Study of Orofacial Function in Preschool Children Born Prematurely
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menon, R. Preterm birth: A global burden on maternal and child health. Pathog. Glob. Health 2012, 106, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslau, N.; Chilcoat, H.D.; Johnson, E.O.; Andreski, P.; Lucia, V.C. Neurologic soft signs and low birthweight: Their association and neuropsychiatric implications. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; Doyle, L.W.; Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Neurobehavioral outcomes of school-age children born extremely low birth weight or very preterm in the 1990s. JAMA 2003, 289, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnari, S.; Yliherva, A.; Paavola, L.; Peltoniemi, O.M. Expressive language skills in Finnish two-year-old extremely-and very-low-birth-weight preterm children. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2012, 64, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayraud, F.; Kern, S. Influence of preterm birth on early lexical and grammatical acquisition. First Lang. 2007, 27, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, M.S.; Barbosa, T.D.S.; Gavião, M.B.D. Assessment of orofacial functions in Brazilian children using the Nordic Orofacial Test-Screening (NOT-S). Rev. Odonto Ciência 2012, 27, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bakke, M.; Bergendal, B.; McAllister, A.; Sjögreen, L.; Asten, P. Development and evaluation of a comprehensive screening for orofacial dysfunction. Swed. Dent. J. 2007, 31, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson, C.; Skoglund, C.; Thelin, H. Normering av Nordiskt Orofacialt Test-Screening (NOT-S) för Barn i Åldrarna 3 Till 6 år; Institutionen för Nervsystem och Rörelseorgan: Linköping, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Trulsson, U.; Klingberg, G. Living with a child with a severe orofacial handicap: Experiences from the perspectives of parents. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2003, 111, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, A.; Lundeborg, I. Oral sensorimotor functions in typically developing children 3 to 8 years old; assessed by the Nordic orofacial test, NOT-S. J. Med. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2013, 21, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Buswell, C.A.; Leslie, P.; Embleton, N.D.; Drinnan, M.J. Oral-motor dysfunction at 10 months corrected gestational age in infants born less than 37 weeks preterm. Dysphagia 2009, 24, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridham, K.; Steward, D.; Thoyre, S.; Brown, R.; Brown, L. Feeding skill performance in premature infants during the first year. Early Hum. Dev. 2007, 83, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergendal, B.; Bakke, M.; McAllister, A.; Sjögreen, L.; Åsten, P. Profiles of orofacial dysfunction in different diagnostic groups using the Nordic Orofacial Test (NOT-S)—A review. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, H.; Harris, G.; Emmett, P. Delayed introduction of lumpy foods to children during the complementary feeding period affects child’s food acceptance and feeding at 7 years of age. Matern. Child Nutr. 2009, 5, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, M.; van Doorn, J.; van den Berg, J. Parents’ perceptions of eating skills of pre-term vs full-term infants from birth to 3 years. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2013, 15, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncelli, N.; Cuomo, G.; Cattani, S.; Mazzi, C.; Pugliese, M.; Coccolini, E.; Zagni, P.; Mordini, B.; Ferrari, F. Oral feeding competences of healthy preterm infants: A review. Int. J. Pediatr. 2012, 2012, 896257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braid, S.; Harvey, E.M.; Bernstein, J.; Matoba, N. Early introduction of complementary foods in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migraine, A.; Nicklaus, S.; Parnet, P.; Lange, C.; Monnery-Patris, S.; Robert, C.D.; Darmaun, D.; Flamant, C.; Amarger, V.; Rozé, J. Effect of preterm birth and birth weight on eating behavior at 2 y of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, N.; Yassaei, S.; Moghadam, M.G. Abnormal oral habits: A review. J. Dent. Oral Hyg. 2012, 4, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, N.M.; Salama, F.; Pedo, C. Sucking habits in Saudi children: Prevalence, contributing factors and effects on the primary dentition. Pediatr. Dent. 1997, 19, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrini, F.R.D.O.; Marba, S.T.M.; Gavião, M.B.D. Oral conditions in very low and extremely low birth weight children. J. Dent. Child. 2008, 75, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Gallardo, M.A.; Rojas Contreras, D.P.; Vargas Keith, J.F. Development of feeding skills in preterm infants: A critical literature review. Rev. CEFAC 2017, 19, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törölä, H.; Lehtihalmes, M.; Yliherva, A.; Olsén, P. Feeding skill milestones of preterm infants born with extremely low birth weight (ELBW). Inf. Behav. Dev. 2012, 35, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Sheena, H.R.; Shulman, R.J.; Schanler, R.J. Oral feeding in low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 1997, 130, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Smith, E.; Schanler, R. Coordination of suck-swallow and swallow respiration in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2003, 92, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.H.; Tan, C.T. Morphology of the palatal vault of primary dentition in transverse view. Angle Orthodont. 2004, 74, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Révérend, B.J.; Edelson, L.R.; Loret, C. Anatomical, functional, physiological and behavioural aspects of the development of mastication in early childhood. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.; Bax, M.; Stevenson, J. The evaluation of home based speech therapy for language delayed pre-school children in an inner city area. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 1982, 17, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.B.; Bendersky, M.; Chapman, T. The early utterances of preterm infants. Br. J. Disord. Commun. 1986, 21, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvedson, J.; Clark, H.; Lazarus, C.; Schooling, T.; Frymark, T. Evidence-based systematic review: Effects of oral motor interventions on feeding and swallowing in preterm infants. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2010, 19, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodrill, P.; McMahon, S.; Ward, E.; Weir, K.; Donovan, T.; Riddle, B. Long-term oral sensitivity and feeding skills of low-risk pre-term infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2004, 76, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, J.A.B.; Ferguson, A.; Cho, C.; Oh, W.; Vohr, B.R. The oral motor development of low-birth-weight infants who underwent orotracheal intubation during the neonatal period. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1993, 147, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaTuga, M.S.; Mittelstaedt, G.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Murray-Keane, L.; Si, W.; Havranek, T. Clinical characteristics of premature infants who orally feed on continuous positive airway pressure. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 139, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, L.; Bidiwala, A.; Sher, I.; Pirzada, M.; Barlev, D.; Islam, S.; Rosenfeld, W.; Crowley, C.C.; Hanna, N. Effect of nasal continuous positive airway pressure on the pharyngeal swallow in neonates. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery-Downs, H.E.; Young, M.E.; Ross, M.A.; Polak, M.J.; Ritchie, S.K.; Lynch, S.K. Sleep-disordered breathing symptoms frequency and growth among prematurely born infants. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, N.; Michaud, A.; Othman, R.; Nadeau, C.; Nault, S.; Cantin, D.; Sage, M.; Catelin, C.; Praud, J.P. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure influences bottle-feeding in preterm lambs. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Reid, S.; Lutz, T.; Malcolm, G.; Oliver, S.; Osborn, D.A. Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway pressure. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogårdh-Roth, S.; Paulsson, L.; Larsson, P.; Ekberg, E. Do preterm-born adolescents have a poorer oral health-related quality of life? BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, D.; Tighe, R.; Petrick, L.; Cobourne, M.T.; Rabe, H. Palatal Development and Orofacial Function: Possible Effects of Preterm Care. Neoreviews 2011, 12, e308–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Characteristics | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Gulping | Swallowing food after chewing | |
| Swallowing food without chewing | ||
| Choke (water and liquid classes) | Non-choke: No coughing during eating | |
| Choke: Coughing more than 3 times during eating | ||
| The amount of open mouth | 21–30 mm | |
| 31 mm or more | ||
| Occlusal force | Normal: Can chew ordinary diet | |
| Abnormal: Can only chew soft food | ||
| Open bite | ≦2 mm | |
| >4 mm | ||
| Dental arch form | Circular shape | |
| Non-Circular shape | ||
| Palate vault | Normal Palate | |
| Abnormal Palate | ||
| Dysarthria | Normal: clear articulation of phonemes | |
| Abnormal: poor articulation of phonemes | ||
| Conscious cough | Good: Strong contraction of abdominal muscles, exercise accompanied by cough sounds | |
| Poor: Abdominal muscle contraction, coughing sound without accompanying movement | ||
| Modified Water Swallowing Test (MWST) | Normal: 3 mL water, swallow more than 3 times within 30 s | |
| Abnormal: 3 mL of water, swallowed less than 2 times within 30 s |
| Variable | GA < 37 Weeks | GA ≥ 37 Weeks | p-Value | BBW < 1501 g | BBW > 1500 g | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 101) | (N = 142) | (N = 65) | (N = 178) | |||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |||
| Average age of the first time eating pureed food (Month) | ||||||
| Fruits | 4.0 ± 1.3 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | <0.001 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.8 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Minced-Toast | 6.5 ± 2.5 | 7.5 ± 2.1 | <0.001 | 6.7 ± 2.9 | 7.2 ± 2.1 | 0.025 |
| Vegetable | 8.0 ± 2.8 | 9.4 ± 2.2 | <0.001 | 8.1 ± 3.1 | 9.1 ± 2.3 | 0.006 |
| Meat | 10.2 ± 3.6 | 11.0 ± 2.0 | <0.001 | 10.3 ± 4.2 | 10.8 ± 2.1 | 0.006 |
| Current status of development | ||||||
| Weight growth curve (%) | 33.4 ± 30.2 | 46.0 ± 31.9 | 0.002 | 33.0 ± 30.4 | 45.0 ± 31.3 | 0.003 |
| Weight growth curve < 3% 1 | 14 (13.9) | 10 (7.0) | 0.079 | 12 (18.5) | 12 (6.7) | 0.007 |
| Height growth curve (%) | 33.3 ± 28.7 | 47.8 ± 31.5 | <0.001 | 36.8 ± 32.8 | 42.2 ± 31.5 | 0.161 |
| Height growth curve < 3% 1 | 23 (22.8) | 15 (10.6) | 0.010 | 14 (21.5) | 24 (13.5) | 0.126 |
| BMI growth curve (%) | 42.7 ± 32.0 | 52.4 ± 33.5 | 0.033 | 40.0 ± 31.8 | 51.4 ± 33.6 | 0.018 |
| BMI growth curve < 3% 1 | 12 (11.9) | 14 (9.9) | 0.615 | 11 (16.9) | 15 (8.4) | 0.058 |
| Variable | Total | BBW 1001–1500 g | BBW < 1001 g | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 65) | (N = 50) | (N = 15) | ||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Apgar 1 min | 5.9 ± 1.6 | 6.2 ± 1.3 | 5.1 ± 1.9 | 0.043 |
| Apgar 5 min | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 7.9 ± 1.3 | 7.2 ± 1.0 | 0.011 |
| Day of intubation | 12.7 ± 19.7 | 6.5 ± 15.0 | 26.7 ± 22.7 | <0.001 |
| Day of NCPAP | 26.7 ± 19.7 | 22.9 ± 17.9 | 39.5 ± 20.4 | 0.005 |
| Day of NG tube placement | 51.9 ± 31.0 | 43.6 ± 24.1 | 79.6 ± 35.8 | <0.001 |
| Day of hospitalization | 71.5 ± 333.8 | 60.5 ± 26.7 | 108.2 ± 29.3 | <0.001 |
| Variable | GA < 37 Weeks | GA ≥ 37 Weeks | p-Value | BBW < 1501 g | BBW > 1500 g | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 101) | (N = 142) | (N = 65) | (N = 178) | |||
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| NOT-S | ||||||
| Breathing-snoring while sleeping | 12 (11.9) | 20 (14.1) | 0.617 | 9 (13.8) | 23 (12.9) | 0.850 |
| Habits (oral habits) | 36 (35.6) | 76 (53.5) | 0.006 | 21 (32.3) | 91 (51.1) | 0.009 |
| Grinding teeth while sleeping | 15 (14.9) | 38 (26.8) | 0.027 | 7 (10.8) | 46 (25.8) | 0.012 |
| Abnormal chewing and swallowing | 61 (60.4) | 97 (68.3) | 0.202 | 39 (60.0) | 119 (66.9) | 0.321 |
| Speech- Pronunciation is not standard | 22 (21.8) | 19 (13.4) | 0.085 | 16 (24.6) | 25 (14.0) | 0.051 |
| Assessment of chewing and swallowing in children | ||||||
| Abnormal gulping | 19 (18.8) | 46 (32.4) | 0.018 | 10 (15.4) | 55 (30.9) | 0.016 |
| Choke | 12 (11.9) | 5 (3.5) | 0.012 | 11 (16.9) | 6 (3.4) | <0.001 |
| The abnormal amount of open mouth | 6 (5.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0.003 | 6 (9.2) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Abnormal occlusal force | 43 (42.6) | 51 (35.9) | 0.294 | 34 (52.3) | 60 (33.7) | 0.008 |
| Abnormal open bite | 6 (5.9) | 5 (3.5) | 0.371 | 4 (6.2) | 7 (3.9) | 0.461 |
| Abnormal dental arch form | 29 (28.7) | 21 (14.8) | 0.008 | 24 (36.9) | 26 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Abnormal palate vault | 25 (24.8) | 14 (9.9) | 0.002 | 21 (32.3) | 18 (10.1) | <0.001 |
| Dysarthria | 21 (20.8) | 15 (10.6) | 0.027 | 16 (24.6) | 20 (11.2) | 0.009 |
| Abnormal conscious cough | 26 (25.7) | 49 (34.5) | 0.145 | 13 (20.0) | 62 (34.8) | 0.270 |
| Abnormal MWST | 34 (33.7) | 49 (34.5) | 0.891 | 19 (29.2) | 64 (36.6) | 0.328 |
| Variable | Gestational Age (Weeks) | p -Value | Birth Weight (g) | p -Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | |||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |||
| NOT-S | ||||||
| Breathing-snoring while sleeping | 35.9 ± 4.1 (211) | 35.6 ± 4.9 (32) | 0.742 | 2505.2 ± 890.2 (211) | 2530.3 ± 957.0 (32) | 0.883 |
| Bad oral habits | 35.3 ± 4.3 (131) | 36.5 ± 4.0 (112) | 0.018 | 2364.2 ± 899.1 (131) | 2677.4 ± 869.0 (112) | 0.006 |
| Grinding teeth during sleep | 35.7 ± 4.3 (190) | 36.7 ± 3.5 (53) | 0.044 | 2437.0 ± 922.5 (190) | 2765.2 ± 53.6 (53) | 0.018 |
| Chewing and swallowing | 35.5 ± 4.2 (85) | 36.1 ± 4.2 (158) | 0.311 | 2473.8 ± 912.2 (85) | 2527.2 ± 891.5 (158) | 0.659 |
| Speech—Pronunciation is not standard | 36.1 ± 4.0 (202) | 34.8 ± 4.9 (41) | 0.065 | 2558.8 ± 856.5 (202) | 2260.7 ± 1053.2 (41) | 0.052 |
| The assessment chewing and swallowing in children | ||||||
| Gulping | 35.5 ± 4.3 (178) | 36.9 ± 3.7 (65) | <0.017 | 2407.0 ± 909.8 (178) | 2786.7 ± 804.8 (65) | 0.003 |
| Choke | 36.0 ± 4.1 (226) | 32.8 ± 4.5 (17) | <0.001 | 2556.9 ± 875.8 (226) | 1865.6 ± 959.1 (17) | 0.002 |
| The abnormal amount of open mouth | 36.0 ± 4.0 (237) | 28.2 ± 2.3 (6) | <0.001 | 2544.8 ± 877.5 (237) | 1077.5 ± 318.2 (6) | <0.001 |
| Occlusal force | 36.3 ± 3.8 (149) | 35.2 ± 4.7 (94) | 0.057 | 2602.4 ± 818.1 (149) | 2359 ± 996.7 (94) | 0.040 |
| Open bite | 35.9 ± 4.1 (232) | 34.7 ± 4.8 (11) | 0.361 | 2522.6 ± 895.8 (232) | 2211.7 ± 919.0 (11) | 0.262 |
| Dental arch form | 36.3 ± 3.9 (193) | 34.1 ± 4.8 (50) | 0.001 | 2610.6 ± 847.4 (193) | 2114.4 ± 981.3 (50) | <0.001 |
| Palate vault | 36.3 ± 4.0 (204) | 33.6 ± 4.5 (39) | <0.001 | 2603.9 ± 840.7 (204) | 2009.7 ± 1023.7 (39) | <0.001 |
| Dysarthria | 36.1 ± 4.0 (207) | 34.3 ± 5.1 (36) | 0.014 | 2572.5 ± 860.4 (207) | 2140.5 ± 1022.9 (36) | 0.007 |
| Conscious cough | 35.5 ± 4.3 (168) | 36.7 ± 3.9 (75) | 0.041 | 2442.8 ± 937.2 (168) | 2140.5 ± 1022.9 (75) | 0.092 |
| MWST | 35.7 ± 4.2 (160) | 36.1 ± 4.0 (83) | 0.511 | 2466.3 ± 931.3 (160) | 2655.5 ± 787.3 (83) | 0.593 |
| Variable | Day of Intubation (N = 65) | p-Value | Day of NCPAP (N = 65) | p-Value | Day of NG Tube Placement (N = 65) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | ||||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||||
| NOT-S | |||||||||
| Breathing-snoring while sleeping | 11.4 ± 17.4 | 21.3 ± 29.6 | 0.158 | 24.7 ± 18.1 | 39.6 ± 25.0 | 0.034 | 51.1 ± 32.7 | 53.7 ± 27.7 | 0.755 |
| Bad oral habits | 10.2 ± 17.4 | 13.1 ± 22.1 | 0.556 | 25.3 ± 20.3 | 29.7 ± 18.4 | 0.401 | 25.3 ± 20.3 | 29.7 ± 18.4 | 0.401 |
| Grinding teeth during sleep | 11.4 ± 19.9 | 9.0 ± 9.1 | 0.756 | 26.6 ± 20.2 | 28.0 ± 15.6 | 0.857 | 51.4 ± 32.2 | 56.4 ± 19.7 | 0.686 |
| Chewing and swallowing | 9.8 ± 17.3 | 12.0 ± 20.1 | 0.66 | 26.4 ± 20.3 | 26.9 ± 19.5 | 0.911 | 47.3 ± 23.7 | 55.0 ± 35.0 | 0.332 |
| Speech—Pronunciation is not standard | 9.4 ± 16.0 | 16.4 ± 25.8 | 0.203 | 26.6 ± 20.2 | 27.1 ± 18.5 | 0.937 | 53.0 ± 30.9 | 48.7 ± 32.2 | 0.636 |
| The assessment chewing and swallowing in children | |||||||||
| Gulping | 10.4 ± 16.3 | 14.9 ± 30.5 | 0.497 | 25.5 ± 18.1 | 33.4 ± 27.0 | 0.246 | 52.0 ± 31.1 | 51.5 ± 32.1 | 0.964 |
| Choke | 10.8 ± 18.8 | 15.6 ± 22.5 | 0.586 | 26.1 ± 19.5 | 34.8 ± 22.4 | 0.343 | 51.5 ± 31.1 | 57.4 ± 32.9 | 0.683 |
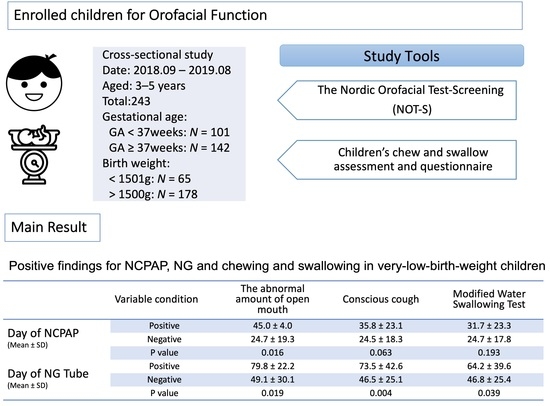
| The abnormal amount of open mouth | 10.6 ± 18.8 | 16.3 ± 22.5 | 0.483 | 24.7 ± 19.3 | 45.0 ± 4.0 | 0.016 | 49.1 ± 30.1 | 79.8 ± 22.2 | 0.019 |
| Occlusal force | 7.0 ± 14.4 | 14.9 ± 21.8 | 0.091 | 23.7 ± 18.5 | 29.5 ± 20.5 | 0.241 | 45.5 ± 21.7 | 57.836.9 | 0.109 |
| Open bite | 11.3 ± 19.2 | 8.3 ± 15.2 | 0.757 | 27.2 ± 20.0 | 19.3 ± 11.6 | 0.437 | 52.9 ± 31.4 | 37.3 ± 21.0 | 0.333 |
| Dental arch form | 12.5 ± 21.4 | 8.8 ± 13.8 | 0.451 | 26.7 ± 21.8 | 26.8 ± 15.7 | 0.983 | 50.7 ± 34.4 | 54.0 ± 24.6 | 0.666 |
| Palate vault | 10.9 ± 19.8 | 11.7 ± 17.4 | 0.874 | 28.0 ± 20.1 | 24.0 ± 16.9 | 0.437 | 49.5 ± 27.6 | 56.9 ± 37.4 | 0.378 |
| Dysarthria | 9.4 ± 16.0 | 16.4 ± 25.8 | 0.203 | 26.6 ± 20.2 | 27.1 ± 18.5 | 0.937 | 53.0 ± 30.8 | 48.7 ± 32.2 | 0.636 |
| Conscious cough | 11.1 ± 19.5 | 11.2 ± 17.1 | 0.955 | 24.5 ± 18.3 | 35.8 ± 23.1 | 0.063 | 46.5 ± 25.1 | 73.5 ± 42.6 | 0.004 |
| MWST | 11.6 ± 20.3 | 9.8 ± 15.2 | 0.718 | 24.7 ± 17.8 | 31.7 ± 23.3 | 0.193 | 46.8 ± 25.4 | 64.2 ± 39.6 | 0.039 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, M.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Chen, H.-L. Study of Orofacial Function in Preschool Children Born Prematurely. Children 2022, 9, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9030360
Chang M-C, Liu H-Y, Huang S-T, Chen H-L. Study of Orofacial Function in Preschool Children Born Prematurely. Children. 2022; 9(3):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9030360
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Mei-Chen, Hsiu-Yueh Liu, Shun-Te Huang, and Hsiu-Lin Chen. 2022. "Study of Orofacial Function in Preschool Children Born Prematurely" Children 9, no. 3: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9030360
APA StyleChang, M.-C., Liu, H.-Y., Huang, S.-T., & Chen, H.-L. (2022). Study of Orofacial Function in Preschool Children Born Prematurely. Children, 9(3), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9030360