Evaluation of 5 μm Superficially Porous Particles for Capillary and Microfluidic LC Columns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Glass Chip Fabrication
2.3. Column Preparation
2.4. Column Characterization and Analysis
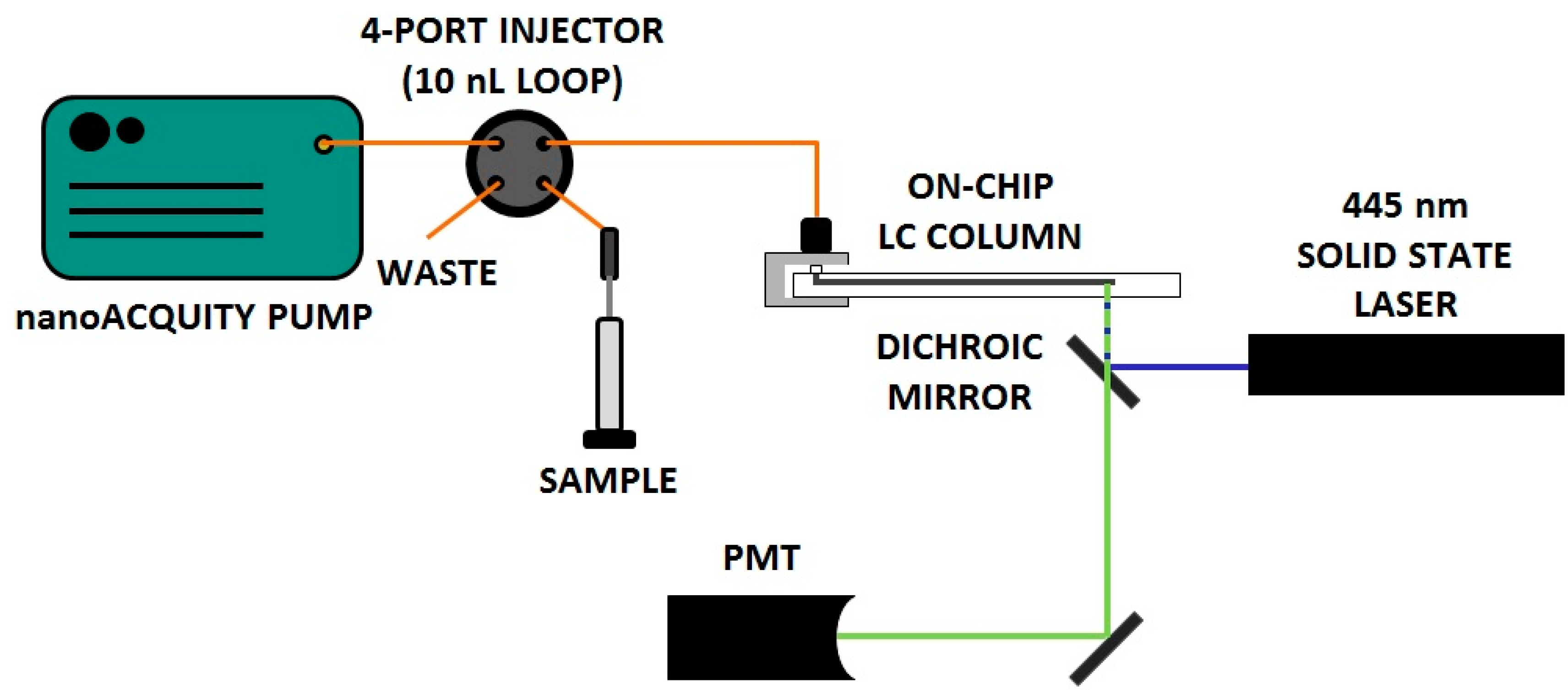
3. Results and Discussion
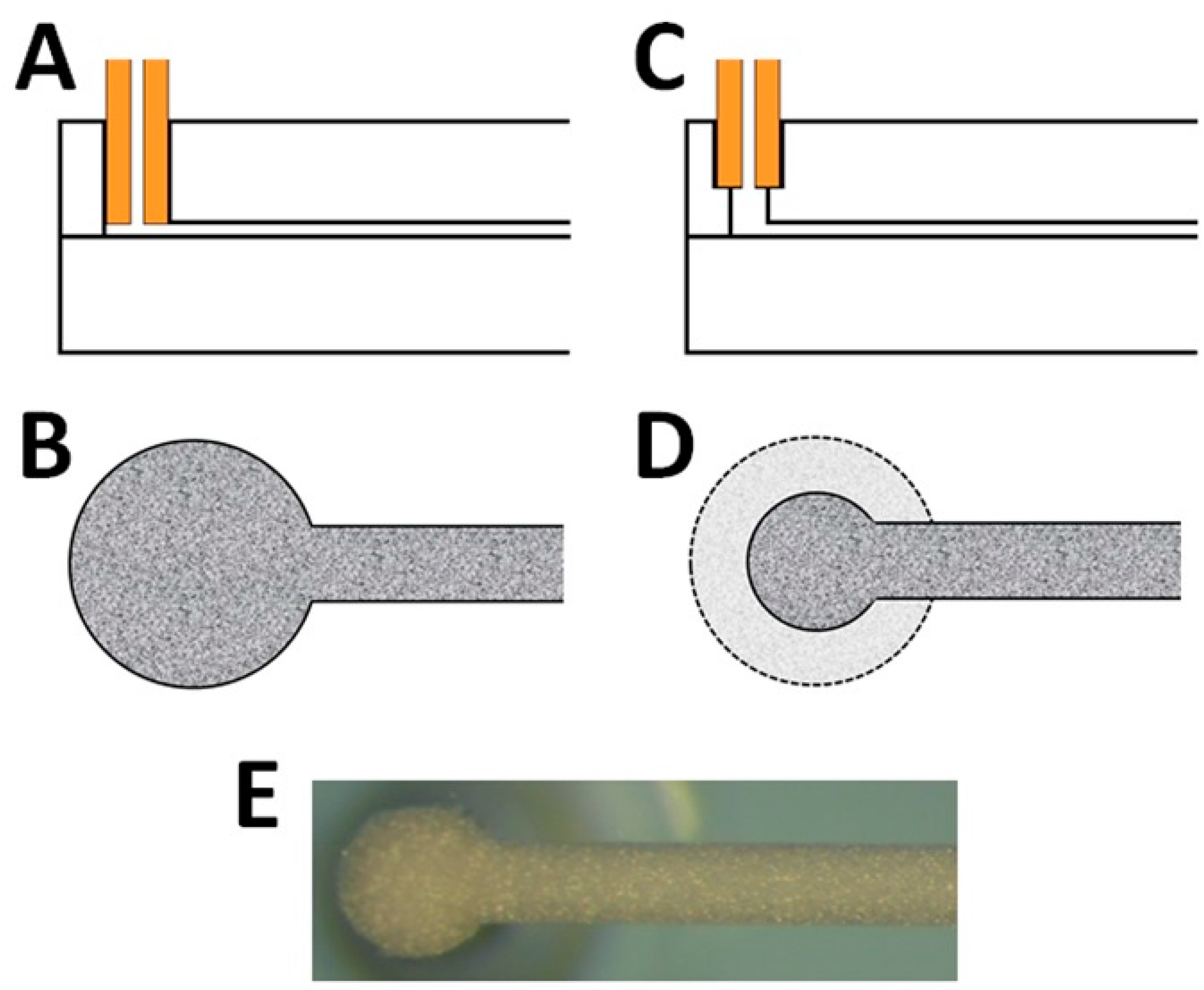
3.1. Preparation and Use of Chip-LC Columns
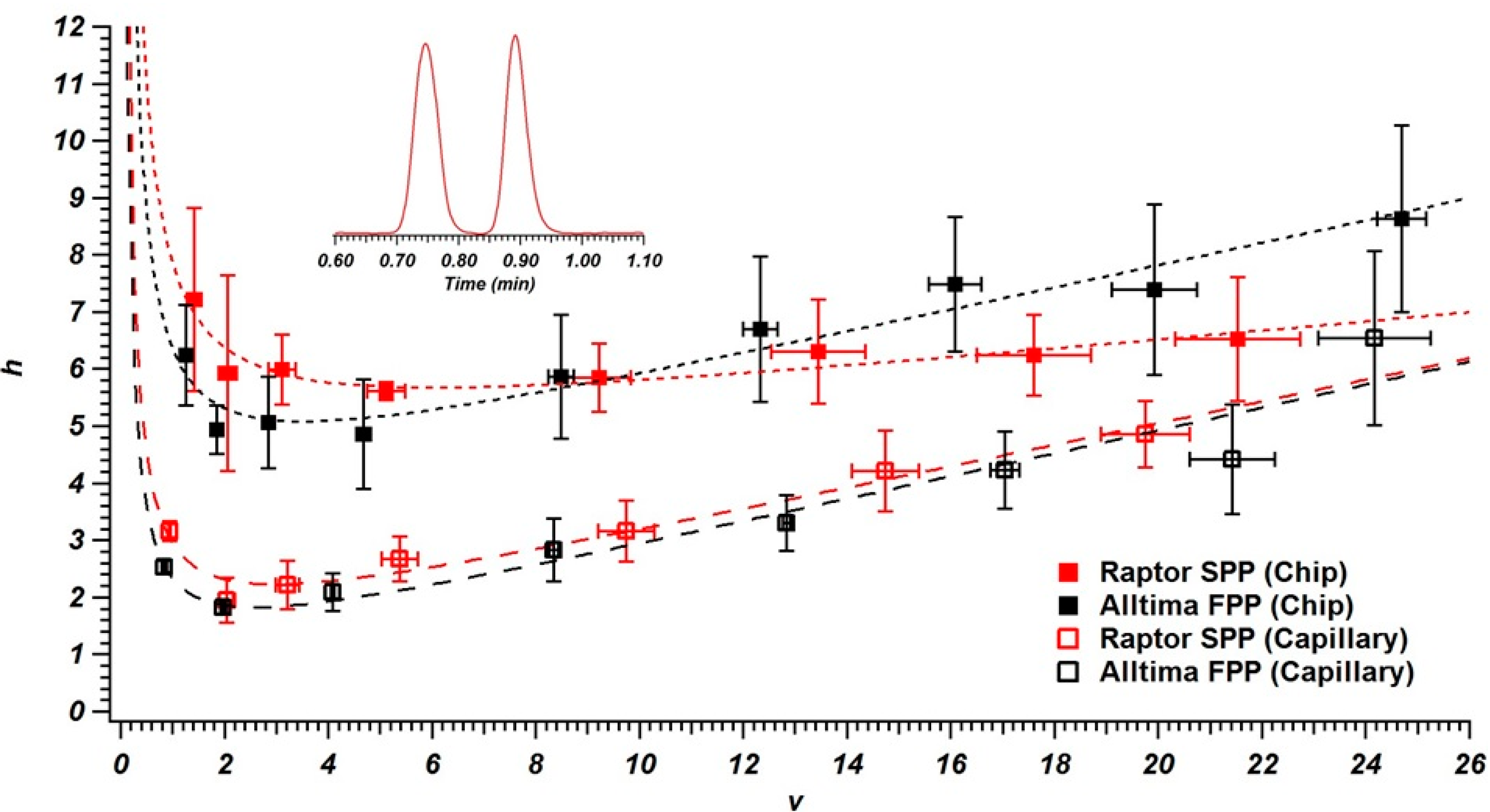
3.2. Column Performance in Chips and Capillaries
| Particle | Structure | Size a | Capillary Efficiency b | Chip Efficiency b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alltima C18 | Fully Porous | 4.97 ± 0.66 µm | 110,000 | 41,400 |
| Raptor C18 | Superficially Porous | 4.24 ± 0.16 µm | 121,000 | 41,900 |
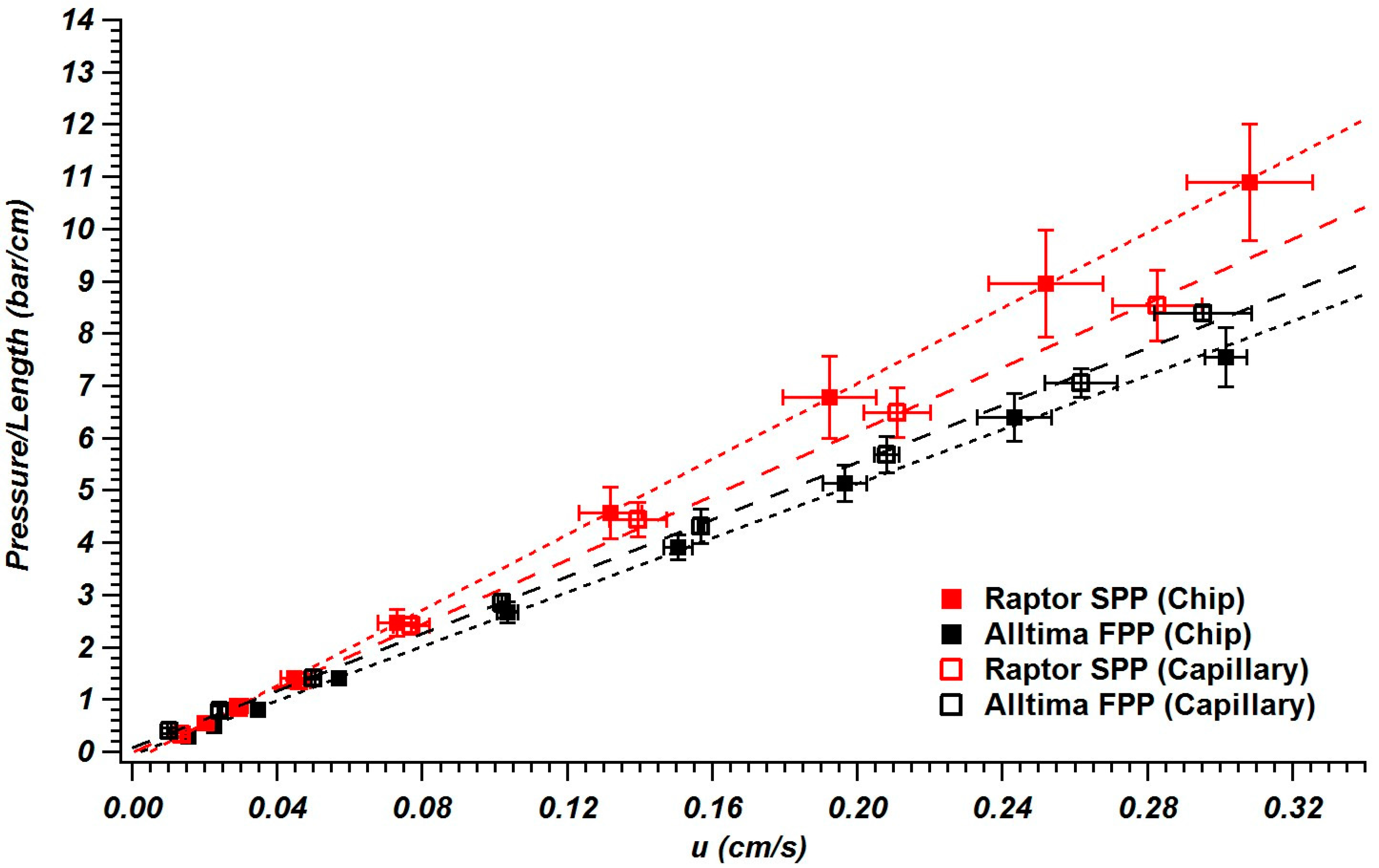
3.3. Column Permeability in Chips and Capillaries
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirkland, J.J.; DeStefano, J.J.; Langlois, T.J. Fused Core Particles for HPLC Columns. Am. Lab. 2007, 39, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano, J.J.; Langlois, T.J.; Kirkland, J.J. Characteristics of Superficially-Porous Silica Particles for Fast HPLC: Some Performance Comparisons with Sub-2-µm Particles. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiochon, G.; Gritti, F. Shell particles, trials, tribulations and triumphs. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1915–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; AL-Othman, Z.A.; Nagae, N.; Gaitonde, V.D.; Dutta, K.K. Recent trends in ultra-fast HPLC: New generation superficially porous silica columns. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 3235–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majors, R.E. The Increasing Role of Superficially Porous Particles in HPLC. LCGC Nor. Am. 2010, 28, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, R.; Ahmed, A.; Edge, T.; Zhang, H. Core–shell particles: Preparation, fundamentals and applications in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1357, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ruiz, V.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A. Core-shell particles lead the way to renewing high-performance liquid chromatography. Tr. Anal. Chem. 2015, 64, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D.; Dong, M.W. Superficially Porous Particles: Perspectives, Practices, and Trends. LCGC Nor. Am. 2014, 32, 420–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chester, T.L. Recent Developments in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phases. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmet, G.; Eeltink, S. Fundamentals for LC Miniaturization. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, S.; Schappler, J.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. Current and future trends in UHPLC. Tr. Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckhoven, K.; Desmet, G. The future of UHPLC: Towards higher pressure and/or smaller particles? Tr. Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Rapid development of core–shell column technology: Accurate measurements of the intrinsic column efficiency of narrow-bore columns packed with 4.6 down to 1.3 µm superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1333, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D. Kinetic evaluation of new generation of column packed with 1.3 µm core–shell particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1308, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Shiner, S.J.; Fairchild, J.N.; Guiochon, G. Evaluation of the kinetic performance of new prototype 2.1 mm × 100 mm narrow-bore columns packed with 1.6 µm superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1334, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Mass transfer resistance in narrow-bore columns packed with 1.7 µm particles in very high pressure liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5069–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeStefano, J.J.; Schuster, S.A.; Lawhorn, J.M.; Kirkland, J.J. Performance characteristics of new superficially porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1258, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Speed-resolution properties of columns packed with new 4.6 µm Kinetex-C18 core–shell particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1280, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeckhoven, K.; Cabooter, D.; Desmet, G. Kinetic performance comparison of fully and superficially porous particles with sizes ranging between 2.7 µm and 5 µm: Intrinsic evaluation and application to a pharmaceutical test compound. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 3, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderheyden, Y.; Cabooter, D.; Desmet, G.; Broeckhoven, K. Isocratic and gradient impedance plot analysis and comparison of some recently introduced large size core–shell and fully porous particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1312, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahsay, G.; Broeckhoven, K.; Adams, E.; Desmet, G.; Cabooter, D. Kinetic performance comparison of fully and superficially porous particles with a particle size of 5 µm: Intrinsic evaluation and application to the impurity analysis of griseofulvin. Talanta 2014, 122, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanali, C.; Rocco, A.; Aturki, Z.; Mondello, L.; Fanali, S. Analysis of polyphenols and methylxantines in tea samples by means of nano-liquid chromatography utilizing capillary columns packed with core–shell particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1234, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, G.; Rocchi, S.; Fanali, S. Nano-liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry: Separation of sulfonamides employing non-porous core–shell particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1255, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, S.; Stoeckel, D.; Smarsly, B.M.; Tallarek, U. Influence of particle properties on the wall region in packed capillaries. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1268, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanali, S.; D’Orazio, G.; Farkas, T.; Chankvetadze, B. Comparative performance of capillary columns made with totally porous and core–shell particles coated with a polysaccharide-based chiral selector in nano-liquid chromatography and capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1269, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, S.; Franklin, E.G.; Grinias, J.P.; Godinho, J.M.; Jorgenson, J.W.; Tallarek, U. Slurry concentration effects on the bed morphology and separation efficiency of capillaries packed with sub-2 µm particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchi, S.; Fanali, S.; Farkas, T.; Chankvetadze, B. Effect of content of chiral selector and pore size of core–shell type silica support on the performance of amylose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate)-based chiral stationary phases in nano-liquid chromatography and capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1363, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blue, L.E.; Jorgenson, J.W. 1.1 μm Superficially porous particles for liquid chromatography: Part II: Column packing and chromatographic performance. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1380, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutter, J.P. Liquid phase chromatography on microchips. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1221, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrik, N.V.; Taylor, L.T.; Sepaniak, M.J. Nanotechnology and chip level systems for pressure driven liquid chromatography and emerging analytical separation techniques: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 694, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, K. Liquid chromatography on chip. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2499–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruim, P.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Kok, W.T. Microfluidic Pressure Driven Liquid Chromatography of Biologically Relevant Samples. Chromatographia 2012, 75, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.J.; Fluri, K.; Seiler, K.; Fan, Z.; Effenhauser, C.S.; Manz, A. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science 1993, 261, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.C.; Hergenroder, R.; Koutny, L.B.; Warmack, R.J.; Ramsey, J.M. Effects of Injection Schemes and Column Geometry on the Performance of Microchip Electrophoresis Devices. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, M.G.; Shackman, J.G.; Dahlgren, G.M.; Kennedy, R.T. Microfluidic chip for continuous monitoring of hormone secretion from live cells using an electrophoresis-based immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, P.C.; Roach, D.; Woolley, A.T.; Thorsen, T.; Johnston, R.; Sensabaugh, G.F.; Mathies, R.A. High-throughput genetic analysis using microfabricated 96-sample capillary array electrophoresis microplates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, G.T.; Wang, M.; Shultz, K.N.; Jennings, C.; Kennedy, R.T. Sampling and Electrophoretic Analysis of Segmented Flow Streams Using Virtual Walls in a Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8231–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriotti, L.; de Rooij, N.F.; Verpoorte, E. An integrated fritless column for on-chip capillary electrochromatography with conventional stationary phases. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.G.; Mellors, J.S.; Henley, W.H.; Ramsey, J.M. Monolithic Integration of Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography−Capillary Electrophoresis and Electrospray Ionization on a Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurmann, S.; Dittmar, A.; Belder, D. A low pressure on-chip injection strategy for high-performance chip-based chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1340, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, R.T.; Jorgenson, J.W. Preparation and evaluation of packed capillary liquid chromatography columns with inner diameters from 20 to 50 micrometers. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zubieta, J.-K.; Kennedy, R.T. Practical Aspects of in Vivo Detection of Neuropeptides by Microdialysis Coupled Off-Line to Capillary LC with Multistage MS. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiolica, A.; Borsotti, D.; Rappsilber, J. Self-made frits for nanoscale columns in proteomics. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3847–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, M.C.; Stearns, S.D. HPLC Sample Injection Using Electric Valve Actuators. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1983, 21, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.; Jorgenson, J.W. Preparation and Evaluation of Slurry-Packed Liquid Chromatography Microcolumns with Inner Diameters from 12 to 33 µm. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, F.; Felinger, A.; Guiochon, G. Influence of the errors made in the measurement of the extra-column volume on the accuracies of estimates of the column efficiency and the mass transfer kinetics parameters. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1136, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neue, U.D. HPLC Columns: Theory, Technology, and Practice; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, C.R.; Chang, P. Correlation of diffusion coefficients in dilute solutions. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bings, N.H.; Wang, C.; Skinner, C.D.; Colyer, C.L.; Thibault, P.; Harrison, D.J. Microfluidic devices connected to fused-silica capillaries with minimal dead volume. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3292–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khirevich, S.; Höltzel, A.; Hlushkou, D.; Tallarek, U. Impact of Conduit Geometry and Bed Porosity on Flow and Dispersion in Noncylindrical Sphere Packings. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 9340–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khirevich, S.; Höltzel, A.; Ehlert, S.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Tallarek, U. Large-Scale Simulation of Flow and Transport in Reconstructed HPLC-Microchip Packings. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4937–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Höltzel, A.; Ehlert, S.; Mora, J.-A.; Kraiczek, K.; Dittmann, M.; Rozing, G.P.; Tallarek, U. Impact of Conduit Geometry on the Performance of Typical Particulate Microchip Packings. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10193–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grinias, J.P.; Kennedy, R.T. Evaluation of 5 μm Superficially Porous Particles for Capillary and Microfluidic LC Columns. Chromatography 2015, 2, 502-514. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030502
Grinias JP, Kennedy RT. Evaluation of 5 μm Superficially Porous Particles for Capillary and Microfluidic LC Columns. Chromatography. 2015; 2(3):502-514. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030502
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrinias, James P., and Robert T. Kennedy. 2015. "Evaluation of 5 μm Superficially Porous Particles for Capillary and Microfluidic LC Columns" Chromatography 2, no. 3: 502-514. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030502
APA StyleGrinias, J. P., & Kennedy, R. T. (2015). Evaluation of 5 μm Superficially Porous Particles for Capillary and Microfluidic LC Columns. Chromatography, 2(3), 502-514. https://doi.org/10.3390/chromatography2030502





