Abstract
In order to investigate the effects of Cl− and SO42− based fertilizers on the accumulation of cadmium (Cd) in rice plants, a long-term experiment, which has been conducted since 1975, and a short-term pot experiment were designed. The results of the long-term experiment showed that the highest total grain Cd was found in the treatment of fertilizers with rich Cl−, which was 72.7% higher compared to conventional fertilization (CF). However, there was no significant difference between the CF and fertilization with rich SO42− treatments. This phenomenon can be explained by the concentrations of the EDTA extractable Cd being significantly increased by 60% under Cl− treatment, while SO42− treatment showed no significant effect. In the short-term trial, compared to CF, Cd concentrations in the roots increased by 1.07 and 0.93 times in the Cl− and SO42− treated soils, respectively, under Cd1.2 exposure. Meanwhile, Cd concentrations in the shoots enhanced by 96% in Cl− treated soil but decreased by 34.6% in SO42− treated soil. It was therefore concluded that fertilizer-borne Cl− significantly increased the Cd concentration in rice grains in the long-term experiment, but fertilizer-borne SO42− had no significant effect on the Cd concentration in rice grains. However, in the pot experiment, SO42− based fertilizers decreased Cd transport to the shoots of a rice plant grown in a Cd contaminated soil. These findings will improve the rational fertilization of Cd contaminated soils and the production of safer rice.
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) is a non-essential element for crop growth and is a soil pollutant [1]. It can enter the human body through the consumption of Cd contaminated crops and agricultural products, leading to potential health problems [2]. Potassium chloride and potassium sulfate are commonly used as fertilizers in agriculture. It has been reported that the amount of Cd transferred from soil to rice is affected by many factors, such as the total soil Cd and its activity, soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), cation exchange capacity (CEC), other ions, and different genotypes of rice [3,4,5]. However, the impact of Cl− and SO42− on cadmium in crops has also been studied [1,6,7,8], but the long-term effects of fertilizer-borne chloride and sulfate anions on Cd in rice have rarely been reported [8,9,10,11].
Cd pollution in agricultural soils has become a major issue in China [12,13]. Since the 1990 survey, Cd levels in Chinese soil have risen and are constantly increasing. Cd contamination was found on 20,000 ha of agricultural land in China [14]. Cd levels in rice grain produced on heavily contaminated soil have surpassed the worldwide threshold limits of 0.4 mg kg−1, leaving the grains unsafe for consumption [15]. The Cd content in rice across China ranged from 0.01 to 5.50 mg kg−1, while the maximum median value of 0.73 mg kg−1 was noted in the Hunan Province [16,17]. In Qiyang, a total of 0.56 mg kg−1 Cd was detected in soil and after two years of study it was found that brown rice of the wild type variety exceeded the Chinese Cd limit by 2.5–3 times [18]. The Qiyang agriculture investigation station has used long term fertilization of rice acreage for nearly half a century [19]. Red soil is a common soil taxon in China’s subtropical zone, while it is the country’s principal acidic farmland soil, with greater heavy metal availability and up-take [19,20].
Other research found that long term fertilizers and manure inputs contaminated red soil with Cd, suggesting that Cd might be agglomerated in edible sections of crops [21]. It was reported that Cd concentration in cattle dung was as high as 1.15 mg kg−1 [19]. This amount of Cd in manure is remarkable comparable to that obtained by [22] in a long term fertilization trial in Qiyang, where 1.13 mg kg−1 Cd was found in swine dung. According to [23], four years of the application of phosphate fertilizers resulted in an annual soil Cd agglomeration of 0.0007 to 0.032 mg kg−1. The authors of [22] reported that 17 years of NPK supplementation enhanced aqua regia extractable Cd in top-soils by 18.9-fold in northeast China. Another study found that the long term addition of NPK + green manure, NPK + swine manure, and solely swine manure raised the total Cd concentrations in rice grain by 202%, 146%, and 100%, respectively [24].
It is well-known that Cl− and SO42− have a remarkable influence on Cd movement in paddy soil to rice grains. Chloride-containing fertilizers can alter the Cd activity of soil by increasing the mobility of Cd via the formation of chloro-Cd complexes [25] and increasing the Cd concentration in the soil solution [26]. Thus, chloride can also improve the bioavailability of Cd. It was reported that the Cl content in the soil solution phase was shown to enhance Cd solubility and thus, resulted in its accumulation in plants [11]. The CdCl+ activity in the soil solution has been shown to be strongly correlated with the Cd uptake of plants [11], and the complexation of Cl− with Cd2+ can form the CdCln(2−n) complex, which might increase the bioavailability of Cd [27].
Cl− and SO42− are common anions that can potentially affect the bioavailability of Cd by plant roots in soil [28]. These ions can freely complex Cd2+; thus, enhancing the mobility of Cd2+ in soils [29]. It has been observed that with the rising Cl− levels in solution from 0.01 mM to 120 mM, a remarkably raised amount of Cd2+ was found in both below and above ground plant parts in Swiss chard in the solution [27]. Chloride-Cd complexing may shift Cd from the solid to the solvable fraction, thus improving solvability and bioavailability [30,31]. Thus, a chloro-Cd conglomeration not only enhances its transportation to roots but direct uptake by plant roots may also occur, although this process is distinct from the agglomeration of unassociated Cd2+ [25]. Sulfur could also promote the mobility of Cd as it enhances absorption and agglomeration of Cd in plants due to the release of SO42− from fertilizers [32,33]. Two possible mechanisms are responsible for higher Cd taken up by SO42− fertilization: First, sulfur can lower soil pH, hence increase Cd bioavailability that would be helpful to plant absorption [32,33]. Second, sulfur may provide the raw materials for methionine (MT), gluthatione (GSH), phytochelations (PC), and non-protein thiols (NPT) in plants, which can chelate intracellularly with Cd, boosting Cd uptake, transport, and detoxification [34,35,36,37]. Conversely, (NH4)2SO4 fertilizer remarkably enhanced rice grain production while lessening the available Cd content in soil compared to (CO(NH2)2), whereas NH4Cl showed the opposite effect [38]. This might be because sulfur can enhance the acidic condition of soils, which triggers calcium, which in return improves soil pH for better element uptake by plants [39,40]. Sulfur may increase the Cd adsorption capability by encouraging the formation of cell wall constituents, preventing Cd from being transported through the apoplastic tract [41]. In addition, greater expression of cation/proton exchanger 3 (CAX3) and ABC transporters, in addition to a higher amount of cysteine as well as the GSH/GSSR value, lead to the detoxification and enhancement of Cd compartmentalization in root vacuoles, thus reducing the transportation of Cd to the shoots through the symplastic system [41]. Furthermore, S-induced the promotion of PC in rice roots under low Cd soil, thus limiting and hindering Cd transportation in brown rice [6]. However, the effect of the long-term application of Cl− and SO42− ions has not yet been clarified, with contradictory results reported in the literature. Thus, we hypothesized that the long-term Cl− and SO42− application in the field, as well as short-term application in pots, could increase Cd accumulation in rice plants by increasing its bioavailability in soil. Therefore, the aim of this experiment was to investigate how the long-term application of Cl− and SO42− fertilizers affected the buildup of Cd in soil and paddy rice grains. Further, the study aimed to determine the influence of short-term Cl− and SO42− fertilizer application on Cd accumulation in roots and shoots in rice plants at two Cd concentrations.
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Site and Design
The long-term experiment of a double rice cropping system began in 1975 at the Qiyang Red Soil Experimental Station, Hunan Province, China (Figure 1) [21,42]. The amounts of fertilizer used in the three treatments are shown in Table 1 and they were applied to every plot before sowing for each rice season, with the same nutrient rates of N = 150 kg ha−1, P2O5 = 75 kg ha−1, and K2O = 225 kg ha−1 in each plot. The experimental plots in the field were 25 m2 in size and were randomly arranged with three replications per treatment. Urea, superphosphate, and KCl treatments were used to represent conventional fertilization (CF), the SO42− treatment was a fertilizer rich in SO42− ions ((NH4)2SO4 + superphosphate + K2SO4), while the Cl− treatment was a fertilizer rich in Cl− ions (NH4Cl + KCl + KH2PO4). The experimental area was cultivated every year using a double rice cropping system (one year two rice crops, early rice and later rice). The soil properties are shown in the next section of the changes in soil physicochemical characteristics following long-term Cl− and SO42− application. The samples of field soil and rice grains were collected in October 2018.

Figure 1.
Anion long-term experiment at the Qiyang Red Soil Experimental Station, Hunan Province, China.

Table 1.
Fertilizer amounts used in the three treatments in the long-term experiment (plot area: 25 m2) and the pot experiment.
2.2. Soil Pot Experiment
To further observe the effects of Cl− and SO42− on Cd uptake by rice, a soil pot experiment was designed. The short-term trial was carried out in the glasshouse of CAAS in Beijing in order to explore the impact of Cl− as well as SO42− fertilizers on the bioavailability and transformation of Cd in soil and plants. During 2018, soil samples were obtained from the long-term experimental CF, Cl−, and SO42− treatment plots at a depth of 0–20 cm in Qiyan, Hunan Province, China. The treatments consisted of three soils from the long-term experimental treatments (CF, Cl, and SO42−) and two rates of cadmium as CdSO4 (which are expressed by Cd0 and Cd1.2, separately). The soil amount for each pot was 200 g after it had been air-dried and passed through a 2 mm sieve. There were a total of six different treatments with three soil samples (from CF, Cl−, and SO42− long-term treatment plots) with two Cd exposures (Cd0 and Cd1.2). The factorial pot experiment had two factors: main factors included “without Cd spiked soil (i.e., 0 mg kg−1 donated as Cd0) and Cd spiked soil (i.e., 1.2 mg kg−1 donated as Cd1.2).” Meanwhile, the three treatments CF, Cl−, and SO42− served as sub-factors. The pot experiment fertilizer application rates were the same as with above long-term experiment treatments (Table 1). The physicochemical characteristics of soil, including background soil Cd, are presented in Table 2. All amendments were repeated three times. Rice seeds (Oryza sativa L.) of the “Huang Hua Zhan” variety from Changsha City were disinfected in 30% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for 20 min, cleansed completely by ultrapure water, then grown for 10 days in quartiz sand treated with acid. After germination, young plantlets were transplanted into pots and grown for 30 days.

Table 2.
Physicochemical properties of the soil following long-term applications of Cl−- and SO42−-based fertilizers.
2.3. Soil and Plant Analyses
2.3.1. Processing of the Total Cd Concentration in Plant Samples
The air-dried rice grains from the long-term experiment were separated from the glumes. Plant roots and shoots from the soil pot experiment were cleansed with normal water then with distilled water. Then the samples were oven dried at 100 °C to reach a constant weight. The dried rice plant materials (roots, shoots, and grains) were crushed into thin particles, then precisely balanced having weight of 0.5 g and placed into contaminant free dehydrated ingestion tubes. Subsequently, 6 mL of conc. nitric acid as well as 3 mL H2O2 was poured into the digestion tubes, and they were left overnight. Thereafter, the tubes were subjected to excessive compression-wrapped microwave fragmentation where the heat remained raised to 200 °C and kept for 2 h. After digestion, the pipes remained placed onto a warming chunk at 80 °C for about 2–3 h. The solution was allowed to cool to ambient temp. After dilution to 50 mL with deionized water and adding 5% HNO3, the solution was gently shaken and filtered. The overall cadmium concentration in the digested solution was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) Perkin Elmer NexION 2000 [43].
2.3.2. Processing of the Total Cd Concentration in Soil Samples
Soil samples from the long-term trial taken at depths of 0–20 cm and from the pot experimentation were desiccated in air at the ambient temp. The samples were then crushed and sieved via a 0.15 mm mesh sieve. Zero point five grams of soil samples was precisely weighed and placed into 100 mL cleansed, dehydrated ingestion pipes, following the addition of 9 mL HNO3 as well as 3 mL hydrofluoric acid (HF). Then the samples remained over night at room temp. The samples were then subjected to excessive compression-wrapped microwave digestion where the heat remained raised to 200 °C and was maintained for 2 h. Following digestion, the samples were placed onto a heating block at 80 °C for 2–3 h. The digested solutions were transferred into 50 mL tubes after cooling and samples were diluted by deionized distilled water comprising 5% HNO3.The samples were thoroughly shaken and filtered, and then analyzed by ICP-MS [43].
2.3.3. Processing of the Soil Samples for the EDTA-Cd Concentration
One-gram of soil was accurately weighed and placed into a 50 mL polypropylene tube and then 5 mL of 0.05 M EDTA-Na2 was added. The samples were shaken in a reciprocal shaker, rotating at 200 rpm min−1 for 30 min at a temperature of 20 °C. Then the samples were centrifuged at 2000 g min−1 for 15 min. The supernatant was filtered through a filter paper and analyzed by ICP-MS [44].
2.3.4. Quality Assurance and Control
Each soil sample from the three replicates was digested and analyzed. The accuracy of the results was determined by subjecting the data to a Q-test, which removed asymmetrical errors from the observations (n = 3) at a 95% confidence level. The quality of the results was assured by comparing them to standard reference materials for soil (GBW07605) [45] and plants (GBW08513) [46] from the National Research Center for Standards of China. The Cd retrieval percentage from the soil was 94.7%.
2.3.5. Determination of Total Cl− in Soil
Total Cl− was determined by accurately weighing a 10 g soil sample, adding 0.5 g activated carbon, and then 50 mL deionized water. The solutions were shaken in an oscillator for 5 min and the filtrate remaining after centrifugation was collected. After filtration, a 20 mL sample solution was extracted using a pipette and placed in a 100 mL conical bottle. Two drops of phenolphthalein indictor were added together with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution or 0.05 mol L−1 sulfuric acid to cause the red color of the solution to fade, and then four drops of potassium chromate indicator were added. Finally, a titration was performed using a silver nitrate standard solution [47,48].
2.3.6. Determination of Total SO42− in Soil
Total SO42− was measured by accurately weighing a 10 g soil sample and placing it in a 100 mL centrifuge tube. After adding 50 mL deionized water and 0.5 g activated carbon, the samples were shaken in an oscillator for 5 min. The samples were centrifuged and filtrated. Using a pipette, a 25 mL sample solution was extracted and placed in a 50 mL colorimetric tube. Then, 1 mL stabilizer and 1 g barium chloride were added, and the tube was immediately shaken until the grains were dissolved. Within 15 min, readings were conducted at 420 or 480 nm. To obtain a calibration curve, SO42− standard solutions were prepared [49].
2.3.7. Soil Characterization
The basic physicochemical properties of the test soil are presented in (Table 2). Statistically, no remarkable change was noted in soil pH amongst the Cl− plus SO42− treatments, but pH in both treatments remained markedly lower compared to CF treatment. The soil OC, TN, TP, TK, and total Cd were not significantly different (p < 0.05) in any of the treatments. Compared to CF, the total Cl− significantly increased by 100% and the soil pH decreased by 0.33 in the Cl− plots, and the total SO42− significantly increased by 74.6%, and the soil pH decreased by 0.37 in the SO42− plots. The results showed that the long-term use of Cl−- and SO42−-based fertilizers led to an accumulation of Cl− and SO42− in the soil. It is also noteworthy that one of the fertilizers used in the CF treatment was KCl, resulting in a Cl− addition of 0.42 kg per plot, which was 2.5 times lower than the Cl− treatment but significantly greater than the SO42− treatment. However, there was no difference in total soil Cl content between the CF and SO42− treatments. The highest total Cd content (0.44 mg kg−1) in soil was found in the SO42− treatment followed by the Cl− and CF treatments (0.40 and 0.39 mg kg−1, respectively), which were not significantly different from each other. This indicates that Cl−- and SO42−-based fertilizers showed no remarkable impact on the agglomeration of Cd in soil.
2.3.8. Statistical Analysis
An analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted using XLSTAT v. 2015 software [50]. The means were compared by a Duncan test at the 5% level of significance. Correlation analysis was performed by using the principal component test (PCA) in IBM SPSS Statistics software. Meanwhile, a generalized linear model (GLM) was used to predict the enhancement or declination of Cd in rice grain by fertilizers treatments.
3. Results
3.1. Available and Total Cd in the Soil and Rice Grains
The EDTA-Cd was determined so that the Cd availabilities could be compared. The EDTA-Cd levels increased by 60% in the Cl− treatment compared to CF, but no substantial variation was observed amid SO42− and CF amendments (Figure 2).
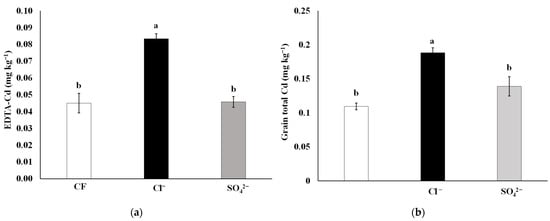
Figure 2.
Effects of long-term field Cl− and SO42− fertilizer applications on (a) EDTA extractable Cd in the soil and (b) Cd concentrations in the rice grains. Vertical bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3). Different lower-case letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 according to Duncan’s test.
The grain total Cd was significantly different among the three treatments. The lowest grain total Cd (0.11 mg kg−1) was found in the CF treatment, while the highest (0.19 mg kg−1) was found in the Cl− treatment, which was 72.7% higher than in the CF treatment. There was no significant difference in the grain total Cd between the CF and SO42− treatments (Figure 2).
3.2. Effects of Cl−- and SO42−-Based Fertilizers on Cd Concentrations in the Pot Experiment Rice Roots and Shoots
The purpose of the pot experiment was to investigate the Cl, and SO42− treatment effects on the transfer of Cd from soil to rice. The results showed that Cd levels in the roots and shoots were enhanced by the Cl− treatment (Figure 3). Compared to the CF in the Cd0 treatment, the Cd concentrations in roots increased by 36.5 and 24 times, and in shoots by 45 and 15.5 times when the Cl−- and SO42−-based fertilizers were applied, respectively. Under Cd1.2, compared to CF, the Cd concentrations in the roots increased by 1.07 and 0.93 times in the Cl− and SO42− treated soil, respectively; whereas in shoots, the Cd concentration increased by 96% in Cl− treated soil, but decreased by 34.6% in SO42− treated soil under Cd1.2 exposure (Figure 2). This demonstrates that cadmium transference over the soil to rice was higher in the Cl− treatment than in the SO42− treatment.
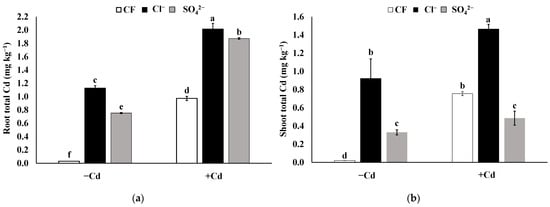
Figure 3.
Effect of Cl−- and SO42−-based fertilizers on rice root and shoot total Cd in the Cd1.2 (1.2 mg Cd kg−1) and Cd0 (0 mg Cd kg−1) treatments. (a) In the roots and (b) in the shoots. Vertical bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3). Different lower-case letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 according to Duncan’s test.
3.3. Prediction of Cd Accumulation in Rice Grain in Long Term Experiment
Equation (1) shows the GLM model for the variables. The GLM model revealed that Cl− fertilization increased Cd levels in rice grain, while SO42− levels decreased Cd content in rice grain. According to GLM model, the Cd content in rice grain reduced by 0.02 and 1.90 units, respectively, with each unit increase in CF and SO42− fertilization, whereas with a one unit increase in Cl− fertilizer the Cd amount in rice grain increased by 0.52 unit.
Cd grain (mg kg−1) = −0.96 log10 + (0.02 CF) + (0.52 Cl−) + (−1.90 SO42−), Adj. R2 = 0.97
3.4. Prediction of Cd Accumulation in Rice Shoot in Short Term Experiment
For the short-term experiment, the GLM model was also used, and the following questions were set. According to the model, the content of Cd in rice grain declined by 13.6 and 4.50 units after Cd0 exposure with one unit rise in CF and SO42− treatments. Whereas, in Cd0 plots the Cd level increased by 2.96 units for every one unit rise in Cl− fertilization. Meanwhile, a one unit increase in CF and Cl− treatments raised the amount of Cd in rice grain by 4.35, and 3.16 units, respectively, under Cd1.2 exposure. On the contrary, a one unit increase in SO42− fertilization reduced Cd levels in grains by 4.53 units under Cd1.2 exposure.
Cd0S (mg kg−1) = −0.61+ log10 (−13.6 CF) + (2.96 Cl−) + (−4.50 SO42−), Adj. R2 = 0.97
Cd0S (mg kg−1) = −0.44 + log10 (4.35 CF) + (3.16 Cl−) + (−4.53 SO42−), Adj. R2 = 0.97
3.5. PCA Analysis
The results of PCA analysis for the long-term experiment showed that pH displayed a weak negative correlation with Cl−, EDTA-Cd, as well as Cd, in rice grain. SOC showed a relatively strong positive relationship with soil Cd, and negative with Cd amount in rice grain. Most notably, the Cd content in rice grain had a strong positive association with Cl− and EDTA-Cd (Figure 4).
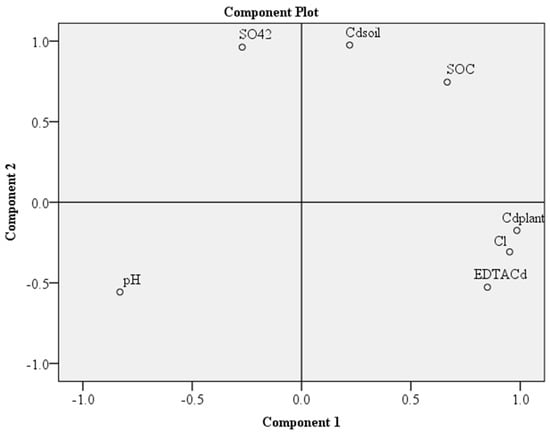
Figure 4.
PCA analysis for the long-term experiment exhibited biplots for total 7 variables which showed that the first principle component (PC1) accounted for 55.0% and the second principle component (PC2) accounted for 45.0%. pH = soil pH, SOC = soil organic carbon, EDTA Cd = EDTA extractable Cd in soil, Cl = total Cl− contents in soil, SO42 = total SO42− content in soil, Cd plant = total Cd in rice grain.
Meanwhile, in short-term pot experiment, pH exhibited a weak and high negative correlation with Cl−, EDTA-Cd, and Cd in shoots under Cd0, as well as Cd1.2 exposure (Figure 5), whereas SOC positively correlated to Cd in soil and root under Cd0 and Cd1.2 exposure. Cl− also exhibited a positive and strong relation with EDTA-Cd as well as Cd in shoot under Cd0 and Cd1.2 exposures in the short-term experiment.
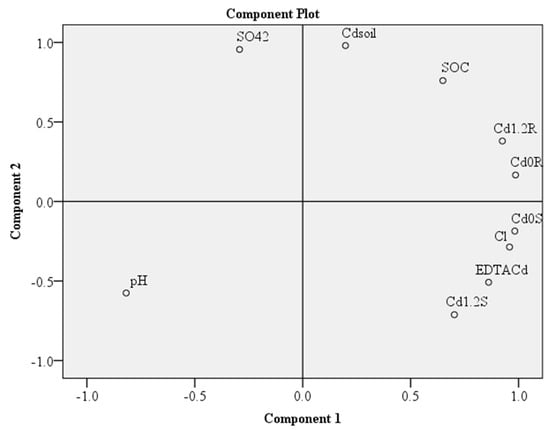
Figure 5.
PCA analysis for long term experiment exhibited biplots for total 10 variables which showed that the first principle component (PC1) accounted for 61.2% and the second principle component (PC2) accounted for 38.7%. pH = soil pH, SOC = soil organic carbon, EDTA Cd = EDTA extractable Cd in soil, Cl = total Cl− contents in soil, SO42 = total SO42− content in soil, Cd0R = total Cd in rice root under Cd0 exposure, Cd1.2R = total Cd in rice root under Cd0 exposure, Cd0S = total Cd in rice shoot under Cd0 exposure, Cd1.2S = total Cd in rice shoot under Cd1.2 exposure.
4. Discussion
There are some interesting findings in the soil physicochemical parameters after long-term fertilizer supplementation. For instance, SO42−-soil have more Cl− than CF, despite the fact that no Cl− was applied (Table 2). The possible explanation could be the leaching of Cl into the deeper layers due to precipitation [51]. There is a downward migration of Cl when rainfall exceeds evaporation. Rainfall, on the other hand, may cause the reverse tendency in Cl, namely upward migration, resulting in a higher Cl concentration in the soil. Thus, Cl movement in soil is mostly influenced by water fluxes [52]. Liu et al. reported that the Cl level in soil enhanced significantly after being fertilized with Cl-borne fertilizer at depth (0–60 cm), but the Cl concentration in the soil could not rise during continuous addition over 5 years with an average precipitation of 1475 mm in the field trial [53]. Due to the heavy rains, Cl-containing fertilizer disintegrated quickly, causing diffusion and leaching. These processes are most common during the rainy season, which lasts from March to August [53]. During the months of June to September, the Cl dissolving rate was higher than the leaching rate, but the converse was true from September to December, which helps to explain why the soil Cl concentration was highest in September [53]. There was a difference (although minor) in SO42− concentration between CF and Cl− treatments (Table 2). The ionic strength is related to the charge equilibrium in the soil that is dependent on the reaction of ion exchange and elemental loss resulting from soil leaching and acidification [54]. The discharge of cations rose, thus leach loss further improved in the acidic soil [55] containing Cl, N-NO3, as well as S as the key concomitant anions [56]. Thus, it indicated that Cl and S contents were remarkably greater compared to other cations in the leachate [53]. In addition, the bioavailable form of S in the soil was SO42−, thus fluctuation in cationic migration might be due to the lower solubility of CaSO4, causing a slower migration of SO42− in the soil than Cl [53]. Another reason is the strong absorption capability of iron and aluminum oxides for SO42−, which may be higher in acidic soil [57]. SO42− also makes complexes with metal cations (i.e., Ca, Fe, A, etc.), thus resulting in its storage in the soil, leading to more absorption of S by plants [53]. Soil Cd content in the Cl− fertilized field was non-significantly lower than CF and SO42− treatments, even though there was increased Cd mobilization due to the Cl− addition (Table 2). This may be due to the long-term addition of phosphate fertilizers, which are the biggest source of Cd in soil. There was an increase in total and bioavailable Cd in soil observed when N and P fertilizers were continuously applied [19,21]. Although Cl could make comparatively stable complexes with soil Cd in solution, it caused Cd to migrate from a solid to solution (i.e., CdCl+, CdCl20, CdCl3−, and CdCl42−) and enhanced Cd solubility [58]. It was also shown that K fertilizers reduced the abundance of some soil microbe indices that lowered soil acidity and CEC, while increasing the abundance of other microbes that increased soil total organic matter (TOM) and CEC [59]. As a result, soil microbes were observed to alleviate the decline in soil pH, TOM, as well as CEC, resulting in a decrease in soil-bioavailable Cd [59]. That is why, despite the fact that fertilizers increased total Cd in soil, it was non-significantly lower in the current experiment due to higher Cd mobility caused by Cl− anions.
In the long-term experiment, EDTA-Cd was significantly increased by Cl− addition, while SO42− addition had no significant effect (Figure 2). Wang et al. (2020) also reported that by using NH4Cl over for 7 years in soil, DTPA-extracted cadmium in sewage-borne Cd contaminated soil compared to urea application was remarkably enhanced; however, the amount of DTPA extractable Cd in soil was significantly decreased by (NH4)2SO4 application compared with urea application. Unfortunately, the amount of Cd taken up by rice was not reported in [38], although the expression of Cd transport genes was tested. Compared with conventional fertilization (such as urea), the long-term application of (NH4)2SO4 will not increase the soil Cd extractability by EDTA or DTPA. The slightly increased concentration of Cd in rice grains may result from the decrease in soil pH due to the long-term application of (NH4)2SO4. Attention should be paid to the reactions and transformation of SO42− in paddy soils, and effects of the application of SO42− on the transfer of Cd from the soil–root–shoot–grain in rice which will be discussed later on. Compared with conventional fertilization (such as urea), the long-term application of NH4Cl significantly increased the soil Cd extractability by EDTA in the current study or DTPA [38], resulting in the increased concentration of Cd in rice grains. Cd increased in rice by Cl− addition to soil may attributed to the formation of Cd-Cl complexes in soil and plant which can improve solubility and movement of Cd from the binding sites in soil to the root surfaces and plant interior [30]. In addition, the application of Cl− might result in a decreased soil Cd-sorption capacity by increasing the ionic strength in the soil solution [8,38]. However, the results from the current study first proved the concentration of Cd in rice and extractability of Cd in soil can be significantly increased by fertilizer-borne chloride after long-term application over 43 years.
In the long-term field experiment, KCl in the CF treatment was employed, but the Cd uptake in the rice grain did not increase. This might be due to application of KH2PO4 fertilizer in the CF treatment. Moreover, there may be two possible reasons: First, due to Cd-Cl complexes and cation competition resulting in the formation of CdCl+ and CdCl2. As a result, CdCl may leach down from the soil surface to the subsoil surface [60,61]. The second may be the effect of KH2PO4 because phosphate fertilizers can change the physicochemical characteristics of soil, such as soil available phosphate, soil particle surface charge, and soil pH [62]. P fertilizers can also directly precipitate Cd content in soils. Furthermore, H2PO4− is considered as a dominant form in the acidic soil solution. H2PO4− could exchange and desorb the OH ion already adsorb in soil colloids. As a result, soil pH increased. The increased in soil pH might cause immobilization and precipitation of Cd in soils in the form of Cd-carbonates complexes, thus decrease soil Cd uptake by plants [38,63].
In the pot experiment with the soils of long-term application of fertilizer-borne chloride and sulfate anions, long-term supplementation of Cl− to soil significantly raised the total Cd in roots and shoots with and without Cd addition (Figure 3). There is some evidence to suggest that supplying soluble Cl− can increase the bioavailability of Cd in field soil for wheat, Swiss chart, and potato tubers [64] and in a solution culture system for Swiss chard [27]. Furthermore, it is noted that the Cd-Cl complexation improved the bioavailability of biosolids and released Cd close to the extent as released by soil fertilizer cadmium [11]. However, the experiments mentioned above are mostly the addition of Cl− through fertilization of Cd contaminated soil. Not many long-term field experiments have been conducted to know the effects of fertilizer-borne chloride on the intrinsic soil properties as well as on the bioavailability of Cd added to soil. The results from the pot experiment indicated that continued supplementation of chloride-containing nutrients significantly raised the bioavailability of Cd in soil. In other words, the soil with long-term application of fertilizer-borne chloride had a higher ability to supply Cd to plants.
In the pot experiment with the soils of long-term application of fertilizer-borne chloride and sulfate anions, the SO42− treatment without Cd addition increased the Cd content in below- and above-ground plant parts, whereas it remarkably lessened the Cd level in shoots compared to the corresponding conventional fertilization (Figure 3). First, the findings showed the behavior of cadmium in soil is different from Cd added freshly to soil. Second, the continued supply of sulfate-containing fertilizers can increase the uptake of Cd by roots but not by shoots when Cd was added to soil. McLaughlin et al. (1998) observed sulfate complexation of cadmium inside nutrient solvability had a lesser influenced on Cd taken up by plants, and the Cd level in stems of 19-day-old seedling of Swiss chard was slightly, yet markedly, enhanced with improving the amount of SO42− in soil. In the current study, it was found that the continued supplementation of sulfate-containing fertilizer raised Cd inside roots and shoots for the soils without Cd addition, which is consistent with previous findings [28], but the long-term application of fertilizer-borne sulfate significantly decreased the Cd concentration in shoots in the soils with Cd addition, which suggested that the results may depend on the pedogenic or anthropogenic sources of soil Cd. Moreover, the complexed reactions and transformations cannot be ignored. However, Zhang et al. [65] reported that the application of sulfur to soil showed the potential to reduce Cd transfer from roots to shoots, which may be similar to sulfate, although sulfur may reduce the soil pH and increase Cd bioavailability [63]. In addition, sulfate fertilizers increased Heavy Metal ATPase 3 (HMA3) expression in the roots. This could have improved iron plaque formation, which can sequester Cd into cell walls and vacuoles [38,65,66,67]. Therefore, fertilizer-borne SO42− decreased Cd transport to the shoots of a rice plants grown in a Cd contaminated soil but had no significant effect on the Cd concentration in rice grains in the long-term experiments.
Empirical soil–plant transfer models outperform compared to other models in terms of predicting Cd concentration in crops. GLM models are increasingly being employed in environmental science and agro-ecology research. According to GLM models in Equations (1)–(3), it can be observed that Cl− fertilization increased the amount of Cd in rice grains, whereas SO42− levels decreased Cd in rice under both long-term field and short-term pot experiments. Zhang et al. (2021) used the GLM model and reported that the simultaneous impact of pH and Cd in porewater displayed a good prediction for the amount of Cd in soybean grain [68]. Earlier studies explained that an increase in soil Cl may increase the movement of Cd from binding sites in soil to root surfaces by forming Cd-Cl complexes, such as CdCl+ and CdCl2, in pore water. In addition, the application of Cl might resulted in a decreased soil Cd-sorption capacity by increasing the ionic strength in the soil solution [8,38]. Similar results were reported by [7], who observed that Cl application enhanced the availability of soil Cd. The possible mechanism may be due to the high concentration of Cl− in the soil solution increasing Cd2+ free ion activity by complexation reactions [7]. The decrease in shoot Cd concentration by SO42− fertilizer under 1.2 mg Cd kg−1 stress in the present experiment may be due to the accumulation and subcellular distribution of Cd by rice seedlings in presence of S. Moreover, the localization of Cd in the cell-wall fraction followed by the soluble fraction (mainly contain of vacuoles) in both shoots and roots [9,67] has been observed. Consistent with our findings, [65] noted that Cd was mainly accumulated in the roots of rice plant, ranging from 6.57 to 9.46 mg kg−1, while stem and leaf Cd concentrations ranged from 0.53 to 1.82 mg kg−1 at the maturation stage. Furthermore, the application of gypsum reduced the stem and leaf Cd concentrations compared to control during the entire rice growth cycle. Rice roots are the main organ which absorb and accumulate Cd. During the tillering period, gypsum treatment significantly enhanced root Cd accumulation, which might be due to absorption of Cd ions by iron and manganese oxide on the root surface with mobile sulfate, or because of a reduction in soil mobile Cd speciation [65,69].
The findings of PCA analysis for the long-term experiment revealed that the pH in rice grain had a weak negative association with Cl−, EDTA-Cd, and Cd. The amount of Cd in rice grains, in particular, demonstrated a strong positive relationship with Cl and EDTA-Cd (Figure 4). Meanwhile, in the short-term pot experiment, pH in shoots exposed to Cd0 and Cd1.2 showed a relatively strong negative connection to Cl−, EDTA-Cd, and Cd. Cl had a positive and strong relationship with EDTA-Cd as well as Cd in shoots under Cd0 and Cd1.2 exposures in the short-term experiment (Figure 5). The results are consistent in that the Cd concentration in rice shoot was significantly and positively correlated with the supplementation of Cl− to the soil [7]. The possible reasons may be the increased concentration of Cl− decreased the soil pH, increased the dissolve organic carbon in soil pore water, or enhanced the complexes of Cd2+ and Cl−, consequently releasing Cd from the solid phase into the solution phase; the Cl ions in the soil increased the uptake of CdCl+ rather than Cd2+ by the roots, thus enhancing the translocation of Cd in rice tissues [7]. Another explanation is that the soil DTPA-Cd concentrations showed a nearly opposite pattern to the changes in soil pH under Cl− treated plots compared to the CF treatment [38].
SOC displayed a positive correlation with total Cd in soil under the long-term experiment (Figure 4), while it also showed a positive correlation with total Cd in soil as well as in root under Cd0 and Cd1.2 exposures (Figure 5). Previous studies also showed that Cd agglomeration in rice grain was remarkably affected by SOM and pH [70,71]. SOM is a significant source of trace metals in interchangeable fractions in soil, thus facilitating metal uptake by roots. It has been reported that organic fertilizers in China often contain high amounts of metals that might explain the positive link amid SOM and DTPA-Cd in agricultural soils [71,72]. SOM contain many fractions, including dissolved OM (DOM) and fulvic/humid acids, function as both source and an active surface buffer, acting as chelates and increasing metals availability [71,73]. Furthermore, DOM may improve plant nutrients bioavailability by boosting CEC in soils, supplying metal chelators, thus enhancing nutrient solvability in the soils [71,73].
5. Conclusions
Large amounts of Cl− and SO42− accumulated in the soils through long-term Cl− and SO42− fertilizer applications remarkably raised the amount of cadmium in rice grains, while SO42−-based fertilizers had no significant effect on the total Cd concentrations in rice grains. This could be attributed to chloro-Cd complexation, which increased Cd availability in soil solution and consequently uptake. The EDTA-Cd concentration was significantly increased by Cl− addition, whereas SO42− addition showed no substantial impact. The Cd transfer ability from soil to rice remained greater in the Cl−-based fertilizer amendments as compared to SO42−-based fertilizer amendments. The results suggest that the application of Cl−-based fertilizers in paddy fields should be avoided because Cl− ions not only increased Cd uptake and translocation by rice, but they are also emerging environmental pollutants.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the study, B.H., Y.M., J.L. and J.G.; formal analysis, methodology, and investigation, B.H., A.U. and N.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.H.; writing—review and editing, B.H. and Y.M., supervision and funding, Y.M., J.L. and J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800406) and the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (0159/2019/A3).
Data Availability Statement
The data may be available after request from corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support from the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (0159/2019/A3) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800406).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declares no conflict of interest.
References
- de Livera, J.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Kirby, J.K.; Beak, D.G. Cadmium solubility in paddy soils: Effects of soil oxidation, metal sulfides and competitive ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-H.; Wang, S.-L.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, M.-K. Dynamics of cadmium concentration in contaminated rice paddy soils with submerging time. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 11, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Camara, A.Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhu, L.; Li, H. Cadmium dynamics in soil pore water and uptake by rice: Influences of soil-applied selenite with different water managements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Deng, D.-M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C. Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: The effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, F.; Cao, W.; Yang, Z.; Hu, M.; Sun, W. Cadmium solubility in paddy soil amended with organic matter, sulfate, and iron oxide in alternative watering conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Hu, Z. Residual effects of sulfur application prior to oilseed rape cultivation on cadmium accumulation in brown rice under an oilseed rape–rice rotation pot experiment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Khaliq, M.A.; Xie, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G. Chlorine weaken the immobilization of Cd in soil-rice systems by biochar. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, T.; Kawabata, M.; Sase, A.; Fukami, M. Cadmium and Nutrient Heavy Metals Uptake by Rice, Barley, and Spinach as Affected by Four Ammonium Salts. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q. Cadmium accumulation, sub-cellular distribution and chemical forms in rice seedling in the presence of sulfur. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, N. Chemical speciation of cadmium and sulfur K-edge XANES spectroscopy in flooded paddy soils amended with zerovalent iron. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weggler, K.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Graham, R.D. Effect of Chloride in Soil Solution on the Plant Availability of Biosolid-Borne Cadmium. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, B.; Ashraf, M.N.; Abbas, A.; Li, J.; Farooq, M. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: Effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Shao, S.; Ni, H.; Fu, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Min, X.; She, S.; Chen, S.; Huang, M.; et al. Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Molecular mechanism of rice responses to cadmium stress. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2013, 27, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, L.; Liao, X.; Chen, T.; Yan, X.; Xie, H.; Wu, B.; Wang, L. Regional assessment of cadmium pollution in agricultural lands and the potential health risk related to intensive mining activities: A case study in Chenzhou City, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2016, 92, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L. Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 17941–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z.; Huang, X.Y.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.J. Producing cadmium-free Indica rice by overexpressing OsHMA3. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, F. Effects of nearly four decades of long-term fertilization on the availability, fraction and environmental risk of cadmium and arsenic in red soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ros, G.; Cai, Z.; Wen, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Calculation of spatially explicit amounts and intervals of agricultural lime applications at county-level in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Lv, J.; Sun, N. Accumulation, availability, and uptake of heavy metals in a red soil after 22-year fertilization and cropping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 15154–15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Tan, C.; Liu, L.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Cadmium bioavailability in surface soils receiving long-term applications of inorganic fertilizers and pig manure. Geoderma 2012, 173, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Su, D.; Li, H. Effects of continuous fertilization on bioavailability and fractionation of cadmium in soil and its uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, B.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Ullah, A.; Tahir, N. A Field Evidence of Cd, Zn and Cu Accumulation in Soil and Rice Grains after Long-Term (27 Years) Application of Swine and Green Manures in a Paddy Soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; Lambregts, R.M.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Tiller, K.G. Effect of soil solution chloride on cadmium availability to Swiss chard. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Bailey, L.D.; Therrien, M.C. The effect of N, P and KCI fertilizers on grain yield and Cd concentration of malting barley. Fertil. Res. 1996, 45, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; McLaughlin, M.J. Chloride Increases Cadmium Uptake in Swiss Chard in a Resin-buffered Nutrient Solution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Lambrechts, R.M.; Smolders, E.; Smart, M.K. Effects of sulfate on cadmium uptake by Swiss chard: II. Effects due to sulfate addition to soil. Plant Soil 1998, 202, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Li, H.-Y.; Smith, S.E.; Smith, F.A. Effects of forms and rates of potassium fertilizers on cadmium uptake by two cultivars of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norvell, W.A.; Wu, J.; Hopkins, D.G.; Welch, R.M. Association of Cadmium in Durum Wheat Grain with Soil Chloride and Chelate-Extractable Soil Cadmium. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Tiller, K.; Smart, M. Speciation of cadmium in soil solutions of saline/sodic soils and relationship with cadmium concentrations in potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.). Soil Res. 1997, 35, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, Q.B.; Hui, W.; Shi, J.Y.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, Y.X. Effect of sulphur on soil Cu/Zn availability and microbial community composition. J. Hazardous. Mater. 2018, 159, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefer, C.; Santner, J.; Puschenreiter, M.; Wenzel, W.W. Localized metal solubilization in the rhizosphere of salix smithiana upon sulfur application. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4522–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldi, F.R.; Gratao, P.L.; Reis, A.R.; Lima, L.W.; Azevedo, R.A. Sulfur metabolism and stress defense responses in plants. Trop. Plant Biol. 2015, 8, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Zhao, J.M.; Chen, X.B.; Yu, J.B.; Wu, H.F. Pathways of cadmium fluxes in the root of the halophyte Suaeda salsa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Kopriva, S.; Giordano, M.; Saito, K.; Hell, R. Sulfur assimilation in photosynthetic organisms: Molecular functions and regulations of transporters and assimilatory enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, D. The responses of cadmium phytotoxicity in rice and the microbial community in contaminated paddy soils for the application of different long-term N fertilizers. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugford, S.G.; Lee, B.-R.; Koprivova, A.; Matthewman, C.; Kopriva, S. Control of sulfur partitioning between primary and secondary metabolism. Plant J. 2011, 65, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakari, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Allakonon, M.G.B.; Singh, A.K.; Chen, C.; Zou, X.; Akponikpè, P.B.I.; Dossa, G.G.O.; et al. Influence of sulfur amendments on heavy metals phytoextraction from agricultural contaminated soils: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Fu, H.-L.; Liao, Q.; Huang, B.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Xin, J.-L.; Huang, Y.-Y. Transcriptome analysis and physiological indicators reveal the role of sulfur in cadmium accumulation and transportation in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARRP. National Farmland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Qiyang. Available online: https://iarrp.caas.cn/en/research/supportdepartmentsorganizations/289714.htm (accessed on 24 April 2022).
- da Silva, Y.J.; do Nascimento, C.W.; Biondi, C.M. Comparison of USEPA digestion methods to heavy metals in soil samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burridge, J.C.; Hewitt, I.J. A comparison of two soil-extraction procedures for the determination of EDTA-extractable copper and manganese. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1987, 18, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yang, X.; Beiyuan, J.; Yin, M.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, W.; et al. Emerging risks of toxic metal(loid)s in soil-vegetables influenced by steel-making activities and isotopic source apportionment. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, W.; Zhang, N.; Su, D.; Zeer, L.; Du, H.; Hu, K. Collaborative Assessment and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils and Tea Leaves in the Southwest Region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Liang, C.-H. A modified colorimetric method to determine the chloride profile from the ponding test. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2014, 37, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Chiang, C.T. Relation between the chloride migration coefficients of concrete from the colourimetric method and the chloride profile method. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2009, 32, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, L.L.; Gehrke, C.W.; Suzuki, J. An automated turbidimetric method for total sulfur in plant tissue and sulfate sulfur in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1980, 11, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XLSTAT, A. Data Analysis and Statistics Software for Microsoft Excel; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, N.; Ishioka, G.; Yanaka, M.; Takata, K.; Murakami, M. Effects of Ammonium Chloride Fertilizer and its Application Stage on Cadmium Concentrations in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Grain. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.; Beaton, J.D.; Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers. An Introduction to Nutrient Management; Pearson Education: Bengaluru, India, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Riaz, M.; Liu, X.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Tan, Z.; Tan, Q. Migration of Chlorine in Plant–Soil–Leaching System and Its Effects on the Yield and Fruit Quality of Sweet Orange. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 744843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.R.; Quaggio, J.A.; Silva, G.O. Dinâmica de íons e acidificação do solo nos sistemas de fertirrigação e adubação sólida na citricultura. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2006, 28, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaggio, J.A. Acidez e Calagem em Solos Tropicais; Instituto Agronômico: Londrina, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-y.; Liu, Z.-d.; Zhao, W.-z.; Masud, M.; Xu, R.-k. Alkaline slag is more effective than phosphogypsum in the amelioration of subsoil acidity in an Ultisol profile. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 149, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Curtin, D. Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 5–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils; Boca Ratón: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Qiu, L.; Guo, L.; Man, J.; Shang, B.; Pu, R.; Ou, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. K Fertilizers Reduce the Accumulation of Cd in Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. by Improving the Quality of the Microbial Community. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasa, K.; Peltovuori, T.; Hartikainen, H. Effects of de-icing chemicals sodium chloride and potassium formate on cadmium solubility in a coarse mineral soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Takano, H.; Kamiya, T.; Itou, T.; Sekiya, N.; Inahara, M.; Sakurai, Y. Restoration of cadmium-contaminated paddy soils by washing with ferric chloride: Cd extraction mechanism and bench-scale verification. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liang, C.H. Evaluation of Phosphate Fertilizers for the Immobilization of Cd in Contaminated Soils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Shen, L.; Pan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Effects of sulfur application on cadmium bioaccumulation in tobacco and its possible mechanisms of rhizospheric microorganisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weggler-Beaton, K.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Graham, R.D. Salinity increases cadmium uptake by wheat and Swiss chard from soil amended with biosolids. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Chen, D.; Shi, G.; Rao, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, D. Effect of elemental sulfur and gypsum application on the bioavailability and redistribution of cadmium during rice growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Lei, X. Sulfur application modifies cadmium availability and transfer in the soil-rice system under unstable pe + pH conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Qin, M.L.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.W.; Chen, M.X. Sulfur supply reduces cadmium uptake and translocation in rice grains (Oryza sativa L.) by enhancing iron plaque formation, cadmium chelation and vacuolar sequestration. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z. Worldwide cadmium accumulation in soybean grains and feasibility of food production on contaminated calcareous soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, D.-c.; Rao, W.; Du, G.-H.; Yang, J.; Hua, D.-l. Influence of Sulfur on the Formation of Fe-Mn Plaque on Root and Uptake of Cd by Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, B. The bioaccumulation of Cd in rice grains in paddy soils as affected and predicted by soil properties. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Song, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, W. Cadmium threshold for acidic and multi-metal contaminated soil according to Oryza sativa L. Cadmium accumulation: Influential factors and prediction model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.-C.; Gao, P.-d.; Wang, B.-Q.; Lin, W.-P.; Jiang, N.-H.; Cai, K.-Z. Impacts of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic amendments supplementation on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and heavy metal content. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Soil pH and organic matter. Nutr. Manag. Modul. 2009, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).