Urinary Protein Array Analysis to Identify Key Inflammatory Markers in Children with IgA Vasculitis Nephritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions and Patient Selection
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Membrane Antibody Arrays
2.3.1. Human Kidney Biomarker Array—Kit K
2.3.2. Human XL Cytokine Array Kit—Kit C
2.3.3. Creatinine Quantification
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Paediatric Cohort
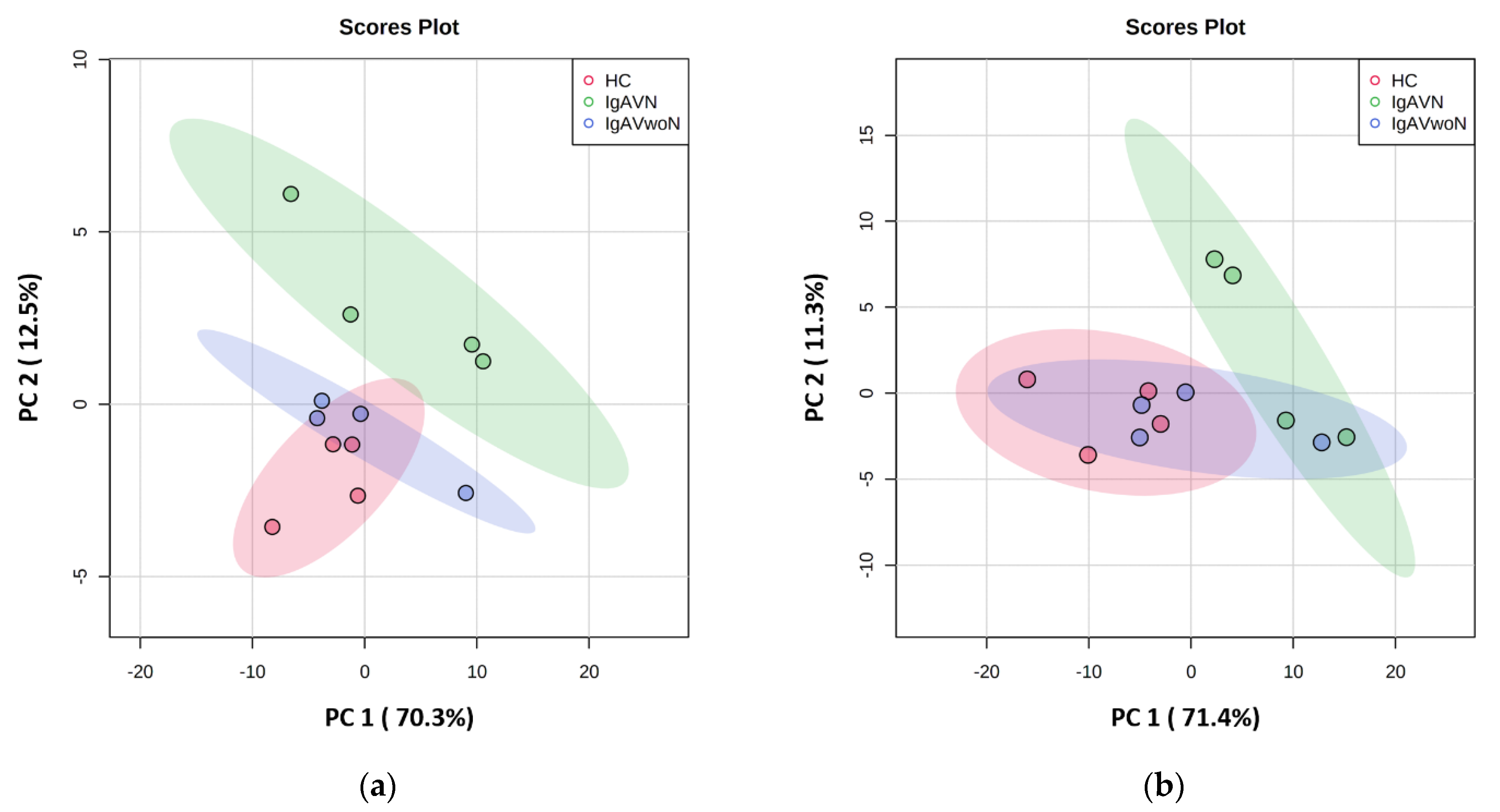
3.2. Exploratory Data Analysis
3.3. Comparison between IgAVN and IgAVwoN
3.4. Comparison between IgAVN and the HCs
3.5. Comparison between IgAVwoN and the HCs
3.6. Correlation between the Kit K and C
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunderkötter, C.; Lamprecht, P.; Mahr, A.; Metze, D.; Zelger, B. Nomenclature of cutaneous vasculitides—German translation of the dermatologic addendum to the 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2018, 16, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner-Medwin, J.M.; Dolezalova, P.; Cummins, C.; Southwood, T.R. Incidence of Henoch-Schönlein purpura, Kawasaki disease, and rare vasculitides in children of different ethnic origins. Lancet 2002, 360, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Pistorio, A.; Iusan, S.M.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Herlin, T.; Brik, R.; Buoncompagni, A.; Lazar, C.; Bilge, I.; Uziel, Y.; et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for Henoch–Schönlein purpura, childhood polyarteritis nodosa, childhood Wegener granulomatosis and childhood Takayasu arteritis: Ankara 2008. Part II: Final classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oni, L.; Sampath, S. Childhood IgA Vasculitis (Henoch Schonlein Purpura)-Advances and Knowledge Gaps. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, S.; Marks, S.D.; Brogan, P.; Groot, N.; de Graeff, N.; Avcin, T.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Dolezalova, P.; Feldman, B.M.; Kone-Paut, I.; et al. European consensus-based recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of immunoglobulin A vasculitis—the SHARE initiative. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.; Tang, Y.L.; Lv, X.H.; Zhang, G.F.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.P.; Li, Q. Risk Factors Associated with Renal Involvement in Childhood Henoch-Schönlein Purpura: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikibakhsh, A.A.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Karamyyar, M.; Hejazi, S.; Noroozi, M.; Macooie, A.A. Treatment of severe henoch-schonlein purpura nephritis with mycophenolate mofetil. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2014, 25, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Chan, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Q. Risk factors associated with IgA vasculitis with nephritis (Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis) progressing to unfavorable outcomes: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narchi, H. Risk of long term renal impairment and duration of follow up recommended for Henoch-Schonlein purpura with normal or minimal urinary findings: A systematic review. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, L.; Richardson, A.R.; Holt, R.C.; Jones, C.A.; Beresford, M.W. Henoch schonlein purpura--a 5-year review and proposed pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, G.; Qiao, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J. Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis: An Up-To-Date Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 771619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.E.C.; Toner, A.; Wright, R.D.; Oni, L. A systematic review of urine biomarkers in children with IgA vasculitis nephritis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 3033–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asano, K.; Iwasaki, H.; Fujimura, K.; Ikeda, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Matsubara, A.; Yano, K.; Irisawa, H.; Kono, F.; Kanbe, M.; et al. Automated microanalysis of creatinine by coupled enzyme reactions. Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. 1992, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, G.; Henault, E. Protein array analyzer for ImageJ. In Proceedings of the ImageJ User and Developer Conference 2010, Mondorf-les-Bains, Luxembourg, 27–29 October 2010; pp. 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blighe, K.; Rana, S.; Lewis, M. EnhancedVolcano: Publication-Ready Volcano Plots with Enhanced Colouring and Labeling. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/kevinblighe/EnhancedVolcano (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Moisini, I.; Davidson, A. BAFF: A local and systemic target in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 158, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Peña, D.; Genre, F.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Pulito-Cueto, V.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Llorca, J.; Sevilla-Pérez, B.; Ortego-Centeno, N.; Lera-Gómez, L.; Leonardo, M.T.; et al. BAFF, APRIL and BAFFR on the pathogenesis of Immunoglobulin-A vasculitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, N.; Li, W. BAFF is involved in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy by activating the TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, F.B.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Hoi, A.Y.; Slavin, L.; Godsell, J.D.; Kitching, A.R.; Harris, J.; Nelson, C.L.; Jenkins, A.J.; Chrysostomou, A.; et al. Urinary B-cell-activating factor of the tumour necrosis factor family (BAFF) in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.D.; Chiu, S.; Gao, Y.; Summers-deLuca, L.E.; Gommerman, J.L. BAFF induces a hyper-IgA syndrome in the intestinal lamina propria concomitant with IgA deposition in the kidney independent of LIGHT. Cell. Immunol. 2006, 241, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.D.; Kujawa, J.; Wilson, C.; Papandile, A.; Poreci, U.; Porfilio, E.A.; Ward, L.; Lawson, M.A.; Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. Mice overexpressing BAFF develop a commensal flora-dependent, IgA-associated nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phatak, S.; Chaurasia, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Gupta, R.; Agrawal, V.; Aggarwal, A.; Misra, R. Urinary B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL): Potential biomarkers of active lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klauzinska, M.; Bertolette, D.; Tippireddy, S.; Strizzi, L.; Gray, P.C.; Gonzales, M.; Duroux, M.; Ruvo, M.; Wechselberger, C.; Castro, N.P.; et al. Cripto-1: An extracellular protein—connecting the sequestered biological dots. Connect. Tissue Res. 2015, 56, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-m.; Bao, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-m.; Song, Z.-B. Cripto-1 modulates macrophage cytokine secretion and phagocytic activity via NF-κB signaling. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, H.; Sawada, Y.; Nakamura, M. IgA Vasculitis: Etiology, Treatment, Biomarkers and Epigenetic Changes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, B.; Winters, S.J. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin in Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Sakoda, H.; Fujishiro, M.; Yamamotoya, T.; Nakatsu, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Kaneko, S.; Tanaka, H.; Asano, T. Protective Effect of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin against Metabolic Syndrome: In Vitro Evidence Showing Anti-Inflammatory and Lipolytic Effects on Adipocytes and Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3062319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simó, R.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Sáez-Lopez, C.; Lecube, A.; Hernandez, C.; Selva, D.M. Molecular Mechanism of TNFα-Induced Down-Regulation of SHBG Expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simó, R.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Hernandez, C.; Selva, D.M. IL1β down-regulation of sex hormone-binding globulin production by decreasing HNF-4α via MEK-1/2 and JNK MAPK pathways. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pugeat, M.; Nader, N.; Hogeveen, K.; Raverot, G.; Déchaud, H.; Grenot, C. Sex hormone-binding globulin gene expression in the liver: Drugs and the metabolic syndrome. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urushihara, M.; Kagami, S. Role of the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system in the progression of renal disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Astor, B.C.; Fox, C.H.; Isakova, T.; Lash, J.P.; Peralta, C.A.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Feldman, H.I. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2012 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Békássy, Z.D.; Kristoffersson, A.-C.; Rebetz, J.; Tati, R.; Olin, A.I.; Karpman, D. Aliskiren inhibits renin-mediated complement activation. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.H.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Associations between the angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and susceptibility to vasculitis: A meta-analysis. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012, 13, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantelme, P.; Rohrwasser, A.; Gociman, B.; Hillas, E.; Cheng, T.; Petty, G.; Thomas, J.; Xiao, S.; Ishigami, T.; Herrmann, T.; et al. Effects of dietary sodium and genetic background on angiotensinogen and Renin in mouse. Hypertension 2002, 39, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiyama, A.; Konishi, Y.; Ohashi, N.; Morikawa, T.; Urushihara, M.; Maeda, I.; Hamada, M.; Kishida, M.; Hitomi, H.; Shirahashi, N.; et al. Urinary angiotensinogen reflects the activity of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi-fei, M.; Yu-feng, L.; Gui-mei, G.; Ya-ju, Z.; Ying-liang, G.; Yu, D. Changes of new urinary biomarkers in children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 841. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.N.; Liu, W.E.I.; Li, Y.G.; Jia, G.C.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Y.J.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.F. Urinary angiotensinogen levels in relation to renal involvement of Henoch-Schonlein purpura in children. Nephrology 2012, 17, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurari, M.; Kafoury, R.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Ndebele, K. The Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone system in vascular inflammation and remodeling. Int. J. Inflam. 2014, 2014, 689360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vorst, E.P.C. High-Density Lipoproteins and Apolipoprotein A1. In Vertebrate and Invertebrate Respiratory Proteins, Lipoproteins and Other Body Fluid Proteins; Hoeger, U., Harris, J.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 399–420. [Google Scholar]
- Kon, V.; Yang, H.-C.; Smith, L.E.; Vickers, K.C.; Linton, M.F. High-Density Lipoproteins in Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgila, K.; Vyrla, D.; Drakos, E. Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, A.J.; Jabs, K.; Hunley, T.E.; Jones, D.P.; VanDeVoorde, R.G.; Anderson, C.; Du, L.; Zhong, J.; Fogo, A.B.; Yang, H.; et al. Urinary apolipoprotein AI in children with kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2019, 34, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Tsai, I.J.; Chang, C.-J.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chiang, B.-L. The Interaction between Circulating Complement Proteins and Cutaneous Microvascular Endothelial Cells in the Development of Childhood Henoch-Schönlein Purpura. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.-C.; Ten Berge, I.J.; Weening, J.J. What is the difference between IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis? Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, J.S.; Zandbergen, M.; Wolterbeek, R.; Baelde, H.J.; van Es, L.A.; de Fijter, J.W.; Bruijn, J.A.; Bajema, I.M. Complement-mediated microangiopathy in IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.F.; Ward, P.A. Role of C5a in inflammatory responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Di, Y.; Shen, M.; Ying, Q.; Fu, S.; Li, Y. Urinary Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor as a Noninvasive Biomarker in Pediatric Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Nephritis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 23, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.-H.; Zhou, T.-B.; Lei, F.-Y.; Huang, W.-F.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Lin, F.-Q.; Su, L.-N. Cut-off values for serum matrix metalloproteinase-9: Is there a threshold to predict renal involvement for Henoch–Schonlein purpura in children? Nephrology 2011, 16, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillebout, E.; Jamin, A.; Ayari, H.; Housset, P.; Pierre, M.; Sauvaget, V.; Viglietti, D.; Deschenes, G.; Monteiro, R.C.; Berthelot, L.; et al. Biomarkers of IgA vasculitis nephritis in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyga, K.; Machura, E.; Świętochowska, E.; Szczepańska, M. Analysis of the association between kidney injury biomarkers concentration and nephritis in immunoglobulin A vasculitis: A pediatric cohort study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, J.; Prayogo, G.W.; Cao, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. Understanding kidney injury molecule 1: A novel immune factor in kidney pathophysiology. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.; Christensen, E.I.; Birn, H. Megalin and cubilin in proximal tubule protein reabsorption: From experimental models to human disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Singh, A.B.; Harris, R.C. The role of the EGF family of ligands and receptors in renal development, physiology and pathophysiology. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramkumar, N.; Kohan, D.E. Proximal tubule angiotensinogen modulation of arterial pressure. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Overall | IgAVN | IgAVwoN | HC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 12 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - |
| Male/female | 6/6 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 1.000 |
| Age, years a | 7.6 [4.0–13.4] | 9.9 [5.2–12.2] | 5.1 [4.0–6.8] | 8.8 [7.5–13.4] | 0.058 |
| Time from diagnosis to sample (weeks) a | 14.8 [1.0–32.0] | 14.8 [5.3–25.3] | 19.2 [1.0–32.0] | - | 0.773 |
| Hypertension b | 2 | 2 | 0 | - | 0.102 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL a | 42.0 [32.0–54.0] | 43.5 [33.0–54.0] | 32.0 [32.0–32.0] c | - | 0.400 |
| Urinary creatinine, mmol/L a | 7.8 [1.2–19.9] | 6.6 [1.6–13.2] | 7.8 [1.2–9.4] ± 3.6 | 9.3 [6.8–19.9] | 0.668 |
| UACR, mg/mmol a,d | 0.0 [0.0–2357.7] | 542.2 [110.4–2357.7] | 0.0 [0.0–0.0] | 0.0 [0.0–0.0] | - |
| Biopsy proven nephritis b | - | 4 | 0 | - | - |
| ISKDC Grade II b IIIb b | - - | 1 3 | - - | - - | - - |
| Medications b | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | - |
| Corticosteroids b | 2 | Prednisolone (2) | - | - | - |
| DMARDs b | 1 | Azathioprine (1) | - | - | - |
| Other b | 1 | - | - | Somatropin (1) | - |
| Follow up at 12 months | |||||
| Discharged | 5 | 1 | 4 | - | |
| Still under follow up | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| Protein | IgAVN vs. IgAVwoN | IgAVN vs. HCs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | p-Value | Fold Change | p-Value | |
| BAFF | 9.7 | 0.026 * | 26.5 | 0.004 * |
| Cripto-1 | 7.8 | 0.015 * | 7.1 | 0.026 * |
| SHBG | 7.6 | 0.008 * | 13.3 | 0.004 * |
| Angiotensinogen | 6.5 | 0.010 * | 22.6 | 0.007 * |
| ApoA1 | 6.0 | 0.020 * | 6.0 | 0.035 * |
| EGF-R | 5.8 | 0.002 * | 7.8 | <0.001 * |
| C5/C5a | 4.6 | 0.033 * | 6.5 | 0.012 * |
| KIM-1 | 4.1 | 0.004 * | 4.1 | 0.001 * |
| ICAM-1 | 4.0 | 0.012 * | 10.2 | <0.001 * |
| ENA-78 | 3.7 | 0.059 | 7.4 | 0.016 * |
| CXCL16 | 3.7 | 0.013 * | 4.5 | 0.013 * |
| IGFBP-3 | 3.4 | 0.023 * | 10.7 | <0.001 * |
| MCP-1 | 3.4 | 0.047 * | 12.0 | 0.001 * |
| ST2 | 3.3 | 0.014 * | 8.2 | <0.001 * |
| CD40 Ligand | 3.0 | 0.045 * | 7.2 | 0.008 * |
| PF4 | 2.9 | 0.261 | 7.5 | 0.036 * |
| CFD | 2.6 | 0.009 * | 3.4 | 0.005 * |
| GH | 2.6 | 0.067 | 6.3 | 0.004 * |
| IL-6 | 2.6 | 0.196 | 5.5 | 0.036 * |
| Serpin E1 | 2.5 | 0.034 * | 8.1 | <0.001 * |
| LIF | 2.4 | 0.008 * | 5.5 | 0.001 * |
| MIF | 2.2 | 0.015 * | 3.1 | 0.006 * |
| Fas Ligand | 2.1 | 0.086 | 3.8 | 0.008 * |
| IL-5 | 2.0 | 0.047 * | 4.6 | 0.003 * |
| CXCL1 | 2.0 | 0.022 * | 4.3 | <0.001 * |
| IL-4 | 2.0 | 0.078 | 4.6 | 0.004 * |
| TfR | 1.9 | 0.087 | 5.6 | <0.001 * |
| RANTES | 1.9 | 0.128 | 4.4 | 0.011 * |
| IL-8 | 1.9 | 0.117 | 2.9 | 0.039 * |
| MCP-1 | 1.9 | 0.061 | 4.1 | 0.006 * |
| IL-22 | 1.8 | 0.248 | 4.4 | 0.020 * |
| HGF | 1.8 | 0.028 * | 4.3 | 0.001 * |
| IP-10 | 1.8 | 0.128 | 2.8 | 0.023 * |
| IGFBP-2 | 1.8 | 0.203 | 4.9 | 0.011 * |
| Endoglin | 1.8 | 0.021 * | 2.7 | 0.014 * |
| MIG | 1.7 | 0.110 | 3.8 | 0.001 * |
| Flt-3 Ligand | 1.7 | 0.131 | 2.7 | 0.019 * |
| Leptin | 1.7 | 0.268 | 4.3 | 0.009 * |
| IL-10 | 1.7 | 0.288 | 3.3 | 0.032 * |
| IL-19 | 1.5 | 0.320 | 3.8 | 0.009 * |
| G-CSF | 1.5 | 0.220 | 3.6 | 0.003 * |
| PDGF-AA/BB | 1.5 | 0.236 | 4.2 | 0.007 * |
| TARC | 1.5 | 0.340 | 4.1 | 0.011 * |
| GM-CSF | 1.4 | 0.234 | 3.2 | 0.016 * |
| Angiopoietin-1 | 1.4 | 0.326 | 3.5 | 0.034 * |
| MIP-1α/MIP-1β | 1.4 | 0.277 | 2.6 | 0.014 * |
| IL-15 | 1.4 | 0.289 | 3.2 | 0.011 * |
| IL-33 | 1.4 | 0.363 | 3.7 | 0.007 * |
| IL-31 | 1.4 | 0.371 | 3.3 | 0.015 * |
| IL-23 | 1.4 | 0.431 | 3.3 | 0.024 * |
| MCP-3 | 1.3 | 0.377 | 3.2 | 0.016 * |
| MIP-3α | 1.3 | 0.349 | 2.5 | 0.018 * |
| IL-16 | 1.3 | 0.374 | 2.7 | 0.016 * |
| I-TAC | 1.2 | 0.370 | 2.9 | 0.009 * |
| Relaxin-2 | 1.2 | 0.510 | 2.9 | 0.048 * |
| IL-24 | 1.2 | 0.504 | 3.2 | 0.019 * |
| IL-13 | 1.2 | 0.603 | 3.4 | 0.016 * |
| IFN-γ | 1.2 | 0.609 | 3.2 | 0.030 * |
| IL-34 | 1.2 | 0.554 | 2.6 | 0.025 * |
| Pentraxin-3 | 1.1 | 0.732 | 3.0 | 0.035 * |
| IL-27 | 1.1 | 0.570 | 3.3 | 0.023 * |
| TNF-α | 1.1 | 0.469 | 2.3 | 0.023 * |
| Dkk-1 | 1.1 | 0.562 | 2.5 | 0.011 * |
| IL-32 | 1.1 | 0.558 | 3.5 | 0.004 * |
| BDNF | 1.0 | 0.757 | 2.6 | 0.020 * |
| PDGF-AA | 1.0 | 0.735 | 2.2 | 0.027 * |
| MIP-3b | 0.9 | 0.484 | 3.5 | 0.013 * |
| Thrombospondin-1 | 0.9 | 0.781 | 2.6 | 0.029 * |
| TGF-α | 0.9 | 0.929 | 2.3 | 0.028 * |
| Protein | IgAVN vs. IgAVwoN | IgAVN vs. HC | IgAVwoN vs. HC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kit K | Kit C | Kit K | Kit C | Kit K | Kit C | |
| CXCL1 | 1.8 (0.534) | 2.0 (0.022) | 5.0 (0.206) | 4.3 (<0.001) | 2.8 (0.539) | 2.1 (0.017) |
| IL-6 | 2.6 (0.196) | 1.8 (0.293) | 5.5 (0.036) | 3.3 (0.052) | 2.1 (0.496) | 1.8 (0.197) |
| IL-10 | 1.6 (0.659) | 1.7 (0.288) | 4.8 (0.346) | 3.3 (0.032) | 3.1 (0.642) | 2.0 (0.203) |
| MCP-1 | 3.4 (0.047) | 1.9 (0.061) | 12.0 (0.001) | 4.1 (0.006) | 3.5 (0.001) | 2.2 (0.134) |
| Thrombospondin-1 | 1.4 (0.719) | 0.9 (0.781) | 3.7 (0.397) | 2.6 (0.029) | 2.6 (0.673) | 2.9 (0.153) |
| TNF-α | 1.6 (0.446) | 1.1 (0.469) | 2.7 (0.366) | 2.3 (0.023) | 1.6 (0.963) | 2.1 (0.385) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marro, J.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Wright, R.D.; Dliso, S.; Oni, L. Urinary Protein Array Analysis to Identify Key Inflammatory Markers in Children with IgA Vasculitis Nephritis. Children 2022, 9, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9050622
Marro J, Chetwynd AJ, Wright RD, Dliso S, Oni L. Urinary Protein Array Analysis to Identify Key Inflammatory Markers in Children with IgA Vasculitis Nephritis. Children. 2022; 9(5):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9050622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarro, Julien, Andrew J. Chetwynd, Rachael D. Wright, Silothabo Dliso, and Louise Oni. 2022. "Urinary Protein Array Analysis to Identify Key Inflammatory Markers in Children with IgA Vasculitis Nephritis" Children 9, no. 5: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9050622
APA StyleMarro, J., Chetwynd, A. J., Wright, R. D., Dliso, S., & Oni, L. (2022). Urinary Protein Array Analysis to Identify Key Inflammatory Markers in Children with IgA Vasculitis Nephritis. Children, 9(5), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9050622






