Static Voltage Stability Assessment Using a Random UnderSampling Bagging BP Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Local Voltage Stability Index
3. Random Under-Sampling Bagging BP Method for VSA
3.1. BP Neural Network for Regression of VSA
3.1.1. Model of BP Neural Network for Regression of VSA
3.1.2. Algorithm of BP Neural Network for Regression of VSA
3.2. Random Under-Sampling Bagging for Improving Model Accuracy of VSA
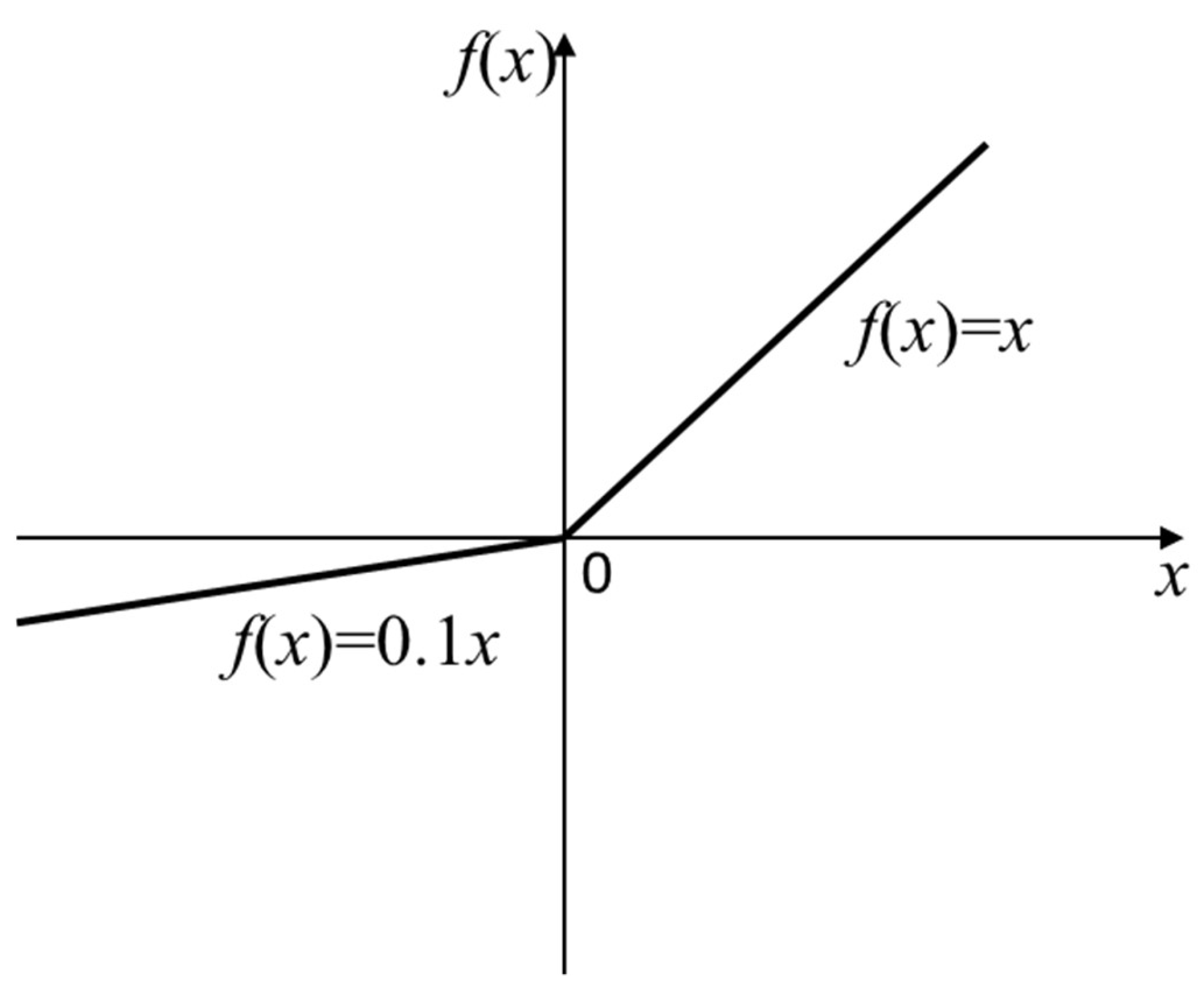
3.2.1. Random Under-Sampling Method for Solving Class Imbalance Problem in VSA
3.2.2. Bagging with Random Under-Sampling for Improving Model Accuracy of VSA
4. Modeling of Static Voltage Stability Assessment Based on Machine Learning
- (1)
- Activation function
- (2)
- Loss function
- (3)
- Optimization algorithm
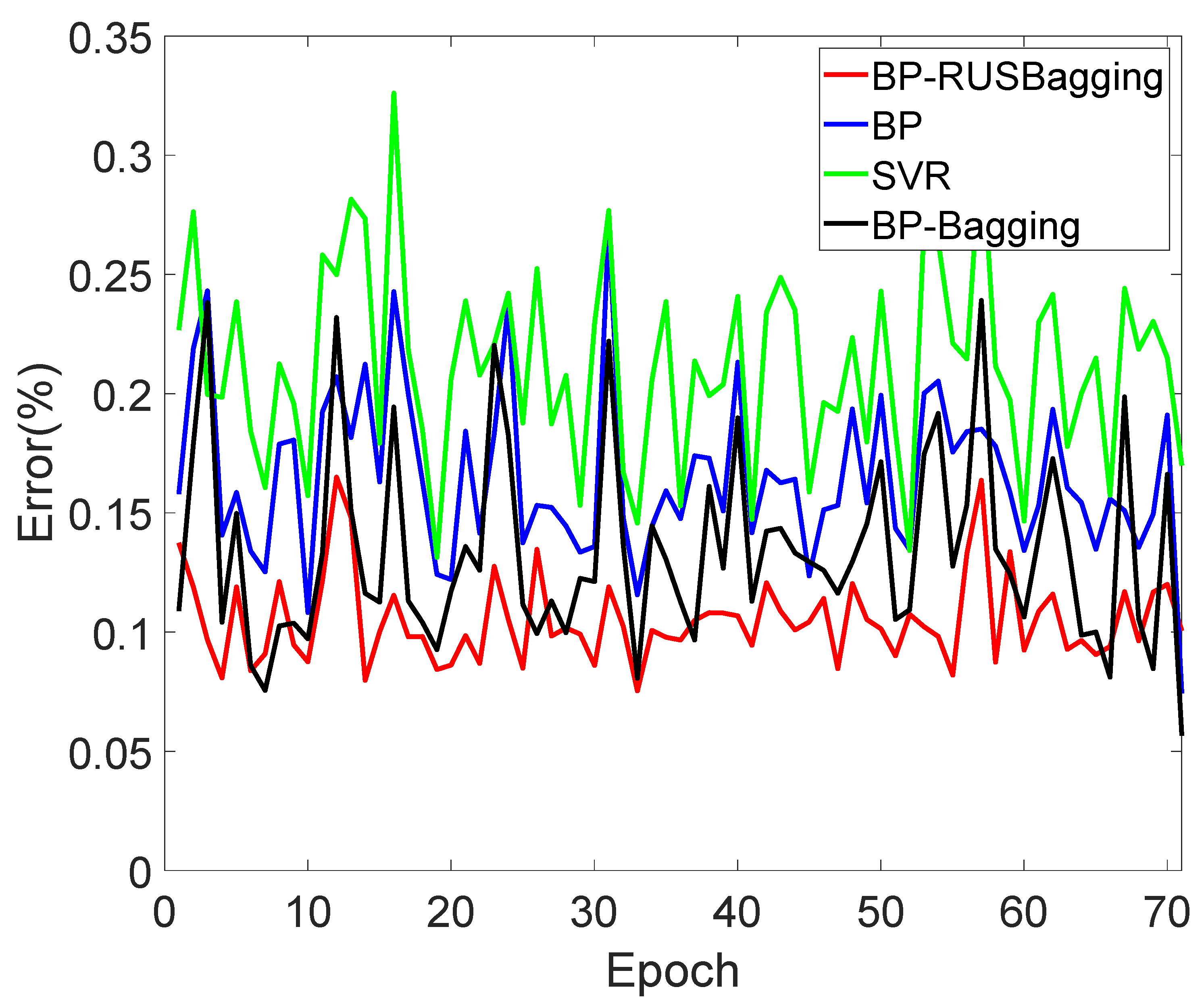
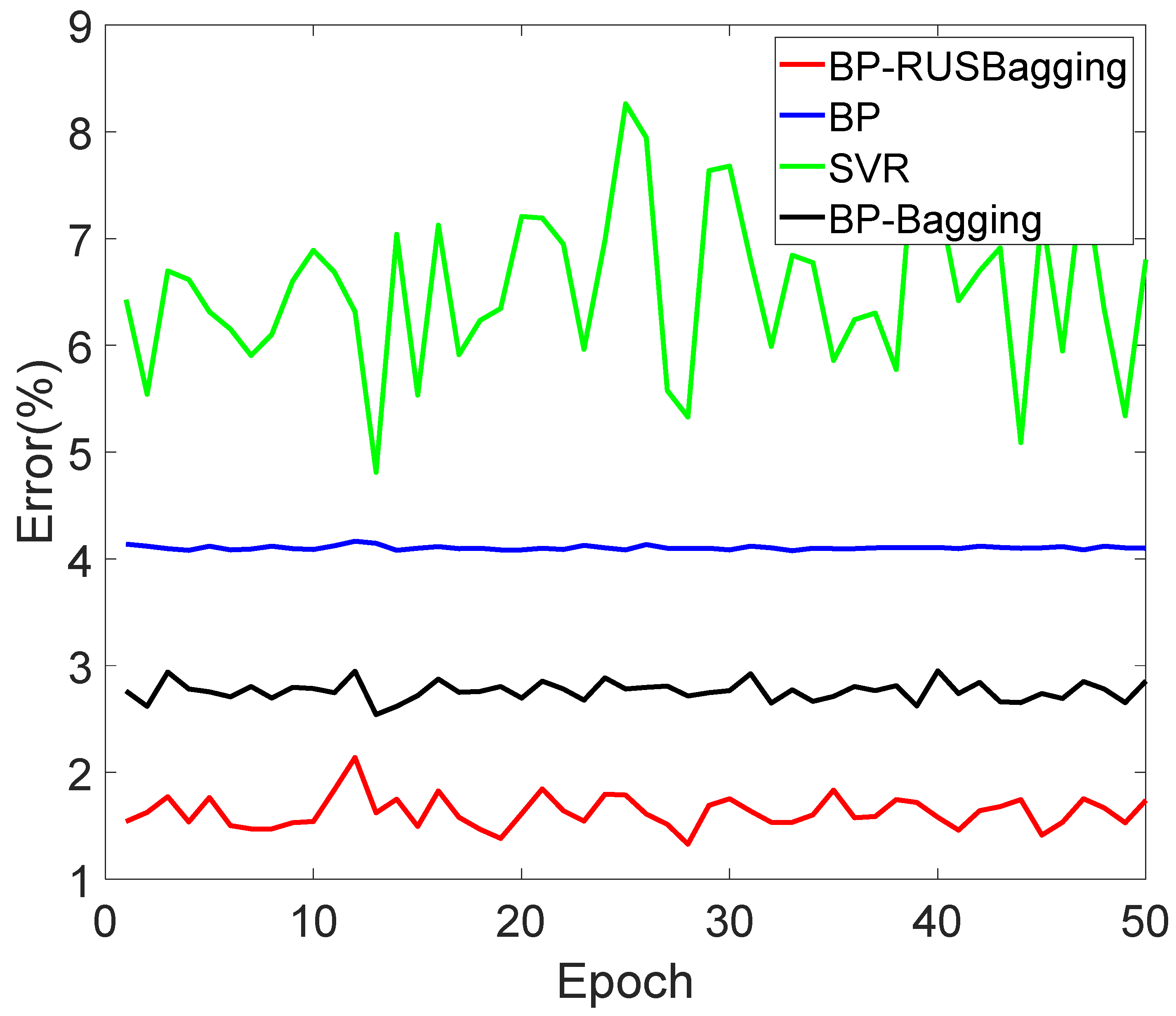
5. Results
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the sample preparation stage, various operating scenarios such as load demand, new energy output power, and EV status were considered, which greatly improved the scenario applicability of the model.
- (2)
- Defining the static voltage stability assessment problem as a regression problem of machine learning, which essentially improves the model assessment accuracy, provides voltage stability information with a quantitative index, and helps grid operators to better observe the grid state.
- (3)
- Using the random under-sampling bagging framework provides a method to solve the problem of imbalanced data in the field of power system operating, which comprehensively improves the accuracy of the model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundur, P. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem, T.; Vournas, C. Voltage Stability of Electric Power Systems; Kluwer: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, L.; Singh, S.N.; Sharma, J. Estimation of loadability margin using parallel self-organizing hierarchical neural network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2000, 26, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganyadevi, M.V.; Babulal, C.K. Online Voltage Stability Assessment of Power System by Comparing Voltage Stability Indices and Extreme Learning Machine; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, W.; Hao, C.; Lian, L. Static Voltage Stability Margin Prediction Based on Natural Gradient Boosting and Its Influencing Factors Analysis. In Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–25 June 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiocel, S.G.; Chow, J.H. A Power Flow Method Using a New Bus Type for Computing Steady-State Voltage Stability Margins. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Dong, Z.Y.; Chen, G.; Xu, Y.; Meng, K.; Chen, Y.Y. Advanced pattern discovery-based fuzzy classification method for power system dynamic security assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2015, 11, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Sanjari, M.J.; Safari, M.; Akbari, M.; Kamali, M.R. Static security assessment of power systems: A review. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, N.; Mao, D.; Shi, R. A data-driven approach for online dynamic security assessment with spatial-temporal dynamic visualization using random bits forest. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 124, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, P.; Meng, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Online Evaluation on Static Voltage Stability Margin Based on Classification and Regression Tree Algorithm. Proc. CSU-EPSA 2020, 32, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wenqing, L.; Qingwu, G.; Chunhui, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Liuchuang, W.U. Transient voltage stability evaluation based on feature and convolutional neural network. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 52, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Xiurui, L.; Daowei, L.; Hongying, Y. Data-Driven Situation Assessment of Power System Static Voltage Stability. Electr. Power Constr. 2020, 41, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, C.; Dong, Z.Y. Imbalance learning machine-based power system short-term voltage stability assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, C. A Deep-Learning intelligent system incorporating data augmentation for Short-Term voltage stability assessment of power systems. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haixiang, G.; Yijing, L.; Shang, J.; Mingyun, G.; Yuanyue, H.; Bing, G. Learning from class-imbalanced data: Review of methods and applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 73, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malave, N.; Nimkar, A.V. A survey on effects of class imbalance in data pre-processing stage of the classification problem. Int. J. Comput. Syst. Eng. 2020, 6, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Hayat, M.; Bennamoun, M.; Sohel, F.; Togneri, R. Cost-sensitive learning of deep feature representations from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 3573–3587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.A.; Vijaya, P.; Kowsalya, M. Voltage stability indices for stability assessment: A review. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2021, 42, 829–845. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, H.S.; Vokony, I. Voltage stability indices–A comparison and a review. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 98, 107743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, P.; Glavitsch, H. Estimating the Voltage Stability of a Power System. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 1, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xu, Y. Deterministic convergence of an online gradient method for neural networks. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2002, 144, 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, T.; Xu, B. A constrained optimization method based on BP neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 29, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, G.; Shen, F. Solving the data imbalance problem of P300 detection via random under-sampling bagging SVMs. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Killarney, Ireland, 12–17 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Błaszczyński, J.; Stefanowski, J. Actively balanced bagging for imbalanced data. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Methodologies for Intelligent Systems, Graz, Austria, 23–25 September 2017; pp. 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Bühlmann, P. Bagging, boosting and ensemble methods. In Handbook of Computational Statistics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 985–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning. MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, N.; Lei, S.; Yang, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, M. Delay Compensated Asynchronous Adam Algorithm for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications and 2017 IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications (ISPA/IUCC), Guangzhou, China, 12–15 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sriyanyong, P.; Song, Y.H. Unit commitment using particle swarm optimization combined with Lagrange relaxation. In Proceedings of the Power Engineering Society General Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 16 June 2005. [Google Scholar]


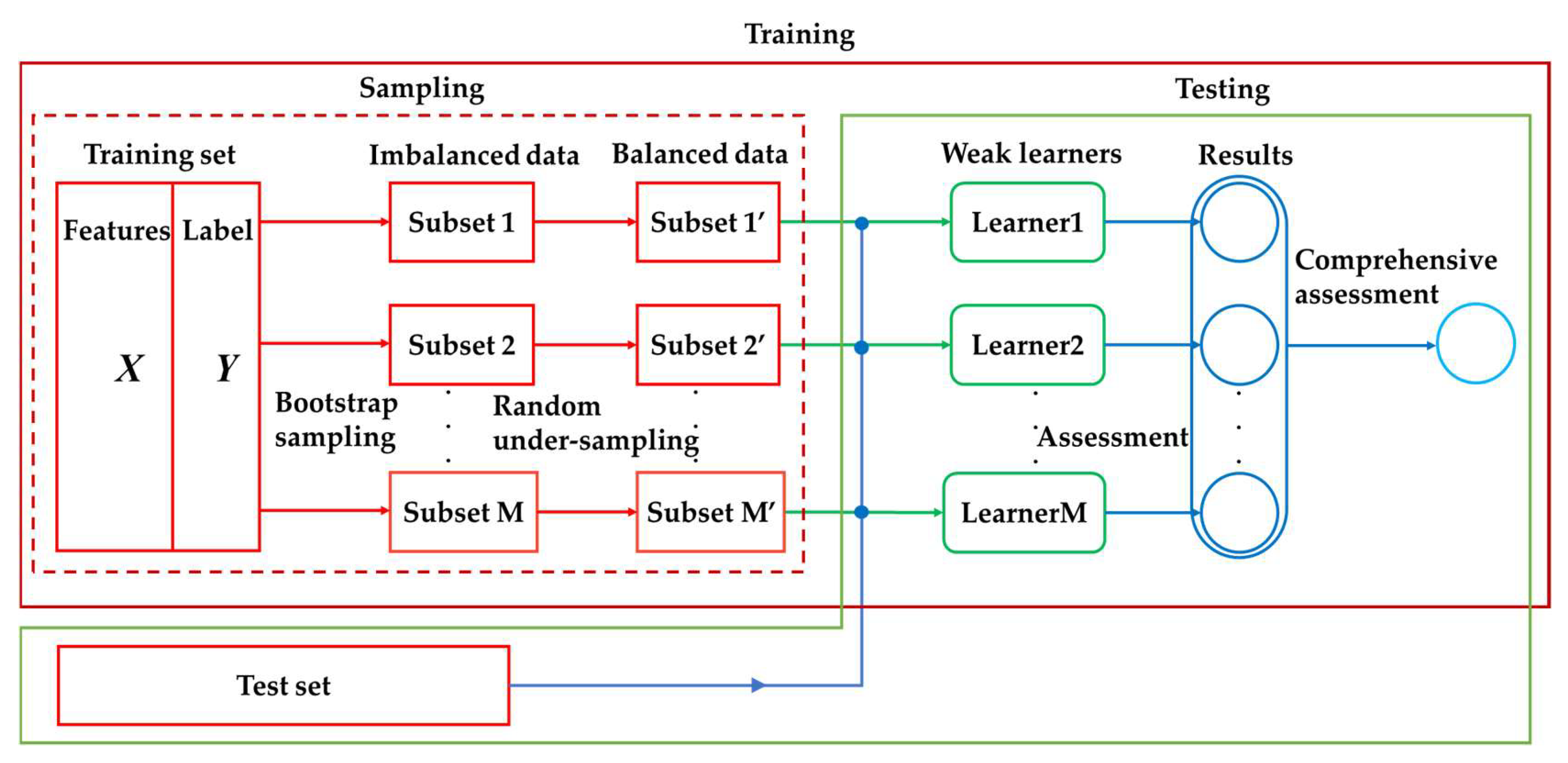


| Input: dataset , weak learner algorithm, number of weak learner M For i = 1, 2, …, M: Using the bootstrap sampling method on the dataset to generate a subsampled set Using the random under-sampling method on the dataset to generate a balanced subsample set Training the ith weak learner with a balanced subsample set End Output: the final model |
| Num | Methods | Train-Time/s | MSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BP-RUSBagging | 312.44 | 6.0252 × 10−7 | 0.0011 |
| 2 | BP-Bagging | 290.35 | 4.7632 × 10−7 | 0.0014 |
| 3 | BP | 213.54 | 2.2391 × 10−6 | 0.0018 |
| 4 | SVR | 564.21 | 9.3797 × 10−6 | 0.0022 |
| Num | Methods | Train-Time/s | MSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BP-RUSBagging | 312.44 | 1.7763 × 10−5 | 0.0167 |
| 2 | BP-Bagging | 290.35 | 8.1022 × 10−5 | 0.0284 |
| 3 | BP | 213.54 | 2.2391 × 10−4 | 0.0411 |
| 4 | SVR | 564.21 | 1.4397 × 10−3 | 0.0622 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Static Voltage Stability Assessment Using a Random UnderSampling Bagging BP Method. Processes 2022, 10, 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101938
Zhu Z, Zhang P, Liu Z, Wang J. Static Voltage Stability Assessment Using a Random UnderSampling Bagging BP Method. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101938
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhujun, Pei Zhang, Zhao Liu, and Jian Wang. 2022. "Static Voltage Stability Assessment Using a Random UnderSampling Bagging BP Method" Processes 10, no. 10: 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101938
APA StyleZhu, Z., Zhang, P., Liu, Z., & Wang, J. (2022). Static Voltage Stability Assessment Using a Random UnderSampling Bagging BP Method. Processes, 10(10), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101938









