Combination of Ultrasound and Heat in the Extraction of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Mucilage: Impact on Yield and Technological Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Purification of Chia Seed Mucilage
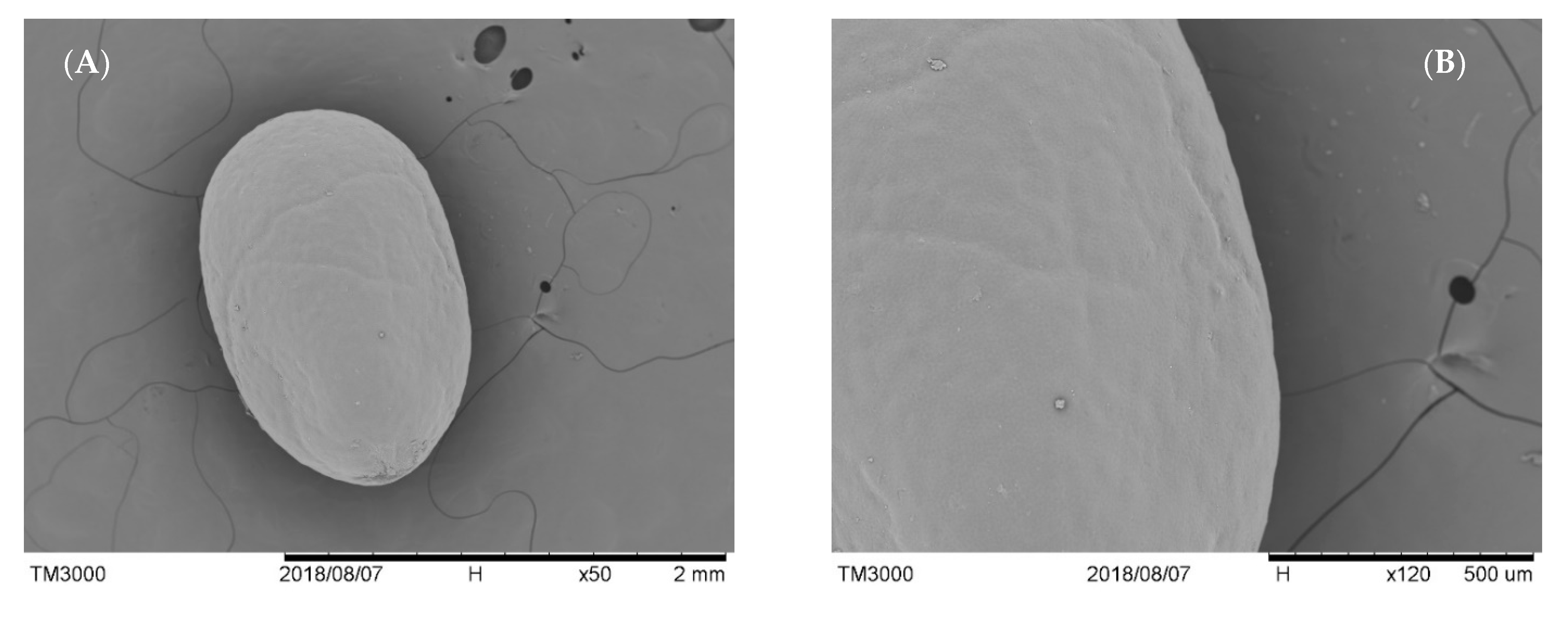
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis of Chia Seed
2.4. Color Analysis
2.5. Proximal Composition
2.6. Solubility
2.7. Water Holding Capacity and Oil Holding Capacity
2.8. Emulsifying Property
2.9. Flow Behavior
2.10. Phase Diagram Construction
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Raw and Treated Chia Seed
3.2. Extraction Yield of Chia Seed Mucilage
3.3. Appearance and Color of Chia Seed Mucilage
3.4. Proximate Composition of Chia Seed Mucilage
3.5. Technological Properties of Chia Seed Mucilage
3.5.1. Solubility
3.5.2. Water Holding Capacity and Oil Holding Capacity
3.5.3. Emulsifying Property
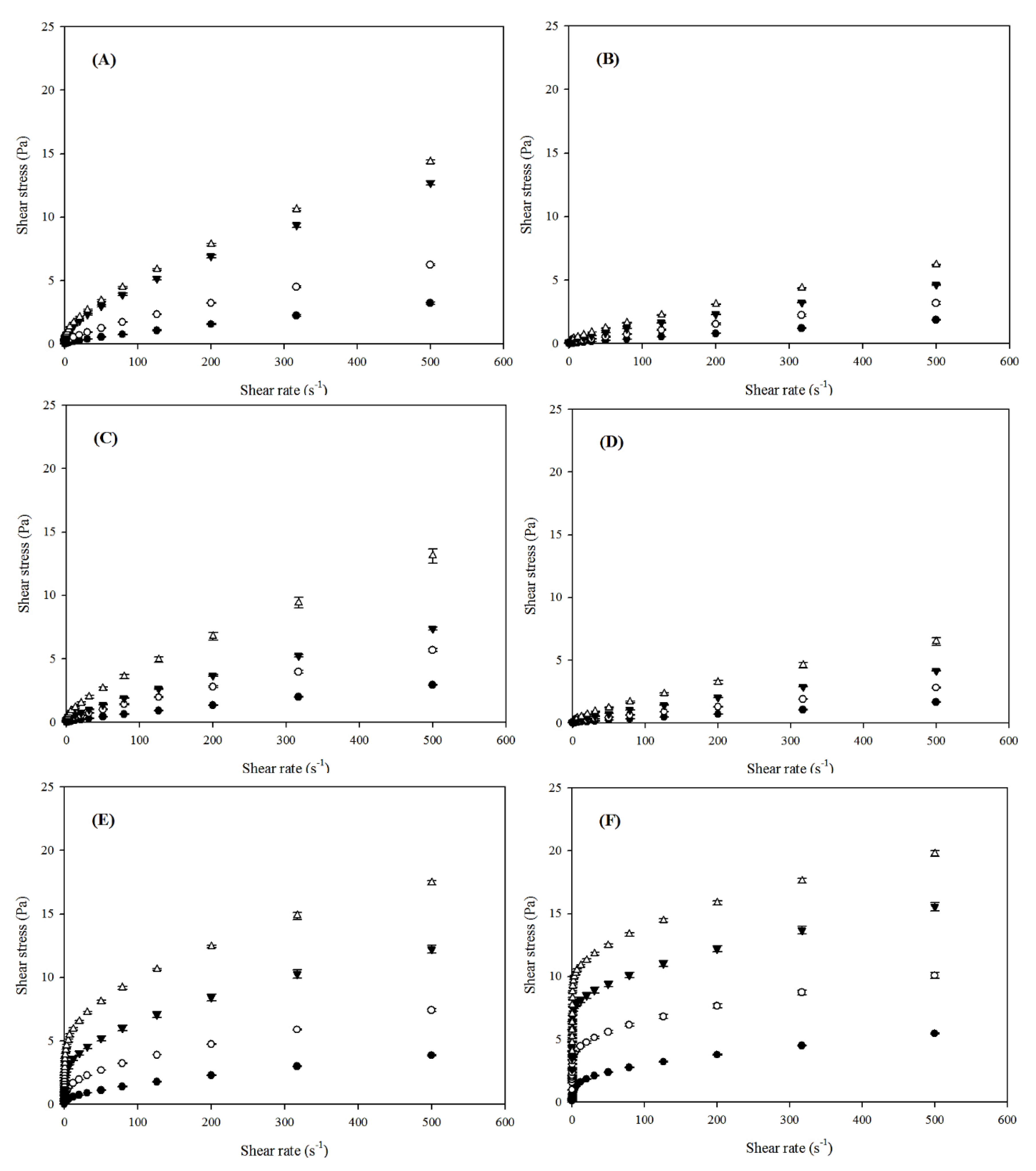
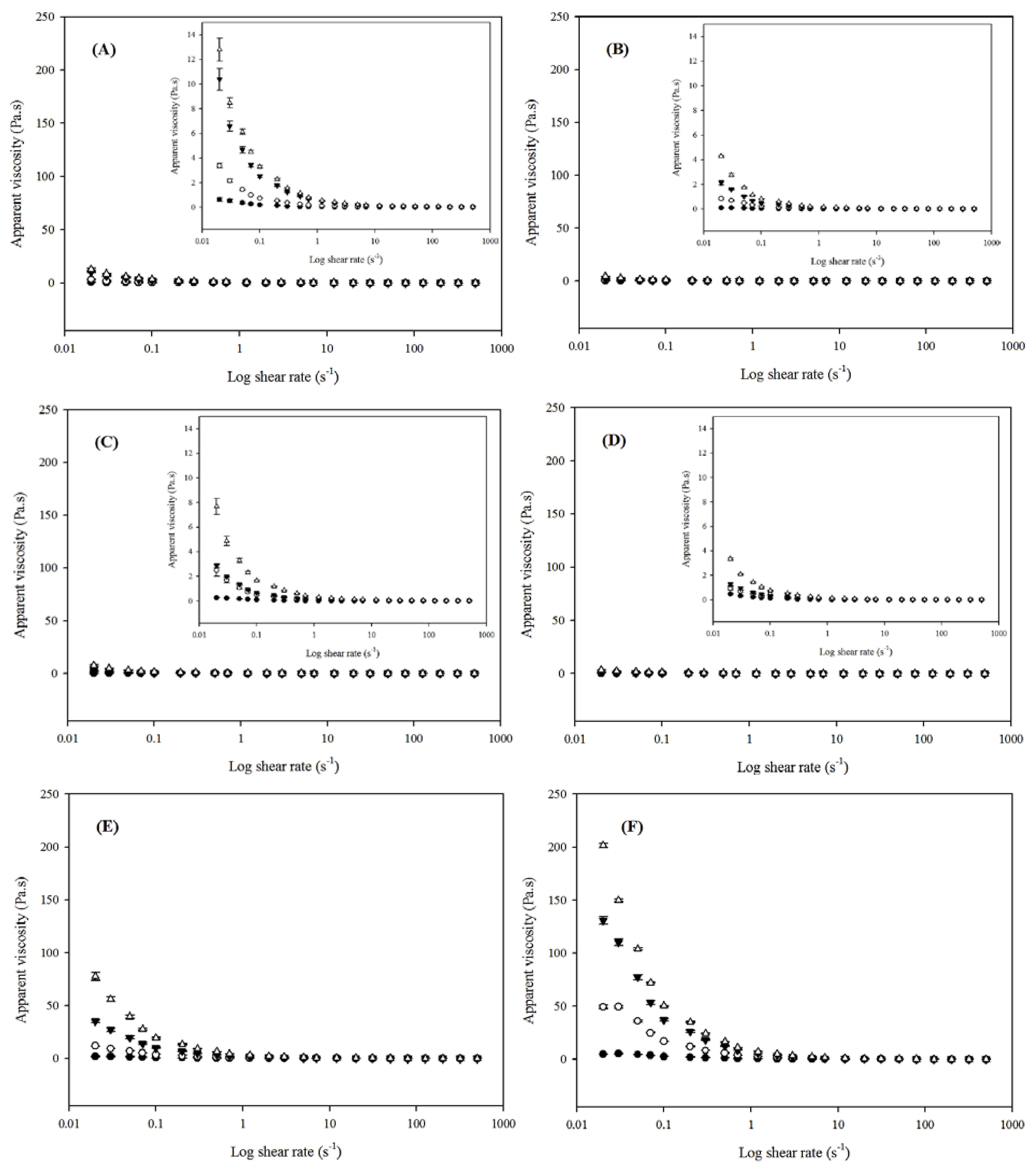
3.5.4. Flow Behavior
3.5.5. Phase Behavior
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, L.A.; Cobos, A.; Diaz, O.; Aguilera, J.M. Chia seed (Salvia hispanica): An ancient grain and a new functional food. Food. Rev. Int. 2013, 29, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushway, A.A.; Belyea, P.R.; Busheay, R.J. Chia seed as a source of oil, polysaccharide, and protein. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, K.; Krejpcio, Z. Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica): Health promoting properties and therapeutic applications—A review. Rocz. Państwowego Zakładu Hig. 2017, 68, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.M.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Tan, S.W.; Tan, S.G. The promising future of chia, Salvia hispanica L. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. 2012, 2012, 171956. [Google Scholar]
- Rabail, R.; Khan, M.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Kieliszek, M.; Khalid, A.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Aadil, R.M. An overview of chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) bioactive peptides’ deriation and utilization as an emerging nutraceutical food. Font. Biosci. 2021, 26, 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Segura-Campos, M.R.; Ciau-Solís, N.; Rosado-Rubio, G.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Chemical and functional properties of chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) gum. Int. J. Food Sci. 2014, 2014, 241053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.Y.; Daniel, L.R.; Whistler, R.L. Structure of chia seed polysaccharide exudate. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 23, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Kasapis, S.; Adhikari, B. Molecular and functional characteristics of purified gum from Australian chia seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, L.A.; Cobos, A.; Diaz, O.; Aguilera, J.M. Chia seeds: Microstructure, mucilage extraction and hydration. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orifici, S.C.; Capitani, M.I.; Tomás, M.C.; Nolasco, S.M. Optimization of mucilage extraction from chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.) using response surface methodology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4495–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.E.; Ruivo, T.D.; Scapim, M.R.S.; Madrona, G.S.; Bergamasco, R.C. Optimization of the mucilage extraction process from chia seeds and application in ice cream as a stabilizer and emulsifier. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coorey, R.; Tjoe, A.; Jayasena, V. Gelling properties of chia seed and flour. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E859–E866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitani, M.I.; Corzo-Rios, L.J.; Chel-Guerrero, L.A.; Betancur-Ancona, D.A.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C. Rheological properties of aqueous dispersions of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.K.T.; Matia-Merino, L.; Chiang, J.H.; Quek, R.; Soh, S.J.B.; Lentle, R.G. The physicochemical properties of chia seed polysaccharide and its microgel dispersion rheology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, L.S.; Junqueira, L.A.; de Qliveira Guimaraes, I.C.; de Resende, J.V. Cold extraction method of chia seed mucilage (Salvia hispanica L.): Effect on yield and rheological behavior. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, F.M.; Acevedo, M.J.; Tamez, R.M.; Nevero, M.J.; Garay, A.L. Method for Obtaining Mucilage from Salvia hispanica L. WO/2008/0044908c 29 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kentish, S.; Feng, H. Applications of power ultrasound in food processing. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, Y.; Cui, W.; Wang, Q. Extraction, purification and physicochemical characterization of fenugreek gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC internationl. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- CNS. The National Standards of the Republic of China; Bureau of Standards, Methodology & Inspection: Taipei, Taiwan, 1984.
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Kasapis, S.; Adhikari, B. Rheological and microstructural properties of the chia seed polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiorgos, V.; Tosh, S.M.; Wood, P.J. Phase behaviour of high molecular weight oat β-glucan whey protein isolate binary mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ixtaina, V.Y.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C. Physical properties of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 28, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, M.I.; Ixtaina, V.Y.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C. Microstructure, chemical composition and mucilage exudation of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) nutlets from Argentina. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3856–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S.; Khan, M.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Maan, A.A.; Khan, M.K.I.; Nadeem, M.; Khalil, A.A.; Din, A.; Aadil, M. An inclusive overview of advanced thermal and nonthermal extraction techniques for bioactive compounds in food and food-related matrices. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnaky, A.; Bakhshizadeh-Shirazi, S.H.; Mesbahi, G.H.; Majzoobi, M.; Rezvani, E.; Schleining, G. Ultrasound-assisted isolation of mucilaginous hydrocolloids from Salvia macrosiphon seeds and studying their functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ren, D.; Yang, N.; Yang, X. Optimization for ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides with chemical composition and antioxidant activity from the Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Salcedo, Á.J.; Torres-Vargas, O.L.; del Real, A.; Contreras-Jiménez, B.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Pasting, viscoelastic, and physicochemical properties of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) flour and mucilage. Food Strcut. 2018, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B. Physicochemical and functional properties of protein isolate produced. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivos-Lugo, B.L.; Valdivia-López, M.Á.; Tecante, A. Thermal and physicochemical properties and nutritional value of the protein fraction of mexican chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, D.; Zhu, K.; Ye, Z. Manosonication assisted extraction and characterization of pectin from different citrus peel wastes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agricul. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garti, N.; Leser, M.E. Emulsification properties of hydrocolloids. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2001, 12, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, G.S. Rheology of concentrated xanthan gum solutions: Steady shear flow behavior. Fibers Polym. 2006, 7, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doublier, J.L.; Garnier, C.; Renard, D.; Sanchez, C. Protein–polysaccharide interactions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
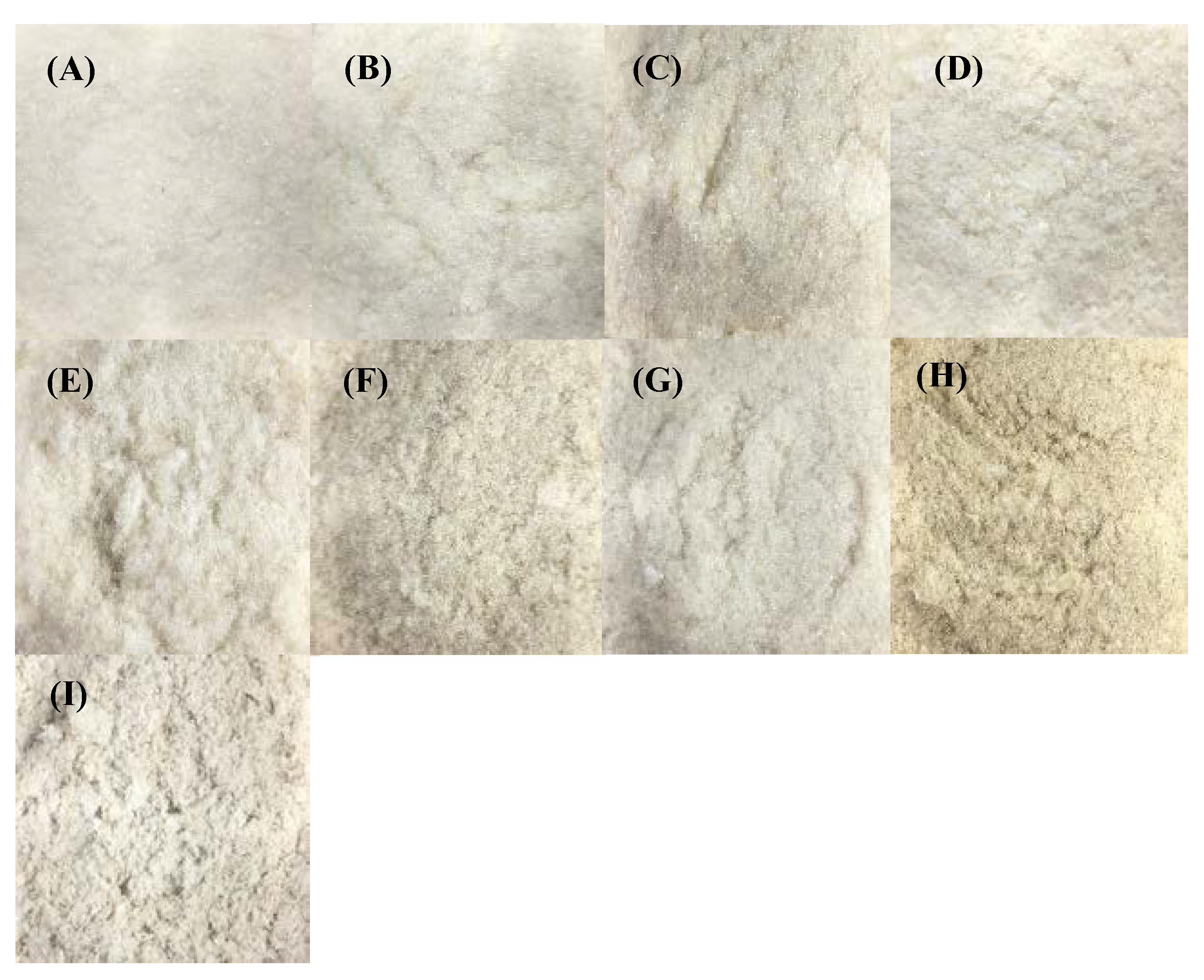
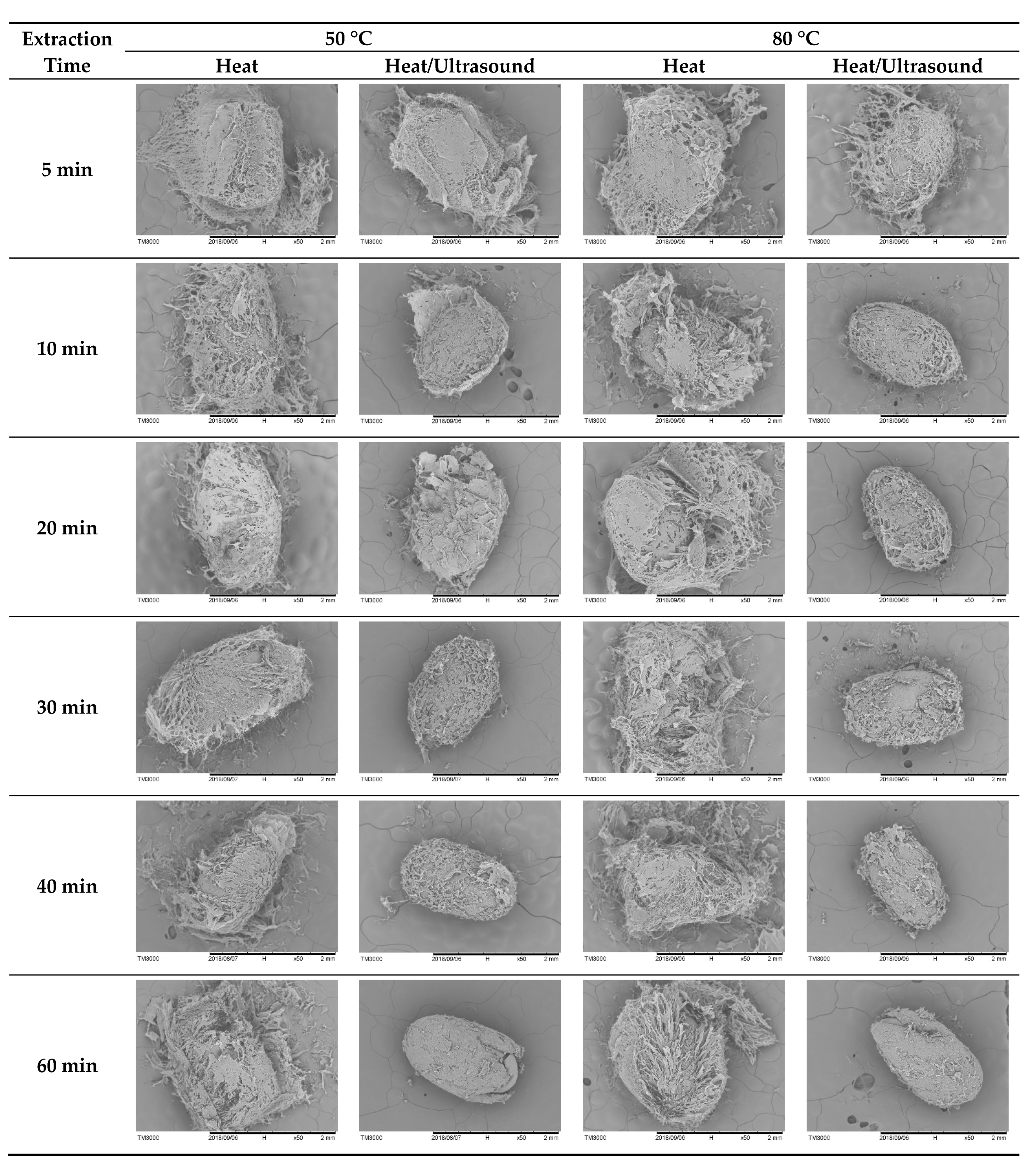

 Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
 Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).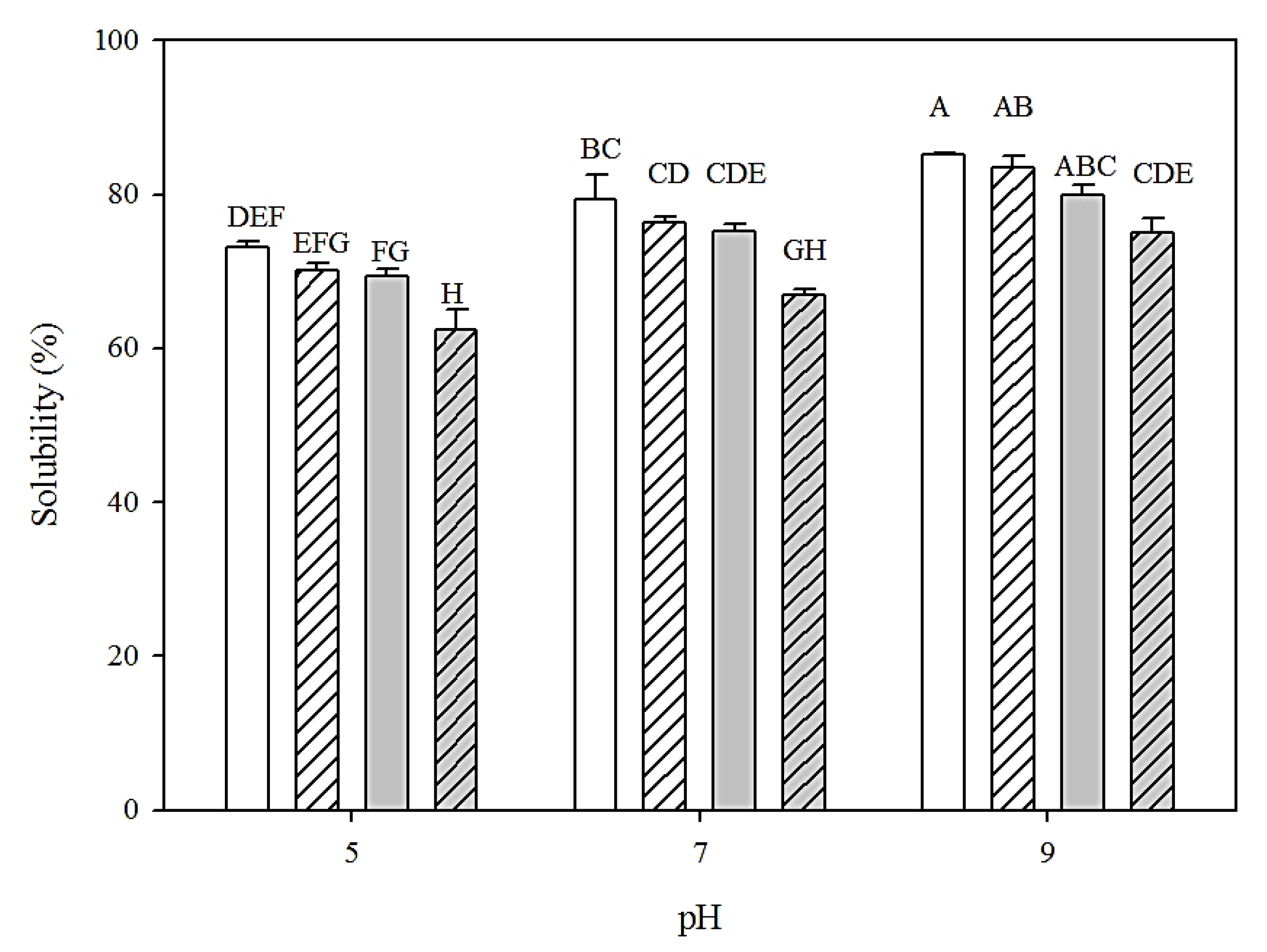
 ) and oil holding capacity (OHC,
) and oil holding capacity (OHC,  ) of chia seed mucilage extracted by ultrasound in combination with heat. Error bars represent standard deviations. Means with different superscript capital letters and lowercase letters denote significant difference among WHC and OHC (p < 0.05), respectively.
) of chia seed mucilage extracted by ultrasound in combination with heat. Error bars represent standard deviations. Means with different superscript capital letters and lowercase letters denote significant difference among WHC and OHC (p < 0.05), respectively.
 ) and oil holding capacity (OHC,
) and oil holding capacity (OHC,  ) of chia seed mucilage extracted by ultrasound in combination with heat. Error bars represent standard deviations. Means with different superscript capital letters and lowercase letters denote significant difference among WHC and OHC (p < 0.05), respectively.
) of chia seed mucilage extracted by ultrasound in combination with heat. Error bars represent standard deviations. Means with different superscript capital letters and lowercase letters denote significant difference among WHC and OHC (p < 0.05), respectively.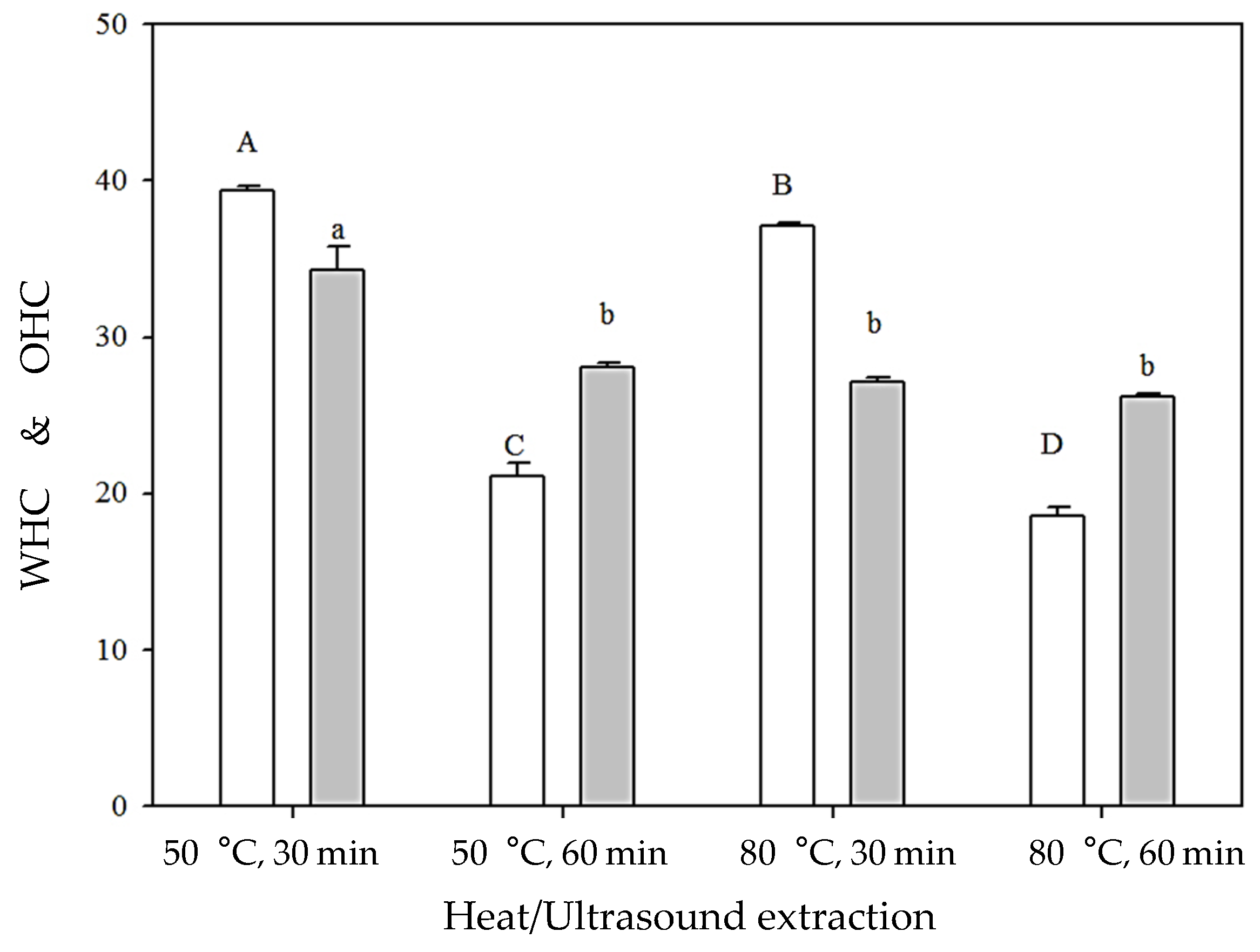
 Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
 Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-50 °C/60 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/30 min;  Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).
Heat/Ultrasound-80 °C/60 min).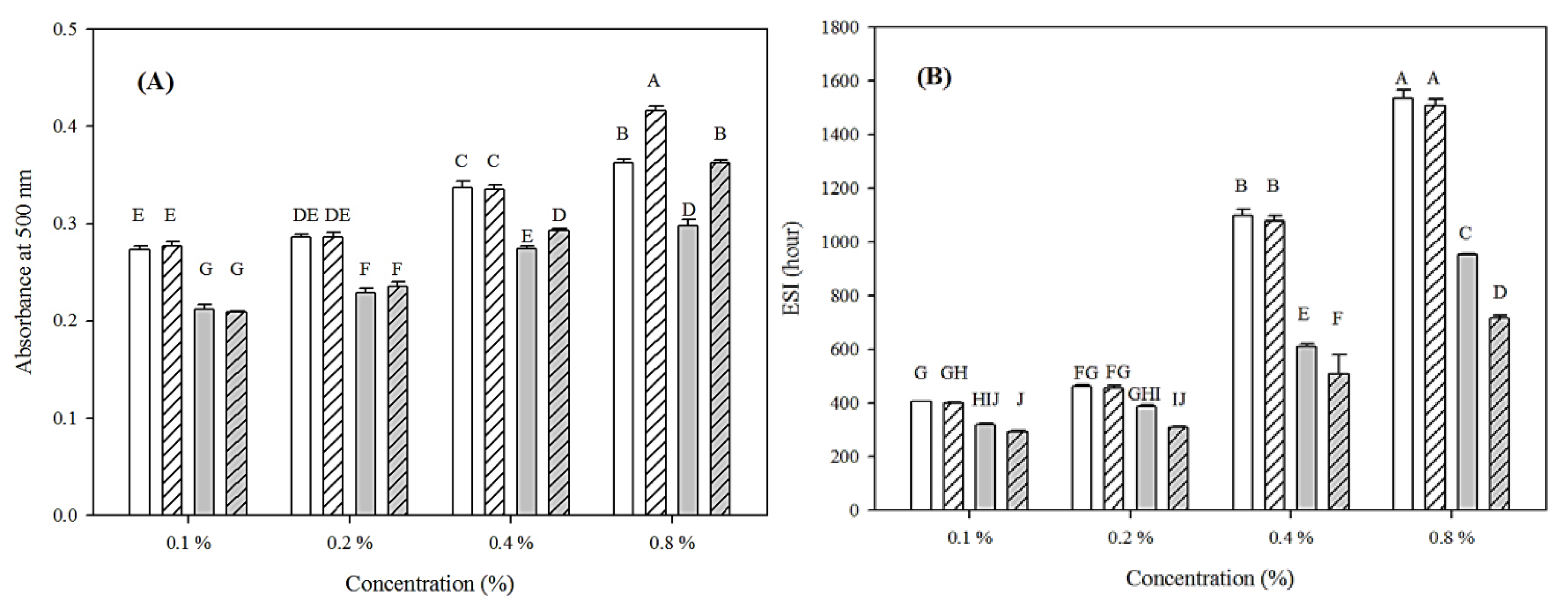

| Extraction Conditions | Purification | Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat | 50 °C/30 min | No | 1.03 ± 0.27 D |
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 1.09 ± 0.02 D | |
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 1.79 ± 0.13 C | |
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 1.86 ± 0.09 C | |
| Heat/Ultrasound | 50 °C/30 min | No | 6.92 ± 0.33 B |
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 10.39 ± 0.57 A | |
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 6.98 ± 0.23 B | |
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 10.52 ± 0.61 A | |
| 50 °C/60 min | Yes | 2.11 ± 0.07 C | |
| Extraction Conditions | Purification | L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat | 50 °C/30 min | No | 41.22 ± 0.11 A | 1.79 ± 0.00 E | 5.26 ± 0.02 G |
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 39.91 ± 0.95 AB | 2.75 ± 0.02 CD | 5.83 ± 0.17 F | |
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 32.98 ± 0.06 C | 2.59 ± 0.06 D | 9.52 ± 0.05 B | |
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 30.80 ± 0.09 D | 3.62 ± 0.06 B | 9.64 ± 0.12 B | |
| Heat/Ultrasound | 50 °C/30 min | No | 38.42 ± 0.68 B | 1.90 ± 0.03 E | 5.77 ± 0.06 F |
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 21.78 ± 0.15 E | 2.78 ± 0.05 C | 7.07 ± 0.10 D | |
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 31.08 ± 0.27 D | 2.64 ± 0.02 CD | 7.56 ± 0.09 C | |
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 21.23 ± 0.24 E | 4.26 ± 0.02 A | 10.85 ± 0.07 A | |
| 50 °C/60 min | Yes | 21.59 ± 0.45 E | 2.61 ± 0.10 CD | 6.60 ± 0.22 E | |
| Heat/Ultrasound Extraction Conditions | Purification | Moisture (%) | Dry Weight Basis (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Lipid | Ash | Carbohydrate * | |||
| 50 °C/30 min | No | 7.10 ± 0.47 A | 5.12 ± 0.22 D | 2.70 ± 0.10 A | 8.73 ± 0.13 C | 83.45 ± 0.27 A |
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 6.83 ± 0.31 A | 5.72 ± 0.09 C | 2.68 ± 0.09 A | 10.07 ± 0.09 B | 81.53 ± 0.16 B |
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 7.06 ± 0.64 A | 7.91 ± 0.03 B | 2.69 ± 0.13 A | 10.60 ± 0.26 AB | 78.80 ± 0.29 C |
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 6.83 ± 0.52 A | 12.05 ± 0.15 A | 2.79 ± 0.03 A | 11.32 ± 0.47 A | 73.84 ± 0.49 D |
| 50 °C/60 min | Yes | 7.03 ± 0.08 A | 0.72 ± 0.08 E | 1.22 ± 0.09 B | 7.68 ± 0.06 D | 90.38 ± 0.13 E |
| Heat/Ultrasound Extraction Conditions | Purification | Concentration (%) | Yield Stress (σy) (mPa) | Consistency Index (k) (mPa × sn) | Flow Behavior Index (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 °C/30 min | No | 0.25 | 23 ± 4 G | 23 ± 1 J | 0.794 ± 0.004 CD |
| 0.5 | 86 ± 2 FG | 70 ± 2 HIJ | 0.721 ± 0.004 H | ||
| 0.75 | 300 ± 9 DE | 202 ± 11 HI | 0.661 ± 0.007 I | ||
| 1 | 385 ± 11 D | 226 ± 6 GH | 0.662 ± 0.003 I | ||
| 50 °C/60 min | No | 0.25 | 9 ± 1 G | 6 ± 0 J | 0.911 ± 0.003 A |
| 0.5 | 29 ± 3 G | 22 ± 2 J | 0.800 ± 0.009 C | ||
| 0.75 | 60 ± 3 FG | 39 ± 2 IJ | 0.766 ± 0.008 EFG | ||
| 1 | 106 ± 1 FG | 58 ± 1 HIJ | 0.749 ± 0.003 FG | ||
| 80 °C/30 min | No | 0.25 | 16 ± 1 G | 16 ± 1 J | 0.839 ± 0.004 B |
| 0.5 | 69 ± 9 FG | 47 ± 2 IJ | 0.770 ± 0.062 EF | ||
| 0.75 | 83 ± 0 FG | 70 ± 1 HIJ | 0.747 ± 0.003 G | ||
| 1 | 204 ± 13 EF | 148 ± 7 HIJ | 0.718 ± 0.003 H | ||
| 80 °C/60 min | No | 0.25 | 25 ± 3 G | 6 ± 1 J | 0.910 ± 0.019 A |
| 0.5 | 46 ± 11 FG | 16 ± 0 J | 0.833 ± 0.005 B | ||
| 0.75 | 43 ± 4 G | 34 ± 1 IJ | 0.772 ± 0.006 DE | ||
| 1 | 98 ± 3 FG | 59 ± 1 HIJ | 0.752 ± 0.004 EFG | ||
| 50 °C/60 min | Yes | 0.25 | 87 ± 5 FG | 118 ± 1 HIJ | 0.555 ± 0.003 J |
| 0.5 | 352 ± 4 DE | 397 ± 7 G | 0.459 ± 0.005 K | ||
| 0.75 | 873 ± 35 C | 981 ± 59 E | 0.390 ± 0.007 L | ||
| 1 | 1685 ± 93 A | 1684 ± 19 D | 0.355 ± 0.002 M | ||
| Xanthan gum | 0.25 | 36 ± 0 G | 651 ± 10 F | 0.336 ± 0.000 M | |
| 0.5 | 842 ± 53 C | 2140 ± 13 C | 0.224 ± 0.004 N | ||
| 0.75 | 1074 ± 62 B | 5002 ± 178 B | 0.156 ± 0.002 O | ||
| 1 | 1138 ± 153 B | 6982 ± 115 A | 0.144 ± 0.003 O | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.-H.; Lu, C.-P.; Kuo, M.-I. Combination of Ultrasound and Heat in the Extraction of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Mucilage: Impact on Yield and Technological Properties. Processes 2022, 10, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030519
Wang W-H, Lu C-P, Kuo M-I. Combination of Ultrasound and Heat in the Extraction of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Mucilage: Impact on Yield and Technological Properties. Processes. 2022; 10(3):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030519
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wen-Huei, Chun-Ping Lu, and Meng-I Kuo. 2022. "Combination of Ultrasound and Heat in the Extraction of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Mucilage: Impact on Yield and Technological Properties" Processes 10, no. 3: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030519
APA StyleWang, W.-H., Lu, C.-P., & Kuo, M.-I. (2022). Combination of Ultrasound and Heat in the Extraction of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Mucilage: Impact on Yield and Technological Properties. Processes, 10(3), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10030519






