Spray Drying of PEG6000 Suspension: Reaction Engineering Approach (REA) Modeling of Single Droplet Drying Kinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
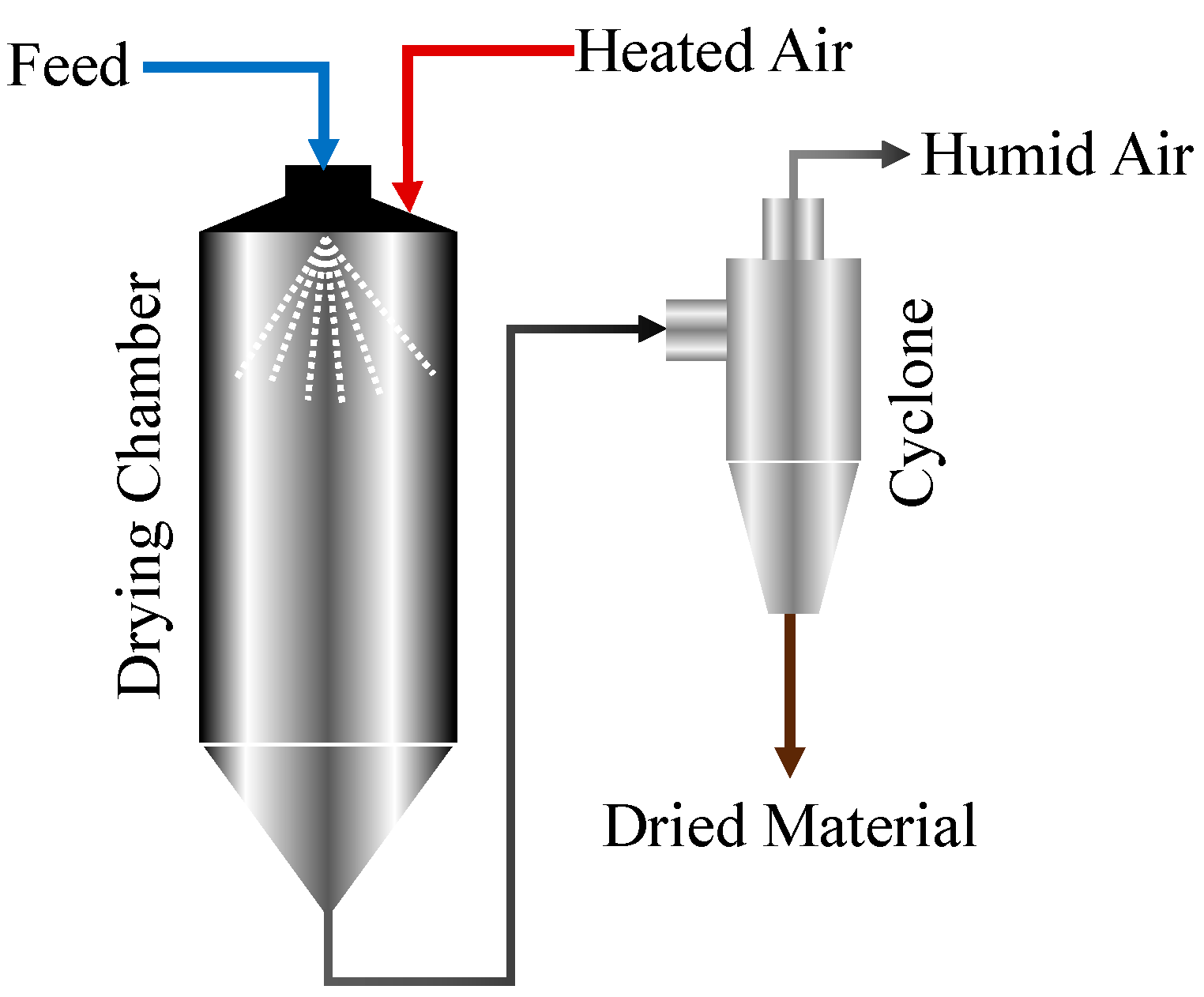
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Method and Procedure
2.2. Drying Kinetics Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
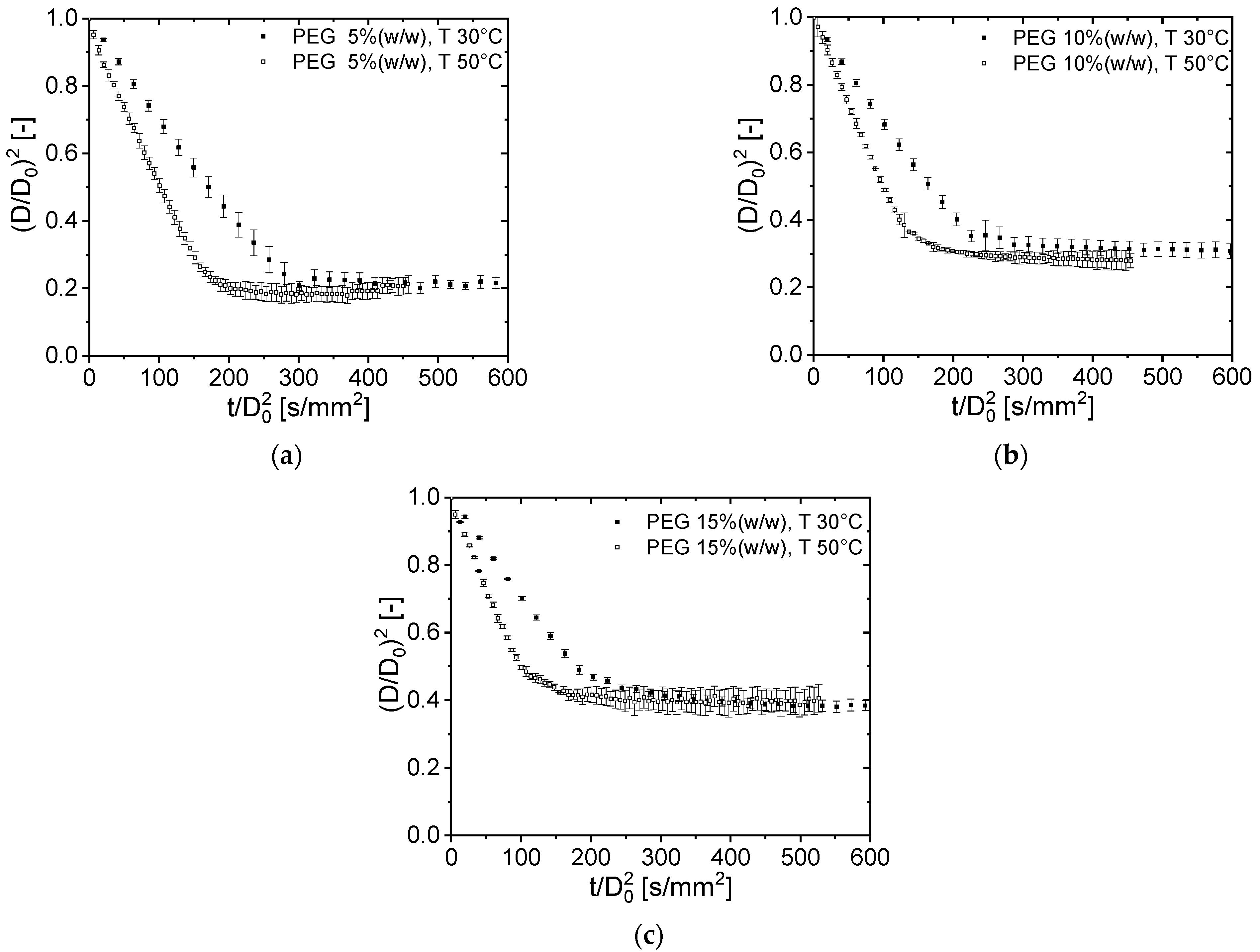
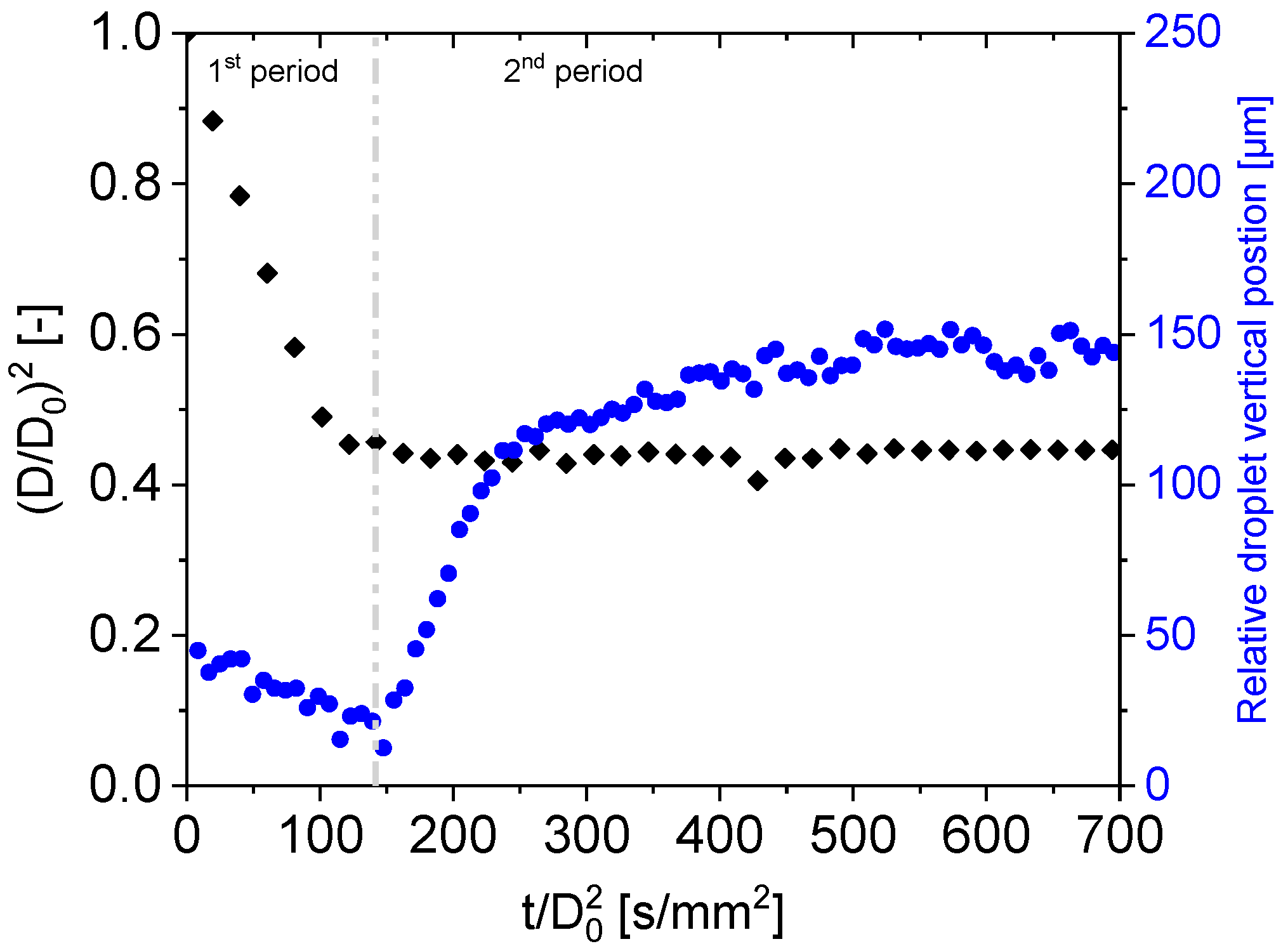
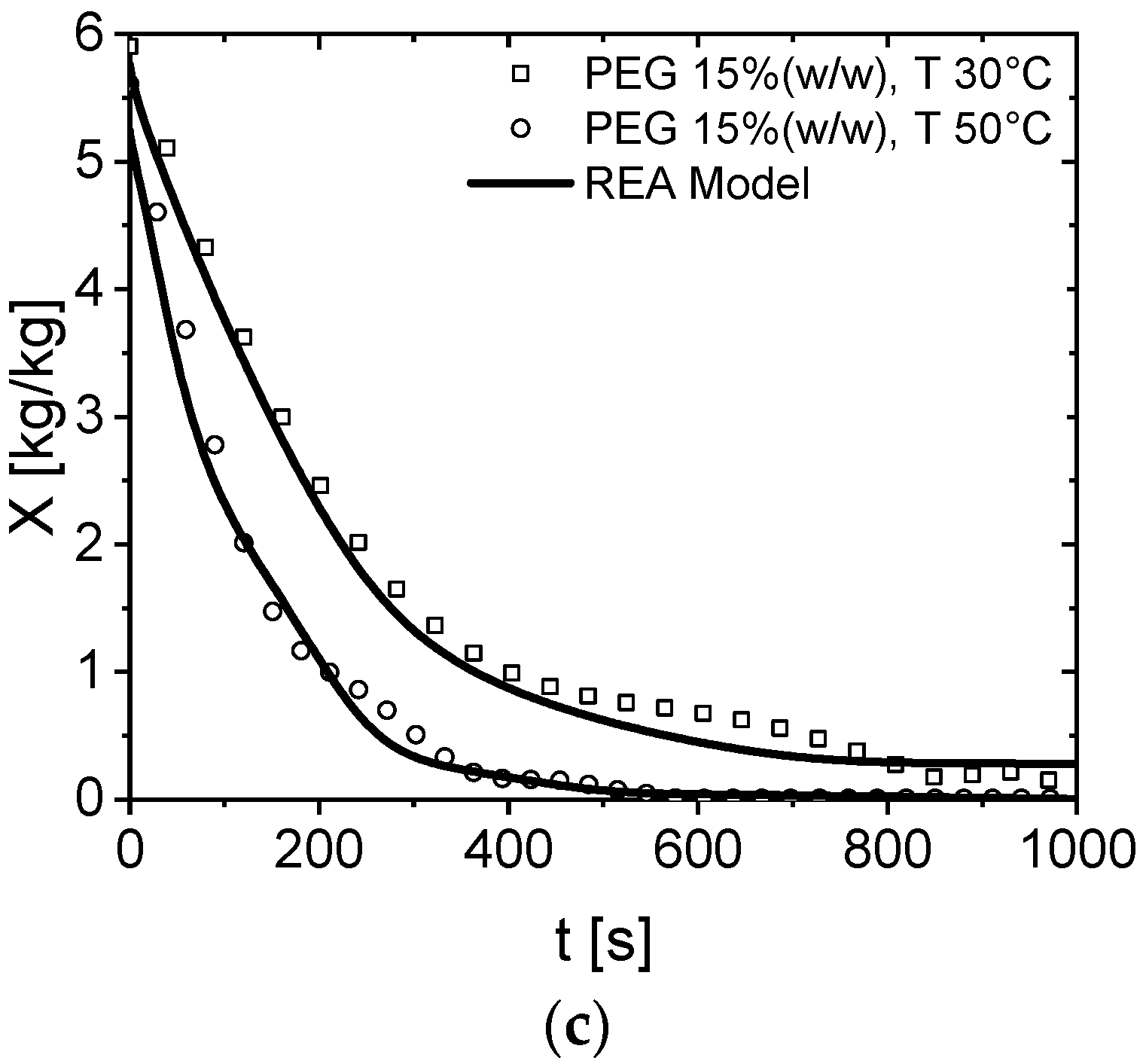
3.1. Drying Curves of Aqueous PEG Droplets at a Different Initial Solids Content
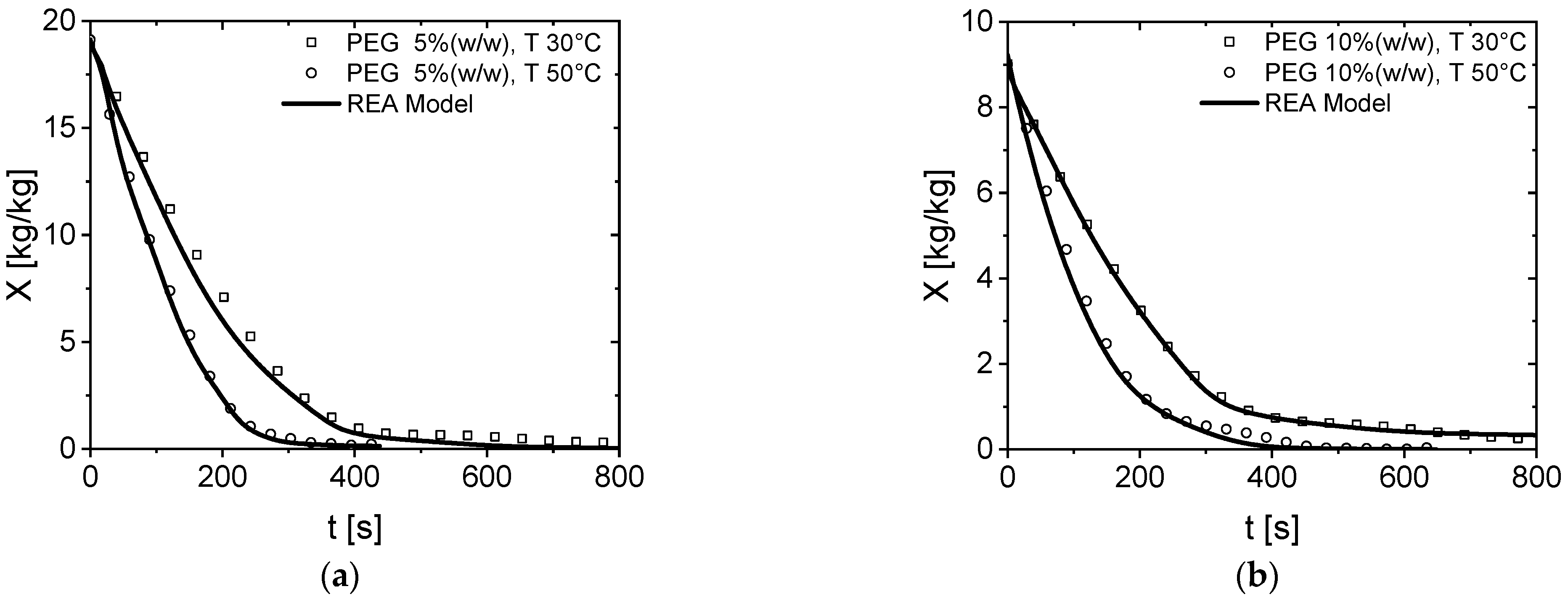
3.2. Modeling of PEG600 Drying Behavior via the REA Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | (m2) | the surface area of the droplet |
| A0e | (N m−2) | sound pressure amplitude |
| B | (m s−1) | gas particle velocity |
| D | (m) | droplet diameter |
| D0 | (m) | initial droplet diameter |
| (J mol−1) | activation energy | |
| hm | (m s−1) | mass transfer coefficient |
| (kg s−1) | the mass flow rate of A | |
| (kg) | the total mass of the droplet | |
| (kg) | mass of the liquid inside the droplet | |
| (kg) | mass of the solids inside the droplet | |
| Nu | (-) | Nusselt number |
| RHg | (-) | relative humidity of drying air |
| Sh | (-) | Sherwood number |
| SPL | (dB) | sound pressure level |
| T | (k) | temperature |
| vs | (m s−1) | sound velocity |
| X | (kg kg−1) | dry basis moisture content |
| Greek symbol | ||
| αg | (m2 s−1) | thermal diffusivity of the gas |
| (J kg−1) | latent heat of vaporization | |
| ρ | (kg m−3) | mass concentration of the droplet |
| (kg m−3) | vapor mass concentration at the droplet surface | |
| (kg m−3) | saturated vapor mass density | |
| ρg | (kg m−3) | the density of the air |
| (m s−2) | diffusion coefficient of vapor | |
| ωA | (-) | mass fraction of the vapor |
| ωsolids | (-) | mass fraction of the solids |
| (Hz) | angular frequency | |
| (-) | fractionality coefficient | |
| Subscripts | ||
| e | equilibrium | |
| g | gas | |
| L | liquid | |
| s | surface of droplet | |
References
- De Mohac, L.M.; Raimi-Abraham, B.; Caruana, R.; Gaetano, G.; Licciardi, M. Multicomponent solid dispersion a new generation of solid dispersion produced by spray-drying. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weuts, I.; Kempen, D.; Verreck, G.; Decorte, A.; Heymans, K.; Peeters, J.; Brewster, M.; Mooter, G.V.d. Study of the physicochemical properties and stability of solid dispersions of loperamide and PEG6000 prepared by spray drying. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, S.A.; Barmpalexis, P.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Optimizing the ability of PVP/PEG mixtures to be used as appropriate carriers for the preparation of drug solid dispersions by melt mixing technique using artificial neural networks: I. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, S.; de Armas, H.N.; Roberts, C.J.; Van den Mooter, G. Characterization of ternary solid dispersions of itraconazole, PEG 6000, and HPMC 2910 E5. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, S.; Paul, S.K.; Chauhan, H. Ternary solid dispersions: Classification and formulation considerations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Sun, Y.; Ding, D.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, R.; He, Z.; Wang, J. Study on enhanced dissolution of azilsartan-loaded solid dispersion, prepared by combining wet milling and spray-drying technologies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poozesh, S.; Lu, K.; Marsac, P.J. On the particle formation in spray drying process for bio-pharmaceutical applications: Interrogating a new model via computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Spray drying formulation of amorphous solid dispersions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thybo, P.; Hovgaard, L.; Lindeløv, J.S.; Brask, A.; Andersen, S.K. Scaling up the spray drying process from pilot to production scale using an atomized droplet size criterion. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, K. Spray Drying Handbook; Longman Scientific & Technical: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasundera, M.; Adhikari, B.; Aldred, P.; Ghandi, A. Surface modification of spray dried food and emulsion powders with surface-active proteins: A review. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadiwinoto, G.D.; Kwok, P.C.L.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Wong, S.N.; Chow, S.F.; Lakerveld, R. Integrated continuous plug-flow crystallization and spray drying of pharmaceuticals for dry powder inhalation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16843–16857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, P.; Bulusu, R.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W.; Singh, M. Amorphous solid dispersions: An update for preparation, characterization, mechanism on bioavailability, stability, regulatory considerations and marketed products. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, D.O.; Healy, A.M.; Corrigan, O.I. The effect of spray drying solutions of polyethylene glycol (PEG) and lactose/PEG on their physicochemical properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishad, J.; Selvan, C.J.; Mir, S.A.; Bosco, S.J.D. Effect of spray drying on physical properties of sugarcane juice powder (Saccharum officinarum L.). J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thybo, P.; Hovgaard, L. Droplet size measurements for spray dryer scale-up. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2008, 13, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaga, S.P.; Nikjoo, D.; Vuddanda, P.R. Experimental studies and modeling of the drying kinetics of multicomponent polymer films. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Zaitone, B.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Al-Shahrani, S.; Lamprecht, A. Drying of a single droplet of dextrin: Drying kinetics modeling and particle formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zaitone, B.; Lamprecht, A. Single droplet drying step characterization in microsphere preparation. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragon, R.; Hernandez, L.; Julia, J.E.; Jarque, J.C.; Chiva, S.; Zaitone, B.; Tropea, C. Study of the drying behavior of high load multiphase droplets in an acoustic levitator at high temperature conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2734–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, S.; Wu, J.X.; Laackmann, J.; Moritz, H.U.; Rantanen, J.; Rades, T.; Leopold, C.S. A case study of real-time monitoring of solid-state phase transformations in acoustically levitated particles using near infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zaitone, B.; Al-Zahrani, A. Modeling drying behavior of an aqueous chitosan single droplet using the reaction engineering approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner, O.; Brenn, G.; Rensink, D.; Tropea, C. Mass transfer from multiple droplets during drying in a tube levitator. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Liquid Automization and Spray Systems, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–20 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, I.J. Models of crystallisation in evaporating droplets. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1996, 398, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.W.; Jeffreys, G.V.; Mumford, C.J. A receding interface model for the drying of slurry droplets. AIChE J. 1986, 32, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handscomb, C.S.; Kraft, M. Simulating the structural evolution of droplets following shell formation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregson, F.K.A.; Robinson, J.F.; Miles, R.E.H.; Royall, C.P.; Reid, J.P. Drying kinetics of salt solution droplets: Water evaporation rates and crystallization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haque, M.A.; Hosain Oliver, M.M.; Putranto, A.; Adhikari, B. Drying and denaturation kinetics of Beta-Lactoglobulin during convective drying. J. Food Eng. 2018, 237, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.D.; Putranto, A. Reaction engineering approach (REA) to modeling drying problems: Recent development and implementations. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zaitone, B.; Al-Zahrani, A. Spray drying of cellulose nanofibers: Drying kinetics modeling of a single droplet and particle formation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021, 44, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putranto, A.; Chen, X.D. Drying of a system of multiple solvents: Modeling by the reaction engineering approach. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lierke, E.G. Akustische positionierung—Ein umfassender überblick über grundlagen und anwendungen. Acustica 1996, 82, 220–237. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H. Boundary Layer Theory; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zaitone, B.; Tropea, C. Evaporation of pure liquid droplets: Comparison of droplet evaporation in an acoustic field versus glass-filament. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3914–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M. A new approach to modelling of single droplet drying. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Xie, G.Z. Fingerprints of the drying behaviour of particulate or thin layer food materials established using a reaction engineering model. Food Bioprod. Processing 1997, 75, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, E.N.; Schettler, P.D.; Giddings, J.C. New method for prediction of binary gas-phase diffusion coefficients. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1966, 58, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Lin, S.X.Q. Air drying of milk droplet under constant and time-dependent conditions. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D. The basics of a reaction engineering approach to modeling air-drying of small droplets or thin-layer materials. Dry. Technol. 2008, 26, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.l.; Brenn, G.; Kastner, O.; Rensink, D.; Tropea, C. Evaporation of acoustically levitated droplets. Fluid Mech. 1999, 399, 151–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morse, P.M. Vibration and Sound, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.D.; Sidhu, H.; Nelson, M. Theoretical probing of the phenomenon of the formation of the outermost surface layer of a multi-component particle, and the surface chemical composition after the rapid removal of water in spray drying. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6375–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, O.; Brenn, G.n.; Rensink, D.; Tropea, C. The acoustic tube levitator—A novel device for determining the drying kinetics of single droplets. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2001, 24, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.; Ahmadlouiedarab, M.; Ghasemzadeh, K. CFD approach for the moisture prediction in spray chamber for drying of salt solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poozesh, S.; Bilgili, E. Scale-up of pharmaceutical spray drying using scale-up rules: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Zaitone, B.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Ahmed, O.; Saeed, U.; Taimoor, A.A. Spray Drying of PEG6000 Suspension: Reaction Engineering Approach (REA) Modeling of Single Droplet Drying Kinetics. Processes 2022, 10, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071365
Al Zaitone B, Al-Zahrani A, Ahmed O, Saeed U, Taimoor AA. Spray Drying of PEG6000 Suspension: Reaction Engineering Approach (REA) Modeling of Single Droplet Drying Kinetics. Processes. 2022; 10(7):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071365
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Zaitone, Belal, Abdulrahim Al-Zahrani, Osama Ahmed, Usman Saeed, and Aqeel Ahmad Taimoor. 2022. "Spray Drying of PEG6000 Suspension: Reaction Engineering Approach (REA) Modeling of Single Droplet Drying Kinetics" Processes 10, no. 7: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071365
APA StyleAl Zaitone, B., Al-Zahrani, A., Ahmed, O., Saeed, U., & Taimoor, A. A. (2022). Spray Drying of PEG6000 Suspension: Reaction Engineering Approach (REA) Modeling of Single Droplet Drying Kinetics. Processes, 10(7), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071365





