Learning to Cycle: Is Velocity a Control Parameter for Children’s Cycle Patterns on the Balance Bike?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection and Protocols
2.4. Data and Statistical Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Categorization of Cycle Patterns
3.2. Cycle Patterns Pre and Post Intervention
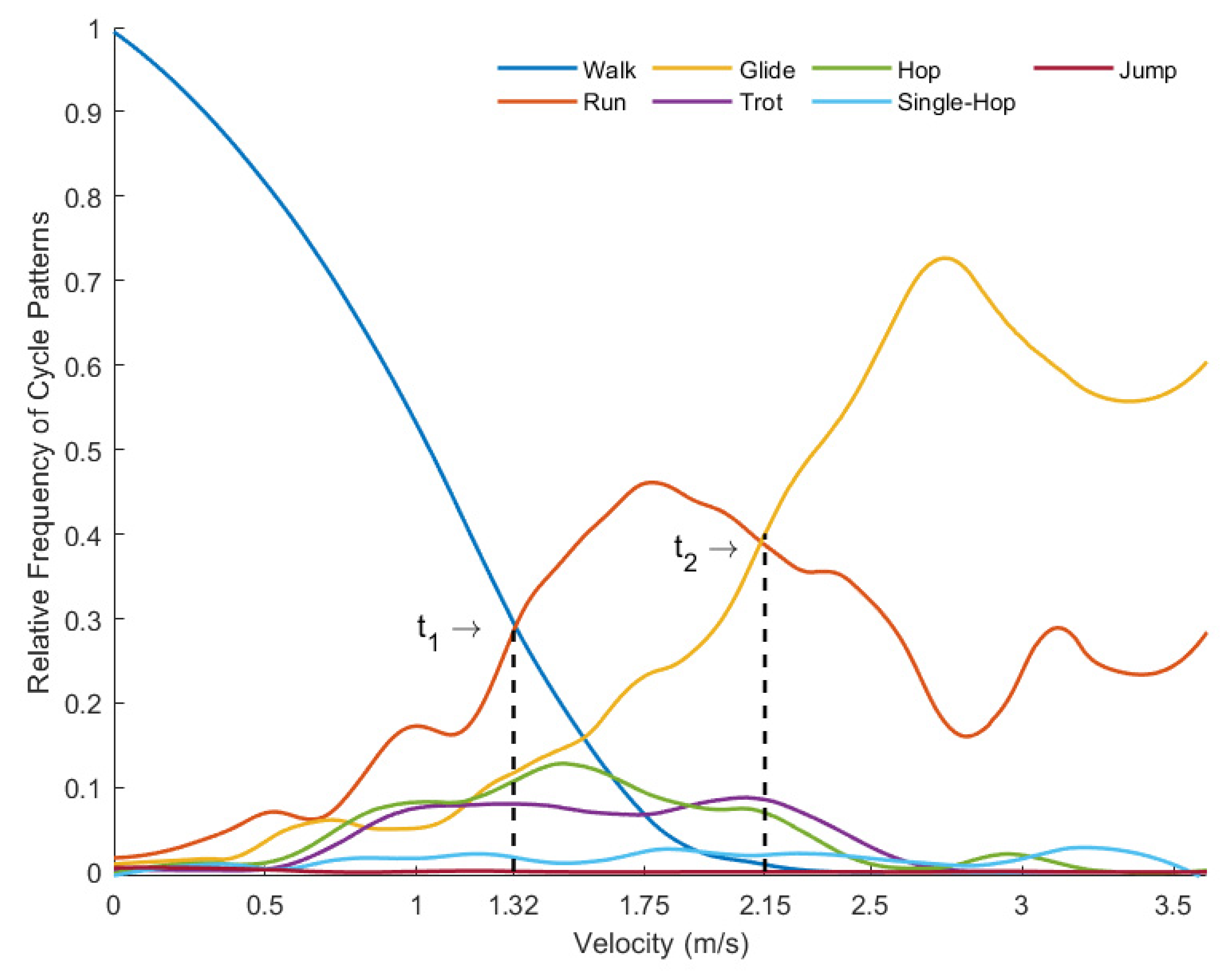
3.3. Velocity as a Control Parameter
4. Discussion
4.1. Categorization of Cycle Patterns
4.2. Evolution of Locomotor Patterns from Pre- to Post-Intervention
4.3. Velocity as a Control Parameter
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulteen, R.M.; Morgan, P.J.; Barnett, L.M.; Stodden, D.F.; Lubans, D.R. Development of Foundational Movement Skills: A Conceptual Model for Physical Activity Across the Lifespan. Sport. Med. 2018, 48, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oja, P.; Titze, S.; Bauman, A.; de Geus, B.; Krenn, P.; Reger-Nash, B.; Kohlberger, T. Health benefits of cycling: A systematic review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2011, 21, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; García-Hermoso, A.; Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Mota, J.; Santos, R.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Amaya-Tambo, D.C.; Villa-González, E. Cycling to School and Body Composition, Physical Fitness, and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2017, 188, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, S. Coordination Dynamics. In Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1537–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Kelso, J.A.S. Dynamic Patterns: The Self-Organization of Brain and Behavior; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Corbetta, D.; Vereijken, B. Understanding development and learning of motor coordination in sport: The contribution of dynamic systems theory. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 1999, 30, 507–530. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, K.M. Constraints on the development of coordination. In Motor Development in Children: Aspects of Coordination and Control; Wade, H.T.A.W.M.G., Ed.; Martinus Nijhoff: Dordrech, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 341–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, S.; Fink, P.W.; Legg, S.J.; Ali, A.; Shultz, S.P. What factors determine the preferred gait transition speed in humans? A review of the triggering mechanisms. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, L.; Chollet, D.; Bardy, B.G. Effect of swimming velocity on arm coordination in the front crawl: A dynamic analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potdevin, F.; Bril, B.; Sidney, M.; Pelayo, P. Stroke frequency and arm coordination in front crawl swimming. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, D.F.; Taylor, C.R. Gait and the energetics of locomotion in horses. Nature 1981, 292, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercê, C.; Branco, M.; Catela, D.; Lopes, F.; Rodrigues, L.P.; Cordovil, R. Learning to Cycle: Are Physical Activity and Birth Order Related to the Age of Learning How to Ride a Bicycle? Children 2021, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercê, C.; Branco, M.; Catela, D.; Lopes, F.; Cordovil, R. Learning to Cycle: From Training Wheels to Balance Bike. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercê, C.; Pereira, J.V.; Branco, M.; Catela, D.; Cordovil, R. Training programmes to learn how to ride a bicycle independently for children and youths: A systematic review. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercê, C.; Branco, M.; Catela, D.; Cordovil, R. Aprender a andar de bicicleta: Padrões de locomoção na bicicleta de equilíbrio, composição corporal e competência motora. In Estudos de Desenvolvimento Motor da Criança XIV; Matias, A.R., Almeida, G., Veiga, G., Marmeleira, J., Eds.; Universidade de Évora: Évora, Portugal, 2021; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine, R. The Ultimate Bicycle Book; Bantam Dell Pub Group: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, A.L.; Norman, S. Incorporating Pedal-less Bicycles into a Pre-K through Third-grade Curriculum to Improve Stability in Children. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2015, 86, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, S.M.; Ulrich, D.A.; Perkins, N.C. Using Measured Bicycle Kinematics to Quantify Increased Skill as a Rider Learns to Ride a Bicycle. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 5th Annual Dynamic Systems and Control Conference Joint with the JSME 2012 11th Motion and Vibration Conference, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 17–19 October 2012; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hallgren, K.A. Computing Inter-Rater Reliability for Observational Data: An Overview and Tutorial. Tutor Quant. Methods Psychol. 2012, 8, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, C.H. The Strategy of the Genes; George Unwin & Unwin: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Jenny, S.E. No Need for Training Wheels: Ideas for Including Balance Bikes in Elementary Physical Education. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2017, 88, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, A.; Davis, W.; Newman, D.; Abbey, B.; Garafalo-Peterson, J. The Effects of a Pedal-less Bicycle Intervention on Stability Scores among Preschool Aged Children. J. Mot. Behav. 2021, 53, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debarnot, U.; Castellani, E.; Valenza, G.; Sebastiani, L.; Guillot, A. Daytime naps improve motor imagery learning. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 11, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Chan, J.S.Y.; Yan, J.; Peng, K. Brain plasticity and motor practice in cognitive aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseh, W.; Bennett, J.; Caputo, J.; Morgan, D. Comparison between preferred and energetically optimal transition speeds in adolescents. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 88, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prilutsky, B.I.; Gregor, R.J. Swing- and support-related muscle actions differentially trigger human walk-run and run-walk transitions. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, R. Catastrophe Theory for Scientists and Engineers; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, N.; Downs, J.; Morris, S. “The problem with running”—Comparing the propulsion strategy of children with Developmental Coordination Disorder and typically developing children. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaeger, D.; Willems, P.A.; Heglund, N.C. The energy cost of walking in children. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2001, 441, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patterns | Description and Ground Contact Phases |
|---|---|
| Walk | Based on walking pattern. Composed of a single support phase, which is followed by a double support phase and no flight phase. Single supports are alternated |
| Run | Based on run pattern. Composed of single support phase, which is followed by flight phase and a new single support, single supports are alternated |
| Glide | The child propels itself (through a single or double support) and maintains balance on the bicycle for at least two-wheel revolutions |
| Hop | The child is propelled through a single support, which is followed by flight and a new single support on the same side. For it to be considered a hop, at least two consecutive simple supports are needed |
| Single Hop | The child is propelled through a single support, which is followed by flight phase |
| Trot | The child is propelled through a single support, which is followed by a double support phase and a flight phase |
| Jump | The child is propelled through a double support, which is followed by a flight phase |
 single support;
single support;  double support;
double support;  single or double support;
single or double support; 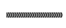 bicycle trace.
bicycle trace.| Velocities (m/s) | Observation 1 | Observation 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Mean | Maximum | N | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | N | |||
| M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | |||||
| Global | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.26 | 1.31 ± 0.41 | 12 | 0.13 ± 0.30 | 1.60 ± 0.47 | 2.52 ± 0.49 | 12 | ||
| Walk | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.25 | 1.28 ± 0.39 | 12 | 0.17 ± 0.41 | 1.12 ± 0.24 | 1.95 ± 0.19 | 11 | ||
| Run | 0.99 ± 0.41 | 1.36 ± 0.25 | 1.72 ± 0.03 | 2 | 0.58 ± 0.57 | 1.75 ± 0.44 | 2.48 ± 0.52 | 12 | ||
| Glide | 1.78 a | 1.86 a | 1.90 a | 1 | 0.85 ± 0.57 | 1.75 ± 0.42 | 2.31 ± 0.60 | 12 | ||
| Trot | 0 | 0.93 ± 0.71 | 1.68 ± 0.43 | 2.17 ± 0.43 | 12 | |||||
| Hop | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 1.11 ± 0.25 | 1.35 ± 0.49 | 2 | 0.93 ± 0.63 | 1.68 ± 0.44 | 2.30 ± 0.40 | 12 | ||
| Single Hop | 0 | 1.04 ± 0.56 | 1.70 ± 0.45 | 2.20 ± 0.57 | 12 | |||||
| Jump | 0 | 1.23 ± 0.89 | 1.61 ± 0.70 | 1.91 ± 0.60 | 8 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercê, C.; Cordovil, R.; Catela, D.; Galdino, F.; Bernardino, M.; Altenburg, M.; António, G.; Brígida, N.; Branco, M. Learning to Cycle: Is Velocity a Control Parameter for Children’s Cycle Patterns on the Balance Bike? Children 2022, 9, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121937
Mercê C, Cordovil R, Catela D, Galdino F, Bernardino M, Altenburg M, António G, Brígida N, Branco M. Learning to Cycle: Is Velocity a Control Parameter for Children’s Cycle Patterns on the Balance Bike? Children. 2022; 9(12):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121937
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercê, Cristiana, Rita Cordovil, David Catela, Flávia Galdino, Mafalda Bernardino, Mirjam Altenburg, Gonçalo António, Nancy Brígida, and Marco Branco. 2022. "Learning to Cycle: Is Velocity a Control Parameter for Children’s Cycle Patterns on the Balance Bike?" Children 9, no. 12: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121937
APA StyleMercê, C., Cordovil, R., Catela, D., Galdino, F., Bernardino, M., Altenburg, M., António, G., Brígida, N., & Branco, M. (2022). Learning to Cycle: Is Velocity a Control Parameter for Children’s Cycle Patterns on the Balance Bike? Children, 9(12), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121937









