Pragmatics: Mapping Evidence on Enhancing Children’s Use of Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Capacities for Interactive Communication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Rise of Pragmatics
1.2. The Scope of Pragmatics
1.3. Scientific Contributions for Pragmatics
1.4. Purpose of the Present Study
2. Methods
2.1. Research Methods
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data-Collection and Sample
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Pragmatics Studies from Scopus, Web of Science, and Lens
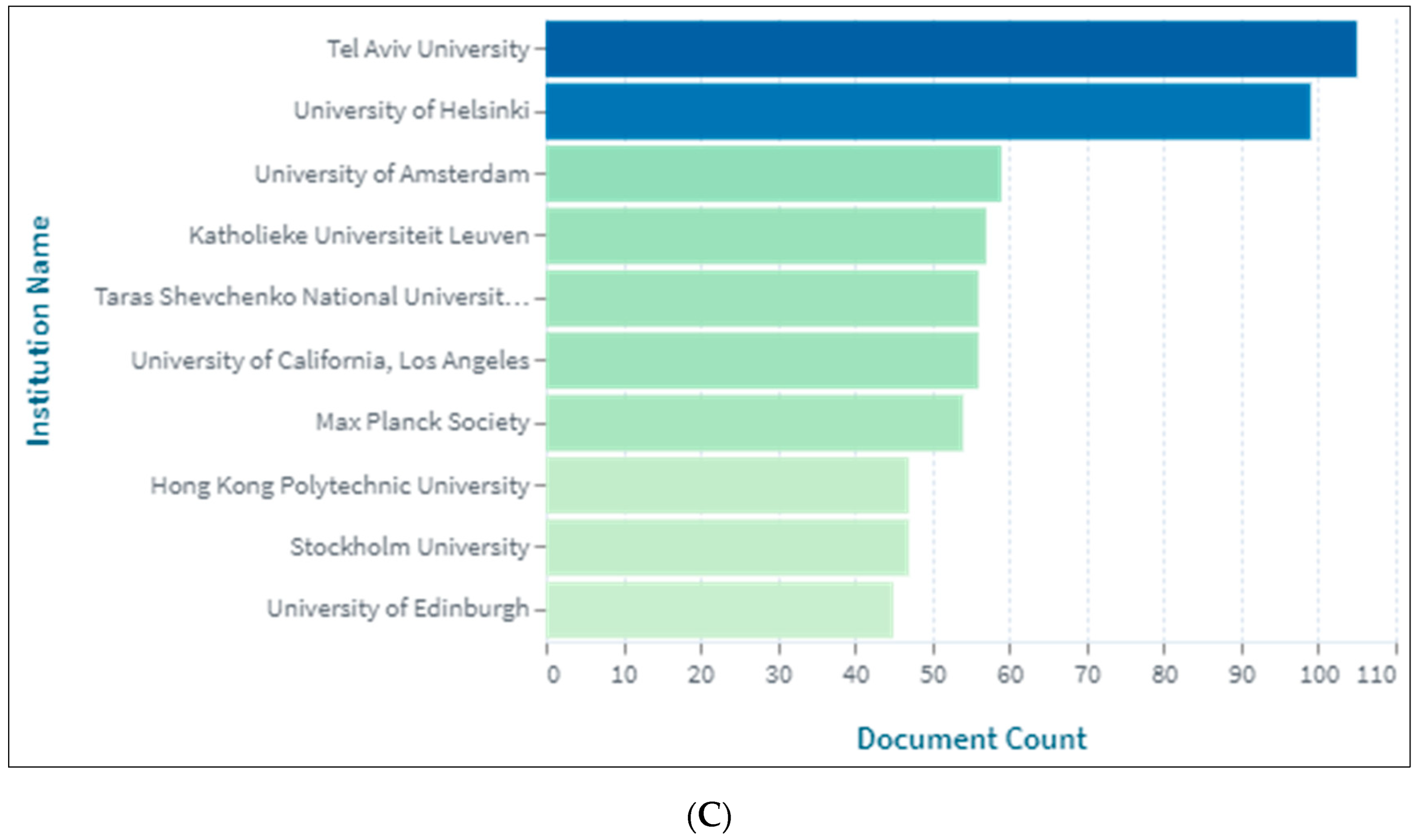
3.2. Production of Pragmatics Research by Country and University
3.3. Production of Pragmatics Research by Journal and Publisher
3.4. Production of Pragmatics by Research Area, Keywords and Cooccurrence
3.5. Production of Pragmatics by Authors
3.6. Impact of Research on Pragmatics
3.7. Impact of Research on Pragmatics by Clusters, Citation Counts, Citation Bursts, Centrality, and Sigma
3.7.1. Clusters
3.7.2. Citation Counts
3.7.3. Bursts
3.7.4. Centrality
3.7.5. Sigma
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Implications
4.2. Practical Implications
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, C.W. Foundations of the Theory of Signs; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, J.L. How to Do Things with Words; Urmson, J.O., Sbisà, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, J. An Essay in the Philosophy of Language. Hist. Pragmat. 1969, 46, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, E. Language and Context: The Acquisition of Pragmatics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, S.C. Pragmatics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983; ISBN 9780521222358. [Google Scholar]
- Grice, P. Studies in the Ways of Words; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Cavell, T. Social Adjustment, Social Performance, and Social Skills: A Tri-Component Model of Social Competence. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 1990, 19, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperber, D.; Wilson, D. Relevance: Communication and Cognition, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1995; ISBN 0631198784. [Google Scholar]
- Yule, G. Pragmatics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Historical Pragmatics; Jucker, A.H. (Ed.) John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; ISBN 1556193289. [Google Scholar]
- Bosco, F.M. Cognitive Pragmatics. In Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Bara, B.G.; Tirassa, M.; Zettin, M. Neuropragmatics: Neuropsychological Constraints on Formal Theories of Dialogue. Brain Lang. 1997, 59, 7–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, L. Clinical Pragmatics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ISBN 9780511581601. [Google Scholar]
- Alduais, A.; Qasem, F.; Alfadda, H.; Alfadda, N.; AlAmri, L. Arabic Validation of the Pragmatic Language Skills Inventory to Assess Pragmatic Language Development in Preschoolers with and without Pragmatic Language Impairment. Children 2022, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, F.; Alduais, A.; Alfadda, H.; Alfadda, N.; AlAmri, L. A Study on the Relationship between Pragmatic Language Development and Socioeconomic Status in Arab Preschoolers with and without Pragmatic Language Impairment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduais, A.M.S. Identifying Typical and Atypical Manifestations of Pragmatic Language Impairment in Arabic: A Multi-Method Study of Individuals with Developmental Dysphasia; King Saud University: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, C.S. What Pragmatism Is. Monist 1905, 15, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mey, J.L. Pragmatics: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Leech, G. Principles of Pragmatics; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781315835976. [Google Scholar]
- Black, M.; Morris, C. Signification and Significance: A Study of the Relations of Signs and Values. Philos. Rev. 1967, 76, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduais, A.M. Conversational Implicature (Flouting the Maxims): Applying Conversational Maxims on Examples Taken from Non-Standard Arabic Language, Yemeni Dialect, an Idiolect Spoken at IBB City. J. Sociol. Res. 2012, 3, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerlich, B. Pragmatics: History. In Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. The Oxford Dictionary of Pragmatics, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- LoCastro, V. Pragmatics for Language Educators: A Sociolinguistic Perspective, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akmajian, A.; Demer, R.A.; Farmer, A.K.; Harnish, R.M. Linguistics: An Introduction to Language and Communication; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.D. Speech Acts. In Sociolinguistics and Language Teaching; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 383–420. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, M. Issues in Applied Linguistics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Celce-Murcia, M.; Olshtain, E.; Olshṭain, I. Discourse and Context in Language Teaching: A Guide for Language Teachers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- El-Okda, M. Developing Pragmatic Competence: Challenges and Solutions. Asian EFL J. 2011, 13, 169–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, G.; Rose, K.R. Pragmatics in Language Teaching. In Pragmatics in Language Teaching; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sperber, D.; Wilson, D. Pragmatics. Cognition 1981, 10, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütz, M.; Neff-van Aertselaer, J. Developing Contrastive Pragmatics: Interlanguage and Cross-Cultural Perspectives; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783110207217. [Google Scholar]
- Stalnaker, R.C. Pragmatics. In Context and Content; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keeffe, A.; Clancy, B.; Adolphs, S. Introducing Pragmatics in Use; Routledge: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 9781136825873. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J. Meaning in Interaction an Introduction to Pragmatics, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mathias, H.K.; Ardo, M.B. Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Actsin President Muhammad Buhari’s Inaugural COVID-19 Address. Voices A J. Engl. Stud. 2021, 4, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Crystal, D. The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Language, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Konur, O. The Evaluation of the Global Research on the Education: A Scientometric Approach. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 47, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappandi, P.; Vijayakumar, C.S. Bibliometrics, Scientometrics, Webometrics/Cybermetrics, Informetrics and Altmetrics—An Emerging Field in Library and Information Science Research. Int. J. Educ. 2018, 7, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glänzel, W.; Schoepflin, U. Little Scientometrics, Big Scientometrics… and Beyond? Scientometrics 1994, 30, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Leydesdorff, L. Scientometrics in a Changing Research Landscape. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egghe, L. Little Science, Big Science… and Beyond. Scientometrics 1994, 30, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, M. The Evaluation of Research by Scientometric Indicators. Libr. Manag. 2011, 32, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Glänzel, W.; Zhang, L. Tracing the Development of Mapping Knowledge Domains. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 6201–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooryamoorthy, R. Scientometrics for the Humanities and Social Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 9780367626860. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, G.D. Data Visualization and Analysis in Second Language Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 9781003032243. [Google Scholar]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfold, R. Using the Lens Database for Staff Publications. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2020, 108, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a Data Source for Research on Scientific and Scholarly Activity. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2020, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, J.F. Scopus Database: A Review. Biomed. Digit. Libr. 2006, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinska, V.; Klimas, R. Mapping Science: Tools for Bibliometric and Altmetric Studies. Inf. Res. an Int. Electron. J. 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. The CiteSpace Manual; Version 1.01; College of Computing and Informatics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual: Manual for VOSviewer, Version 1.6.18; Univeristeit Leiden: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in Social Networks. Soc. Networks 1979, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, J. Bursty and Hierarchical Structure in Streams. In Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining-KDD ’02, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 23–26 July 2002; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace: A Practical Guide for Mapping Scientific Literature; Nova Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781536102956. [Google Scholar]
- Bambini, V. Neuropragmatics: A Foreword. Ital. J. Linguist. 2010, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Capone, A. The Pragmatics of Indirect Reports Socio-Philosophical Considerations; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, S.E.S.; Ostrom, E. A Grammar of Institutions. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 1995, 89, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazden, C. A Pedagogy of Multiliteracies: Designing Social Futures. Harv. Educ. Rev. 1996, 66, 60–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, C. Action and Embodiment within Situated Human Interaction. J. Pragmat. 2000, 32, 1489–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, C.; Goodwin, M.H. Context, Activity and Participation. In The Contextualization of Language; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.V.M. Development of the Children’s Communication Checklist (CCC): A Method for Assessing Qualitative Aspects of Communicative Impairment in Children. J. Child Psychol. PSYCHIATRY 1998, 39, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruner, J.S. From Communication to Language—A Psychological Perspective. Cognition 1974, 3, 255–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C. Information Structure in Discourse: Towards an Integrated Formal Theory of Pragmatics. Semant. Pragmat. 2012, 5, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L. Moment Analysis and Translanguaging Space: Discursive Construction of Identities by Multilingual Chinese Youth in Britain. J. Pragmat. 2011, 43, 1222–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, F.J. Neurophenomenology: A Methodological Remedy for the Hard Problem. J. Conscious. Stud. 1996, 3, 330–349. [Google Scholar]
- Kalfoglou, Y.; Schorlemmer, M. Ontology Mapping: The State of the Art. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2003, 18, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B. Perspectives on Politeness. J. Pragmat. 1990, 14, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorace, A. Pinning down the Concept of “Interface” in Bilingualism. Linguist. Approaches to Biling. 2011, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y. Politeness Phenomena in Modern Chinese. J. Pragmat. 1990, 14, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, J.G.; Corwin, J. Pragmatics of Measuring Recognition Memory: Applications to Dementia and Amnesia. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1988, 117, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperber, D.; Wilson, D. Pragmatics, Modularity and Mind-reading. Mind Lang. 2002, 17, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graneheim, U.; Lundman, B. Qualitative Content Analysis in Nursing Research: Concepts, Procedures and Measures to Achieve Trustworthiness. Nurse Educ. Today 2004, 24, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y. Reexamination of the Universality of Face: Politeness Phenomena in Japanese. J. Pragmat. 1988, 12, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weick, K.E. Small Wins: Redefining the Scale of Social Problems. Am. Psychol. 1984, 39, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darke, P.; Shanks, G.; Broadbent, M. Successfully Completing Case Study Research: Combining Rigour, Relevance and Pragmatism. Inf. Syst. J. 1998, 8, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, A. The Discursive Accomplishment of Normality: On ‘Lingua Franca’ English and Conversation Analysis. J. Pragmat. 1996, 26, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selic, B. The Pragmatics of Model-Driven Development. IEEE Softw. 2003, 20, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culpeper, J. Towards an Anatomy of Impoliteness. J. Pragmat. 1996, 25, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B. What Are Discourse Markers? J. Pragmat. 1999, 31, 931–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noveck, I.A. When Children Are More Logical than Adults: Experimental Investigations of Scalar Implicature. Cognition 2001, 78, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes, P.B.; Staudinger, U.M. Wisdom: A Metaheuristic (Pragmatic) to Orchestrate Mind and Virtue toward Excellence. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, P. Logic and Conversation. In Speech Acts; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1975; pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, J.L. How to Do Things with Words; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975; ISBN 9780198245537. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.; Levison, S. Politeness: Some Universals in Language Usage; Cambridge University Press: Cambrdige, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.V. The Children’s Communication Checklist; Psychological Corporation: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, C.L. How (Not) to Be Rude: Facilitatingthe Acquisition of L2 (Im)Politeness. Intercult. Pragmat. 2018, 15, 651–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, V.; Arcara, G.; Martinelli, I.; Bernini, S.; Alvisi, E.; Moro, A.; Cappa, S.F.; Ceroni, M. Communication and Pragmatic Breakdowns in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Brain Lang. 2016, 153, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catani, M.; Bambini, V. A Model for Social Communication And Language Evolution and Development (SCALED). Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 28, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, J. Pragmatics in the Last Quarter Century: The Case of Conditional Perfection. J. Pragmat. 1997, 27, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, M. Intention in Pragmatics. Intercult. Pragmat. 2008, 5, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macagno, F.; Capone, A. Uncommon Ground. Intercult. Pragmat. 2016, 13, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, S.C. Presumptive Meanings: The Theory of Generalized Conversational Implicature, Speech, and Communication; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, N. Instructed Pragmatics at a Glance: Where Instructional Studies Were, Are, and Should Be Going. Lang. Teach. 2015, 48, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeleri, R.; Bosco, F.; Zettin, M.; Sacco, K.; Colle, L.; Bara, B. Communicative Impairment in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Complete Pragmatic Assessment. Brain Lang. 2008, 107, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Bishop, D.V.M. Conversational Characteristics of Children with Semantic-Pragmatic Disorder. I: Exchange Structure, Turntaking, Repairs and Cohesion. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 1989, 24, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasher, A. Mood Implicatures: A logical way of doing generative pragmatics. Theor. Linguist. 1974, 1, 6–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, A. On Grice’s Circle (a Theory-Internal Problem in Linguistic Theories of the Gricean Type). J. Pragmat. 2006, 38, 645–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.M.; Kliegl, R.; Vasishth, S.; Baayen, H. Parsimonious Mixed Models. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04967. [Google Scholar]
- Kádár, D.Z.; Márquez-Reiter, R. (Im)Politeness and (Im)Morality: Insights from Intervention. J. Politeness Res. 2015, 11, 239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Goffman, E. La Condition de Félicité—1. Actes Rech. Sci. Soc. 1986, 64, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, M. Indexical Order and the Dialectics of Sociolinguistic Life. Lang. Commun. 2003, 23, 193–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschueren, J. Reflections on Presupposition Failure: A Contribution to an Integrated Theory of Pragmatics. J. Pragmat. 1978, 2, 107–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, K.; Harnish, R.M. Linguistic Communication and Speech Acts; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kecskes, I. Intercultural Pragmatics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780199892655. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.O. Sociobiology: The New Synthesis; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S. Gender and Politeness; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; ISBN 9780521810845. [Google Scholar]
- Degen, J.; Goodman, N.D. Lost Your Marbles? The Puzzle of Dependent Measures in Experimental Pragmatics. Proc. Annu. Conf. Cogn. Sci. Soc. 2014, 36, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Szabolcsi, A.; Bott, L.; McElree, B. The Effect of Negative Polarity Items on Inference Verification. J. Semant. 2008, 25, 411–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerlich, B.; Clarke, D.D. Language, Action and Context Linguistic Pragmatics in Europe and America (1800–1950). J. Pragmat. 1994, 22, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicone, M.; Wapner, W.; Foldi, N.; Zurif, E.; Gardner, H. The Relation between Gesture and Language in Aphasic Communication. Brain Lang. 1979, 8, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.M.; MacWhinney, B.; Mayhew, D. Pragmatics in Memory: A Study of Natural Conversation. J. Verbal Learning Verbal Behav. 1977, 16, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsos, N.; Bishop, D.V.M. Pragmatic Tolerance: Implications for the Acquisition of Informativeness and Implicature. Cognition 2011, 120, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohlberg, M.M.; MacDonald, S.; Byom, L.; Iwashita, H.; Lemoncello, R.; Meulenbroek, P.; Ness, B.; O’Neil-Pirozzi, T.M. Social Communication Following Traumatic Brain Injury Part I: State-of-the-Art Review of Assessment Tools. Int. J. Speech. Lang. Pathol. 2019, 21, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.R. Toward a New Taxonomy for Pragmatic Inference: Q-Based and R-Based Implicature. In Meaning, Form Use Context; Georgetown University Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, J. The Pragmatics of Humor Support. Humor–Int. J. Humor Res. 2001, 14, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, T. Pragmatics and Non-Verbal Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ISBN 9780521691444. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, L. Pragmatic Impairment. In The Handbook of Language and Speech Disorders; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, 2021; pp. 192–208. ISBN 9781119606987. [Google Scholar]
- Cherpas, C. Natural Language Processing, Pragmatics, and Verbal Behavior. Anal. Verbal Behav. 1992, 10, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyner, L.; Cohen, A.D. Second Language Pragmatic Ability: Individual Differences According to Environment. Stud. Second Lang. Learn. Teach. 2015, 5, 519–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, R.H. A discourse-pragmatic analysis of illocutionary speech acts in dickens ‘hard times’. Int. J. Humanit. Educ. Res. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpashri, H.; Shyamala, K. Pragmatic Skills during Mother-Child Interaction in Children with Autism. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 244–250. [Google Scholar]
- Dervan, M.; Egan, M. I Want to Say so I Can Play: An Examination of a Pragmatic Language Intervention for Children with Specific Speech and Language Disorder. Reach 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.; Maniam, M. A Review Article of the Pragmatics-Based-Curriculum in EFL Context: Focus on the Curriculum in Iraq. Bp. Int. Res. Crit. Linguist. Educ. J. 2020, 3, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takkaç Tulgar, A. The Role of Pragmatic Competence in Foreign Language Education. Turk. Online J. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2016, 1, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisna, A.; Husein, R.; Pulungan, A.H. Learning Pragmatic Aspects Acquired by a Three-Year-Old Indonesian Child. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual International Seminar on Transformative Education and Educational Leadership (AISTEEL 2020), Medan, Indonesia, 22 September 2020; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Haugh, M. Intention(Ality) and the Conceptualization of Communication in Pragmatics. Aust. J. Linguist. 2009, 29, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, N. 11. Longitudinal Studies in Interlanguage Pragmatics. In Pragmatics across Languages and Cultures; De Gruyter Mouton: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 333–362. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, S.M. A Pragmatic Study of the Recognition and Interpretation of Verbal Irony by Malaysian ESL Learners. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, H.P. Logic and Conversation. In Syntax and Semantics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- House, J.; Kádár, D.Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Xia, Z.; Jiao, L. Interaction, Speech Acts and Ritual: An Integrative Model. Lingua 2021, 257, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, N. Dispreferred Speech Acts in Virtual Reality: Analysis of Tone Choices and Hesitations. System 2022, 106, 102793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, V.; Agostoni, G.; Buonocore, M.; Tonini, E.; Bechi, M.; Ferri, I.; Sapienza, J.; Martini, F.; Cuoco, F.; Cocchi, F.; et al. It Is Time to Address Language Disorders in Schizophrenia: A RCT on the Efficacy of a Novel Training Targeting the Pragmatics of Communication (PragmaCom). J. Commun. Disord. 2022, 97, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrset, A. ‘You Could Win Masterchef with This Soup. Can I Get Some More?’ Request Production and the Impact of Instruction on Young EFL Learners. J. Pragmat. 2022, 192, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal, P.; Bischetti, L.; Bertini, C.; Ricci, I.; Lecce, S.; Bambini, V. N400 Differences between Physical and Mental Metaphors: The Role of Theories of Mind. Brain Cogn. 2022, 161, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.; Won, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.M. L2 Pragmatic Comprehension of Aural Sarcasm: Tone, Context, and Literal Meaning. System 2022, 105, 102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, L. No Straight Talk Here: A Multi-Level Analysis of Hedging Strategies Employed by the Fed Chair in Press Conferences. J. Pragmat. 2022, 188, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marocchini, E.; Domaneschi, F. “Can You Read My Mind?” Conventionalized Indirect Requests and Theory of Mind Abilities. J. Pragmat. 2022, 193, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaneschi, F.; Di Paola, S.; Pouscoulous, N. The Development of Presupposition: Pre-Schoolers’ Understanding of Regret and Too. Intercult. Pragmat. 2022, 19, 345–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotzke, A.; Czypionka, A. The Pragmatics of Surprise-Disapproval Questions: An Empirical Study. Linguist. Vanguard 2022, 8, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, R.; Schulz, K. Causal Relevance of Conditionals: Semantics or Pragmatics? Linguist. Vanguard 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Lloret, M. Technology-Mediated Tasks for the Development of L2 Pragmatics. Lang. Teach. Res. 2022, 26, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, J.; Taguchi, N. Using L2 Interactional-Pragmatic Resources in CMC: A Case of Japanese Orthography and Emoji. Lang. Teach. Res. 2022, 26, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M. The Multilingual Pragmatics of New Englishes: An Analysis of Question Tags in Nigerian English. Front. Commun. 2022, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, P. Directives and Politeness in SPICE-Ireland. Corpus Pragmat. 2022, 6, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, N. Immersive Virtual Reality for Pragmatics Task Development. TESOL Q. 2022, 56, 308–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, M.H.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Goodman, N.D. Logic, Probability, and Pragmatics in Syllogistic Reasoning. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2022, 14, 574–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilviu, D.; Parola, A.; Vivaldo, S.; Di Lisi, D.; Consolino, P.; Bosco, F.M. Children with Hearing Impairment and Early Cochlear Implant: A Pragmatic Assessment. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotila, A.; Tohka, J.; Kauppi, J.P.; Gabbatore, I.; Mäkinen, L.; Hurtig, T.M.; Ebeling, H.E.; Korhonen, V.; Kiviniemi, V.J.; Loukusa, S. Neural-Level Associations of Non-Verbal Pragmatic Comprehension in Young Finnish Autistic Adults. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2021, 80, 1909333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macuch Silva, V.; Franke, M. Pragmatic Prediction in the Processing of Referring Expressions Containing Scalar Quantifiers. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsos, N.; Andrés-Roqueta, C. Where next for Pragmatics and Mind Reading? A Situation-Based View (Response to Kissine). Language 2021, 97, e184–e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarella, D.; Noveck, I. Pragmatics and Mind Reading: The Puzzle of Autism (Response to Kissine). Language 2021, 97, e198–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, V.; Van Looy, L.; Demiddele, K.; Schaeken, W. What Is the Contribution of Executive Functions to Communicative-Pragmatic Skills? Insights from Aging and Different Types of Pragmatic Inference. Cogn. Process. 2021, 22, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing Bibliometric Networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 285–320. ISBN 9783319103761. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L.; Dekker, R.; van den Berg, J. A Comparison of Two Techniques for Bibliometric Mapping: Multidimensional Scaling and VOS. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Muñoz, J.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Cobo, M.J. Software Tools for Conducting Bibliometric Analysis in Science: An up-to-Date Review. Prof. De La Inf. 2020, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





















| Source Journal | Host Country | Publisher | Span | Volumes | Web Address | Scope of the Journal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Journal of Pragmatics | Netherlands | Elsevier | 1977–2020 | 191 | https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-pragmatics | Innovative pragmatic studies from all perspectives. |
| Intercultural Pragmatics | Germany | De Gruyter Mouton | 2004–2020 | 18 | https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-pragmatics | General theoretic issues, multiple languages and cultures, or various varieties of a language. |
| Pragmatics and Cognition | Netherlands | John Benjamins Publishing Company | 1993–2014, 2016–2019 | 27 | https://benjamins.com/catalog/pc | Linguistics, semiotics, cognitive science, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, philosophy, ethology and cognitive anthropology. |
| Pragmatics | Belgium | International Pragmatics Association | 1986–2020 | 31 | https://benjamins.com/catalog/prag | Linguistics, anthropology, sociology, psychology or computation. |
| Journal of Historical Pragmatics | Netherlands | John Benjamins Publishing Company | 2000–2019 | 22 | https://benjamins.com/catalog/jhp | Socio-historical and pragmatic aspects of historical texts within the context of socio-cultural communication as well as diachronic pragmatics. |
| Pragmatics and Society | Netherlands | John Benjamins Publishing Company | 2010–2020 | 12 | https://benjamins.com/catalog/ps | Language use and social normativity, such as in education, political discourse as well as discriminatory language use. |
| Perspectives in Pragmatics, Philosophy and Psychology | Switzerland | Springer International Publishing AG | 2013–2014, 2016–2020 | 12 | https://www.springer.com/series/11797 | Theoretical pragmatics and pragmatics. |
| International Review of Pragmatics | Netherlands | Brill Academic Publishers | 2014–2020 | 13 | https://brill.com/view/journals/irp/irp-overview.xml | Different topics in pragmatics |
| Lodz Papers in Pragmatics | Germany | Versita (Central European Science Publishers) | 2015–2018, 2020 | 16 | https://www.degruyter.com/journal/key/lpp/html | Human communication, both in everyday interactions and in the media, whether verbal or written, institutional or interpersonal. |
| Current Research in the Semantics/Pragmatics Interface | Netherlands | Brill Academic Publishers | 2007–2016, 2018 | https://brill.com/view/serial/CRISPI?lang=en | Different topics in semantics and pragmatics | |
| Pragmatics and Beyond New Series | Netherlands | John Benjamins Publishing Company | 2018–2020 | https://benjamins.com/catalog/pbns | Different topics in pragmatics, linguistic and sociocultural contexts and different theoretical and methodological perspectives. | |
| Studies in Pragmatics | Netherlands | Brill Academic Publishers | 2009–2010, 2012, 2014–2017 | https://brill.com/view/serial/SIP | Theoretical, analytical, and applied pragmatic studies. | |
| East Asian Pragmatics | United Kingdom | Equinox Publishing Ltd. | 2018–2020 | 6 | https://journal.equinoxpub.com/EAP | East Asian language use contributing to pragmatics. |
| Wednesday, 9 March 2022 Scopus TITLE-ABS-KEY ({pragmatics}) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)) 6554 document results from 1939 to 2022 |
| WOS TS=(“pragmatics”) and Web of Science Core Collection (Database) and English (Languages) and Articles or Early Access (Document Types) 6597 results from Web of Science Core Collection from 1966 to February 2022 WOS (To get most cited authors and references in CiteSpace) “pragmatics” (Topic) and Articles (Document Types) and English (Languages) and 2022 or 2021 or 2020 or 2019 or 2018 (Publication Years) 2222 results from Web of Science Core Collection from 2018 to February 2022 |
| Lens source.title:pragmatics Filters: Publication Type Scholarly Works (11,230) from 1966 to 2022 |
| No. | Source Title | Citation | Citations by Database | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scopus | WOS | Lens | |||
| 1 | A grammar of institutions | [59] | 694 | X | X |
| 2 | A pedagogy of multiliteracies: Designing social futures | [60] | 2892 | 2114 | X |
| 3 | Action and embodiment within situated human interaction | [61] | X | X | 1927 |
| 4 | Context, Activity and Participation | [62] | X | X | 574 |
| 5 | Development of the Children’s Communication Checklist (CCC): A method for assessing qualitative aspects of communicative impairment in children | [63] | X | 390 | Χ |
| 6 | From communication to language-a psychological perspective | [64] | 594 | X | X |
| 7 | Information Structure in Discourse: Towards an Integrated Formal Theory of Pragmatics | [65] | X | X | 719 |
| 8 | Moment analysis and translanguaging space: discursive construction of identities by multilingual Chinese youth in Britain | [66] | X | X | 765 |
| 9 | Neurophenomenology: A methodological remedy for the hard problem | [67] | 821 | X | X |
| 10 | Ontology mapping: The state of the art | [68] | 861 | X | X |
| 11 | Perspectives on politeness | [69] | X | X | 699 |
| 12 | Pinning down the concept of interface in bilingualism | [70] | X | 379 | X |
| 13 | Politeness phenomena in modern Chinese | [71] | X | X | 715 |
| 14 | Pragmatics of measuring recognition memory-applications to dementia and amnesia | [72] | 2437 | 2437 | X |
| 15 | Pragmatics, modularity and mind-reading | [73] | X | 484 | X |
| 16 | Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: Concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness | [74] | 9320 | 8781 | X |
| 17 | Reexamination of the universality of face: Politeness phenomena in Japanese | [75] | X | X | 653 |
| 18 | Small wins: Redefining the scale of social problems | [76] | 624 | X | X |
| 19 | Successfully completing case study research: combining rigour, relevance and pragmatism | [77] | X | 371 | X |
| 20 | The discursive accomplishment of normality: On ?€?lingua franca?€? English and conversation analysis | [78] | X | X | 768 |
| 21 | The pragmatics of model-driven development | [79] | 841 | 555 | X |
| 22 | Towards an anatomy of impoliteness | [80] | X | X | 859 |
| 23 | What are discourse markers | [81] | X | Χ | 745 |
| 24 | When children are more logical than adults: experimental investigations of scalar implicature | [82] | X | 388 | X |
| 25 | Wisdom: A metaheuristic (pragmatic) to orchestrate mind and virtue toward excellence | [83] | 715 | 571 | X |
| Cluster ID | Size | Silhouette | Label (LSI) | Label (LLR) | Label (MI) | Average Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 154 | 0.827 | pragmatic competence | speech act (741.32, 1.0 × 104) | syntax-discourse interface (3.68) | 1997 |
| 1 | 133 | 0.748 | case study | relevance-theoretic approach (542.65, 1.0 × 104) | syntax-discourse interface (2.87) | 1994 |
| Scopus | ||||||
| 0 | 418 | 0.663 | natural language processing | autism spectrum disorder (5841.56, 1.0 × 104) | character equivalence (6.1) | 2004 |
| 1 | 297 | 0.472 | autism spectrum disorder | pragmatic disorder (1561.88, 1.0 × 104) | character equivalence (0.87) | 1991 |
| 2 | 212 | 0.785 | autism spectrum disorder | pragmatic language (3311.06, 1.0 × 104) | character equivalence (1.47) | 2001 |
| WoS | Scopus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citation | Reference | Cluster ID | Citation | Reference | Cluster ID |
| 231 | Grice [84] | 3 | 25 | Bambini [90] | 0 |
| 154 | Brown [86] | 0 | 19 | Der Van [91] | 1 |
| 115 | Grice [6] | 1 | 19 | Haugh [92] | 4 |
| 100 | Leech [19] | 0 | 18 | Macagno [93] | 93 |
| 100 | Levinson [94] | 1 | 16 | Taguchi [95] | 14 |
| 100 | Sperber [8] | 1 | 15 | Bosco [96] | 3 |
| 96 | Austin [85] | 0 | 13 | Adams [97] | 5 |
| 92 | Levinson [5] | 2 | 12 | Kasher [98] | 10 |
| 81 | Deirdre [8] | 1 | 12 | Capone [99] | 93 |
| 56 | Bates [100] | 2 | 11 | Kadar [101] | 4 |
| WoS | Scopus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burst | Reference | Cluster ID | Burst | Reference | Cluster ID |
| 4.52 | Brown [86] | 0 | 6.33 | Haugh [92] | 4 |
| 3.77 | Goffman [102] | 0 | 5.71 | Taguchi [95] | 14 |
| 3.72 | Austin [85] | 1 | 4.63 | Capone [99] | 93 |
| 3.45 | Silverstein [103] | 1 | 4.24 | Verschueren [104] | 89 |
| 3.44 | Harnish [105] | 1 | 3.96 | Der Van [91] | 1 |
| 3.18 | Kecskes [106] | 0 | 3.91 | Kadar [101] | 4 |
| 3.18 | Wilson [107] | 1 | 3.62 | Kasher [98] | 10 |
| 3.18 | Mills [108] | 0 | 3.06 | Goodman [109] | 11 |
| 3.11 | Grice [6] | 1 | 2.91 | Bott [110] | 13 |
| 2.92 | Bishop [87] | 3 | 2.87 | Nerlich [111] | 77 |
| WoS | Scopus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centrality | Reference | Cluster ID | Centrality | Reference | Cluster ID |
| 314 | Grice [84] | 3 | 14 | Bambini [90] | 0 |
| 242 | Brown [86] | 0 | 12 | Der Van [91] | 1 |
| 224 | Levinson [5] | 2 | 10 | Zurif [112] | 2 |
| 221 | Grice [6] | 1 | 9 | Bosco [96] | 3 |
| 221 | Levinson [94] | 1 | 8 | Arcara [89] | 0 |
| 219 | Sperber [8] | 1 | 8 | MacWhinney [113] | 2 |
| 196 | Deirdre [8] | 1 | 7 | Katsos [114] | 1 |
| 175 | Austin [85] | 0 | 7 | O’Neil-Pirozzi [115] | 6 |
| 170 | Leech [19] | 0 | 7 | Ness [115] | 6 |
| 148 | Horn [116] | 1 | 7 | Byom [115] | 6 |
| WoS | Scopus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma | Reference | Cluster ID | Sigma | Reference | Cluster ID |
| 0 | Grice [84] | 3 | 0 | Bambini [90] | 0 |
| 0 | Brown [86] | 0 | 0 | Der Van [91] | 1 |
| 0 | Levinson [5] | 2 | 0 | Zurif [112] | 2 |
| 0 | Grice [6] | 1 | 0 | Bosco [96] | 3 |
| 0 | Levinson [94] | 1 | 0 | Arcara [89] | 0 |
| 0 | Sperber [8] | 1 | 0 | MacWhinney [113] | 2 |
| 0 | Deirdre [8] | 1 | 0 | Katsos [114] | 1 |
| 0 | Austin [85] | 0 | 0 | O’Neil-Pirozzi [115] | 6 |
| 0 | Leech [19] | 0 | 0 | Ness [115] | 6 |
| 0 | Horn [116] | 1 | 0 | Byom [115] | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alduais, A.; Al-Qaderi, I.; Alfadda, N.; Alfadda, H. Pragmatics: Mapping Evidence on Enhancing Children’s Use of Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Capacities for Interactive Communication. Children 2022, 9, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091318
Alduais A, Al-Qaderi I, Alfadda N, Alfadda H. Pragmatics: Mapping Evidence on Enhancing Children’s Use of Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Capacities for Interactive Communication. Children. 2022; 9(9):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091318
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlduais, Ahmed, Issa Al-Qaderi, Najla Alfadda, and Hind Alfadda. 2022. "Pragmatics: Mapping Evidence on Enhancing Children’s Use of Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Capacities for Interactive Communication" Children 9, no. 9: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091318
APA StyleAlduais, A., Al-Qaderi, I., Alfadda, N., & Alfadda, H. (2022). Pragmatics: Mapping Evidence on Enhancing Children’s Use of Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Capacities for Interactive Communication. Children, 9(9), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9091318







