Removal of Thallium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Gamma-Alumina Nanoparticles (γ-ANPs)
2.2.2. Determination of pHZPC of the Adsorbent (γANPs)
2.2.3. Determination of Thallium (I) Ions Concentration
2.3. Batch Adsorption Investigations of Thallium (I)
2.4. Temperature Effect
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized γANPs
3.2. Batch Investigations of Thallium Adsorption onto γANPs
3.2.1. Effect of Initial pH
3.2.2. Effect of the Agitation Time on Tl(I) Adsorption and Adsorption Kinetics
Effect of the Agitation Time on Tl(I) Adsorption
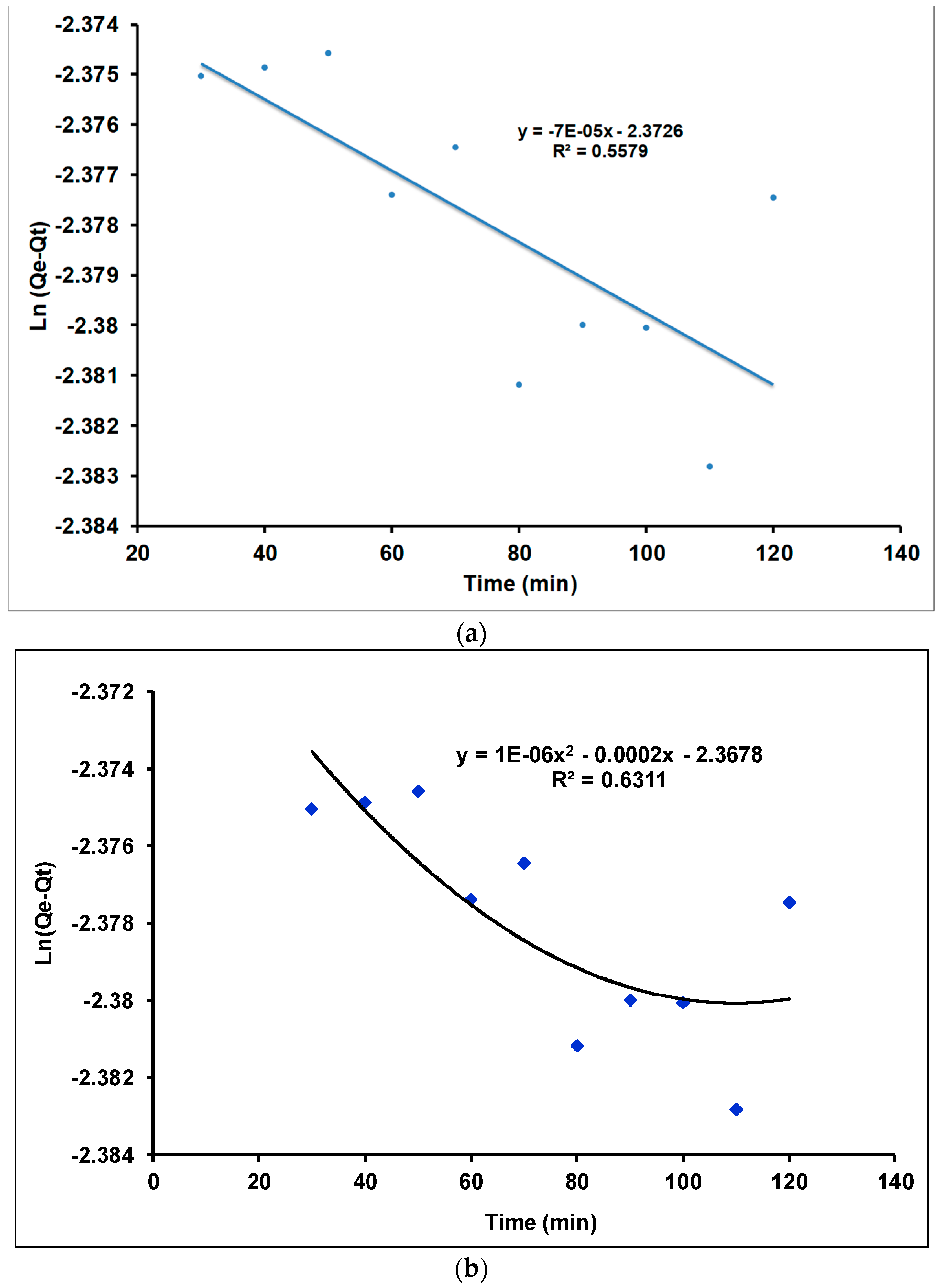
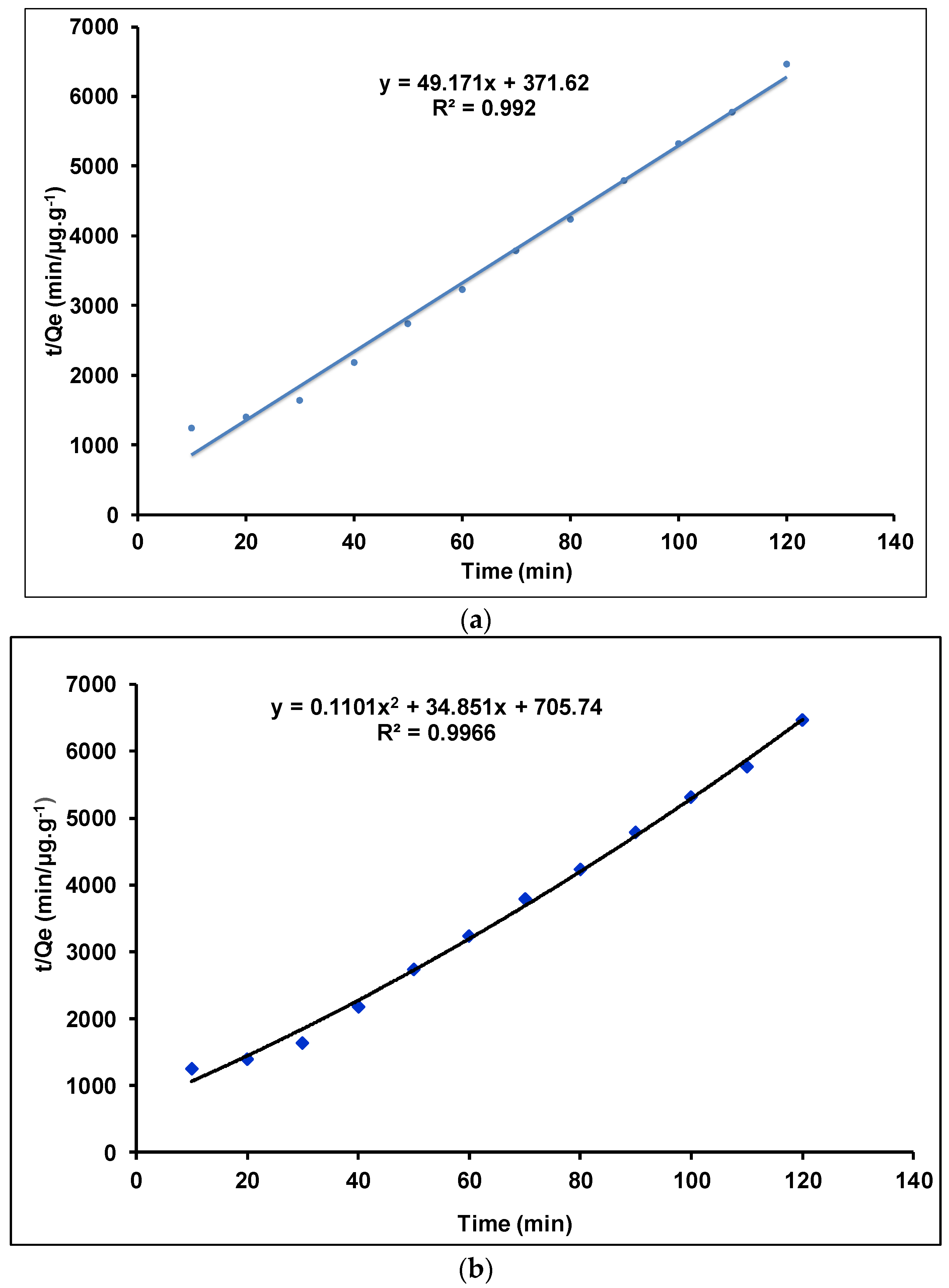
Investigation of Adsorption Kinetics Using Linear and Quadratic Models
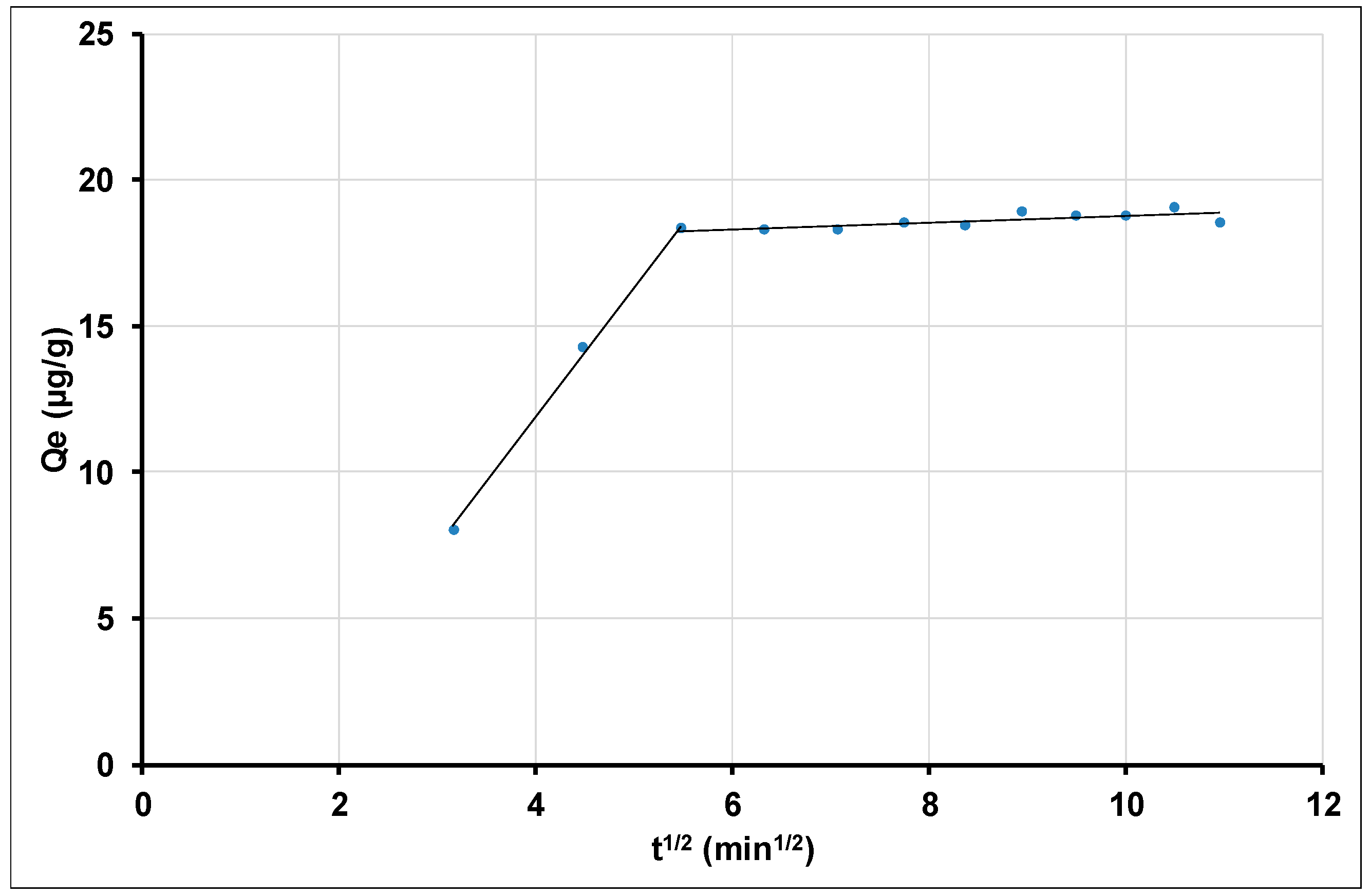
Intraparticle Diffusion of Thallium Adsorption by Gamma Nano Alumina
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.2.4. Effect of Initial Concentration of Tl Solution and Isotherms
Effect of Initial Concentration of Tl(I) Solution
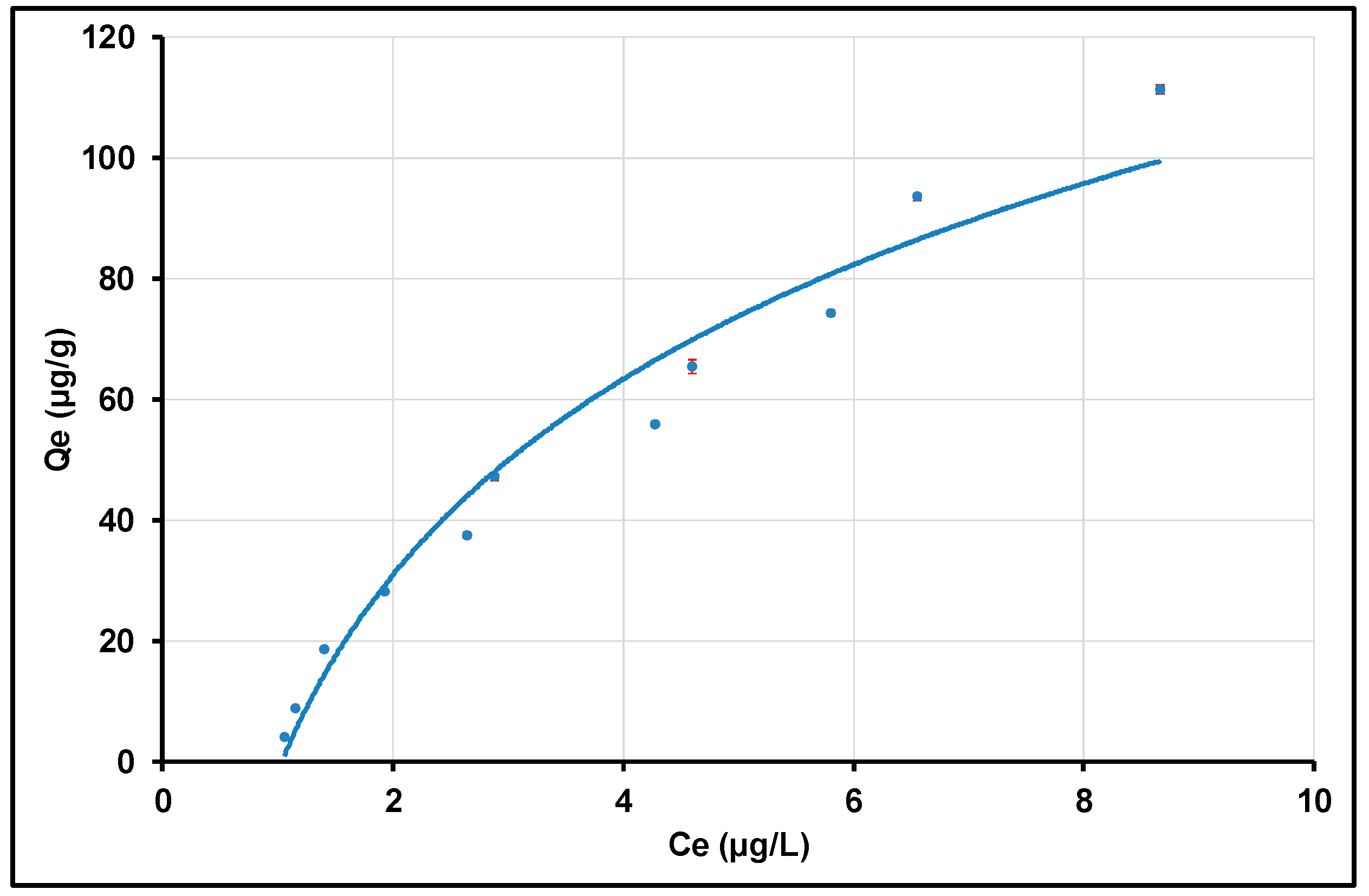
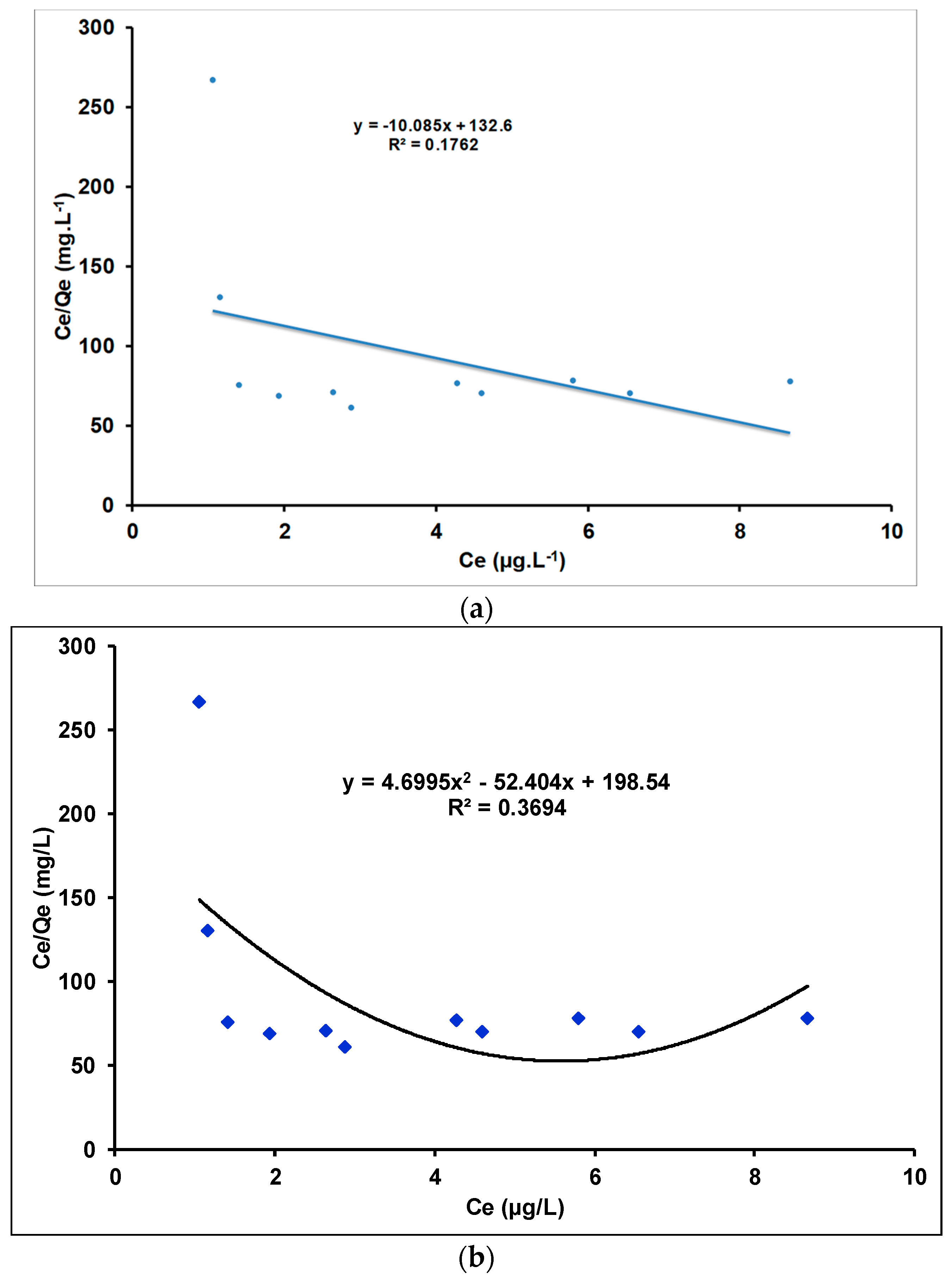
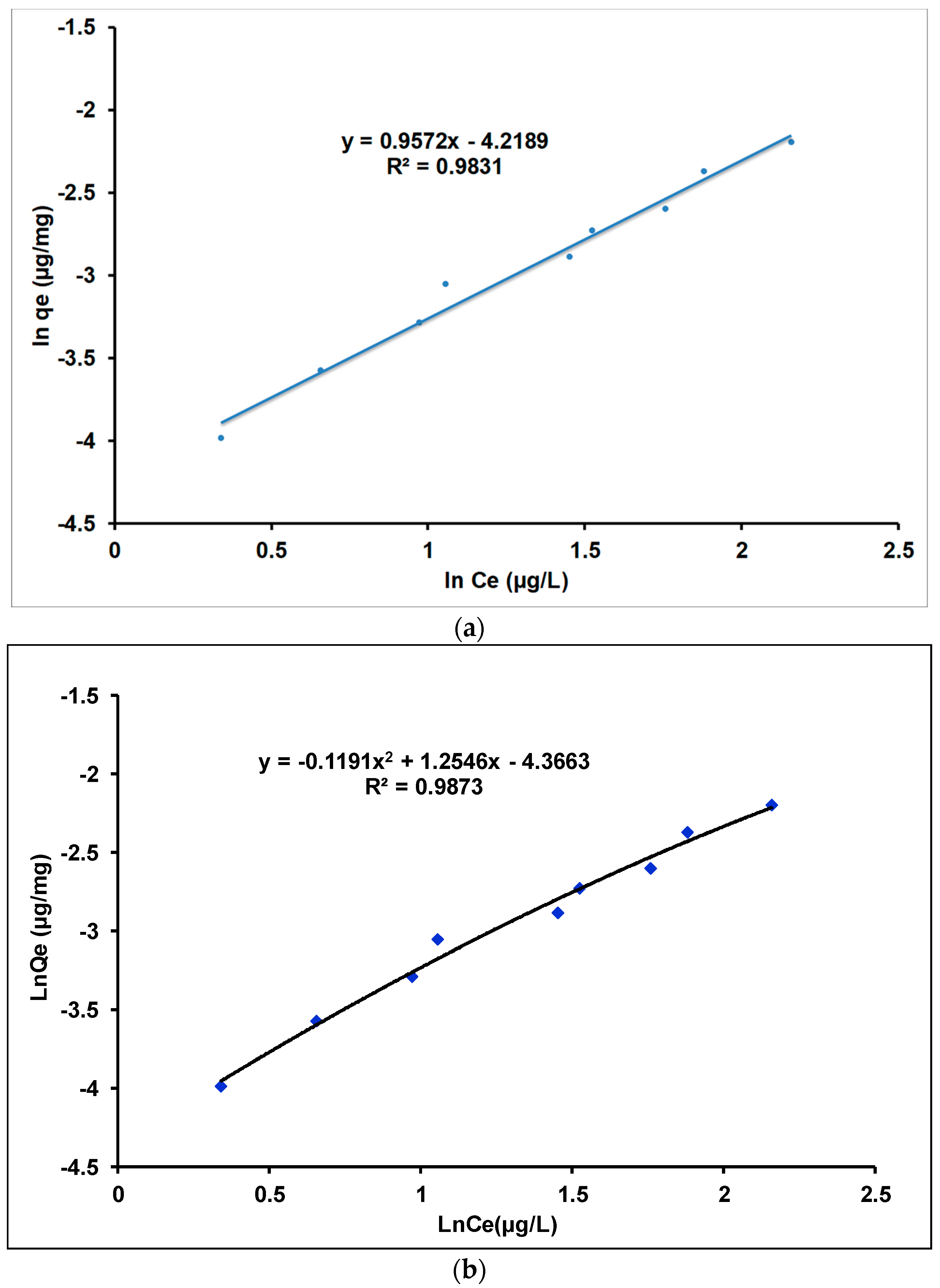
Investigations of Adsorption Isotherms Using Linear and Quadratic Models
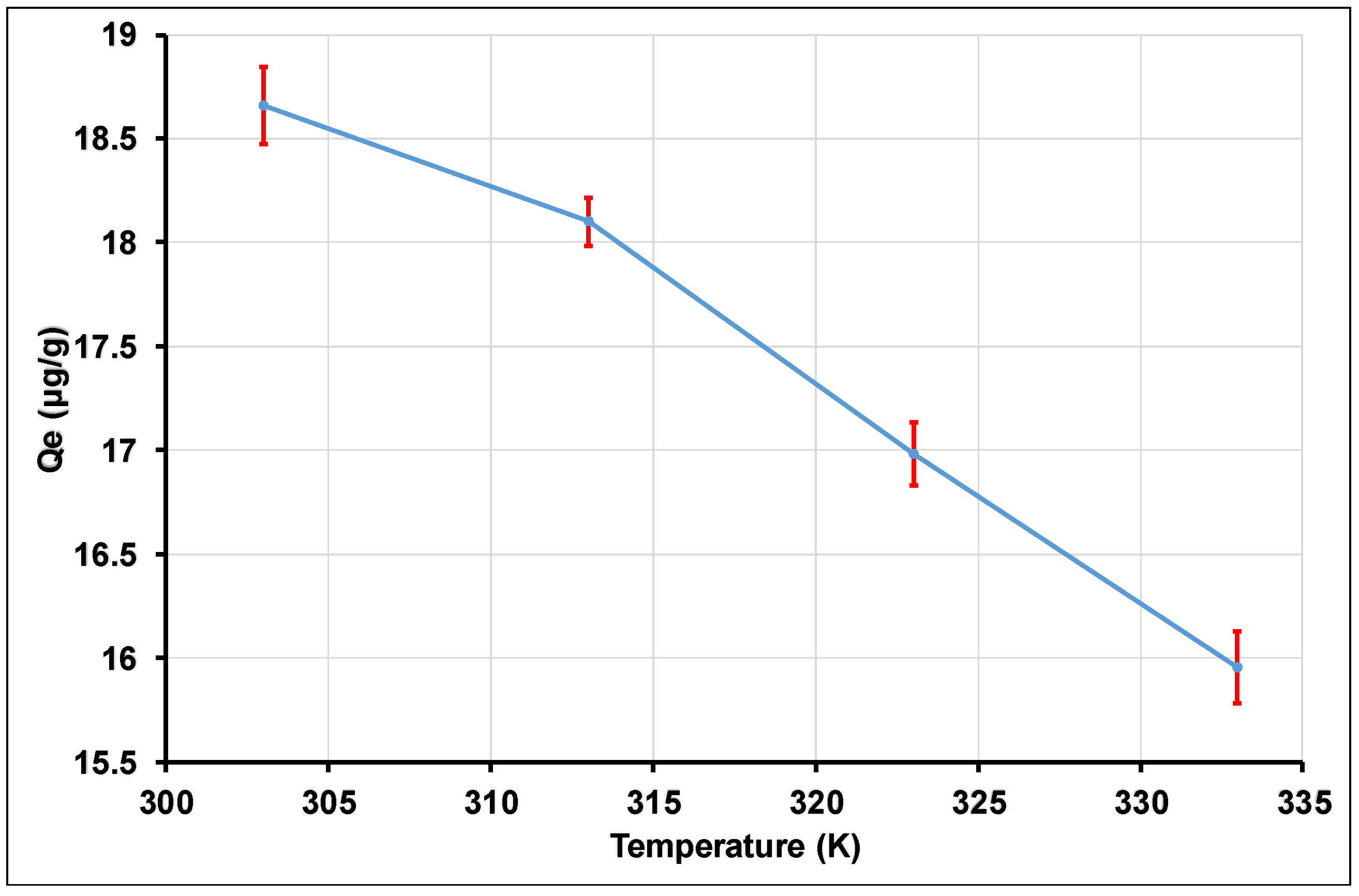
3.3. Temperature Effect and Thermodynamic Parameters of Tl(I) Adsorption on γANPs
3.4. Mechanism of Thallium Adsorption onto γANPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karbowska, B. Presence of thallium in the environment: Sources of contaminations, distribution and monitoring methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Thallium in the environment : A critical review focused on natural waters, soils, sediments and airborne particles. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 84, 218–243. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, L.; Xuwen, L.; Yuqing, S.; Daniel, C.W.; Jianying, Q.; Weilong, Z.; Nuo, L.; Meiling, Y.; Jin, W.; Holger, L.; et al. Thallium pollution in China and removal technologies for waters: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 771–790. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, A.L.J.; Viraraghavan, T. Thallium: A review of public health and environmental concerns. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Lai, Y.; Liang, C.; Yan, S.; Huang, K.; Pan, W.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, P.; Hao, J.; et al. Prenatal thallium exposure and poor growth in early childhood: A prospective birth cohort study. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Removal of thallium in water/wastewater: A review. Water Res. 2019, 165, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.F.; Yang, F.; Li, S.H.; Zheng, B.S.; Ning, Z.P. Thallium pollution in China: A geo-environmental perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, A.; Mahmood, C.; Mohammad, H.; Entezari, M.J.H.; Narjes, G. On-line preconcentration of ultra-trace thallium (I) in water samples with titanium dioxide nanoparticles and determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2012, 9, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Viraraghavan, T.; Asha, S. Thallium: Environmental Pollution and Health Effects. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, S.H.; Robert, H. Thallium Poisoning During Pregnancy: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 767–775. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, J.; Cao, H.; Hu, S.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, X. Highly efficient removal of thallium (I) by facilely fabricated amorphous titanium dioxide from water and wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatrice, C.; Massimo, O.; Alessandro, U.; Roberto, G.; Massimo, O.; Riccardo, P.; Emilia, B. Human exposure to thallium through tap water: A study from Valdicastello Carducci and Pietrasanta (northern Tuscany, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cristian, B.; Massimo, O.; Giovanni, O.; Lepore, F.A.; Simone, V. Thallium-rich rust scales in drinkable water distribution systems: A case study from northern Tuscany, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, B.; Casiot, C.; Onor, M.; Perotti, M.; Petrini, R.; Bramanti, E. Thallium release from acid mine drainages: Speciation in river and tap water from Valdicastello mining district (northwest Tuscany). Talanta 2017, 171, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lippold, H.; Lippmann-Pipke, J.; Chen, Y. Sorption of thallium (I) onto geological materials: Influence of pH and humic matter. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvolone, D.; Petri, D.; Aprea, M.C.; Bertelloni, S.; Voller, F.; Aragona, I. Thallium Contamination of Drinking Water: Health Implications in a Residential Cohort Study in Tuscany (Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Office of Water U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 3–8.
- Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Q. Comparative investigation on removal of thallium (Ⅰ) from wastewater using low-grade pyrolusite and pyrolysis residue derived from oily sludge: Performance, mechanism and application. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twidwell, L.G.; Williams-Beam, C. Potential Technologies for Removing Thallium from Mine and Process Wastewater: An Abbreviated Annotation of the Literature. Eur. J. Miner. Processing Environ. Prot. 2002, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Cooke, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. A preliminary investigation and evaluation of the thallium environmental impacts of the unmined Xiangquan thallium-only deposit in Hexian. China Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamane, A.A.; Guel, B. Caractérisations physico-chimiques des eaux souterraines de la localité de Yamtenga (Burkina Faso). Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 9, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kam, O.R.; Bakouan, C.; Zongo, I.; Guel, B. Assessing the Source of Thallium Contamination in Ground and Surface Waters in the Locality of Yamtenga (Burkina Faso): Correlation with Some Heavy Metal Ions. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, M.; Xiao, T.; Long, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liao, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; et al. Highly efficient removal of thallium (I) from wastewater via hypochlorite catalytic oxidation coupled with adsorption by hydrochar coated nickel ferrite composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hou, X.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Y.; You, J.; Xu, L. Adsorptive removal of trace thallium (I) from wastewater: A review and new perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, S.; Cao, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Beiyuan, J.; Peng, Y.; Fang, F.; She, J.; Yin, M.; Shen, N.; et al. Highly efficient removal of thallium in wastewater by MnFe2O4-biochar composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Figueroa, L.; Wildeman, T.; Bucknam, C. The oxidative precipitation of thallium at alkaline pH for treatment of mining influenced water. Mine Water Environ. 2016, 35, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, T.; Zhao, X.; Qi, J.; Ma, J. Highly efficient removal of trace thallium from contaminated source waters with ferrate: Role of in situ formed ferric nanoparticle. Water Res. 2017, 124, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, Z.; Xu, C.; Guo, G.; He, H.; Ma, J. Treatment of trace thallium in contaminated source waters by ferrate peroxidation and poly aluminium chloride coagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sinyakova, M.A.; Semenova, E.A.; Gamuletskaya, O.A. Ion exchange of copper (II), lanthanum (III), thallium (I), and mercury (II) on the “polysurmin” substance. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2014, 84, 2516–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chena, Y.; Long, J.; Jiang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Qi, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Gong, J.; et al. Simultaneous removal of thallium and chloride from a highly saline industrial wastewater using modified anion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Yin, G.Y.; Hu, Z.G. Extraction and separation of gallium, indium and thallium with several carboxylic acids from chloride media. Talanta 2003, 59, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, M.M.; Kenawy, I.M.; Mostafa, M.R.; El-Dellay, H. Extraction of gallium, indium and thallium from aquatic media using amino silica gel modifed by gallic acid. Microchim. Acta 2011, 172, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaf, A. Adsorption of cesium, thallium, strontium and cobalt radionuclides using activated carbon. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 1, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, D.; Su, Y.; He, J. Adsorption and desorption of thallium (I) on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, H.H.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Ye, H.P. Adsorption of Tl (I) on Na-montmorillonite and kaolinite from aqueous solutions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, S.; Baeyens, B.; Fernandes, M.M.; Voegelin, A. Thallium adsorption onto illite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birungi, Z.S.; Chirwa, E.M.N. The adsorption potential and recovery of thallium using green micro-algae from eutrophic water sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangvanich, T.; Sukwarotwat, V.; Wiacek, R.J.; Grudzien, R.M.; Fryxell, G.E.; Addleman, R.S.; Timchalk, C.; Yantasee, W. Selective capture of cesium and thallium from natural waters and simulated wastes with copper ferrocyanide functionalized mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.; Taulemesse, J.-M.; Dauvergne, A.; Chanut, T.; Testa, F.; Guibal, E. Thallium (I) sorption using Prussian blue immobilized in alginate capsules. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 99, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Ma, M.; Lu, L.; Qian, L.; Xu, S.; Xue, Y.; Ma, Z. Selective capture of thallium (I) ion from aqueous solutions by amorphous hydrous manganese dioxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.C.; Wan, S.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Guo, Q.W.; Xu, Z.C.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W.M. Recyclable polymer-based nano-hydrous manganese dioxide for highly efficient Tl (I) removal from water. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, X.; Jiang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, S.-Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Adsorption and oxidation of thallium (I) by a nanosized manganese dioxide. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Xiao, T.; Long, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of manganese dioxide with different morphologies for thallium removal from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, S.; Pena, J.; Voegelin, A. Thallium sorption onto manganese oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13168–13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Chen, H.; Ni, J.R. Adsorption mechanisms of thallium (I) and thallium (III) by titanate nanotubes: Ion-exchange and co-precipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 423, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Fan, F.; Li, X.P.; Qi, J.Y.; Chen, Y.H. Superior adsorption of thallium (I) on titanium peroxide: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Su, Z.; Deng, N.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Huang, C.; Xiao, T. Removal of thallium (I) from aqueous solutions using titanate nanomaterials: The performance and the influence of morphology. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Effective heavy metal removal from aqueous systems by thiol functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.J. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Kaushal, R. Treatment of wastewater with low cost adsorbent—A review. Int. J. Tech. Non-Tech. Res. 2013, 4, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, U.; Wittmann, G.T.W. Metals Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfa, O.M.; Yalcinkaya, O.; Turker, A.R. Synthesis of nano B2O3/TiO2 composite material as a new solid phase extractor and its application to preconcentration and separation of cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, P.; Guo, L. Nanometer titanium dioxide immobilized on silica gel as sorbent for preconcentration of metal ions prior to their determination by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 2005, 68, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R.H.; Monthioux, M.; Kane, A. Toxicology of carbon nanomaterials: Status, trends and perspectives on the special issues. Carbon 2006, 44, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisz, I.; Dombi, A.; Mogyorósi, K.; Dékány, I. Photocatalytic water treatment with different TiO2 nanoparticles and hydrophilic/hydrophobic layer silicate adsorbents. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 230, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, B.; Sarah, M.L.; Guillaume, N.; Muriel, P.; Jean, L.; Daniel, R.T.; Charles, T. Metal Phosphonates Applied to Biotechnologies: A Novel Approach to Oligonucleotide Microarrays. Chemistry 2005, 11, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Taiba, N.; Tayyiba, D. The role of some important metal oxide nanoparticles for wastewater and antibacterial applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 3, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y.; Mou, S.; Jiang, G. Adsorption of di-ethylphthalate from aqueous solutions with surfactant-coated nano/microsized alumina. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 140, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, T.A.-R.; Omar, F. A-R.; Noor, M.A. Preparation of a Modified Nanoalumina Sorbent for the Removal of Alizarin Yellow R and Methylene Blue Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- RIBEIRO, A.P. Alumines Macro- Mésoporeuses Produites par Procédé Sol-Gel Pour une Application en Catalyse Hétérogène. Doctoral Thesis, PARIS-SUD University, Bures-sur-Yvette, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siahpoosh, S.M.; Salahi, E.; Hessari, F.A.; Mobasherpour, I. Synthesis of γ-Alumina Nanoparticles with High-Surface-Area via Sol-Gel Method and Their Performance for the Removal of Nickel from Aqueous Solution. Bull. Société R. Sci. Liège 2016, 85, 912–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Hua, T.; Tang, G.; Peng, X.Q.; Hao, M.H.; Zuo, Q.T. Adsorption characteristics of Cu (II) and Zn (II) by nano-alumina material synthesized by the sol-gel method in batch mode. Environ Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, P.; Asghari, A.; Hemmati, M. Efficient determination of some potentially toxic metal ions from real samples via modified nano-γ-alumina-based solid-phase extraction followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometric analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koju, N.K.; Xin, S.; Qing, W.; Zhihao, H.; Claudio, C. Cadmium removal from simulated groundwater using alumina nanoparticules: Behaviors and mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Ting, H.; Min, Z.; Xingjia, G.; Zhu, Y. Studies on the capability and behavior of adsorption of thallium on nano-Al2O3. J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 157, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, O.R.; Garikoé, I.; Bakouan, C.; Guel, B. Low-Cost Synthesis of Alumina Nanoparticles and Their Usage for Bisphenol-A Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2021, 9, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarif, D.G.; Prajitno, D.H.; Umar, E. Synthesis of A12O3 Nanoparticles from Local Bauxite for Water-A12O3 Nanofluids egy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 799, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Manivasakan, P.; Rajendran, V.; Rauta, P.R.; Sahu, B.B.; Panda, B.K. Direct synthesis of nano alumina from natural bauxite. Adv.Mater. Res. 2009, 67, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, G.; Tamilarasan, R.; Dharmendirakumar, M. Adsorption, Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic studies on the removal of basic dye Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution by the use of natural adsorbent perlite. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Musah, M.; Azeh, Y.; Mathew, J.T.; Umar, M.T.; Abdulhamid, Z.; Muhammad, A.I. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm Models: A Review. CaJoST 2022, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; and Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption of carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Lee, D.J.; Wong, C.J.W. Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption equilibrium of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater with low-cost adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 291, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rahman, K.M.A.; El-Kamash, A.M.; El-Sourougy, M.R.; Abdel-Moniem, N.M. Thermodynamic modeling for the removal of Cs, Sr, Ca and Mg ions from aqueous waste solutions using zeolite. A. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 268, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.F.; Mendes, M.F.; Coelho, G.L.V. Thermodynamic study of fatty acids adsorption on different adsorbents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2007, 39, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S. Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. In Thermodynamics; Tadashi, M., Ed.; InTechOpen: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 350–364. Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/thermodynamics/insight-into-adsorption-thermodynamics (accessed on 14 January 2011).
- Bawa, S.G.; Ahmed, A.S.; Okonkwo, P.C. The study of Thermal effect on the surface properties of Gamma-Alumina synthesized from Kankara Kaolin. Niger. J. Technol. 2016, 35, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Paranjpe, K.Y. Alpha, Beta and Gamma Alumina as a catalyst—A Review. Pharma Innov. J. 2017, 6, 236–238. [Google Scholar]
- Meteab, H.S.; Karem, H.A.; Salih, W.K. Synthesis and characterization of nano gamma aluminium oxide from iraqi bauxite using extraction method. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 814–818. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; García, M.F. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Oxide Nanomaterials; John Wiley & Sons: Hobeken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanpour, O.; Shariati, A.; Nikou, M.R.K. New Method for Synthesis Nano Size γ-Al2O3 Catalyst for Dehydration of Methanol to Dimethyl Ether. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin, L.; Dianqing, L.; Pinggui, T.; Yongjun, F. A simple and promoter free way to synthesize spherical γ-alumina with high hydrothermal stability. Mater. Lett. 2015, 155, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bazyari, A.; Mortazavi, Y.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Thompson, L.T.; Tafreshi, R.; Zaker, A.; Ajenifujah, O.T. Effects of alumina phases as nickel supports on deep reactive adsorption of (4,6-dimethyl) dibenzothiophene: Comparison between γ, δ, and θ-alumina. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ysla, F.A.; Martins, A.R.; Rodrigo Estevam, C.; Cesário, F.d.V.; Adriana, D.B.; Carvalho, L.S. A Simple Way to Produce γ-Alumina from Aluminum Cans by Precipitation Reactions. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 977–982. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, E.; Kaur, S.; Dave, P.N. Mechanistic study of adsorption of acid orange-7 over aluminum oxide nanoparticles. J. Eng. 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C.; Srivastava, V.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Weng, C.H. Alumina nanoparticles for the removal of Ni (II) from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8095–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Saber-Tehrani, M.; Bagheri, H. Simultaneous removal of heavy-metal ions in wastewater samples using nanoalumina modified with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cao, C.Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Ge, M.F.; Song, W.G. Superb fluoride and arsenic removal performance of highly order mesoporous aluminas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Weng, C.H.; Singh, V.K.; Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption of nickel ions from aqueous solutions by nano alumina: Kinetic, mass transfer, and equilibrium studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2011, 56, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Beam, C.; Twidwell, L.G. Removal of thallium from wastewater. Hydrometallurgy. 2003, 2, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Qu, J. Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 335, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metivier, R.; Leray, I.; Lefevre, J.P.; Roy-Auberger, M.; Zanier-Szydlowskic, N.; Valeur, B. Characterization of alumina surfaces by fluorescence spectroscopy Part 2. Photophysics of a bound pyrene derivative as a probe of the spatial distribution of reactive hydroxyl groups. Phys. Chem. 2003, 5, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y. Interfacial characterization of α-alumina with small surface area by streaming potential and chromatography. Colloids Surf. A. 2013, 436, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.S.; Nriagu, J. Revised hydrolysis constants for thallium (I) and thallium (III) and the environmental Implications. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1998, 48, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavlieva, M.P.; Genieva, S.D.; Georgieva, V.G.; Vlaev, L.T. Kinetic study of brilliant green adsorption from aqueous solution onto white rice husk ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 409, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.Q.; Memon, N.; Solangi, A.R.; Memon, J.U.R. Sawdust: A green and economical sorbent for thallium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 140, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, Z.M.; Ulusoy, U. Thallium adsorption onto polyacryamide-aluminosilicate composites: A Tl isotope tracer study. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiking, C.; Pingxiao, W.; Langfen, Y.; Shuai, L.; Bo, R.; Haihui, H.; Nengwu, Z.; Zhang, L. FeOOH-loaded MnO2 nano-composite: An efficient emergency material for thallium pollution incident. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Vithanage, M.; Mayakaduwa, S.; Herath, I.; Ok, Y.S.; Mohan, D. Kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanistic studies of carbofuran removal using biochars from tea waste and rice husks. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Wasim, A.A.; Fazal-Ur-Rehmangu, S. Statistically Optimized Adsorption of Pb (II) Ion on Corn Husk Activated Carbon—An Application of Response Surface Method. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2022, 35, 421–432. [Google Scholar]
- Co¸skun, Y.I.; Aksuner, N.; Yanik, J. Sandpaper wastes as adsorbent for the removal of brilliant green and malachite green dye. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betianu, C.S.; Cozma, P.; Rosca, M.; Ungureanu, C.E.-D.; Mămăligă, I.; Gavrilescu, M. Sorption of Organic Pollutants onto Soils: Surface Diffusion Mechanism of Congo Red Azo Dye. Processes 2020, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K.; Mishra, I.M. Removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyaraman, P.M.; Karan, S.; Ponnusamy, S.K.; Vaidyanathan, V.; Vasanthakumar, S.; Dhanasekaran, A.; Subramanian, S. Adsorption of an anionic dye onto native and chemically modified agricultural waste. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Makhlouf, M.; Hamacha, R.; Villièras, F.; Bengueddach, A. Kinetics and thermodynamics adsorption of phenolic compounds on organic-inorganic hybrid mesoporous material. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2013, 3, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Habumugisha, T.; Eric, C.; Luo, Z.; Kayiranga, A.; Nkinahamira, F.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Yan, C. Thallium removal by the montmorillonite biochar composite: Insights and environmental implications. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.S.; Li, X.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Long, J.Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Xiao, T.F.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.L.; Zhuang, L.Z.; Huang, W.Y. Removal and recovery of thallium from aqueous solutions via a magnetite-mediated reversible adsorption-desorption process. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Li, X.W.; Xiao, T.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Long, J.Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.L.; Zhuang, L.Z.; Li, K.K. Efficient removal of thallium (I) from wastewater using flower-like manganese dioxide coated magnetic pyrite cinder. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Long, J.Y.; Li, X.W.; Jiang, D.Q.; Zhang, P.; Qi, J.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Liu, J.; Xu, R.B.; et al. Removal of thallium from aqueous solutions using Fe-Mn binary oxides. J. Hazard Mater. 2017, 338, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavidaki, H.D.; Fekri, M.H. Removing thallium (I) ion from aqueous solutions using modified ZnO nanopowder. J. Adv. Chem. 2015, 11, 3777–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabermahani, F.; Mahani, N.M.; Noraldiny, M. Removal of thallium (I) by activated carbon prepared from apricot nucleus shell and modified with rhodamine B. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Xiong, J.F.; Xiao, T.F.; Long, J.Y.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, K.K.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, H.G. Biochar derived from watermelon rinds as regenerable adsorbent for efficient removal of thallium (I) from wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 127, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimibofa, A.; Augustus, N.E.; Donbebe, W. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Coopern, C.; Ouki, S. Comparison of modified montmorillonite adsorbents-part I: Preparation, characterization and phenol adsorption. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.R.; Ahmad, K.; Aziz, A.A.; Chik, Z. Geoenvironmental Aspects of Tropical Residual Soils. In Tropical Residual Soils Engineering, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hardiljeet, K.B.; Meera, J.; Denis, M.O. kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nanozerovalent iron particles. J. Hasardous Mater. 2011, 186, 458–465. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.H. Statiscal mechanical study on the Freunlich isotherm equation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 208, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, G.B.H.I.; Chan, N.W.; Haliza, A.R.; Nor, A.Z. Freundlich Isotherm Equilibrium Equations in Determining Effectiveness a Low Cost Absorbent to Heavy Metal Removal In Wastewater (Leachate) At Teluk Kitang Landfill, Pengkalan Chepa, Kelantan, Malaysia. J. Geogr. Earth Sci. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, B.; Megharaj, M.; Xi, Y.; Naidu, R. Surface charge characteristics of organopalygorskites and adsorption of p-nitrophenol in flow-through reactor system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.S.; Ozcan, A. Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solutions onto acid activated bentonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, A.; Shreadah, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Heiba, H.F. Multi-component adsorption of Pb (II), Cd (II), and Ni (II) onto Egyptian Na activated bentonite; equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, and application for seawater desalination. J. Environ Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1166–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Fazli, M. Effect of nanostructure alumina on adsorption of heavy metals. Desalination. 2010, 253, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, M. Removal of Pb (II) from water by natural zeolitic tuff: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheela, T.; Nayaka, Y.A.; Viswanatha, R.; Basavanna, S.; Venkatesha, T. Kinetics and thermodynamics studies on the adsorption of Zn (II), Cd (II) and Hg (II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Yang, P.; Zhang, M. Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions by magnetic Schiff base: Kinetic and thermodynamic investigation. Chem Eng J. 2012, 198, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozbeh, S.; Azam, M.; Saeed, S. Facile one-pot synthesis of thiol-functionalized mesoporous silica submicrospheres for Tl (I) adsorption: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 371, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chidozie, C.N.; Akambende, E.A.; Cordelia, N.M.; Praise, G.C.E.; Nkpa, M.O. Equilibrium and thermodynamic investigation of biosorption of nickel from water by activated carbon made from palm kernel chaff. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- El-Eswed, R.I.Y.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H. Adsorption characteristics of natural zeolites as solid adsorbents for phenol removal from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamics studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.-S.; Zheng, T.; Wang, P.; Jiang, J.P.; Li, N. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnemaie, R.; Hiemstra, T.; van Riemsdijk, W.H. Inner- and outer-sphere complexation of ions at the goethite–solution interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

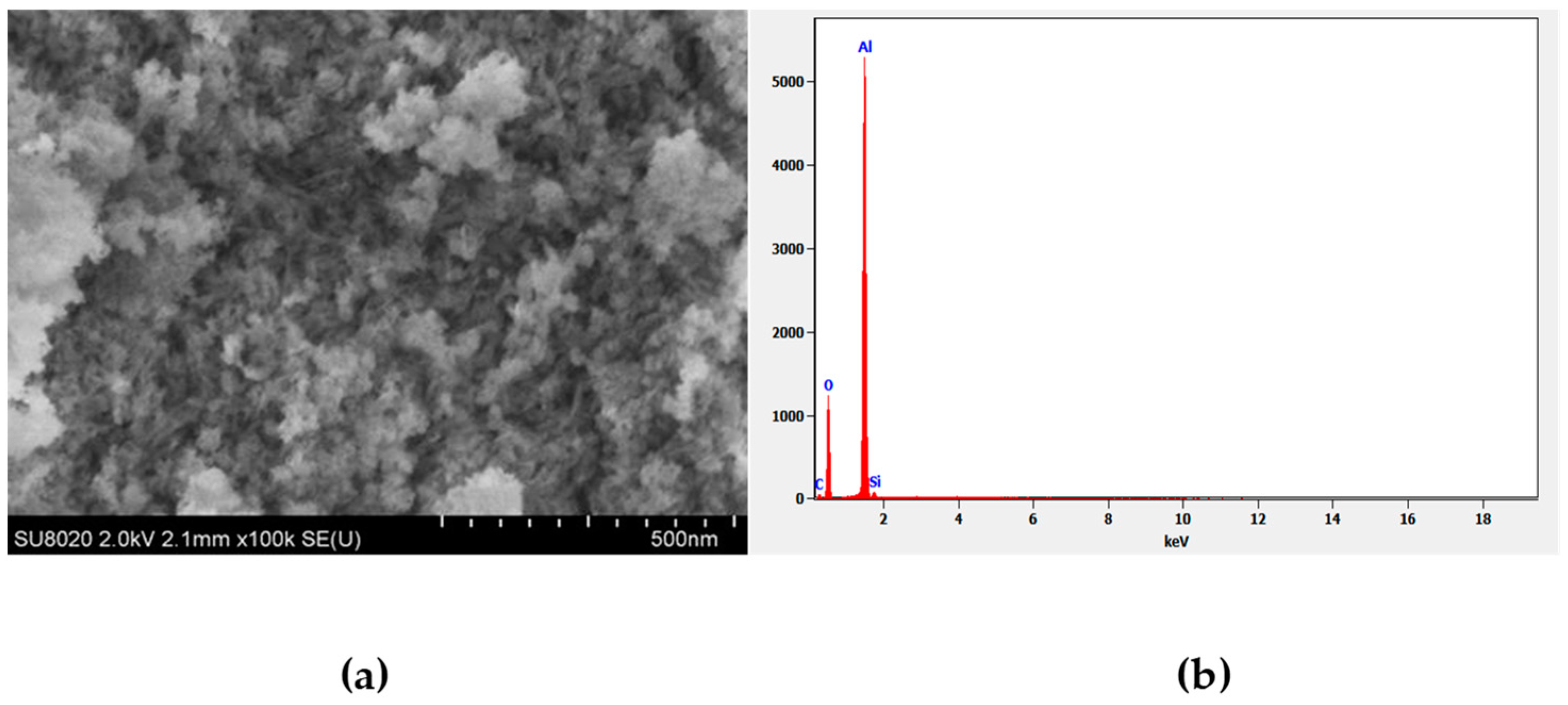

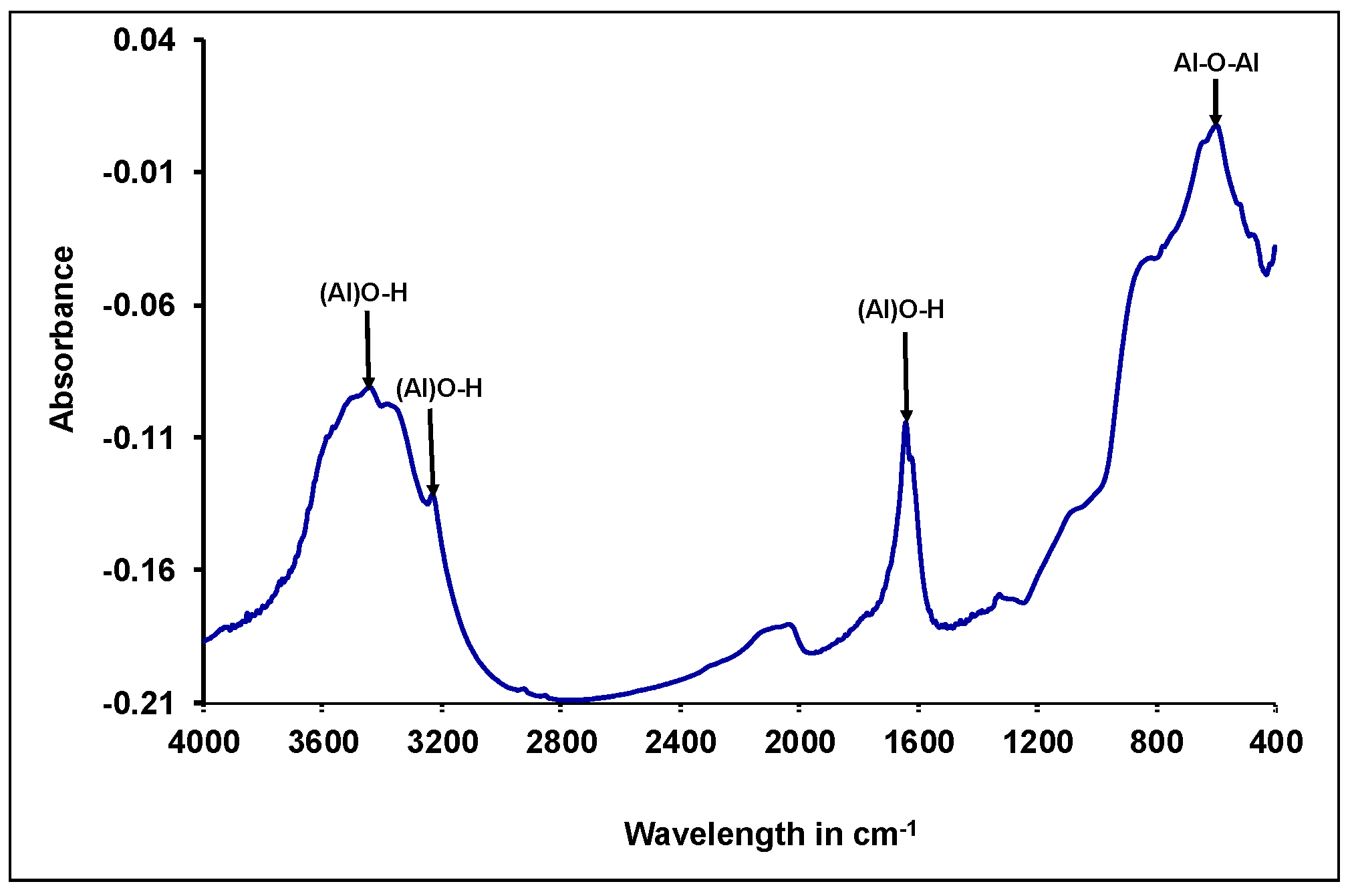

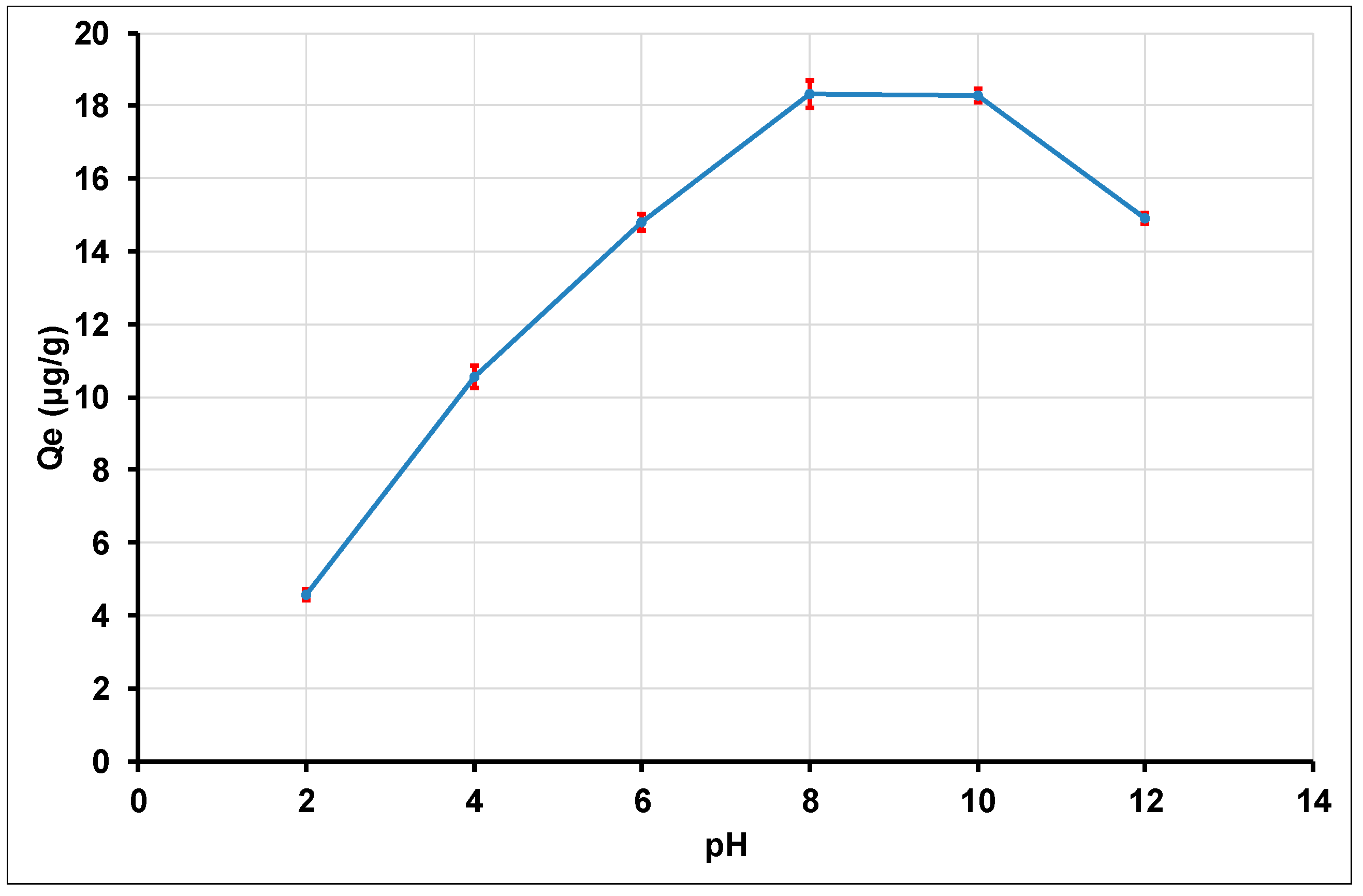
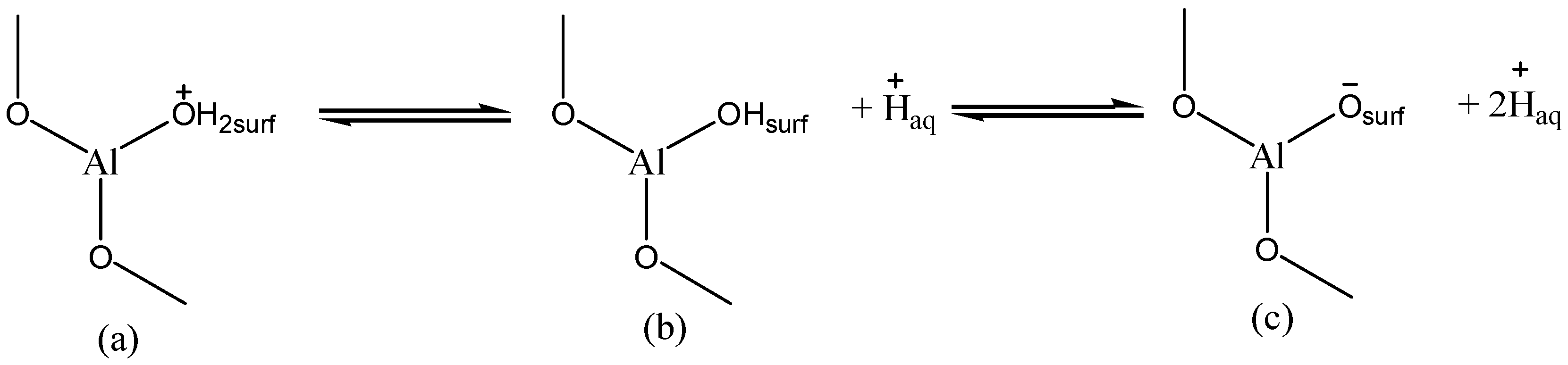


| Oxides | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | P2O5 | V2O5 | Na2O | MgO | K2O | ZnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 88.00 | 5.101 | 0.100 | 0.170 | 0.020 | 0.090 | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.005 |
| Sorbent | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | Qe1 (mg/g) | R2 | K2 (g/mg.min) | Qe2 (mg/g) | R2 | |
| γANPs | 0.0006 | 1666.666 | 0.5579 | 6.506 | 0.023 | 0.992 |
| Adsorbents | Adsorbate | Concentrations Range (µg.L−1) | Dosages (g.L−1) | Residual Concentrations of Tl (µg.L−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis residue | Tl(I) | 1600 | 3 | 104.96 | [18] |
| Low-grade pyrolusite | Tl(I) | 1600 | 3 | 17.5 | [18] |
| Amorphous hydrous manganese dioxide (HMO) | Tl(I) | 50,000 | 0.5 | ˂0.1 | [40] |
| Montmorillonite biochar composite | Tl(I) | 800 | - | 33.2 | [106] |
| Magnetite (Fe3O4) | Tl(I) | 450–10,000 | 2.5 | 29 | [107] |
| MnO2@pyrite | Tl(I) | 10,000–171,000 | 1 | 3.8 | [108] |
| Fe-Mn binary oxides | Tl(I) | 10,000 | 2 | 2 | [109] |
| Nano-alumina | Tl(III) | 10,000 | 3 | 4.4 | [6,66] |
| Modified ZnO Nanopowder | Tl(I) | 5000–50,000 | 2 | 3600 | [110] |
| Titanium peroxide | Tl(I) | 46–20,000 | 0.2 | ˂2 | [46] |
| Modified activated carbon with rhodamine B | Tl(I) | 30–50,000 | 40 | 3.23 | [111] |
| Biochar derived from watermelon rinds | Tl(I) | 20,000–100,000 | 6 | ˂5 | [112] |
| Synthesized γANPs | Tl(I) | 20 | 1 | 0.97 ± 0.23 | Present study |
| Sorbent | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | Qm (mg/g) | R2 | KF (L/g) | n | R2 | |
| γANPs | 0.0144 | 1.0103 | 0.1762 | 1.3388 | 1.0447 | 0.9831 |
| Thermodynamic Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | T(K) | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔHx (kJ/mol) | ΔS (kJ/mol.K) | R2 |
| γAl2O3 | 303 | −24.031 | −36.090 | 31.638 | −0.039 | 0.994 |
| 313 | −23.841 | |||||
| 323 | −23.192 | |||||
| 333 | −22.923 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kam, O.R.; Bakouan, C.; Zongo, I.; Guel, B. Removal of Thallium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091826
Kam OR, Bakouan C, Zongo I, Guel B. Removal of Thallium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles. Processes. 2022; 10(9):1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091826
Chicago/Turabian StyleKam, Ollé Rodrigue, Corneille Bakouan, Inoussa Zongo, and Boubié Guel. 2022. "Removal of Thallium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles" Processes 10, no. 9: 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091826
APA StyleKam, O. R., Bakouan, C., Zongo, I., & Guel, B. (2022). Removal of Thallium from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Alumina Nanoparticles. Processes, 10(9), 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091826









