Abstract
Background: In the medical field, various deep learning (DL) algorithms have been effectively used to extract valuable information from unstructured clinical text data, potentially leading to more effective outcomes. This study utilized clinical text data to classify clinical case reports into tuberculosis (TB) and non-tuberculosis (non-TB) groups using natural language processing (NLP), a pre-processing technique, and DL models. Methods: This study used 1743 open-source respiratory disease clinical text data, labeled via fuzzy matching with ICD-10 codes to create a labeled dataset. Two tokenization methods preprocessed the clinical text data, and three models were evaluated: the existing Text-CNN, the proposed Text-CNN with t-test, and Bio_ClinicalBERT. Performance was assessed using multiple metrics and validated on 228 baseline screening clinical case text data collected from ICMR–NIRT to demonstrate effective TB classification. Results: The proposed model achieved the best results in both the test and validation datasets. On the test dataset, it attained a precision of 88.19%, a recall of 90.71%, an F1-score of 89.44%, and an AUC of 0.91. Similarly, on the validation dataset, it achieved 100% precision, 98.85% recall, 99.42% F1-score, and an AUC of 0.982, demonstrating its effectiveness in TB classification. Conclusions: This study highlights the effectiveness of DL models in classifying TB cases from clinical notes. The proposed model outperformed the other two models. The TF-IDF and t-test showed statistically significant feature selection and enhanced model interpretability and efficiency, demonstrating the potential of NLP and DL in automating TB diagnosis in clinical decision settings.
1. Introduction
In 2023, 8.2 million people worldwide reported a new diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB), surpassing the 7.1 million in 2019, 5.8 million in 2020, and 6.4 million in 2021, as well as the 7.5 million in 2022. India is the country with the highest global burden of TB, accounting for 26% of all TB cases globally in 2023 [1]. Efficient monitoring networks are required to quantify and monitor the burden of the illness and its causes to meet the objective of the End TB strategy and enhance patient care. Many low- and middle-income nations are still struggling to put a functional TB surveillance system in place [2]. TB programs should encourage the use of digital health platforms for patient data collection to save time and effort when filling out paper forms and prevent typical errors like incomplete and inaccurate data. Digital health initiatives can improve program administration, surveillance, and monitoring, and subsequently improve patient care [3]. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare is a rapidly developing field. The availability of a large amount of data in healthcare due to the extensive usage of biological data sources alongside electronic health record (EHR) systems opens up new avenues for clinical studies. Such resources consist of data-rich resources that can be used to enhance physicians’ productivity, quality, and efficiency, as well as to reduce errors in prescribing medicine, reduce healthcare costs, and provide safer treatment [4,5]. According to the United States Department of Health and Human Services, EHR systems enable the collection of patient-level real-world data for clinical care decision-making [6]. Among many other types of clinical narratives, including patient experiences, a significant portion of these data are contained in free text and may be found in radiology reports, discharge summaries, and doctors’ notes. Documenting the complaints and symptoms of the patient, physical examination, diagnostic tests, findings, therapies, and treatment outcomes, this clinical text follows the patient through the process of treatment. Clinical free text is a form of unstructured data, which are difficult to process using automated processing, although there have been several attempts to encode text as structured data [7].
Medical databases often contain structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. While structured and semi-structured data can be mapped to standardized representations with minimal information loss [8], a significant portion of EHRs remain in free text form [9]. Although unstructured medical records are more challenging to handle, they often contain rich patient information that is valuable for research and modeling [10]. However, as medical databases grow and the variations in clinical texts increase, extracting meaningful insights from unstructured data becomes increasingly difficult [11]. Discussions on the development of machine learning (ML) models to derive representations from free text in EHRs for the automated International Categorization of Diseases (ICD) coding have been ongoing for over 20 years [12]. The World Health Organization (WHO) designed the ICD, a globally standardized illness categorization process. This applies coding to describe illnesses and classifies them systematically based on the disease, etiology, clinical symptoms, and anatomical location [13]. Recent studies using advanced neural network-generated models based on natural language processing (NLP) techniques showed significant improvements in terms of performance [14,15]. Several ML techniques were extensively applied to identify health outcomes from EHRs. These include supervised techniques such as support vector machines and random forest, as well as neural networks and deep learning (DL) models, which can be used in both supervised and unsupervised settings [16,17,18].
Clinical writing frequently uses function words (such as “and”, “the”, or “is”), special characters, misspellings, and acronyms. Therefore, NLP approaches can be utilized to create a more formalized structural representation of a text [19], which can allow for data science, ML, statistics, and medical prediction models to access this information more easily. NLP is one of the most popular big data analysis methods in the healthcare industry, according to Yim W. et al. It is described as “any computer-based algorithm that handles, augments, and transforms natural language so that it can be represented for computation” [20]. Patient identification [21,22], disease classification [23,24], disease history [25], ICD-10 categorization [26], hospital readmission prediction [27], chronic disease prediction [28], text de-identification tools [29], and clinical decision support systems [5] are just a few of the health applications that utilize NLP approaches.
As DL algorithms and NLP techniques evolve, researchers increasingly employ electronic medical record (EMR) data for disease diagnosis. For example, to assist in sepsis identification at an earlier stage, Kam et al. employed a deep neural network (DNN) model to build a prediction network following EMR data extraction of several biological signal variables from the Multiparameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care II (MIMIC II) database [30]. Using EHRs as well as knowledge-based convolutional neural networks (CNNs), Wang et al. developed a prediction model to calculate the distant recurrence rate for breast cancer patients [31]. DL methods, predominantly CNN-based models [32], as well as several others, such as transformer models [33] and recurrent neural network (RNN)-based models [34], were successful in text classification. To extract important information for the CNN method, convolutional networks may convolve text on the word vector dimensions and perform pooling layer operations. With this method, significant data can be used for classification tasks.
In this study, we demonstrate that the integration of DL techniques, particularly Bio_ClinicalBERT and the Text CNN model, is effective in classifying clinical notes into “TB” or “non-TB” categories. Initially, the data consisted of unlabeled text-based clinical notes. To assign labels, we employed fuzzy matching with ICD-10 codes, which enabled the categorization of each clinical note as either “TB” or “non-TB”. Following this, NLP techniques were applied to preprocess the text data, preparing it in a suitable format for DL model training. Preprocessing is a crucial step for the Text CNN model, as it facilitates the model’s ability to learn meaningful patterns within the clinical text. Finally, we compared the performance metrics of the three models to evaluate their effectiveness in classifying the clinical notes.
The prime aim of employing statistical feature selection to carry out keyword selection using a statistical t-test for the Text CNN model is to select the important keywords from the clinical text data and reduce the false positives (FP) and false negatives (FN). The article’s research focus is as follows: “This study addresses by evaluating the performance of the models, and comparison of the models like: Existing Text CNN, proposed Text CNN with t-test model, and Bio_ClinicalBERT models for TB classification from the clinical notes”.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Labeling and Preprocessing
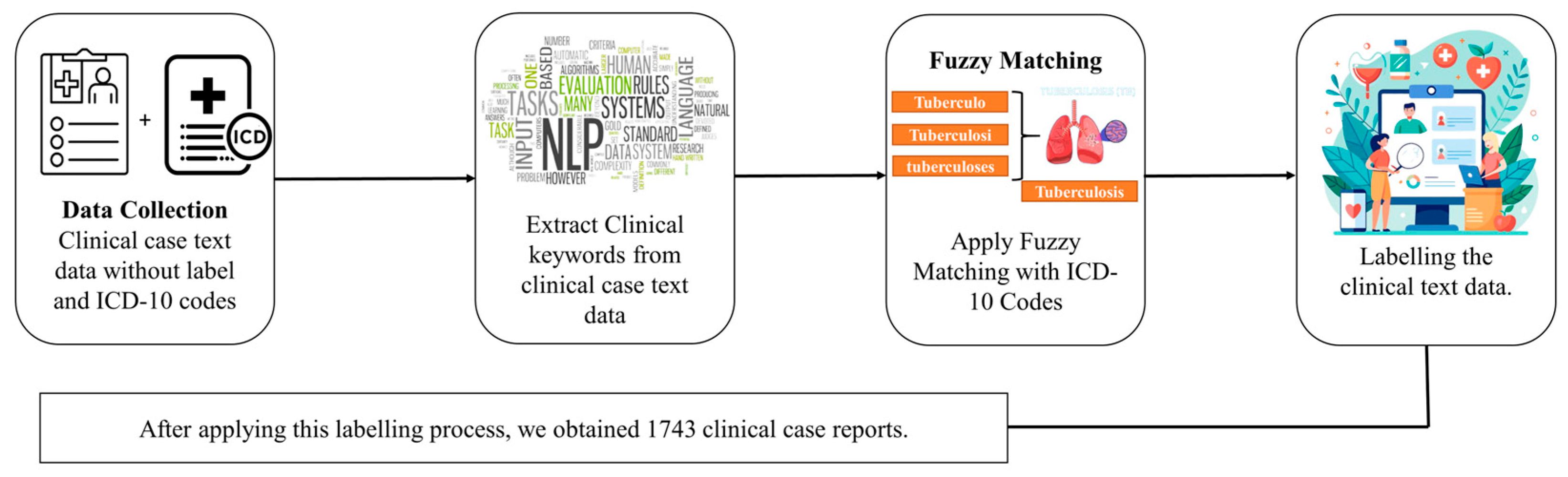
The dataset was collected from an openly available source [35] and comprises multi-modal data from over 75,000 clinical case reports. We mapped unstructured clinical notes to ICD-10 codes using fuzzy matching with the FuzzyWuzzy Python library version 0.18.0, which uses Levenshtein distance to compute string similarity. A similarity criterion of ≥85% was used to ensure accurate and meaningful matches. Clinical notes were then categorized into two categories based on the ICD-10 codes: “A15–A19”, classified as “Tuberculosis”, and “J00–J99”, categorized as “Non-Tuberculosis”, such as asthma, pneumonia, viral infections, fungal infections, and other lung-related diseases. After applying this labeling process, we obtained 1743 clinical case text data. Figure 1 illustrates the process of converting unlabeled clinical text data into a labeled format using fuzzy matching with ICD-10 codes. This transformation effectively converted the dataset into a labeled format, enabling a structured analysis and model development. In the Supplementary File, Tables S1 and S2 present the distribution of clinical notes labeled as TB and non-TB using the fuzzy matching technique with ICD-10 codes. The data were split into 80% training and 20% testing data.
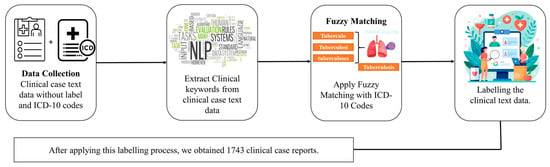
Figure 1.
Workflow for labeling clinical notes using ICD–10 codes; fuzzy matching was used for conversion from an unlabeled to a labeled format.
2.2. Challenges of Handling Clinical Notes
Clinical notes present several challenges, particularly when applying ML and DL algorithms. Since these notes are unstructured, they must be converted into a structured format. This transformation procedure requires the use of the NLP technique to quantify the medical terms and terminologies, which are key characteristics of the clinical text dataset. Preprocessing is the crucial initial step in cleaning and preparing clinical notes for any ML and DL analysis. This is especially important when handling medical vocabulary, which requires specialized techniques. To the best of our knowledge, no prior study has utilized clinical notes on respiratory diseases, particularly for TB classification in low-resource settings, using DL models, including transformer-based models such as Bio_ClinicalBERT. In this study, we evaluated the models using a validation dataset consisting of 228 clinical case report text data obtained from the Indian Council of Medical Research—National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis (ICMR—NIRT), Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
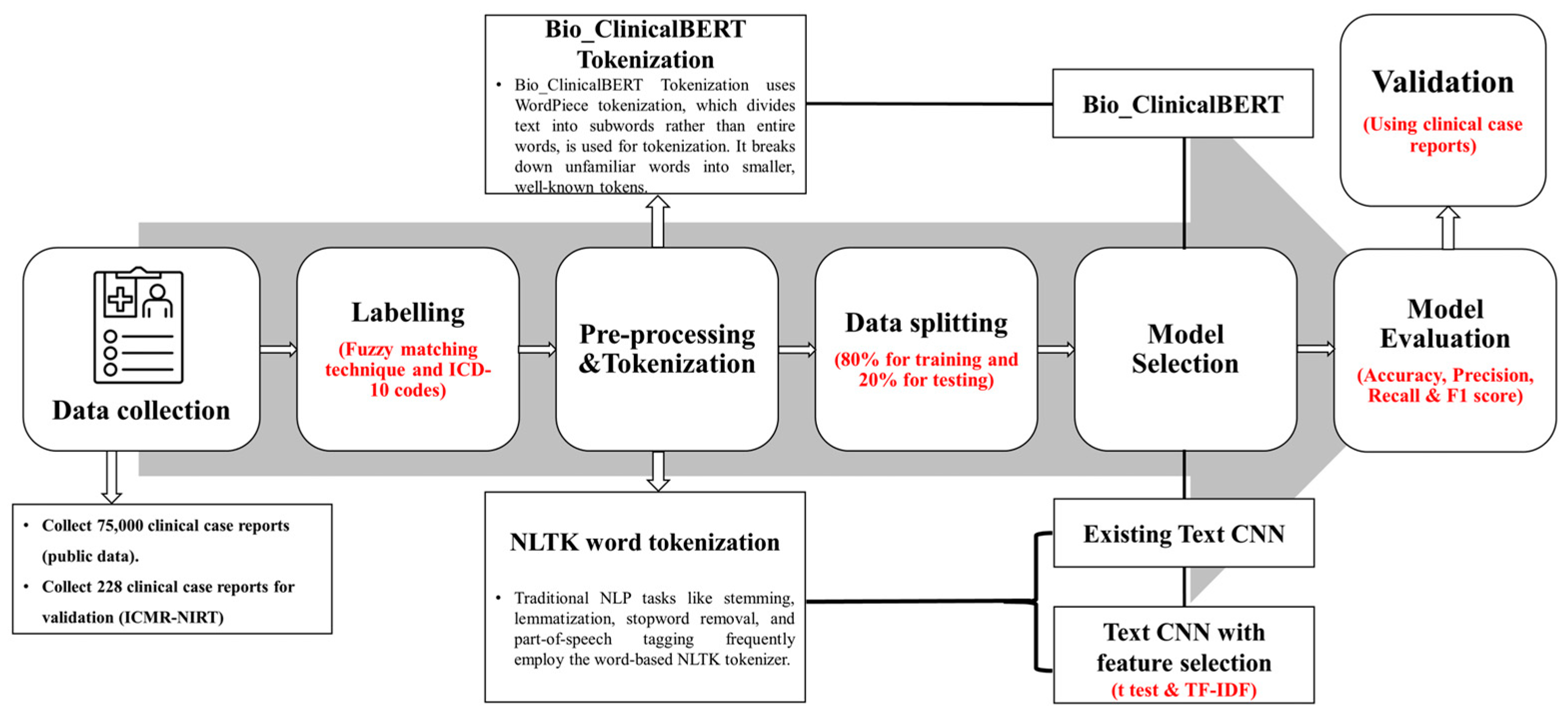
In the pre-processing steps, we employed the NLP rule-based pre-processing of the clinical notes for the two models, which are the existing Text CNN and proposed Text CNN with t-test models, such as lowercase text to convert all the texts into lowercase to ensure uniformity and reduce variability. Numerical values were replaced with their word equivalents for consistency, and medical measurement units were converted into their full word forms for standardization. Lemmatization was applied to reduce words to their base or dictionary forms. Common, non-informative words (stop words) and possessive markers like “s” were removed, and the text was tokenized into individual words or tokens for further analysis. A detailed summary of the text pre-processing steps applied before the model training is provided in the Supplementary File, Table S3. In contrast, the Bio_ClinicalBERT model does not require manual pre-processing, as its transformer-based architecture automatically handles text normalization using a self-attention mechanism to process the text. The framework of this study is illustrated in Figure 2.
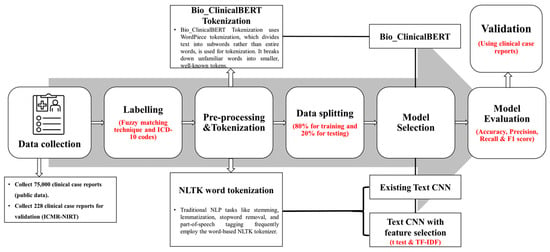
Figure 2.
Study framework to identify patients with TB or non-TB using the EHR dataset; the models were validated using the institutional clinical notes. This framework consists of data labeling, preprocessing and tokenization, and model training, testing, and validation. Finally, the models were evaluated using various performance metrics.
2.3. Model Architectures
2.3.1. Text CNN
Text-CNN is a modified CNN designed specifically for text data, making it well-suited to tasks such as sentiment analysis and text classification. Due to their strong performance, especially in processing lengthy texts, CNNs have gained attention for use in NLP tasks [36,37,38]. In Text CNN, a pre-trained word vector serves as the input, from which the model generates relevant word embeddings. Unlike CNN [39], the convolution kernel’s width must match the word vector’s size when applying the convolution. This ensures that the model effectively captures the contextual information in text sequences. Text CNN plays a crucial role in extracting text features from EHRs by employing various techniques to enhance feature extraction from medical texts, minimize the inclusion of patient privacy-related information, highlight key features relevant to downstream clinical tasks, and ensure privacy protection while retaining critical textual insights.
2.3.2. Bio_ClinicalBERT
We utilized Bio_ClinicalBERT [40], a domain-adapted version of BioBERT v1.0, for the clinical text classification task. BioBERT v1.0 extends the original BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) via pre-training on 200 k PubMed abstracts and 270 k PMC full-text articles, enabling it to understand biomedical language. The Bio_ClinicalBERT model builds upon this foundation through an additional pretraining on approximately 880 million words from the clinical notes in the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) database, significantly enhancing its contextual understanding of clinical language. This extensive domain adaptation makes Bio_ClinicalBERT particularly effective in clinical NLP applications, including the analysis and classification of clinical text data. In this study, we employed Bio_ClinicalBERT to examine its capability in clinical tasks that involve identifying meaningful insights from clinical text data.
2.3.3. Proposed Text CNN with Feature Selection
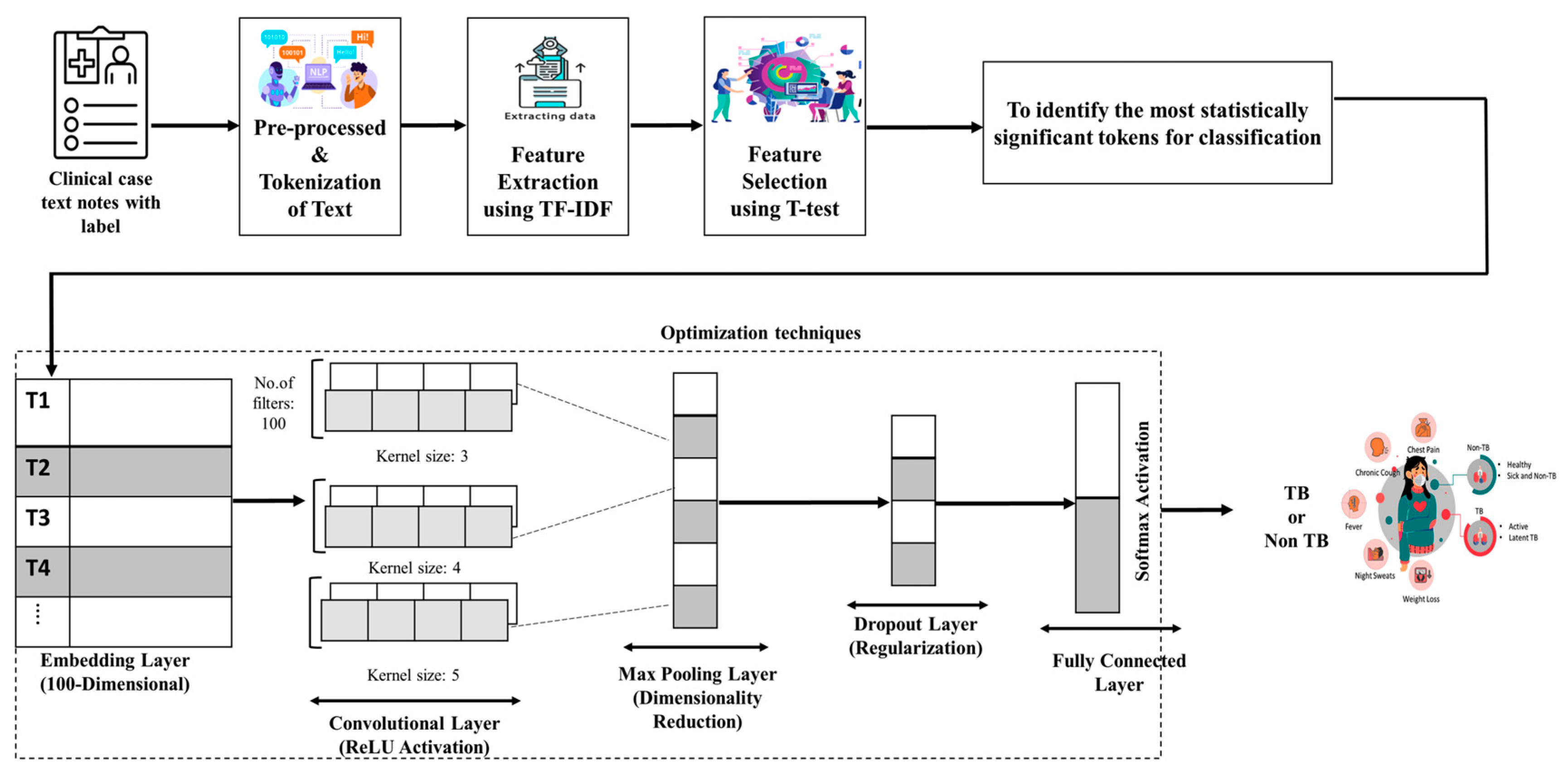
To further refine the input features for the Text CNN model, we applied a combination of Term Frequency–Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF)- and t-test-based feature selection. TF-IDF was used to quantify the importance of words within the clinical test corpus, while the t-test was employed to identify statistically significant terms that contribute to distinguishing between TB and non-TB clinical case reports. This approach helped to eliminate irrelevant words, reduce noise, and enhance the performance of the model. Figure 3 illustrates the framework of the proposed model, enhanced via t-test feature selection.
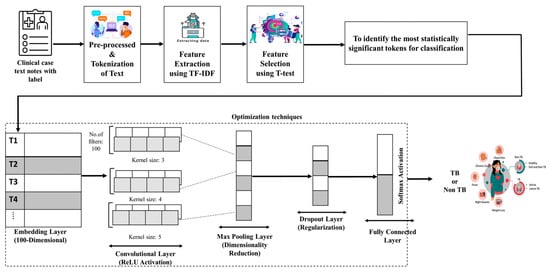
Figure 3.
Model architecture for the proposed Text CNN with feature selection.
2.3.4. TF-IDF
TF-IDF is an unsupervised word-weighting technique that is widely used for text-mining and information retrieval. It evaluates the importance of a word in a document relative to a collection of documents (the corpus). The term frequency (TF) component measures how often a word appears in a specific document, while the inverse document frequency (IDF) component downweights words that occur frequently across many documents. This combination ensures that words which are common within a particular document but rare across multiple documents are assigned higher weights. TF-IDF is particularly useful in clinical text analysis for identifying discriminative and contextually significant words [41,42].
2.3.5. T-Test
To refine the feature set, we applied a t-test to identify words with statistically significant differences between the TB and non-TB categories [43]. Keywords with p < 0.05 were retained in the vocabulary, effectively filtering out irrelevant or redundant terms. Each selected term was assigned a unique index. By combining TF-IDF with t-test-based feature selection, this approach ensured that the CNN model focused on the most relevant features, thereby reducing noise and dimensionality. This not only enhanced classification accuracy but also improved model interpretability and generalization, making it a robust tool for TB detection in clinical text analysis. After developing the analysis framework, we validated the model using retrospective baseline screening clinical text data collected from the ICMR—NIRT. The validation data comprised 228 clinical case notes, offering a reliable assessment of the model’s performance in a real-world clinical setting.
2.4. Model Setup Details
We aim to compare the performance of several models of analysis through distinct hyperparameters and training configurations. The Text CNN model is an existing model, and Text CNN with t-test was a proposed model that was utilized in this study, with an embedding dimension of 100, 100 filters, and filter sizes of (3, 4, 5). It was designed for two classes, with a dropout rate of 0.5 and Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) as the activation function. The model was trained using the Adam optimizer with a batch size of 16, eight epochs, and a learning rate of 0.001. The total number of parameters for this model was 1.12 million. Bio_ClinicalBERT model is a pre-trained model employed in our study, featuring an embedding dimension of 768 and 12 encoder layers. It was configured for binary classification with a dropout rate of 0.1. The activation functions used were Gaussian error linear unit (GeLU) in the Transformer Layers and Softmax in the final layer. We employed the associated WordPiece tokenizer with a maximum sequence length of 512 tokens to preprocess the input data. All 12 transformer encoder layers and the classification head were jointly fine-tuned. The classification head consisted of a fully connected dense layer with SoftMax activation applied to the [CLS] token representation. Fine-tuning was performed on 1743 clinical cases, each with an average input length of 553 tokens (truncated to 512). The model was trained using the Adam optimizer over three epochs, with a batch size of eight, and a learning rate of 5 × 10−5. Despite the absence of GPU acceleration, training was conducted on an Intel® CoreTM i7-7700 CPU @ 3.60 GHz with 16 GB RAM, using PyTorch version 2.2.0 and the Hugging Face Transformers library. The total number of model parameters was 108 million. The entire training process, including data loading and evaluation, was completed in approximately 60 min, demonstrating the feasibility of CPU-based fine-tuning for small to moderately sized clinical text datasets. The hyperparameters for each model are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Hyperparameters and training parameters used for three different models.
2.5. Model Evaluation
To assess model performance, we evaluated the models using the key metrics of precision, recall, and F1-score to determine the best-performing model.
Precision: A widely used metric for evaluating a model’s ability to correctly identify relevant cases. It is calculated as the ratio of true positives (TP) to the sum of TP and false positives (FP). This metric represents the proportion of correctly predicted positive cases out of all predicted positive cases, as shown in Equation (1):
Recall or Sensitivity: Measures the model’s ability to correctly identify the actual positive cases. This is calculated as the ratio of TP to the sum of TP and false negatives (FN). This metric represents the proportion of correctly predicted positive cases out of all actual positive cases in the dataset, as shown in Equation (2):
F1-Score: The F1-score provides a balanced measure of precision and recall by computing their harmonic mean. It accounts for both FP and FN, making it particularly useful when dealing with imbalanced datasets. The metric is computed using Equation (3):
True Positive (TP): The number of TB-related clinical case reports that are correctly identified as TB cases by the model.
False Positive (FP): The number of non-TB-related clinical case reports that are incorrectly identified as TB cases by the model.
True Negative (TN): The number of non-TB-related clinical case reports that are correctly identified as non-TB cases by the model.
False Negative (FN): The number of TB-related clinical case reports that are incorrectly identified as non-TB cases by the model.
3. Results
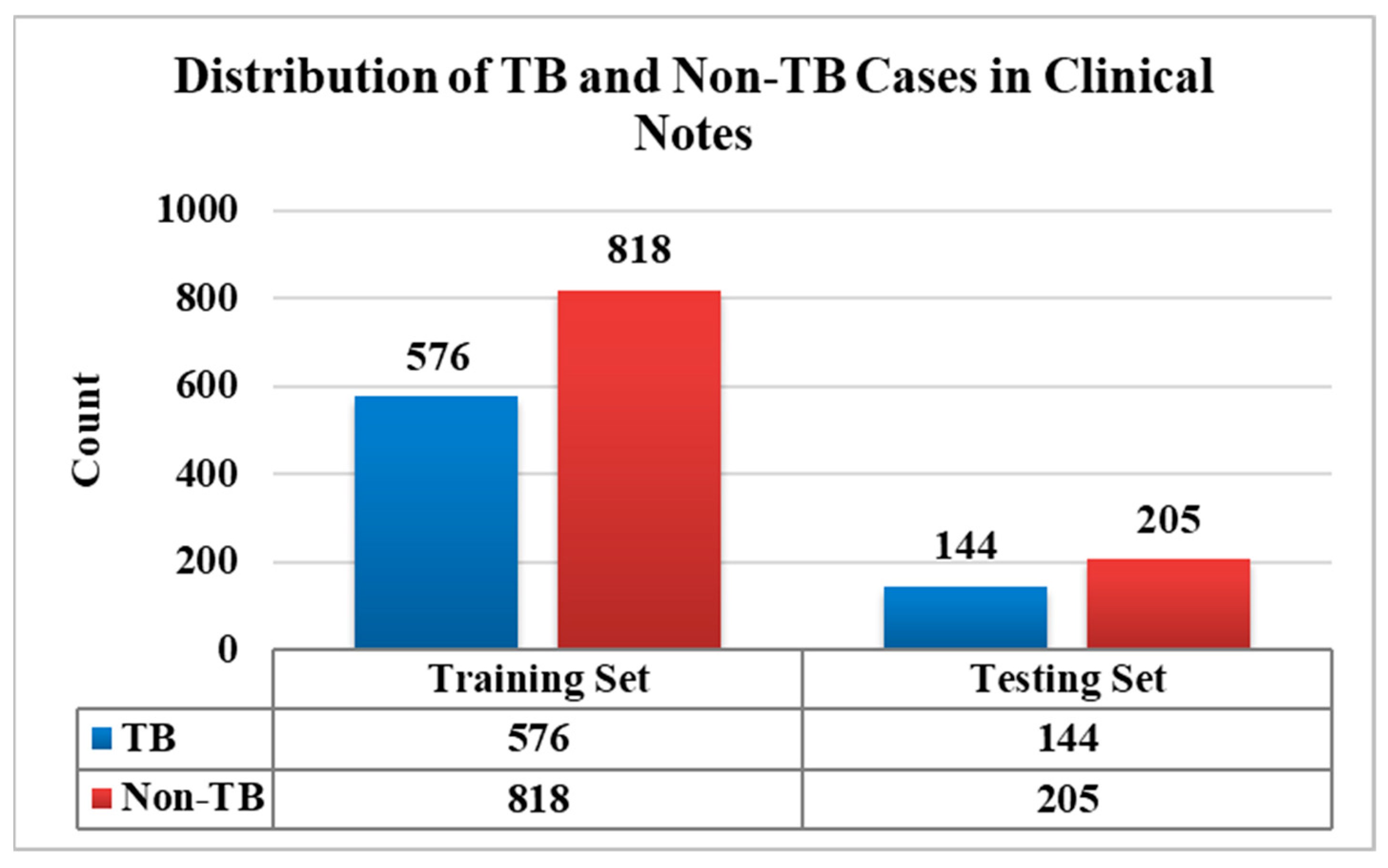
A proper and precise diagnosis is essential for improving patient outcomes and preventing the spread of TB, which remains a major worldwide health burden. Clinical, radiographic, and microbiological examinations have been used to diagnose TB; however, a greater amount of patient information is now stored in EHRs, often in the form of unstructured clinical notes. In the present study, we utilized a dataset comprising 1743 clinical notes, which was split into 80% (1394 clinical notes) for training while the remaining 20% (349 clinical notes) were used for testing the models, as depicted in Figure 4. All the analyses were carried out in Python version 3.11, using several essential libraries that support DL and NLP. The Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) facilitated the initial text-preprocessing tasks. The Hugging Face Transformers libraries provide access to pre-trained language models, such as Bio_ClinicalBERT, which are made especially for processing medical text data, enabling the extraction of meaningful features for clinical notes. DL frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow were used to train and fine-tune neural networks on unlabeled data. Keras, with a high-level Application Programming Interface (API), supports flexible and accessible model implementation. Scikit-learn played an essential part in statistical feature selection (t-test), model assessment (using precision, recall, and F1-score), and validation. The integration of DL with statistical feature selection techniques improved the clinical text analysis, resulting in a more reliable and effective approach to TB prediction from unstructured clinical case data.
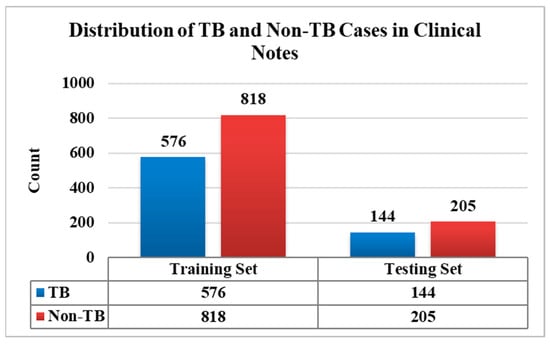
Figure 4.
Distribution plot of the TB and non-TB clinical notes.
The models evaluated were the existing Text CNN, the proposed Text CNN with t-test, and Bio_ClinicalBERT models. The models trained with an average sentence length of 553 words. We pre-processed the text data using NLTK, applying word tokenization, stopword removal, stemming, and lemmatization for the Text CNN and the Text CNN with t-test models. After preprocessing, the Text CNN model utilized 27,454 tokens; for the Bio_ClinicalBERT model, approximately 30,522 tokens were used, with WordPiece tokenization, a subword-based method designed to handle out-of-vocabulary terms.
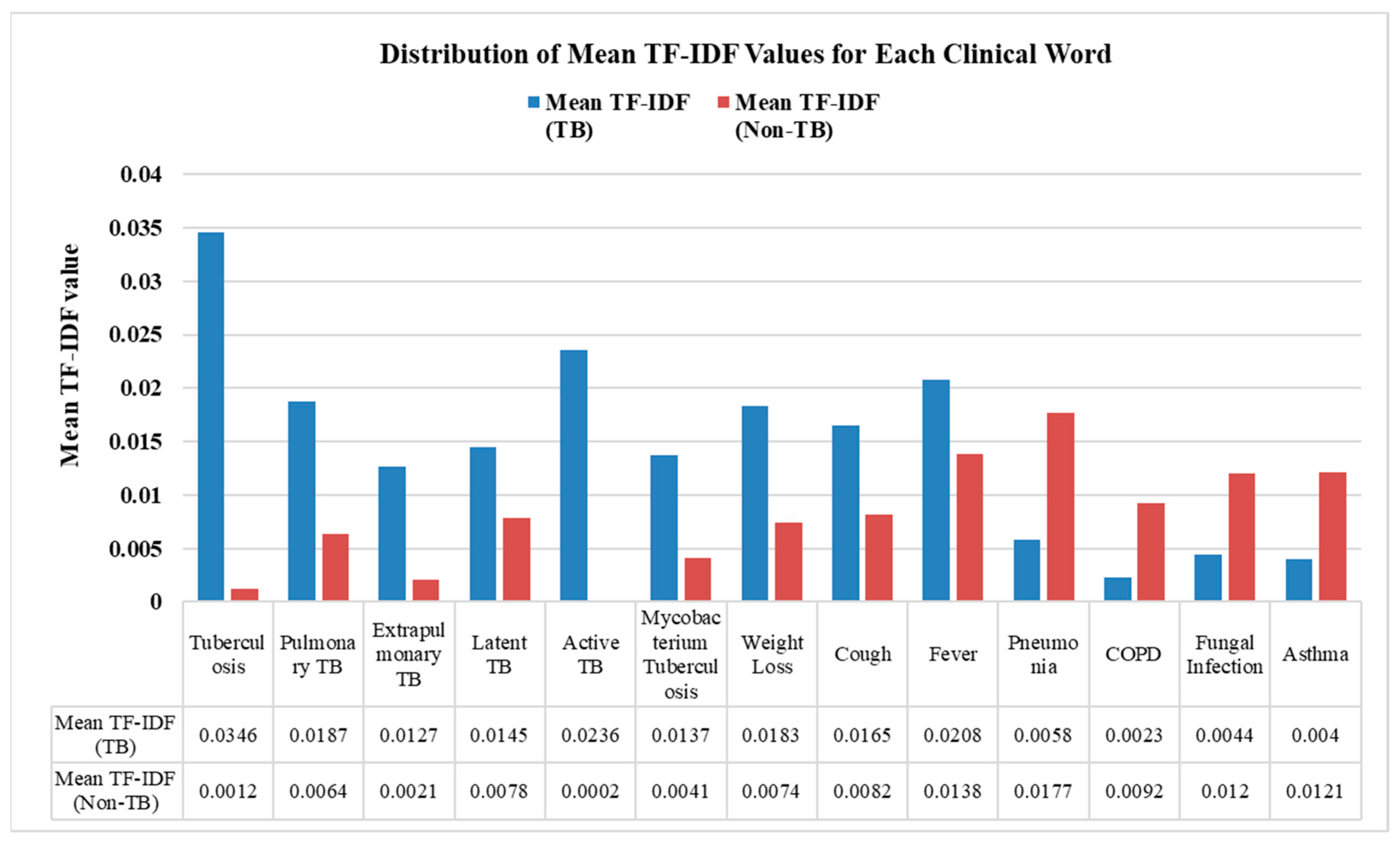
The Text CNN with the t-test model enhanced the input by selecting 1741 statistically significant tokens for training. To assess the statistical significance of these differences, we conducted a t-test comparing the TF-IDF distributions for each keyword across the TB and non-TB groups, identifying terms with significant differences (p < 0.05). This test determines whether the observed differences were statistically meaningful or likely due to random chance. The mean TF-IDF values of each clinical keyword associated with TB and non-TB patients are shown in Figure 5. Blue bars represent the mean TF-IDF values for TB-related keyword terms, while red bars represent those found in non-TB clinical notes. These differences highlight the distinct importance of certain terms in TB versus non-TB. For instance, keywords such as “Tuberculosis”, “Active TB”, and “Mycobacterium tuberculosis” have notably higher mean TF-IDF values, of 0.0346, 0.0236, and 0.0137, respectively, in TB-related clinical notes. In contrast, terms like “Pneumonia”, “Fungal Infection”, and “Asthma” show higher relevance in non-TB cases, with mean TF-IDF values of 0.0177, 0.012, and 0.0121. By retaining only statistically and clinically relevant terms, this feature selection step improves both the robustness and interpretability of the model, allowing it to leverage validated linguistic markers in the classification of TB and non-TB clinical notes.
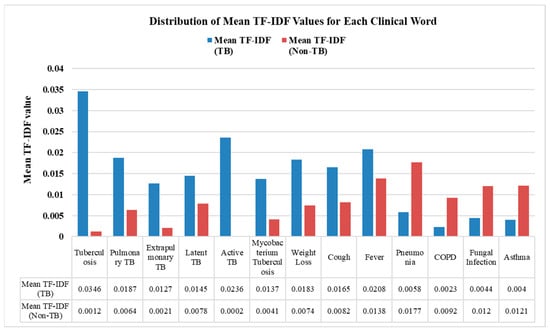
Figure 5.
Distribution of mean TF-IDF values for each clinical word in the TB and non-TB categories.
The test dataset comprises 349 clinical cases, of which 144 were TB and 205 were non-TB instances. Table 2 summarizes the model-specific performance measures: precision, recall, F1-score, and Area under the Curve (AUC). The trained models of Text CNN, Bio_ClinicalBERT, and Text CNN with t-test feature selection were assessed on a test dataset. The Text CNN model achieved a precision of 72.22%, indicating a high rate of false positives (FP) in which non-TB cases were misclassified as TB. However, its recall of 88.89% suggests it successfully identifies most TB cases, although with some compromise in specificity. An AUC of 0.86 reflects a reasonably strong overall classification performance. The Bio_ClinicalBERT improved upon the Text CNN in terms of precision, achieving 83.33%, thereby reducing the FP. However, its recall dropped to 80.54%, suggesting it misses more actual TB cases. In contrast, the Text CNN with t-test feature selection outperforms the other two models across all the evaluation metrics. It achieved the highest precision of 88.19%, indicating the effective minimization of FP, and the highest recall of 90.71%, meaning it correctly identifies the majority of TB cases. The F1-score of 89.44% reflects a strong balance between precision and recall, while its AUC of 0.91 demonstrates the best overall classification performance. These results suggest that feature selection techniques, such as the t-test, can greatly enhance model performance by removing irrelevant attributes and concentrating on the most informative attributes.

Table 2.
Performance metrics of different models on the test set.
To evaluate a classification model’s performance, a confusion matrix for the test set is presented in Table 3. The confusion matrix provides insights into the distribution of correct and incorrect predictions, allowing for a deeper understanding of each model’s classification behavior. Among the models, the proposed Text CNN model demonstrated the best performance. It correctly identified 127 (TP) TB cases and made only 17 (FP) errors, misclassifying non-TB cases as TB. Additionally, it recorded just 13 (FN), meaning that it missed the fewest actual TB cases, thus making it the most reliable model. The Bio_ClinicalBERT model showed improved precision over the existing Text CNN model by reducing the (FP) to 24. However, it missed 29 actual TB cases (FN), which negatively affected its recall. The Text CNN model achieved a low number of (FN) of 13, showing strong sensitivity in identifying TB cases. However, it had the highest number of (FP) of 40, meaning it frequently misclassified non-TB cases as TB, which reduces its overall precision.

Table 3.
Confusion matrix for the test set.
The validation dataset comprises 228 clinical notes, which were evaluated by each model to predict the TB cases. The performance metrics of the three different models on the validation set are summarized in Table 4. The evaluation of the validation dataset showed that the Text CNN with the t-test model achieved the best performance, with 100% precision, 98.85% recall, and 99.42% F1-score, and an AUC of 0.982. These results indicate that it perfectly identified all non-TB cases while detecting nearly all TB cases, making it the most reliable model. The Bio_ClinicalBERT model achieved 100% precision, correctly identifying all TB cases. However, its recall was considerably lower, at 76.11%, indicating that it failed to detect many actual non-TB cases. This imbalance led to an F1-score of 86%, suggesting that while the model effectively avoids false positives, it is not effective in detecting TB cases. It obtained an AUC of 0.877; although higher than that of the Text CNN, it remained lower than the Text CNN with the t-test model, making it a weaker overall choice. The Text CNN model demonstrated a high recall of 98.66%, successfully identifying most TB cases. However, its precision was lower, at 85.47%, indicating a higher rate of FP, meaning some non-TB cases were incorrectly classified as TB. With an AUC of 0.835, it was the least effective of the three models in distinguishing between TB and non-TB cases.

Table 4.
Performance metrics for the different models of a validation set.
Table 5 presents the confusion matrix results for the validation dataset, providing a detailed insight into model performance during the validation phase. By comparing these results with the test sets’ confusion matrix, it assists in the identification of any overfitting or underfitting problems. The confusion matrix helps evaluate each model’s ability to correctly classify TB and non-TB cases, offering a comprehensive view of their predictive accuracy. The proposed Text CNN with t-test model demonstrated the strongest performance, correctly identifying 172 (TP), with only two (FN) and zero (FP). This indicates that it accurately detects nearly all TB cases while avoiding any misclassification of non-TB cases, making it the most clinically effective model. The Bio_ClinicalBERT model also achieved zero (FP). However, it recorded 54 actual non-TB cases (FN), meaning it failed to detect a significant number of actual TB cases, which limits its reliability for TB detection. The Text CNN model detects 147 TB cases correctly (TP) and misses only 2 (FN). However, it achieved 25 (FP), misclassifying several non-TB cases as TB. This notable reduction in misclassifications by the proposed model highlights the value of feature selection, which significantly enhances classification accuracy by emphasizing the most informative features.

Table 5.
Confusion matrix for the validation set.
The test and validation dataset results show that the Text CNN with t-test model outperformed the others; it achieved the highest precision, recall, and F1-score, while also minimizing the FP and FN. It is the most clinically accurate model for the identification of TB in unlabeled clinical notes. The Text CNN model recorded good recall while recording more false positives, which could lead to overdiagnosis. Bio_ClinicalBERT model, while having high precision, has low recall, in the sense that it misses many TB cases, making it less suitable for this application. From the findings, the proposed model is suggested for TB classification in clinical text analysis for small samples.
4. Discussion
Employing DL techniques, this study demonstrates how clinical text data can be utilized for disease prediction. We propose a Text CNN model with t-test-based feature selection for classifying TB from clinical text data. Yao (2019) et al. [44] introduced a new method for classifying clinical texts, with a particular focus on the Obesity Challenge. In their study, they employed a CNN model integrated with rule-based feature engineering and knowledge-guided DL to classify medical texts related to obesity and its comorbidities. Incorporating findings from earlier studies on the CNN-based classification of medical texts and biomedical text classification, Rios and Kavuluru (2015) [45] demonstrated that CNNs outperform conventional models, like logistic regression and Support Vector Machines. However, they noted that the absence of explicit feature selection could introduce noise during feature extraction. Similarly, Liang et al. (2017) further highlighted that CNNs often capture redundant and irrelevant features, recommending the use of statistical feature selection methods to enhance efficiency [46]. Addressing this limitation, our model integrates t-test based feature selection before CNN model training, ensuring that only statistically significant and clinically meaningful features are used. This approach effectively reduces noise, improves classification accuracy, and enhances the clinical relevance of TB detection.
The proposed model achieved a strong performance in predicting TB from clinical note descriptions, with an AUC of 0.91, F1-score of 89.44%, recall of 90.71%, and precision of 88.19%. On the validation dataset, the model performed even better, achieving an AUC of 0.982, an F1-score of 99.42%, a recall of 98.55%, and a precision of 100%. These results were obtained after applying the NLTK word tokenization method as part of the preprocessing pipeline. Overall, the findings demonstrated the effectiveness of DL models in predicting TB from clinical notes and highlighted the critical role of feature selection in enhancing the predictive performance of DL models.
The study also has several important implications for healthcare. Firstly, the use of DL models for disease prediction holds great promise for transforming healthcare by enhancing remote diagnostic capabilities. Additionally, we demonstrated how a fuzzy matching approach can be used to extract keywords from clinical notes that match ICD-10 codes, thereby automating the conversion of unlabeled clinical notes into labeled data for disease prediction. To fully harness the potential of DL models for illness prediction, further research is required, especially research exploring alternative models and methodologies. By enabling earlier detection and expanding remote diagnostic capabilities, DL-based healthcare solutions have the potential to improve patient outcomes and enable more effective disease management.
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated three DL-based models for the classification of TB from the clinical text notes: the existing Text CNN, the Text CNN with t-test, and the Bio_ClinicalBERT models. Among these, the proposed model emerged as the most reliable, achieving an optimal balance between recall and precision. It effectively minimized both FP and FN, significantly enhancing classification precision. Moreover, the model’s generalizability and robustness were validated using an institutional dataset, validating its effectiveness in real-world clinical settings. The Text CNN model exhibited a higher number of Type I errors, leading to an increase in FP, while the Bio_ClinicalBERT model showed a higher number of Type II errors, resulting in TB cases being missed.
Therefore, the proposed model significantly improves the classification accuracy while reducing both FP and FN, making it the most effective framework for accurate TB classification from clinical text data. This advancement supports improved clinical decision-making and contributes to public health initiatives. Although the Bio_ClinicalBERT model demonstrated excellent precision, its poor recall resulted in undetected TB cases, a major risk in disease diagnosis.
Limitations: A key limitation of this study is the computational demand required to train DL models like Text CNN and Bio_ClinicalBERT. High-performance hardware such as GPUs or TPUs are essential, but not always accessible in every healthcare facility. Furthermore, real-time clinical deployment may require additional fine-tuning and validation by physicians to ensure optimal performance. The Text CNN and proposed Text CNN with t-test performed well on a relatively small dataset due to the robust pre-processing of text, which standardized medical terminology and reduced noise. Although Bio_ClinicalBERT is powerful model, it may struggle with smaller datasets due to its complexity and reliance on extensive pre-training. The limited data may restrict its ability to capture nuanced clinical variations, contributing to lower recall in the TB classification. Additionally, while the model was trained on a publicly available dataset and validated using a small institutional dataset, its performance on data from other hospitals or regions has not yet been tested. Domain variations in phrasing, terminology, or abbreviations may require model adaptation for broader applicability.
Future Work: We propose the use of large language models (LLMs) to enhance the model’s capacity to interpret complex clinical text. Fine-tuning domain-specific LLMs on large TB-related datasets may improve contextual understanding and classification accuracy. Additionally, we aim to develop an ontology-based diagnostic system that integrates labeled medical knowledge to support text classification. Incorporating structured clinical data, such as test results, radiographic reports, and symptom descriptions, through semantic reasoning and knowledge graphs could lead to a more precise and interpretable TB diagnostic system. To ensure broader generalizability, we recommend cross-institutional and real-world validation using clinical notes from different hospitals in geographic regions. For practical testing, we plan to integrate the model into EHR systems, facilitating its seamless deployment in clinical workflows and improving TB detection in real-world healthcare settings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/informatics12030064/s1. Table S1: TB-labeled clinical notes after using fuzzy matching with ICD-10 codes; Table S2: Non-TB-labeled clinical notes after using fuzzy matching with ICD-10 codes; Table S3: Text pre-processing steps performed on clinical text data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F.A., S.K. and P.C.; methodology, S.K. and P.C.; software, S.K. and S.F.A.; validation, P.C. and S.F.A.; formal analysis, S.F.A. and S.K.; investigation, P.C. and S.K.; resources, S.K. and P.C.; data curation, S.K. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F.A. and P.C.; writing—review and editing, P.C. and S.K.; visualization, S.F.A. and S.K.; supervision, P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Article Processing Charges (APC) were supported by the ICMR—National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai, India.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available at https://zenodo.org/records/10079370 (accessed on 20 December 2024) or the article titled MultiCaRe: An open-source clinical case dataset for medical image classification and multimodal AI applications.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the authorities of the ICMR-National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Indian Council of Medical Research, Chennai, India, for permitting us to use the data for text classification using clinical notes to validate the models.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| Non-TB | Non-Tuberculosis |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ICD | International Categorization of Diseases |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| MIMIC II | Multiparameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care II |
| MIMIC-III | Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| Text CNN | Text Convolutional Neural Network |
| TP | True Positives |
| TN | True Negatives |
| FP | False Positives |
| FN | False Negatives |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| TF-IDF | Term Frequency–Inverse Document Frequency |
| IDF | Inverse Document Frequency |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| GeLU | Gaussian Error Linear Unit |
| NLTK | Natural Language Toolkit |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
References
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240101531 (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Falzon, D.; Timimi, H.; Kurosinski, P.; Migliori, G.B.; Van Gemert, W.; Denkinger, C.; Isaacs, C.; Story, A.; Garfein, R.S.; Bastos, L.G.D.V.; et al. Digital Health for the End TB Strategy: Developing Priority Products and Making Them Work. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.J.A.; Arinaminpathy, N.; Bloom, A.; Bloom, B.R.; Boehme, C.; Chaisson, R.; Chin, D.P.; Churchyard, G.; Cox, H.; Ditiu, L.; et al. Building a Tuberculosis-Free World: The Lancet Commission on Tuberculosis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1331–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A. Text Mining in Healthcare: Bringing Structure to Electronic Health Records. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.T.; Pincock, D.; Baumgart, D.C.; Sadowski, D.C.; Fedorak, R.N.; Kroeker, K.I. An Overview of Clinical Decision Support Systems: Benefits, Risks, and Strategies for Success. npj Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Health & Human Services. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Spasic, I.; Nenadic, G. Clinical Text Data in Machine Learning: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2020, 8, e17984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenivtseva, Y.; Kopanitsa, G. Investigation of Content Overlap in Proprietary Medical Mappings. In ICT for Health Science Research; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Ginige, J.A. Analysing Effectiveness of Multi-Label Classification in Clinical Coding. In Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 29–31 January 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Rastegar-Mojarad, M.; Moon, S.; Shen, F.; Afzal, N.; Liu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Mehrabi, S.; Sohn, S.; et al. Clinical Information Extraction Applications: A Literature Review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 77, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, A.; Hulth, A.; Megyesi, B. General-Purpose Text Categorization Applied to the Medical Domain. 2007. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:40971 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Larkey, L.S.; Croft, W.B. Automatic Assignment of Icd9 Codes to Discharge Summaries; Technical report; University of Massachusetts at Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA, 1995; Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/30740467/10.1.1.49.816.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Available online: https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classification-of-diseases (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Li, F.; Yu, H. ICD Coding from Clinical Text Using Multi-Filter Residual Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 8180–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullenbach, J.; Wiegreffe, S.; Duke, J.; Sun, J.; Eisenstein, J. Explainable Prediction of Medical Codes from Clinical Text. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Past, Present and Future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, e000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, M.; Sonnessa, M.; Tànfani, E.; Testi, A. Unsupervised Neural Networks for Clustering Emergent Patient Flows. Oper. Res. Health Care 2018, 18, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Giachanou, A.; Mosteiro, P.; Verberne, S. Natural Language Processing and Text Mining (Turning Unstructured Data into Structured). In Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Real-World Data; Asselbergs, F.W., Denaxas, S., Oberski, D.L., Moore, J.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, W.; Yetisgen, M.; Harris, W.P.; Kwan, S.W. Natural Language Processing in Oncology: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, R.J.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Sun, J.; Ebadollahi, S.; Stewart, W.F. Automatic Identification of Heart Failure Diagnostic Criteria, Using Text Analysis of Clinical Notes from Electronic Health Records. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2014, 83, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamian, L.; Wheless, L.; Crofford, L.J.; Barnado, A. Rule-Based and Machine Learning Algorithms Identify Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Accurately in the Electronic Health Record. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, B.; Karimi, S.; Nguyen, A.; McGuire, R.; Muscatello, D.; Kemp, M.; Truran, D.; Zhang, M.; Thackway, S. Automatic Classification of Diseases from Free-Text Death Certificates for Real-Time Surveillance. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocbek, S.; Cavedon, L.; Martinez, D.; Bain, C.; Mac Manus, C.; Haffari, G.; Zukerman, I.; Verspoor, K. Text Mining Electronic Hospital Records to Automatically Classify Admissions against Disease: Measuring the Impact of Linking Data Sources. J. Biomed. Inform. 2016, 64, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Sammani, A.; Van Der Heijden, P.G.M.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Oberski, D.L. ETM: Enrichment by Topic Modeling for Automated Clinical Sentence Classification to Detect Patients’ Disease History. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2020, 55, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammani, A.; Bagheri, A.; van der Heijden, P.G.; Te Riele, A.S.; Baas, A.F.; Oosters, C.A.J.; Oberski, D.; Asselbergs, F.W. Automatic Multilabel Detection of ICD10 Codes in Dutch Cardiology Discharge Letters Using Neural Networks. npj Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Altosaar, J.; Ranganath, R. ClinicalBERT: Modeling Clinical Notes and Predicting Hospital Readmission. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnagaddala, J.; Liaw, S.-T.; Ray, P.; Kumar, M.; Chang, N.-W.; Dai, H.-J. Coronary Artery Disease Risk Assessment from Unstructured Electronic Health Records Using Text Mining. J. Biomed. Inform. 2015, 58, S203–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, V.; Scheepers, F.; van Wijk, L.M.; Spruit, M. DEDUCE: A Pattern Matching Method for Automatic de-Identification of Dutch Medical Text. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, H.J.; Kim, H.Y. Learning Representations for the Early Detection of Sepsis with Deep Neural Networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Luo, Y. Prediction of Breast Cancer Distant Recurrence Using Natural Language Processing and Knowledge-Guided Convolutional Neural Network. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 110, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y. Convolutional Neural Network for Sentence Classification. 2015. Available online: https://uwspace.uwaterloo.ca/items/42654efd-45e2-4c67-b906-158e7e349188 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent Neural Network Regularization. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievas Offidani, M.A.; Delrieux, C.A. Dataset of Clinical Cases, Images, Image Labels and Captions from Open Access Case Reports from PubMed Central (1990–2023). Data Brief 2024, 52, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, Y.-S. Sentiment Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Li, I.; Kotoulas, S.; Suzumura, T. Medical Text Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Informatics for Health: Connected Citizen-Led Wellness and Population Health; IOS Press: Amsterdam, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, N.I. Convolution Neural Network for Text Mining and Natural Language Processing. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 662, p. 052010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xi, X.; Chen, J.; Sheng, V.S.; Ma, J.; Cui, Z. A Survey of Deep Learning for Electronic Health Records. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilyalsentzer/Bio_ClinicalBERT Hugging Face. Available online: https://huggingface.co/emilyalsentzer/Bio_ClinicalBERT (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Lam, S.L.Y.; Lee, D.L. Feature Reduction for Neural Network Based Text Categorization. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Systems for Advanced Applications, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 21 April 1999; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Weng, J.; Zhang, J. Feature Selection for Text Classification: A Review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 3797–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Lv, W.; Wang, D. T-Test Feature Selection Approach Based on Term Frequency for Text Categorization. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Mao, C.; Luo, Y. Clinical Text Classification with Rule-Based Features and Knowledge-Guided Convolutional Neural Networks. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, A.; Kavuluru, R. Convolutional Neural Networks for Biomedical Text Classification: Application in Indexing Biomedical Articles. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–12 September 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Y. Text Feature Extraction Based on Deep Learning: A Review. J. Wirel. Com. Netw. 2017, 2017, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).