe2O4 samples reveal decrease in full width half maxima (FWHM) with the increase in sintering temperature. The MgFe2O4 grain size for powder samples calcined at a temperature range from 500 to 1000 °C was obtained from Scherrer’s formula using FWHM and peak position of the sample after correcting for instrumental broadening and is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The grain size from XRD for MgFe2O4 samples calcined at different temperatures.
The grain size was estimated to be around 10.2 nm for the ultra-disperse MgFe2O4 sample calcined at 500 °C. With the increase in sintering temperature, the grain size of MgFe2O4 increases dramatically and reached the value of around 74.1 nm for crystallites in the MgFe2O4 sample calcined at 1200 °C. For the further increase in sintering temperature to 1300 °C, it was not possible to adequately measure grain size in the prepared MgFe2O4 sample with X-ray diffraction due to instrumental broadening.
It is widely known that since Mg2+ ions are non-magnetic, the magnetic moment of MgFe2O4 is derived from the particular type of cation distribution. It is a known fact that there is a remarkable effect of initial particle size on bulk magnetic properties of sintered product. According to published data, MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite is partly inverse and partly normal and is, therefore, one of the most interesting ferrite spinels [3,4]. At room temperature, MgFe2O4 has an inverse spinel structure in which the divalent and half of the trivalent ions are arranged in the octahedral positions and the remaining trivalent ions fill the tetrahedral positions with the degree of inversion of the structure about 0.90 [21]. This means that its structure is very close to the perfectly inverse one. An increase in temperature above the annealing temperature of 600 °C leads to an increase in the intensity of these reflexes, which indicates an ordering of the crystal structure. At around the temperature of 700 K, the value of MgFe2O4 inversion degree begins to drop and at 1400 K reaches the value of 0.70 [3,4]. As indicated by literature data, the beginning of inversion in the structure of MgFe2O4 occurs within the 573–723 K temperature range [21,22,23].
The measured DC electrical conductivity of MgFe2O4 compacted powder samples obtained at different calcination temperatures (Figure 4) also clearly shows the change in electrical conduction behavior of samples with increased calcination temperatures. The minimum of DC electrical conductivity for MgFe2O4 powder samples was observed at a 1000–1100 °C calcination temperature range. Possibly this result reflected the grain growth and coalescence of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles. Our data are in accordance with observation that MgFe2O4 is a soft magnetic semiconductor and possesses high resistivity [24].
The MgFe2O4 powder sample calcined at 1200 °C was analyzed by X-ray elemental microanalysis. In the EDX spectra (Figure 5), no impurity elements are seen, except Mg, Fe and O. The calculated atomic ratio of Mg and Fe elements is approximately 1:2.
It was found that the attenuation of electromagnetic waves in nanosized MgFe2O4 based materials above 1000 MHz mainly comes from magnetic loss [25,26], and in the frequency range of 7–18 GHz the MgFe2O4 was the dielectric loss materials [27]. We found that in our case of used microsized MgFe2O4 powder, the composite MgFe2O4–paraffin materials can dissipate EM-waves from magnetic loss in the 0.5–4 GHz range (Figure 6).
The calculated dielectric constant and loss tangent of the used paraffin and PLA matrix presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Calculated dielectric constant and loss tangent of the paraffin and PLA.
According to collected data in Figure 7, the prepared by FDM 3D-printing process with 40% (wt.) MgFe2O4–PLA materials have moderate microwave absorption properties in the 4G cell phone communication range. The observed microwave absorption peak resonance is located at a frequency of about 3.0 GHz. Thus, we can suggest that FDM 3D-printed 40% (wt.) MgFe2O4–PLA composites are appropriate for application as magnetodielectric ferrite substrates for printed and microstrip antenna miniaturization with enhanced radiation performance attractive for practical applications such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Further, we can conclude that as a microwave-absorbing filler, produced MgFe2O4 powder is inferior to domestic magnetic microwave-absorbing materials previously studied by us such as magnetic microspheres [28], Fe-Si-Al alloy micropowders [29] or ferrite powders of spinel series [13,30,31,32,33] (Table 4). However, MgFe2O4 is a practical, easily produced, low-cost, ecological microwave-absorbing material.

Table 4.
Microwave absorption characteristics of magnetodielectric composites.
Thus, an additive manufacturing FDM 3D-printing process with self-developed MgFe2O4–PLA composite filament for fabricating magnetic microwave-absorbing components was also demonstrated. Therefore, the investigated 3D-printed MgFe2O4–PLA composite prepared based on FDM has moderate microwave-absorbing properties and good bearing capacity and it is a promising microwave-absorbing material for 3D printing by the FDM method.
5. Conclusions
Magnesium spinel-type ferrite MgFe2O4 magnetic powder material was successfully synthesized by the glycine–nitrate sol–gel auto-combustion method. Crystallinity and grain size of the MgFe2O4 powder samples products increase with the increase in sintering temperatures. A single cubic phase of MgFe2O4 was achieved after calcinations at 900 °C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction study confirmed the formation of a pure phase MgFe2O4 space group of Fd3 ̅m (cubic spinel) with a parameter of a = 8.4004 Å at 1000 °C. The DC electrical conductivity of MgFe2O4 also clearly shows the change in conduction behavior of samples with increase calcination temperatures and reflects high resistivity of MgFe2O4. The electromagnetic microwave properties of micron-sized particles of MgFe2O4 ferrite powder for 1200 °C annealing temperatures was studied for composites in paraffin with produced magnetic filler mass concentration from 40% and 50%. In this regard, we can conclude that MgFe2O4-based polymer composite materials can effectively dissipate EM-waves from magnetic loss in the 0.5–4 GHz range. The filament composites of polylactic acid with MgFe2O4 ferrite powder samples were prepared by the FDM 3D-printing process and their microwave-absorbing properties were investigated. The application of developed PLA–MgFe2O4 ferrite filament for fabricating magnetic microwave-absorbing components also was demonstrated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B. and S.I.; methodology, V.B. and A.G.; validation, V.B., S.I., I.P. and P.P.; formal analysis, V.B., S.I. and A.G.; investigation, V.B., I.S., S.I. and A.G.; resources, V.B., S.I., I.S., I.P. and P.P.; data curation, V.B., S.I., A.G. and I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, V.B. and S.I.; writing—review and editing, V.B., S.I., I.P. and P.P.; visualization, V.B., S.I. and I.P.; supervision, V.B. and I.P.; project administration, V.B.; funding acquisition, V.B. and S.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the state task of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (state task project FZEN-2020-0022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The research was partially carried out on the basis of the scientific and educational center “Center perspective technologies and nanomaterials” of the center for collective use “KubSTU” and scientific and educational center “Diagnostics of the structure and properties of nanomaterials” of the center for collective use “KubSU”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no identified financial interest or relationship that could be used for the work presented in this article.
References
- Aliyan, N.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Akbari, S. The effect of post-calcination on cation distributions and magnetic properties of the coprecipitated MgFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, D.K.; Majumder, S.; Banerjee, S. Large polaron tunneling, magnetic and impedance analysis of magnesium ferrite nanocrystallite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.; Araujo-Barbosa, S.; Souza, A.; Iglesias, C.; Xavier, J.; Souza, P.; Cid, C.P.; Azevedo, S.; da Silva, R.; Correa, M.; et al. Tuning structural, magnetic, electrical, and dielectric properties of MgFe2O4 synthesized by sol-gel followed by heat treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 2021, 154, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampiva, R.Y.S.; Kaufmann, C.G., Jr.; Alve, A.K.; Bergmann, C.P. Influence of the Fuel Composition and the Fuel/Oxidizer Ratio on the Combustion Solution Synthesis of MgFe2O4 Catalyst Nanoparticles. FME Trans. 2018, 46, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gerle, A.; Piotrowski, J.; Podworny, J. The Influence of Order in the Cation Sublattice of MgAl2O4, MgCr2O4 and MgFe2O4 Spinels on the Kinetics of Topochemical Reactions with Sulphur Oxides. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- De Hoyos-Sifuentes, D.H.; Reséndiz-Hernández, P.J.; Díaz-Guillén, J.A.; Ochoa-Palacios, R.M.; Altamirano-Guerrero, G. Synthesis and characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles and PEG-coated MgFe2O4 nanocomposite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3130–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, M. Comparative studies on impact of synthesis methods on structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 8, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.I.; Elkady, A.S.; Rashad, M.M.; Mostafa, A.G.; Megahid, R.M. Structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles prepared via EDTA-based sol–gel reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 379, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, S.K.; Naz, S.; Mehmood, M.; Nadeem, M.; Siddique, M. Structural, impedance and Mössbauer studies of magnesium ferrite synthesized via sol–gel auto-combustion process. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easwari, M.; Jesurani, S. Synthesis & Magnetic Properties of Magnesium Ferrite (MgFe2O4) Nanoparticles Via Sol Gel Method. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, V.; Seeni, S.M.; Maraikkayar, M.A.; Sivaranjani, S.; Kalpana, M.; Jeeva, R.K.; Pandian, S. Engineered meta magneto dielectric substrate for microstrip patch antenna miniaturization with reduced return loss. Int. J. Appl. Eng. 2015, 10, 30474–30479. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-K.; McGhee, J.; Tsipogiannis, C.; Zhang, S.; Cadman, D.; Goulas, A.; Whittaker, T.; Gheisari, R.; Engstrom, D.; Vardaxoglou, J.; et al. Evaluation of Microwave Characterization Methods for Additively Manufactured Materials. Designs 2019, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamray, I.I.; Buz’Ko, V.Y.; Goryachko, A.I. Changes in the Structure and Properties of Nickel-Zinc Spinel Nanoferrites Series for 3D-Printing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 969, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Castles, F.; Grant, P.S. 3D Printing of NiZn ferrite/ABS Magnetic Composites for Electromagnetic Devices. MRS Proc. 2015, 1788, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yao, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhou, J. Mechanical and microwave absorption properties of 3D-printed Li0.44Zn0.2Fe2.36O4/polylactic acid composites using fused deposition modeling. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 19296–19307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicong, Y.; Qi, G.; Enyi, H.; Chao, Y.; Bin, O.; Peng, Y.; Haihua, W. Mechanical and microwave absorbing properties of Mn-Zn ferrite/polylactic acid composites formed by fused deposition modeling. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2022, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Haihua, W.; Zhenglang, H.; Yutian, L.; Peng, Q.; Li, L.; Jianxin, Z. Electromagnetic absorption properties and mechanical properties of Fe-Ni alloy/polylactic acid composites fabricated by fused deposition modeling. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2022, 39, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Khot, V.M.; Salunkhe, A.B.; Phadatare, M.R.; Pawar, S.H. Formation, microstructure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline MgFe2O4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, E.J.; Frasch, J.L.; Ellison, S.M.; Chahal, P.; Ouedraogo, R.O. Analysis of the Nicolson-Ross-Weir Method for Characterizing the Electromagnetic Properties of Engineered Materials. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2016, 157, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antao, S.M.; Hassan, I.; Parise, J.B. Cation ordering in magnesioferrite, MgFe2O4, to 982 °C using in situ synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gateshki, M.; Petkov, V.; Pradhan, S.K.; Vogt, T. Structure of nanocrystalline MgFe2O4 from X-ray diffraction, Rietveld and atomic pair distribution function analysis. J. Appl. Cryst. 2005, 38, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O‘Neil, H.; Annersten, H.; Virgo, D. The temperature dependence of the cation distribution in magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) from powder XRD structural refinements and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1992, 77, 725–740. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.J.; Putnis, A. Determination of the mechanism of cation ordering in magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) from the time and temperature-dependence of magnetic susceptibility. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1999, 26, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Wang, J.W.; Li, F.; Mei, Z.; Lu, Z.X.; Ge, L.L.; You, C.Y. Enhanced microwave absorption of Fe flakes with magnesium ferrite cladding. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 4175–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, J. Synthesis for powder of nano-MgFe2O4/Fe2O3 by citrate sol-gel and absorbs characteristic of electromagnetic wave. J. Func. Mater. 2005, 36, 1839–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Fu, M. One-step in situ growth of magnesium ferrite nanorods on graphene and their microwave-absorbing properties. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.G. MgFe2O4 nanoparticles preparation and its electromagnetic properties. J. Func. Mater. 2013, 44, 776–779. [Google Scholar]
- Vyzulin, S.A.; Buz’ko, V.Y.; Kalikintseva, D.A.; Goryachko, A.I.; Sarin, L.I.; Kolantsov, O.A.; Syr’ev, N.E. Magnetic and dielectric properties of composites based on magnetic microspheres. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1389, 012161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryachko, A.I.; Ivanin, S.N.; Buz’ko, V.Y. Electromagnetic properties of composite materials based on Nd-compound modified Fe-Si-Al alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 969, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyzulin, S.A.; Miroshnichenko, E.L.; Kalikintseva, D.A.; Buz’ko, V.Y. Investigation of microwave absorption properties of nanosized nickel-zinc ferrites powders. In Proceedings of the 2017 Radiation and Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves (RSEMW), Divnomorskoe, Russia, 26–30 June 2017; pp. 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Vyzulin, S.A.; Kalikintseva, D.A.; Miroshnichenko, E.L.; Buz’Ko, V.Y.; Goryachko, A.I. Microwave Absorption Properties of Nickel–Zinc Ferrites Synthesized by Different Means. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2018, 82, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryachko, A.I.; Ivanin, S.N.; Buzko, V.Y. Synthesis, Microstructural and Electromagnetic Characteristics of Cobalt-Zinc Ferrite. Condens. Matter Interphas. 2020, 22, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buz’Ko, V.Y.; Shamrai, I.I.; Ryabova, M.Y.; Kireeva, G.V.; Goryachko, A.I. Properties of Nickel Zinc Ferrite Nanopowders Prepared by Different Methods. Inorg. Mater. 2021, 57, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).