Determinants of Internal Control System Effectiveness: Evidence from Greek Listed Companies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Legislative Framework of Corporate Governance in Greece
3. Literature Review
3.1. Internal Control System
3.2. Controls and Procedures
- (a)
- Efficient business conduct: Controls should be in place to ensure that processes flow smoothly and operations are free from disruptions. This mitigates against the risk of inefficiencies and threats to the creation of value in the organization.
- (b)
- Safeguarding assets: Controls should be in place to ensure that assets are deployed for their proper purposes and are not vulnerable to misuse or theft.
- (c)
- Preventing and detecting fraud and other unlawful acts: Even small businesses with simple organizational structures may fall victim to these violations. However, as organizations increase in size and complexity, the nature of fraudulent practices becomes more diverse, and controls must be capable of addressing these evolving threats.
- (d)
- Completeness and accuracy of financial records: An organization cannot produce accurate financial statements if its financial records are unreliable.
- (e)
- Timely preparation of financial statements: Organizations should be able to fulfill their legal obligations to submit their account accurately and on time. They also have a duty to their shareholders to produce meaningful statements. Internal controls may also be applied to management accounting processes, which are necessary for effective strategic planning, decision-making, and monitoring of organizational performance.
3.3. Risk Management
3.4. Internal Audit
3.5. Compliance
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Sample
4.2. Data Collection
- A section of 3 questions for the characteristics of the listed company.
- A section of 7 questions for the demographic characteristics of the respondent executive.
- A section of 6 questions for the attributes of the BoD of the listed company.
- A section of 47 questions for the ICS of the listed company is analyzed as follows: 5 questions for the effectiveness of the Internal Control System (ICS), 9 questions for the quality of Controls and Procedures (CP), 12 questions for the quality of Internal Audit (IA), 10 questions for the quality of Compliance, 11 questions for the quality of RM.
4.3. Variables and Models
5. Descriptive Statistics
6. Empirical Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CG | Corporate Governance |
| ICS | Internal Control Systems |
| OP | Organizational Performance |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| ESG | Environmental, Social, and Governance |
| OECD | Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| HCGC | Hellenic Corporate Governance Code |
| BoD | Board of Directors |
| M&A | Mergers and Acquisitions |
| CP | Controls and Procedures |
| IA | Internal Audit |
| RM | Risk Management |
| ATHEX | Athens Stock Exchange |
| IPPF | International Professional Practices Framework |
| IIA | Institute of Internal Auditors |
| COSO | Committee of Sponsoring Organizations |
| HCMC | Hellenic Capital Market Commission |
| SA | Sociétés Anonymes |
| CGS | Corporate Governance System |
| C&E | Compliance & Ethics |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| ERM | Enterprise Risk Management |
| ICSE | Internal Control System Effectiveness |
| CPQ | Controls and Procedures Quality |
| RMQ | Risk Management Quality |
| IAQ | Internal Audit Quality |
| CQ | Compliance Quality |
Appendix A
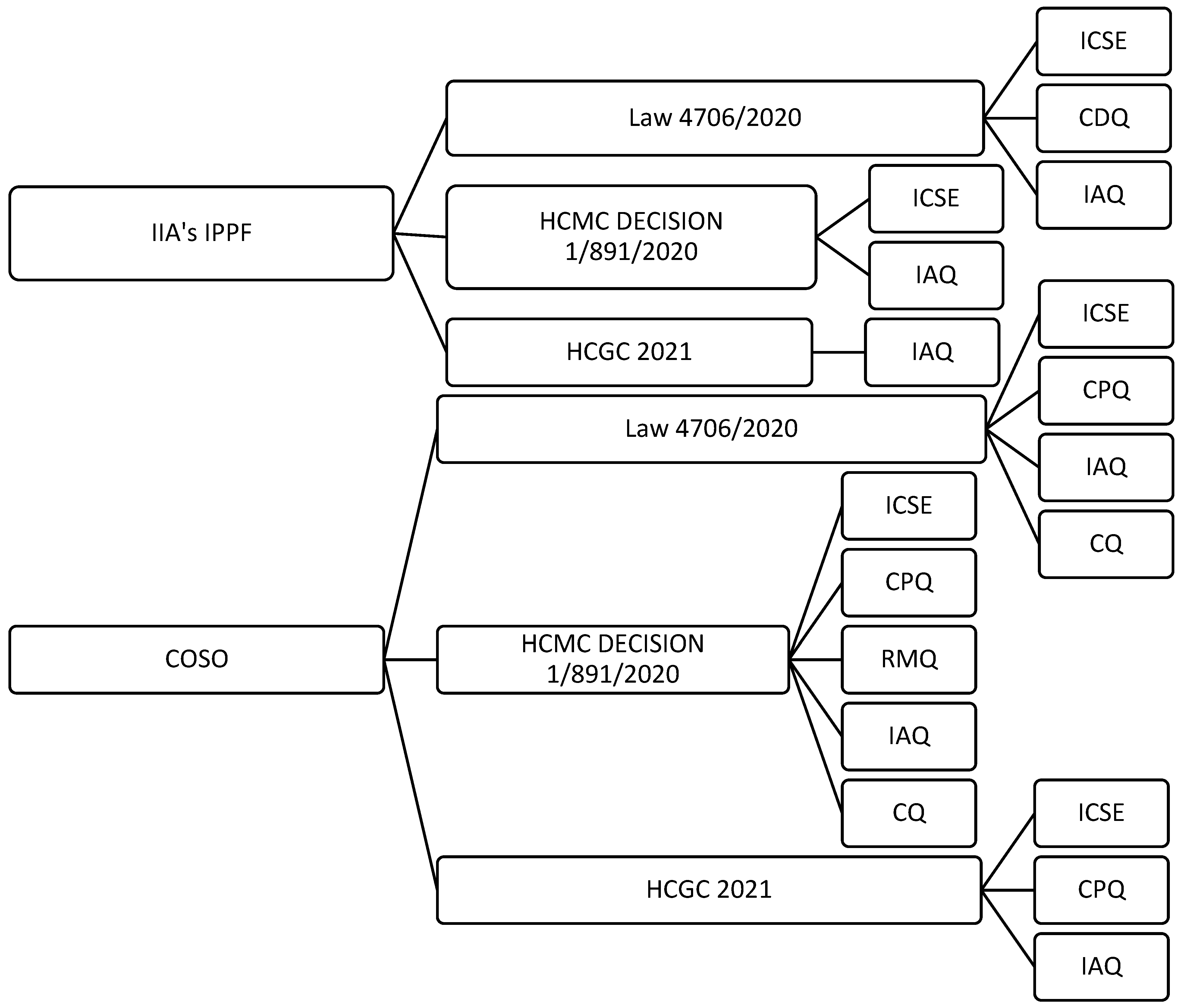
| REGULATORY OVERVIEW MATRIX | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONSTRUCTS | QUALITY FACTORS PER CONSTRUCT | CG FRAMEWORK IN GREECE | COSO | IIA’s IPPF | |||
| LAW 4706/2020 | HCMC DECISION 1/891/2020 | HCGC (2021) | |||||
| DEPENDENT | Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE) | The Board of Directors shall ensure the effectiveness and independence of the functions constituting the ICS by providing the necessary resources and powers (ICSE_1). | Article 4 | N/A | Part C, 6.2 | N/A | N/A |
| Controls and procedures work effectively against risks, ensuring the achievement of management’s objectives (ICSE_2). | N/A | Control Activities | N/A | Control Activities | 2130—Control | ||
| The Internal Audit Unit of the ICS provides objective assurance for the effective operation of the ICS (ICSF_3). | Article 16 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Add Value | ||
| The Compliance Unit implements a practical ethics and compliance program to prevent fraud and corruption risks, and to avoid fines or criminal sanctions (ICSE_4). | Article 13 | Monitoring (Compliance) | N/A | Compliance objectives | N/A | ||
| The Risk Management Unit effectively implements risk assessment, risk response, and risk monitoring procedures (ICSE_5). | N/A | Risk Management | Part C, 6.10 | Risk Assessment | N/A | ||
| INDEPENDENTS | Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ) | How much do you estimate that controls and procedures secure the company’s assets? (CPQ_1) | N/A | 2130-Control | Part C, 6.10 | Operations Objectives | N/A |
| How much do you estimate that controls and procedures help to limit risks to levels acceptable to the company? (CPQ_2) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Control Activities | N/A | ||
| How much do you estimate that the Internal Audit Unit effectively supervises the risk management procedures and controls, contributing to their improvement? (CPQ_3) | 2120—Risk Management | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2130—Control | ||
| Risk Management Quality (RMQ) | How effective do you assess the oversight of Risk Management to be? (RMQ_1) | Article 4 | Risk Management | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| To what extent do you assess that the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_2) | N/A | Risk Management | N/A | Risk Assessment | N/A | ||
| To what extent do you assess that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economical, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country (ies) of activity affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_3) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Risk Assessment | N/A | ||
| Internal Audit Quality (IAQ) | How effective do you think IA supervision is? (IAQ_1) | Article 4 | Monitoring (IA Unit) | Part C, 6.5 | N/A | 1000—Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility | |
| To what extent do you estimate that IA has access to the required sources of information? (IAQ_2) | Article 15 | Monitoring (IA Unit) | N/A | N/A | 1000—Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility | ||
| How much do you estimate that IA uses effective tools and techniques for conducting audits? (IAQ_3) | N/A | Monitoring (IA Unit) | N/A | N/A | 1220—Due Professional Care | ||
| How much do you estimate that the control environment (Company Organizational Structure, Board of Directors, Corporate Responsibility, Human Resources) of your company affects the effectiveness of IA? (IAQ_4) | Article 4 | Control Environment | Part C, 6.9 | Control Environment | Control Environment | ||
| How much more effective do you think IA will become, due to the mandatory external evaluation of the ICS (HCMC Dec. No 1/891/30.09.2020)? (IAQ_5) | Article 4 | Monitoring (IA Unit) | Ν/A | Ν/A | Ν/A | ||
| Compliance Quality (CQ) | How effective do you think Compliance supervision is? (CQ_1) | Article 4 | Monitoring (Compliance) | Ν/A | Principle 1 (COSO ERM 2020) | Ν/A | |
| To what extent do you estimate that Compliance has access to the required sources of information? (CQ_2) | Article 13 | Monitoring (Compliance) | N/A | Principle 18 (COSO ERM 2020) | N/A | ||
| How much do you think the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of Compliance’s work? (CQ_3) | Article 13 | N/A | N/A | Principle 15 (COSO ERM 2020) | N/A | ||
| How much do you estimate that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economic, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country (es) of activity affect the quality of Compliance’s work? (CQ_4) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Principle 6 (COSO ERM 2020) | N/A | ||
| COMPONENT | Governance & Culture | Strategy & Objective- Setting | Performance | Review & Revision | Information, Communication & Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRINCIPLES | 1. Exercises Board Risk Oversight | 6. Analyzes Business Context | 10. Identifies Risk | 15. Assesses Substantial Change | 18. Leverages Information and Technology |
| 2. Establishes Operating Structures | 7. Defines Risk Appetite | 11. Assesses Severity of Risk | 16. Reviews Risk and Performance | 19. Communicates Risk Information | |
| 3. Defines Desired Culture | 8. Evaluates Alternative Strategies | 12. Prioritizes Risks | 17. Pursues improvement in Enterprise Risk Management | 20. Reports on Risk, Culture, and Performance | |
| 4. Demonstrates Commitment to Core Values | 9. Formulates Business Objectives | 13. Implements Risk Responses | |||
| 5. Attracts, Develops, and Retains Capable Individuals | 14. Develops Portfolio View |
Appendix B
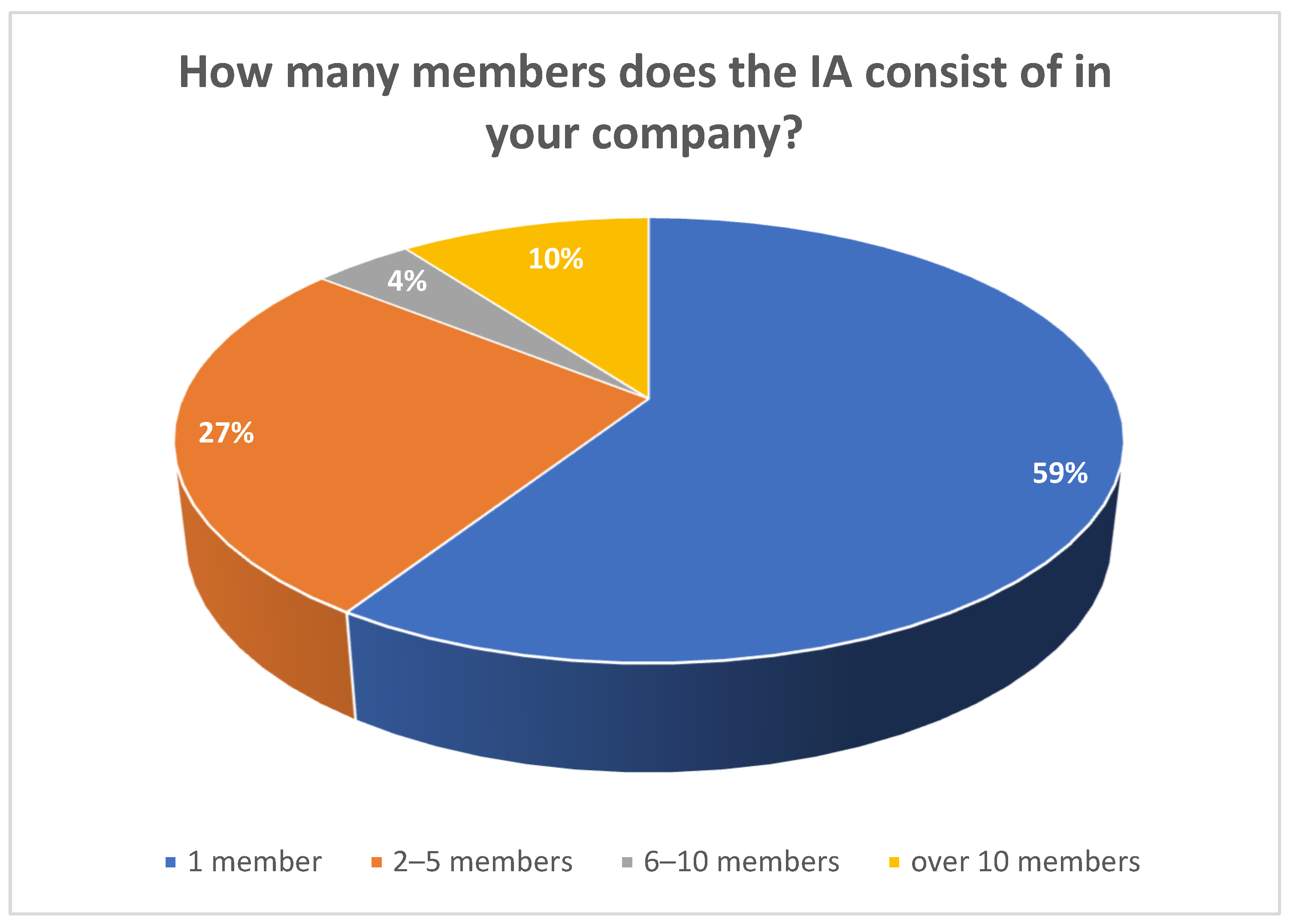
| How Many Members Does the IA Consist of in Your Company? | Frequency | Rates |
|---|---|---|
| 1 member | 29 | 59.18% |
| 2 members | 5 | 10.21% |
| 3 members | 5 | 10.21% |
| 4 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| 5 members | 2 | 4.08% |
| 6 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| 8 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| 17 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| 18 members | 2 | 4.08% |
| 20 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| 37 members | 1 | 2.04% |
| TOTAL | 49 | 100.00% |
| SURVEY RESULTS | COMPLIANCE AUDIT WITH LAW 4706/2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resp. No. (Firms) | How Many Members Does the BoD of Your Company Consist of? (a) | How Many Members of the BoD Are Women? (b) | How Many Members of the BoD Are Executive? (c) | Number of Independent Non-Executive Members of the BoD (d) | Independent Non-Executive Members | Representation by Gender | ||||
| Min. Members/Firm | Min. Members/Firm | |||||||||
| At least 1/3 of Total Members (in Any Case, >2 Members) (a)*1/3 | Decimals Round to the Nearest Whole Number (e) | Compliance Audit # ≥ 0: Comply # < 0: Non-Compliant (d)–(e) | Representation 25% by Gender on the BoD (f) | Decimals Round to the Previous Whole Number (g) | Compliance Audit # ≥ 0: Comply # < 0: Non-compliant (b)–(g) | |||||
| 1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1.67 | 2 | 1 | 1.25 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2.33 | 2 | 2 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3.33 | 3 | 0 | 2.50 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3.67 | 4 | 0 | 2.75 | 2 | 0 |
| 6 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 3.67 | 4 | 3 | 2.75 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | 11 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 3.67 | 4 | 0 | 2.75 | 2 | 0 |
| 8 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3.67 | 4 | 0 | 2.75 | 2 | 0 |
| 10 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | 15 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 5.00 | 5 | 5 | 3.75 | 3 | 0 |
| 12 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 13 | 13 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4.33 | 4 | 1 | 3.25 | 3 | 1 |
| 14 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 4 |
| 15 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.00 | 2 | 0 | 1.50 | 1 | 0 |
| 16 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 0 |
| 17 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 0 |
| 18 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3.67 | 4 | 0 | 2.75 | 2 | 1 |
| 19 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.33 | 3 | 0 | 2.50 | 2 | 1 |
| 20 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 0 |
| 21 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.67 | 2 | 0 | 1.25 | 1 | 0 |
| 22 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3.33 | 3 | 0 | 2.50 | 2 | 0 |
| 23 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2.67 | 3 | 1 | 2.00 | 2 | 1 |
| 24 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 4.00 | 4 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 |
| 25 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 3.33 | 3 | 1 | 2.50 | 2 | 1 |
| 26 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 1 |
| 27 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 1 |
| 28 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.00 | 2 | 0 | 1.50 | 1 | 0 |
| 29 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 1 |
| 30 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.33 | 3 | 0 | 2.50 | 2 | 0 |
| 31 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 32 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2.67 | 3 | 0 | 2.00 | 2 | 0 |
| 33 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2.00 | 2 | 2 | 1.50 | 1 | 1 |
| 34 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 0 |
| 35 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5.00 | 5 | 0 | 3.75 | 3 | 2 |
| 36 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2.67 | 3 | 0 | 2.00 | 2 | 0 |
| 37 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.67 | 2 | 0 | 1.25 | 1 | 0 |
| 38 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 39 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.67 | 2 | 0 | 1.25 | 1 | 0 |
| 40 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 41 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1.67 | 2 | 0 | 1.25 | 1 | 0 |
| 42 | 15 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 5.00 | 5 | 1 | 3.75 | 3 | 0 |
| 43 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2.00 | 2 | 0 | 1.50 | 1 | 1 |
| 44 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 | 2.25 | 2 | 0 |
| 45 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2.33 | 2 | 0 | 1.75 | 1 | 2 |
| 46 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3.67 | 4 | 0 | 2.75 | 2 | 1 |
| 47 | 12 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 4.00 | 4 | 0 | 3.00 | 3 | 0 |
| 48 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
| 49 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.33 | 2 | 1 | 1.75 | 1 | 0 |
References
Archival Sources
Law 4706/2020, Corporate governance of Sociétés Anonymes, modern capital market, incorporation into Greek Law of Directive (EU) 2017/828 of the European Parliament and of the Council, measures for the implementation of Regulation (EU) 2017/1131 and other provisions (Government Gazette A’ 136/17.07.2020).1/891/30.9.2020,Decision of the BoD of the HCMC, “Specializations of Article 14 para. 3 approx. i and para. 4, Evaluation of the Internal Control System (ICS) and the Implementation of the provisions on Corporate Governance of Law 4706/2020” (Government Gazette B’4556/15.10.2020).Law 4548/2018, Reform of the Law of Sociétés Anonymes (Government Gazette A’ 104/13.06.2018).Law 3016/2002, Hellenic Capital Market Commission, “On corporate governance, payroll issues and other provisions” (Government Gazette 110/17.05.2002).Published Sources
- Aguilera, Chen Tien, Tien Waheed Niroula, and Chung Kwang Zhang. 2023. Influence of internal control systems on governance among parastatals in Taiwan. Journal of Public Policy & Governance 11: 105–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Raja Adzrin Raja, Norhidayah Abdullah, Nur Erma Suryani Mohd Jamel, and Normah Omar. 2015. Board Characteristics and Risk Management and Internal Control Disclosure Level: Evidence from Malaysia. Procedia Economics and Finance 31: 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, Abitya, and Siti Choiriah. 2025. The effect of good corporate governance, internal control system, and human resource competence on financial reporting quality. Research Horizon 5: 183–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Astal, Ahmad Y.M., Ali Ateeq, Marwan Milhem, and Dalili I. Shafie. 2025. Corporate Governance and Internal Control Mechanisms: Developing a Strategic Framework. In Business Sustainability with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Challenges and Opportunities. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control. Edited by Esra AlDhaen, Ashley Braganza, Allam Hamdan and Weifeng Chen. Cham: Springer, vol. 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaiti, Hani. 2023. Influences of internal control on enterprise performance: Does an information system make a difference? Journal of Risk and Financial Management 16: 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Chartered Certified Accountants, The Internal Audit Foundation and The Institute of Management Accountants. 2022. Internal Control and the Transformation of Entities. Available online: https://www.accaglobal.com/gb/en/professional-insights/technology/transformation-of-internal-control.html (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Bekiaris, Michalis, Thanasis Efthymiou, and G. Andreas Koutoupis. 2013. Economic crisis impact on corporate governance and internal audit: The case of Greece. Corporate Ownership and Control 11: 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burca, Olteanu, Andreea Larisa, Badea Florea, Elena Claudia, and Madalina Preda. 2024. Role of audit committees and internal audit in the context of the evolution of ESG indicators. Polish Journal of Management Studies 29: 123–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Yu-Tzu, Hanchung Chen, Rainbow K. Cheng, and Wuchun Chi. 2019. The impact of internal audit attributes on the effectiveness of internal control over operations and compliance. Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics 15: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, Joe, Gerrit Sarens, and Philomena Leung. 2009. A critical analysis of the independence of the internal audit function: Evidence from Australia. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal 22: 200–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Jeffrey., Krishnamoorthy Ganesh, and M. Arnold Wright. 2002. Corporate governance and the audit process. Contemporary Accounting Research 9: 573–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinan, Charles P., Lois S. Mahoney, and Pamela Roush. 2016. Corporate social responsibility and shareholder support for corporate governance changes. Social Responsibility Journal 12: 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamshidovna, Akhmedova Latifa. 2025. Auditing and internal controls: Enhancing organizational governance and performance. Multidisciplinary Journal of Science and Technology 5: 542–46. [Google Scholar]
- Drogalas, George. 2010. Evaluation of the Implementation and Contribution of Internal Control Systems from the Point of View of Accounting and Finance in Hotel Businesses in Greece. Ph.D. thesis, University of Macedonia, Thessaloniki, Greece. [Google Scholar]
- Drogalas, George, and Stiliani Siopi. 2017. Risk Management and Internal Audit: Evidence from Greece. Risk Governance & Control: Financial Markets & Institutions 7: 104–10. [Google Scholar]
- Drogalas, George, Iordanis Eleftheriadis, Michail Pazarskis, and Evgenia Anagnostopoulou. 2017. Perceptions about effective risk management. The crucial role of internal audit and management. Evidence from Greece. Investment Management and Financial Innovations 14: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogalas, George, Karagiorgos Theofanis, and Konstantinos Arampatzis. 2015. Factors associated with Internal Audit Effectiveness: Evidence from Greece. Journal of Accounting and Taxation 7: 113–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, Houdini, and Christo Ackerman. 2013. The impact of COSO control components on internal control effectiveness: An internal audit perspective. South African Journal of Accountability and Audit Research 14: 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin-Stewart, Jenny, and Pamela Kent. 2006. The use of internal audit by Australian companies. Managerial Auditing Journal 21: 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, Sean J. 2016. Corporate Governance in an Era of Compliance. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2766661 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Hakimi, Natalia, Salwa Zolkaflil, Khalid, and Nurliyana Haji. 2023. The role of internal audit, internal control systems, and corporate governance practices toward financial report quality. MAHSA International Journal of Business & Social Sciences 3: 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Heier, Jan R., Michael T. Dugan, and David L. Sayers. 2005. A Century of Debate for Internal Controls and their Assessment: A Study of Reactive Evolution. Accounting History 10: 39–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Corporate Governance Council. 2021. Hellenic Corporate Governance Code—HCGC. Available online: https://www.esed.org.gr/web/guest/code-listed (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Hossain, Mohammad Kamal, Fazlur Rahman, Uttam Golder, and Humayun Kabir. 2025. Effectiveness of internal corporate governance mechanisms in controlling NPLs in an emerging economy. Schmalenbach Journal of Business Research 77: 560–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, Michael, and William Meckling. 1976. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs, and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics 3: 305–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Like, Andre, Paul, Richard, and Chrystelle. 2017. An International Study of Internal Audit Function Quality. Accounting and Business Research 48: 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johl, Shireenjit K., Satirenjit Kaur Johl, Nava Subramaniam, and Barry Cooper. 2013. Internal audit function, board quality and financial reporting quality: Evidence from Malaysia. Managerial Auditing Journal 28: 780–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, Henry F. 1974. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika 39: 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiorgos, Theofanis, George Drogalas, and Nikolaos Giovanis. 2011. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Internal Audit in Greek Hotel Business. International Journal of Economic Sciences and Applied Research 4: 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Koutoupis, Andreas. 2009. The Effects of the Institutional Framework of Corporate Governance and Best Practices on the Development of Internal Audit Systems of Enterprises. The case of companies listed on the Athens Stock Exchange. Ph.D. thesis, Panteion University of Social and Political Sciences, Athens, Greece. [Google Scholar]
- Koutoupis, Andreas, and Evangelia Pappa. 2018. Corporate Governance and Internal Controls: A Case Study. Greece Journal of Governance and Regulation 7: 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Syou-Ching, Hungchih Li, Henghsiu Lin, and Frederick Wu. 2017. The influence of internal control weaknesses on firm performance. Journal of Accounting and Finance 17: 82–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, Rainer, and John Chesshire. 2023. Rethinking internal audit: Governance needs gardening. EDPACS 68: 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussii, Ahmed Atef, and Neila Boulila Taktak. 2018. The impact of internal audit function characteristics on internal control quality. Managerial Auditing Journal 33: 450–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paape, Leen, Scheffe Johan, and Pim Snoep. 2003. The relationship between the Internal Audit Function and Corporate Governance in the EU—A Survey. International Journal of Auditing 7: 247–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Yanhong, and Qing Li. 2013. Game Analysis of Internal Control and Risk Management. International Journal of Business and Management 8: 103–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangastuti, and Leli Agustina. 2023. The role of internal auditing in upholding corporate governance standards. Advances in Managerial Auditing Research 1: 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawitt, Douglas F., Jason L. Smith, and David A. Wood. 2009. Internal Audit Quality and Earnings Management. The Accounting Review 84: 1255–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, Kirsten, John Stephen Sands, and Nava Subramaniam. 2017. Associations among the Five Components within COSO Internal Control-Integrated Framework as the Underpinning of Quality Corporate Governance. Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal 11: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoliosi, Carlo, and Alessandro d’Eri. 2014. “Good” corporate governance and the quality of internal auditing departments in Italian listed firms: An exploratory investigation in Italian listed firms. Journal of Management & Governance 18: 891–920. [Google Scholar]
- Sarens, Gerrit, and Mohammad J. Abdolmohammadi. 2011. Monitoring Effects of the Internal Audit Function: Agency Theory versus other Explanatory Variables. International Journal of Auditing 15: 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, Mohsen, and Reg Dennick. 2011. Making Sense of Cronbach’s Alpha. International Journal of Medical Education 2: 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasi, Christina. 2018. Internal Audit and the Quality of Accounting Reporting: Corporate Governance and Quality of Internal Audit in Listed Companies of the Athens Stock Exchange. Ph.D. thesis, University of the Aegean, Chios, Greece. [Google Scholar]
- Vadasi, Christina, Michalis Bekiaris, and Andreas Andrikopoulos. 2021. Internal Audit Function Quality and Corporate Governance: The Case of Greece. Multinational Finance Journal 25: 1–61. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3866954 (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Van Der Nest, Daniel P., Louis Smidt, and Dave Lubbe. 2017. The use of generalised audit software by internal audit functions in a developing country: A maturity level assessment. Risk Governance and Control: Financial Markets & Institutions 7: 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Xiaotong. 2024. The impact of internal control on the quality of corporate governance from an audit perspective. Paper presented at the ICEMCI 2023, Beijing, China, 17–19 November 2023; Dordrecht: Atlantis Press, pp. 450–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Zhiyi. 2025. The relationship among corporate governance, internal control, and M&A performance. SHS Web of Conferences 218: 03031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| COMPONENT | Control Environment | Risk Assessment | Control Activities | Information & Communication | Monitoring Activities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRINCIPLES | 1. Demonstrates commitment to integrity and ethical values | 6. Specifies suitable objectives | 10. Selects and develops control activities | 13. Uses relevant information | 16. Conducts ongoing and/or separate evaluations |
| 2. Exercises oversight responsibility | 7. Identifies and analyzes risk | 11. Selects and develops general controls over technology | 14. Communicates internally | 17. Evaluates and communicates deficiencies | |
| 3. Establishes structure, authority, and responsibility | 8. Assesses fraud risk | 12. Deploys through policies and procedures | 15. Communicates externally | ||
| 4. Demonstrates commitment to competence | 9. Identifies and analyzes significant change | ||||
| 5 Enforces accountability |
| Study (Year) | Context/Sample | Methods | Main Findings | Limitations | The Gap Addressed by the Current Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Koutoupis (2009) | Greek listed firms (doctoral thesis) | Questionnaire, descriptive analysis | Corporate governance is positively associated with internal audit activities and the adoption of ICS. | Outdated regulatory context; focuses solely on IA; lacks psychometric validation. | Updates the Greek context under Law 4706/2020 and assesses multiple ICS components |
| Drogalas (2010) | Greek hotel sector | Mixed methods: questionnaire and financial data | ICS contributes added value and operational efficiency in hotels | Single-sector focus; small sample; limited generalizability | Extends analysis across ATHEX-listed sectors for broader representativeness |
| Karagiorgos et al. (2011) | 52 large Greek hotels | Survey: COSO-based evaluation | High overall ICS scores; the monitoring component is the weakest | Sector focus; descriptive approach; cross-sectional design | Examines IA staffing adequacy and independence across listed companies |
| Prawitt et al. (2009) | Various international contexts | Construct validation and empirical testing | IAF quality linked to internal control effectiveness | Scale development requires replication; limited context detail | Adopts IAQ measures and reports Cronbach’s alpha for transparency |
| Drogalas et al. (2015, 2017) | Greek listed firms/employees | Questionnaire; multiple regression | Top management support, risk-based IA, and IA involvement improve RM effectiveness. | Cross-sectional design; self-reported measures | Tests the joint effects of CPQ, RMQ, IAQ, and CQ using GLMM and Ridge Regression |
| Rae et al. (2017) | Australian organizations | COSO component analysis | Links between control environment, information flow, and RM monitoring | Descriptive focus; lacks regulatory integration | Integrates Greek Law 4706/2020 and HCGC 2021 within the COSO framework |
| Lai et al. (2017) | U.S.-listed firms | Secondary data: regression on control weaknesses and performance | IC weaknesses negatively affect firm performance | Historical dataset; limited to financial outcomes | Examines perceived control quality and operational features (e.g., IA staffing) |
| Z. Xu (2025); Olteanu Burca et al. (2024) | Multinational samples | Regression/mixed methods | Strong governance and controls linked to ESG and financial outcomes | Heterogeneous measures and institutional settings | Positions Greek compliance and ICS quality in an international governance context |
| Total listed companies | 157 |
| Companies under suspension | −8 |
| Financial sector/corporate bonds/public sector | −28 |
| Research population | =121 |
| Unsent questionnaires | −3 |
| Sent questionnaires | =118 |
| Responses | 51 |
| Invalid responses | −2 |
| Valid responses (sample) | =49 |
| Response rate % | 43% |
| Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE): |
| The Board of Directors shall ensure the effectiveness and independence of the functions constituting the ICS by providing the necessary resources and powers (ICSF_1). |
| Controls and procedures work effectively against risks, ensuring the achievement of management’s objectives (ICSF_2). |
| The Internal Audit Unit of the ICS provides objective assurance for the effective operation of the ICS (ICSF_3). |
| The Compliance Unit implements a practical ethics and compliance program to prevent fraud and corruption risks, and to avoid fines or criminal sanctions (ICSF_4). |
| The Risk Management Unit effectively implements risk assessment, risk response, and risk monitoring procedures (ICSF_5). |
| Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ): |
| How much do you estimate that the controls and procedures secure the company’s assets? (CPQ_1) |
| How much do you estimate that controls and procedures help to limit risks to levels acceptable to the company? (CPQ_2) |
| How much do you estimate that the Internal Audit Unit effectively supervises the risk management procedures and controls, contributing to their improvement? (CPQ_3) |
| Risk Management Quality (RMQ): |
| How effective do you assess the oversight of Risk Management to be? (RMQ_1) |
| To what extent do you assess that the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_2) |
| To what extent do you assess that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economical, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country (ies) of activity affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_3) |
| Internal Audit Quality (IAQ): |
| How effective do you think IA supervision is? (IAQ_1) |
| To what extent do you estimate that IA has access to the required sources of information? (IAQ_2) |
| How much do you estimate that IA uses effective tools and techniques for conducting audits? (IAQ_3) |
| How much do you estimate that the control environment (Company Organizational Structure, Board of Directors, Corporate Responsibility, Human Resources) of your company affects the effectiveness of IA? (IAQ_4) |
| How much more effective do you think IA will become, due to the mandatory external evaluation of the ICS (HCMC Dec. No 1/891/30.09.2020)? (IAQ_5) |
| Compliance Quality (CQ): |
| How effective do you think Compliance supervision is? (CQ_1) |
| To what extent do you estimate that Compliance has access to the required sources of information? (CQ_2) |
| How much do you think the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of Compliance’s work? (CQ_3) |
| How much do you estimate that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economic, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country (es) of activity affect the quality of Compliance’s work? (CQ_4) |
| Variable | Dimensions | Indicators/Items (Questionnaire Codes) | Reference Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE) | Effectiveness of Internal Control System | ICSE_1: The Board of Directors ensures ICS effectiveness and independence; ICSE_2: Controls and procedures mitigate risks; ICSE_3: The Internal Audit Unit provides objective assurance; ICSE_4: The Compliance Unit implements practical ethics and anti-fraud programs; ICSE_5: The Risk Management Unit effectively assesses and monitors risks | COSO (2013); Law 4706/2020, Art. 4 & 13; HCMC Decision 1/891/30.9.2020; Institute of Internal Auditors [IIA], IPPF (2017); Vadasi (2018) |
| Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ) | Safeguarding of assets, risk limitation, and audit oversight | CPQ_1: Controls secure company assets; CPQ_2: Controls limit risks to acceptable levels; CPQ_3: Internal Audit supervises controls and contributes to improvement | COSO (2013); IIA (Standard 2130, 2017); ACCA, IIA, & IMA (2022); Koutoupis and Pappa (2018) |
| Risk Management Quality (RMQ) | Oversight, contextual influence, external environment | RMQ_1: Effectiveness of Risk Management oversight; RMQ_2: Impact of size, complexity, and nature of activities; RMQ_3: Influence of PESTEL factors on Risk Management quality | COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework (2020); IIA (Standard 2120, 2019); Fourie and Ackerman (2013); Drogalas et al. (2017) |
| Internal Audit Quality (IAQ) | Supervision, access to information, tools and techniques, organizational environment, and regulatory enhancement | IAQ_1: Effectiveness of Internal Audit supervision; IAQ_2: Access to required information sources; IAQ_3: Use of audit tools and techniques; IAQ_4: Effect of control environment on Internal Audit effectiveness; IAQ_5: Expected improvement from external ICS evaluation | IIA (2019); Prawitt et al. (2009); Regoliosi and d’Eri (2014); Drogalas et al. (2015); HCMC Decision 1/891/30.9.2020 |
| Compliance Quality (CQ) | Oversight, access to information, organizational, and environmental influence | CQ_1: Effectiveness of Compliance supervision; CQ_2: Access to required information; CQ_3: Impact of company size and complexity; CQ_4: Effect of PESTEL factors on Compliance quality | COSO (2013, 2017); International Organization for Standardization [ISO] (2014, 2020); Griffith (2016); UK Ministry of Justice (2010) |
| Control Variables | Company characteristics, respondent profile | Multi: Internationalization (domestic vs. international operations); Size: Number of employees; Gender: Respondent gender; Age: Respondent age category | Law 4706/2020, Art. 13 (proportionality principle); Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD] (2021); Drogalas et al. (2017); Vadasi (2018) |
| In which sector does your company operate? | Frequency | Rates |
| Industrial | 16 | 32.65% |
| Commercial | 12 | 24.49% |
| Construction | 5 | 10.20% |
| Fuels/Energy | 1 | 2.04% |
| Technology/Telecommunications | 5 | 10.21% |
| Services | 10 | 20.41% |
| Total | 49 | 100.00% |
| How many employees does your company employ? | Frequency | Rates |
| Up to 50 | 10 | 20.41% |
| 51–100 | 3 | 6.12% |
| 101–250 | 14 | 28.57% |
| More than 251 | 22 | 44.90% |
| Total | 49 | 100.00% |
| Please select your position in the company. | Frequency | Rates |
| Head of Internal Audit | 32 | 65.31% |
| Head of Compliance | 1 | 2.04% |
| Head of Risk Management | 2 | 4.08% |
| Internal Auditor | 13 | 26.53% |
| Other (Response: IA Manager of 2 countries) | 1 | 2.04% |
| Total | 49 | 100.00% |
| Is IA a purely independent organizational unit in your company? | Frequency | Rates |
| Yes | 42 | 85.71% |
| No | 7 | 14.29% |
| TOTAL | 49 | 100.00% |
| Is RM a purely independent organizational unit in your Company? | Frequency | Rates |
| Yes | 19 | 38.78% |
| No (Co-exists with Compliance) | 10 | 20.41% |
| No (Co-exists with Internal Audit) | 10 | 20.41% |
| No (Co-exists with Compliance and Internal Audit) | 3 | 6.12% |
| No (Co-exists with Finance Division) | 2 | 4.08% |
| No (Co-exists with Information Security) | 1 | 2.04% |
| No (Risk Committee) | 2 | 4.08% |
| No (Risk Management does not exist at all) | 2 | 4.08% |
| TOTAL | 49 | 100.00% |
| Is Compliance a purely independent organizational unit in your company? | Frequency | Rates |
| Yes | 18 | 36.73% |
| No | 14 | 28.57% |
| No (Co-exists with RM) | 10 | 20.41% |
| Νο (Compliance co-exists with Internal Audit) | 1 | 2.04% |
| No (Compliance co-exists with Legal Service) | 1 | 2.04% |
| Compliance does not exist at all | 5 | 10.21% |
| TOTAL | 49 | 100.00% |
| Please Rate the Following Factors of Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE): | N | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Skewness (γ1) | Kurtosis (γ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Board of Directors shall ensure the effectiveness and independence of the functions constituting the ICS by providing the necessary resources and powers (ICSE_1). | 49 | 3.90 | 4.00 | 0.984 | −1.156 | 1.620 |
| Controls and procedures work effectively against risks, ensuring the achievement of management’s objectives (ICSE_2). | 49 | 3.96 | 4.00 | 0.889 | −1.589 | 3.811 |
| The Internal Audit Unit, in collaboration with the ICS, provides objective assurance of the ICS’s effective operation (ICSE_3). | 49 | 4.20 | 4.00 | 0.816 | −1.359 | 3.496 |
| The Compliance Unit implements an effective program of ethics and compliance to prevent risks of fraud and corruption, and to avoid fines or criminal sanctions (ICSE_4). | 49 | 3.92 | 4.00 | 1.057 | −1.264 | 1.663 |
| The Risk Management Unit effectively implements risk assessment, risk response, and risk monitoring procedures (ICSE_5). | 49 | 3.84 | 4.00 | 0.874 | −1.034 | 1.623 |
| ICSE_ave | 49 | 3.96 | 4.00 | 0.791 | −1.255 | 3.085 |
| Please Rate the Following Factors of Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ): | N | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Skewness (γ1) | Kurtosis (γ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| How much do you estimate that the controls and procedures secure the company’s assets? (CPQ_1) | 49 | 3.94 | 4 | 0.719 | −1.661 | 5.766 |
| How much do you estimate that controls and procedures help to limit risks to levels acceptable to the company? (CPQ_2) | 49 | 3.90 | 4 | 0.895 | −1.427 | 3.167 |
| How much do you estimate that the Internal Audit Unit effectively supervises the risk management procedures and controls, contributing to their improvement? (CPQ_3) | 49 | 4.20 | 4 | 0.735 | −1.655 | 6.341 |
| CPQ_ave | 49 | 4.01 | 4.00 | 0.690 | −1.919 | 7.066 |
| Please Rate the Factors of Risk Management Quality (RMQ): | N | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Skewness (γ1) | Kurtosis (γ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| How effective do you assess the oversight of Risk Management to be? (RMQ_1) | 49 | 3.65 | 4 | 0.879 | −0.970 | 0.968 |
| To what extent do you assess that the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_2) | 49 | 3.90 | 4 | 0.714 | −1.278 | 4.667 |
| To what extent do you assess that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economical, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country(ies) of activity affect the quality of the Risk Management work? (RMQ_3) | 49 | 3.73 | 4 | 0.861 | −1.083 | 2.570 |
| RMQ_ave | 49 | 3.76 | 4 | 0.649 | −1.551 | 6.069 |
| Please Rate the Factors of Internal Audit Quality (IAQ): | N | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Skewness (γ1) | Kurtosis (γ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| How effective do you think IA supervision is? (IAQ_1) | 49 | 3.84 | 4.00 | 0.874 | −1.034 | 1.623 |
| To what extent do you estimate that IA has access to the required sources of information? (IAQ_2) | 49 | 4.41 | 5.00 | 0.814 | −1.862 | 5.091 |
| How much do you estimate that IA uses effective tools and techniques for conducting audits? (IAQ_3) | 49 | 4.02 | 4.00 | 0.750 | −1.271 | 4.346 |
| How much do you estimate that the control environment (Company Organizational Structure, Board of Directors, Corporate Responsibility, Human Resources) of your company affects the effectiveness of IA? (IAQ_4) | 49 | 3.98 | 4.00 | 0.721 | −1.358 | 5.086 |
| How much more effective do you think IA will become, due to the mandatory external evaluation of the ICS (HCMC Dec. No 1/891/30.09.2020)? (IAQ_5) | 49 | 3.71 | 4.00 | 0.957 | −0.721 | 0.310 |
| IAQ_ave | 49 | 3.99 | 4.00 | 0.488 | −0.381 | 1.834 |
| Please Rate the Factors of Compliance Quality (CQ): | N | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Skewness (γ1) | Kurtosis (γ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| How effective do you think Compliance supervision is? (CQ_1) | 49 | 3.55 | 4.00 | 1.062 | −1.064 | 0.799 |
| To what extent do you estimate that Compliance has access to the required sources of information? (CQ_2) | 49 | 3.96 | 4.00 | 1.079 | −1.574 | 2.518 |
| How much do you think the size, complexity, and nature of your company’s activities affect the quality of Compliance’s work? (CQ_3) | 49 | 3.73 | 4.00 | 0.93 | −1.538 | 2.937 |
| How much do you estimate that the PESTEL factors (P: Political, E: Economic, S: Social, T: Technological, E: Environmental, L: Legal) of the company’s country (ies) of activity affect the quality of the Compliance’s work? (CQ_4) | 49 | 3.73 | 4.00 | 0.995 | −1.019 | 1.557 |
| CQ_ave | 49 | 3.74 | 4.00 | 0.776 | −1.703 | 4.984 |
| Variable | Cronbach’s Alpha Standardized Items | F Test | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE) | 0.906 | 2.983 | 0.029 |
| Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ) | 0.856 | 4.652 | 0.014 |
| Risk Management Quality (RMQ) | 0.520 | 4.609 | 0.003 |
| Internal Audit Quality (IAQ) | 0.762 | 5.458 | 0.003 |
| Compliance Quality (CQ) | 0.717 | 3.752 | 0.031 |
| Variable | KMO | Bartlett’s Test (Sig.) | No of Components | Eigenvalue | % of Variances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Control System Effectiveness (ICSE) | 0.846 | 161.51 (<0.001) | 1 | 3.650 | 73.01 |
| Controls and Procedures Quality (CPQ) | 0.623 | 80.43 (<0.001) | 1 | 2.337 | 77.92 |
| Risk Management Quality (RMQ) | 0.536 | 41.74 (<0.001) | 1 | 1.944 | 64.81 |
| Internal Audit Quality (IAQ) | 0.601 | 46.20 (<0.001) | 2 | 1.259 | 66.70 |
| Compliance Quality (CQ) | 0.536 | 97.38 (<0.001) | 2 | 1.254 | 89.70 |
| Multi | Size | Gender | Age | ICSE_ave | CPQ_ave | IAQ_ave | CQ_ave | RMQ_ave | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi | 1 | 0.562 ** | −0.052 | −0.145 | −0.004 | −0.183 | 0.091 | −0.062 | 0.062 |
| Size | 0.651 ** | 1 | −0.119 | −0.029 | 0.111 | −0.046 | 0.142 | 0.073 | 0.052 |
| Gender | −0.052 | −0.091 | 1 | −0.446 ** | −0.025 | −0.048 | 0.127 | −0.101 | 0.058 |
| Age | −0.151 | −0.137 | −0.449 ** | 1 | −0.042 | −0.052 | −0.203 | 0.057 | −0.158 |
| ICSE_ave | 0.015 | 0.126 | −0.031 | −0.056 | 1 | 0.571 ** | 0.563 ** | 0.541 ** | 0.394 ** |
| CPQ_ave | −0.188 | −0.069 | −0.018 | −0.049 | 0.695 ** | 1 | 0.538 ** | 0.371 ** | 0.290 * |
| IAQ_ave | 0.033 | 0.117 | 0.100 | −0.151 | 0.679 ** | 0.689 ** | 1 | 0.557 ** | 0.531 ** |
| CQ_ave | −0.119 | 0.075 | 0.046 | −0.099 | 0.639 ** | 0.593 ** | 0.657 ** | 1 | 0.703 ** |
| RMQ_ave | −0.030 | 0.039 | 0.058 | −0.098 | 0.578 ** | 0.591 ** | 0.686 ** | 0.800 ** | 1 |
| Fixed Effects a | ||||||
| Source | F | df1 | df2 | Sig. | ||
| Corrected Model | 16.294 | 4 | 44 | 0.000 | ||
| CPQ_ave | 7.641 | 1 | 44 | 0.008 | ||
| IAQ_ave | 3.022 | 1 | 44 | 0.089 | ||
| CQ_ave | 3.081 | 1 | 44 | 0.086 | ||
| RMQ_ave | 0.144 | 1 | 44 | 0.706 | ||
| Fixed Coefficients a | ||||||
| Model Term | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Intercept | −0.360 | 0.6341 | −0.568 | 0.573 | −1.638 | 0.917 |
| CPQ_ave | 0.439 | 0.1587 | 2.764 | 0.008 | 0.119 | 0.758 |
| IAQ_ave | 0.431 | 0.2482 | 1.738 | 0.089 | −0.069 | 0.932 |
| CQ_ave | 0.299 | 0.1703 | 1.755 | 0.086 | −0.044 | 0.642 |
| RMQ_ave | −0.079 | 0.2091 | −0.379 | 0.706 | −0.501 | 0.342 |
| Random Effect | ||||||
| Random Effect Covariance | Estimate | Std. Error | Z | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Var(Multi) | 0.008 | 0.039 | 0.201 | 0.840 | 4.63 × 10−7 | 130.232 |
| Var(Size) | 1.234 × 10−12 b | |||||
| Var(Gender) | 0.000 b | |||||
| Var(Age) | 9.537 × 10−7 b | |||||
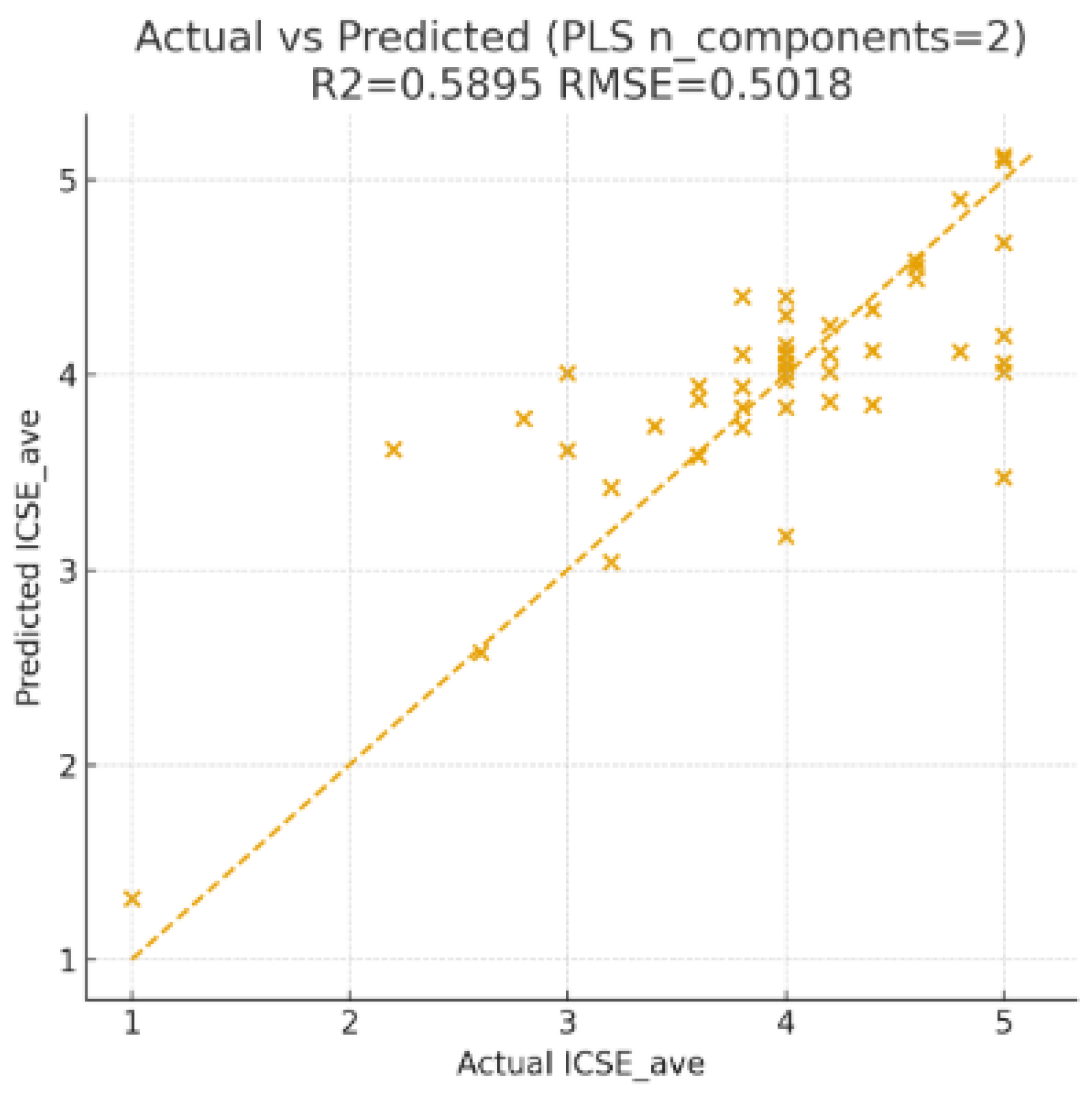
| N | Percent | R2 | ||
| Sample | Training | 37 | 75.5% | 0.593 |
| Holdout | 12 | 24.5% | 0.489 | |
| Valid | 49 | 100.0% | ||
| Alpha | 1.000 | |||
| Standardizing Values c | Standardized Coefficients | Unstandardized Coefficients | ||
| Coefficients a | Mean | Std. Dev. | ||
| Intercept b | 3.919 | −0.437 | ||
| CPQ_ave | 3.991 | 0.729 | 0.335 | 0.460 |
| IAQ_ave | 3.946 | 0.491 | 0.174 | 0.354 |
| CQ_ave | 3.764 | 0.685 | 0.215 | 0.314 |
| RMQ_ave | 3.766 | 0.693 | −0.010 | −0.015 |
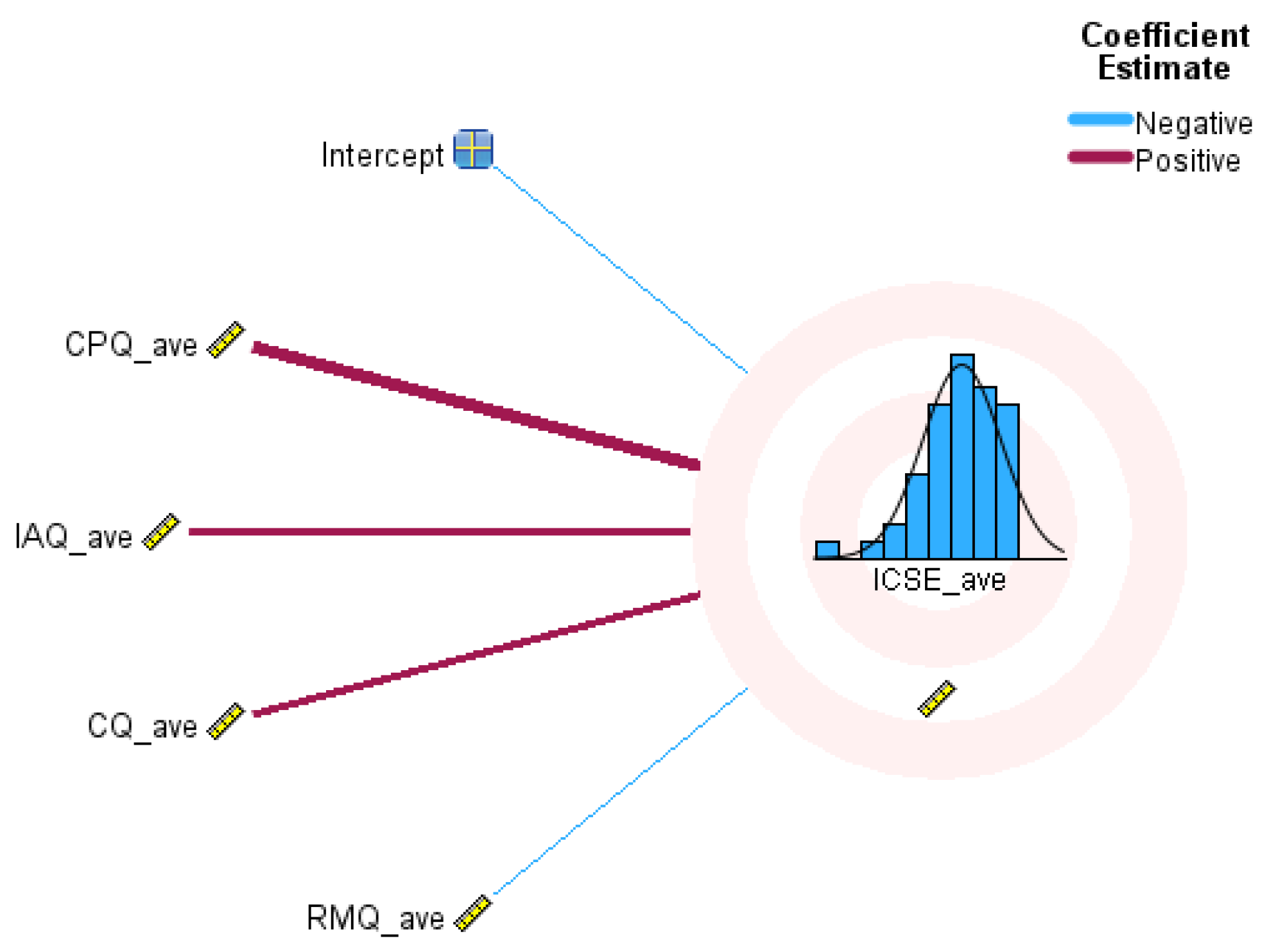
| Feature | original_coef | boot_mean | boot_std | 2.5% | 97.5% | p_approx_two_sided | VIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPQ_ave | 0.4014 | 0.3959 | 0.0997 | 0.208 | 0.5950 | 0.0000 | 1.5567 |
| IAQ_ave | 0.1212 | 0.1208 | 0.0895 | −0.039 | 0.2856 | 0.1240 | 0.7647 |
| CQ_ave | 0.0443 | 0.0451 | 0.0701 | −0.098 | 0.1892 | 0.5520 | 0.3701 |
| RMQ_ave | 0.0207 | 0.0199 | 0.0644 | −0.112 | 0.1632 | 0.7080 | 0.3103 |
| Training R2 (original ICSE_ave): 0.5895 | |||||||
| Training RMSE (original ICSE_ave): 0.5018 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannopoulos, V.; Lymperopoulos, A.; Kariofyllas, S.; Kariofyllas, C. Determinants of Internal Control System Effectiveness: Evidence from Greek Listed Companies. Risks 2025, 13, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks13110219
Giannopoulos V, Lymperopoulos A, Kariofyllas S, Kariofyllas C. Determinants of Internal Control System Effectiveness: Evidence from Greek Listed Companies. Risks. 2025; 13(11):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks13110219
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannopoulos, Vasileios, Antonios Lymperopoulos, Spyridon Kariofyllas, and Charalampos Kariofyllas. 2025. "Determinants of Internal Control System Effectiveness: Evidence from Greek Listed Companies" Risks 13, no. 11: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks13110219
APA StyleGiannopoulos, V., Lymperopoulos, A., Kariofyllas, S., & Kariofyllas, C. (2025). Determinants of Internal Control System Effectiveness: Evidence from Greek Listed Companies. Risks, 13(11), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks13110219








